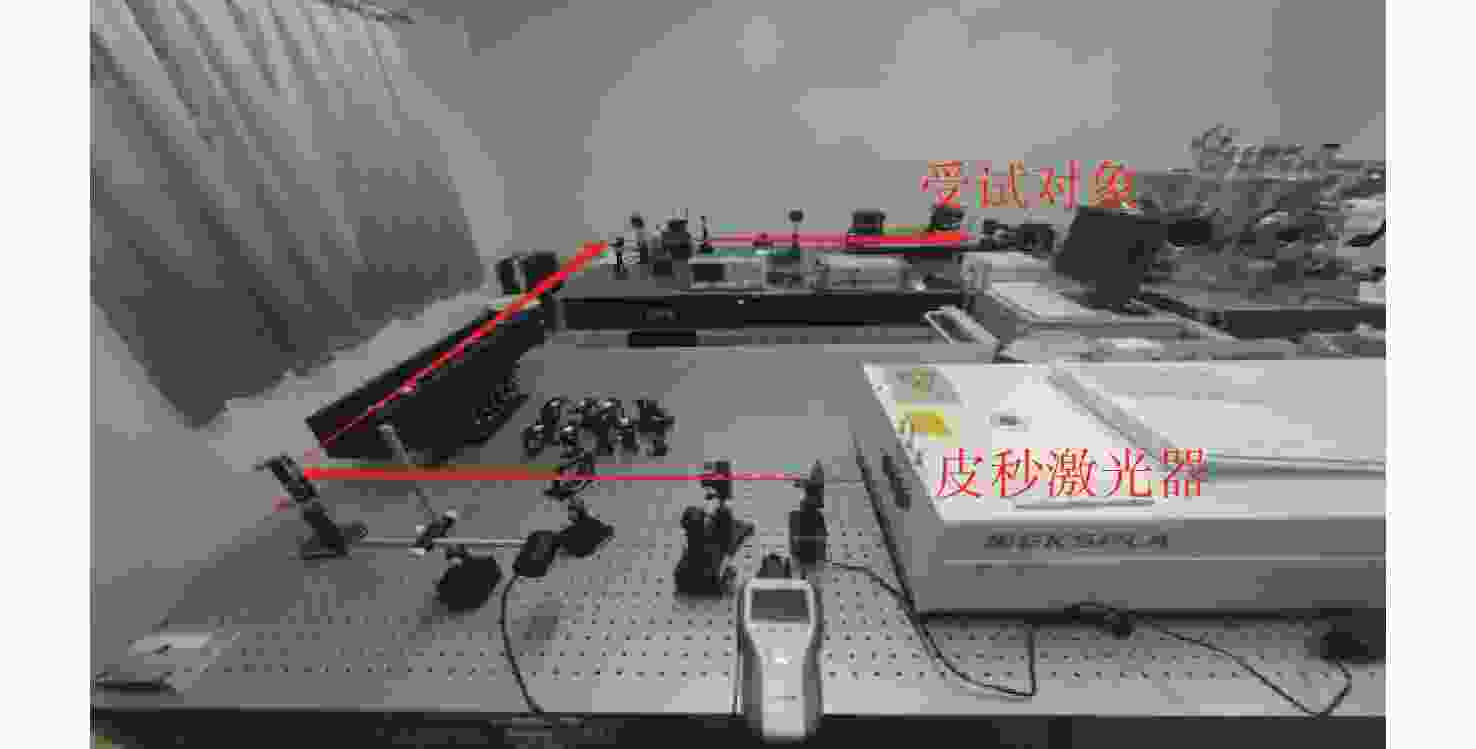
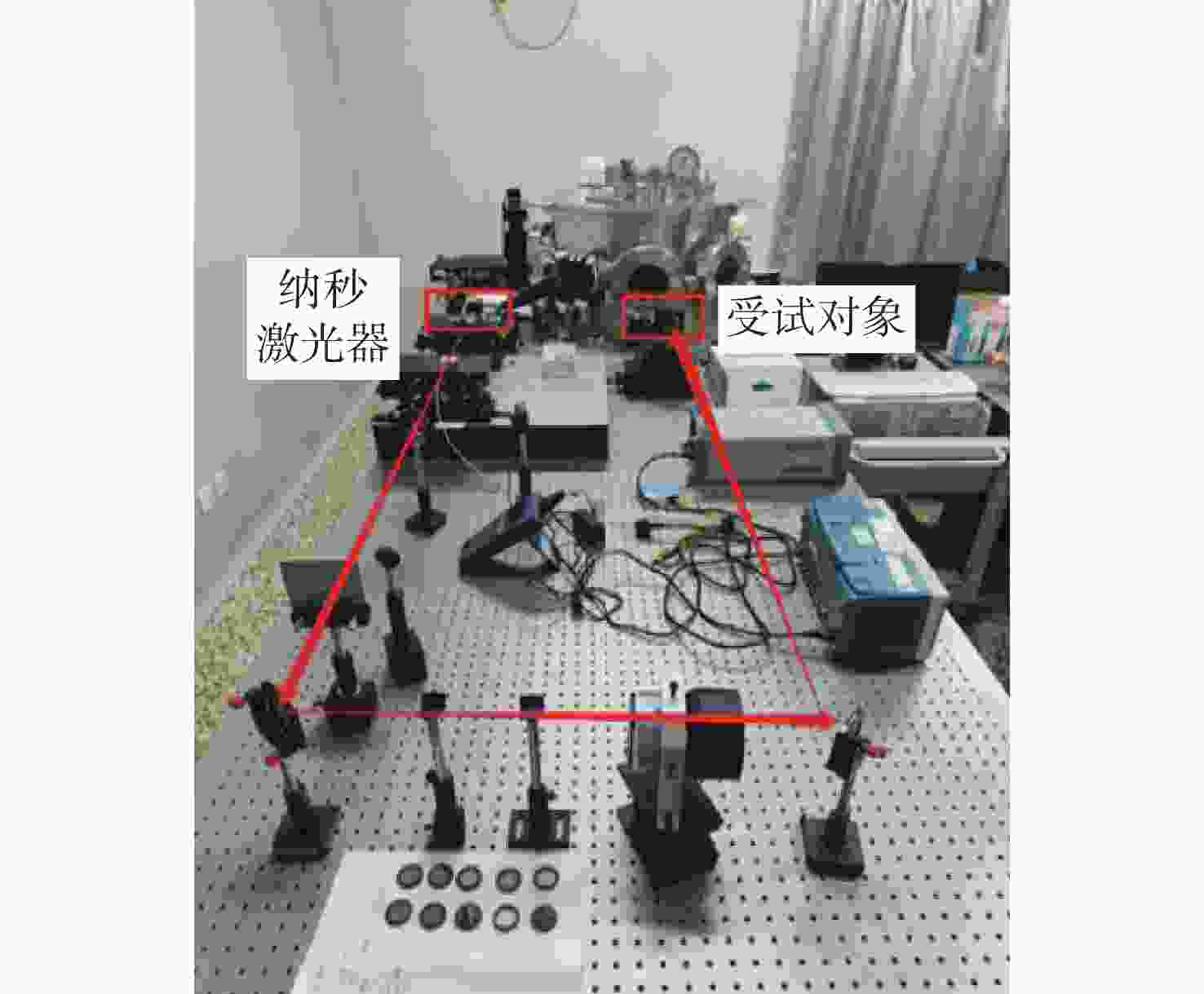
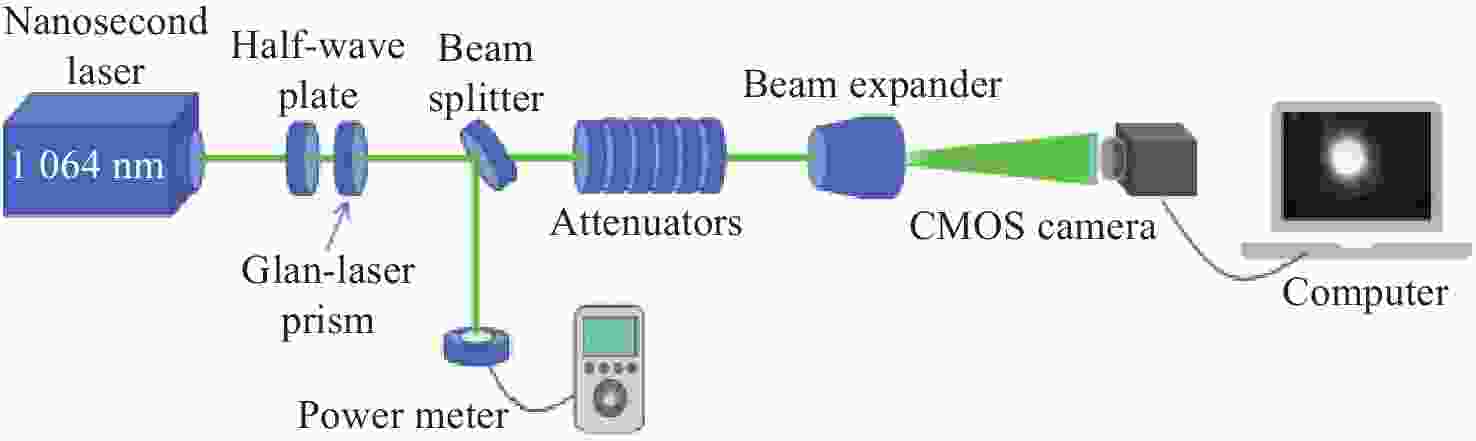
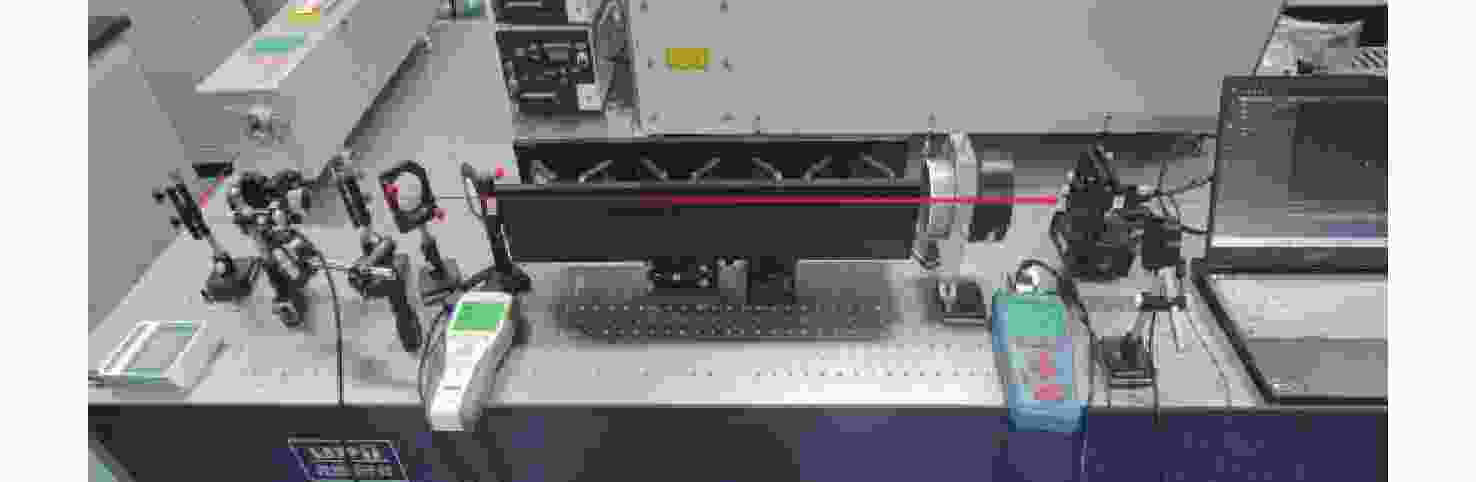
-
摘要:
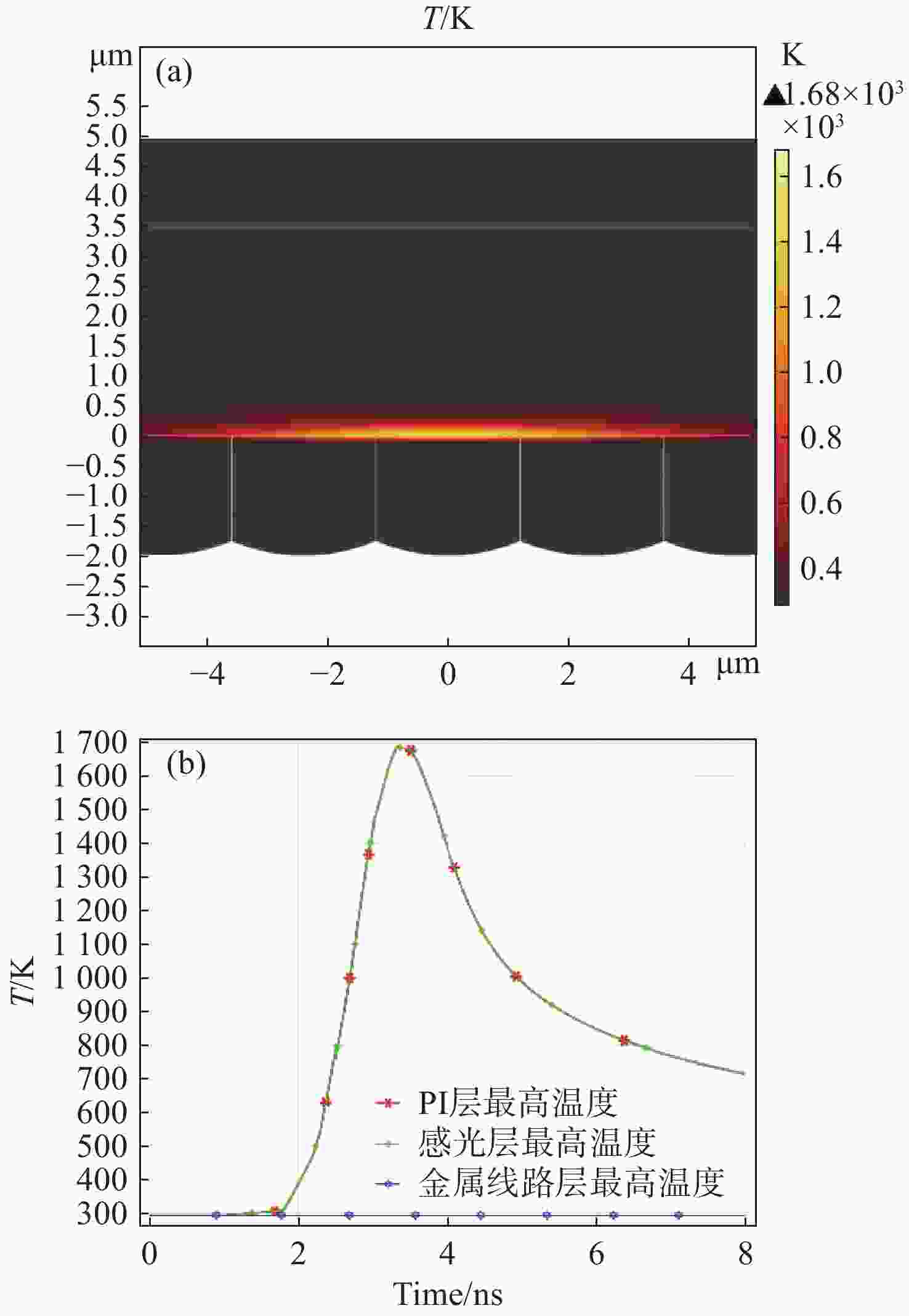
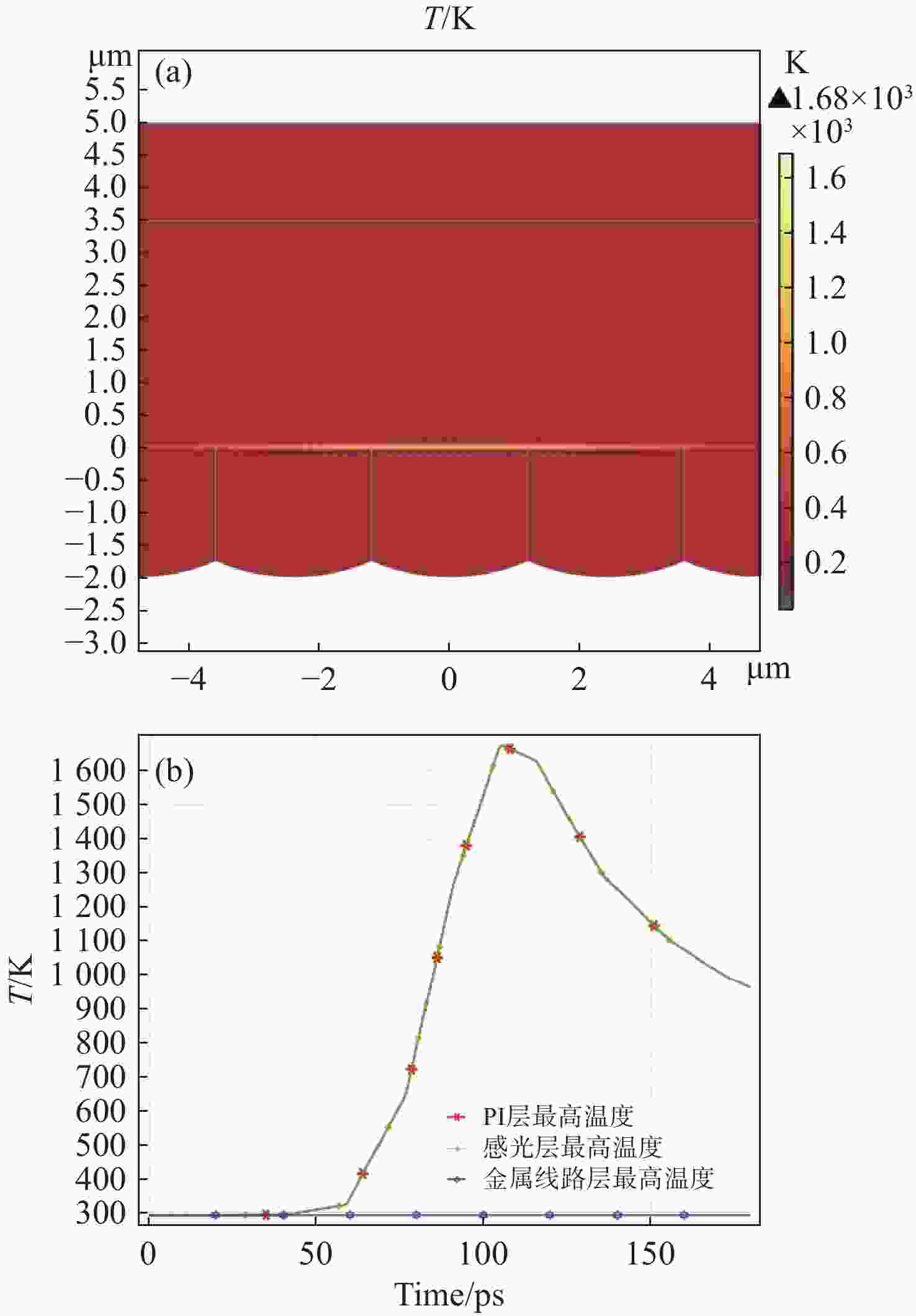
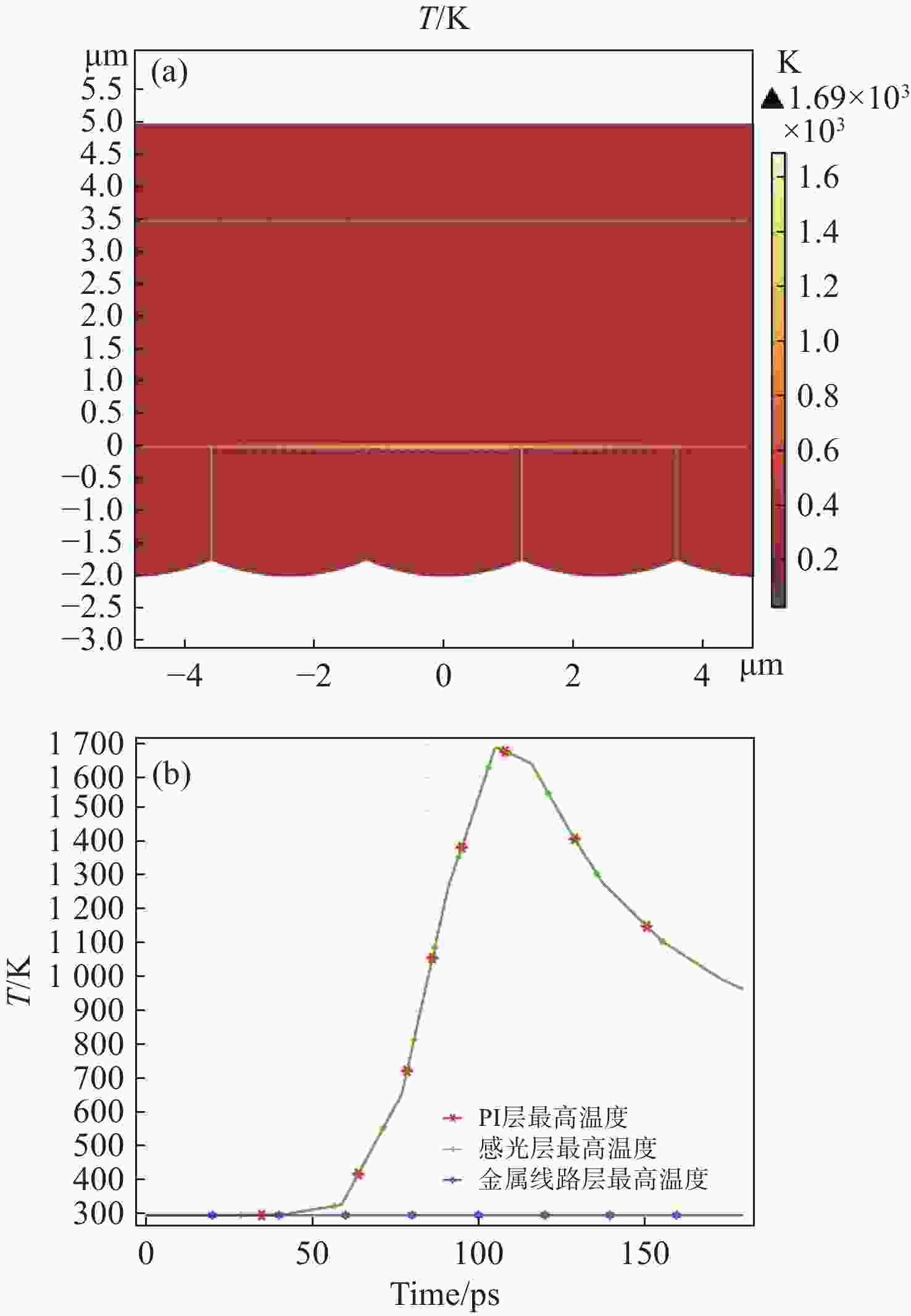
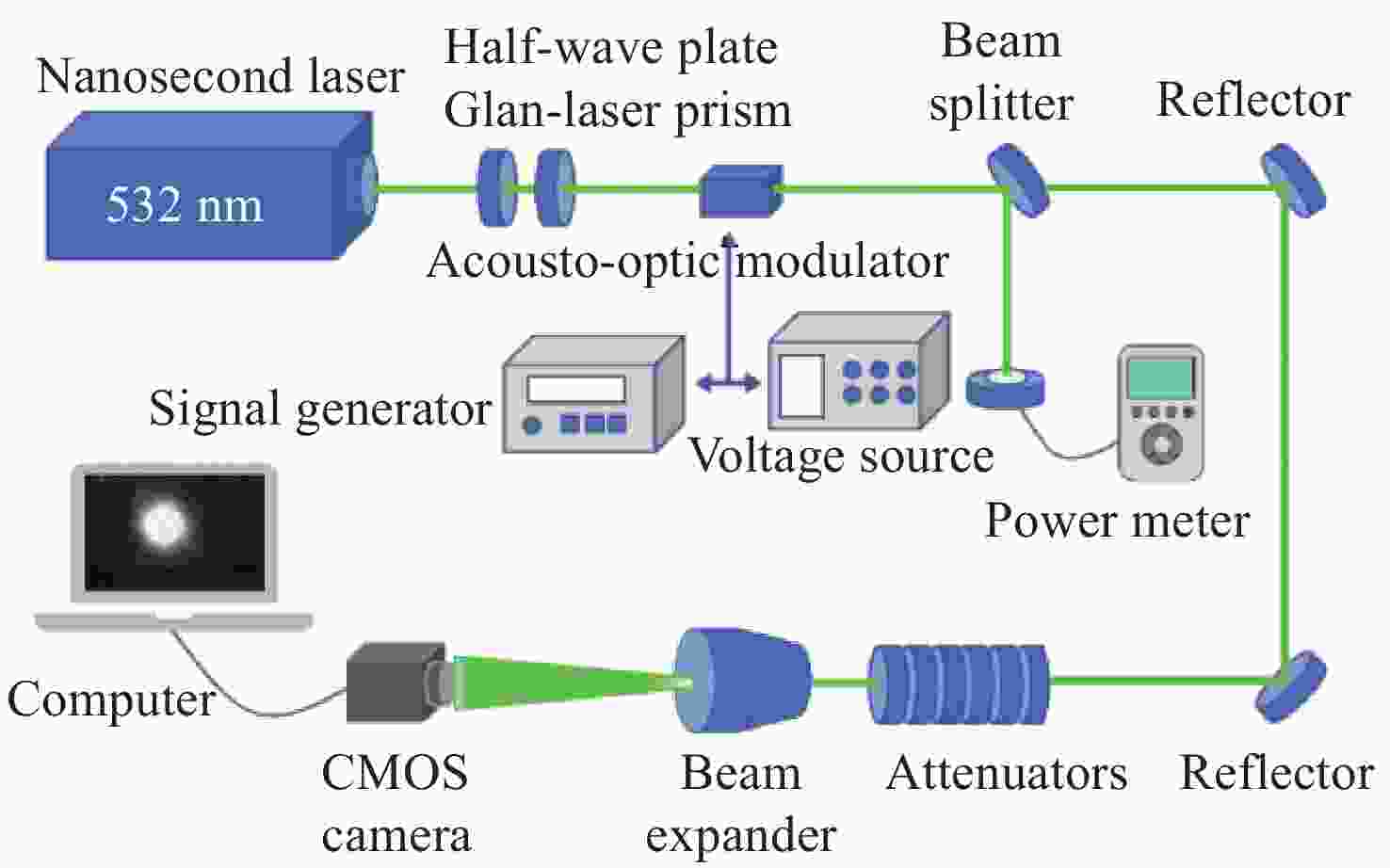
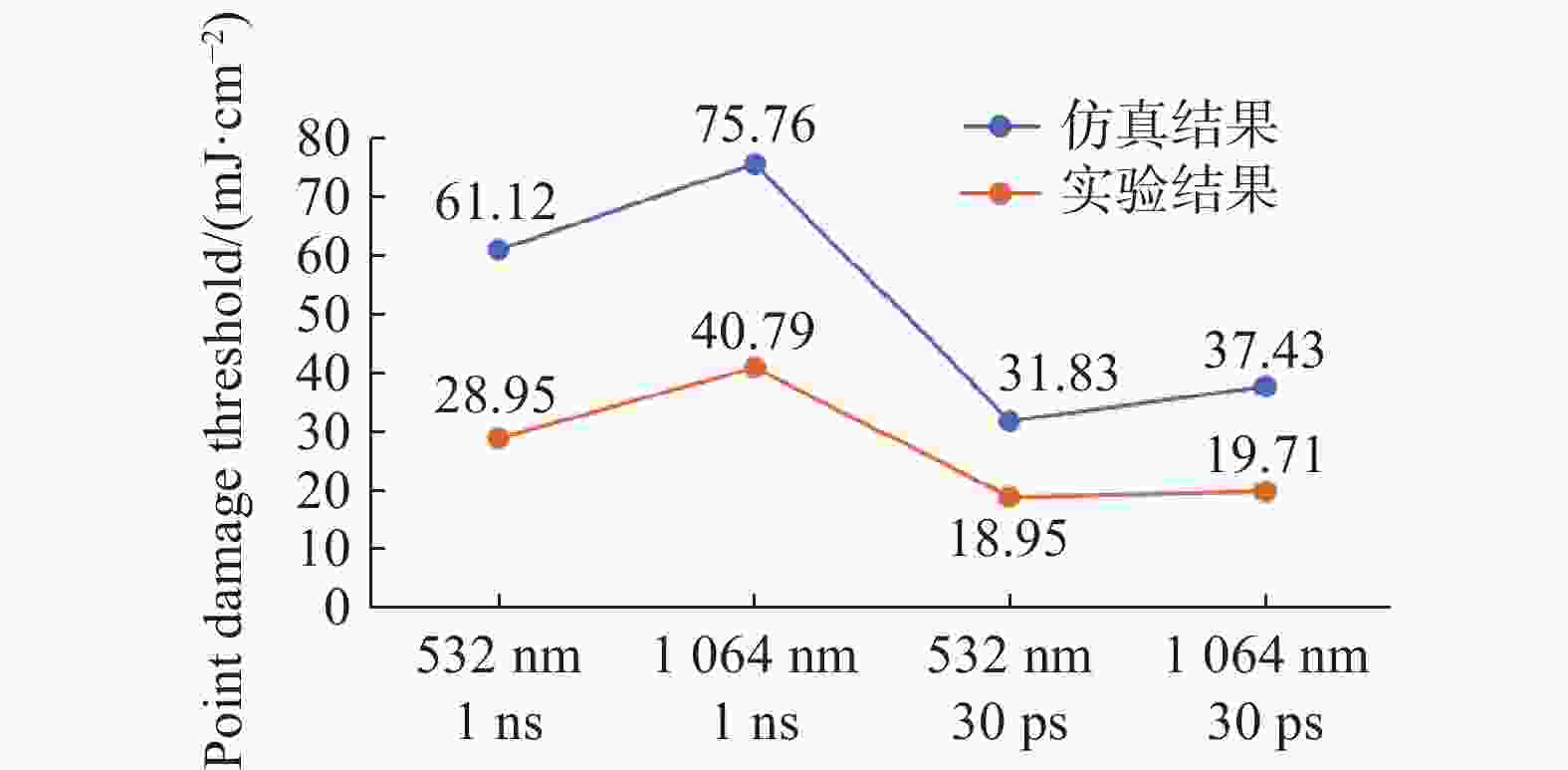
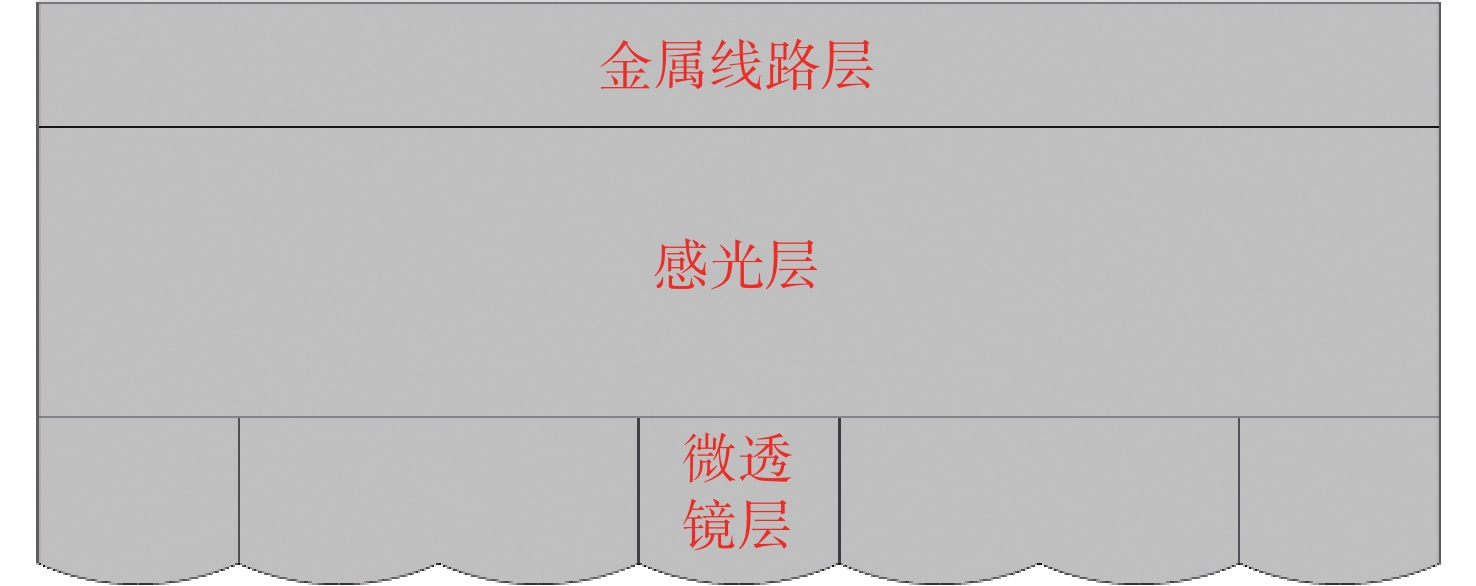
CMOS图像传感器是当今应用最广泛的传感器之一,已应用在航空航天,医学成像,工业检测,军事侦察等领域。然而,CMOS图像传感器的激光干扰和损伤随之也成为国内外相关领域的研究热点。为了研究脉冲激光对背照式CMOS图像传感器的影响,本文选用Sony IMX178背照式CMOS图像传感器作为靶材,基于热传导方程,利用有限元仿真软件COMSOL Multiphysics对比计算了不同参数单脉冲激光辐照下CMOS图像传感器的温度分布。计算结果表明,传感器在532 nm (1 ns)、
1064 nm (1 ns)、532 nm (30 ps)、1064 nm (30 ps)单脉冲激光作用下的点损伤阈值分别为61.12 mJ/cm2、75.76 mJ/cm2、31.83 mJ/cm2、37.43 mJ/cm2。同步开展了背照式CMOS图像传感器的激光辐照效应实验研究。结果表明:相比于1064 nm脉冲激光,532 nm脉冲激光作用下的图像传感器损伤阈值更低;相比于纳秒脉冲激光,皮秒脉冲激光有更高的峰值功率,更容易造成点损伤。本文仿真计算得到的点损伤阈值和实验结果比较吻合。Abstract:The CMOS image sensor is widely used in aerospace, medical imaging, industrial detection, military reconnaissance, and other fields. The laser interference and damage to CMOS image sensors have also become a research hotspot in related fields at home and abroad. To investigate the impact of pulsed laser on back-illuminated CMOS image sensors, we select the Sony IMX178 back-illuminated CMOS image sensor as the target. Based on the heat conduction equation, the finite element simulation software COMSOL Multiphysics is used to compare and calculate the temperature distribution of the CMOS image sensor under the irradiation of single-pulse lasers with different parameters. The calculation results indicate that the point damage thresholds of the sensor under the effects of single-pulse lasers at 532 nm (1 ns), 1064 nm (1 ns), 532 nm (30 ps), and 1064 nm (30 ps) are respectively 61.12 mJ/cm2, 75.76 mJ/cm2, 31.83 mJ/cm2, and 37.43 mJ/cm2. Subsequently, an experimental study is conducted on the laser irradiation effects of back-illuminated CMOS image sensors. The experimental results demonstrate that the image sensor exhibits a lower damage threshold under the influence of 532 nm pulsed lasers compared to 1064 nm pulsed lasers; picosecond pulsed lasers, with higher peak power compared to nanosecond pulsed lasers, are more prone to causing point damage. The calculated point damage thresholds are highly consistent with the experimental results.
-
Key words:
- nanosecond pulse laser /
- picosecond pulse laser /
- thermal effect /
- damage threshold
-
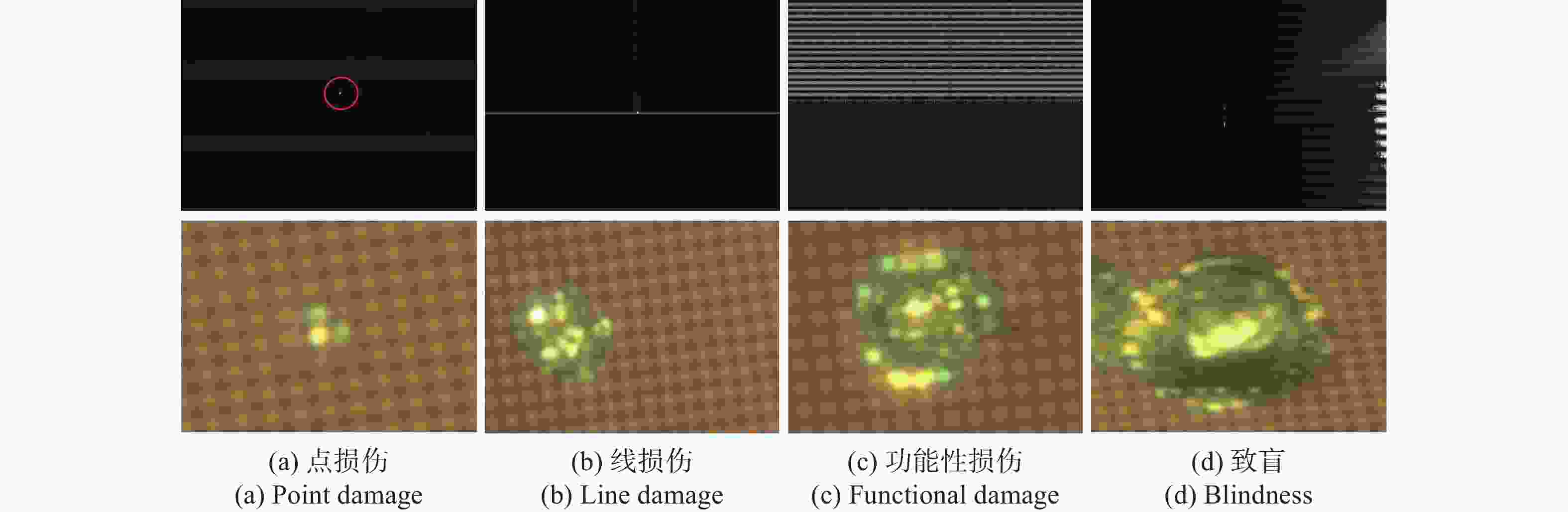
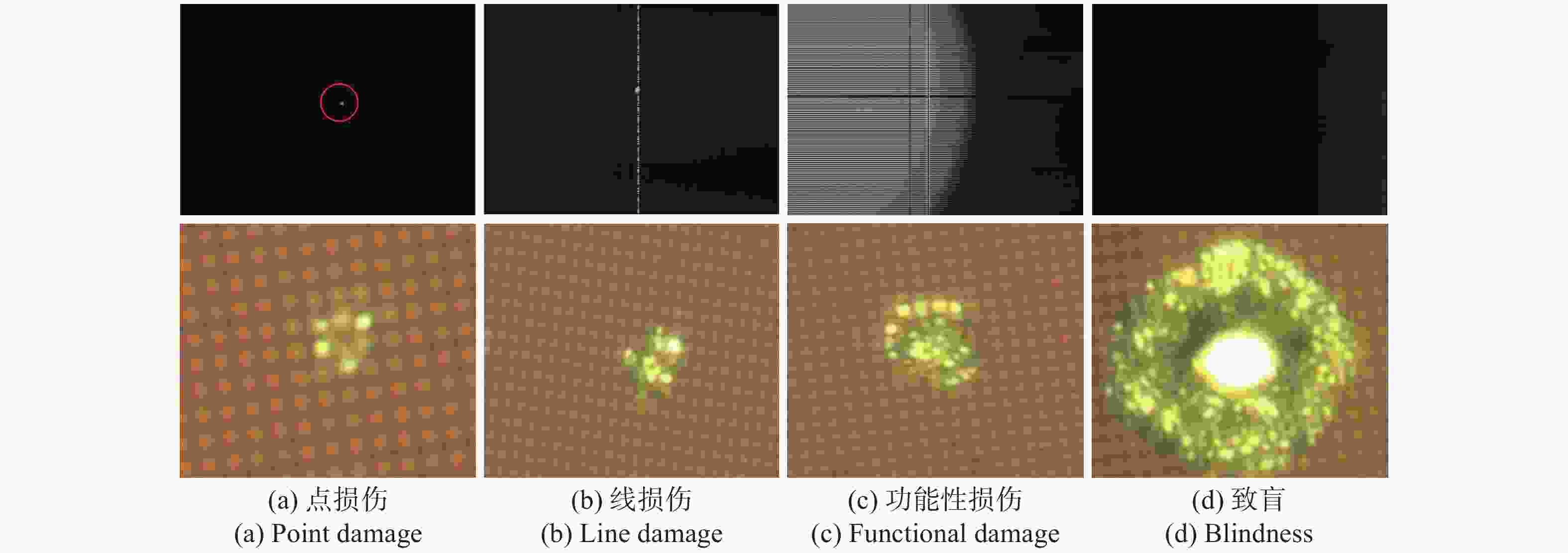
图 8 532 nm 纳秒激光辐照时,CMOS图像传感器的损伤情况,从左到右激光能量密度分别为28.95 mJ/cm2、69.91 mJ/cm2、167.6 mJ/cm2和519.3 mJ/cm2
Figure 8. Damage condition of CMOS image sensors irradiated by 532 nm nanosecond single pulse laser. From left to right, the laser energy densities are 28.95 mJ/cm2, 69.91 mJ/cm2, 167.6 mJ/cm2, 519.3 mJ/cm2, respectively
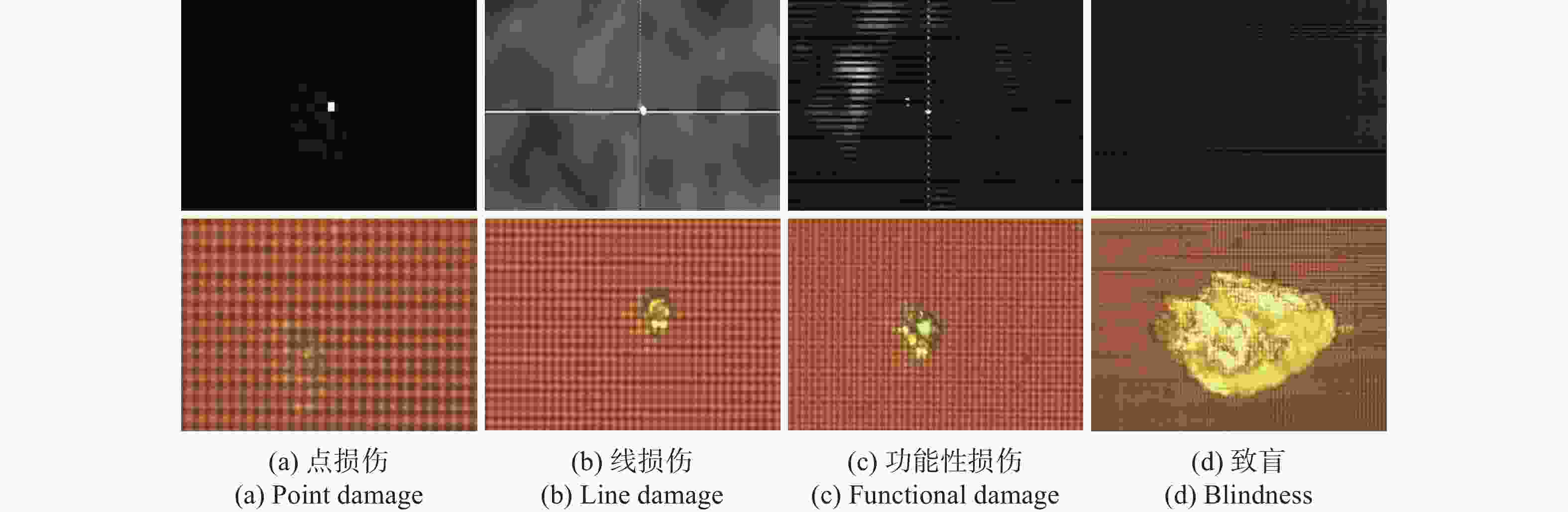
图 11
1064 nm纳秒单脉冲激光辐照CMOS传感器时的激光损伤情况,从左到右的激光能量密度分别为40.79 mJ/cm2,100.6 mJ/cm2,132.4 mJ/cm2和1.24 J/cm2Figure 11. Damage condition of CMOS image sensors irradiated by
1064 nm nanosecond single pulse laser. From left to right, the laser energy densities are 40.79 mJ/cm2, 100.6 mJ/cm2, 132.4 mJ/cm2, 1.24 J/cm2, respectively图 14 532 nm皮秒激光作用下的CMOS图像传感器的损伤情形。从左到右的激光能量密度分别为18.95 mJ/cm2,78.93 mJ/cm2,120.49 mJ/cm2和501.33 mJ/cm2
Figure 14. Damage condition of CMOS image sensor irradiated by 532 nm picosecond pulse laser. From left to right, the laser energy densities are 18.95 mJ/cm2, 78.93 mJ/cm2, 120.49 mJ/cm2, 501.33 mJ/cm2, respectively
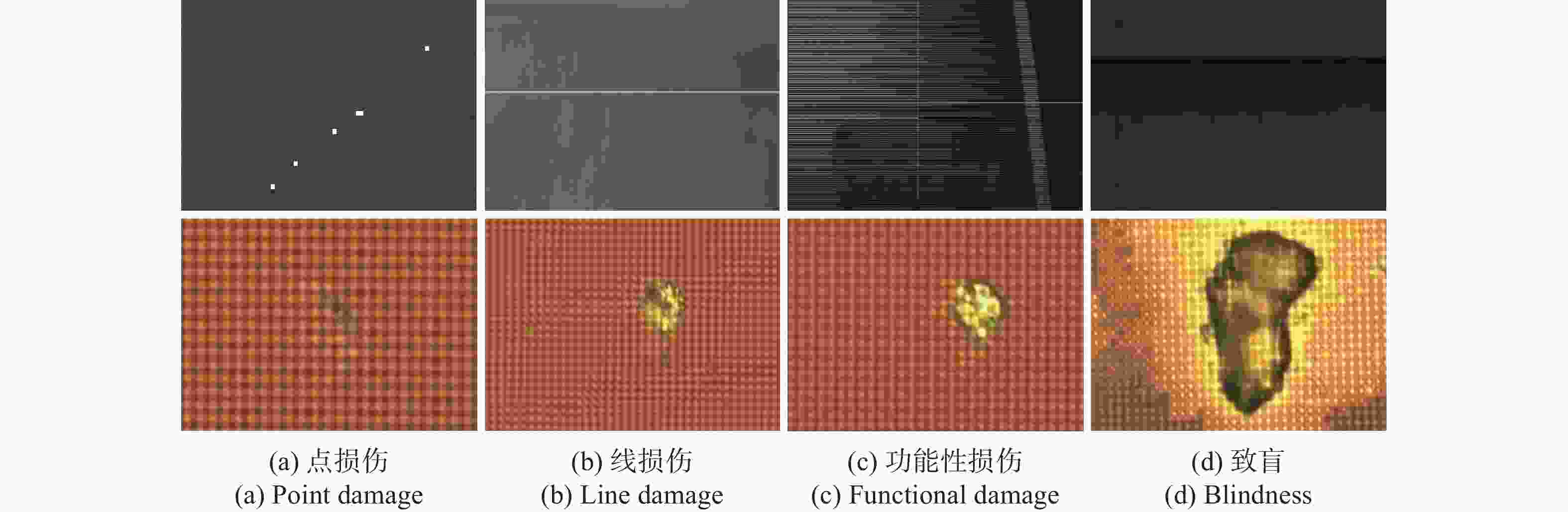
图 15
1064 nm 皮秒单脉冲激光作用下的CMOS图像传感器的损伤情形。从左到右的激光能量密度分别为19.71 mJ/cm2,90.76 mJ/cm2,123.80 mJ/cm2,566.19 mJ/cm2Figure 15. Damage condition of CMOS image sensor irradicatd by
1064 nm picosecond pulse laser. From left to right, the laser energy densities are 19.71 mJ/cm2, 90.76 mJ/cm2, 123.80 mJ/cm2, 566.19 mJ/cm2, respectirely表 1 材料的热力学参数
Table 1. Thermodynamic parameters of materials
PI Si Al 密度/(kg·m−3) 1190 2329 2700 导热系数/(W·m−1K−1) 0.3 27 238 热膨胀系数(1/K) 2×10−5 2.6×10−6 23×10−6 恒压热容/(J·kg−1·K−2) 1510 700 900 杨氏模量(Pa) 3.2×109 170×109 70×109 泊松比 0.35 0.28 0.33 熔点(K) 710 1685 932 表 2 各激光参数下的点损伤阈值
Table 2. Point damage thresholds under various laser parameters
单脉冲激光 点损伤阈值/(mJ·cm−2) 532 nm,1 ns 61.12 1064 nm,1 ns75.76 532 nm,30 ps 31.83 1064 nm,30 ps37.43 表 3 各阶段损伤阈值
Table 3. Damage thresholds for each stage
点损伤 线损伤 功能性损伤 致盲 纳秒 532 nm 28.95 69.91 167.6 519.3 1064 nm40.79 100.6 132.4 1.24×103 皮秒 532 nm 18.95 78.93 120.49 501.33 1064 nm19.71 90.76 123.80 566.19 注:激光能量密度单位为mJ/cm2 -
[1] YOON S, JHANG K Y, SHIN W S. Damage analysis of CMOS electro-optical imaging system by a continuous wave laser[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9983: 99831F. doi: 10.1117/12.2235736 [2] SCHWARZ B, RITT G, KOERBER M, et al. Laser-induced damage threshold of camera sensors and micro-optoelectromechanical systems[J]. Optical Engineering, 2017, 56(3): 034108. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.56.3.034108 [3] SANTOS C N, CHRÉTIEN S, MERELLA L, et al. Visible and near-infrared laser dazzling of CCD and CMOS cameras[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10797: 107970S. [4] SCHWARZ B, RITT G, EBERLE B. Impact of threshold assessment methods in laser-induced damage measurements using the examples of CCD, CMOS, and DMD[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(22): F39-F49. doi: 10.1364/AO.423791 [5] THÉBERGE F, AUCLAIR M, DAIGLE J F, et al. Damage thresholds of silicon-based cameras for in-band and out-of-band laser expositions[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(10): 2473-2482. doi: 10.1364/AO.450317 [6] 王雪. 光电传感器激光致盲与损毁技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2018.WANG X. Study on laser blindness and damage technology of photoelectric sensors[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2018. (in Chinese). [7] 向洪刚. CMOS面阵探测器强光辐照效应若干问题研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2020.XIANG H G. Research on the High-light irradiation effects of array CMOS detector[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2020. (in Chinese). [8] ZHU R ZH, ZHANG H B, WANG ZH H, et al. Lattice phenomenon and mechanism analysis of CMOS image sensor irradiated by 532 nm laser[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2021, 11763: 1176306. [9] 朱孟真, 刘云, 米朝伟, 等. 复合激光损伤CMOS图像传感器实验研究[J]. 红外与激光工程,2022,51(7):20210537. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210537ZHU M ZH, LIU Y, MI CH W, et al. Experimental study on a CMOS image sensor damaged by a composite laser[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(7): 20210537. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210537 [10] 姜楠, 张雏, 牛燕雄, 等. 脉冲激光辐照CCD探测器的硬破坏效应数值模拟研究[J]. 激光与红外,2008,38(10):1004-1007.JIANG N, ZHANG CH, NIU Y X, et al. Numerical simulation of pulsed laser induced damage on CCD arrays[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2008, 38(10): 1004-1007. (in Chinese). [11] 寇子龙. 短脉冲激光对CCD诱导击穿效应及机理研究[D]. 天津: 河北工业大学, 2022.KOU Z L. Study on the induced breakdown effect and mechanism of CCD by short pulse laser[D]. Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology, 2022. (in Chinese). [12] 袁磊, 王毕艺, 罗超, 等. 红外探测系统的激光辐照热效应仿真分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束,2023,35(2):021003.YUAN L, WANG B Y, LUO CH, et al. Simulation analysis of thermal effect of laser irradiation in infrared detection system[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35(2): 021003. (in Chinese). [13] 张引, 邵俊峰, 汤伟. TEA CO2长波红外激光对红外凝视成像系统探测器组件的损伤效应[J]. 光学 精密工程,2021,6(29):1217-1224.ZHANG Y, SHAO J F, TANG W. Damage effect of TEA CO2 long wave infrared laser on detector assembly of infrared staring imaging system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 6(29): 1217-1224. (in Chinese). [14] 马 彬, 侯志强, 焦宏飞, 等. 脉冲激光损伤阈值测量技术及光学元件损伤性能[J]. 光学 精密工程,2022,30(21):2805-2826. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223021.2805MA B, HOU ZH Q, JIAO H F, et al. Pulsed laser-induced damage threshold measurement and damage performance of optical components[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(21): 2805-2826. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223021.2805 -





 下载:
下载: