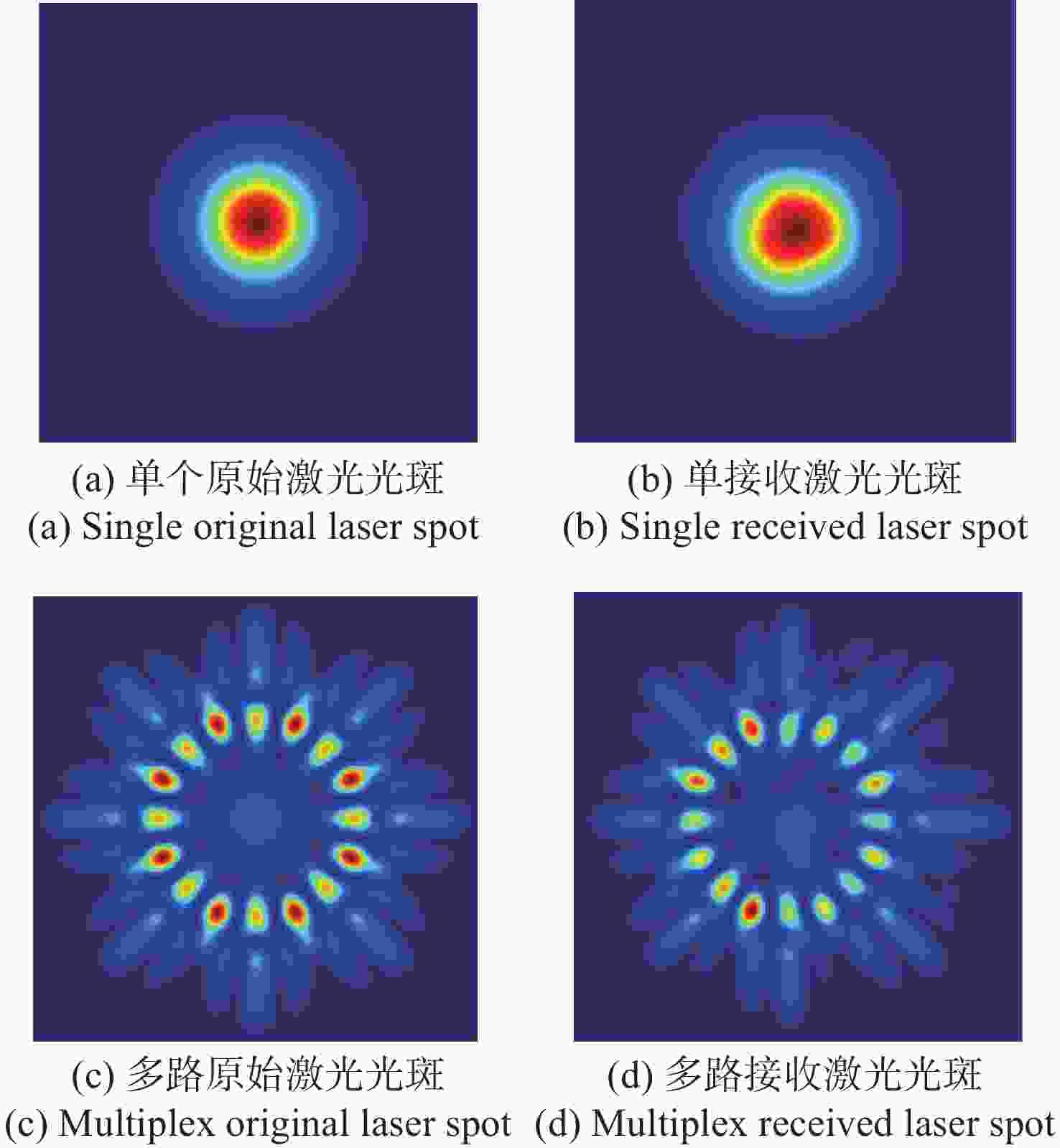
-
摘要:
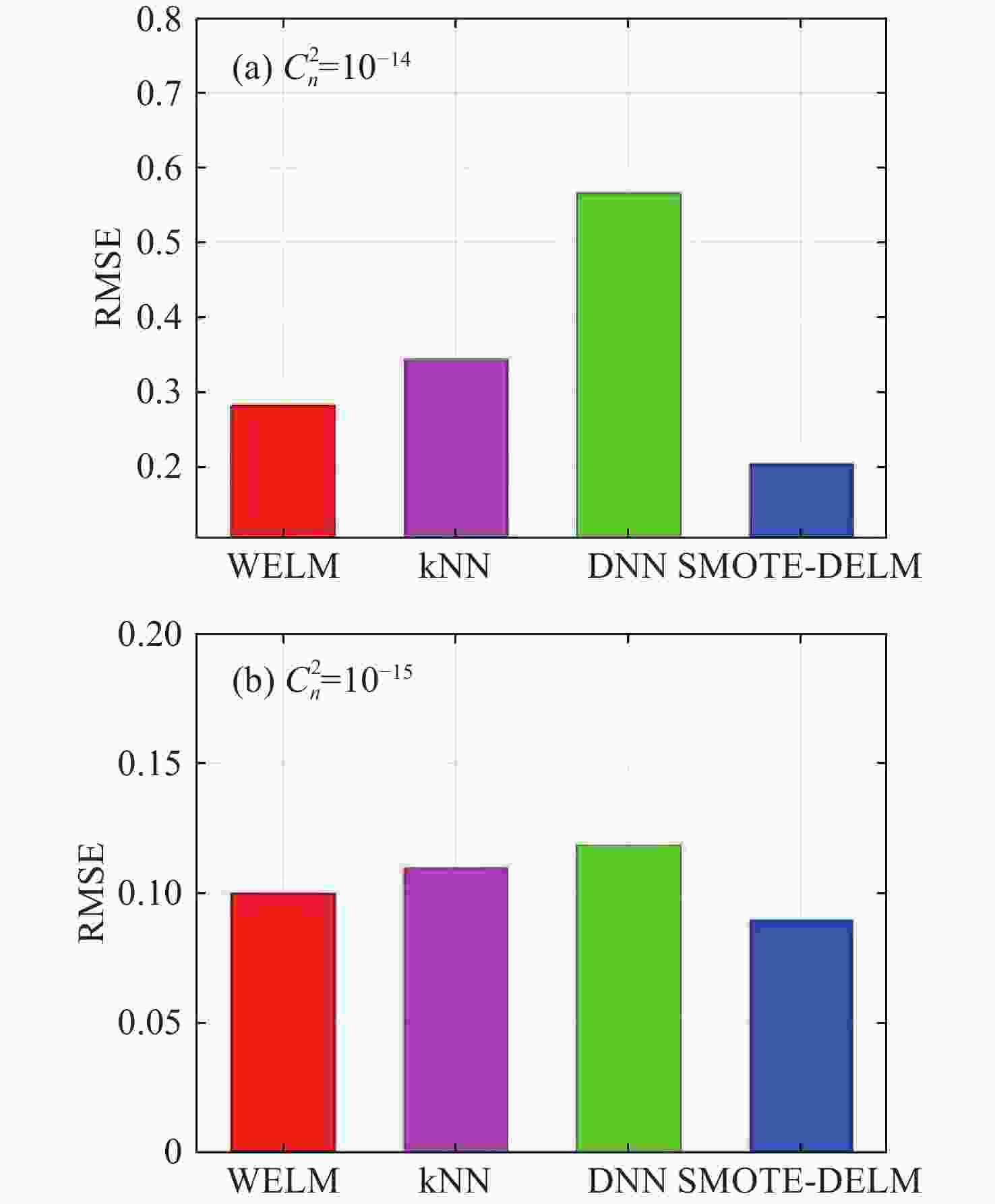
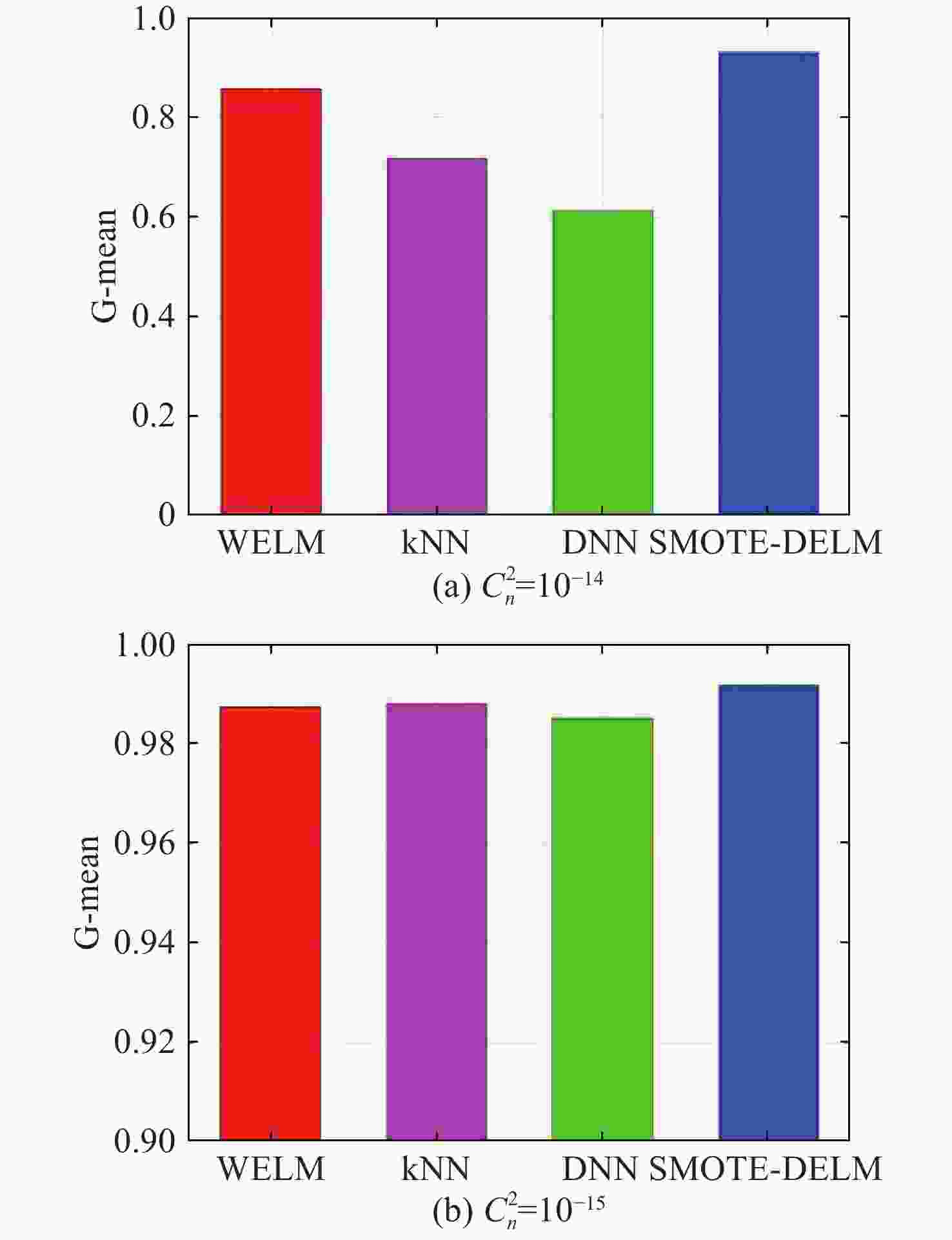
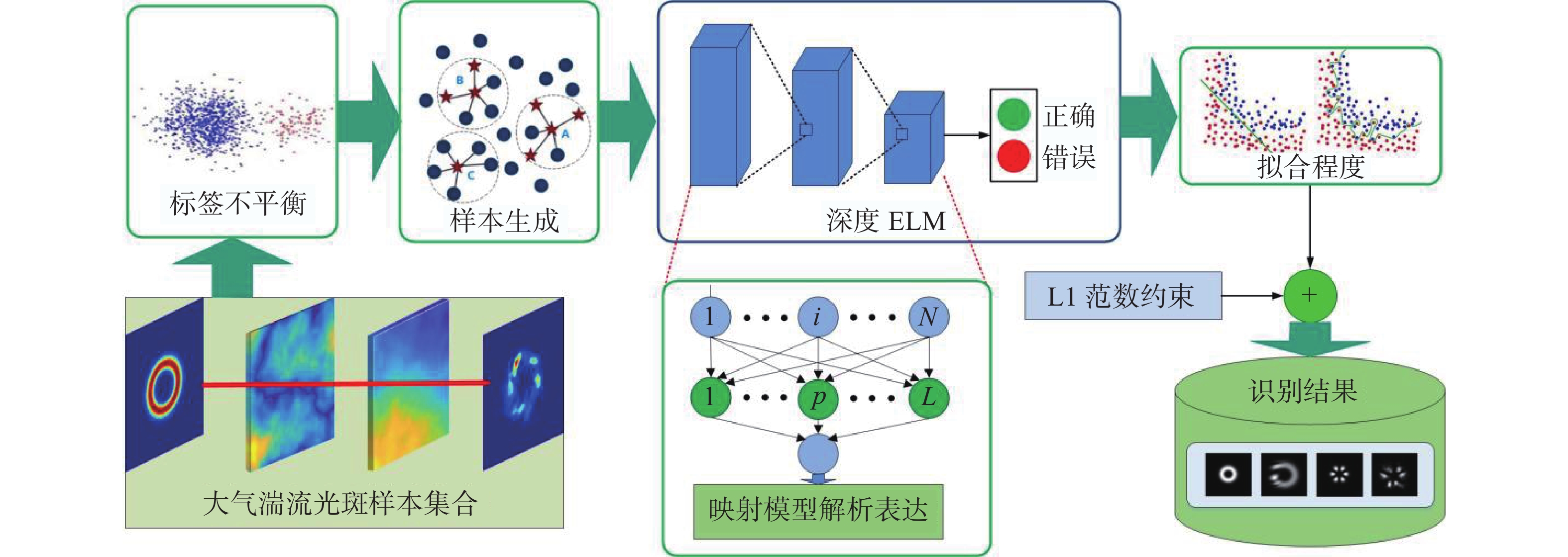
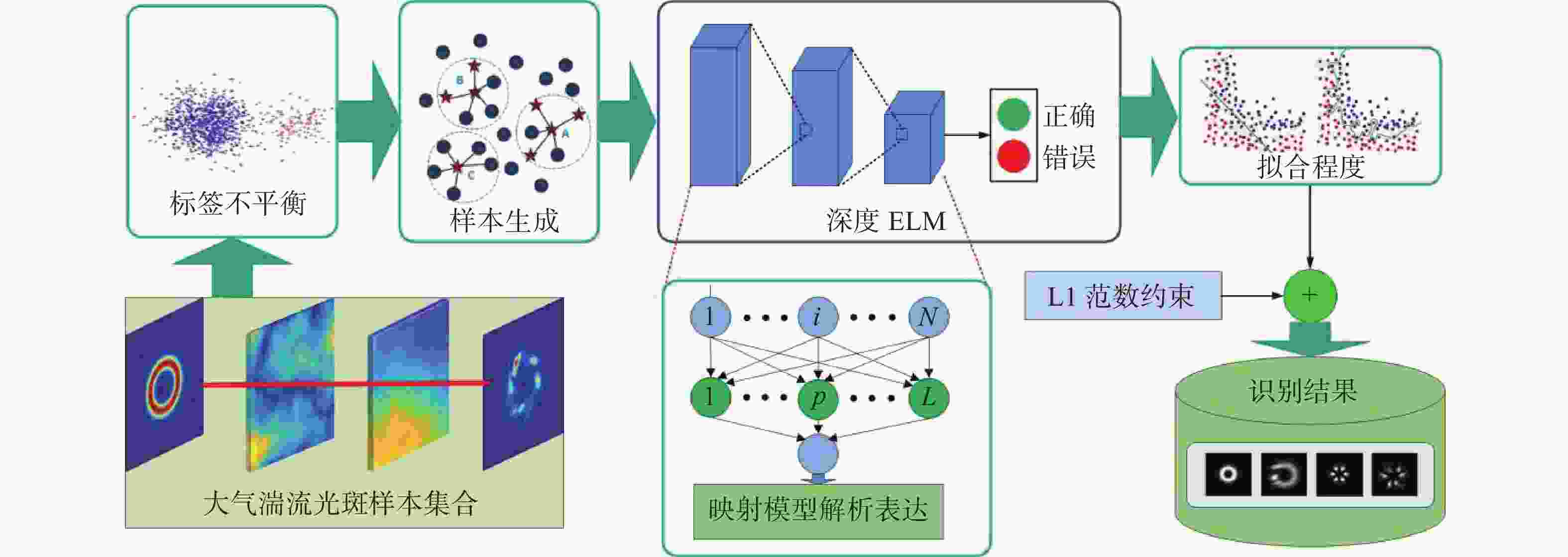
针对标签分布不平衡的涡旋光束轨道角动量(OAM)识别问题,提出了一种基于全局代价的合成少数类过采样技术(SMOTE)的深度极限学习机(DELM)的衍生模型。与典型的机器学习方法不同,本文所提方法能够获得映射模型解析表达,避免了反复的参数优化过程,使模型适用于工程应用。在数据生成阶段,利用协方差的逆矩阵去除量纲的影响,有效度量了同一类样本的差异性。在模型选择阶段,考虑了光信号在大气湍流中的传输特性,采用DELM表征光斑样本和标签之间的映射关系,并用快速迭代收缩阈值FISTA算法计算模型的解析表达式。在不同强度的大气湍流数据集上进行实验,对比了WELM、k近邻等代表性方法性能。实验结果表明,在不同的湍流强度下,所提方法均方根误差达到
0.2049 和0.0894 ,各项评价指标均优于对比方法。证明了所提方法能够充分挖掘了OAM光斑集合的特征,具有更好的识别效果。Abstract:To identify the vortex beams orbital angular momentum (OAM) with imbalanced labels, this paper proposes a derived model based on global cost SMOTE and deep extreme learning machine (DELM). Unlike typical machine learning methods, the proposed model can obtain the analytical expression of the mapping model. It avoids repeated parameter optimization, thus building a suitable model for time-varying engineering applications. In the data generation stage, the inverse matrix of covariance was used to remove the influence of dimensions, and the differences among samples within the same category were effectively measured. In the model selection stage, considering the transmission characteristics of light signals in atmospheric turbulence, the DELM was adopted to quantify the mapping relationship between light spots and labels. Then the FISTA algorithm was used to calculate the model’s analytical expression. Experiments were carried out on different intensity atmospheric turbulence data sets. The representative comparative methods include WELM and k-nearest neighbor. Experimental results show that the proposed method’s root mean square error (RMSE) achieves
0.2049 and0.0894 , which are superior to the comparison methods under different turbulence intensities. This proves that the proposed method can fully explore the characteristics of OAM spot collection and has a better recognition effect. -
表 1 所提方法伪代码
Table 1. Pseudocode of proposed method
(1)数据生成阶段,根据式(11)进行重采样;
(2)if(样本数目<平均样本数目);
(3) 根据式(12)计算马氏距离;
添加新样本到样本集合中sample=[sample s];
(4)end;
(5)利用多层ELM网络构建特征向量与OAM标签关系;
(6)初始化目标函数并根据式(15)制定最优准则;
(7)计算Lipschitz条件的近似函数;
(8)利用FISTA迭代求解每一层输出权重;
(9)利用式(19)计算综合权重;
(10)返回输出层权重的解析解$ {{\boldsymbol{\beta }}_j} $和OAM模态估计值。表 2 混淆矩阵
Table 2. Confusion matrix
真实结果 预测结果 正例 反例 正例 TP (真正例) FN (假反例) 反例 FP (假正例) TN (真反例) 表 3 消融实验
Table 3. Ablation experiment
深度ELM SMOTE-DELM $ C_n^2 = {10^{ - 14}} $ 0.2552 0.2049 $ C_n^2 = {10^{ - 15}} $ 0.0924 0.0894 -
[1] ARYA S, CHUNG Y H. A comprehensive survey on optical scattering communications: current research, new trends, and future vision[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorial, 2024, 26(2): 1446-1477. [2] CHEN R, ZHOU J X, LONG W X, et al. Hybrid circular array and Luneberg lens for long-distance OAM wireless communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(1): 485-497. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3223697 [3] YU H, YANG B W, HU H Y, et al. Propagation characteristics of the vortex beam array through anisotropic non-Kolmogorov maritime atmospheric turbulence[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2023, 11: 1277132. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2023.1277132 [4] 毛红敏, 丁致雅, 杨燕燕, 等. 大气湍流对高分辨率遥感卫星的成像影响研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(1):167-177.MAO H M, DING ZH Y, YANG Y Y, et al. Effect of atmospheric turbulence on imaging quality of high-resolution remote sensing satellites[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(1): 167-177. [5] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [6] JING G Q, CHEN L ZH, WANG P P, et al. Recognizing fractional orbital angular momentum using feed forward neural network[J]. Results in Physics, 2021, 28: 104619. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104619 [7] FU X, BAI Y H, YANG Y J. Measuring OAM by the hybrid scheme of interference and convolutional neural network[J]. Optical Engineering, 2021, 60(6): 064109. [8] 娄岩, 陈纯毅, 赵义武, 等. 高斯涡旋光束在大气湍流传输中的特性研究[J]. 中国光学,2017,10(6):768-776. doi: 10.3788/co.20171006.0768LOU Y, CHEN CH Y, ZHAO Y W, et al. Characteristics of Gaussian vortex beam in atmospheric turbulence transmission[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(6): 768-776. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/co.20171006.0768 [9] ZHOU H Q, WANG Y T, LI X, et al. A deep learning approach for trustworthy high-fidelity computational holographic orbital angular momentum communication[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2021, 119(4): 044104. doi: 10.1063/5.0051132 [10] 吴鹏飞, 贾致远, 雷思琛, 等. 改进CNN-Transformer结合双缝干涉的轨道角动量模态识别方法[J]. 光学学报,2024,10:1-17.WU P F, JIA ZH Y, LEI S CH, et al. A method for orbital angular momentum mode recognition employing an enhanced CNN-transformer model integrated with double-slit interference[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2024, 10: 1-17. [11] ZHU CH X, ZHOU X X, GUO G C, et al. Simulating electrical fields in the orbital angular momentum space of light[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(2): 972-985. doi: 10.1364/OE.446276 [12] 郑崇辉, 王天枢, 刘哲绮, 等. 深度迁移学习方法识别轨道角动量光束[J]. 光电工程,2022,49(6):210409.ZHENG CH H, WANG T SH, LIU ZH Q, et al. Deep transfer learning method to identify orbital angular momentum beams[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2022, 49(6): 210409. (in Chinese). [13] 周旭, 陈纯毅, 于海洋, 等. 基于注意力机制的轨道角动量多叠加态识别方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2023,60(23):2306003.ZHOU X, CHEN CH Y, YU H Y, et al. Orbital angular momentum multi-superposition identification method based on attention mechanism[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(23): 2306003. (in Chinese). [14] CHEN CH Y, YANG H M. Characterizing the statistical distribution for transmission coefficient of turbulent optical orbital-angular-momentum channels[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(20): 28968-28982. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.028968 [15] YANG C H, CHENG K, HUANG H W, et al. Orbital-angular-momentum spectra in coherent optical vortex beam arrays with hybrid states of polarizatio[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(6): 1501-1511. [16] 侯政诚, 张明明, 白胜闯, 等. 一维阵列涡旋光束在海面大气中的传输特性[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(2):300-311.HOU ZH CH, ZHANG M M, BAI SH CH, et al. Propagation properties of one-dimensional array vortex beams in a marine atmosphere[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(2): 300-311. [17] GONG CH L, GU L X. A novel SMOTE-based classification approach to online data imbalance problem[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2016, 2016: 5685970. [18] 王忠震, 黄勃, 方志军, 等. 改进SMOTE的不平衡数据集成分类算法[J]. 计算机应用,2019,39(9):2591-2596.WANG ZH ZH, HUANG B, FANG ZH J, et al. Improved SMOTE unbalanced data integration classification algorithm[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2019, 39(9): 2591-2596. (in Chinese). [19] ZHANG A M, YU H L, HUAN ZH J, et al. SMOTE-RkNN: a hybrid re-sampling method based on SMOTE and reverse k-nearest neighbors[J]. Information Sciences, 2022, 595: 70-88. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.02.038 [20] HUANG G, HUANG G B, SONG SH J, et al. Trends in extreme learning machines: a review[J]. Neural Networks, 2015, 61: 32-48. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2014.10.001 [21] YAN D Q, CHU Y H, ZHANG H Y, et al. Information discriminative extreme learning machine[J]. Soft Computing, 2018, 22(2): 677-689. doi: 10.1007/s00500-016-2372-y [22] YU H Y, CHEN CH Y, HU X J, et al. An efficient recognition method for orbital angular momentum via adaptive deep ELM[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(21): 8737. doi: 10.3390/s23218737 [23] BECK A, TEBOULLE M. A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(1): 183-202. doi: 10.1137/080716542 [24] DELGADO-VENCES F J, FLANDOLI F. A spectral-based numerical method for Kolmogorov equations in Hilbert spaces[J]. Infinite Dimensional Analysis, Quantum Probability and Related Topics, 2016, 19(3): 1650020. doi: 10.1142/S021902571650020X [25] LAI J, WANG X D, XIANG Q, et al. Multilayer discriminative extreme learning machine for classification[J]. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2023, 14(6): 2111-2125. doi: 10.1007/s13042-022-01749-7 [26] 陈纯毅, 杨华民, 任斌, 等. 激光大气湍流传输数值实验建模与计算机模拟[J]. 系统仿真学报,2018,30(6):2133-2143.CHEN CH Y, YANG H M, REN B, et al. Modeling and computer simulation of numerical experiments on laser propagation through atmospheric turbulence[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2018, 30(6): 2133-2143. (in Chinese). [27] 姜楠, 李晓英, 牛春晖, 等. 大气湍流对激光空间传输特性影响的实验研究[J]. 激光技术,2022,46(5):708-712.JIANG N, LI X Y, NIU CH H, et al. Experimental study on the influence of atmospheric turbulence on laser spatial transmission characteristics[J]. Laser Technology, 2022, 46(5): 708-712. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: