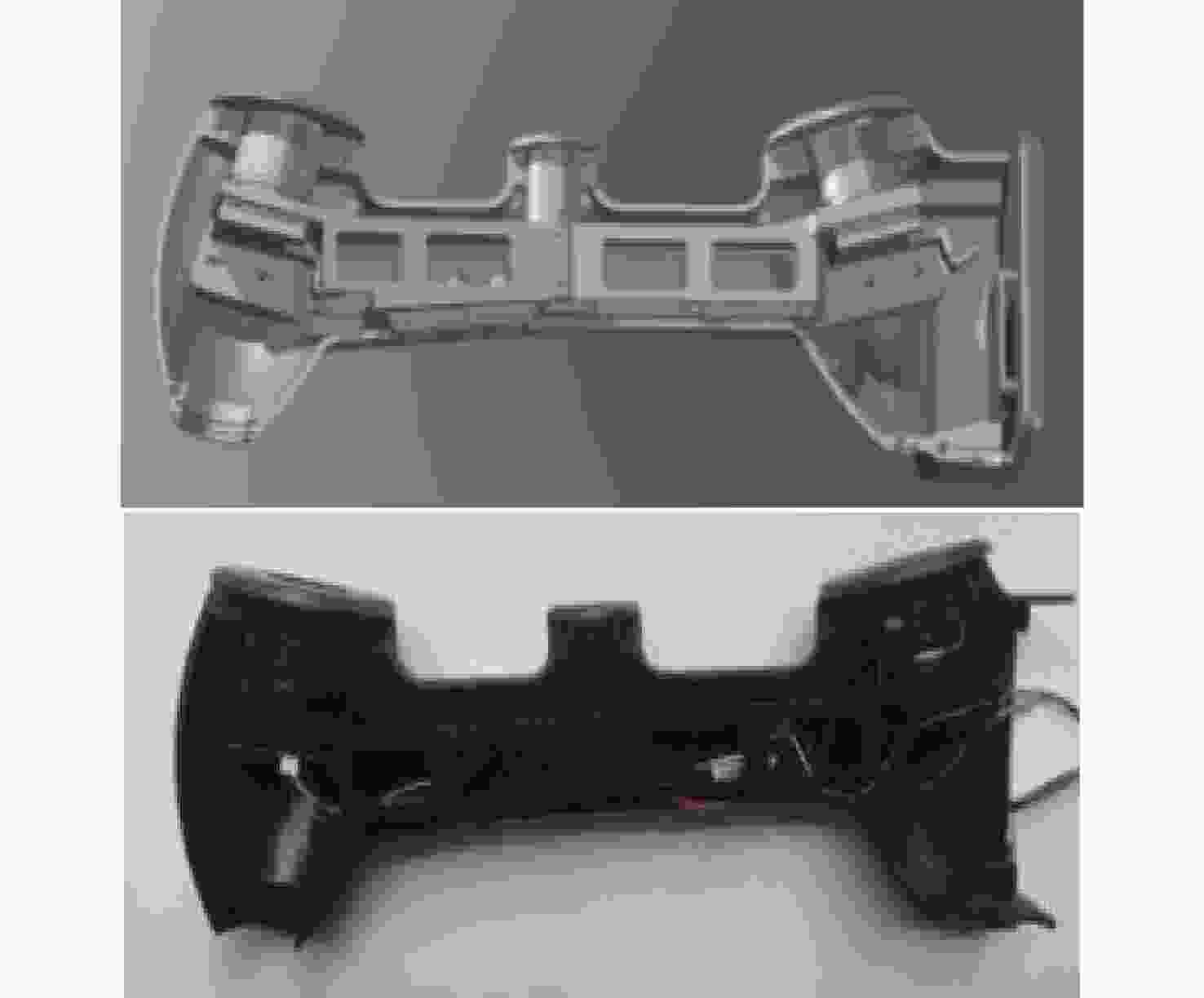
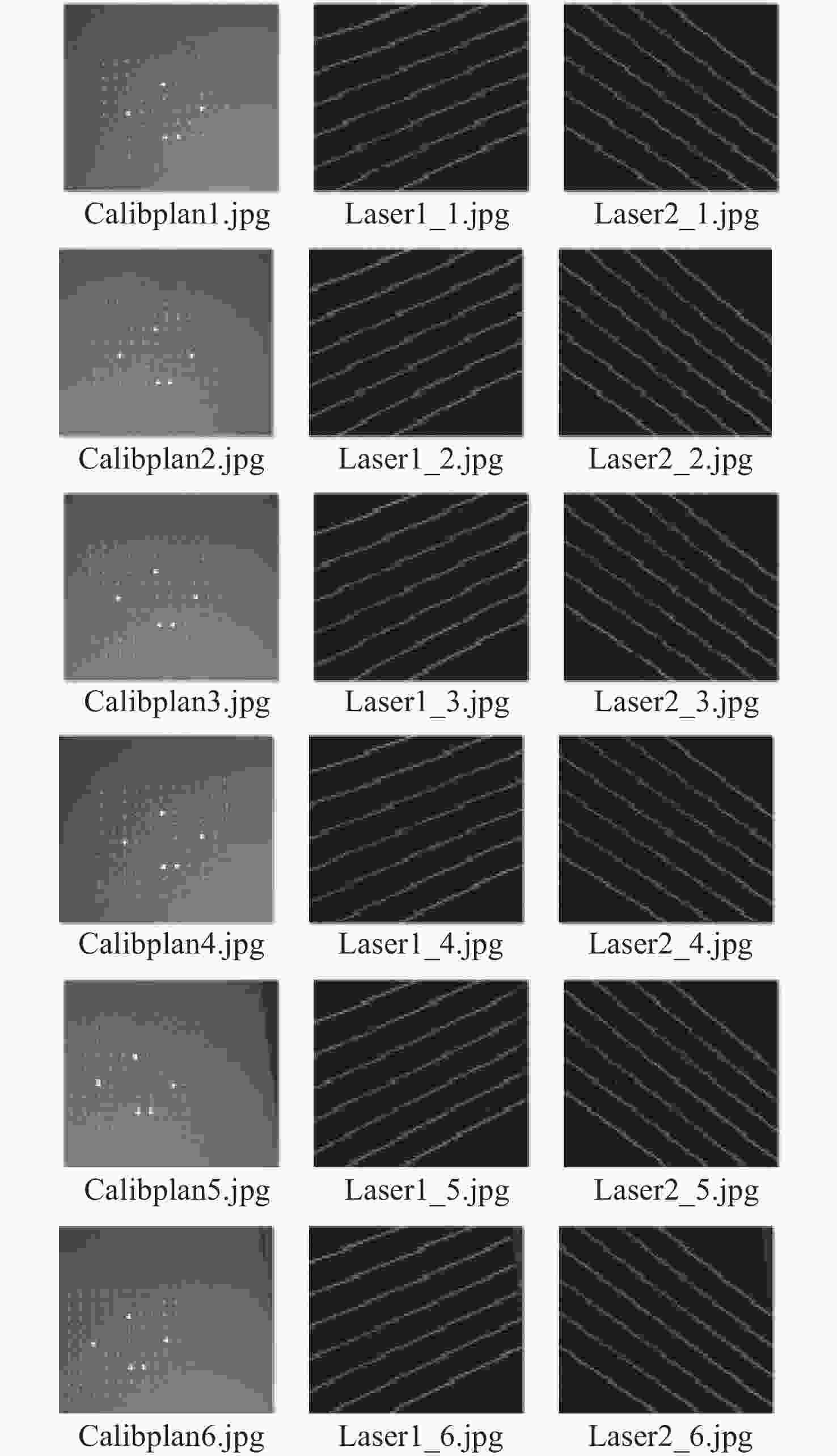
-
摘要:
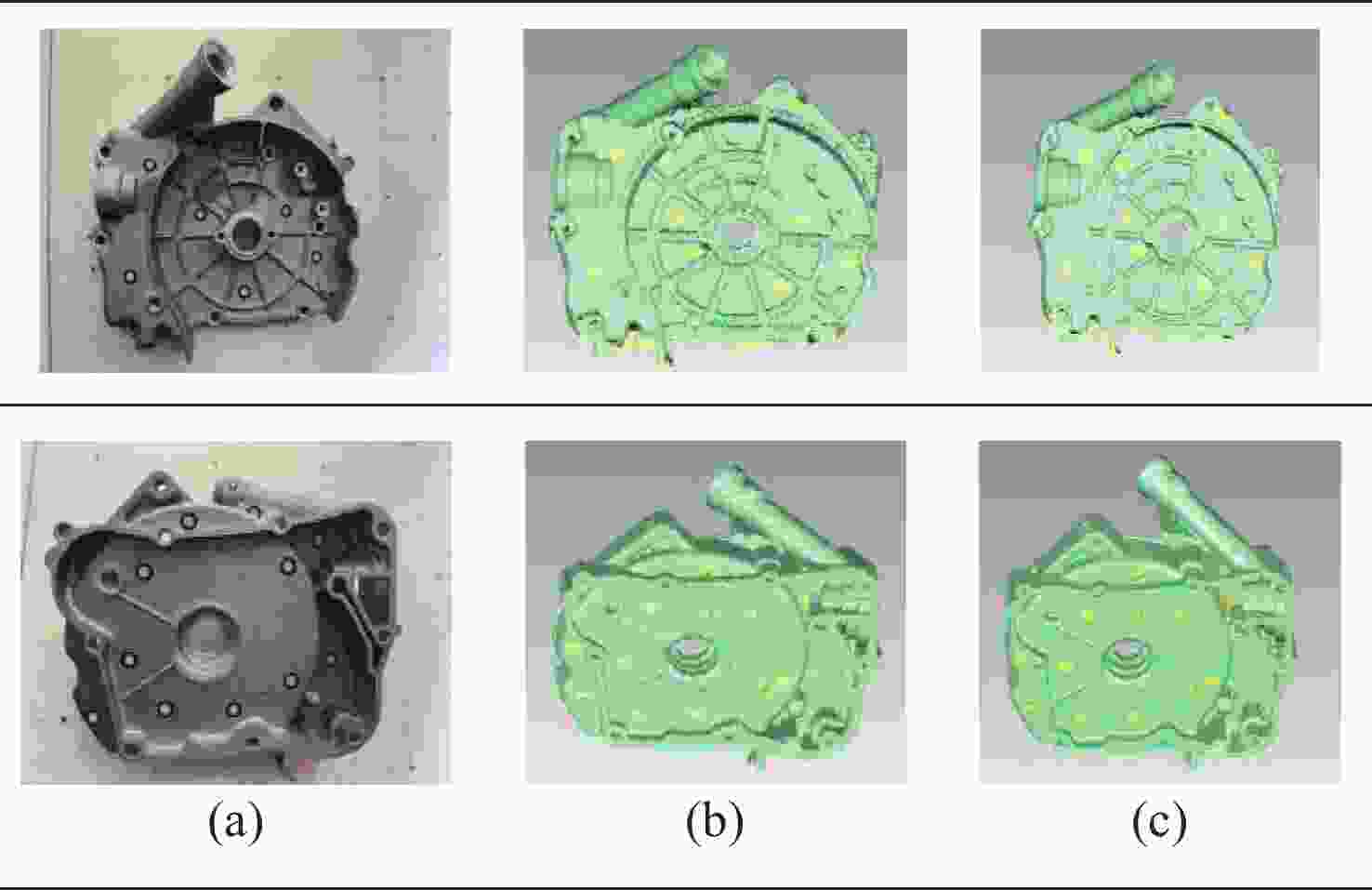
传统的多线激光三维重建技术由于多线激光线不可避免地会受到噪声的影响,导致检测的激光中心坐标存在一定误差,这将导致直接使用基于极线约束找到的匹配点进行三维重建时无法获得高精度的三维数据。为了解决上述问题,本文提出了一种基于几何估计方法来实现多线激光的三维重建。首先,标定出多线激光的二次曲面方程,结合双目极线约束的方法可以计算出多线激光的初始匹配点。在找到正确的初始匹配点之后,利用图像点与双视图极线的关系约束来建立一个几何距离最小化的估计模型。通过这个几何距离最小化的优化估计,可以重新计算出更加符合极线约束的新匹配点,从而提高激光图像点的匹配精度,最后根据这些新的匹配点来完成多线激光的三维重建。实验结果显示:相较于传统方法,本文提出的算法在匹配度和精度方面表现更优,最终的三维重建精度可以达到0.02 mm左右。通过这种方法可以显著提高双目多线激光重建的整体精度,从而获得更加精确和可靠的三维数据。
Abstract:In traditional multi-line laser 3D reconstruction technology, due to the inevitable noise affecting the multi-line laser lines, the extracted laser center coordinates often contain specific errors. These errors can lead to the inability to obtain high-precision 3D data when using matching points found based on epipolar constraints for 3D reconstruction directly. To address this issue, we propose a method based on geometric estimation to achieve 3D reconstruction of multi-line lasers. First, by calibrating the quadratic surface equations of the multi-line laser, combined with the binocular epipolar constraint method, the initial matching points of the multi-line laser can be calculated. After finding the correct initial matching points, a geometric distance minimization estimation model can be established using the distance constraint from points to epipolar lines. This geometric distance refers to the distance from the laser center points in the left and right images to their corresponding epipolar lines. New matching points that better conform to the epipolar constraints can be recalculated through this geometric distance minimization optimization estimation. Finally, these new matching points can be used to complete the 3D reconstruction of the multi-line laser. Compared to the traditional method based on epipolar constraints, the algorithm proposed in this paper performs better in matching and accuracy. The accuracy of the final 3D reconstruction can reach about 0.02 mm. This method can significantly improve the overall accuracy of binocular multi-line laser reconstruction, thereby obtaining more accurate and reliable 3D data.
-
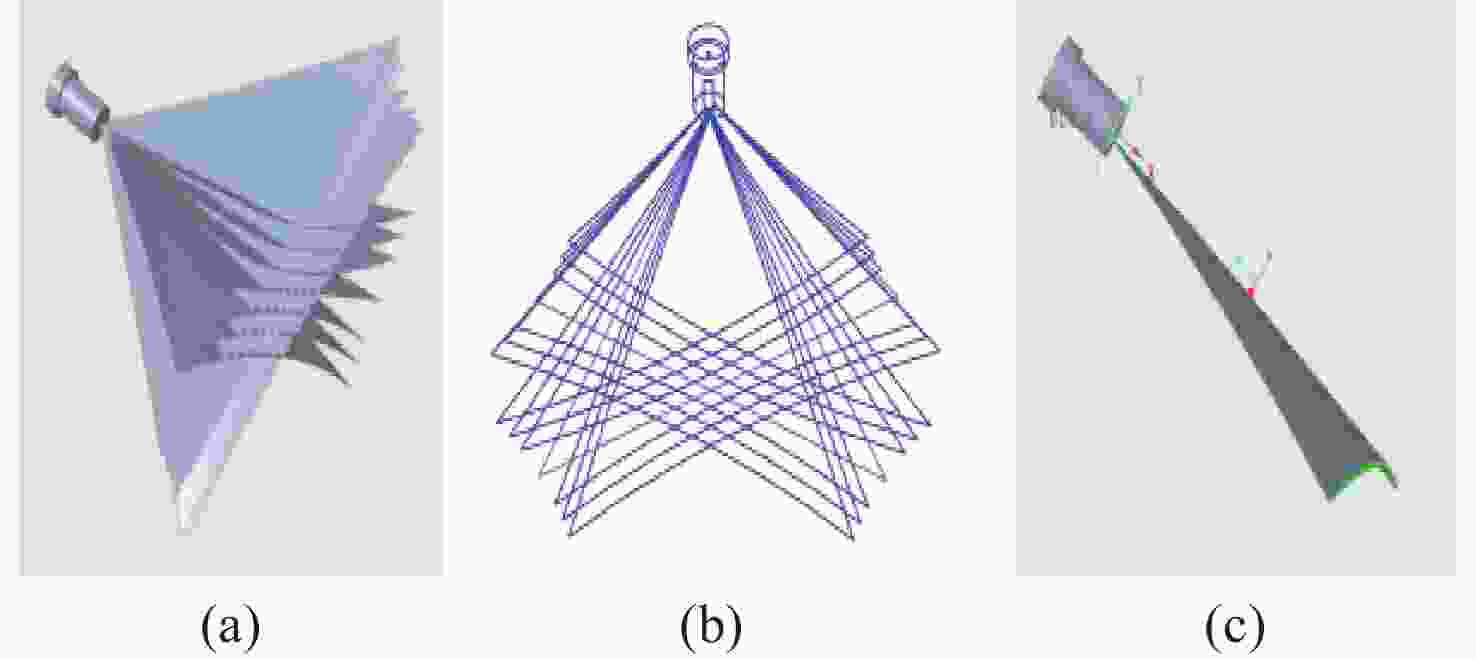
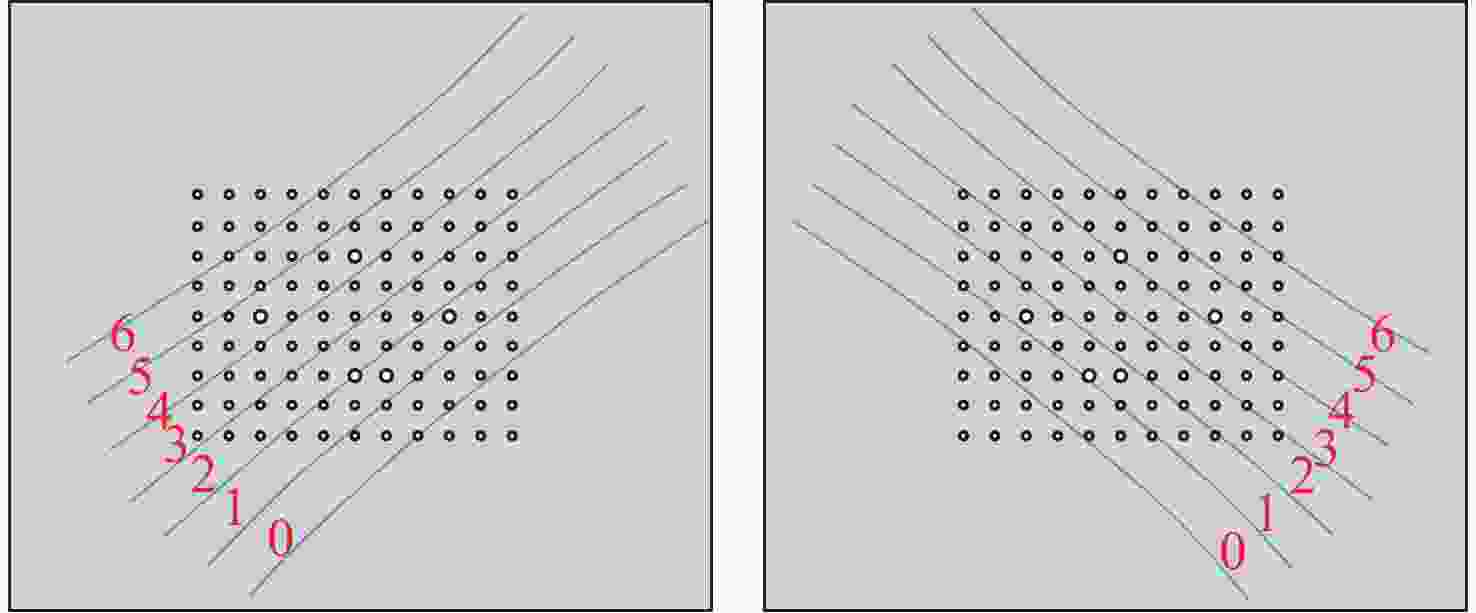
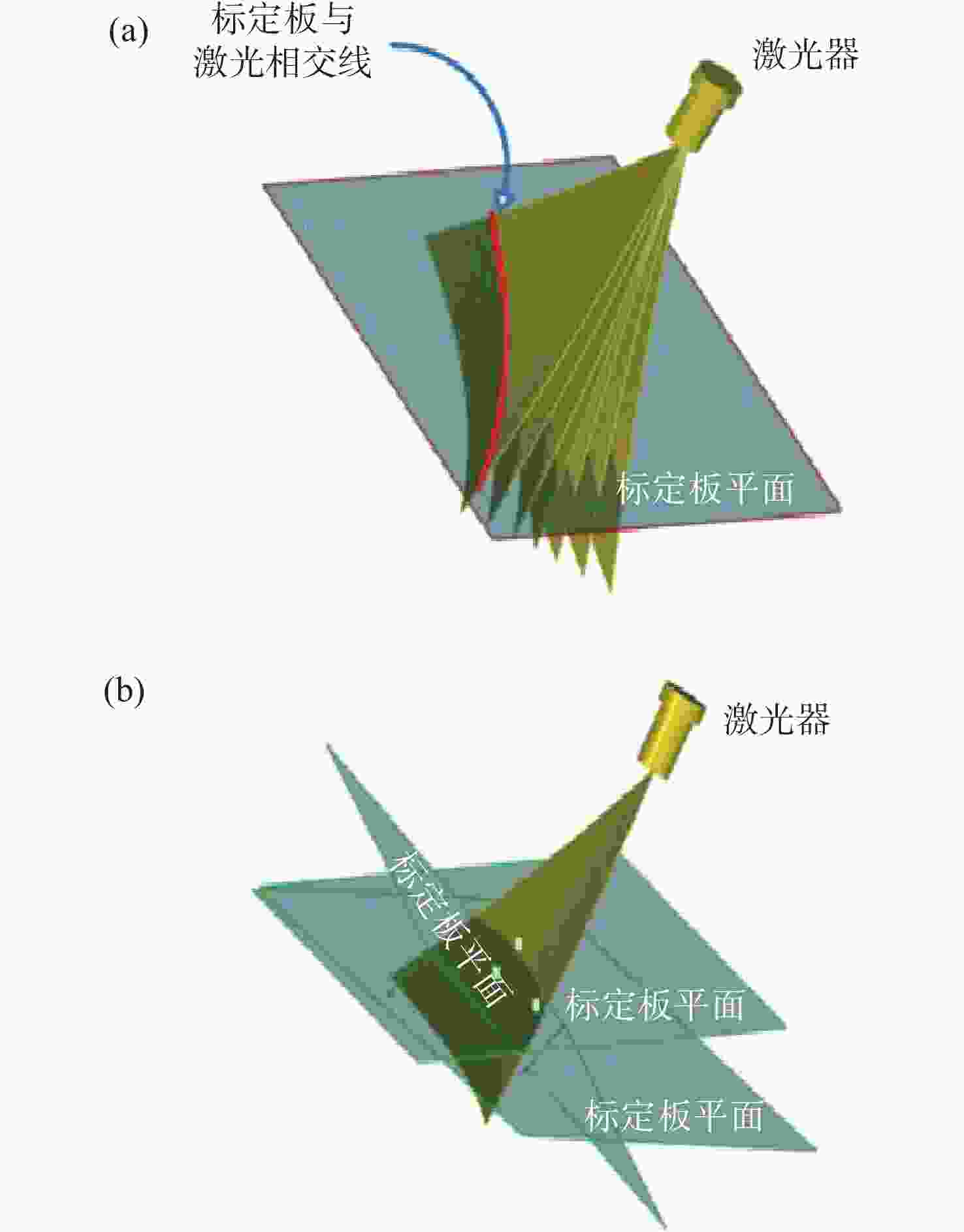
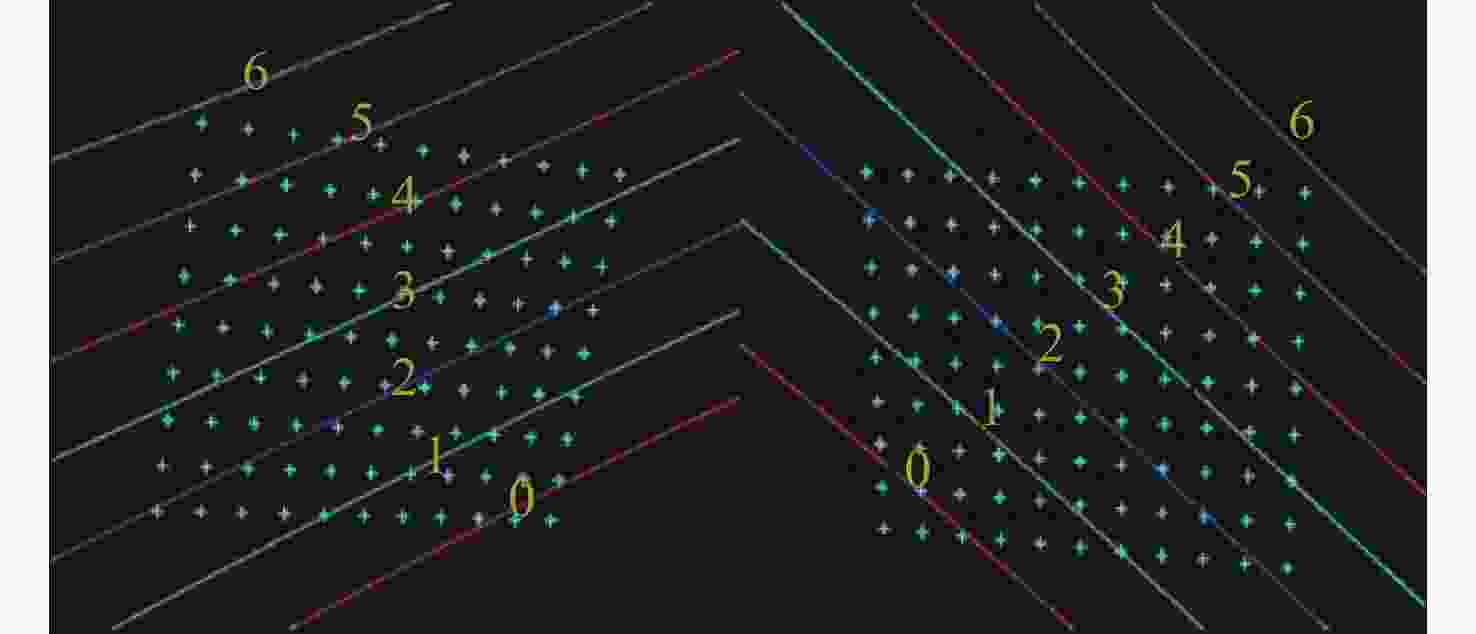
图 4 多线激光曲面与标定平面相交图。(a)多线激光空间二次曲面与标定板相交情况。(b)单个激光二次曲面与多个位置标定相交情况
Figure 4. Intersection diagram of multi-line laser surface and calibration plane. (a) The intersection of the multi-line laser spatial quadratic surface with the calibration plate. (b) The intersection of a single laser quadratic surface with multiple positions
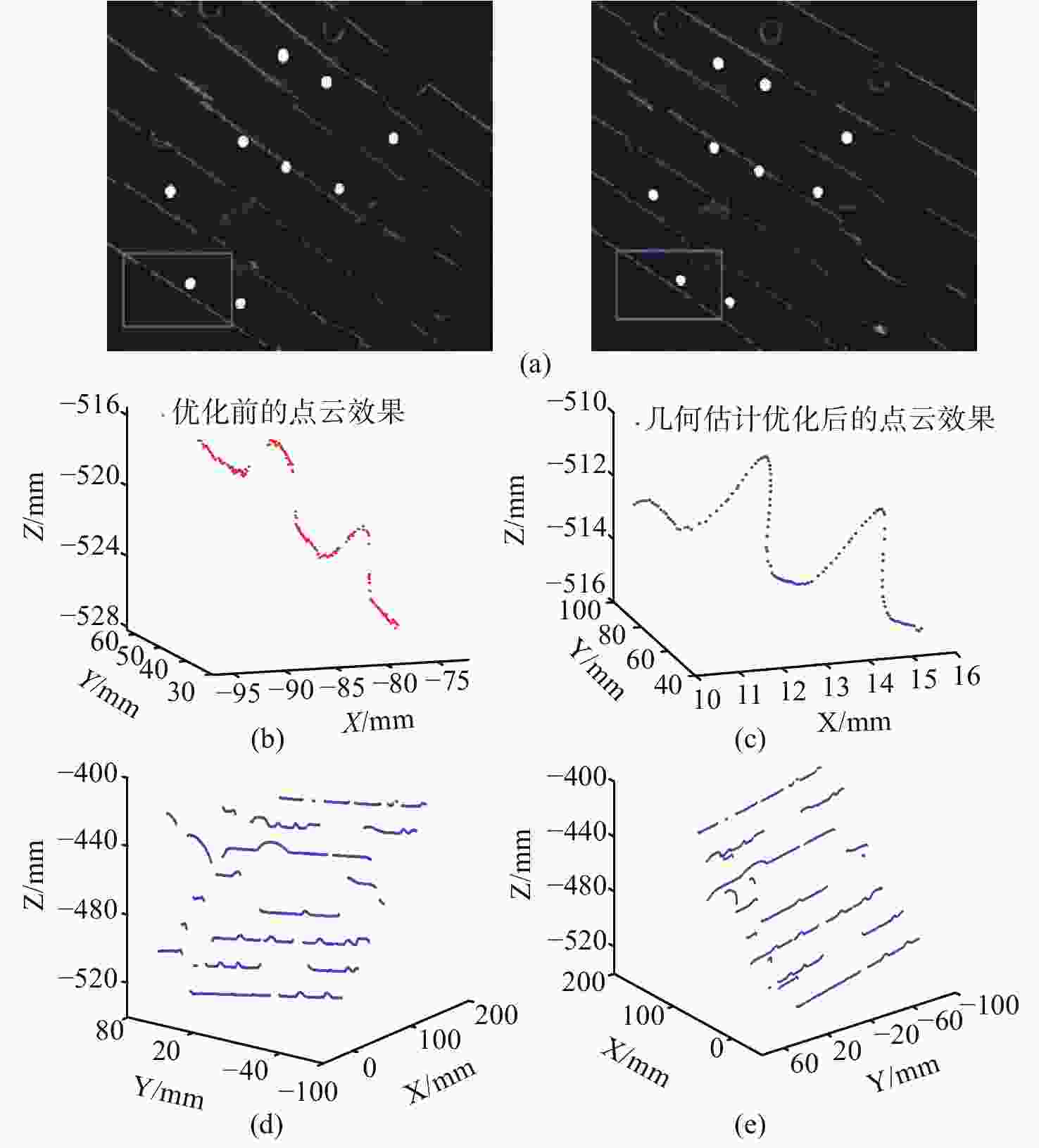
图 13 基于几何估计优化前后的点云效果对比结果。(a)左右多线激光提取效果和框选的区域;(b)框选区域优化前的点云效果;(c)框选区域几何估计优化后的点云效果;(d)(e)几何估计优化后的整体点云重建效果
Figure 13. Comparison of point cloud effect before and after optimization based on geometric estimation. (a) Left and right multi-line laser extraction effect and box selection area; (b) the point cloud effect of box selection area before optimization; (c) geometrically estimated point cloud effect after optimization; (d) and (e) overall point cloud reconstruction effect after geometric estimation optimization
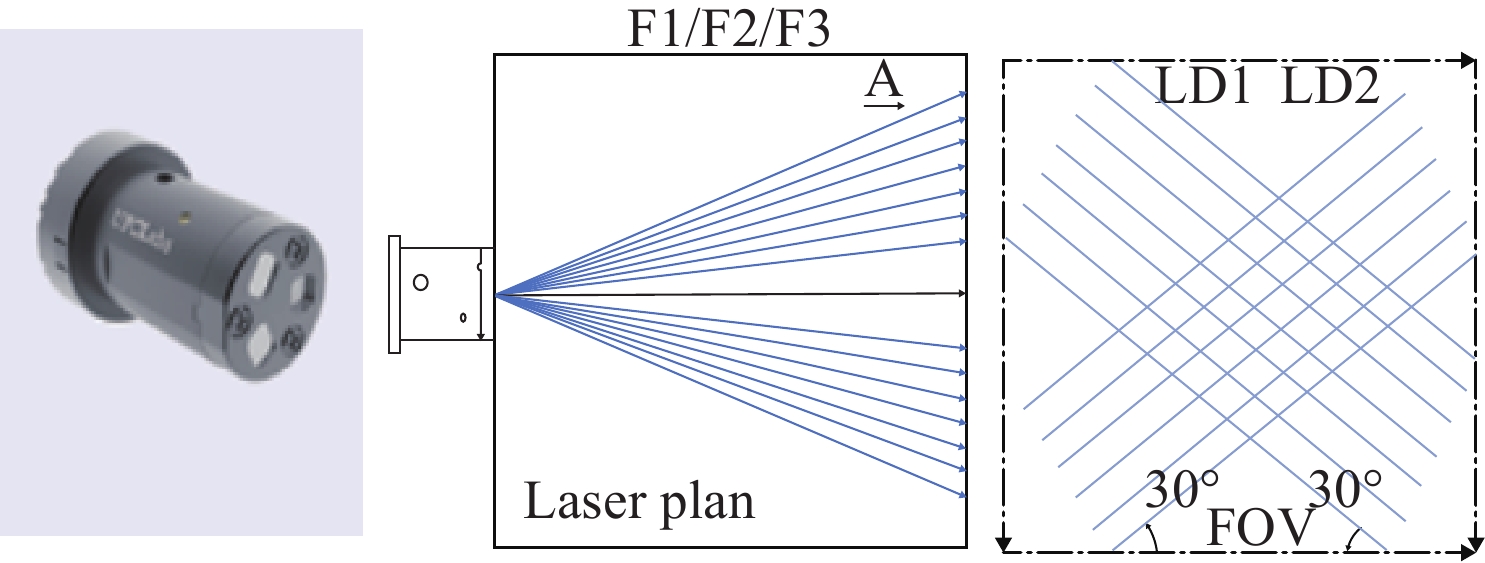
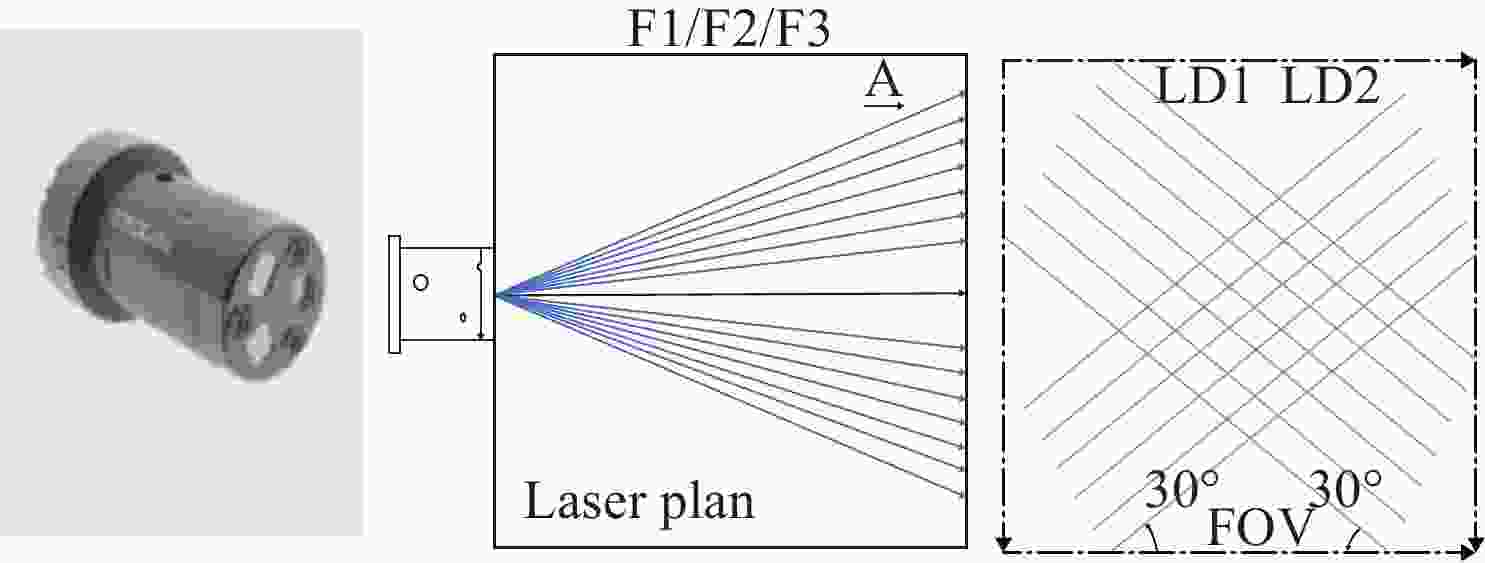
表 1 手持多线激光硬件参数
Table 1. Parameters of the handheld multi-line laser hardware
多线激光 相机 波长(nm) 450 分辨率 1280 ×1024 交叉角度 120 焦距 12 mm 通道数 2 角度 120 投射范围 300~400 mm 投诉距离 400 mm 表 2 左斜七线激光的激光线拟合的二次曲面参数
Table 2. Parameters of quadric surface by laser lines fitting
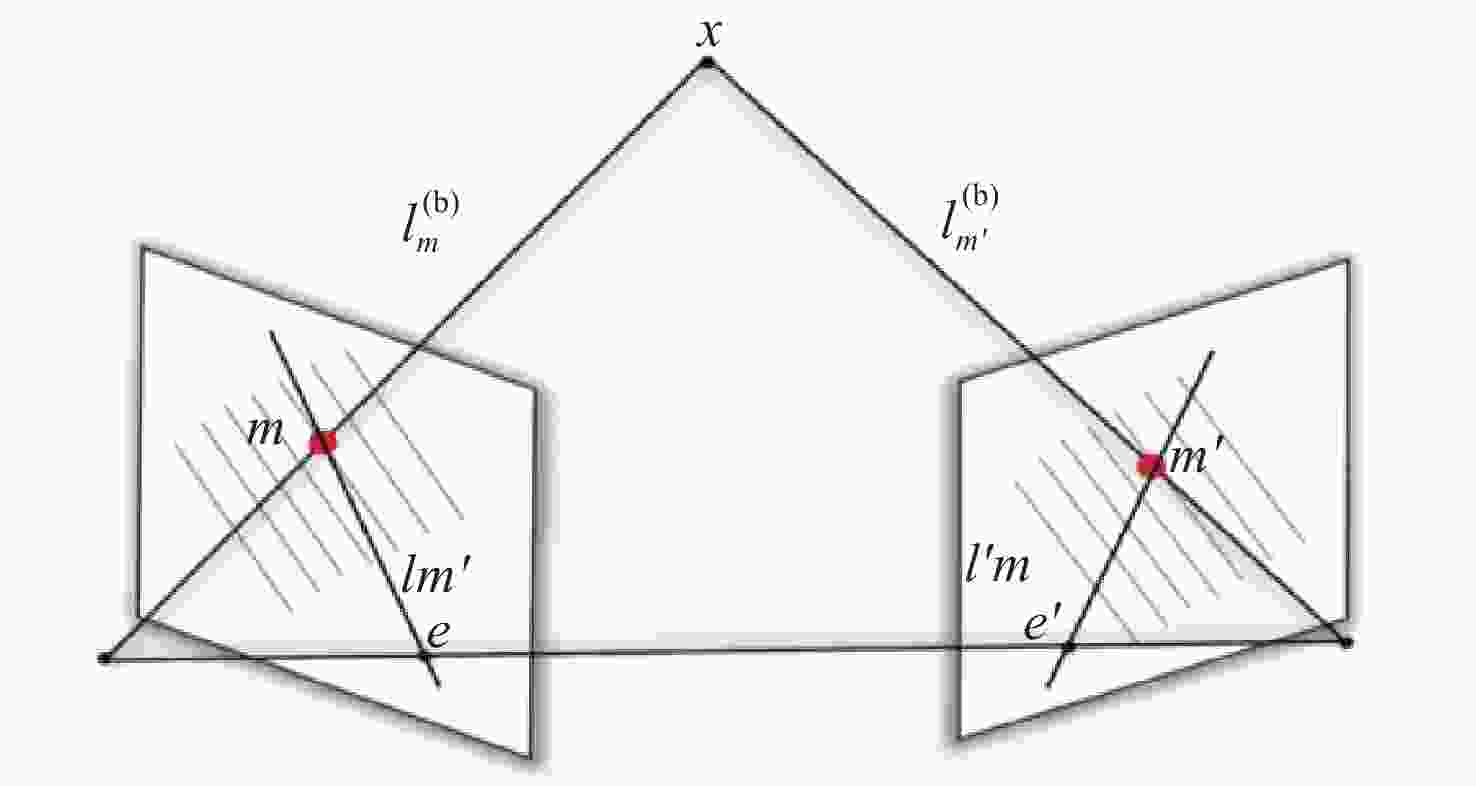
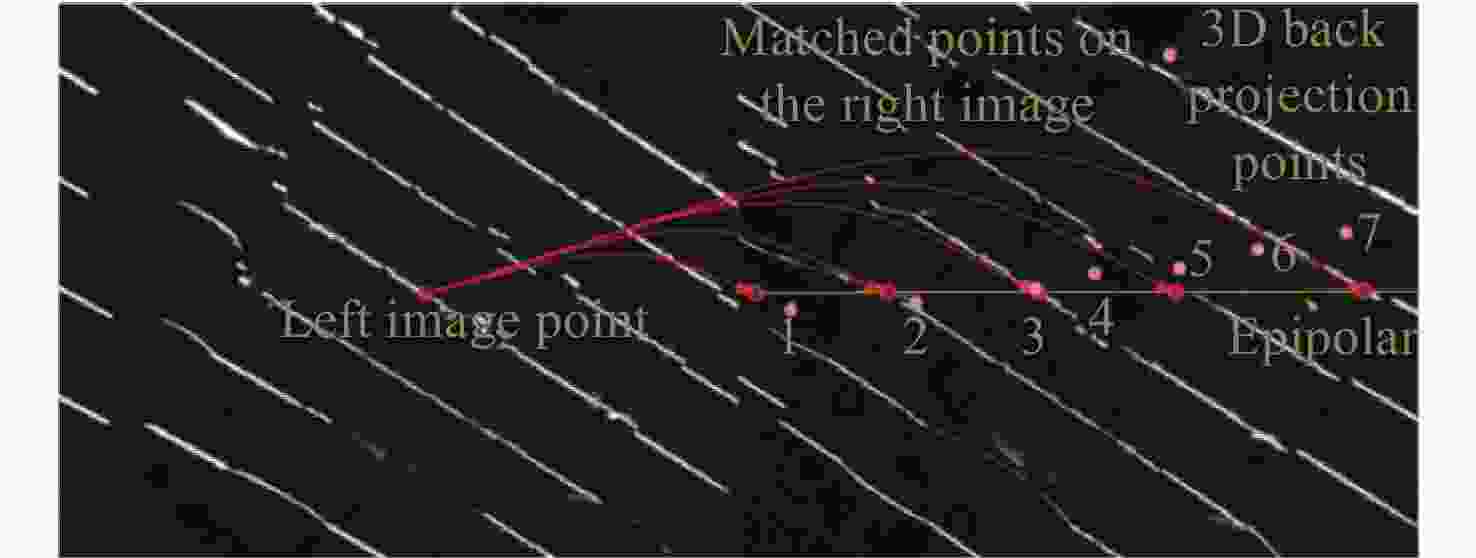
$ f(x,y) = {a_0}{x^2} + {a_1}{y^2} + {a_2}xy + {a_3}x + {a_4}y + {a_5} $ 序号 a0 a1 a2 a3 a4 a5 1 − 0.04355 − 0.17652 − 0.16847 − 4532.34 −846.79 3523.5824 2 1.104494 5.58200 4.95249 −323.814 −730.008 2189.0322 3 0.018882 0.10288 0.08628 − 9.97831 − 23.6556 1133.3425 4 − 0.00124 − 0.01061 − 0.00690 − 3.25750 − 8.05648 502.28098 5 − 0.00003 − 0.00279 0.000062 − 2.12223 − 5.61680 332.88023 6 0.000487 0.00100 0.003433 − 1.36085 − 4.00520 251.74369 7 0.000148 − 0.00015 0.002501 − 0.96619 − 3.22864 200.97273 表 3 图像点到极线的距离
Table 3. The distance from image points to epipolars
初始匹配点 优化后点 极线距离/像素 优化前 优化后 [433.768 ,200.620]
[429.553 ,226.722][432.983 ,200.125]
[428.876 ,226.360]0.28 0.064 [477.079,411.815]
[464.988,426.827][476.825,411.129]
[464.167,426.114]0.41 0.055 [434.472,201.047]
[430.743,227.391][434.018,200.538]
[430.003,226.994]0.37 0.089 [477.767,412.273]
[465.754,427.245][477.380,411.992]
[465.104,426.833]0.28 0.051 [733.345,200.354]
[687.059,204.529][732.914,200.019]
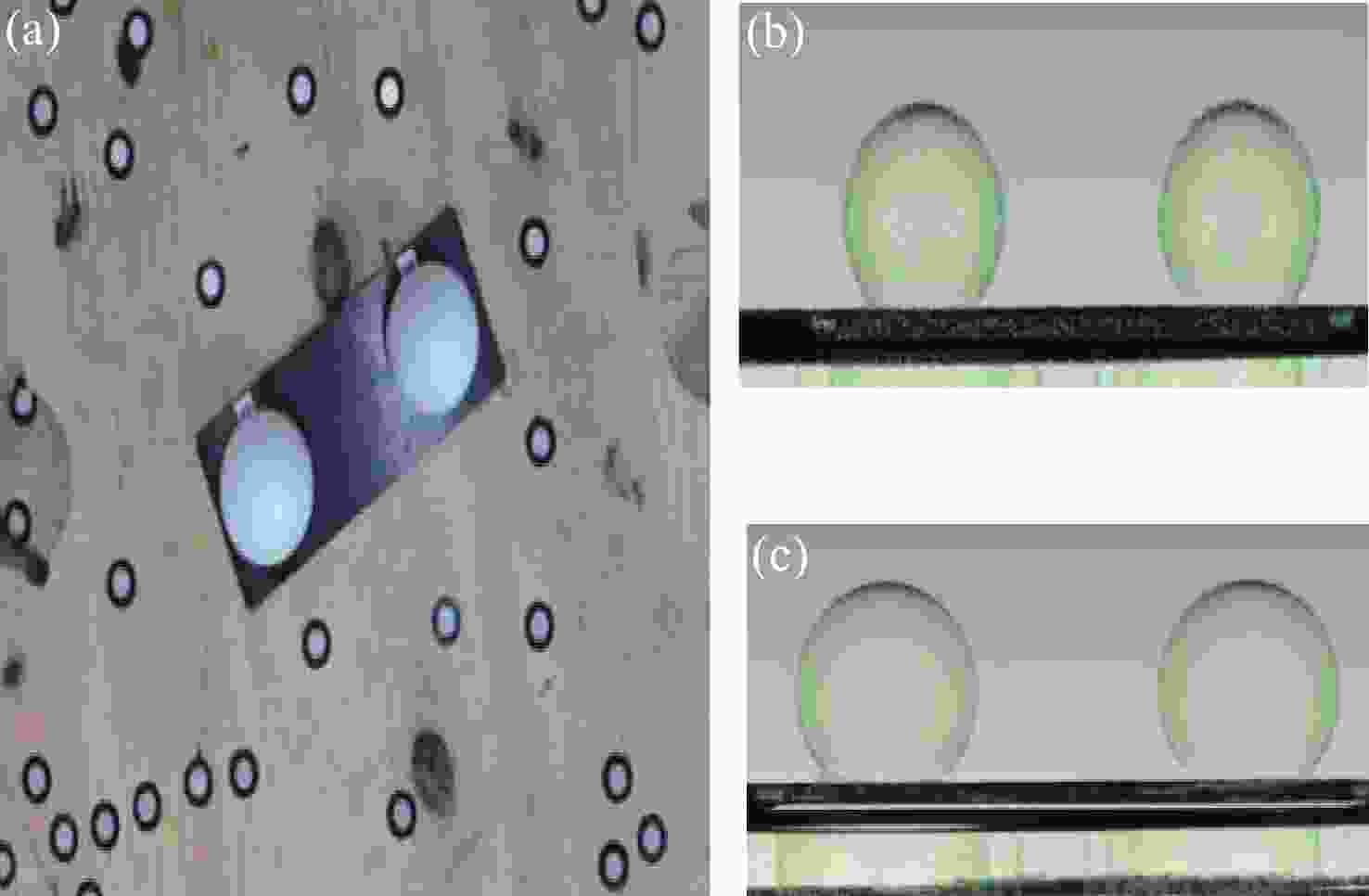
[686.653,204.178]0.32 0.0643 表 4 算法优化前后的球心距和误差
Table 4. The center distance and error before and after optimization by the proposed algorithm
序号 优化前标准球心距离/mm 优化后标准球心距离/mm 1 60.2455 60.0234 2 60.2570 60.0229 3 60.3084 60.0301 4 60.3123 60.0214 5 60.4015 60.0325 平均误差 0.3029 0.0241 -
[1] 许新傲, 李艺璇, 钱佳铭, 等. 基于全局优化的实时高精度模型重建[J]. 液晶与显示,2023,38(6):748-758. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2023-0086XU X A, LI Y X, QIAN J M, et al. Real-time high-precision model reconstruction based on global optimization[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2023, 38(6): 748-758. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2023-0086 [2] LI W G, HOU D M, LUO Z X. Clustering of divergent multi-line structured light stripes based on structural constraint[J]. Optik, 2022, 265: 169178. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.169178 [3] ZHANG J, SUN J, ZHANG Z. Identifying multiple line-structured lights from images via a local-to-global graph representation[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(10): 15611-15624. [4] CUI X ZH, ZHOU X L, LOU J J, et al. Measurement method of asphalt pavement mean texture depth based on multi-line laser and binocular vision[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2017, 18(5): 459-471. doi: 10.1080/10298436.2015.1095898 [5] SUN Q C, REN Z M, ZHU J L, et al. A three-dimensional structured light vision system by using a combination of single-line and three-line lasers[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(1): 13. [6] CUI B, TAO W, ZHAO H. High-precision 3D reconstruction for small-to-medium-sized objects utilizing line-structured light scanning: a review[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(21): 4457. doi: 10.3390/rs13214457 [7] WAN M S, ZHENG R H, WANG S D, et al. Efficient 3D scanning measurement system based on asymmetric trinocular vision and a multi-line laser[J]. Applied Optics, 2023, 62(8): 2145-2153. doi: 10.1364/AO.481406 [8] PING Y S, LIU Y K. A calibration method for line-structured light system by using sinusoidal fringes and homography matrix[J]. Optik, 2022, 261: 169192. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.169192 [9] CAO Y, FENG Y, CHEN Y J, et al. A method of 3D scene reconstruction with vehicle-borne laser scanner based on monocular visual positioning[C]. Proceedings of International Symposium on Photoelectronic Detection and Imaging 2011: Laser Sensing and Imaging; and Biological and Medical Applications of Photonics Sensing and Imaging, SPIE, 2011, doi: 10.1117/12.900981. [10] JIAN X, CHEN X, HE W P, et al. Outdoor 3D reconstruction method based on multi-line laser and binocular vision[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2020, 53(2): 9554-9559. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.2436 [11] OESAU S, LAFARGE F, ALLIEZ P. Indoor scene reconstruction using feature sensitive primitive extraction and graph-cut[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 90: 68-82. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.02.004 [12] KWOCZYŃSKA B, MAŁYSA B. Integration of data obtained from laser scanning and UAV used to develop a 3D model of the building object[J]. Archives of Civil Engineering, 2022, 68(4): 311-330. [13] ZHANG CH B, CUI H H, YIN W, et al. A robust real-time laser measurement method based on noncoding parallel multi-line[C]. Proceedings of Optical Metrology and Inspection for Industrial Applications IV, SPIE, 2016: 1002321. [14] CHIANG P J, LIN C H. Active stereo vision system with rotated structured light patterns and two-step denoising process for improved spatial resolution[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2022, 152: 106958. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2022.106958 [15] 杨洪涛, 刘士萍, 刘月琪, 等. 线扫描齿轮测量机转台基准轴标定方法[J]. 应用激光,2024,44(3):115.YANG H T, LIU S P, LIU Y Q, et al. A calibration method for rotary table reference axis of line scan gear measuring machine[J]. Applied Laser, 2024, 44(3): 115. (in Chinese). [16] 袁小翠, 王咏涛, 刘宝玲, 等. 基于3D线激光传感器的轨道弹条扣件结构缺陷检测方法[J]. 红外与激光工程,2024,53(7):20240176. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20240176YUAN X C, WANG Y T, LIU B L, et al. Detection method for structural defects of railway clip fastener based on 3D line laser sensor[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2024, 53(7): 20240176. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20240176 [17] 韩家杰, 周建平, 薛瑞雷, 等. 线结构光管道焊缝表面形貌重建与质量评估[J]. 中国激光,2021,48(14):1402010. doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.1402010HAN J J, ZHOU J P, XUE R L, et al. Surface morphology reconstruction and quality evaluation of pipeline weld based on line structured light[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2021, 48(14): 1402010. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.1402010 [18] HUANG H M, LIU G H, XIAO C J, et al. Spatial quadric calibration method for multi-line laser based on diffractive optical element[J]. AIP Advances, 2024, 14: 035017. doi: 10.1063/5.0194603 [19] 李伟明, 彭国, 高兴宇, 等. 线激光光条中心快速提取算法[J]. 中国激光,2020,47(3):0304002. doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0304002LI W M, PENG G, GAO X Y, et al. Fast extraction algorithm for line laser strip centers[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(3): 0304002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0304002 [20] 蔡怀宇, 冯召东, 黄战华. 基于主成分分析的结构光条纹中心提取方法[J]. 中国激光,2015,42(3):0308006. doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.0308006CAI H Y, FENG ZH D, HUANG ZH H. Centerline extraction of structured light stripe based on principal component analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015, 42(3): 0308006. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.0308006 -





 下载:
下载: