Research progress in the phenomenon of exceptional point on passive non-Hermitian metasurfaces
-
摘要:
在非厄密系统中,调节系统的增益或损耗可以使系统状态从PT对称向PT对称破缺转变,转变过程中存在一个特殊的状态转变点,使得系统本征值和本征态同时简并,该点称为奇异点。奇异点结合超构表面产生了许多有趣的光学现象:不对称传输、拓扑相位、非厄密趋肤效应等。然而引入增益的有源超构表面在实验上很难实现,因此利用系统损耗构建虚拟增益的无源超构表面成为非厄密研究的有力武器。本文将从无源非厄密超构表面奇异点的理论模型、研究进展、具体应用和实验设计4个方面进行综述,并对该领域未来的发展方向进行展望。
Abstract:In non-Hermitian systems, controlling the gain or loss of the system can enable the system state transition from PT-symmetry to broken PT-symmetry. This transition leads to a special point known as the exceptional point, where the system eigenvalues and eigenstates become simultaneously degenerate. When combined with metasurfaces, the exceptional point leads to various intriguing optical phenomena, such as asymmetric transmission, exceptional topological phase, and the non-Hermitian skinning effect. However, active metasurfaces introducing gains are difficult to realize experimentally. Therefore, designing passive metasurfaces using equivalent gains through loss becomes a powerful tool in non-Hermitian research. In this paper, we review the theoretical models, research progress, specific applications, and experimental design in the study of the exceptional point on passive non-Hermitian metasurfaces and look forward to the future direction of this field.
-
Key words:
- exceptional point /
- non-hermitian /
- metasurfaces /
- passive systems
-
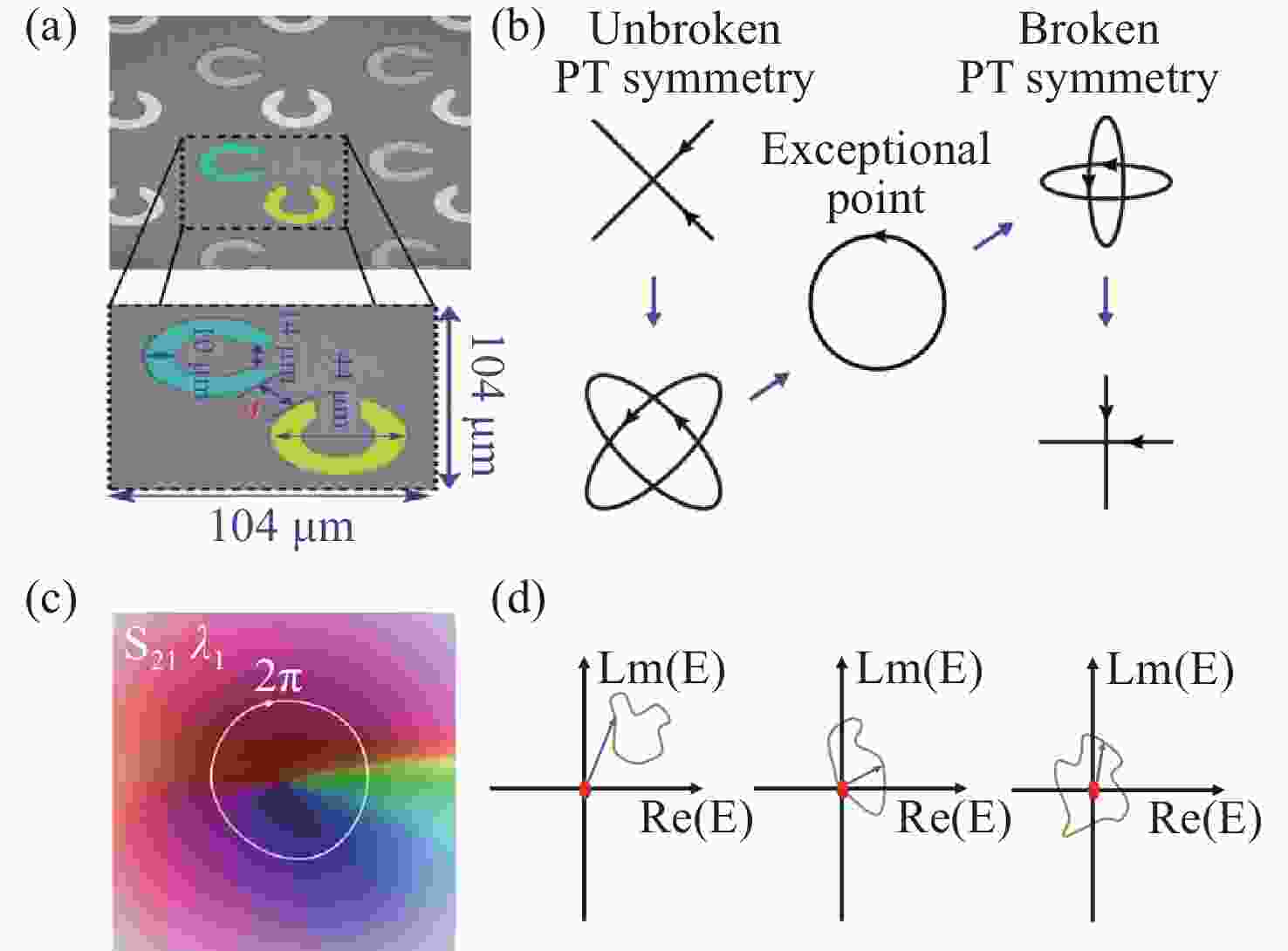
图 1 无源非厄密超构表面的光学性质。(a)双原子PT对称超构表面。(b)系统从PT对称到PT对称破缺转变过程中本征态的变化[20]。(c)拓扑相位[23]。(d)复空间中微扰结构与奇异点相离,相切,包围
Figure 1. Optical properties of passive non-hermitian metasurfaces. (a) Biatomic PT symmetric metasurfaces. (b) Changes in eigenstates during the transition of the system from PT symmetry to broken PT symmetry[20]. (c) Exceptional topological phase[23]. (d) Perturbative structures in complex space separated from EP, tangent to EP, and surrounded by EP
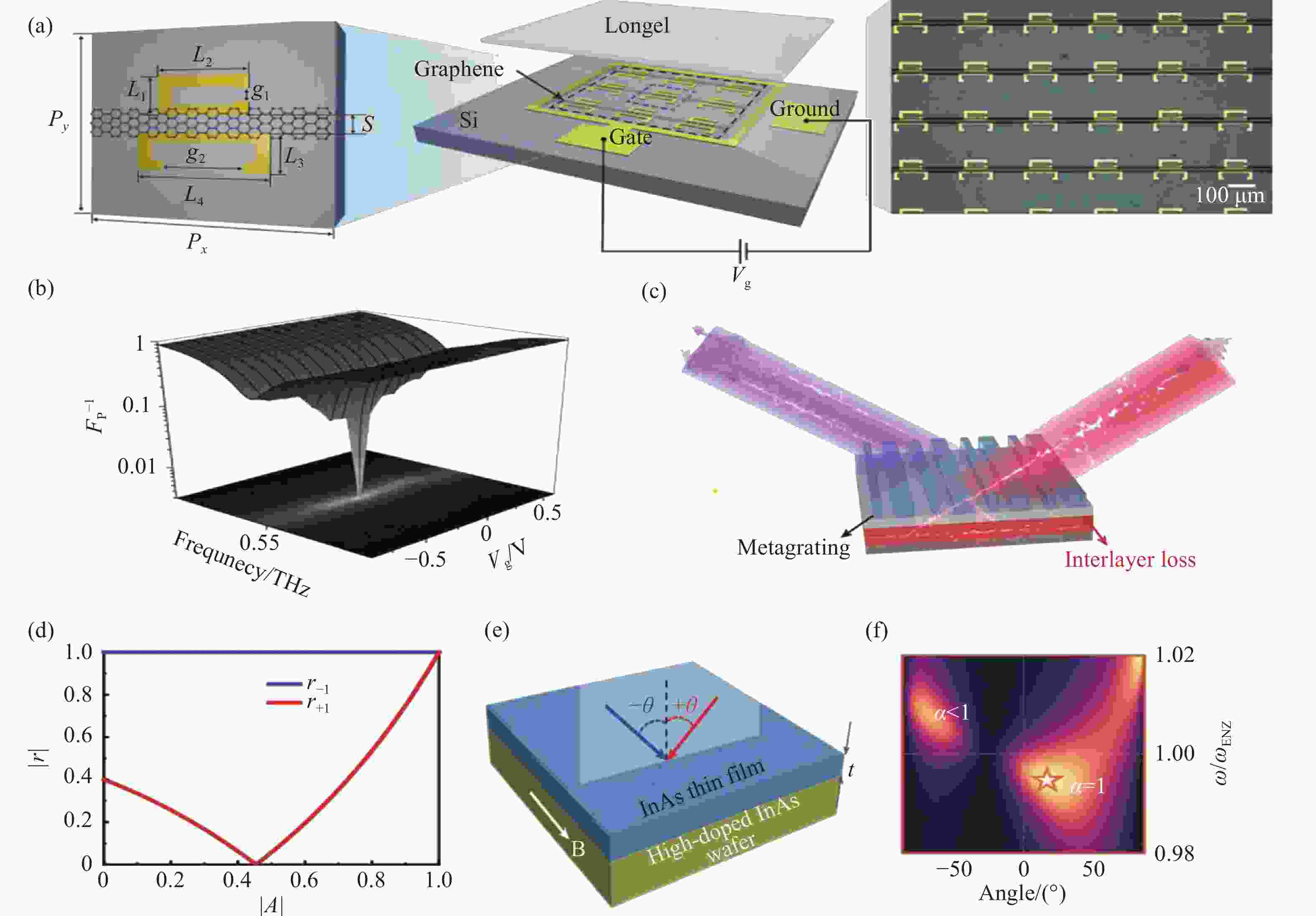
图 2 自由空间光传输的非厄密超构表面器件。(a)石墨烯金属谐振环超构表面示意图。(b)奇异点反射率图[28]。(c)超构光栅示意图。(d)偏振光反射率和复系数A的关系[29]。(e)超构薄膜示意图。(f)光吸收[30]
Figure 2. Passive non-hermitian metasurface devices for free-space optical transmission. (a) Schematic diagram of graphene metal resonant ring metasurface. (b) Exceptional point reflectance map[28]. (c) Metasurface grating. (d) Relationship between polarized light reflectance and complex coefficient A[29]. (e) Metasurface thin films. (f) Light absorption[30].
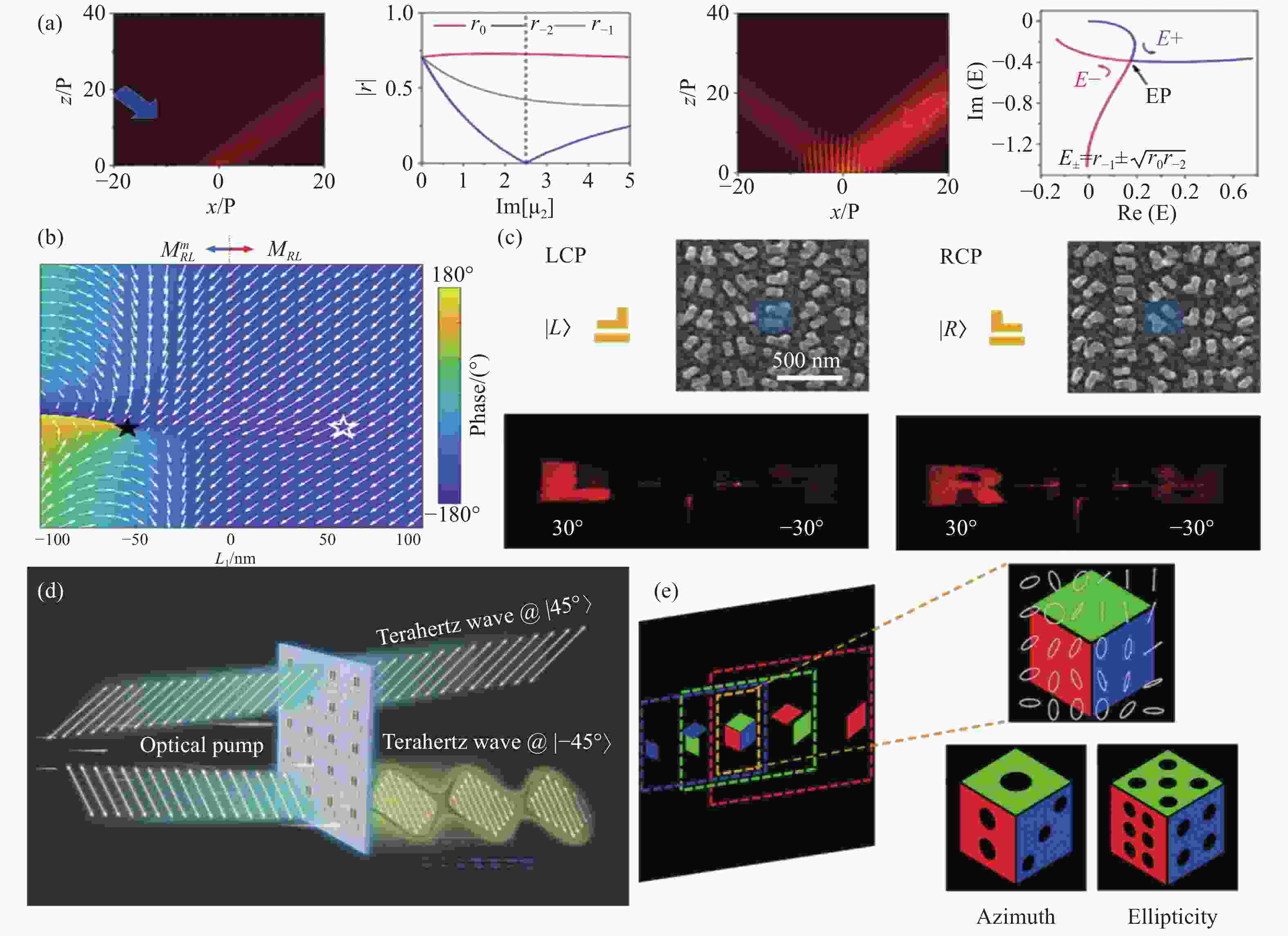
图 4 基于无源非厄密超构表面的奇异光学现象和器件设计。(a)入射方向敏感的不对称传输[36]。(b)奇异拓扑相位。(c)基于拓扑相位的角度不对称全息[37]。(d)奇异点结构实现角度敏感脉冲传输[39]。(e)彩色矢量全息[43]
Figure 4. Exceptional optical phenomena and device design based on passive non-Hermitian metasurfaces. (a) Asymmetric transmission sensitive to incidence direction[36]. (b) Exceptional topological phase. (c) Angular asymmetric holography based on exceptional topological phase[37]. (d) Angle-sensitive pulse transmission realized with EP structure[39]. (e) Color vector holographic[43]
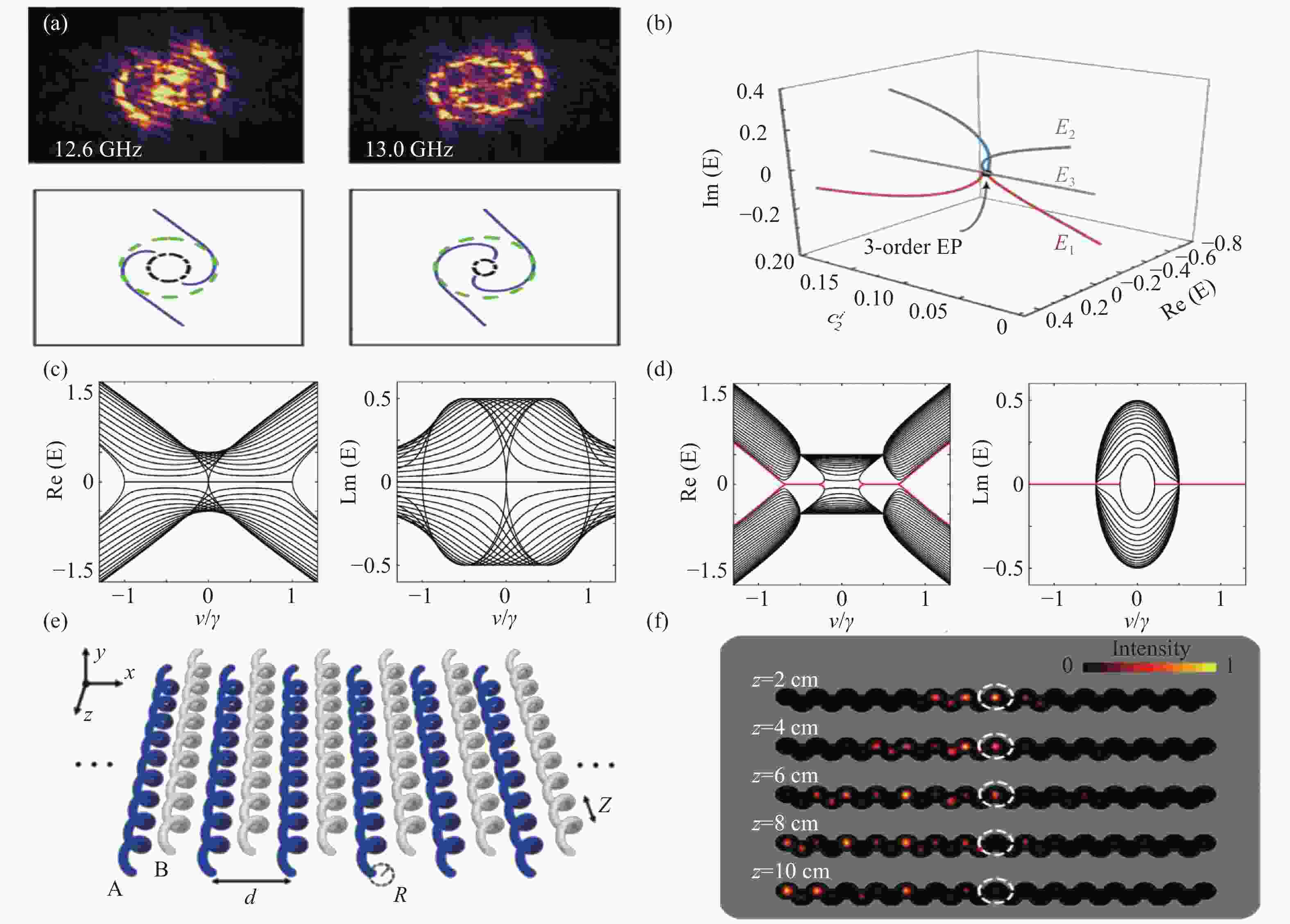
图 6 复杂奇异光学现象。(a)气隙中的费米弧[57]。(b)三阶奇异点[60]。(c)周期边界的能带谱。(d)开放边界的能带谱[62]。(e)Floquet拓扑光子晶格模型。(f)趋肤效应[67]
Figure 6. Complex exceptional optical phenomena. (a) Fermi arcs in the air gap[57]. (b) Third-order EP[60]. (c) Energy band spectrum at periodic boundary. (d) Energy band spectrum with open boundary[62]. (e) Floquet topological photonic lattice models. (f) Skin effect[67]
-
[1] JIE K Q, HUANG H, QIN SH, et al. Electronically controlled time-domain integral average depolarizer based on a barium titanate (BTO) metasurface[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(7): 1228. doi: 10.3390/nano12071228 [2] QIN SH, HUANG H, JIE K Q, et al. Active modulating the intensity of bifocal metalens with electrically tunable barium titanate (BTO) nanofins[J]. Nanomaterials, 2021, 11(8): 2023. doi: 10.3390/nano11082023 [3] QIN SH, XU N, HUANG H, et al. Near-infrared thermally modulated varifocal metalens based on the phase change material Sb2S3[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(5): 7925-7934. doi: 10.1364/OE.420014 [4] YIN Y, YANG Y, LI T, et al. High-dynamic-resolution optical edge detection based on liquid crystal diffractive moiré lenses with a tunable focal length[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(10): 2549-2552. doi: 10.1364/OL.425427 [5] LI Y, FAN X H, GUO X Y, et al. Metasurface for oscillatory spin splitting along the optical path[J]. Photonics Research, 2022, 10(9): B7-B13. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.463041 [6] DONG S Y, ZHANG ZH Y, XIE L Y, et al. Broadband depolarized perfect Littrow diffraction with multilayer freeform metagratings[J]. Optica, 2023, 10(5): 585-593. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.486332 [7] WANG Q, TU CH H, LI Y N, et al. Polarization singularities: progress, fundamental physics, and prospects[J]. APL Photonics, 2021, 6(4): 040901. doi: 10.1063/5.0045261 [8] LI SH Q, WANG ZH, DONG SH H, et al. Helicity-delinked manipulations on surface waves and propagating waves by metasurfaces[J]. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(10): 3473-3481. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2020-0200 [9] QIAN CH, YANG Y, HUA Y F, et al. Breaking the fundamental scattering limit with gain metasurfaces[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 4383. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32067-9 [10] KANG M, CHONG Y D. Coherent optical control of polarization with a critical metasurface[J]. Physical Review A, 2015, 92(4): 043826. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.92.043826 [11] FENG L, EL-GANAINY R, GE L. Non-Hermitian photonics based on parity–time symmetry[J]. Nature Photonics, 2017, 11(12): 752-762. doi: 10.1038/s41566-017-0031-1 [12] EL-GANAINY R, MAKRIS K G, KHAJAVIKHAN M, et al. Non-hermitian physics and PT symmetry[J]. Nature Physics, 2018, 14(1): 11-19. doi: 10.1038/nphys4323 [13] LI A D, WEI H, COTRUFO M, et al. Exceptional points and non-Hermitian photonics at the nanoscale[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2023, 18(7): 706-720. doi: 10.1038/s41565-023-01408-0 [14] WANG CH Q, JIANG X F, ZHAO G M, et al. Electromagnetically induced transparency at a chiral exceptional point[J]. Nature Physics, 2020, 16(3): 334-340. doi: 10.1038/s41567-019-0746-7 [15] WONG Z J, XU Y L, KIM J, et al. Lasing and anti-lasing in a single cavity[J]. Nature Photonics, 2016, 10(12): 796-801. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2016.216 [16] BAI P, DING K, WANG G, et al. Simultaneous realization of a coherent perfect absorber and laser by zero-index media with both gain and loss[J]. Physical Review A, 2016, 94(6): 063841. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.94.063841 [17] HONG X M, HU G W, ZHAO W CH, et al. Structuring nonlinear wavefront emitted from monolayer transition-metal dichalcogenides[J]. Research, 2020, 2020: 9085782. [18] GUAN F X, GUO X D, ZENG K B, et al. Overcoming losses in superlenses with synthetic waves of complex frequency[J]. Science, 2023, 381(6659): 766-771. doi: 10.1126/science.adi1267 [19] FENG L, XU Y L, FEGADOLLI W S, et al. Experimental demonstration of a unidirectional reflectionless parity-time metamaterial at optical frequencies[J]. Nature Materials, 2013, 12(2): 108-113. doi: 10.1038/nmat3495 [20] LAWRENCE M, XU N N, ZHANG X Q, et al. Manifestation of PT symmetry breaking in polarization space with terahertz metasurfaces[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2014, 113(9): 093901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.093901 [21] WU X R, ZHU J X, LIN F, et al. Study of a high-index dielectric non-Hermitian metasurface and its application in holograms[J]. ACS Omega, 2022, 7(49): 44743-44749. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04448 [22] YANG Y, WANG Y P, RAO J, et al. Unconventional singularity in anti-parity-time symmetric cavity magnonics[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2020, 125(14): 147202. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.125.147202 [23] FU P, DU SH, LAN W Z, et al. Deep learning enabled topological design of exceptional points for multi-optical-parameter control[J]. Communications Physics, 2023, 6(1): 254. doi: 10.1038/s42005-023-01380-0 [24] LIU M Q, CHEN W J, HU G W, et al. Spectral phase singularity and topological behavior in perfect absorption[J]. Physical Review B, 2023, 107(24): L241403. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.107.L241403 [25] SONG Q H, ODEH M, ZÚÑIGA-PÉREZ J, et al. Plasmonic topological metasurface by encircling an exceptional point[J]. Science, 2021, 373(6559): 1133-1137. doi: 10.1126/science.abj3179 [26] KANG M, CHEN J, CHONG Y D. Chiral exceptional points in metasurfaces[J]. Physical Review A, 2016, 94(3): 033834. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.94.033834 [27] PARK S H, LEE S G, BAEK S, et al. Observation of an exceptional point in a non-Hermitian metasurface[J]. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(5): 1031-1039. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2019-0489 [28] BAEK S, PARK S H, OH D, et al. Non-hermitian chiral degeneracy of gated graphene metasurfaces[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2023, 12(1): 87. [29] HE T, ZHANG ZH Y, ZHU J Y, et al. Scattering exceptional point in the visible[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2023, 12(1): 229. [30] LIU M Q, XIA SH, WAN W J, et al. Broadband mid-infrared non-reciprocal absorption using magnetized gradient epsilon-near-zero thin films[J]. Nature Materials, 2023, 22(10): 1196-1202. doi: 10.1038/s41563-023-01635-9 [31] RÜTER C E, MAKRIS K G, EL-GANAINY R, et al. Observation of parity–time symmetry in optics[J]. Nature Physics, 2010, 6(3): 192-195. doi: 10.1038/nphys1515 [32] WANG SH B, HOU B, LU W X, et al. Arbitrary order exceptional point induced by photonic spin–orbit interaction in coupled resonators[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 832. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08826-6 [33] QI H X, HU X Y, WANG X Y, et al. Encircling an exceptional point in a multiwaveguide anti–parity-time-symmetry system[J]. Physical Review A, 2021, 103(6): 063520. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.103.063520 [34] ZHANG X L, CHAN C T. Dynamically encircling exceptional points in a three-mode waveguide system[J]. Communications Physics, 2019, 2(1): 63. doi: 10.1038/s42005-019-0171-3 [35] LIU Q J, WANG T T, LEI Q, et al. Nonreciprocal topological mode conversion by encircling an exceptional point in dynamic waveguides[J]. Optics Letters, 2023, 48(15): 4089-4092. doi: 10.1364/OL.496988 [36] DONG SH H, HU G W, WANG Q, et al. Loss-assisted metasurface at an exceptional point[J]. ACS Photonics, 2020, 7(12): 3321-3327. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.0c01440 [37] YANG Z J, HUANG P SH, LIN Y T, et al. Creating pairs of exceptional points for arbitrary polarization control: asymmetric vectorial wavefront modulation[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 232. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44428-z [38] ERGOKTAS M S, SOLEYMANI S, KAKENOV N, et al. Topological engineering of terahertz light using electrically tunable exceptional point singularities[J]. Science, 2022, 376(6589): 184-188. doi: 10.1126/science.abn6528 [39] YU ZH Y, HE W B, HU S Y, et al. Creating anti-chiral exceptional points in non-hermitian metasurfaces for efficient terahertz switching[J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(28): 2402615. doi: 10.1002/advs.202402615 [40] GAO F, JIN G L, LIU H, et al. High-performance full-stokes polarization detection at exceptional point in a non-hermitian metasurface[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2023, 123(1): 011705. doi: 10.1063/5.0155706 [41] LI Y CH, DENG ZH W, QIN CH H, et al. Bifunctional sensing based on an exceptional point with bilayer metasurfaces[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(1): 492-501. doi: 10.1364/OE.478546 [42] YANG J X, XIA D X, ZHI Q J. Optical differential operation near exceptional points[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2024, 169: 109982. [43] YANG Z J, HUANG P SH, LIN Y T, et al. Asymmetric full-color vectorial meta-holograms empowered by pairs of exceptional points[J]. Nano Letters, 2024, 24(3): 844-851. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c03611 [44] YU N F, GENEVET P, KATS M A, et al. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6054): 333-337. doi: 10.1126/science.1210713 [45] SUN SH L, YANG K Y, WANG C M, et al. High-efficiency broadband anomalous reflection by gradient meta-surfaces[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(12): 6223-6229. doi: 10.1021/nl3032668 [46] CHENG F, GAO J, LUK T S, et al. Structural color printing based on plasmonic metasurfaces of perfect light absorption[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 11045. doi: 10.1038/srep11045 [47] YAN CH, LI X, PU M B, et al. Generation of polarization-sensitive modulated optical vortices with all-dielectric metasurfaces[J]. ACS Photonics, 2019, 6(3): 628-633. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.8b01119 [48] PARK J S, ZHANG SH Y, SHE A L, et al. All-glass, large metalens at visible wavelength using deep-ultraviolet projection lithography[J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(12): 8673-8682. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b03333 [49] MAKAROV S V, MILICHKO V, USHAKOVA E V, et al. Multifold emission enhancement in nanoimprinted hybrid perovskite metasurfaces[J]. ACS Photonics, 2017, 4(4): 728-735. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.6b00940 [50] LIU T, AN SH W, GU ZH M, et al. Chirality-switchable acoustic vortex emission via non-Hermitian selective excitation at an exceptional point[J]. Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(11): 1131-1136. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2022.04.009 [51] WANG L, LIU H, LI T, et al. Resonant exceptional points sensing in terahertz metasurfaces[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2024, 124(13): 131701. doi: 10.1063/5.0193106 [52] WU X R, ZHAO X F, LIN Y H, et al. Twins of exceptional points with opposite chirality for non-hermitian metasurfaces[J]. ACS Photonics, 2024, 11(5): 2054-2060. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.4c00196 [53] SHU X Q, ZHONG Q, HONG K, et al. Chiral transmission by an open evolution trajectory in a non-Hermitian system[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2024, 13(1): 65. [54] CERJAN A, HUANG SH, WANG M H, et al. Experimental realization of a Weyl exceptional ring[J]. Nature Photonics, 2019, 13(9): 623-628. doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0453-z [55] SANCHEZ D S, COCHRAN T A, BELOPOLSKI I, et al. Tunable topologically driven Fermi arc van Hove singularities[J]. Nature Physics, 2023, 19(5): 682-688. doi: 10.1038/s41567-022-01892-6 [56] ZHOU H Y, PENG CH, YOON Y, et al. Observation of bulk Fermi arc and polarization half charge from paired exceptional points[J]. Science, 2018, 359(6379): 1009-1012. doi: 10.1126/science.aap9859 [57] CHENG H, GAO W L, BI Y G, et al. Vortical reflection and spiraling Fermi arcs with Weyl metamaterials[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2020, 125(9): 093904. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.125.093904 [58] MANDAL I, BERGHOLTZ E J. Symmetry and higher-order exceptional points[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2021, 127(18): 186601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.186601 [59] XIONG W, LI ZH X, ZHANG G Q, et al. Higher-order exceptional point in a blue-detuned non-Hermitian cavity optomechanical system[J]. Physical Review A, 2022, 106(3): 033518. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.106.033518 [60] FANG X SH, GERARD N J R K, ZHOU ZH L, et al. Observation of higher-order exceptional points in a non-local acoustic metagrating[J]. Communications Physics, 2021, 4(1): 271. doi: 10.1038/s42005-021-00779-x [61] QIN H Y, SHI Y ZH, SU Z P, et al. Exploiting extraordinary topological optical forces at bound states in the continuum[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(49): eade7556. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ade7556 [62] LEE T E. Anomalous edge state in a non-Hermitian lattice[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2016, 116(13): 133903. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.133903 [63] KUNST F K, EDVARDSSON E, BUDICH J C, et al. Biorthogonal bulk-boundary correspondence in non-Hermitian systems[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 121(2): 026808. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.026808 [64] FRANCA S, KÖNYE V, HASSLER F, et al. Non-Hermitian physics without gain or loss: the skin effect of reflected waves[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2022, 129(8): 086601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.129.086601 [65] WEIDEMANN S, KREMER M, HELBIG T, et al. Topological funneling of light[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6488): 311-314. doi: 10.1126/science.aaz8727 [66] FANG ZH N, HU M Y, ZHOU L, et al. Geometry-dependent skin effects in reciprocal photonic crystals[J]. Nanophotonics, 2022, 11(15): 3447-3456. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2022-0211 [67] SUN Y Y, HOU X R, WAN T, et al. Photonic floquet skin-topological effect[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2024, 132(6): 063804. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.063804 [68] JIN L, SONG ZH. Symmetry-protected scattering in non-Hermitian linear systems[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2021, 38(2): 024202. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/38/2/024202 [69] XIA SH Q, KALTSAS D, SONG D H, et al. Nonlinear tuning of PT symmetry and non-hermitian topological states[J]. Science, 2021, 372(6537): 72-76. doi: 10.1126/science.abf6873 [70] YI Y F, YANG ZH S. Non-hermitian skin modes induced by on-site dissipations and chiral tunneling effect[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2020, 125(18): 186802. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.125.186802 [71] JIN L, SONG Z. Bulk-boundary correspondence in a non-Hermitian system in one dimension with chiral inversion symmetry[J]. Physical Review B, 2019, 99(8): 081103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.99.081103 [72] YANG ZH S, ZHANG K, FANG CH, et al. Non-hermitian bulk-boundary correspondence and auxiliary generalized Brillouin zone theory[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2020, 125(22): 226402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.125.226402 -





 下载:
下载: