Infrared and visible image fusion guided by cross-domain interactive attention and contrastive learning
-
摘要:
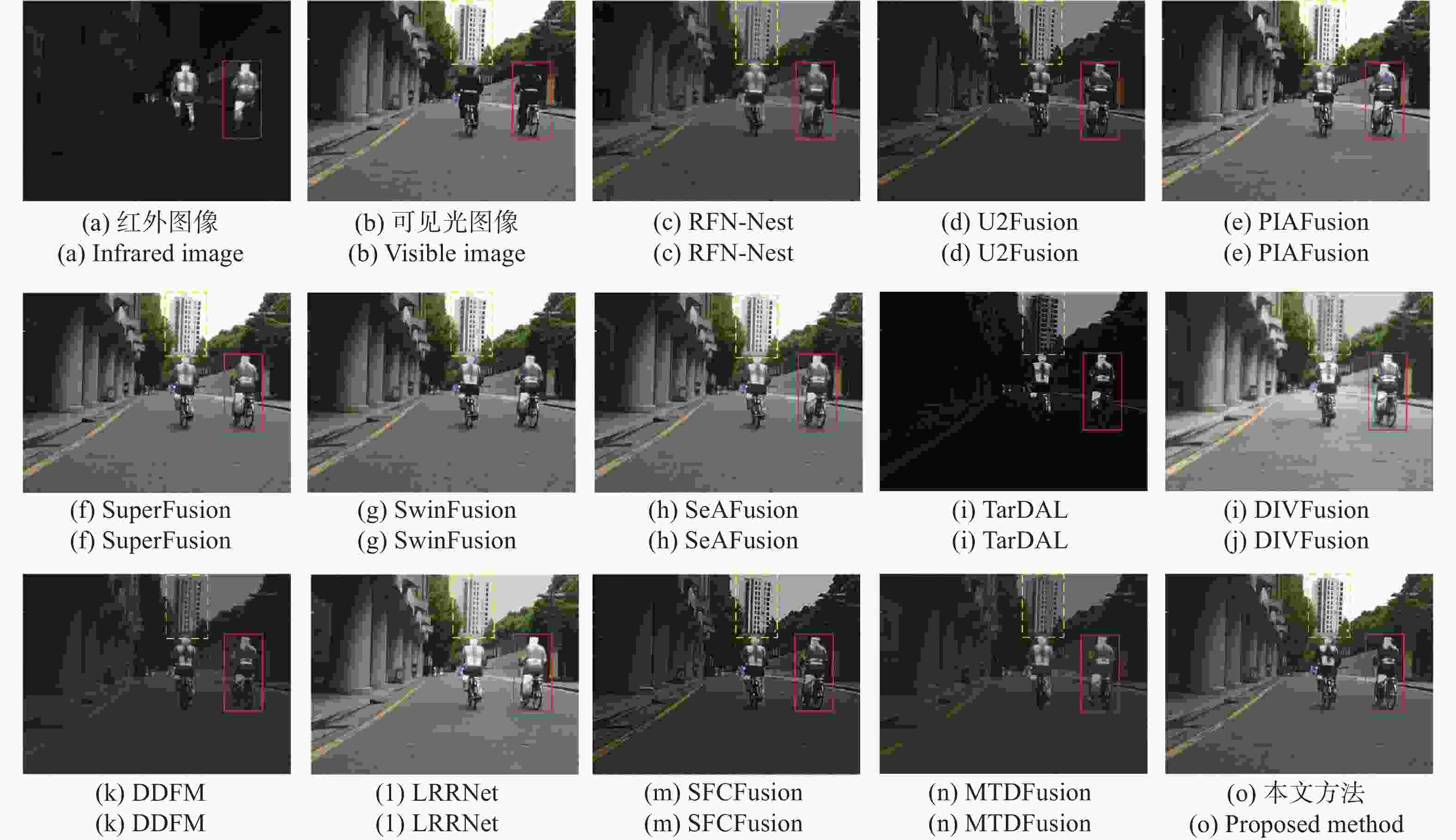
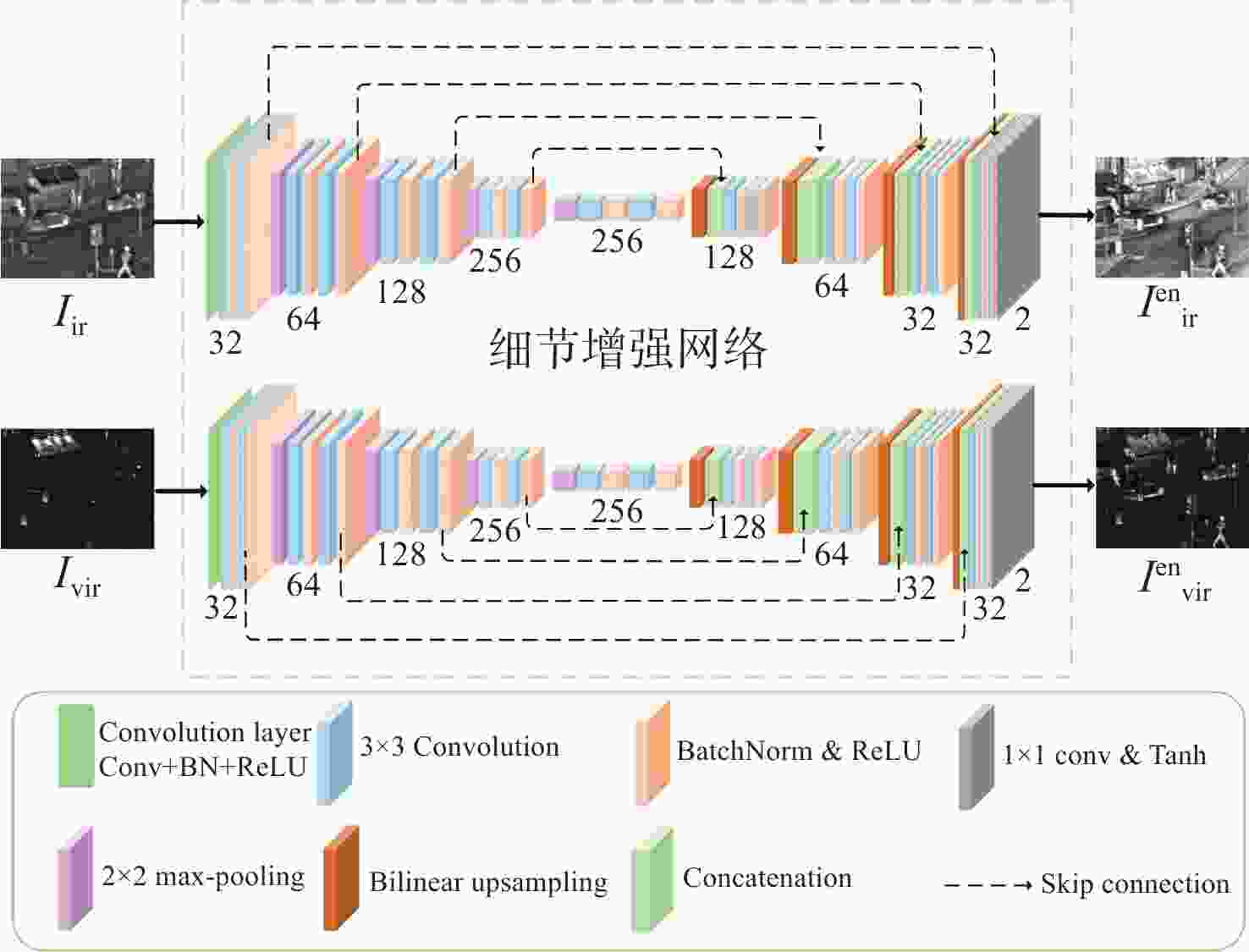
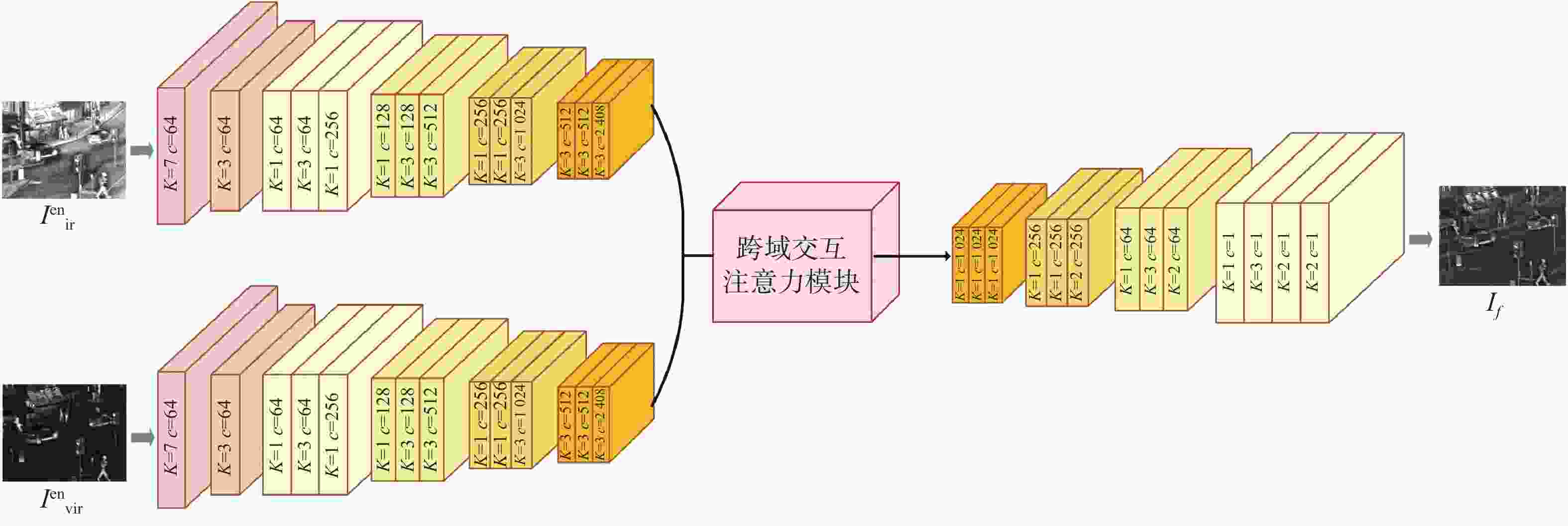
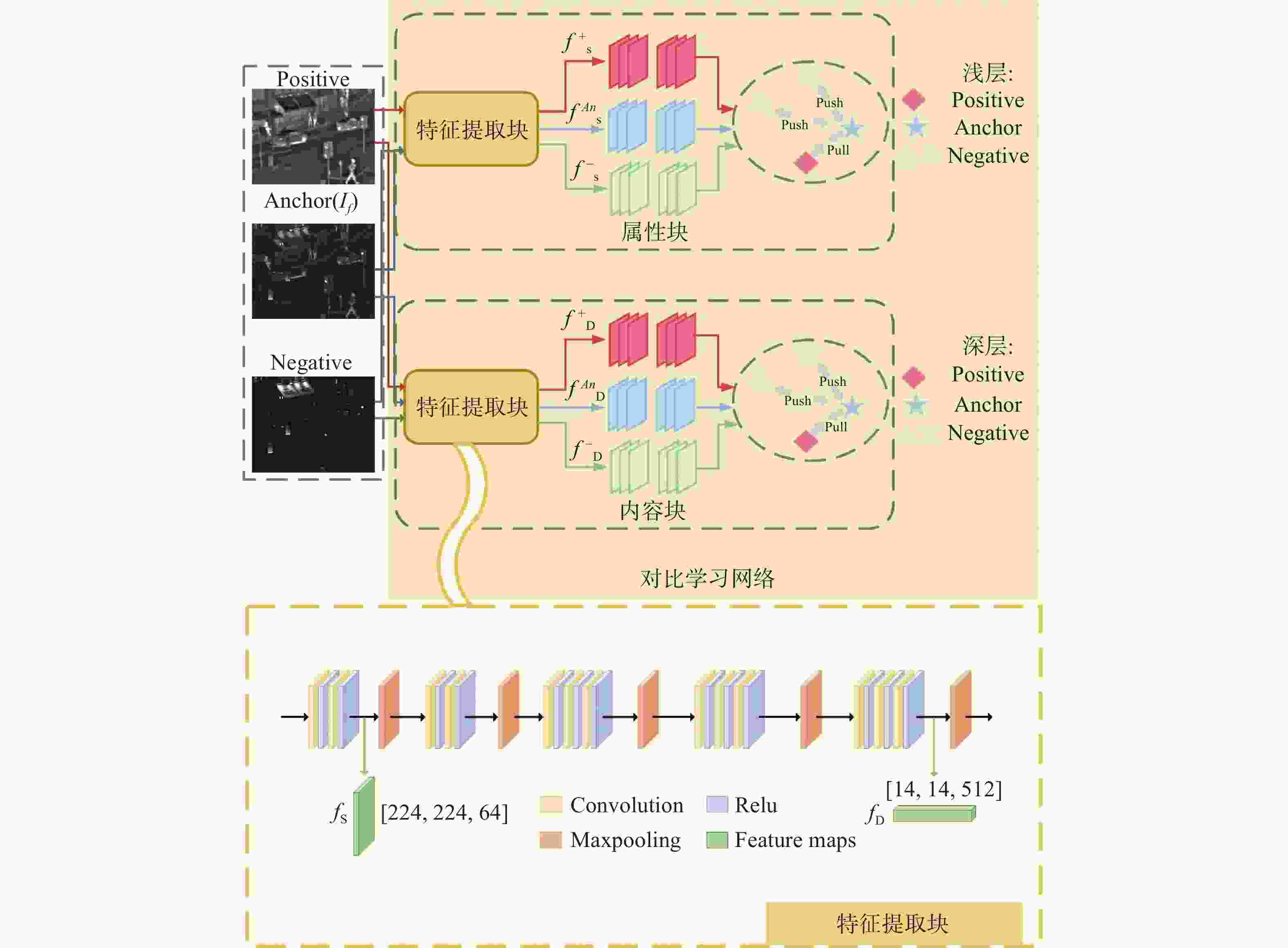
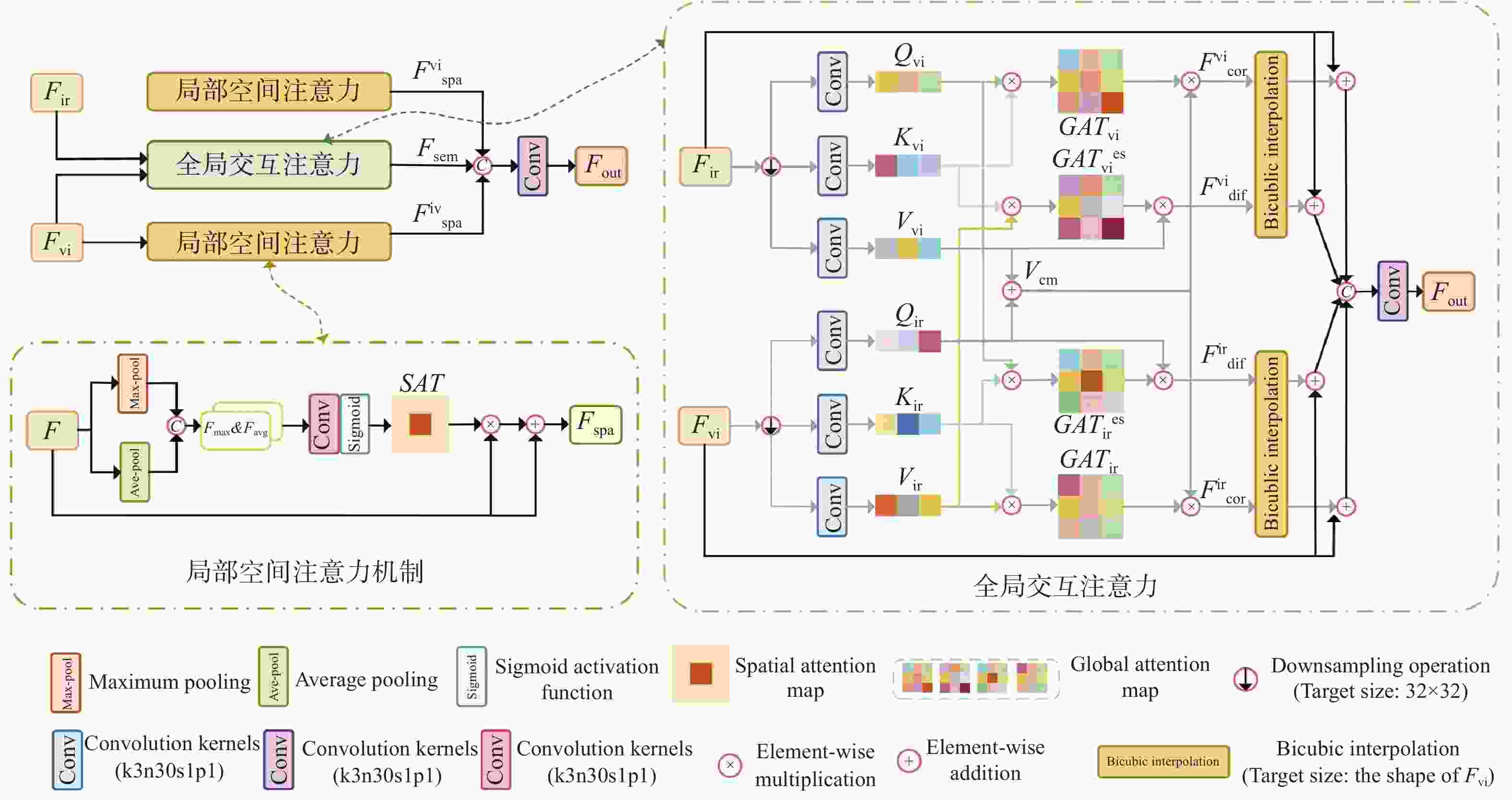
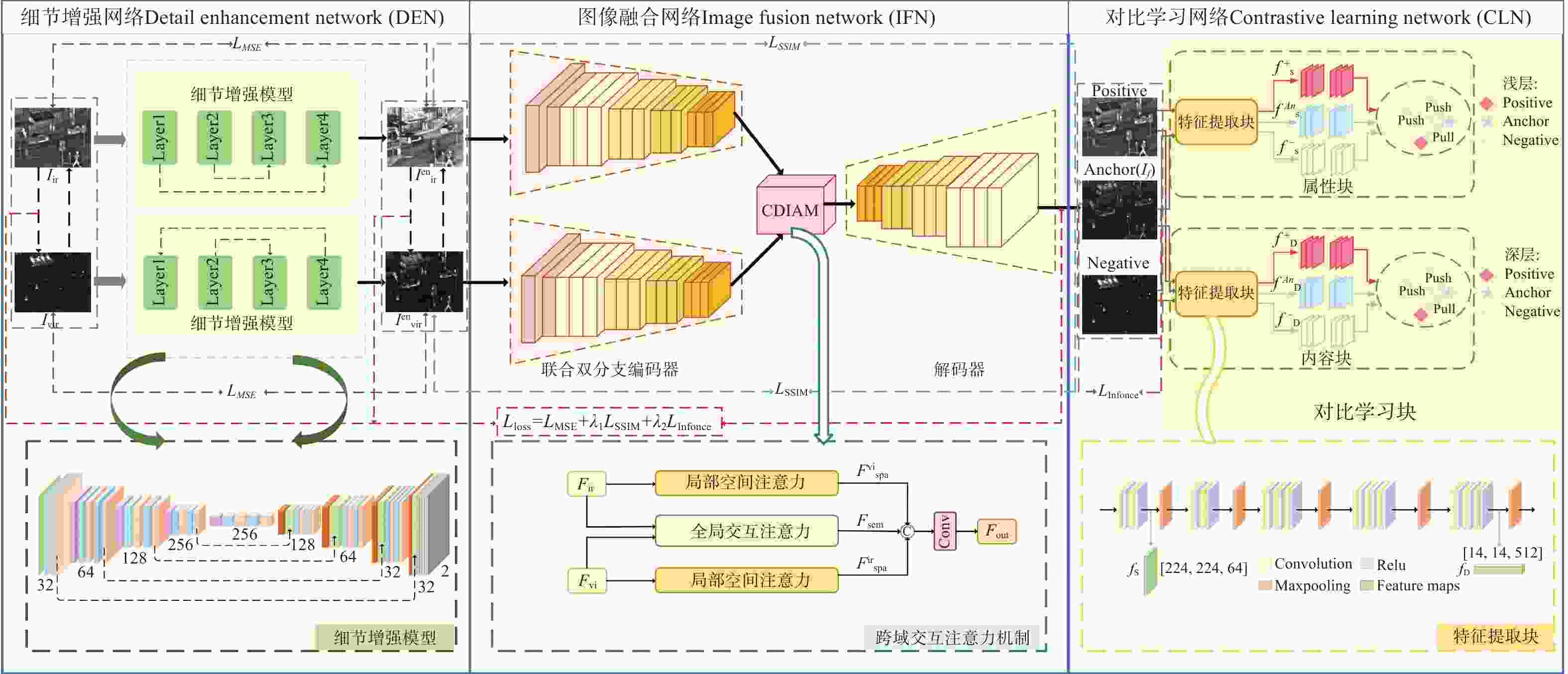
现有红外与可见光图像融合方法难以充分提取和保留源图像细节信息与对比度,导致纹理细节模糊。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种跨域交互注意力和对比学习引导的红外与可见光图像融合方法。首先,设计了双支路跳跃连接的细节增强网络,从红外和可见光图像中分别提取和增强细节信息,并利用跳跃连接避免信息丢失,生成增强后的细节图像。接着,构建了联合双分支编码器和跨域交互注意力模块的图像融合网络,确保特征融合时充分进行特征交互,并通过解码器重建为最终的融合图像。然后,引入了通过对比学习块进行浅层和深层属性和内容的对比学习网络,优化特征表示,进一步提升图像融合网络的性能。最后,为了约束网络训练以保留源图像的固有特征,设计了一种基于对比约束的损失函数,以辅助融合过程对源图像信息的对比保留。将提出方法与前沿融合方法进行了定性和定量的分析比较。在TNO、MSRS、RoadSence数据集上的实验结果表明:本文方法的8项客观评价指标均较对比方法有显著提升。本文方法融合后图像具有丰富的细节纹理、显著的清晰度和对比度,有效提高了道路交通、安防监控等实际应用中的目标识别和环境感知能力。
-
关键词:
- 红外与可见光图像融合 /
- 对比学习 /
- 跨域交互注意力机制 /
- 对比约束损失
Abstract:Aiming at the problems in existing infrared and visible image fusion methods, such as the difficulty in fully extracting and preserving the source image details, contrast, and blurred texture details, this paper proposes an infrared and visible image fusion method guided by cross-domain interactive attention and contrastive learning. First, a dual-branch skip connection detail enhancement network was designed to separately extract and enhance detail information from infrared and visible images, using skip connections to prevent information loss and generate enhanced detail images. Next, a fusion network combining a dual-branch encoder and cross-domain interactive attention module was constructed to ensure sufficient feature interaction during fusion, and the decoder was used to reconstruct the final fused image. Then, a contrastive learning network was introduced, performing shallow and deep attribute and content contrastive learning from the contrastive learning block, optimizing feature representation, and further improving the performance of the fusion network. Finally, to constrain network training and retain the inherent features of the source images, a contrast-based loss function was designed to assist in preserving source image information during fusion. The proposed method is qualitatively and quantitatively compared with current state-of-the-art fusion methods. Experimental results show that the eight objective evaluation metrics of the proposed method significantly outperform the comparison methods on the TNO, MSRS, and RoadSence datasets. The fused images produced by the proposed method have rich detail textures, enhanced sharpness, and contrast, effectively improving target recognition and environmental perception in real-world applications such as road traffic and security surveillance.
-
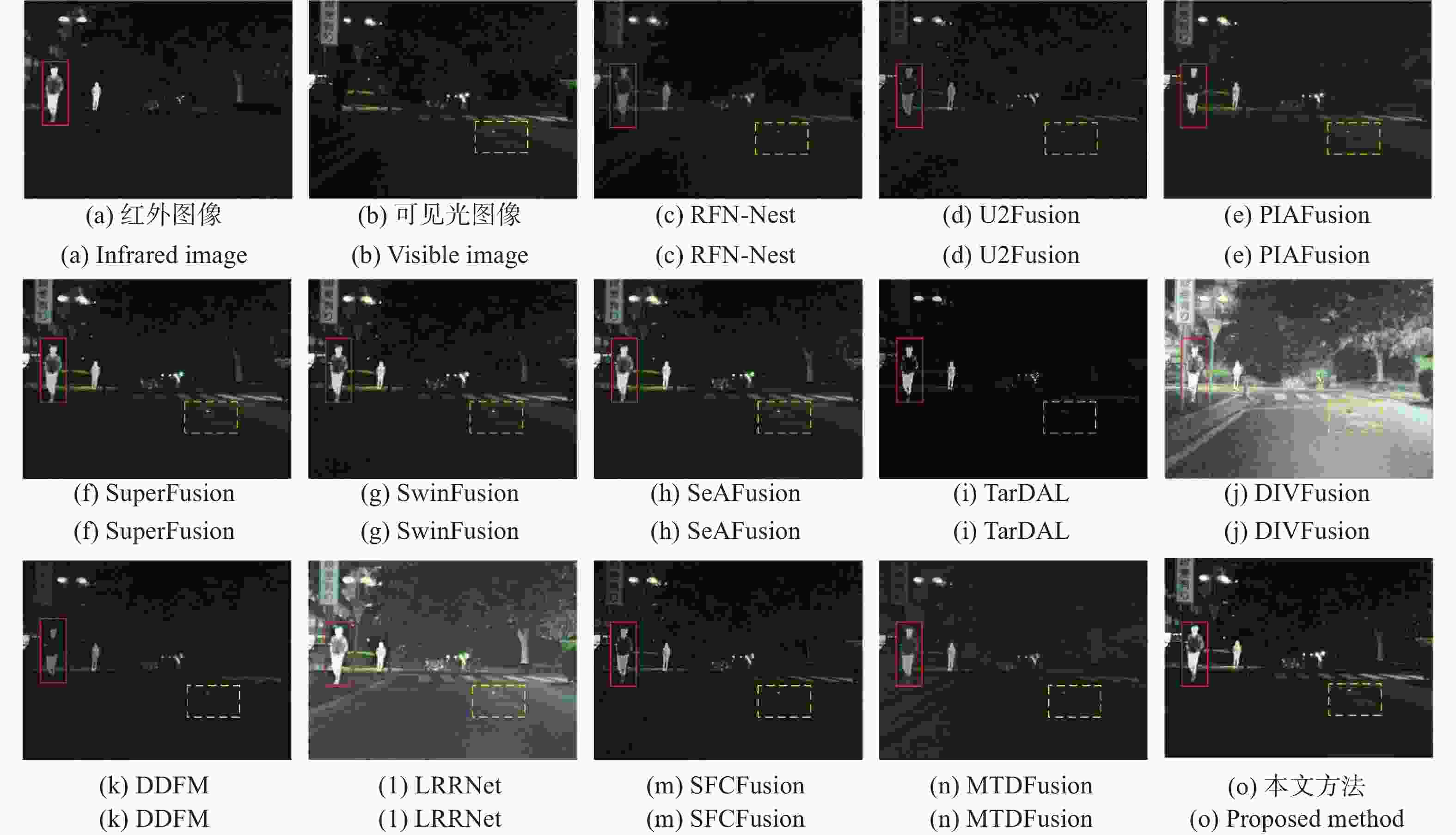
表 1 TNO数据集42组图像的客观评价指标均值
Table 1. Mean values of objective evaluation indices for 42 groups of images in the TNO
方法 评价指标 AG EN SD VIF SF MI PSNR SSIM Time RFN-Nest 2.669 6.963 36.897 0.559 5.874 2.113 62.193 0.649 0.249 U2Fusion ${\underline{\underline{5.023}}} $ 6.997 37.697 0.619 11.864 2.005 62.808 0.605 0.354 PIAFusion 3.828 6.814 37.141 0.740 9.620 3.352 61.776 0.468 0.682 SuperFusion 2.421 6.558 30.663 0.422 6.275 2.330 60.979 ${\underline{\underline{0.753}}} $ 0.715 SwinFusion 3.560 6.819 34.825 0.658 8.985 2.297 62.577 0.686 ${\underline{\underline{0.553}}} $ SeAFusion 4.980 ${\underline{\underline{7.133}}} $ 44.244 ${\underline{\underline{0.704}}} $ 12.253 ${\underline{\underline{2.833}}} $ 61.392 0.628 0.604 TarDAL 2.998 6.840 ${\underline{\underline{45.212}}} $ 0.539 7.959 2.802 62.304 0.597 3.159 DIVFusion 5.560 7.593 47.526 0.625 13.463 2.217 59.979 0.408 2.149 DDFM 5.111 6.854 37.081 0.629 ${\underline{\underline{12.952}}} $ 2.048 63.466 0.618 3.517 LRRNet 3.600 6.838 39.499 0.551 9.331 2.515 62.656 0.546 0.927 SFCFusion 4.324 6.700 31.297 0.675 11.401 1.997 63.133 0.687 2.578 MTDFusion 4.612 6.695 33.669 0.578 11.643 2.256 62.150 0.758 1.597 本文方法 5.601 7.443 50.879 0.792 14.742 3.374 ${\underline{\underline{62.875}}} $ 0.831 0.593 表 2 MSRS数据集40组图像的客观评价指标均值
Table 2. Mean value of objective evaluation indices for 40 groups of images in MSRS
方法 评价指标 AG EN SD VIF SF MI PSNR SSIM Time RFN-Nest 1.557 5.209 25.976 0.555 4.725 2.498 67.123 0.565 0.428 U2Fusion 2.409 5.332 25.303 0.555 7.709 2.244 66.599 0.595 0.536 PIAFusion 3.598 6.536 $\underline{\underline{46.263}} $ 1.008 10.945 3.825 64.464 0.545 0.892 SuperFusion 3.598 6.468 43.469 0.913 9.464 $\underline{\underline{3.999}} $ 64.851 0.545 0.874 SwinFusion 3.598 6.491 44.209 0.913 9.712 4.173 64.821 0.545 0.724 SeAFusion 3.598 6.547 42.902 $\underline{\underline{0.952}} $ 10.047 3.776 64.570 0.581 $\underline{\underline{0.647}} $ TarDAL 3.598 3.312 26.792 0.162 13.973 1.245 63.544 0.278 4.589 DIVFusion 4.313 7.406 54.228 0.784 $\underline{\underline{11.575}} $ 2.545 56.314 0.243 3.248 DDFM 1.848 5.642 21.144 0.561 5.922 2.414 67.088 0.705 3.774 LRRNet 3.508 $\underline{\underline{6.780}} $ 25.976 0.852 10.058 3.202 58.759 $\underline{\underline{0.685}} $ 1.938 SFCFusion $\underline{\underline{3.759}} $ 5.933 30.836 0.636 11.407 2.002 66.788 0.526 2.549 MTDFusion 2.114 5.586 30.836 0.399 6.727 2.090 65.110 0.632 2.874 本文方法 4.731 7.331 56.891 1.138 13.216 4.215 $\underline{\underline{66.821}} $ 0.732 0.698 表 3 RoadSence数据集221组图像的客观评价指标均值
Table 3. Mean value of objective evaluation indices for 221 groups of images in RoadSence
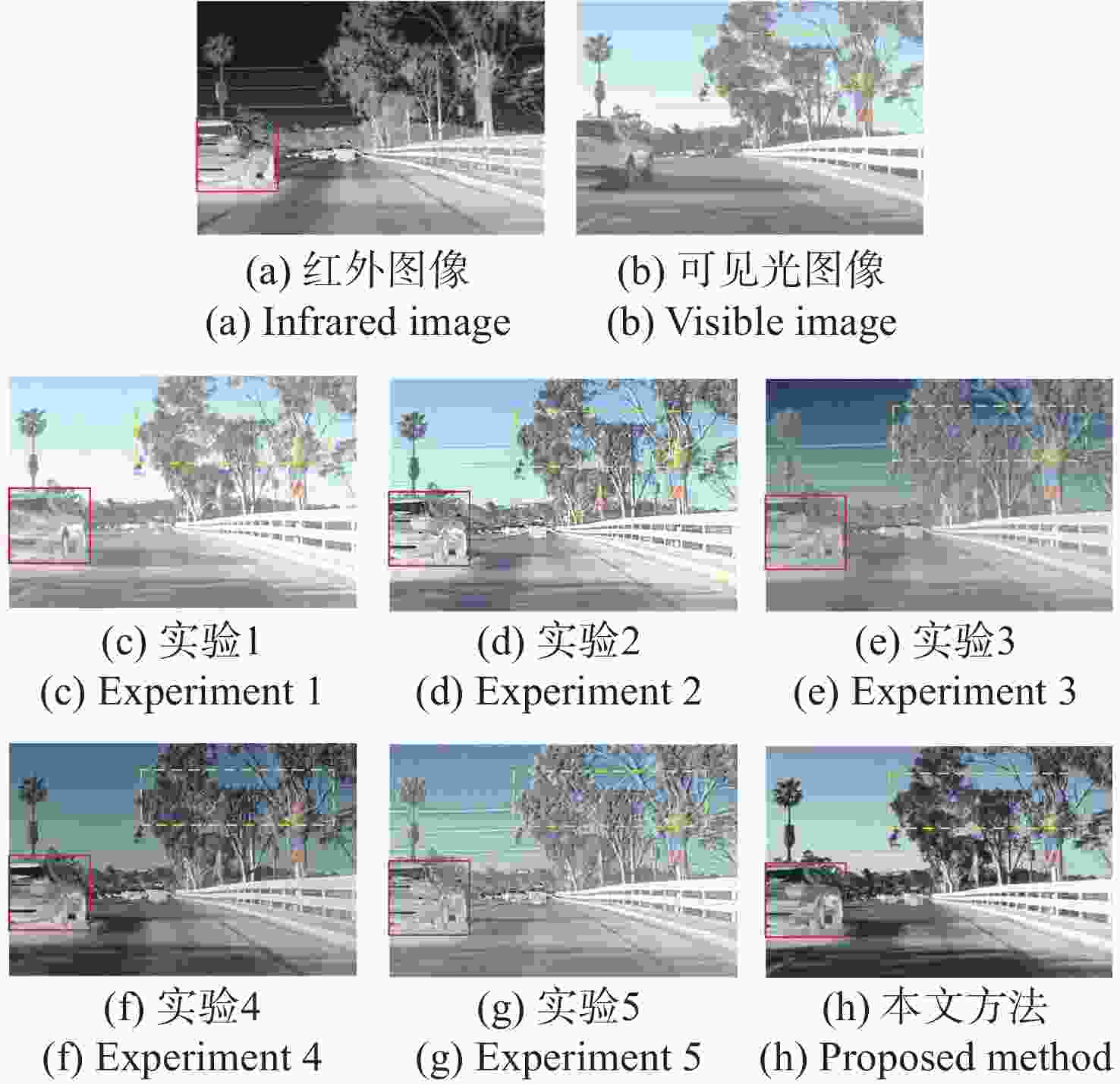
方法 评价指标 AG EN SD VIF SF MI PSNR SSIM Time RFN-Nest 3.362 7.336 46.025 0.500 7.852 2.738 61.366 0.617 0.357 U2Fusion 6.099 7.183 40.092 0.564 15.282 2.578 61.366 0.696 0.684 PIAFusion 4.308 6.981 42.702 0.681 12.132 3.557 61.680 0.659 0.534 SuperFusion 4.469 6.990 41.358 0.608 12.185 $\underline{\underline{3.562}} $ 62.107 0.566 0.824 SwinFusion 4.516 7.000 44.067 0.614 16.720 3.334 61.297 0.529 $\underline{\underline{0.545}} $ SeAFusion $\underline{\underline{6.491}} $ 7.330 49.645 0.600 $\underline{\underline{16.625}} $ 3.022 61.714 0.584 0.657 TarDAL 6.691 7.550 59.398 0.418 16.123 2.191 59.566 0.552 3.924 DIVFusion 5.010 ${\underline{\underline{7.539}}} $ 54.188 0.572 13.295 2.900 61.779 0.441 2.842 DDFM 3.952 6.868 33.551 0.532 10.174 2.845 64.484 0.660 3.667 LRRNet 5.692 7.526 ${\underline{\underline{54.772}}} $ ${\underline{\underline{0.631}}} $ 15.223 3.510 62.025 0.730 1.259 SFCFusion 6.304 7.222 41.496 0.591 15.994 2.842 63.781 0.670 1.842 MTDFusion 4.407 7.059 37.356 0.577 11.417 2.896 ${\underline{\underline{64.440}}} $ ${\underline{\underline{0.728}}} $ 2.067 本文方法 6.924 7.596 60.891 0.703 16.810 4.027 62.303 0.804 0.573 表 4 10组场景消融实验客观评价指标均值
Table 4. Mean values of objective evaluation indices in 10 groups of ablation experiment scenes
模型 AG EN SD VIF SF MI PSNR SSIM 实验1 7.328 7.248 52.314 0.652 16.257 3.628 54.217 0.766 实验2 5.628 6.995 48.302 0.563 18.005 3.495 57.457 0.501 实验3 6.715 7.137 45.541 0.589 18.186 3.214 56.259 0.627 实验4 6.357 7.033 50.249 0.637 17.894 3.455 57.224 0.643 实验5 7.780 7.324 52.413 0.633 17.924 3.527 58.149 0.702 本文方法 8.326 7.421 61.672 0.709 18.259 3.989 59.248 0.791 -
[1] ARCHANA R, JEEVARAJ P S E. Deep learning models for digital image processing: a review[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2024, 57(1): 11. doi: 10.1007/s10462-023-10631-z [2] LI H, WU X J. CrossFuse: a novel cross attention mechanism based infrared and visible image fusion approach[J]. Information Fusion, 2024, 103: 102147. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.102147 [3] YANG B, HU Y X, LIU X W, et al. CEFusion: an infrared and visible image fusion network based on cross-modal multi-granularity information interaction and edge guidance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(11): 17794-17809. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3426539 [4] NAHATA D, OTHMAN K, NAHATA D, et al. Exploring the challenges and opportunities of image processing and sensor fusion in autonomous vehicles: a comprehensive review[J]. AIMS Electronics and Electrical Engineering, 2023, 7(4): 271-321. doi: 10.3934/electreng.2023016 [5] 程博阳, 李婷, 王喻林. 基于视觉显著性加权与梯度奇异值最大的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(4):675-688. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0124CHENG B Y, LI T, WANG Y L. Fusion of infrared and visible light images based on visual saliency weighting and maximum gradient singular value[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(4): 675-688. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0124 [6] ZHANG Y M, LEE H J. Infrared and visible image fusion based on multi-scale decomposition and texture preservation model[C]. Proceedings of 2021 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Artificial Intelligence (ICCEAI), IEEE, 2021: 335-339. [7] GAO M L, ZHOU Y N, ZHAI W ZH, et al. SaReGAN: a salient regional generative adversarial network for visible and infrared image fusion[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2023, 83(22): 61659-61671. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-14393-2 [8] LI X L, LI Y F, CHEN H J, et al. RITFusion: reinforced interactive transformer network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 5000916. [9] CHEN J, LI X J, LUO L B, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on target-enhanced multiscale transform decomposition[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 508: 64-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.08.066 [10] 刘先红, 陈志斌, 秦梦泽. 结合引导滤波和卷积稀疏表示的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 光学 精密工程,2018,26(5):1242-1253. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182605.1242LIU X H, CHEN ZH B, QIN M Z. Infrared and visible image fusion using guided filter and convolutional sparse representation[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(5): 1242-1253. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182605.1242 [11] LI Y H, LIU G, BAVIRISETTI D P, et al. Infrared-visible image fusion method based on sparse and prior joint saliency detection and LatLRR-FPDE[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2023, 134: 103910. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2023.103910 [12] LIU Y, CHEN X, WARD R K, et al. Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(12): 1882-1886. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2618776 [13] PRABHAKAR K R, SRIKAR V S, VENKATESH BABU R. DeepFuse: a deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs[C]. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2017: 4724-4732. [14] LI H, WU X J, DURRANI T. NestFuse: an infrared and visible image fusion architecture based on nest connection and spatial/channel attention models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(12): 9645-9656. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.3005230 [15] LI H, WU X J, KITTLER J. RFN-Nest: an end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images[J]. Information Fusion, 2021, 73: 72-86. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.02.023 [16] MA J Y, TANG L F, FAN F, et al. SwinFusion: cross-domain long-range learning for general image fusion via Swin transformer[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2022, 9(7): 1200-1217. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2022.105686 [17] ZHAO Z X, BAI H W, ZHANG J SH, et al. CDDFuse: correlation-driven dual-branch feature decomposition for multi-modality image fusion[C]. Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2023: 5906-5916. [18] WANG X, GUAN ZH, QIAN W H, et al. CS2Fusion: contrastive learning for self-supervised infrared and visible image fusion by estimating feature compensation map[J]. Information Fusion, 2024, 102: 102039. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.102039 [19] HE K M, FAN H Q, WU Y X, et al. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning[C]. Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2020: 9726-9735. [20] XU H, MA J Y, JIANG J J, et al. U2Fusion: a unified unsupervised image fusion network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(1): 502-518. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3012548 [21] TANG L F, YUAN J T, ZHANG H, et al. PIAFusion: a progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware[J]. Information Fusion, 2022, 83-84: 79-92. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.03.007 [22] TANG L F, DENG Y X, MA Y, et al. SuperFusion: a versatile image registration and fusion network with semantic awareness[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2022, 9(12): 2121-2137. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2022.106082 [23] TANG L F, YUAN J T, MA J Y. Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: a semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network[J]. Information Fusion, 2022, 82: 28-42. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.12.004 [24] LIU J Y, FAN X, HUANG ZH B, et al. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection[C]. Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2022: 5792-5801. [25] TANG L F, XIANG X Y, ZHANG H, et al. DIVFusion: darkness-free infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 91: 477-493. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.10.034 [26] ZHAO Z X, BAI H W, ZHU Y ZH, et al. DDFM: denoising diffusion model for multi-modality image fusion[C]. Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2023: 8048-8059. [27] LI H, XU T Y, WU X J, et al. LRRNet: a novel representation learning guided fusion network for infrared and visible images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(9): 11040-11052. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3268209 [28] CHEN H R, DENG L, CHEN ZH X, et al. SFCFusion: spatial-frequency collaborative infrared and visible image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 5011615. [29] LIU J Y, LIN R J, WU G Y, et al. CoCoNet: coupled contrastive learning network with multi-level feature ensemble for multi-modality image fusion[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2024, 132(5): 1748-1775. doi: 10.1007/s11263-023-01952-1 -





 下载:
下载: