Scintillation index analysis of radial Gaussian vortex beam array propagation in the atmosphere
-
摘要:
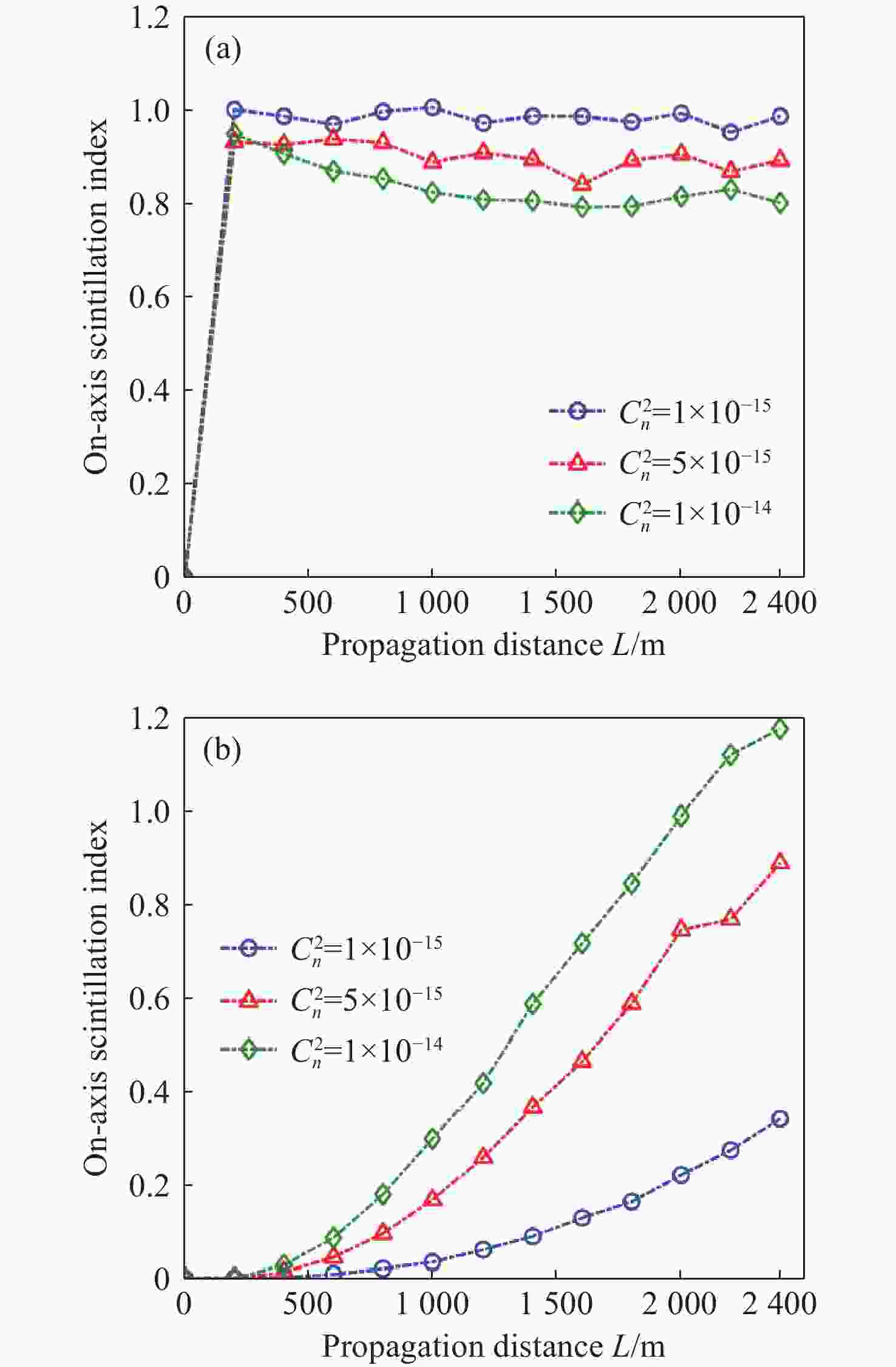
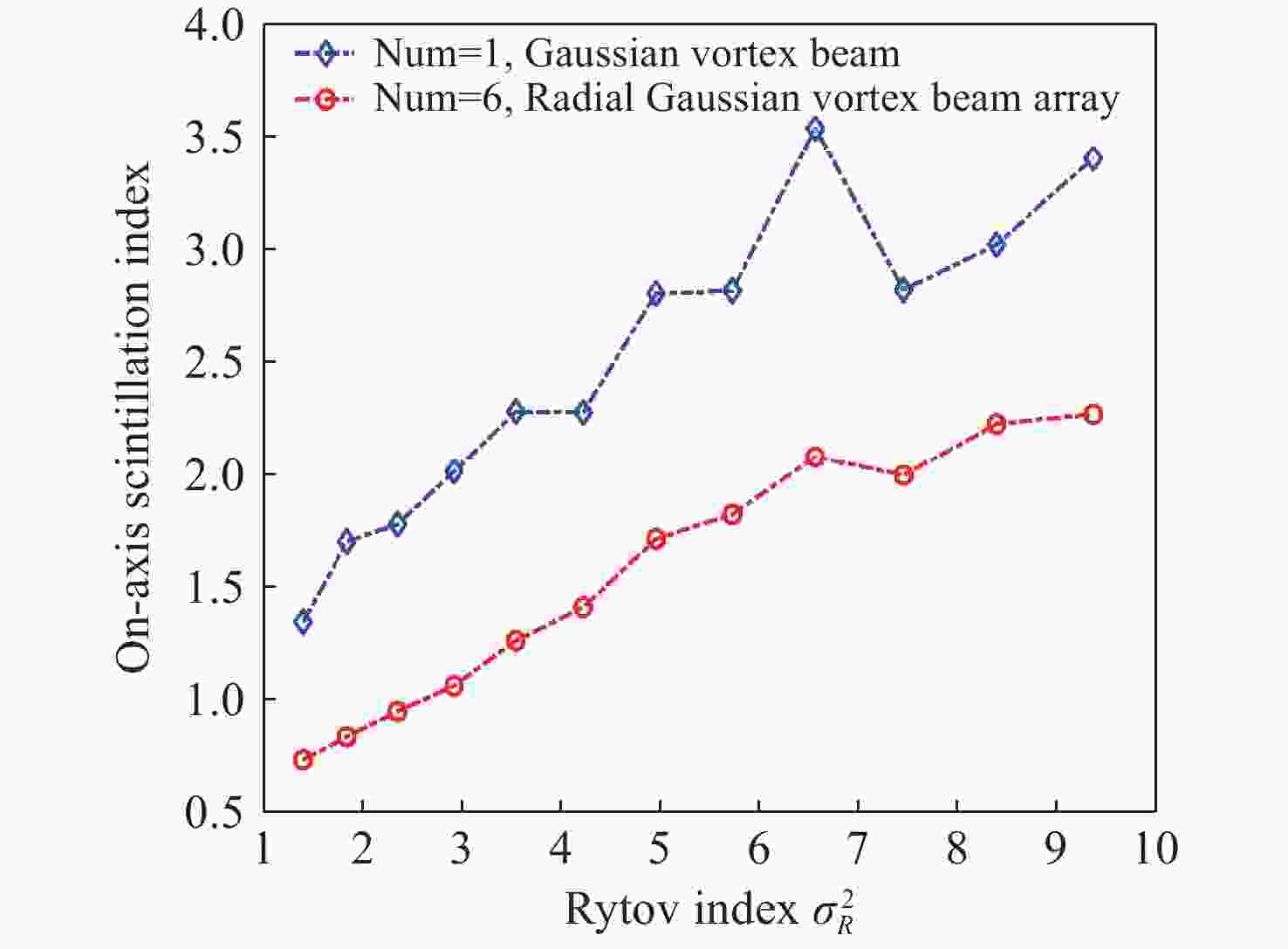
涡旋光束阵列在自由空间光通信领域有很大的应用价值。本文采用多相位屏模拟大气湍流,研究了径向高斯涡旋光束阵列在大气湍流环境中传输的光场演化过程和轴上闪烁特性,分析了不同初始光束参数对径向高斯涡旋光束阵列的轴上闪烁指数的影响,并将其与单束高斯涡旋光束的轴上闪烁指数进行对比。研究结果表明:在弱湍流区域,rytov指数小于0.5时,单束高斯涡旋光束的轴上闪烁指数一直保持在小于1的数值区域,远小于径向高斯涡旋光束的轴上闪烁指数;而在中等强度湍流区域,径向高斯涡旋光束阵列的轴上闪烁指数小于单束高斯涡旋光束的轴上闪烁指数。此外,还发现径向高斯涡旋光束阵列的轴上闪烁指数会随着轨道角动量值的减小和径向阵列半径的增大而减小。研究结果对于大气湍流环境下的涡旋光通信具有一定的理论意义和应用价值。
-
关键词:
- 径向高斯涡旋光束阵列 /
- 轴上闪烁指数 /
- 相位屏仿真
Abstract:Beam arrays have great application value in free-space optical communication. In this paper, the light intensity evolution and the on-axis scintillation index of radial Gaussian vortex beam arrays propagating through atmospheric turbulence are analyzed using multi-phase screen simulation. The effect of initial beam parameters on the on-axis scintillation index of radial Gaussian vortex beam arrays is studied, and the on-axis scintillation index of radial Gaussian vortex beam arrays is compared with that of a single Gaussian vortex beam. The results indicate that in the weak fluctuation regime and when the rytov index is less than 0.5, the on-axis scintillation index of Gaussian vortex beams remains within a numerical range of less than 1, while the on-axis scintillation index of radial Gaussian vortex beam arrays is around 1. In the medium fluctuation regime, the on-axis scintillation index of the radial Gaussian vortex beam arrays is smaller than that of a single Gaussian vortex beam. The on-axis scintillation index of radial Gaussian vortex beam arrays decreases with the decrease of orbital angular momentum and the increase of radial array radius. The research results hold theoretical significance and application value for vortex optical communication in turbulent atmospheric environments.
-
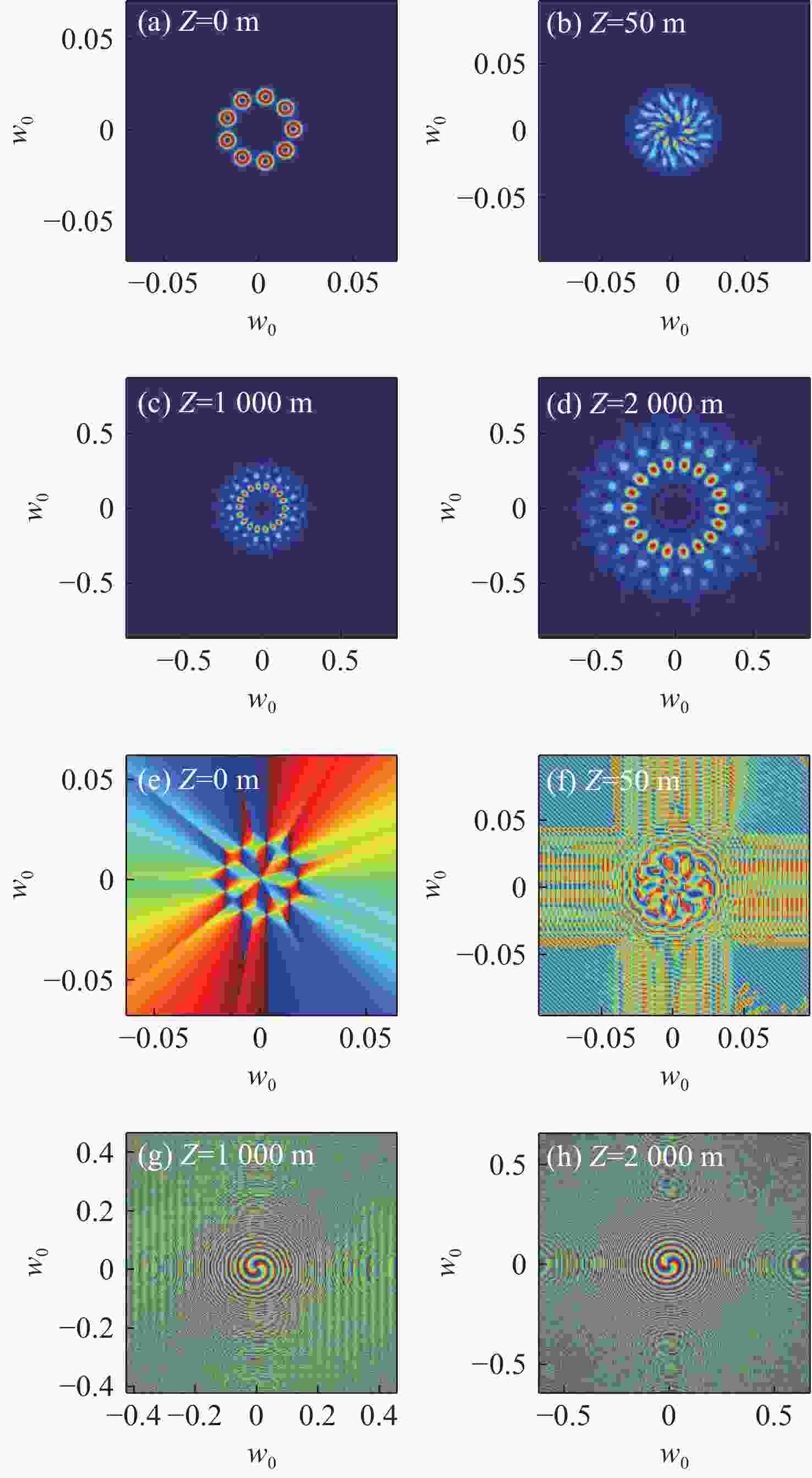
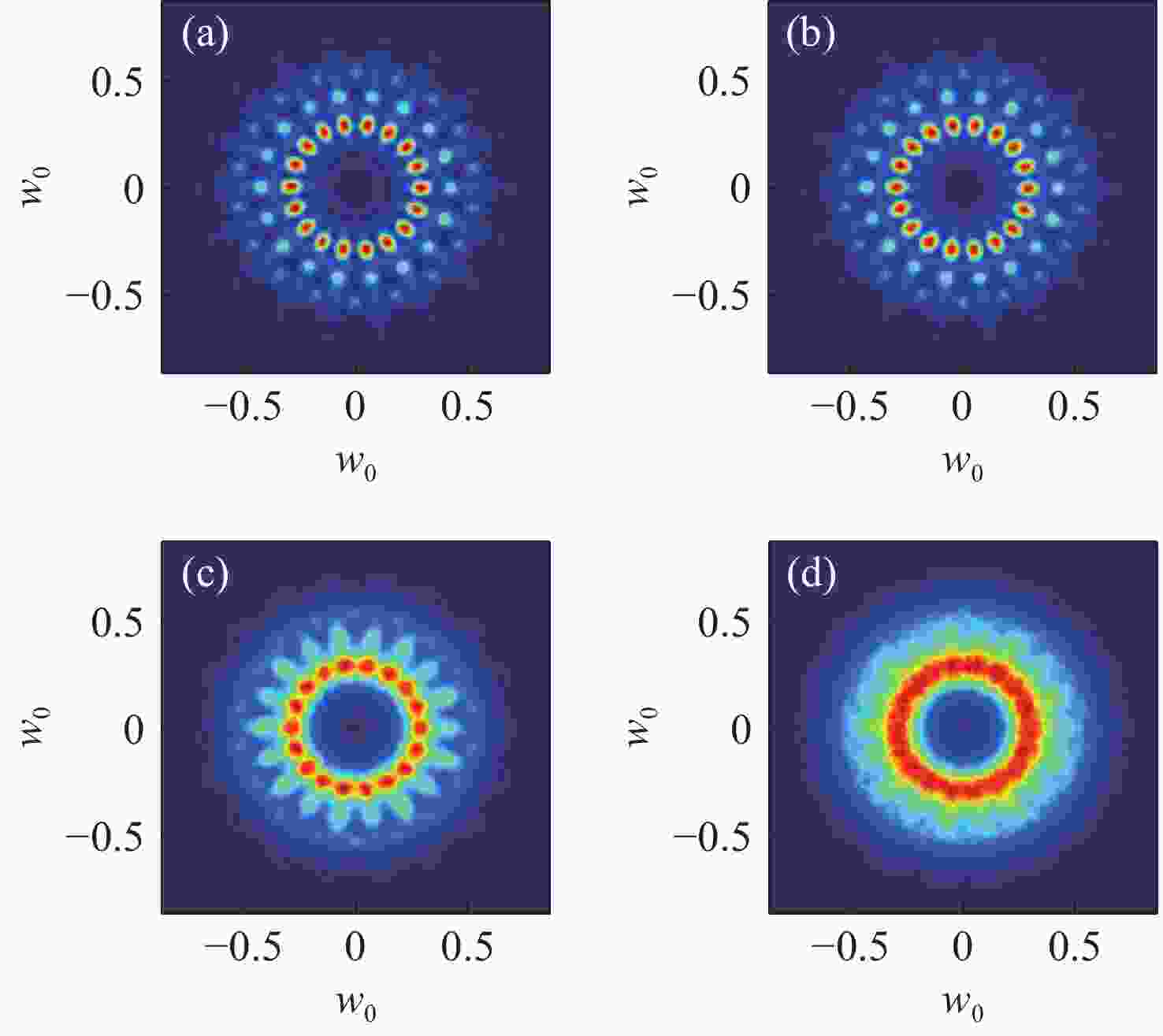
图 4 不同折射率结构常数
$C_n^2$ 下RGVBA的光强分布($l = 2$ ,$Num = 9$ ,Z=2000 m)。(a)$C_n^2 = 0$ ;(b)$ C_n^2 = $ $ 5 \times {10^{ - 15}}{m^{{{ - 2} / 3}}} $ ;(c)$ C_n^2 = 5 \times {10^{ - 14}}{m^{{{ - 2} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{ - 2} 3}} \right. } 3}}} $ ;(d)$ C_n^2 = 1 \times $ $ {10^{ - 13}}{m^{{{ - 2} / 3}}} $ Figure 4. The intensity distribution of RGVBA under different refractive index structure constants
$C_n^2$ ($l = 2$ ,$Num = $ $ 9$ , Z=2000 m). (a)$C_n^2 = 0$ ; (b)$ C_n^2 =5 \times {10^{ - 15}}{m^{{{ - 2} / 3}}} $ ; (c)$ C_n^2 = 5 \times {10^{ - 14}}{m^{{{ - 2} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{ - 2} 3}} \right. } 3}}} $ ; (d)$ C_n^2 = 1 \times {10^{ - 13}}{m^{{{ - 2} /3}}} $ 图 7 相同湍流条件下不同初始光束参数的RGVBA轴上闪烁指数值随子光束数目(Num)的变化情况。 (a)不同OAM值;(b)不同径向阵列半径
${r_0}$ Figure 7. Under the same turbulence conditions, the on-axis scintillation index values of RGVBA with different initial beam parameters as a function of the number of beamlets (Num). (a) With different OAM values; (b) with different radial array radii
${r_0}$ 表 1 相位屏仿真参数
Table 1. Phase screen simulation parameters
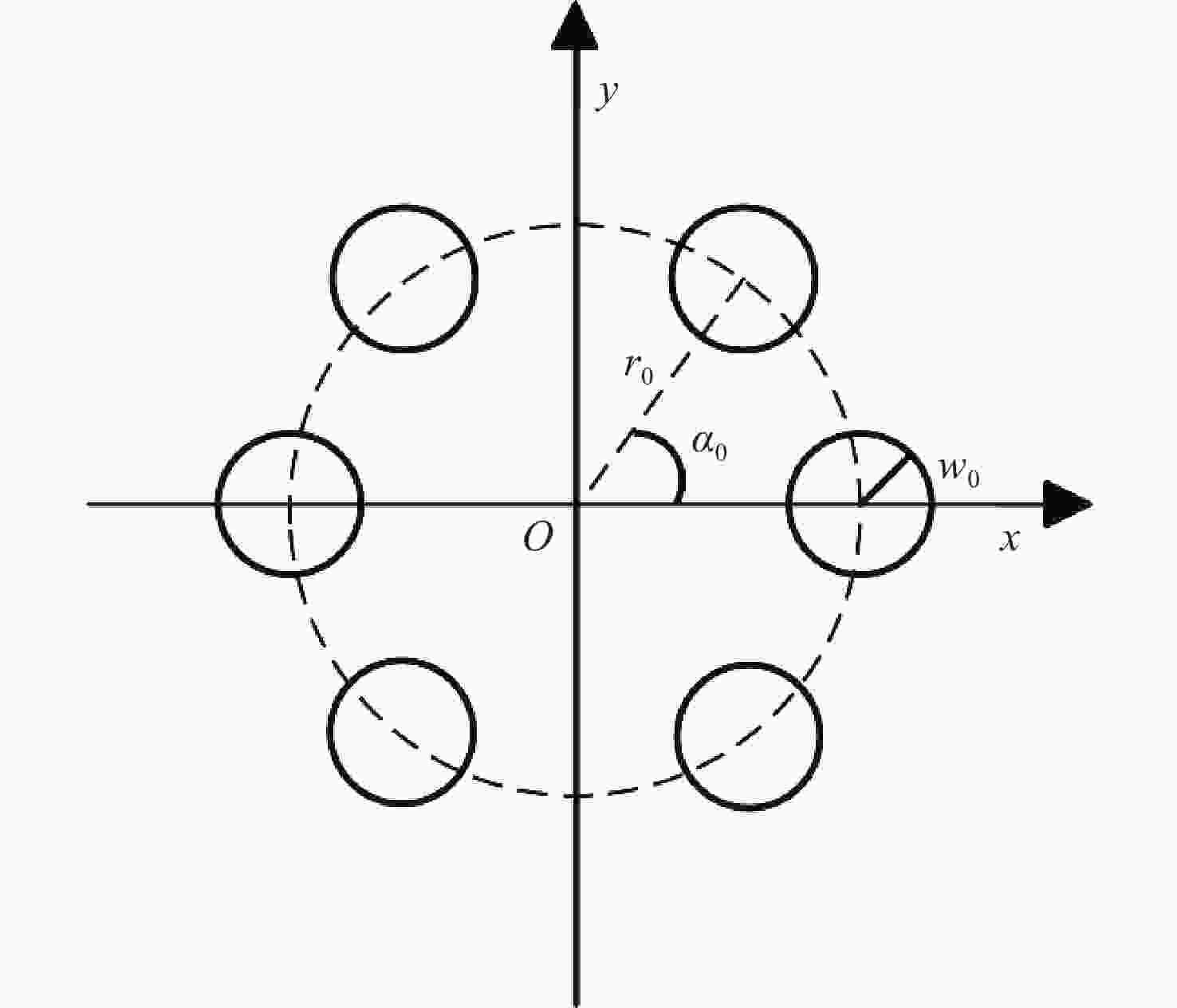
采样网格$N$ 采样间隔$\Delta x$/mm 相位屏间隔$\Delta Z$/m 湍流内尺度${l_0}$/m 湍流外尺度${L_0}$/m 1024 1.7 200 0.01 10 波长$\lambda $/nm OAM值$l$ 子光束半径${w_0}$/mm 阵列半径${r_0}$/cm 子光束数目$Num$ 1550 1~3 3 1.8 6 表 2 不同折射率结构常数和传输距离对应的rytov指数
Table 2. The rytov index corresponding to each refractive index structure constant and transmission distance
折射率结构常数$C_n^2$ 传输距离范围$Z$ rytov指数$\sigma _R^2$ $1 \times {10^{ - 15}}{m^{{{ - 2} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{ - 2} 3}} \right. } 3}}}$ 200~ 2400 m0.0010 ~0.0991 $5 \times {10^{ - 15}}{m^{{{ - 2} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{ - 2} 3}} \right. } 3}}}$ 200~ 2400 m0.0052 ~0.4953 $1 \times {10^{ - 14}}{m^{{{ - 2} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{ - 2} 3}} \right. } 3}}}$ 200~ 2400 m0.0104 ~0.9905 -
[1] ALLEN L, PADGETT M J, BABIKER M. IV The orbital angular momentum of light[J]. Progress in Optics, 1999, 39: 291-372. [2] 郭忠义, 龚超凡, 刘洪郡, 等. OAM光通信技术研究进展[J]. 光电工程,2020,47(3):190593.GUO ZH Y, GONG CH F, LIU H J, et al. Research advances of orbital angular momentum based optical communication technology[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2020, 47(3): 190593. (in Chinese). [3] WANG SH L, XU J P, YANG Y P, et al. Optimization of wireless optical communication using perfect vortex beam[J]. Optics Communications, 2024, 556: 130258. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2023.130258 [4] REN Y X, LI L, WANG ZH, et al. Orbital angular momentum-based space division multiplexing for high-capacity underwater optical communications[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 33306. doi: 10.1038/srep33306 [5] ZHONG W H, LIN ZH ZH, WU L X, et al. Spatial and mode selective switch for orbital angular momentum mode division multiplexing[J]. Optics Letters, 2024, 49(11): 3006-3009. doi: 10.1364/OL.515916 [6] MA R, LUO K H, POKHAREL S, et al. Orbital-angular-momentum-dependent speckles for spatial mode sorting and demultiplexing[J]. Optica, 2024, 11(5): 595-605. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.523846 [7] KOTLYAR V V, KOVALEV A A, PORFIREV A P. Vortex Laser Beams[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2018. [8] 高春清, 付时尧. 涡旋光束[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2019.GAO CH Q, FU SH Y. Vortex Beams[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2019. (in Chinese). [9] DEDO M I, WANG Z K, GUO K, et al. Retrieving performances of vortex beams with GS algorithm after transmitting in different types of turbulences[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(11): 2269. doi: 10.3390/app9112269 [10] REN Y X, WANG ZH, XIE G D, et al. Atmospheric turbulence mitigation in an OAM-based MIMO free-space optical link using spatial diversity combined with MIMO equalization[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(11): 2406-2409. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.002406 [11] 杜芊芊, 韦宏艳, 史晨寅, 等. 基于深度学习的复合贝塞尔高斯光束大气湍流效应补偿[J]. 中国激光,2023,50(22):2206002. doi: 10.3788/CJL221444DU Q Q, WEI H Y, SHI CH Y, et al. Atmospheric turbulence compensation based on deep learning to correct distorted composite Bessel-Gaussian beam[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50(22): 2206002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL221444 [12] 蒋金洋, 刘晓云, 陈永豪, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的涡旋光束拓扑荷数估算[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2024,61(13):1326001.JIANG J Y, LIU X Y, CHEN Y H, et al. Topological charge estimation of vortex beams based on convolutional neural network[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(13): 1326001. (in Chinese). [13] 卢芳, 赵丹, 刘春波, 等. 非Kolmogorov大气湍流对高斯阵列光束光强闪烁的影响[J]. 红外与激光工程,2016,45(7):0711001. doi: 10.3788/irla201645.0711001LU F, ZHAO D, LIU CH B, et al. Influence of non-Kolmogorov atmospheric turbulence on scintillation of Gaussian array beams[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2016, 45(7): 0711001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/irla201645.0711001 [14] LIU H L, LÜ Y F, XIA J, et al. Radial phased-locked partially coherent flat-topped vortex beam array in non-Kolmogorov medium[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(17): 19695-19712. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.019695 [15] LIU Y X, ZHANG K N, CHEN Z Y, et al. Scintillation index of double vortex beams in turbulent atmosphere[J]. Optik, 2019, 181: 571-574. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.12.046 [16] 骆传凯, 卢芳, 苗志芳, 等. 径向阵列涡旋光束在大气中的传输与扩展[J]. 光学学报,2019,39(6):0601004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0601004LUO CH K, LU F, MIAO ZH F, et al. Propagation and spreading of radial vortex beam array in atmosphere[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(6): 0601004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0601004 [17] LUO CH K, LU F, HAN X E. Propagation and evolution of rectangular vortex beam array through atmospheric turbulence[J]. Optik, 2020, 218: 164913. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164913 [18] 侯政诚, 张明明, 白胜闯, 等. 一维阵列涡旋光束在海面大气中的传输特性[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(2):300-311. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0094HOU ZH CH, ZHANG M M, BAI SH CH, et al. Propagation properties of one-dimensional array vortex beams in a marine atmosphere[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(2): 300-311. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0094 [19] 王明军, 张妍. 阵列涡旋光束在不稳定分层海洋中的远距离传输[J]. 中国激光,2024,51(8):0806001. doi: 10.3788/CJL231060WANG M J, ZHANG Y. Long-distance transmission of vortex beam arrays in unstable stratified ocean[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51(8): 0806001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL231060 [20] 刁鲁欣, 王明军, 黄朝军, 等. 海洋湍流下双拉盖尔-高斯涡旋光束的闪烁指数与误码率研究[J]. 光子学报,2024,53(2):0201002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20245302.0201002DIAO L X, WANG M J, HUANG CH J, et al. Scintillation index and bit error rate of double Laguerre-Gaussian vortex beams under ocean turbulence[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2024, 53(2): 0201002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20245302.0201002 [21] SHISHTER Y M, ALI F H, YOUNG R C. Scintillation and bit error rate analysis of zero-order Bessel–Gauss beams in atmospheric turbulence based on the extended Rytov theory[J]. Optical Engineering, 2023, 63(4): 041205. [22] XU Y, XU Y G. Scintillation index and bit error rate of partially coherent twisted Gaussian beams in turbulent atmosphere[J]. Optical and Quantum Electronics, 2023, 55(6): 519. doi: 10.1007/s11082-023-04766-0 [23] BAYKAL Y, EYYUBOǦLU H T. Scintillation index of flat-topped Gaussian beams[J]. Applied Optics, 2006, 45(16): 3793-3797. doi: 10.1364/AO.45.003793 [24] ZHANG G, WANG J, WANG L, et al. Scintillation analysis of pseudo-Bessel-Gaussian Schell-mode beams propagating through atmospheric turbulence with wave optics simulation[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2018, 100: 139-144. [25] AKCAN C I, BAYRAKTAR M, ELMABRUK K. Analysis of finite energy Fresnel Bessel beams scintillation level in turbulent communication links[J]. Physica Scripta, 2024, 99(6): 065505. doi: 10.1088/1402-4896/ad40db [26] EYYUBOĞLU H T, BAYKAL Y, CAI Y. Scintillations of laser array beams[J]. Applied Physics B, 2008, 91(2): 265-271. doi: 10.1007/s00340-008-2966-x [27] YUAN Y SH, CAI Y J. Scintillation index of a flat-topped beam array in a weakly turbulent atmosphere[J]. Journal of Optics, 2011, 13(12): 125701. doi: 10.1088/2040-8978/13/12/125701 [28] 牛超君. 阵列光束在湍流中的传输及合成光束自适应优化整形[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2019.NIU CH Q. Propagation characteristics of array beams through turbulence and adaptive beam shaping[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2019. (in Chinese). [29] 黎芳, 刘慧. 部分相干异常涡旋光束在大气湍流中的传输特性[J]. 激光与红外,2020,50(1):9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2020.01.002LI F, LIU H. Propagation of partially coherent anomalous vortex beams through turbulent atmosphere[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2020, 50(1): 9-12. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2020.01.002 -







 下载:
下载: