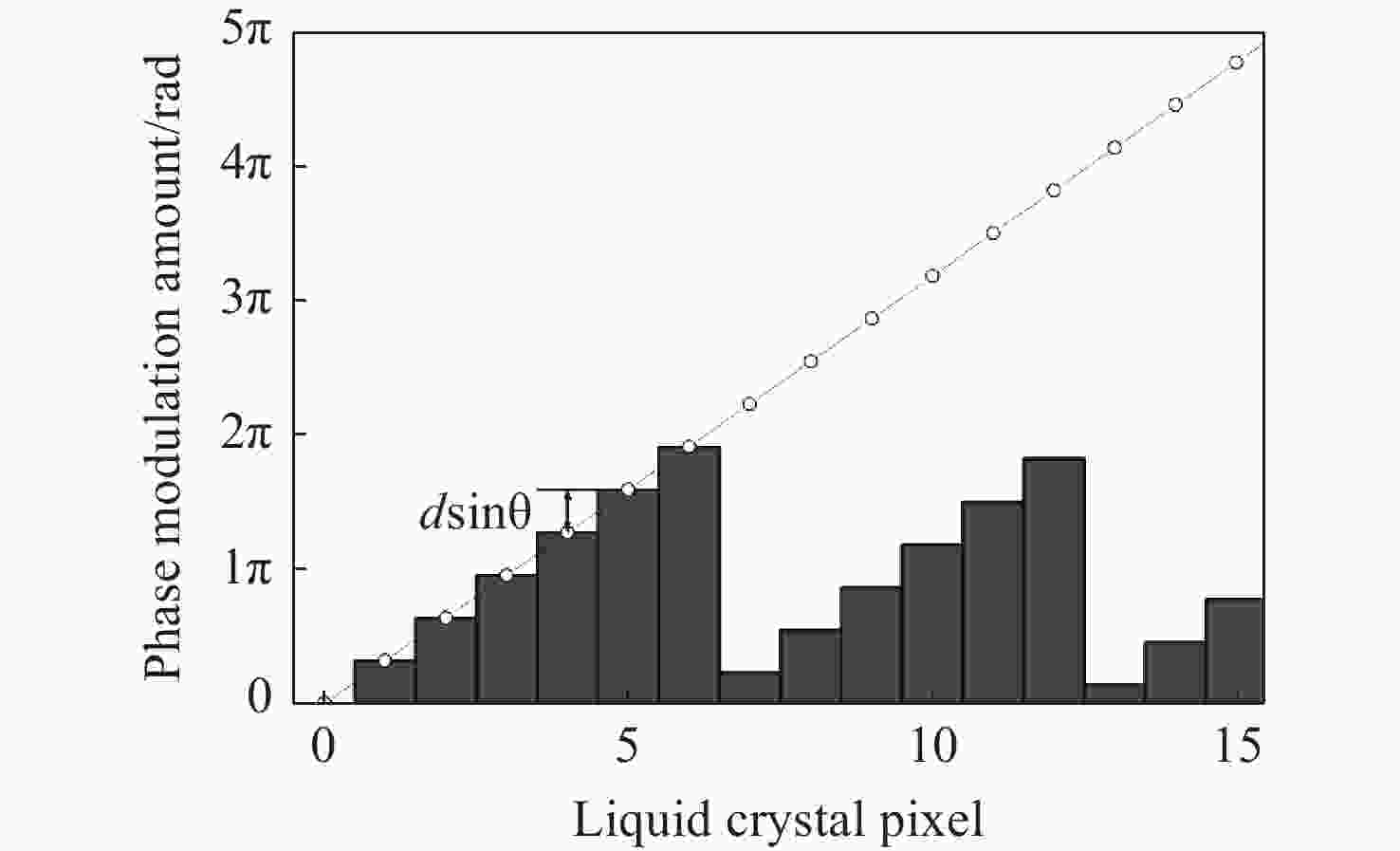
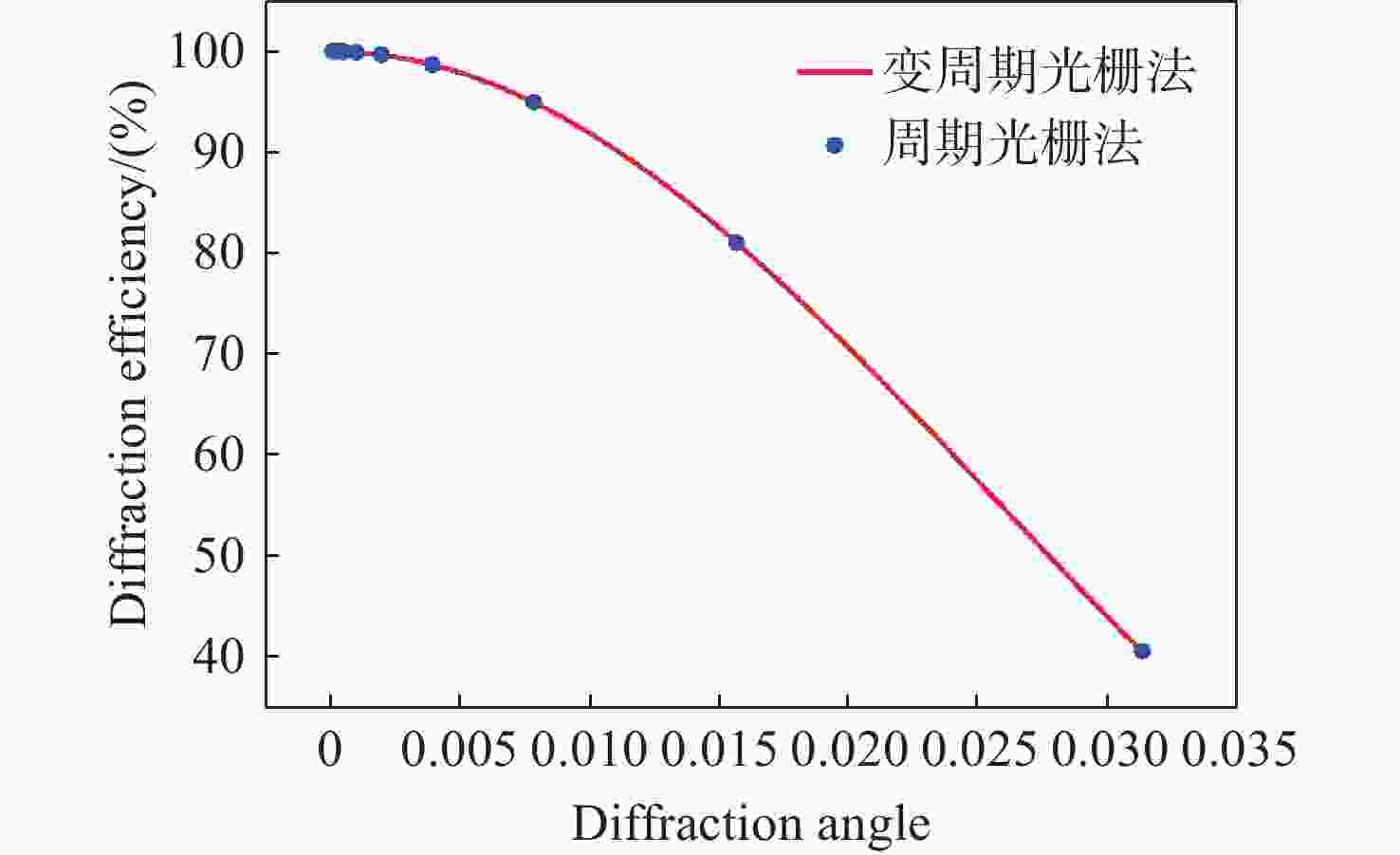
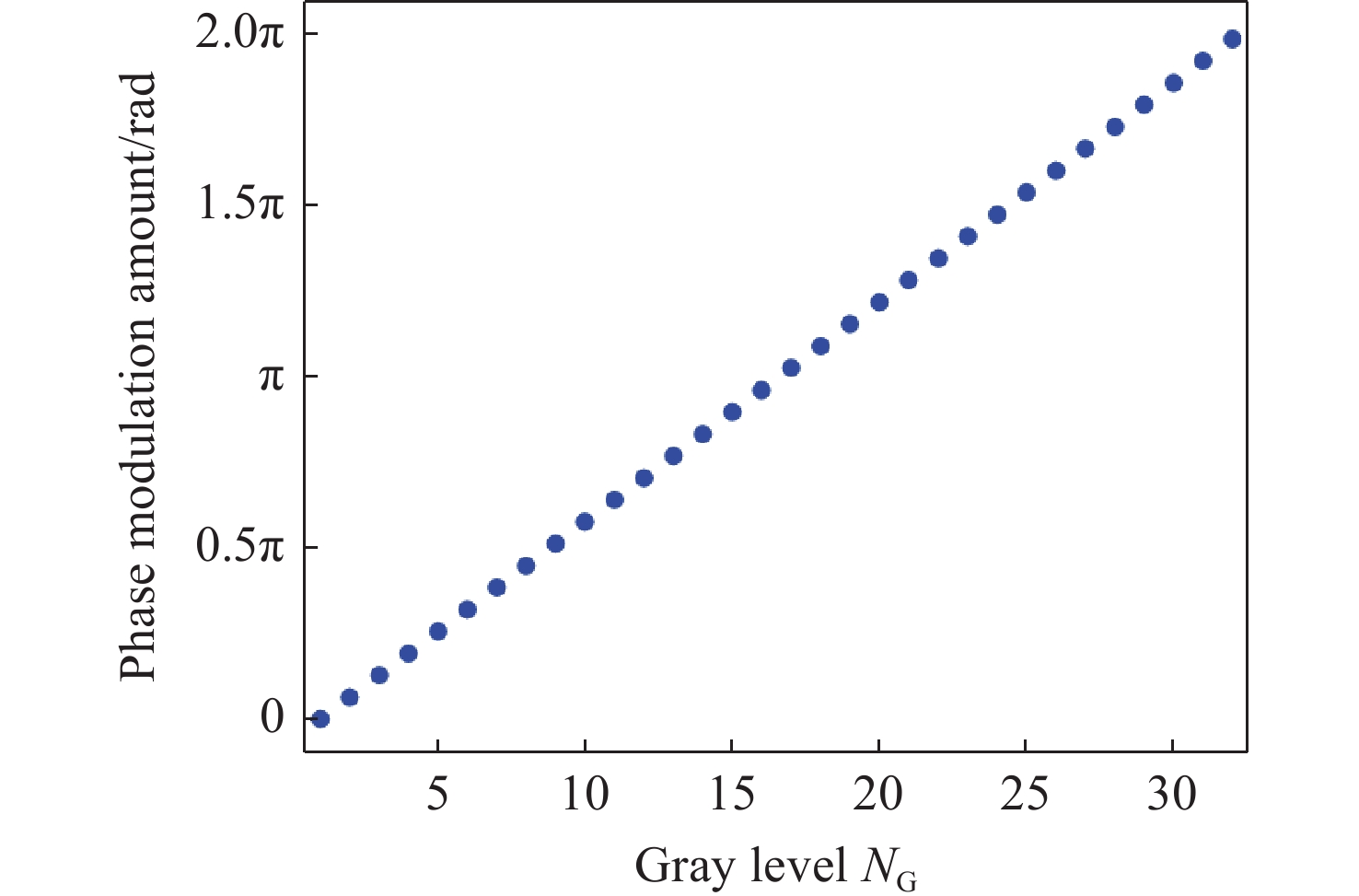
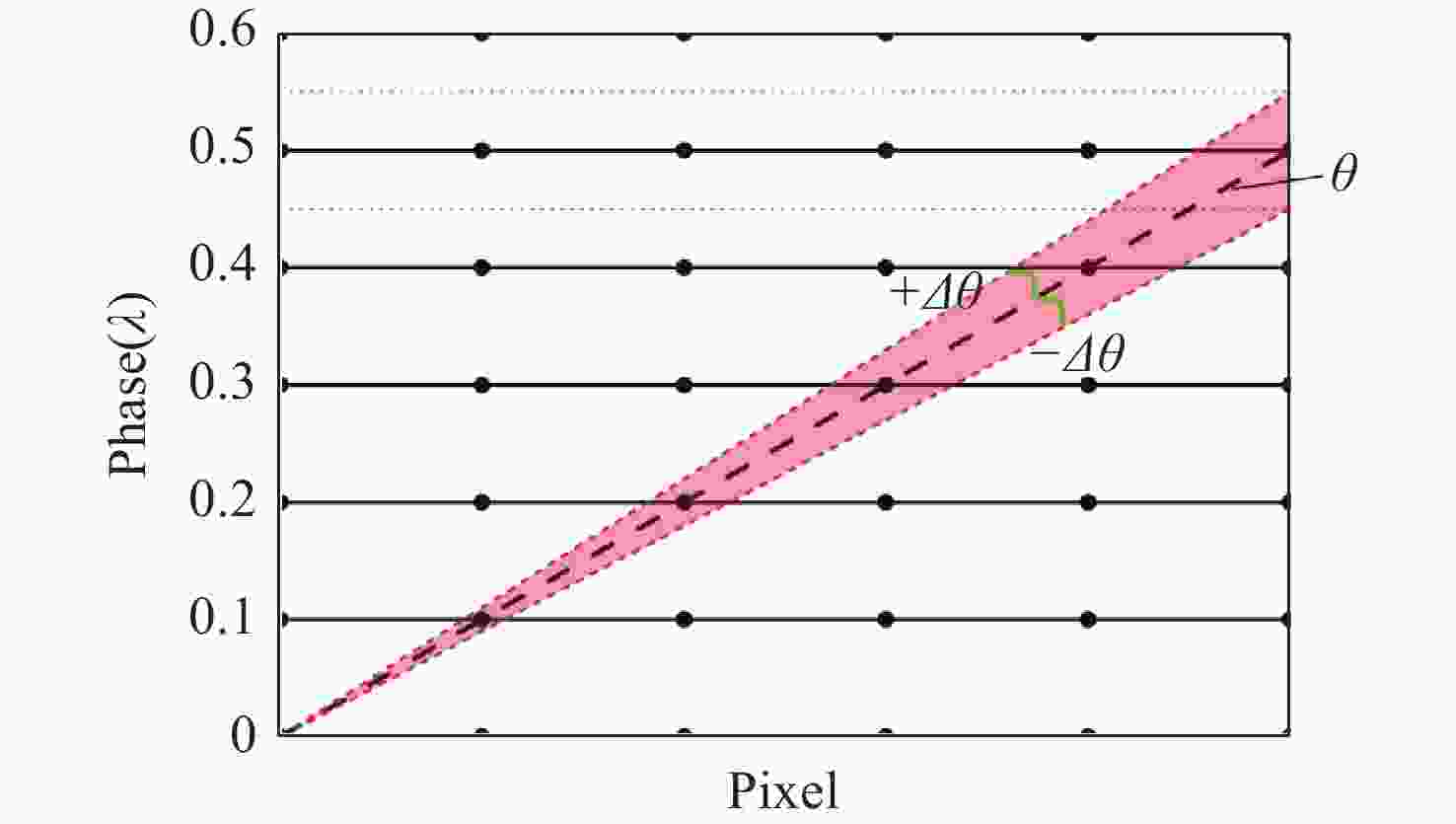
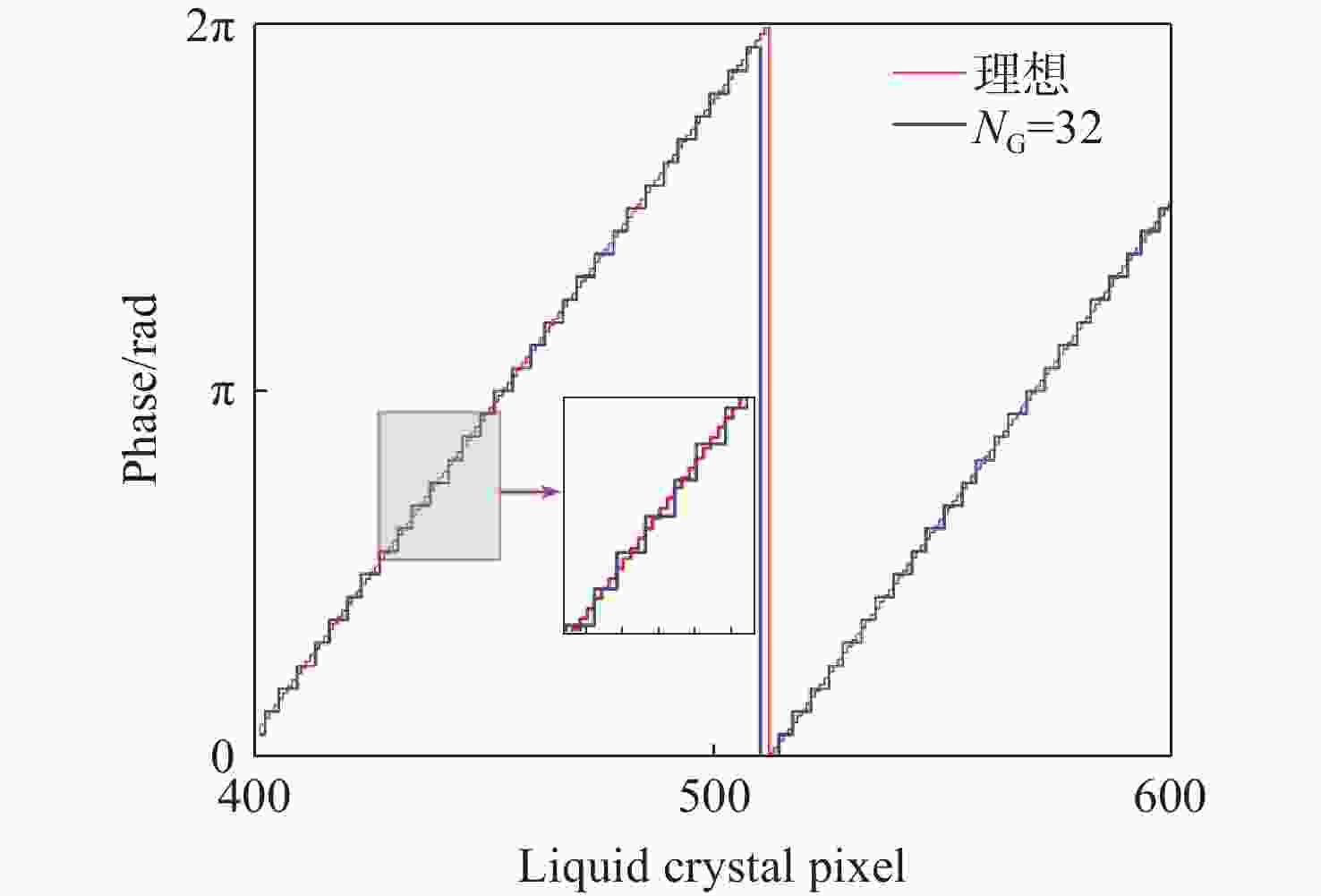
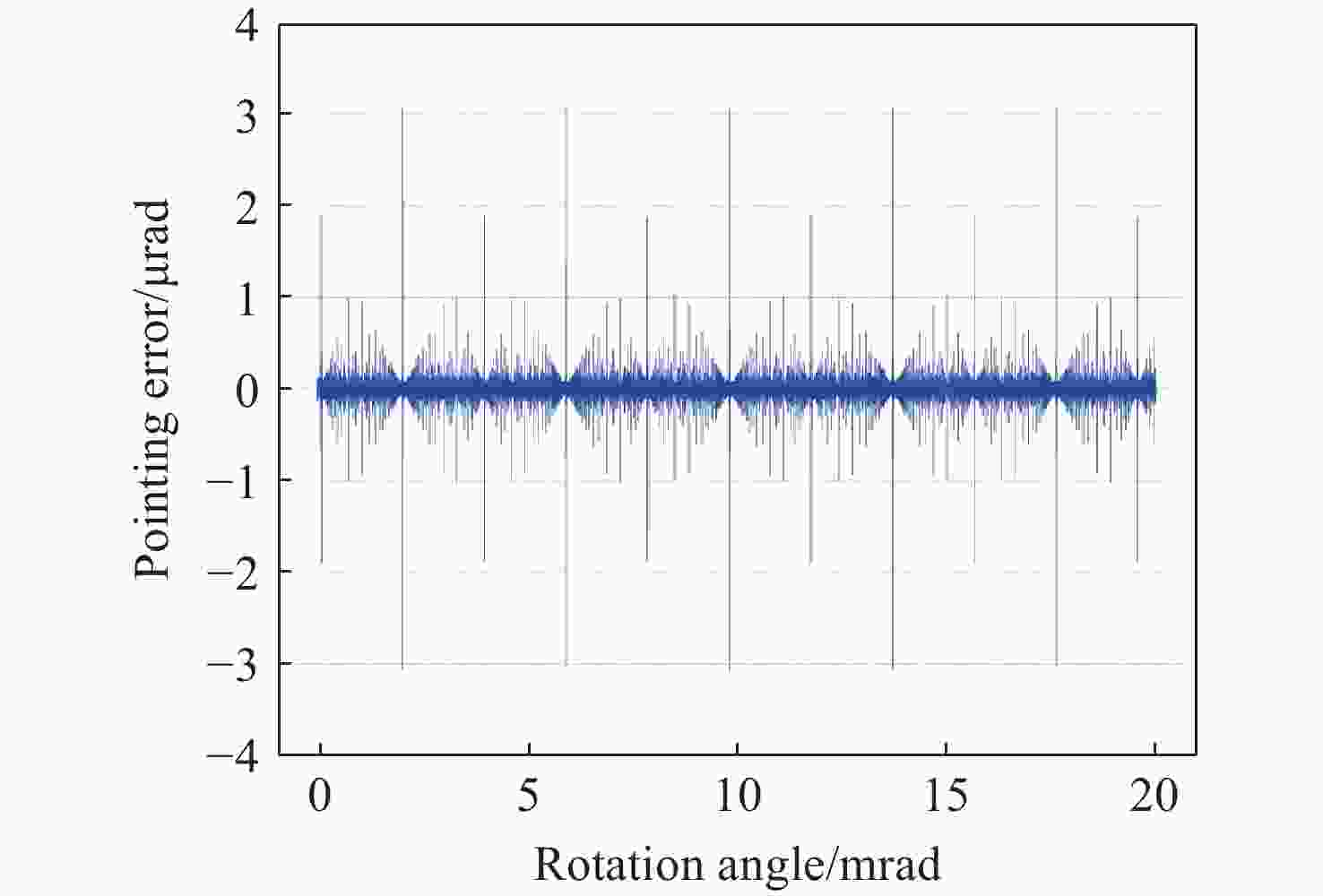
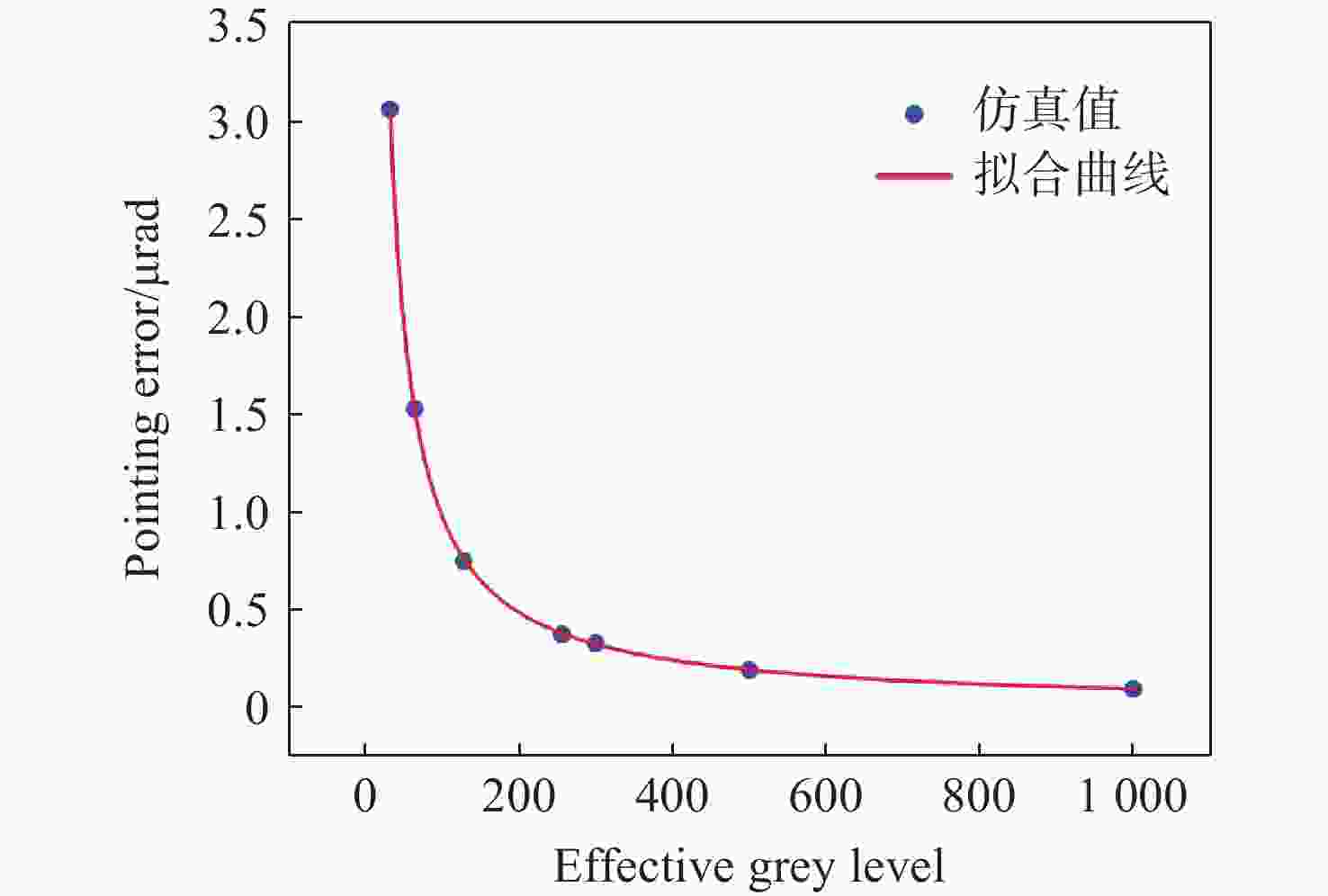
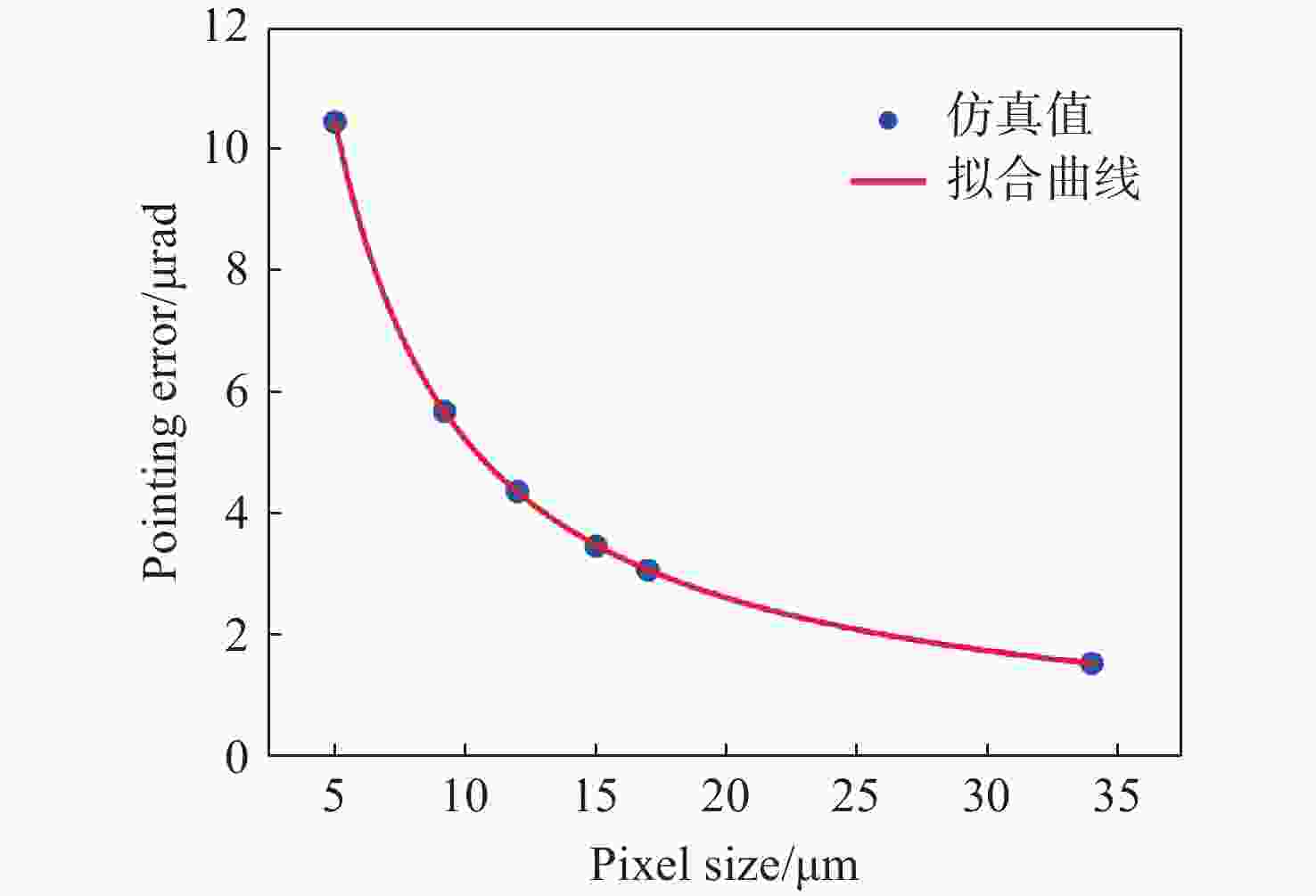
Research on pointing accuracy of liquid crystal phase array based on the variable period grating method
-
摘要:
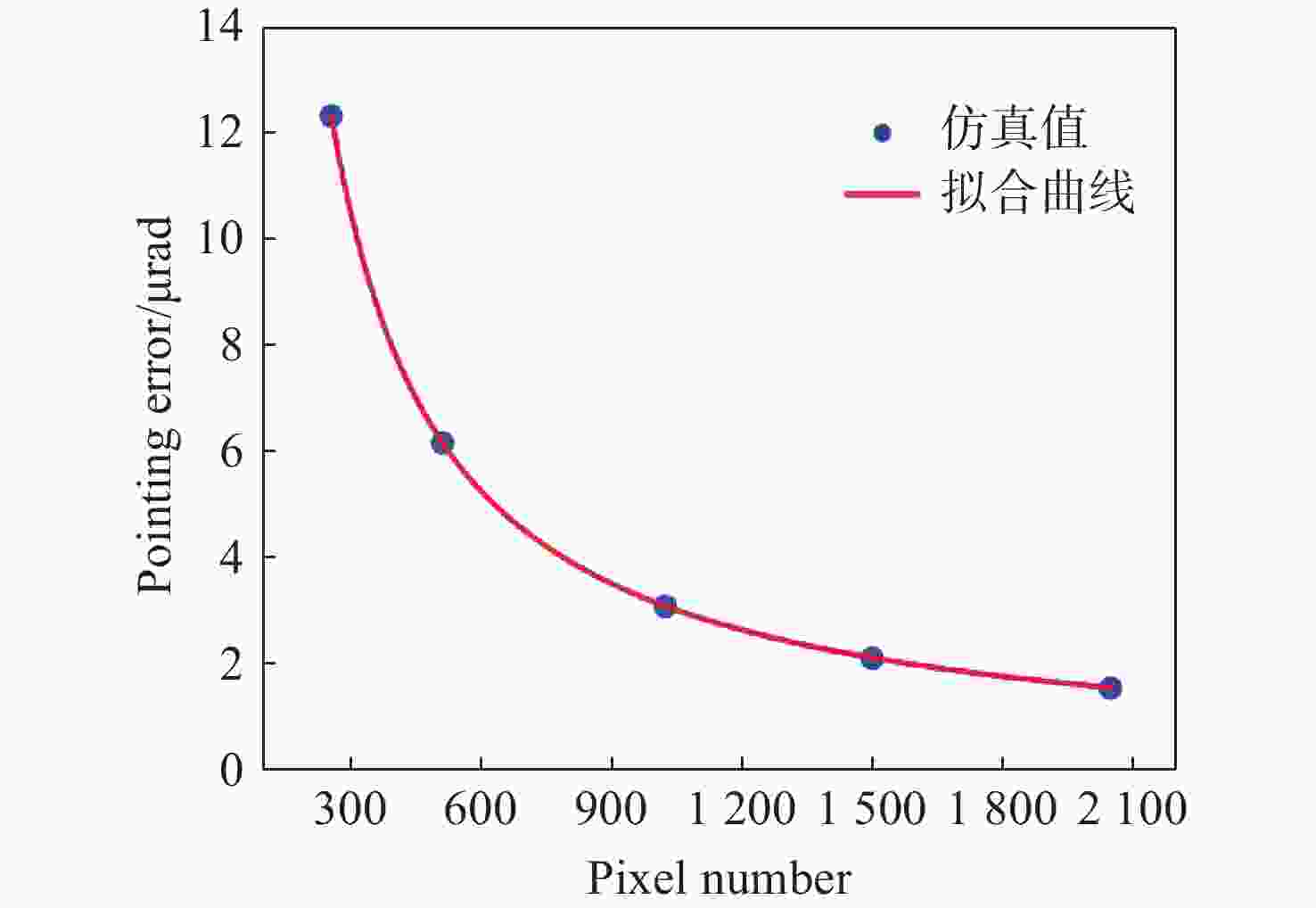
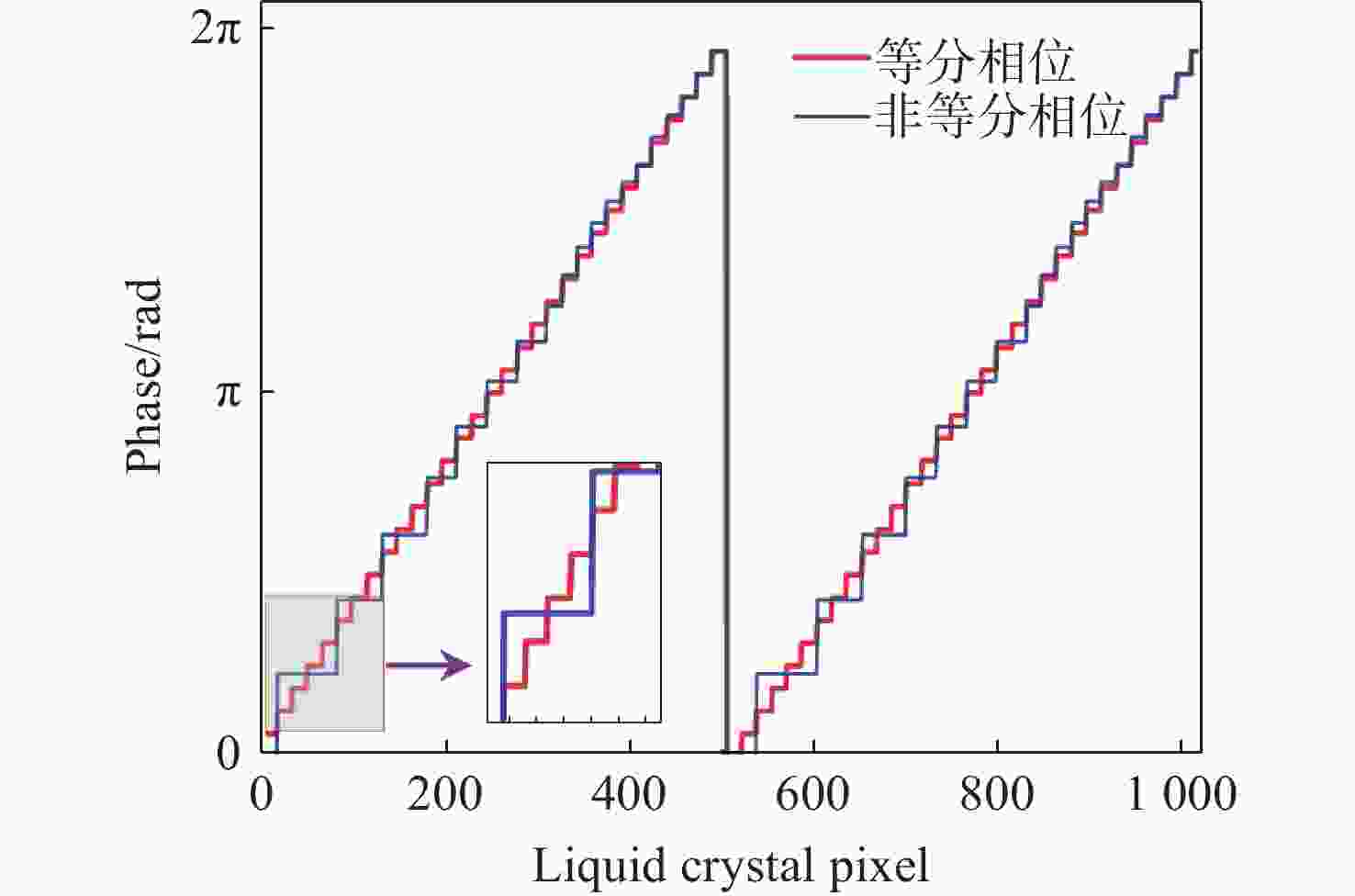
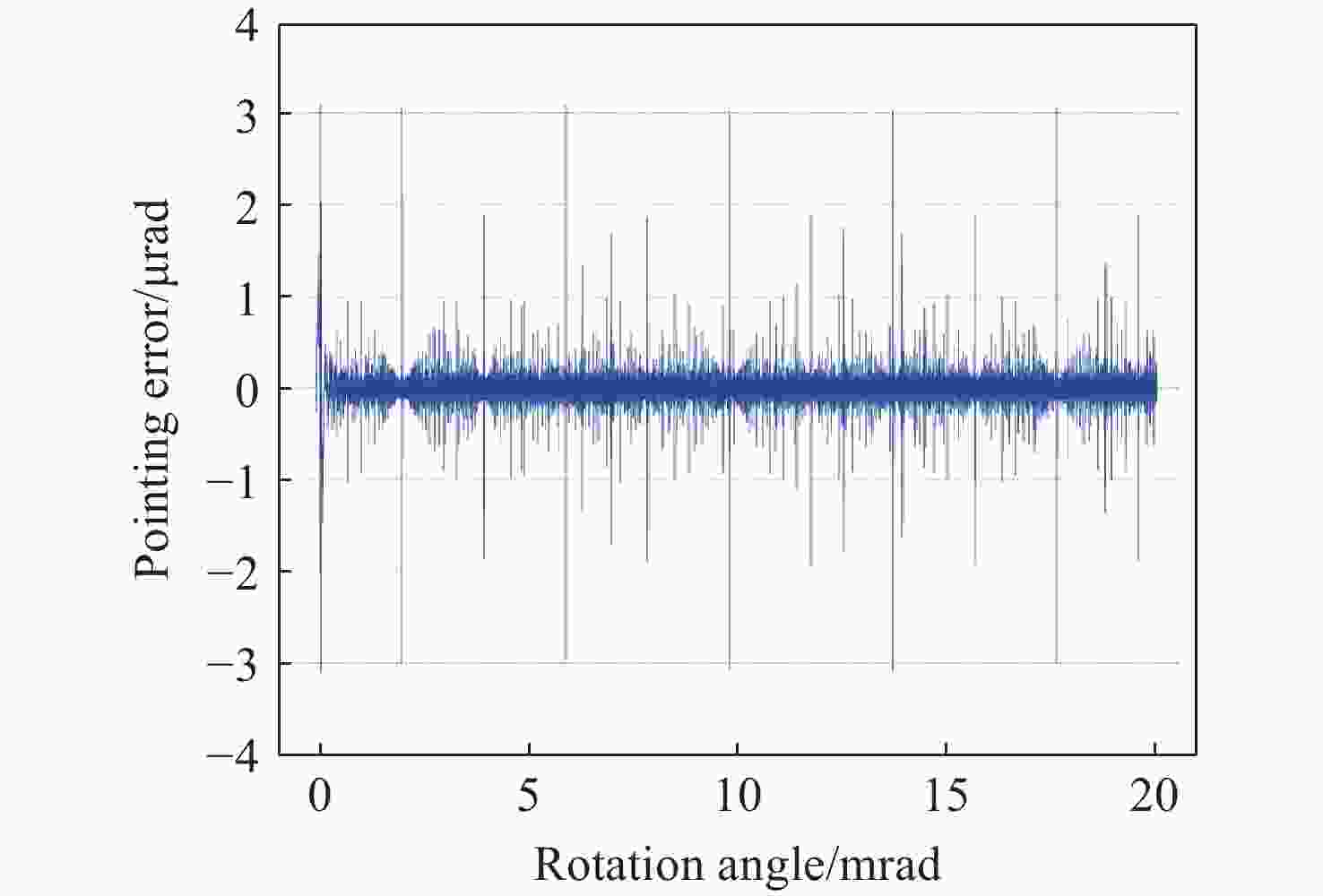
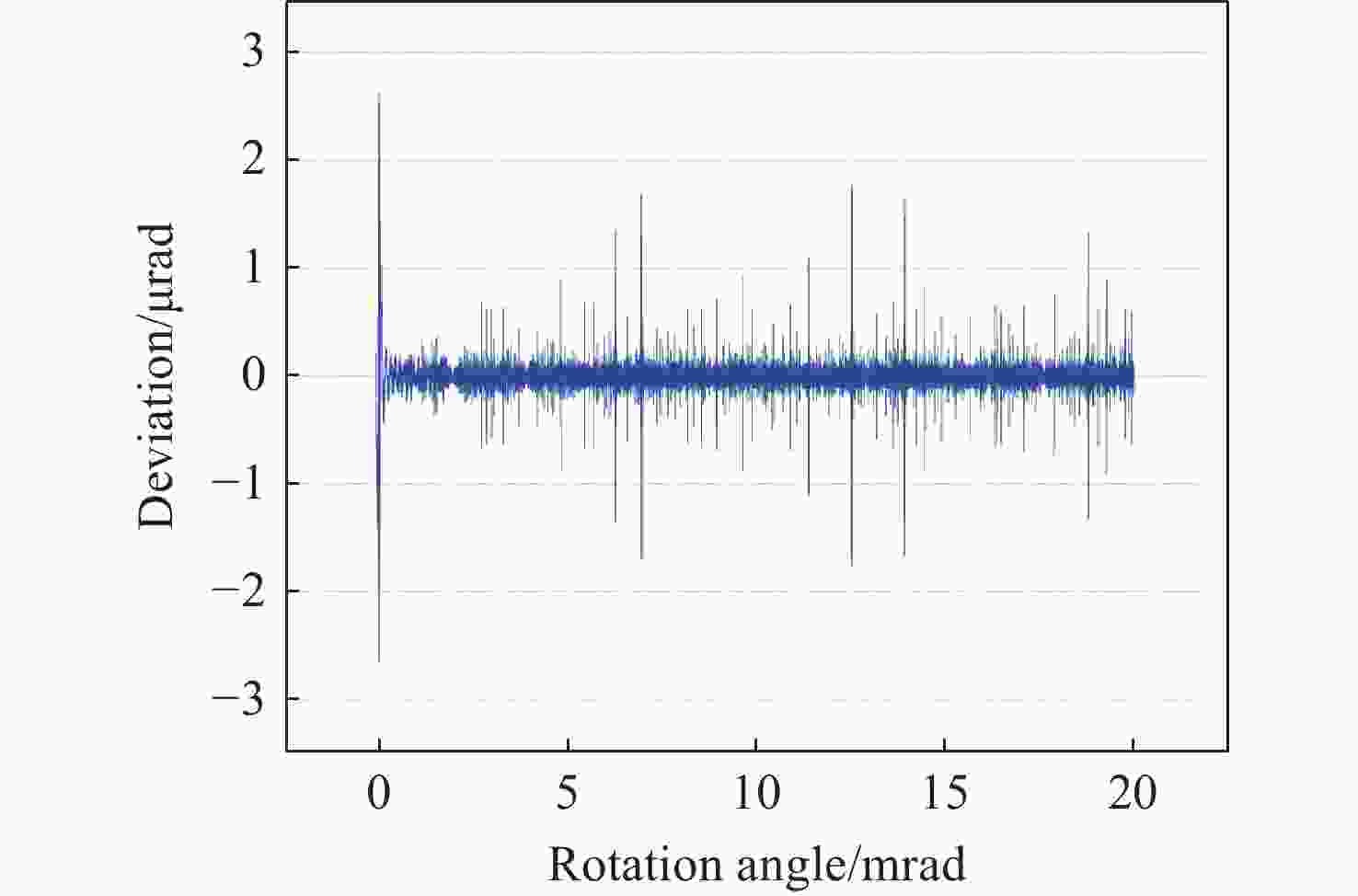
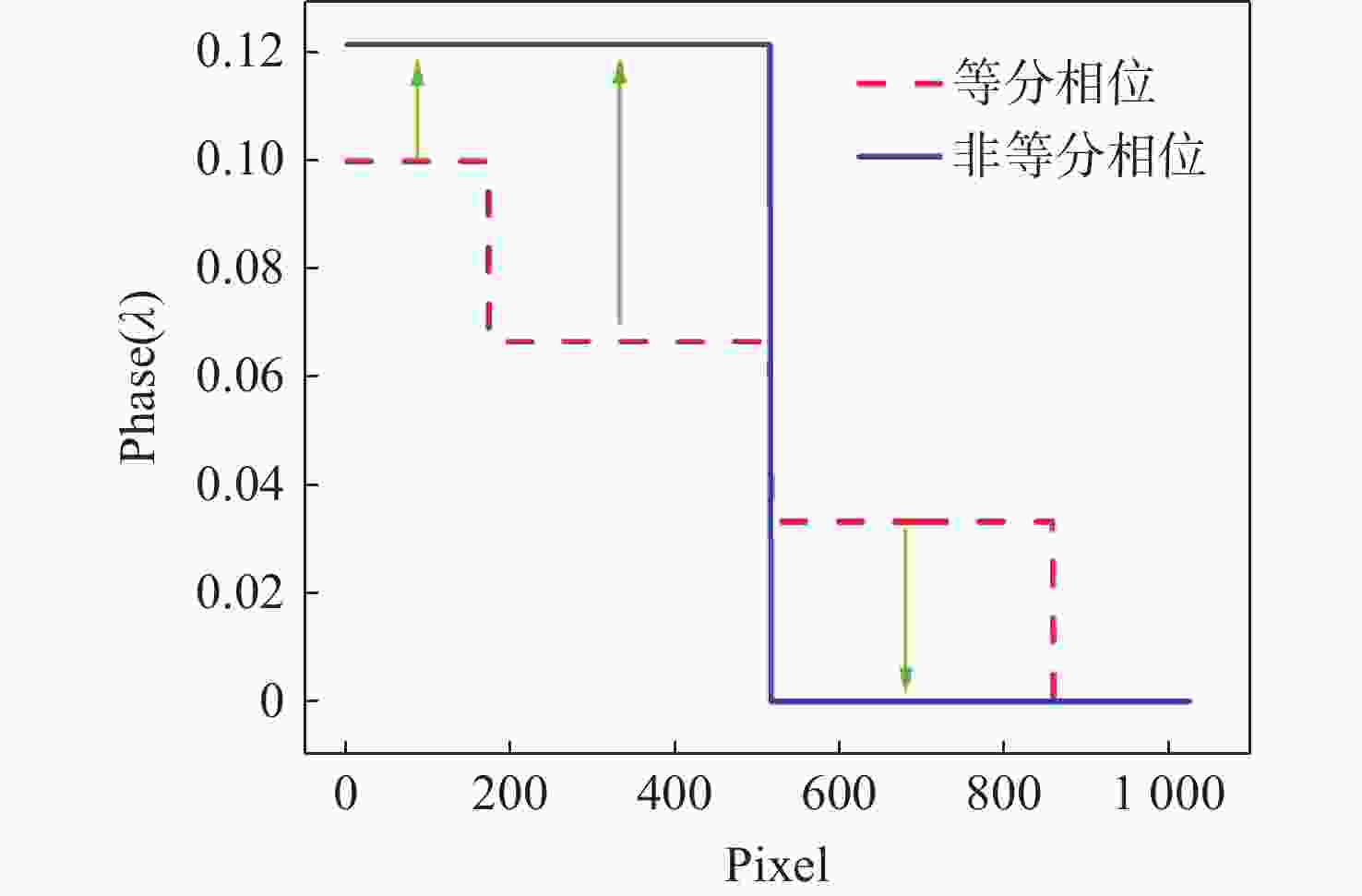
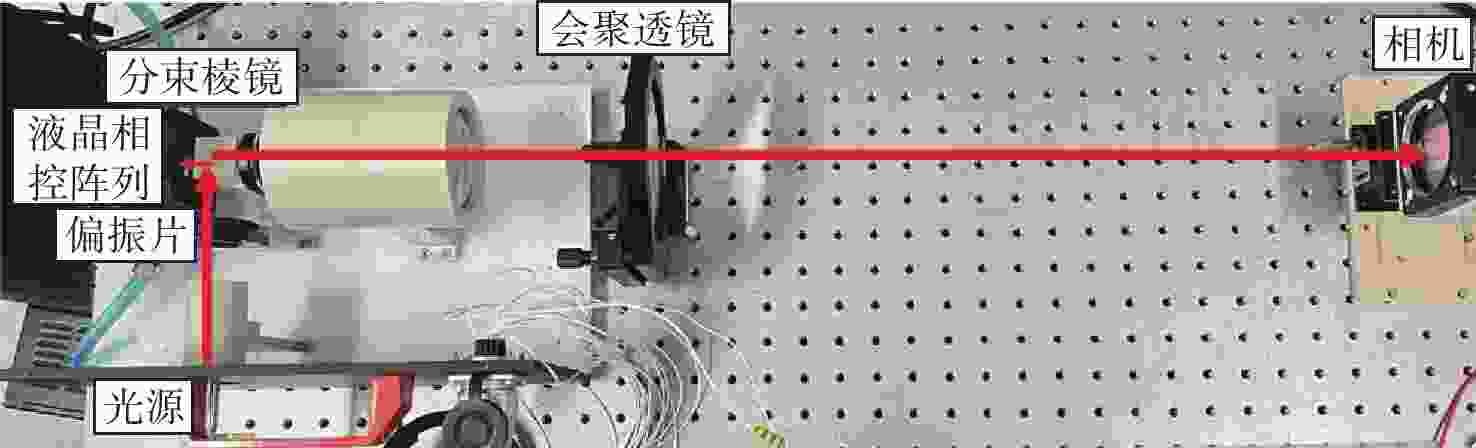
液晶光学相控阵被广泛应用于激光雷达、激光通信以及激光武器,进行激光光束的扫描控制。为了实现液晶相控阵的最优设计和激光光束高精度控制,本文重点研究了工作波长、像素数、像素尺寸及有效灰度数对光束指向精度的影响规律。首先,根据液晶相位调制原理,仿真分析了周期光栅法和变周期光栅法的有效扫描角度和衍射效率;然后,基于驱动电压灰度等分相位调制量,仿真分析了指向误差随工作波长、像素数、像素尺寸以及有效灰度数的变化规律,推导出多变量普适公式;接着,仿真分析了驱动电压灰度非等分相位调制量时的指向精度,并和等分相位调制量的结果进行对比分析;最后,实验验证了有效灰度数、像素数和指向误差的关系,初步证实了经验公式的有效性。本文的研究结果可为液晶相控阵的设计提供理论依据。
Abstract:Liquid crystal optical phase array (LC OPA) is widely used in lidar, laser communication and laser weapons to scan and control laser beams. In order to optimize the design of LC OPA and high-precision laser beam control, we study the influence of working wavelength, number of pixels, pixel size, and effective grey levels on beam pointing accuracy. Firstly, according to the liquid crystal phase modulation principle , the effective scanning angle and diffraction efficiency of the period grating and the variable period grating methods are simulated and analyzed. Secondly, assuming the phase modulation to be equally divided by the driving voltage, the variation law of the pointing error with the working wavelength, the number of pixels, the pixel size, and the effective grey levels is simulated and analyzed. The multivariable universal formula is also derived. Thirdly, the pointing accuracy of the nonuniform phase modulation is simulated, analyzed, and compared with the results of the uniform phase modulation. Finally, the relationship between the effective grey levels and the pointing error is verified by experiments, and the validity of the empirical formula is preliminarily confirmed. The research results can provide a theoretical basis for the design of LC OPA.
-
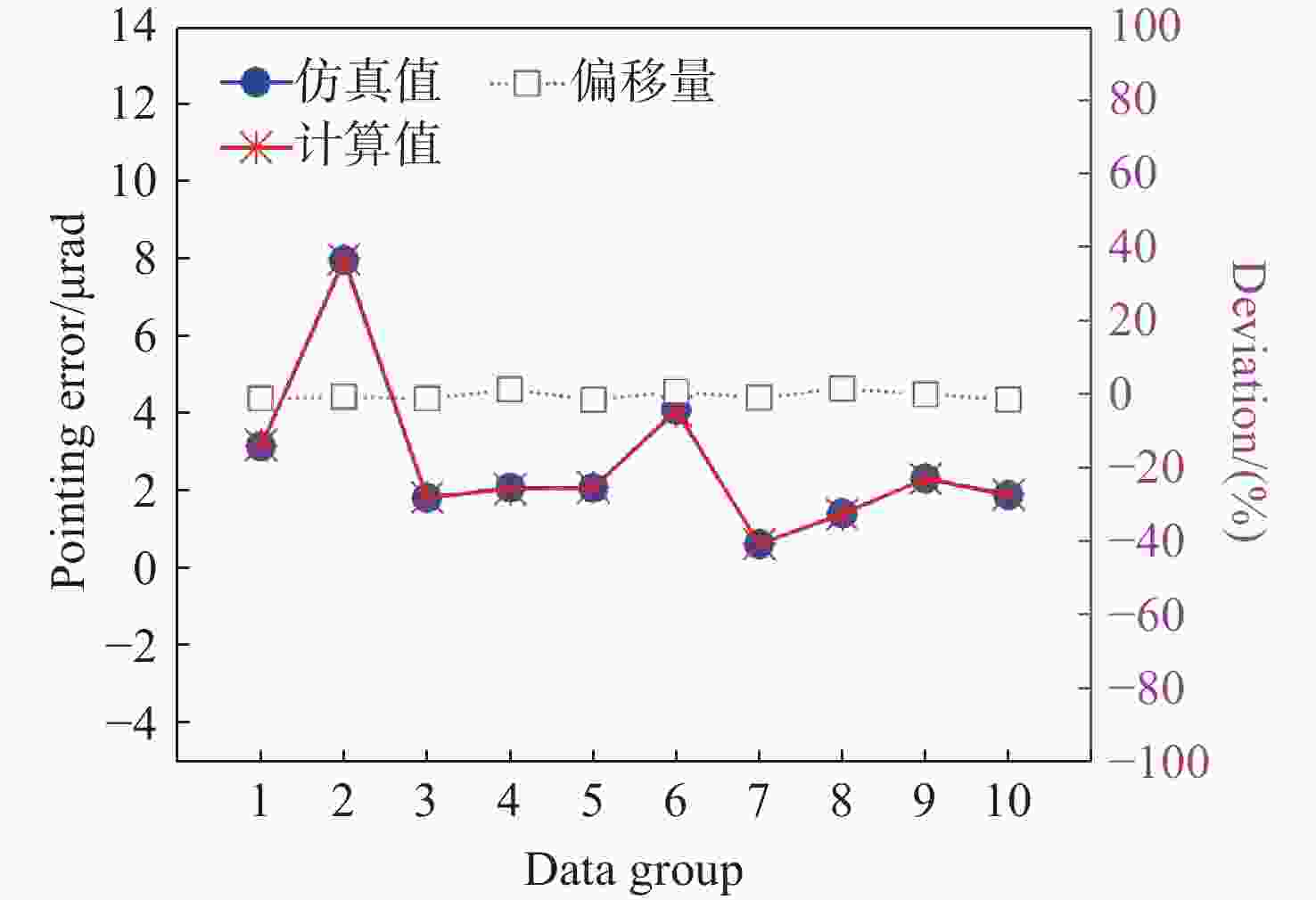
表 1 随机选取的液晶相控阵多变量数据
Table 1. Random selection data for the multivariable of liquid crystal phase array
组别 PS/μm PN NG λ/μm 1 10.0 1000 50 1.000 2 5.0 800 40 0.800 3 8.0 900 60 0.500 4 12.0 512 80 0.635 5 15.0 700 32 0.444 6 9.2 600 64 0.900 7 16.0 888 76 0.456 8 14.0 666 86 0.707 9 18.0 500 90 1.180 10 9.0 1200 100 1.300 -
[1] 王琦, 高旭峰, 张大伟, 等. 液晶光学相控阵技术的研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2021,58(17):1700007.WANG Q, GAO X F, ZHANG D W, et al. Research progress in liquid crystal optical phased array technology[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(17): 1700007. (in Chinese). [2] HE X X, LI M F, LIANG ZH Q, et al. A liquid crystal stackable phased array to achieve fast and precise nonmechanical laser beam deflection[J]. Optics Communications, 2022, 506: 127598. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2021.127598 [3] WANG CH M, WANG Q D, MU Q Q, et al. High-precision beam array scanning system based on liquid crystal optical phased array and its zero-order leakage elimination[J]. Optics Communications, 2022, 506: 127610. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2021.127610 [4] WANG Z SH, WANG CH Y, LIANG SH N, et al. Diffraction characteristics of a non-mechanical beam steering system with liquid crystal polarization gratings[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(5): 7319-7331. doi: 10.1364/OE.452397 [5] STOCKLEY J, SERATI S. Advances in liquid crystal beam steering[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5550: 32-39. doi: 10.1117/12.562595 [6] WANG X R, WU L, LI M, et al. Theoretical and experimental demonstration on grating lobes of liquid crystal optical phased array[J]. International Journal of Optics, 2016, 2016: 7175809. [7] WU L, WANG X R, XIONG C D, et al. Improved high order grating method to realize wide angle beam steering on liquid crystal optical phased array[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9795: 161-169. [8] MCMANAMON P F, DORSCHNER T A, CORKUM D L, et al. Optical phased array technology[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1996, 84(2): 268-298. doi: 10.1109/5.482231 [9] LINNENBERGER A, SERATI S, STOCKLEY J. Advances in optical phased array technology[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6304: 199-207. [10] WINKER B, MAHAJAN M, HUNWARDSEN M. Liquid crystal beam directors for airborne free-space optical communications[C]. SPIE, 2004: 1702-1708. [11] LIN Y H, MAHAJAN M, TABER D, et al. Compact 4 cm aperture transmissive liquid crystal optical phased array for free-space optical communications[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5892: 107-116. [12] 孔令讲, 朱颖, 宋艳, 等. 基于非周期闪耀光栅的液晶相控阵波控方法研究[J]. 光学学报,2011,31(1):0123001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201131.0123001KONG L J, ZHU Y, SONG Y, et al. A beam steering approach of liquid crystal phased array based on nonperiodic blazed grating[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2011, 31(1): 0123001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201131.0123001 [13] LIANG ZH Q, HUANG Y W, HE X X, et al. Four-access, 80 mm aperture all phase-controlled liquid crystal laser antenna[J]. Optical Engineering, 2022, 61(10): 105113. [14] TANG ZH H, WANG X R, HUANG Z Q, et al. Sub-aperture coherence method to realize ultra-high resolution laser beam deflection[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 335: 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2014.08.006 [15] HU L F, XUAN L, LIU Y J, et al. Phase-only liquid-crystal spatial light modulator for wave-front correction with high precision[J]. Optics Express, 2004, 12(26): 6403-6409. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.12.006403 [16] PENG Z H, LIU Y G, YAO L SH, et al. Improvement of the switching frequency of a liquid-crystal spatial light modulator with optimal cell gap[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(18): 3608-3610. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.003608 [17] WANG C, PENG Z, LIU Y, et al. Radial sub-aperture coherence method used to achieve beam steering with high precision and stability[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(5): 6331-6347. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.006331 [18] 刘伯晗, 张健. 纯相位空间光调制器动态控制光束偏转[J]. 中国激光,2006,33(7):899-902.LIU B H, ZHANG J. Dynamical laser beams steering with phase-only spatial light modulator[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2006, 33(7): 899-902. (in Chinese). [19] 徐林. 液晶光学相控阵相位延迟及衍射效率研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2008.XU L. Research on phase delay and diffraction efficiency of liquid crystal optical phased array[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2008. (in Chinese). [20] 张健, 徐林, 吴丽莹, 等. 液晶光学相控阵可编程光束偏转研究[J]. 光子学报,2008,37(8):1497-1502.ZHANG J, XU L, WU L Y, et al. Programmable beam steering based on liquid crystal optical phased array[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2008, 37(8): 1497-1502. (in Chinese). [21] 杜升平, 傅承毓, 黄永梅, 等. 一种液晶相位调制特性的测量方法[J]. 光子学报,2017,46(1):0105001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20174601.0105001DU SH P, FU CH Y, HUANG Y M, et al. A method of measure the liquid-crystal's modulating characteristic[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2017, 46(1): 0105001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20174601.0105001 [22] 杜升平, 黄永梅, 付承毓, 等. 基于相控阵雷达模型的液晶光束偏转波控方法研究[J]. 应用光学,2017,38(4):581-586.DU SH P, HUANG Y M, FU CH Y, et al. Liquid-crystal beam deflection wave control method based on phased array radar[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2017, 38(4): 581-586. (in Chinese). [23] 肖文奔, 黄永梅, 吴琼雁, 等. 基于Wollaston棱镜的大角度液晶光束偏转系统[J]. 光学技术,2012,38(5):588-592.XIAO W B, HUANG Y M, WU Q Y, et al. A wide-angle beam steering system based on Wollaston prisms[J]. Optical Technique, 2012, 38(5): 588-592. (in Chinese). [24] 范佳鑫, 王春阳, 张宁. 液晶相控阵指向精度影响因素分析及优化方法[J]. 长春理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,45(2):65-73.FAN J X, WANG CH Y, ZHANG N. Analysis of factors affecting the steering accuracy of liquid crystal phased array and optimization method[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 45(2): 65-73. (in Chinese). [25] 黄志伟, 王春阳, 彭丽华, 等. 基于蝙蝠算法的液晶光学相控阵波束优化[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2018,55(8):082303.HUANG ZH W, WANG CH Y, PENG L H, et al. Beam optimization of liquid crystal optical phased array based on bat algorithm[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(8): 082303. (in Chinese). [26] 王春阳, 李兰婷, 史红伟, 等. 基于液晶相控阵的光束偏转控制方法研究[J]. 液晶与显示,2018,33(10):857-863. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20183310.0857WANG CH Y, LI L T, SHI H W, et al. Beam deflection control method based on liquid crystal phased array[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2018, 33(10): 857-863. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20183310.0857 [27] BUCK J, SERATI S, HOSTING L, et al. Polarization gratings for non-mechanical beam steering applications[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8395: 159-164. [28] MCMANAMON P F. Agile nonmechanical beam steering[J]. Optics and Photonics News, 2006, 17(3): 24-29. doi: 10.1364/OPN.17.3.000024 [29] MCMANAMON P F, BOS P J, ESCUTI M J, et al. A review of phased array steering for narrow-band electrooptical systems[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2009, 97(6): 1078-1096. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2009.2017218 [30] 丁科, 亓波. 基于二维标量衍射的液晶光束偏转性能仿真[J]. 中国激光,2016,43(2):0205005. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0205005DING K, QI B. Beam steering performance simulation of liquid crystal spatial light modulator based on 2D scalar diffraction[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2016, 43(2): 0205005. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0205005 [31] 郭弘扬, 杜升平. 驱动电压对向列型液晶调制相位的影响[J]. 国外电子测量技术,2017,36(12):28-31.GUO H Y, DU SH P. Influence of driving voltage on phase modulation of nematic liquid crystal[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2017, 36(12): 28-31. (in Chinese). [32] 汪相如, 黄子强. 液晶光学相控阵组件扫描精度分析研究[J]. 光电技术应用,2017,32(4):33-37.WANG X R, HUANG Z Q. Analysis and research on liquid crystal optical phase array component steering presicion[J]. Electro-Optic Technology Application, 2017, 32(4): 33-37. (in Chinese). [33] 王承邈. 基于液晶光学相控阵的高精度光束指向控制技术[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2021.WANG CH M. High precision beam pointing control technology based on liquid crystal optical phased array[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2021. (in Chinese). [34] 曹召良, 穆全全, 胡立发, 等. 液晶波前校正器位相调制非线性及闭环校正研究[J]. 液晶与显示,2008,23(2):157-162.CAO ZH L, MU Q Q, HU L F, et al. Nonlinear phase modulation of liquid crystal wavefront corrector and closed loop correction[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2008, 23(2): 157-162. (in Chinese). [35] 刘禹彤, 曹宗新, 李子凡, 等. 基于液晶偏振光栅的大口径激光光束扫描系统[J]. 应用光学,2024,45(3):557-567. doi: 10.5768/JAO202445.0310010LIU Y T, CAO Z X, LI Z F, et al. Large-aperture laser beam scanning system based on liquid crystal polarization grating[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2024, 45(3): 557-567. (in Chinese). doi: 10.5768/JAO202445.0310010 -





 下载:
下载: