Measurement of atmospheric coherence length for extended targets based on wavefront structure function
-
摘要:
为测量大气相干长度这一表征大气湍流对自由空间光通信链路性能影响的重要指标,本文提出了一种将扩展目标作为信息源的新策略,即结合波前结构函数法与扩展目标偏移量算法直接对大气相干长度进行估计。现有的差分像运动监测器等方法通常依赖于导星目标,但在水平通信链路中难以设置合适的导星目标,其实际应用效果受到显著限制。因此,将扩展目标作为直接测量的信息源,为大气相干长度测量提供了一种可行的解决方案。本文首先回顾了现有主流算法的原理及研究现状,分析了现有算法对导星目标的依赖性及其在水平链路应用中的局限性。在此基础上,提出一种将改进归一化互相关算法与波前结构函数法相结合的测量方案,用于扩展目标场景估计大气相干长度。与传统测量方法相比,该方法能够在水平链路基于扩展目标条件下有效开展测量,同时显著减少了系统的复杂度和设备成本。为验证所提方法的有效性与测量精度,本文设计开展了仿真与实验研究。结果表明,该方法测得相干长度值与差分像运动监测器法及波前相位方差法高度一致,测量精度误差约为4%。这一结果证明了该方法在大气相干长度评估中的有效性,可为提升自由空间激光通信的可靠性提供有效参考。
Abstract:Atmospheric coherence length is a critical indicator of the impact of atmospheric turbulence on free-space optical communication links. This paper proposes a novel strategy for measuring atmospheric coherence length by utilizing extended targets as the information source. Specifically, the method integrates the wavefront structure function approach with the extended target offset algorithm to directly estimate the atmospheric coherence length. Traditional methods, such as the Differential Image Motion Monitor (DIMM), typically rely on guide star targets, which are difficult to set appropriately in horizontal communication links, thereby limiting their effectiveness in practical applications. In contrast, employing extended targets as direct detection targets provides a feasible solution for measuring atmospheric coherence length. The paper first reviews the principles and current research status of mainstream algorithms, emphasizing the reliance of existing algorithms on guide star targets and their limitations in horizontal links. Subsequently, we propose a new measurement scheme that combines the improved normalized cross-correlation algorithm with the wavefront structure function method to estimate atmospheric coherence length under extended targets scenarios. In comparison to traditional measurement methods, our approach enables coherence length measurement based on extended targets in horizontal links, thereby significantly reducing system complexity and equipment costs. To validate the effectiveness and measurement accuracy of the proposed method, both simulations and experiments were designed and conducted. The results demonstrate that the coherence length values measured by this method are highly consistent with those obtained using the DIMM method and the wavefront phase variance method, with a measurement accuracy error of approximately 4%. This indicates that the proposed method can effectively assess atmospheric coherence length, thereby providing a valuable reference for enhancing the reliability of free-space laser communication systems.
-
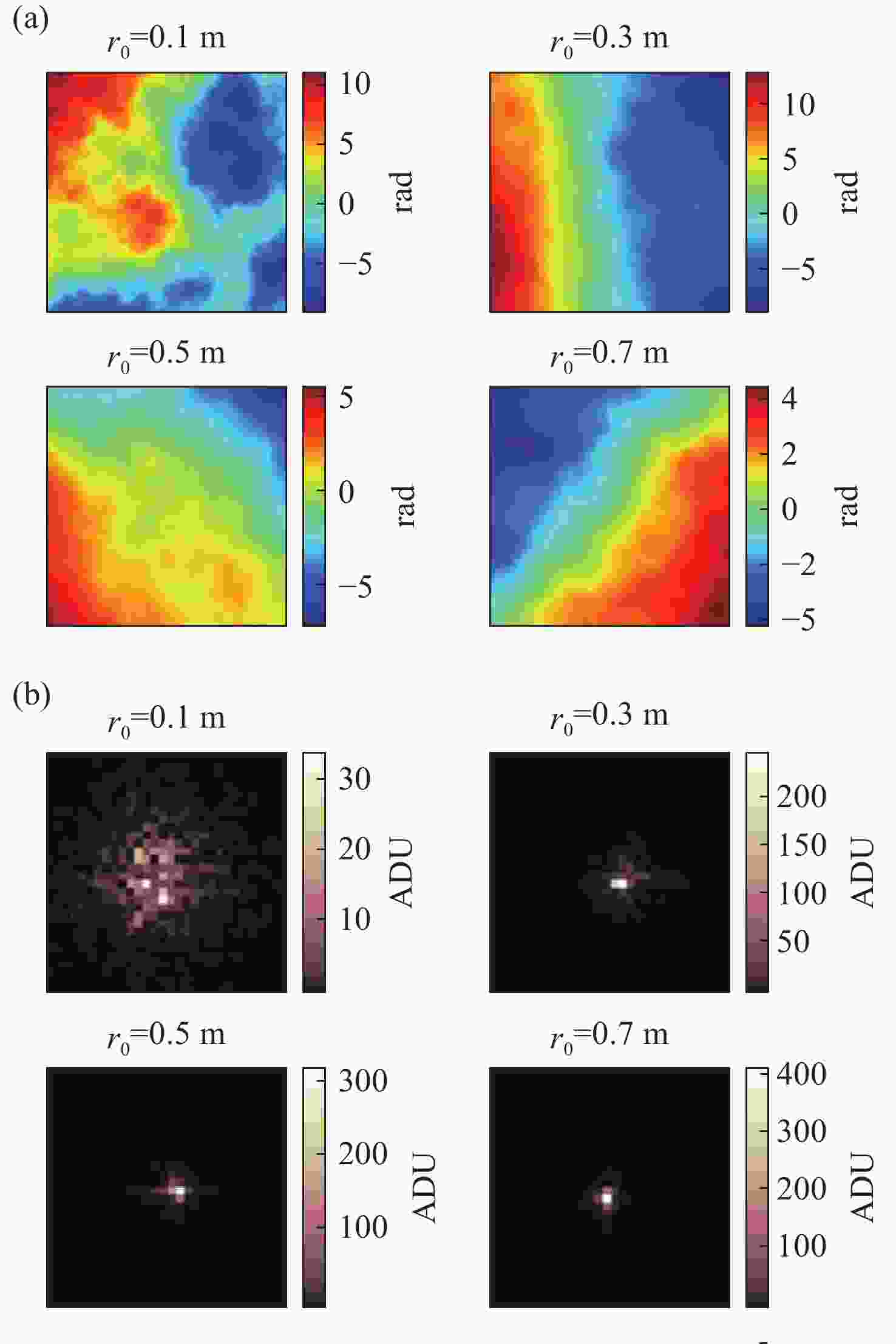
图 2 模拟湍流屏示意图。(a)不同r0下SU算法生成的湍流相位屏;(b)不同强度湍流相位屏对应的远场衍射图案
Figure 2. Illustration of simulated turbulence screens. (a) Turbulence phase screens generated by the SU algorithm under different r0 conditions; (b) Far-field diffraction patterns corresponding to phase screens with different turbulence intensities
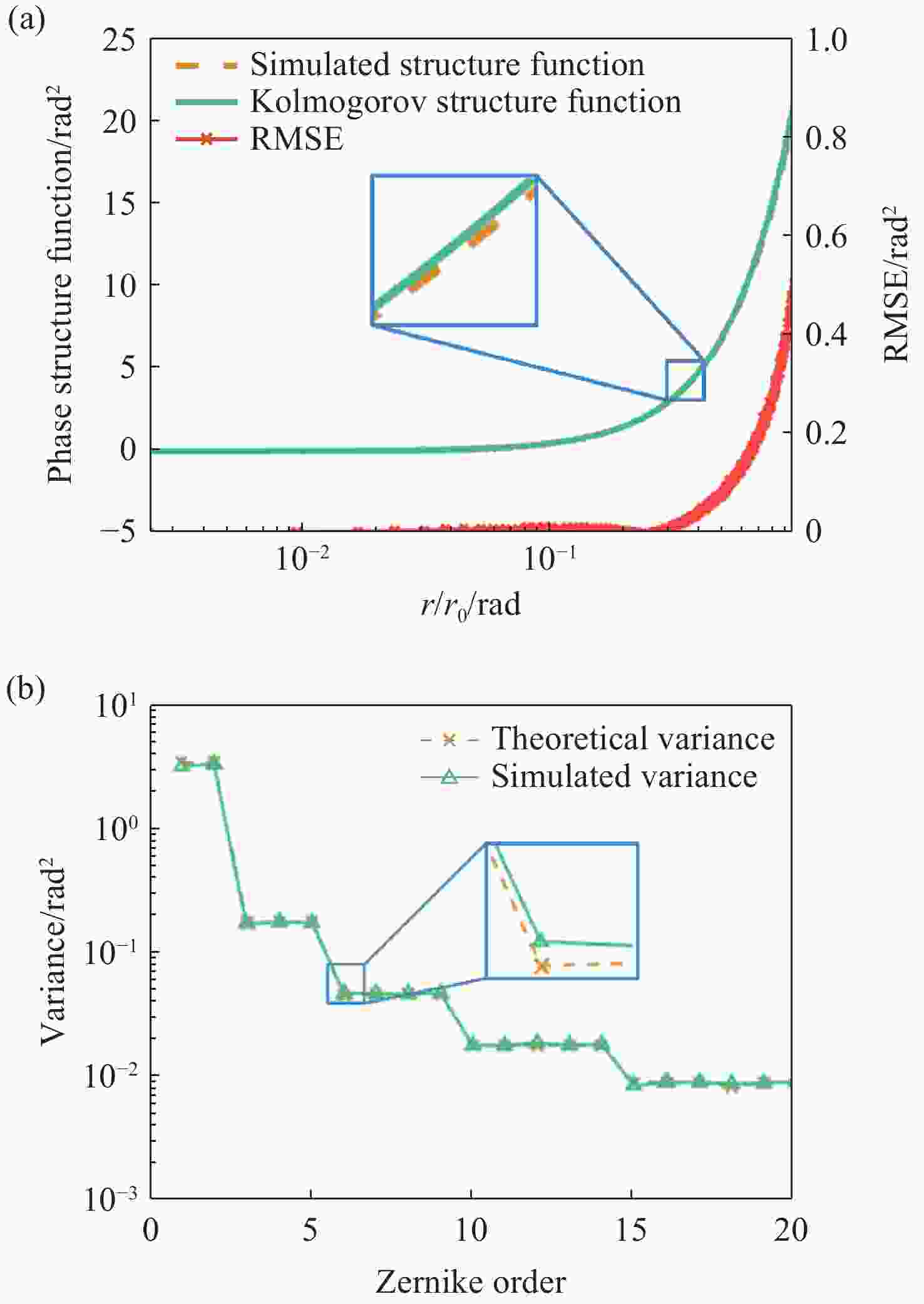
图 3 模拟湍流屏验证。(a)湍流相位屏平均结构函数与理论期望值及RMSE;(b)各阶Zernike系数方差统计分布的测量值与理论值
Figure 3. Validation of simulated turbulence screens. (a) The average structure function of the turbulent phase screen compared to the theoretical expected value, and the RMSE; (b) Measured values and theoretical values of the statistical distribution of variances for each order of Zernike coefficients
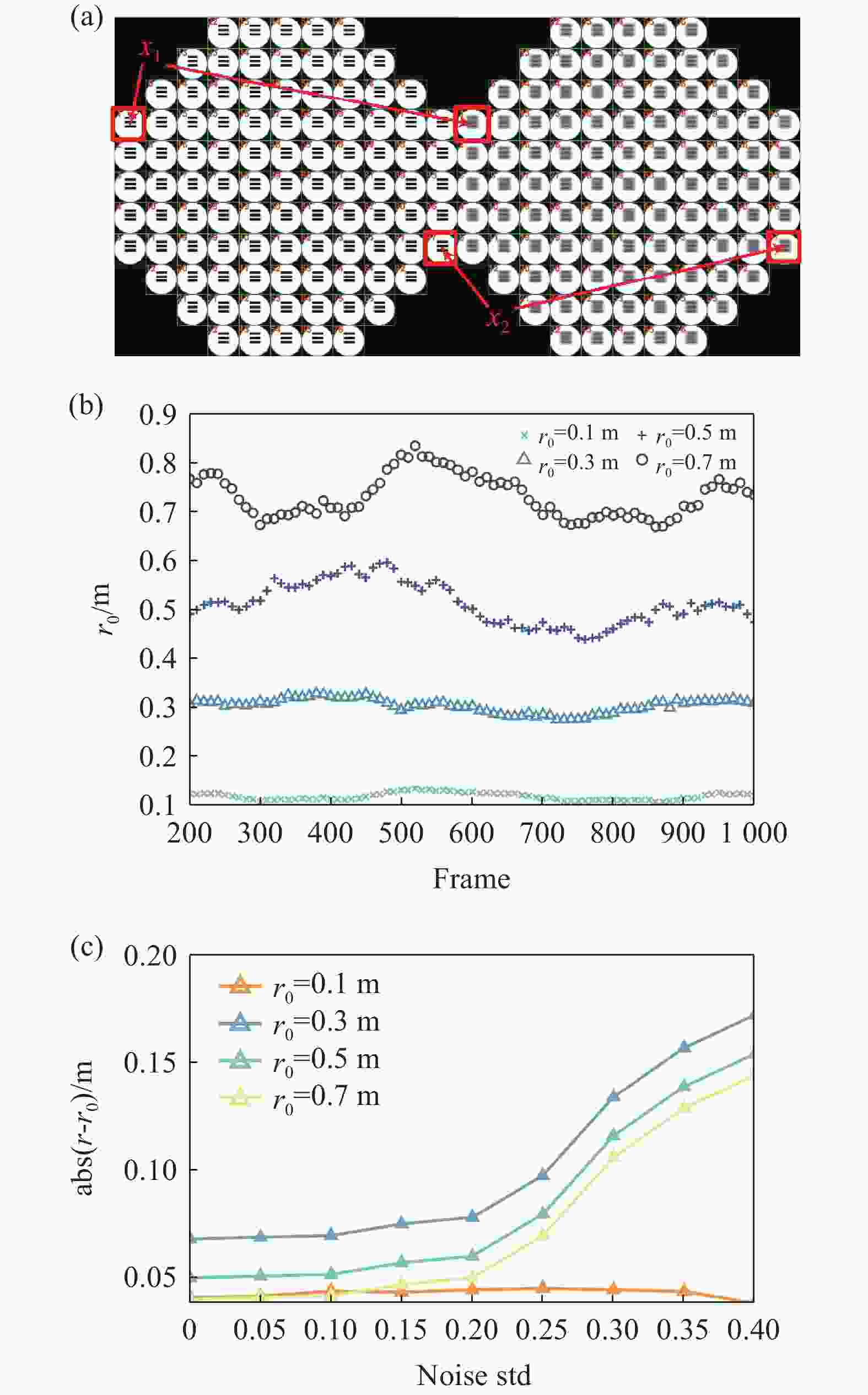
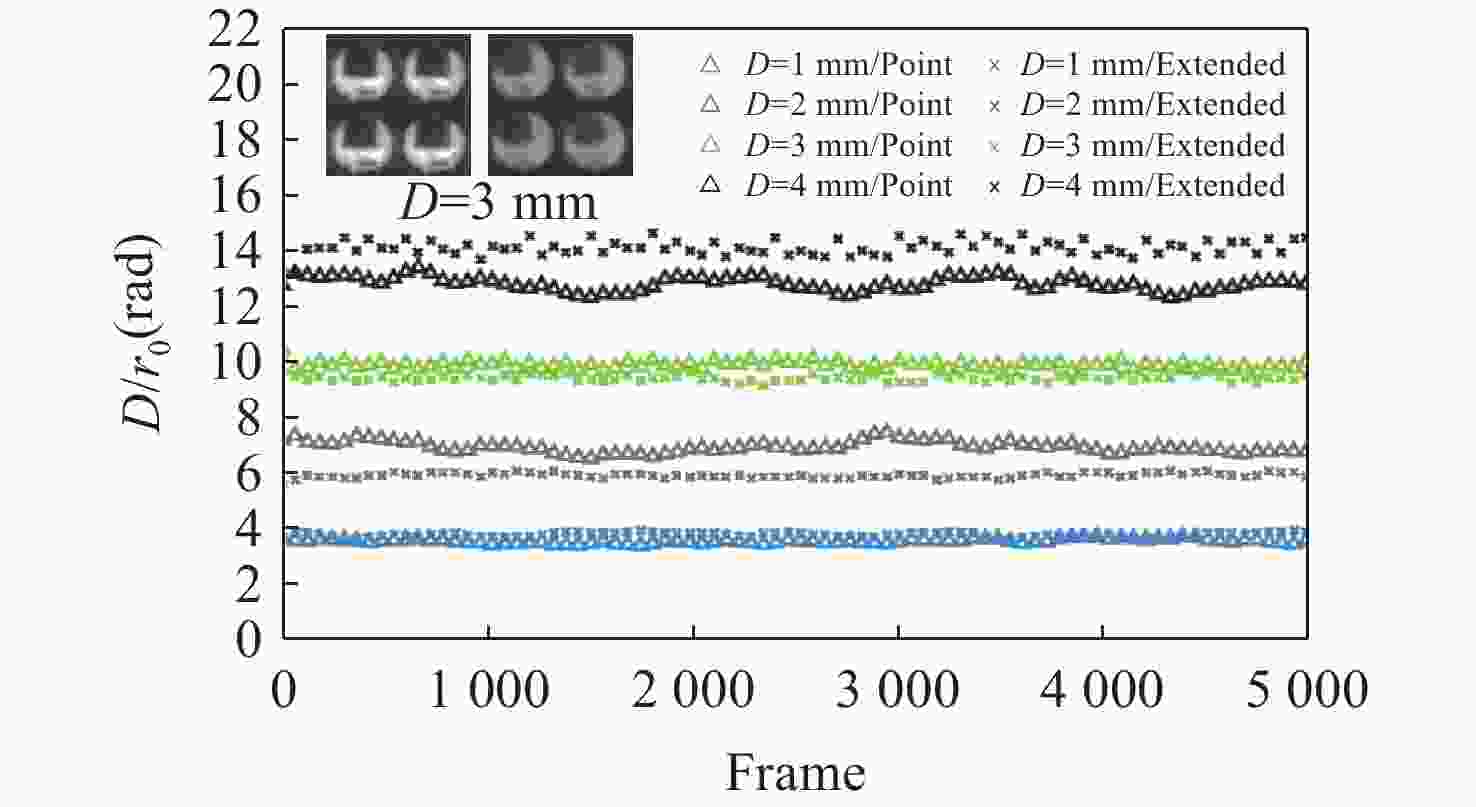
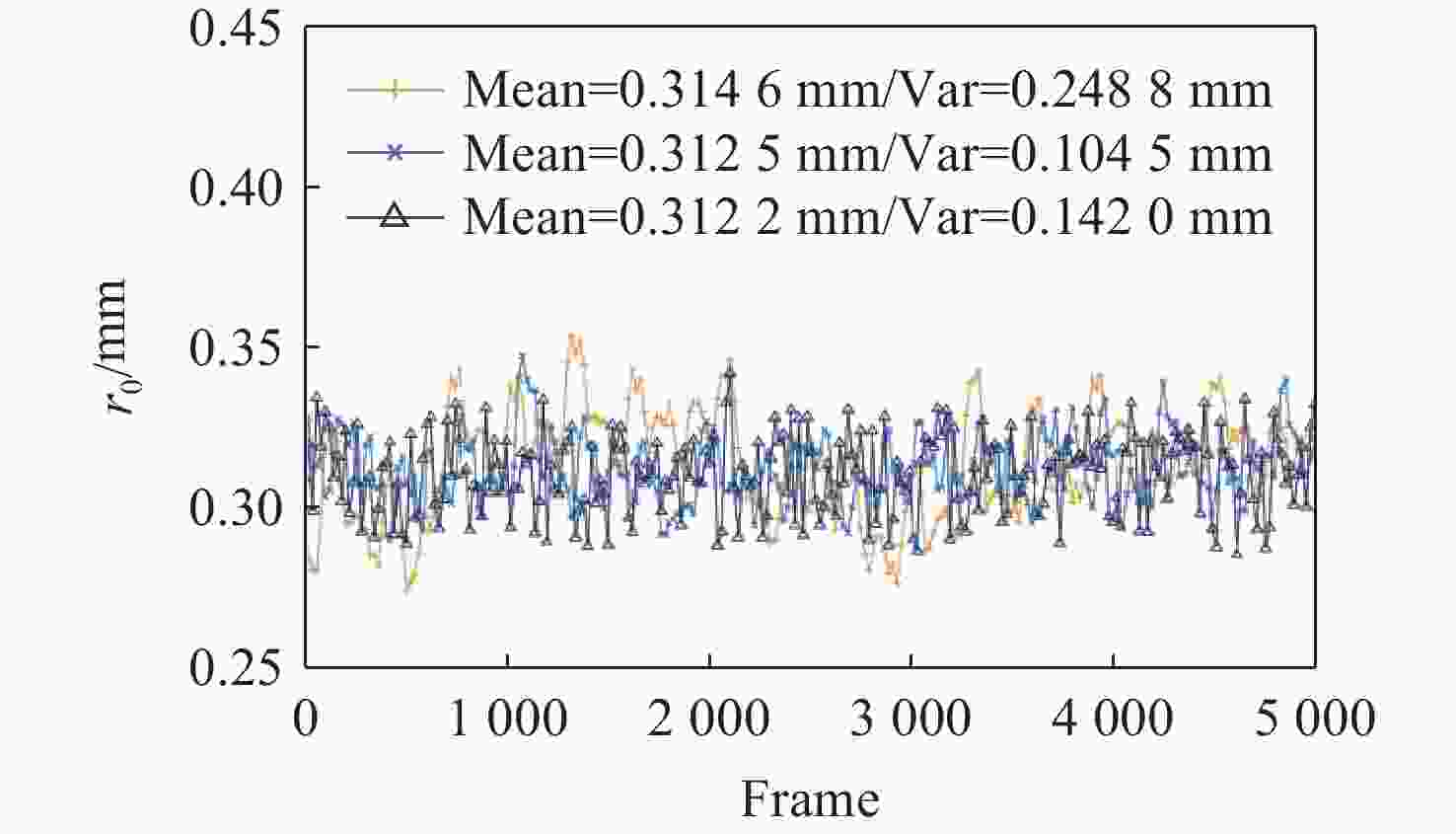
图 5 相干长度仿真结果。(a)加入湍流前后的SHWFS子孔径阵列图像;(b)每200帧波前结构函数测得r0曲线;(c)加入不同标准差的高斯噪声后的r0曲线
Figure 5. Coherence length simulation results. (a) Sub-aperture array images of the SHWFS before and after the introduction of turbulence; (b) r0 curve measured by the wavefront structure function values every 200 frames; (c) r0 curve with added Gaussian noise of different standard deviations
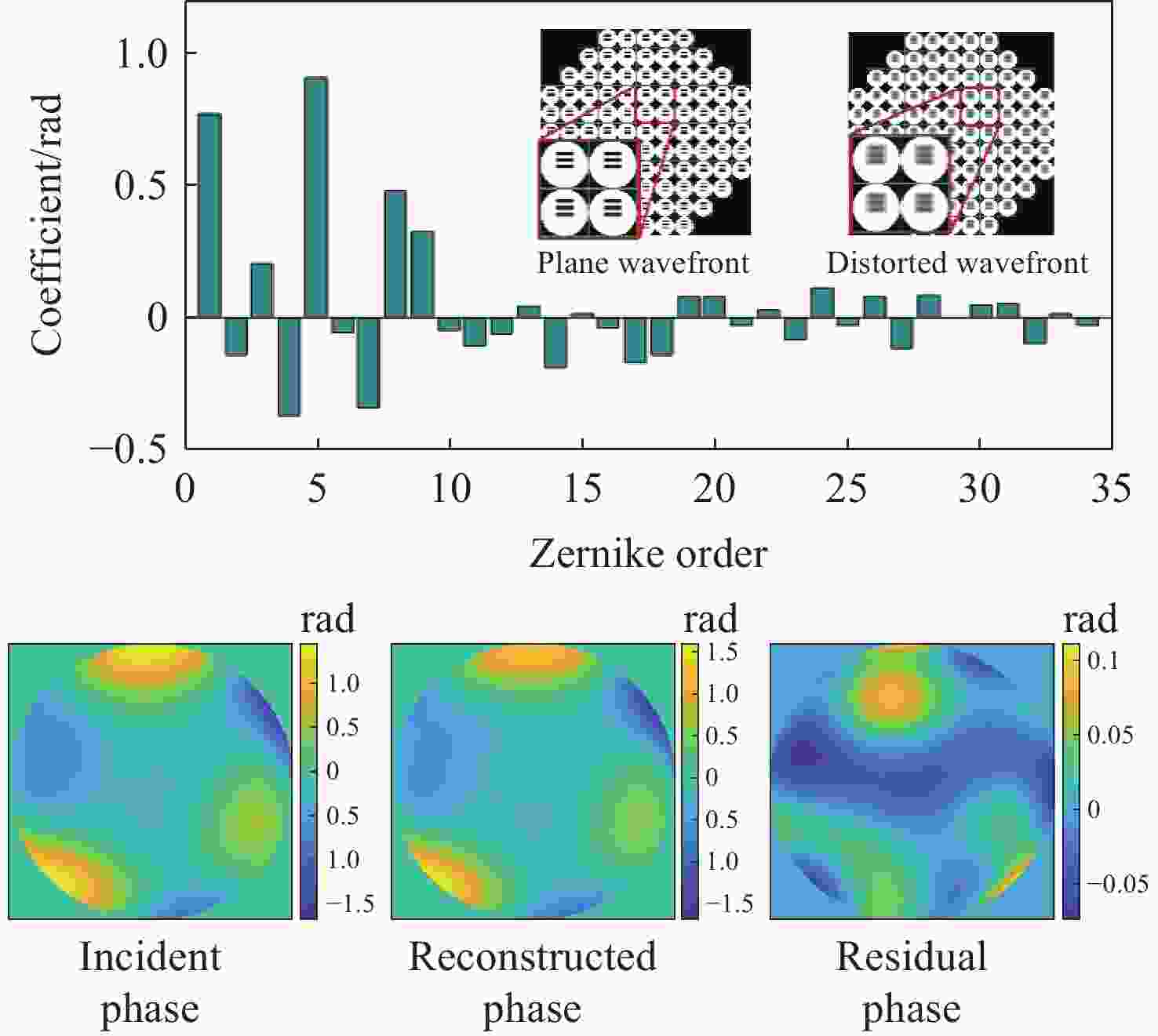
表 1 符合Kolmogorov理论的畸变波前各阶Zernike系数方差
Table 1. Variance of Zernike coefficients of distorted wavefronts at various orders that conform to Kolmogorov theory.
阶数 方差(rad2) 阶数 方差(rad2) 1 0.4479 (D/r0)5/36 0.0061 (D/r0)5/32 0.4480 (D/r0)5/37 0.0062 (D/r0)5/33 0.0230 (D/r0)5/38 0.0062 (D/r0)5/34 0.0230 (D/r0)5/39 0.0062 (D/r0)5/35 0.0232 (D/r0)5/310 0.0024 (D/r0)5/3 -
[1] GUIOMAR F P, FERNANDES M A, NASCIMENTO J L, et al. Coherent free-space optical communications: opportunities and challenges[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2022, 40(10): 3173-3186. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2022.3164736 [2] 刘恒瑞. 自由空间光通信系统中的信道预测技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2024.LIU H R. Channel prediction techniques in free-space optical communication systems[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2024. (in Chinese). [3] JAHID A, ALSHARIF M H, HALL T J. A contemporary survey on free space optical communication: Potentials, technical challenges, recent advances and research direction[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2022, 200: 103311. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2021.103311 [4] 陈丹, 陈昊雅, 王明军, 等. 非理想信道下自由空间光通信自适应星座几何整形[J]. 光学学报,2025,45(3):0306004. doi: 10.3788/AOS241470CHEN D, CHEN H Y, WANG M J, et al. Adaptive constellation geometry shaping for free space optical communication in non-ideal channels[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2025, 45(3): 0306004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS241470 [5] 朱嘉康, 安其昌, 杨飞. 大口径望远镜镜面视宁度检测方法综述[J]. 红外与激光工程,2023,52(2):20220488. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220488ZHU J K, AN Q CH, YANG F. Review on the measurement methods of mirror seeing of large-aperture telescope[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52(2): 20220488. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220488 [6] FRIED D L. Statistics of a geometric representation of wavefront distortion[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1965, 55(11): 1427-1435. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.55.001427 [7] LI M, ZHANG P X, HAN J W. Methods of atmospheric coherence length measurement[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(6): 2980. doi: 10.3390/app12062980 [8] GRIFFITHS R, BARDOU L, BUTTERLEY T, et al. A comparison of next-generation turbulence profiling instruments at Paranal[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 529(1): 320-330. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stae434 [9] SABIL M, HABIB A, BENKHALDOUN Z. Interferential seeing monitor, a seeing monitor for atmospheric turbulence studies: calibration with the differential image motion monitor[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2020, 500(2): 1884-1888. doi: 10.1093/mnras/staa2400 [10] TILLAYEV Y, AZIMOV A, EHGAMBERDIEV S, et al. Astronomical seeing and meteorological parameters at maidanak observatory[J]. Atmosphere, 2023, 14(2): 199. doi: 10.3390/atmos14020199 [11] SUBRAMANIAN S K, RENGASWAMY S, DESHMUKH P G, et al. Daytime turbulence strength profile measurement at Kodaikanal observatory[J]. Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems, 2024, 10(3): 039004. [12] JACKSON O, VAN KOOTEN M A M, PERERA S, et al. SHIMM as an atmospheric profiler on the nickel telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2023, 12680: 126801V. [13] PERERA S, WILSON R W, BUTTERLEY T, et al. SHIMM: a versatile seeing monitor for astronomy[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 520(4): 5475-5486. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad339 [14] ANDRADE P P, GARCIA P J V, CORREIA C M, et al. Estimation of atmospheric turbulence parameters from Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor measurements[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2019, 483(1): 1192-1201. doi: 10.1093/mnras/sty3181 [15] SAUVAGE C, ROBERT C, MUGNIER L M, et al. Near ground horizontal high resolution $ C_{n}^{2} $ profiling from shack-Hartmann slope and scintillation data[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(34): 10499-10519. doi: 10.1364/AO.438170[16] HE Y, BAO M D, CHEN Y W, et al. Accuracy characterization of Shack–Hartmann sensor with residual error removal in spherical wavefront calibration[J]. Light: Advanced Manufacturing, 2023, 4(4): 36. [17] ARISTIDI E, ZIAD A, CHABÉ J, et al. A generalized differential image motion monitor[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2019, 486(1): 915-925. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stz854 [18] DIBAEE B, SHOMALI R, KHALILZADEH J, et al. 4-aperture differential image motion monitor as a new approach for estimating atmospheric turbulence parameters[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 2019, 66(7): 753-763. doi: 10.1080/09500340.2019.1567843 [19] 王子跃, 任德清. 差分像运动视宁度优化监测法[J]. 天文研究与技术,2019,16(1):114-122.WANG Z Y, REN D Q. Improved to differential image motion monitor[J]. Astronomical Research & Technology, 2019, 16(1): 114-122. (in Chinese). [20] KORNILOV V, SAFONOV B. Wave propagation effect on differential image motion monitor measurements[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2019, 488(1): 1273-1281. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stz1783 [21] 毛红敏, 丁致雅, 杨燕燕, 等. 大气湍流对高分辨率遥感卫星的成像影响研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(1):167-177. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0083MAO H M, DING Z Y, YANG Y Y, et al. Effect of atmospheric turbulence on imaging quality of high-resolution remote sensing satellites[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(1): 167-177. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0083 [22] KORNILOV V, SAFONOV B. Differential image motion in the short-exposure regime[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2011, 418(3): 1878-1888. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19604.x [23] MACATANGAY R, RATTANASOON S, BUTTERLEY T, et al. Seeing and turbulence profile simulations over complex terrain at the Thai national observatory using a chemistry-coupled regional forecasting model[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 530(2): 1414-1423. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stae727 [24] 赵文栋, 杨飞, 安其昌. 面向大口径地基望远镜视宁度检测方法综述[J]. 激光与红外,2023,53(9):1299-1308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2023.09.001ZHAO W D, YANG F, AN Q CH. Review on the inspection methods of visibility for large aperture ground based telescope[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2023, 53(9): 1299-1308. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2023.09.001 [25] ZURASKI S M, BEECHER E, MCCRAE J E, et al. Turbulence profiling using pupil plane wavefront data derived Fried parameter values for a dynamically ranged rayleigh beacon[J]. Optical Engineering, 2020, 59(8): 081807. [26] 仇陈祥. 应用于船载平台的湍流廓线激光雷达研制[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2023.QIU CH X. Development of Lidar System for Monitoring Turbulent Profiles on Shipborne Platform[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2023. (in Chinese). [27] 陈亮, 周孟哲, 陈禾. 一种结合边缘区域和互相关的图像配准方法[J]. 北京理工大学学报,2016,36(3):320-325.CHEN L, ZHOU M ZH, CHEN H. A method for image registration combined by edge region and cross correlation[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016, 36(3): 320-325. (in Chinese). [28] CANNY J. A computational approach to edge detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1986, PAMI-8(6): 679-698. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.1986.4767851 [29] CHARNOTSKII M. Four methods for generation of turbulent phase screens: comparison[J]. arXiv: 1911.09185, 2019. (查阅网上资料, 不确定文献类型及格式是否正确, 请确认) . [30] 陈浩, 宣丽, 胡立发, 等. 大气相干长度的稳定测量[J]. 光学 精密工程,2013,21(4):911-918.CHEN H, XUAN L, HU L F, et al. Steady measurement of atmospheric turbulence coherence length[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2013, 21(4): 911-918. (in Chinese). -





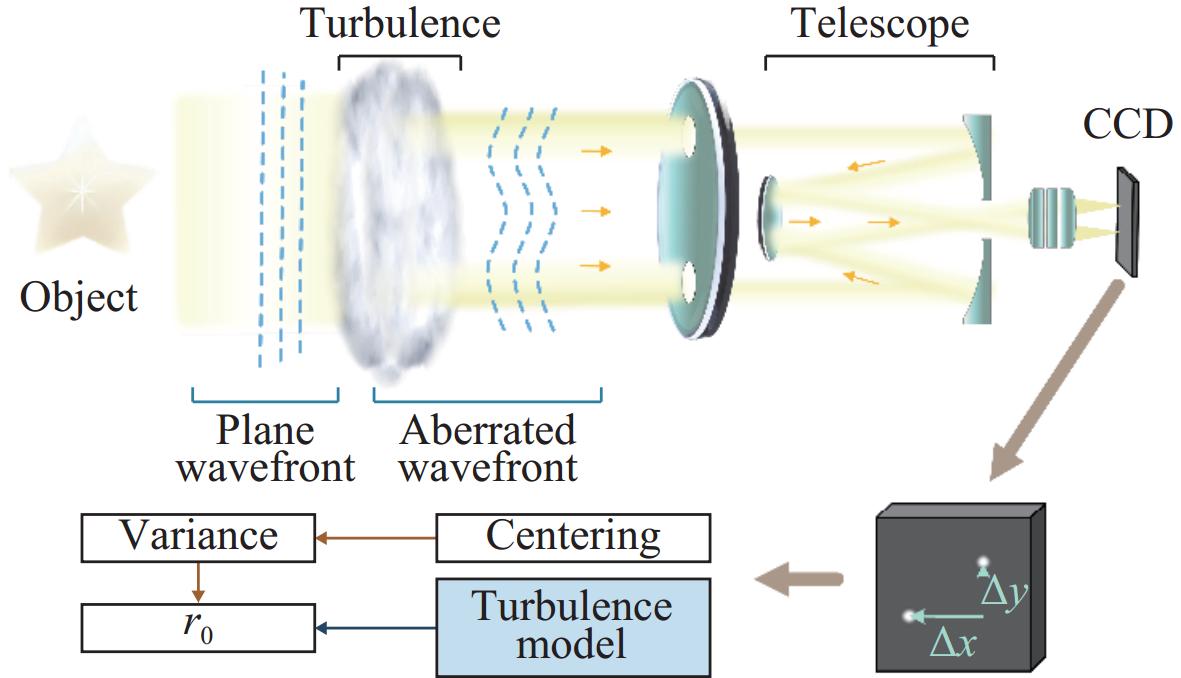
 下载:
下载: