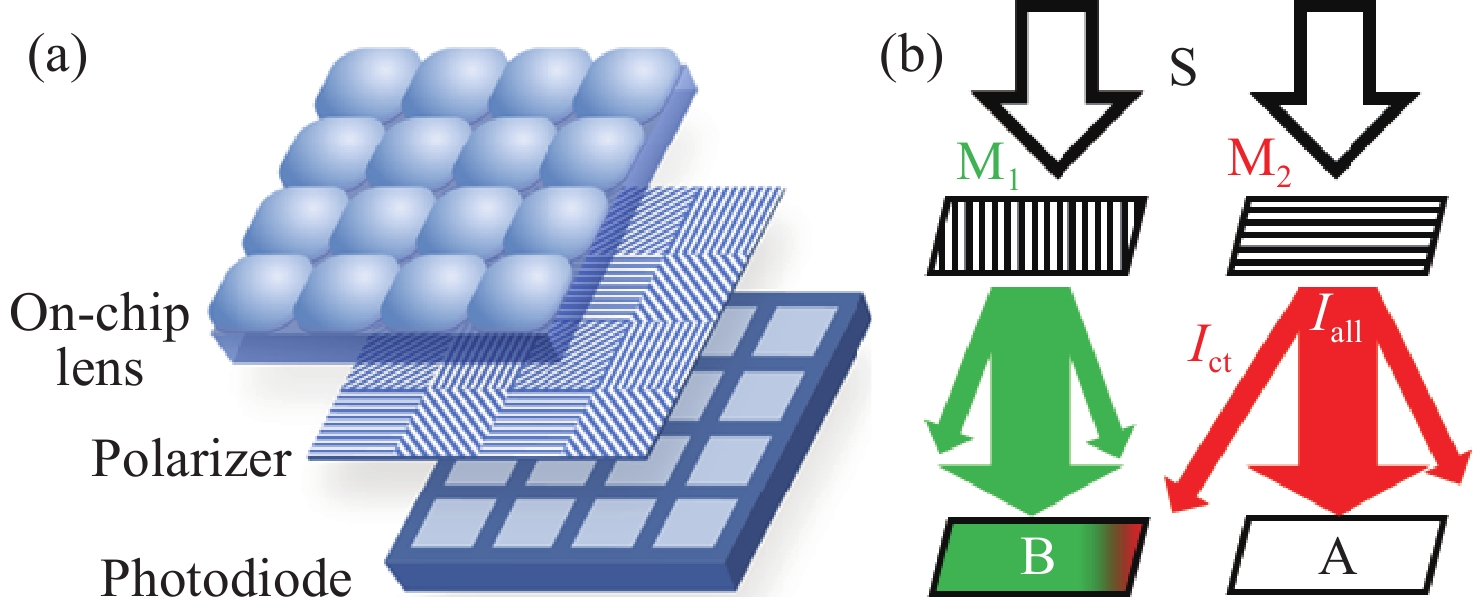
-
摘要:
分焦平面偏振相机是一种应用广泛的集成化偏振成像系统,微偏振片阵列的像素间串扰是此类偏振成像系统特有的干扰因素,且串扰光强随入射光偏振特性的变化而改变,在目标偏振信息测量时会引入误差。本文回顾了偏振串扰模型的发展历程,将相关研究中涉及到的影响串扰的全部因素进行了归纳。以感光芯片参数和光学系统参数为系统关键因素,讨论了相机应用过程中的串扰原因-结果模型以及与时间噪声的关系,分析了串扰导致的各像素检偏参数的变化结果,重点总结了串扰的因素相关性、实验可重复性、误差随机性和参数可标定性,并对串扰模型的未来发展趋势进行了展望。
Abstract:Division of focal plane polarization camera is a widely used integrated polarization imaging system. Crosstalk between pixels of the micro-polarizer arrays (MPAs) is the unique interference factor in such system, and its crosstalk light intensity varies with the polarization characteristics of the incident light, bringing errors to the measurement of the target’s polarization information. This paper reviews the development of polarization crosstalk models and summarizes all the factors affecting crosstalk identified in relevant researchs. Taking sensor parameters and optical system parameters as key factors, this paper discusses the cause-effect model of crosstalk in cameras and its relation to temporal noise. It analyzes the results of parameter changes caused by crosstalk, primarily summarizing the crosstalk’s factor correlation, experimental repeatability, error randomness and parameter calibration. Finally, this paper prospects the future development trends of crosstalk models.
-
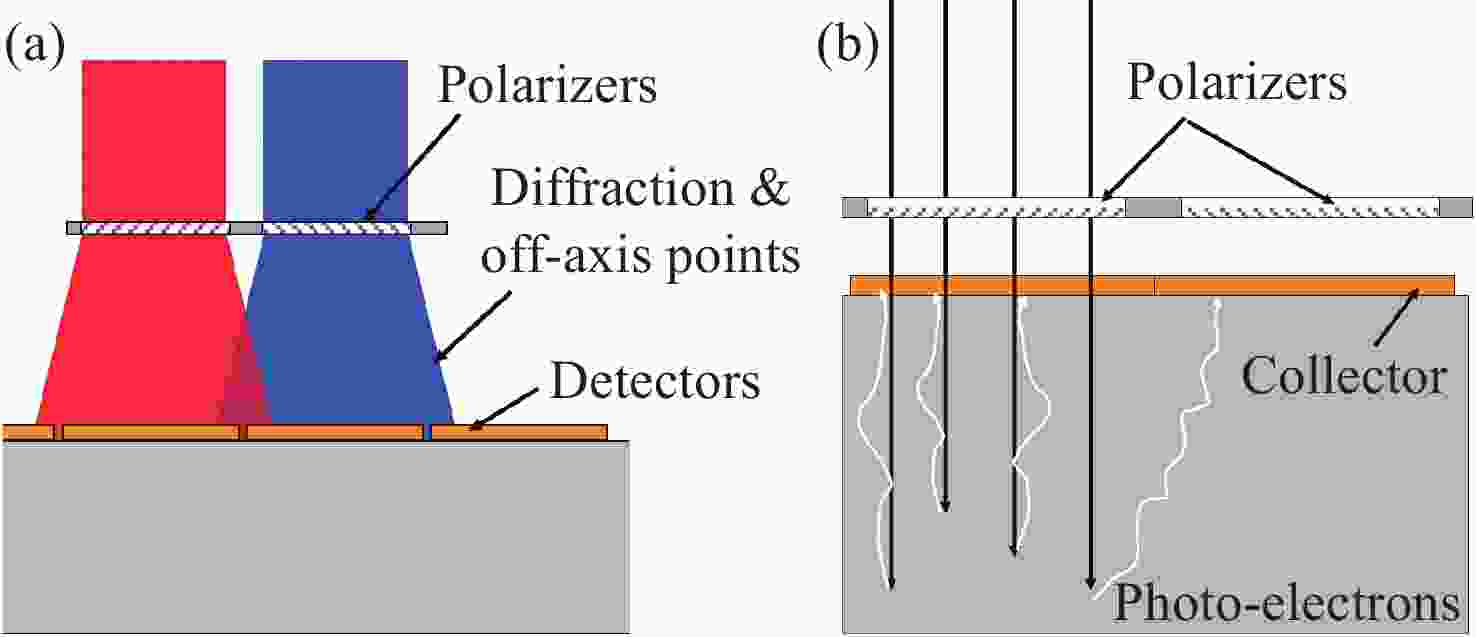
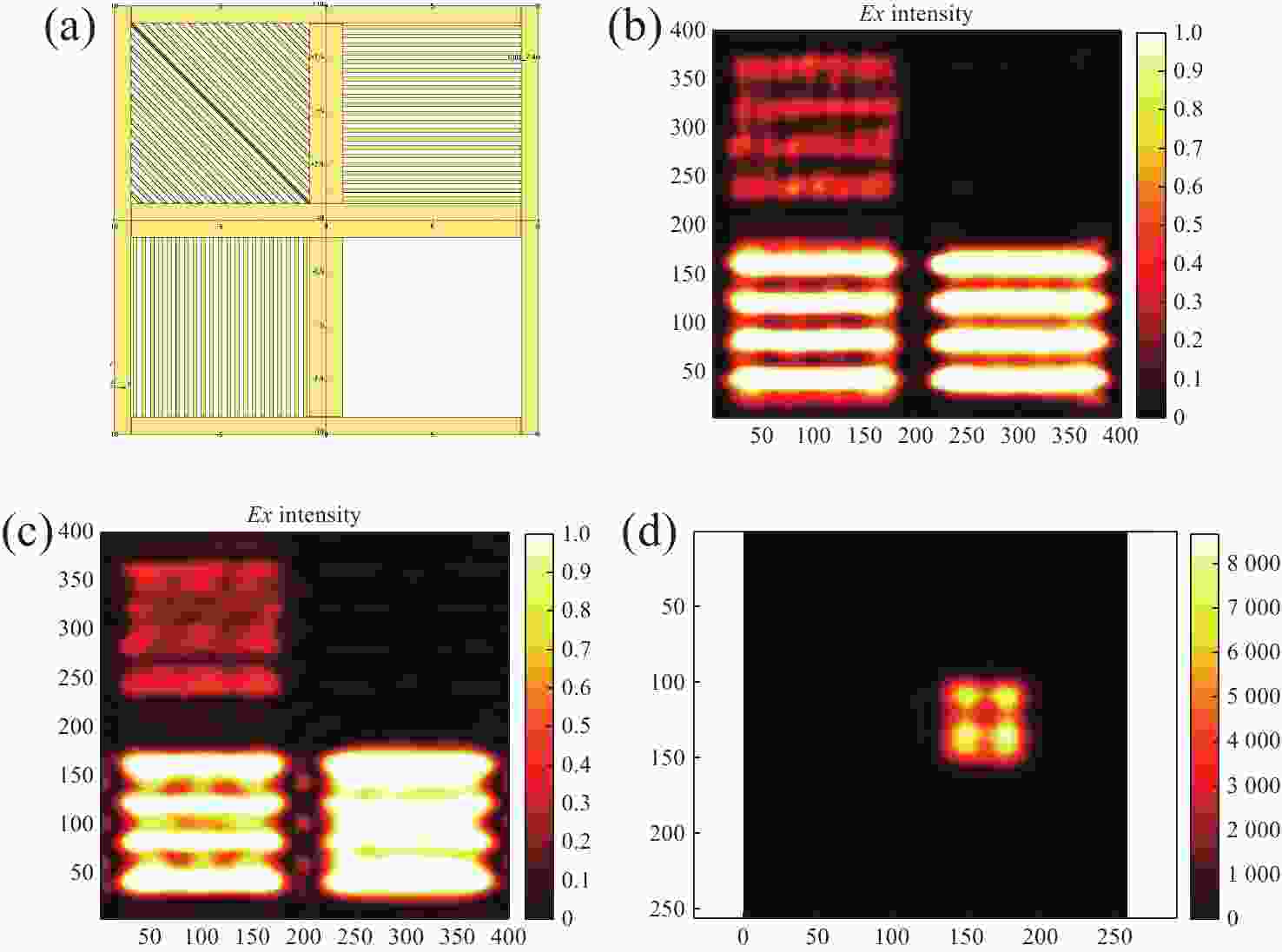
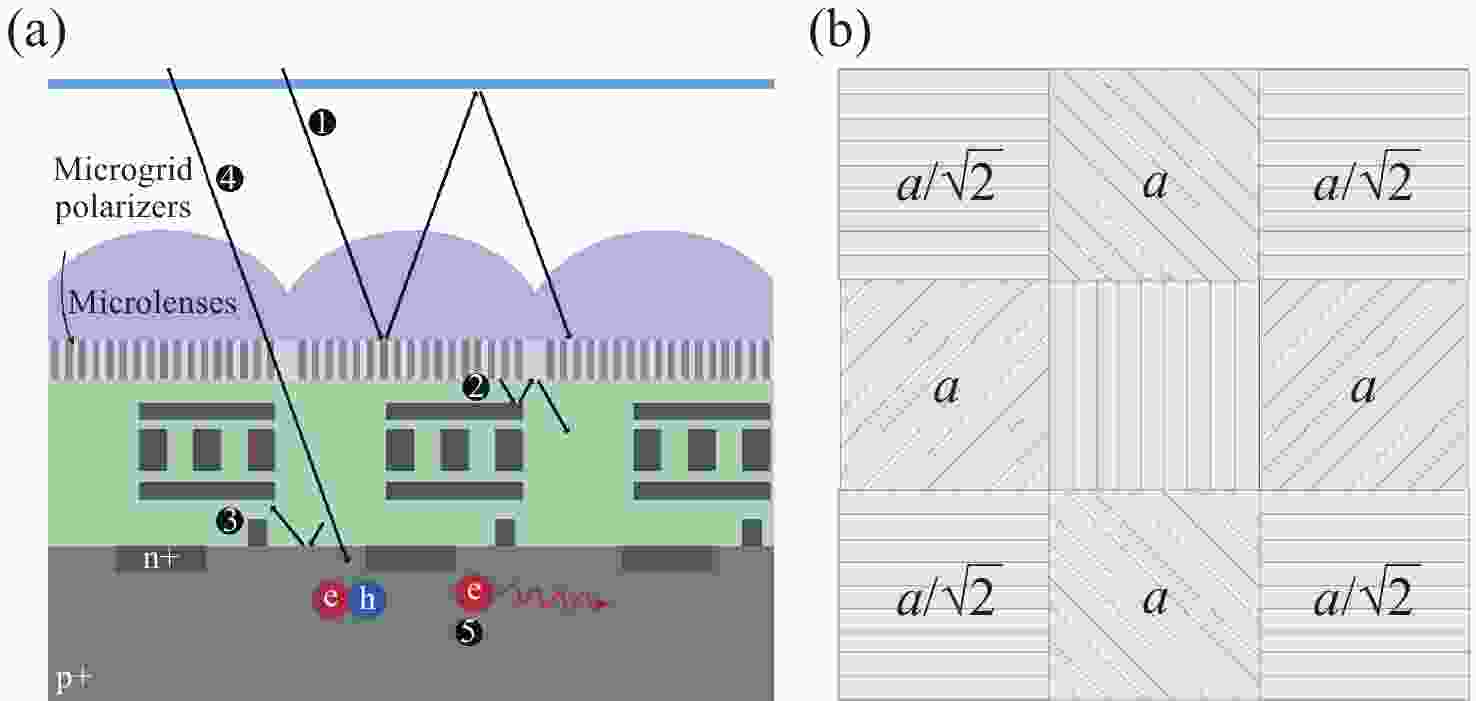
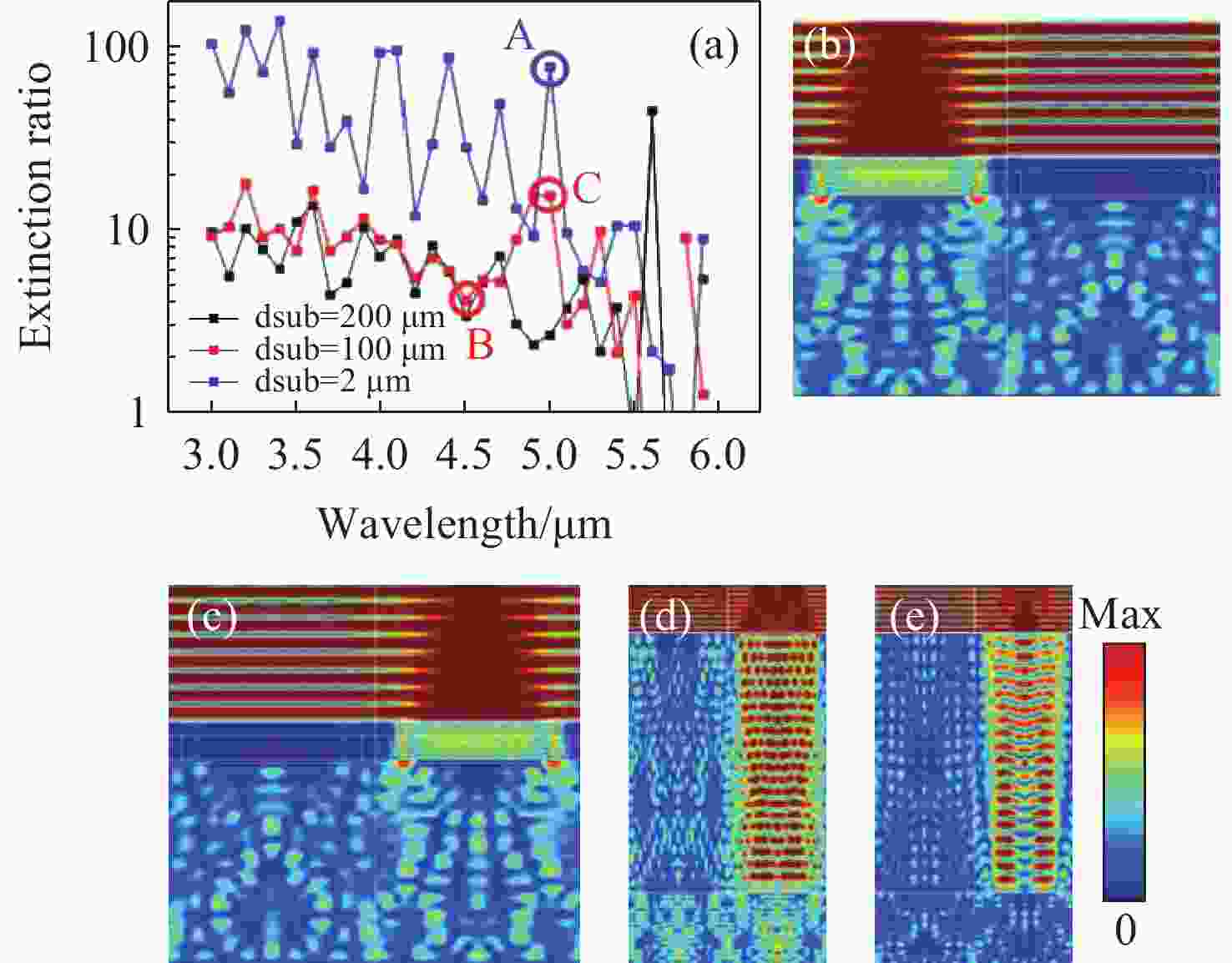
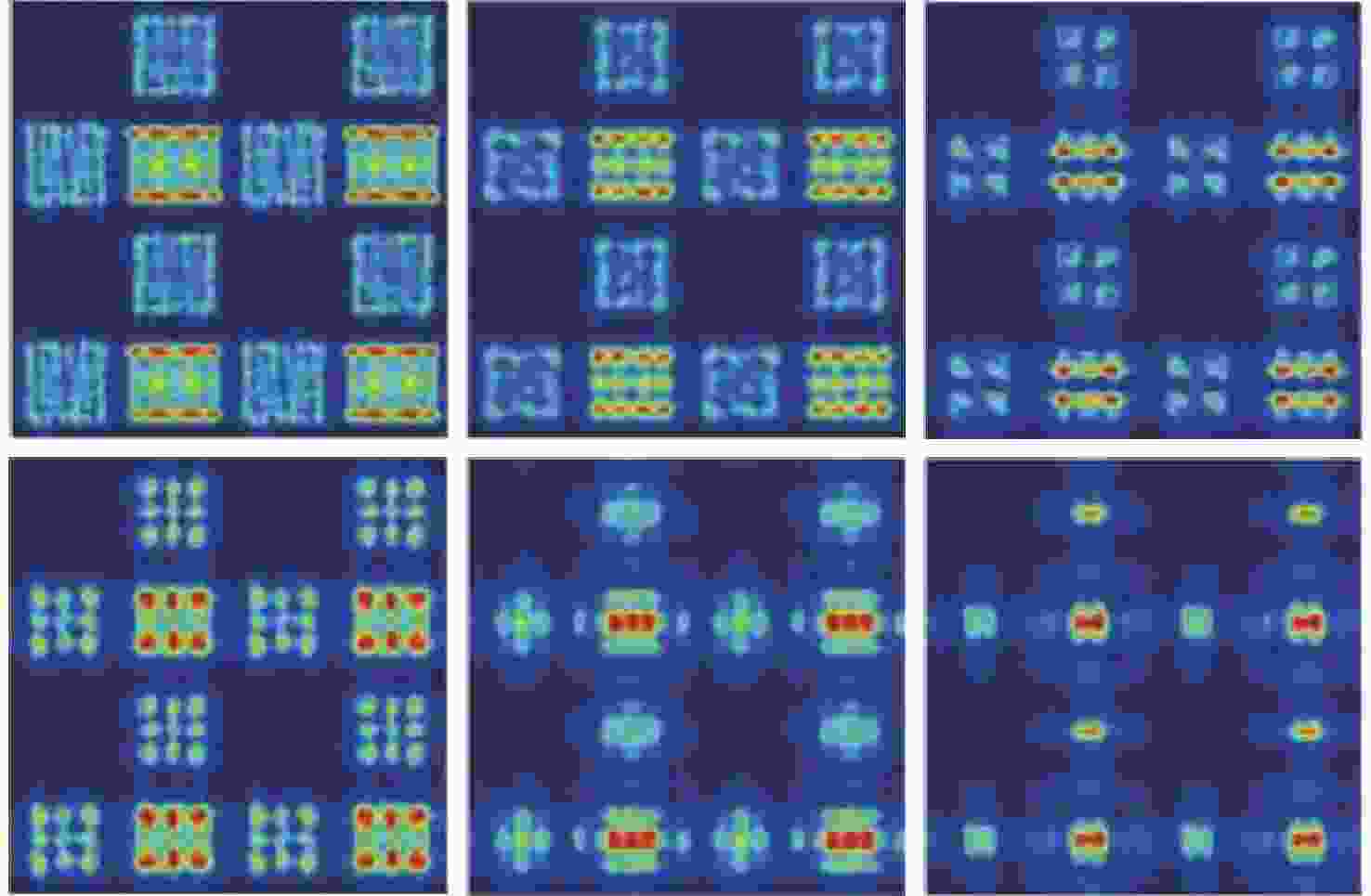
图 15 偏振红外探测器仿真结果[20]。(a) 衬底厚度与消光比关系;(b)波长5 μm的TM和 (c)TE入射光A的光场分布;(d)波长4.5 μm和(e)5 μm的TE入射光B和C的光场分布(A、B和C光在(a)中有标注)
Figure 15. Simulation results of polarization infrared detector[20]. (a) Relationship between extinction ratio and thickness of substrate. The light field distribution of (b) TM and (c) TE incident light A with wavelength of 5 μm, and TE incident light with wavelengths of (d) 4.5 μm B and (e) 5 μm C. Light A, B, and C are marked in (a)
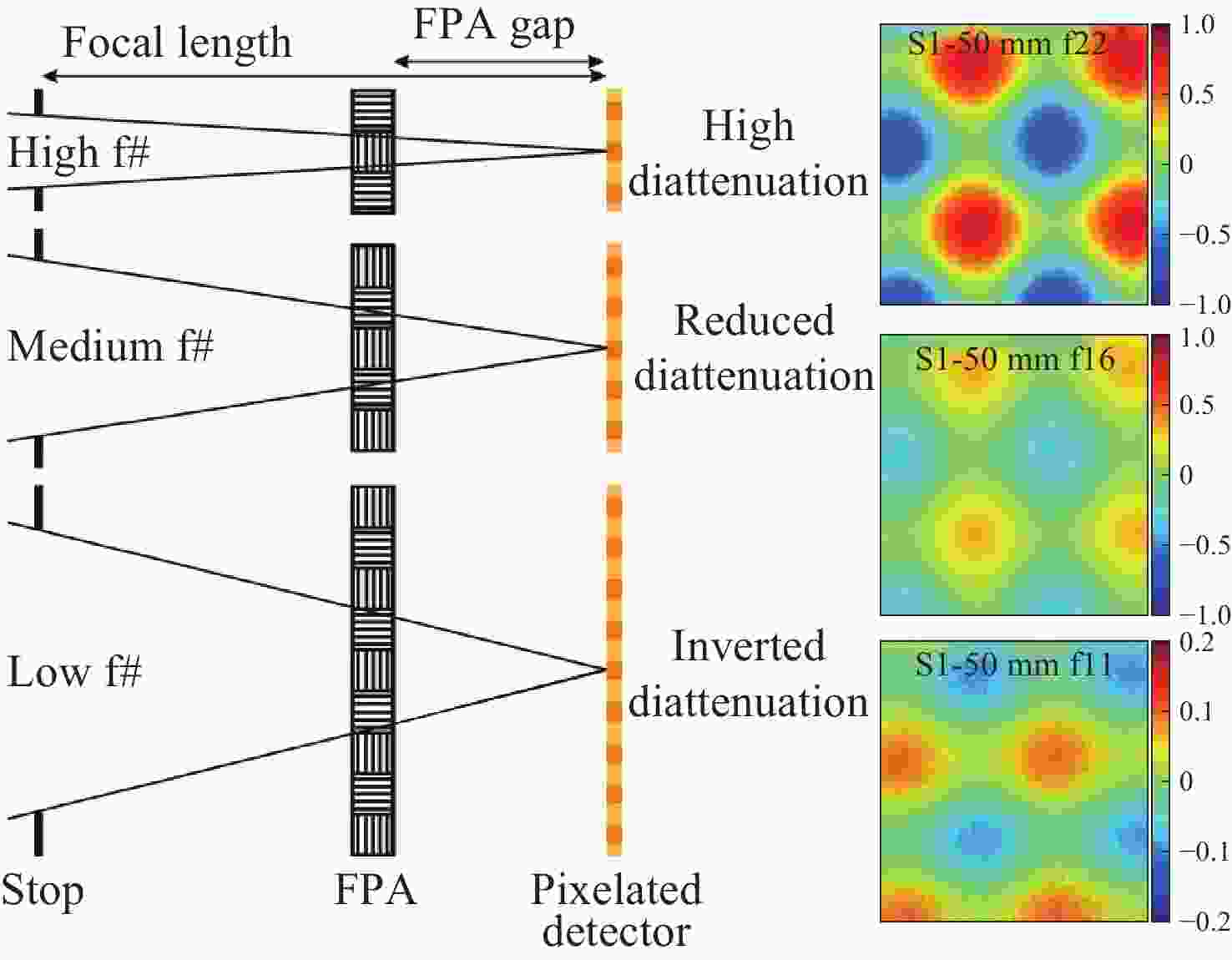
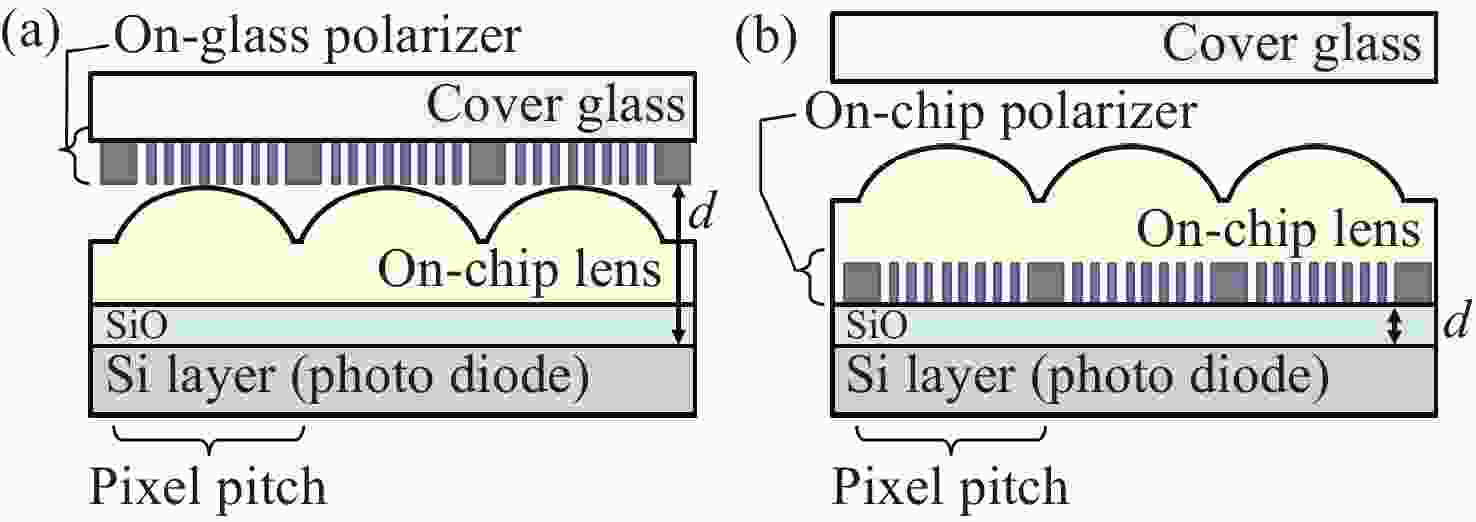
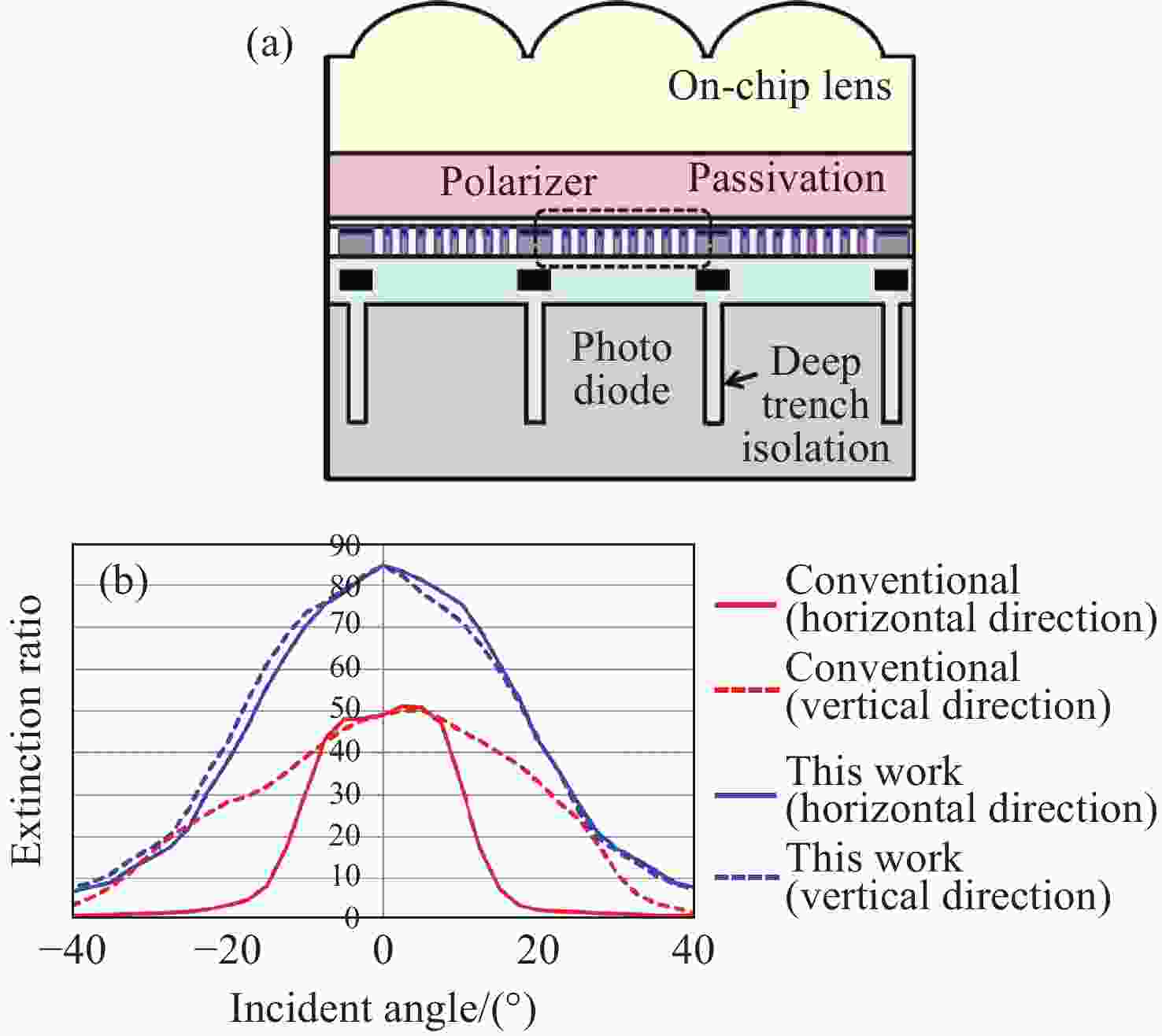
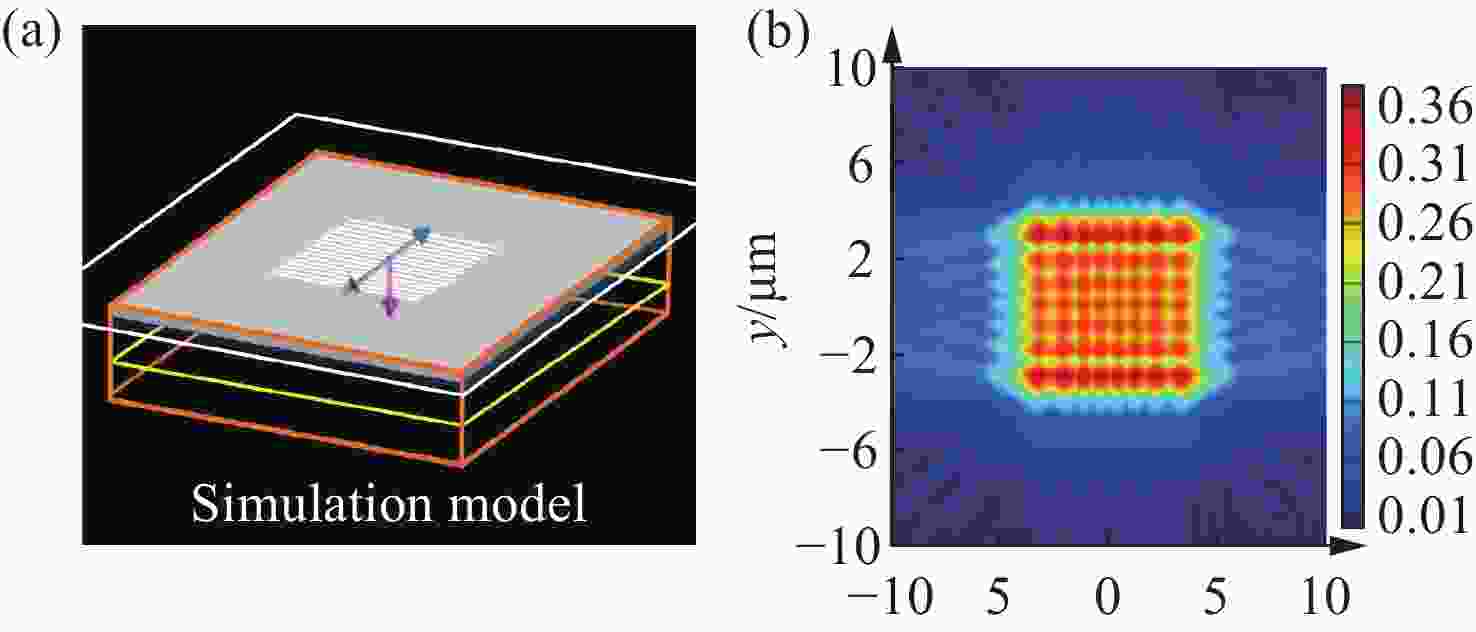
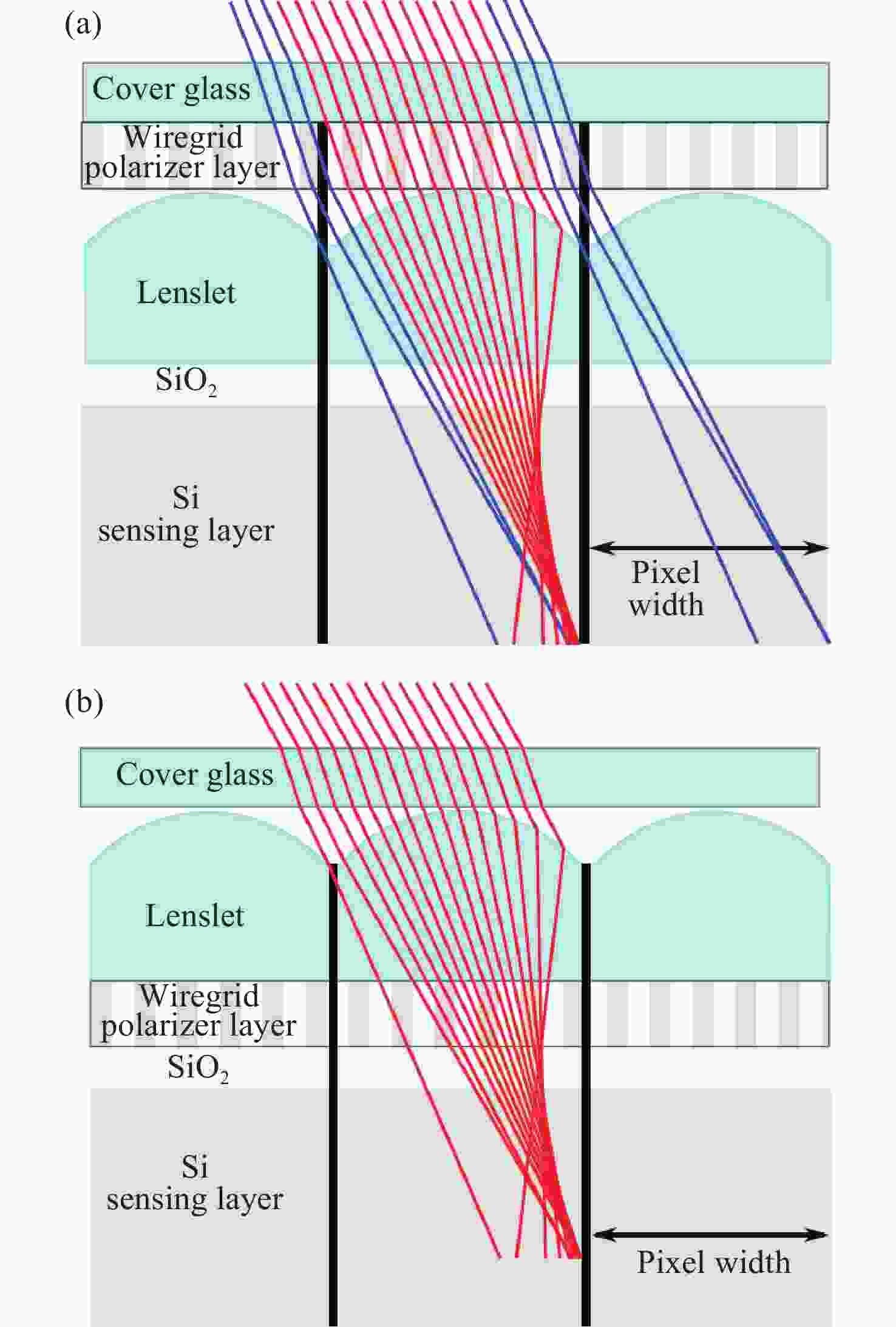
表 1 优化感光芯片参数/结构以抑制串扰的相关研究
Table 1. Studies related to optimization of photoreceptor chip parameters/structure for crosstalk suppression
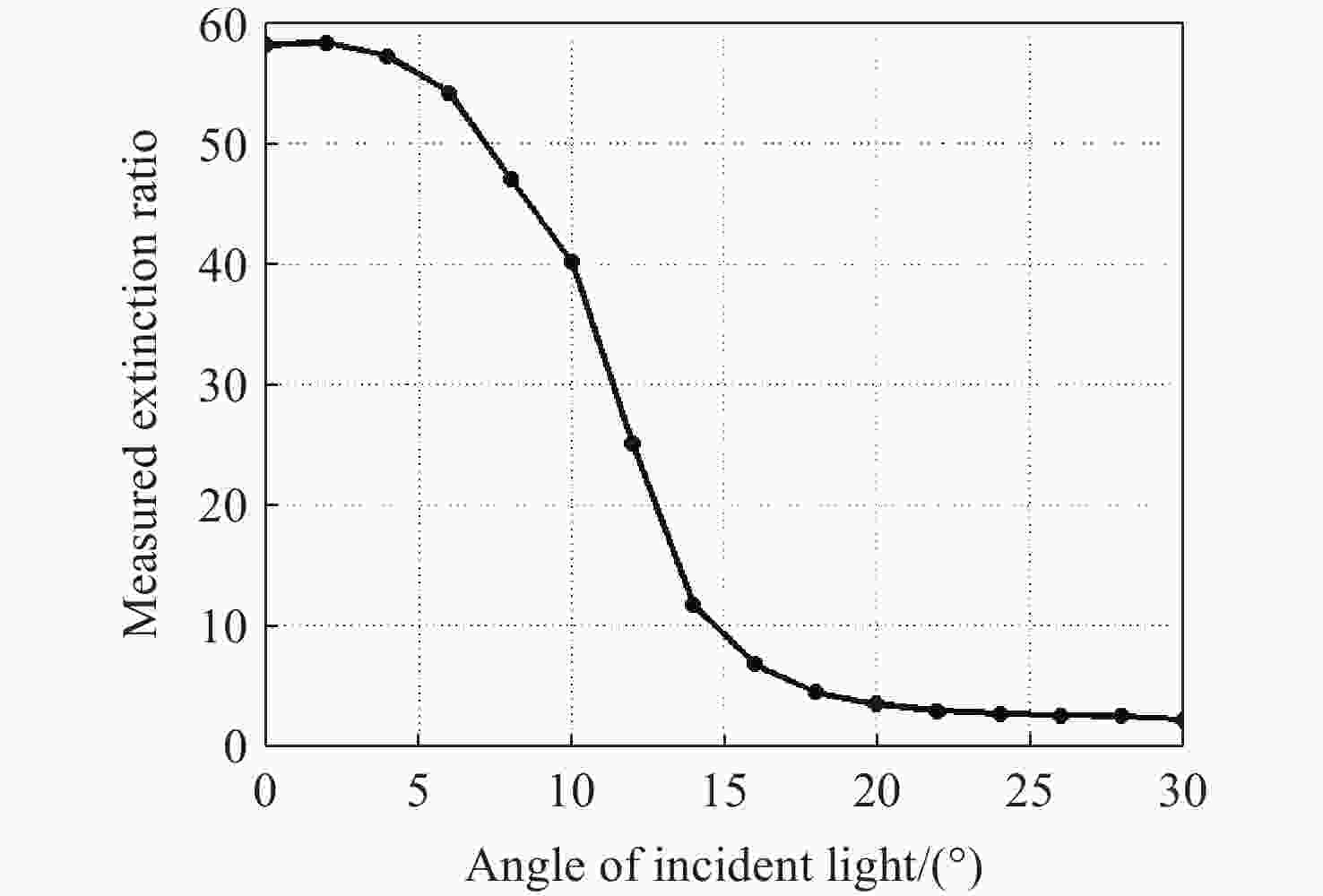
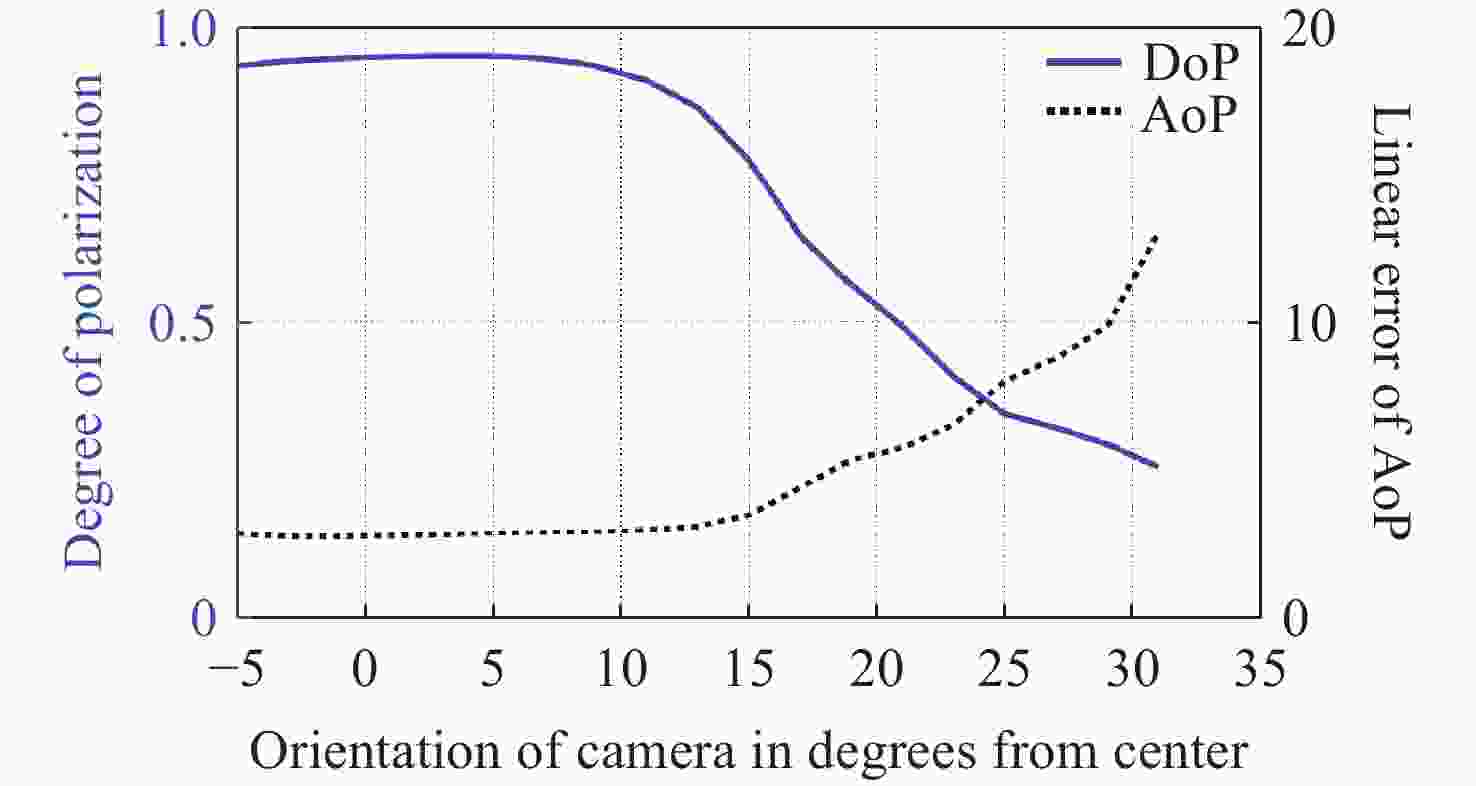
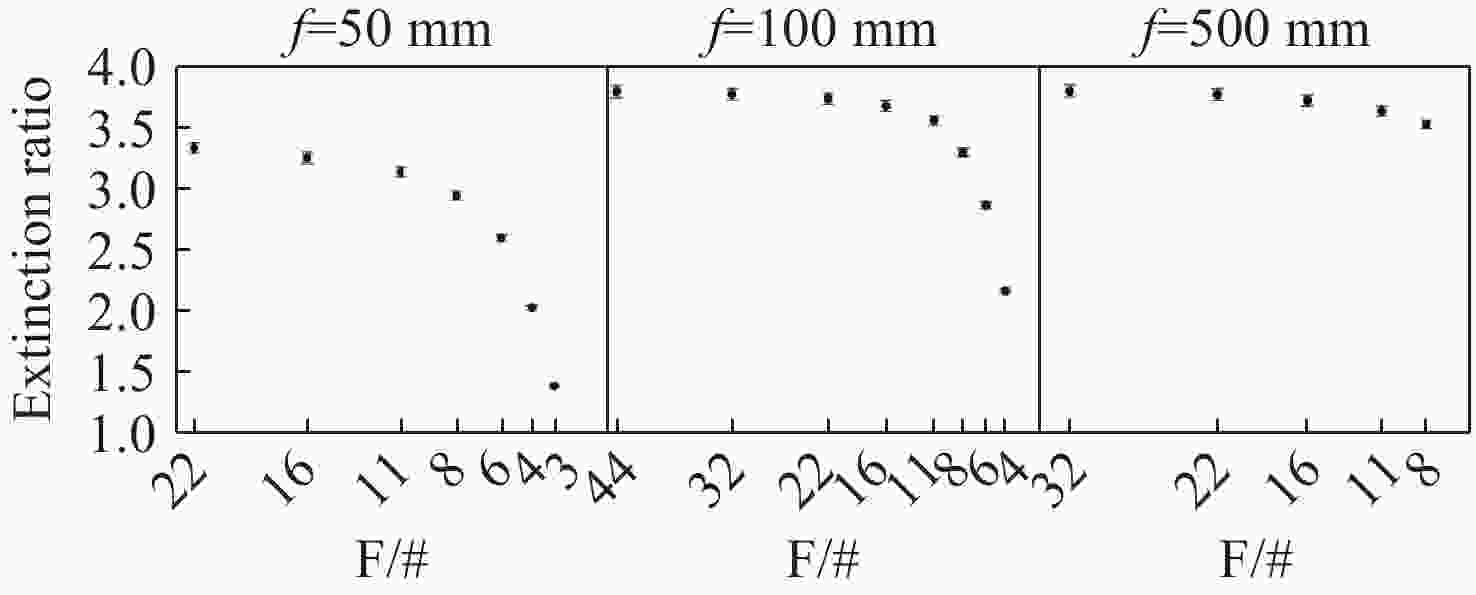
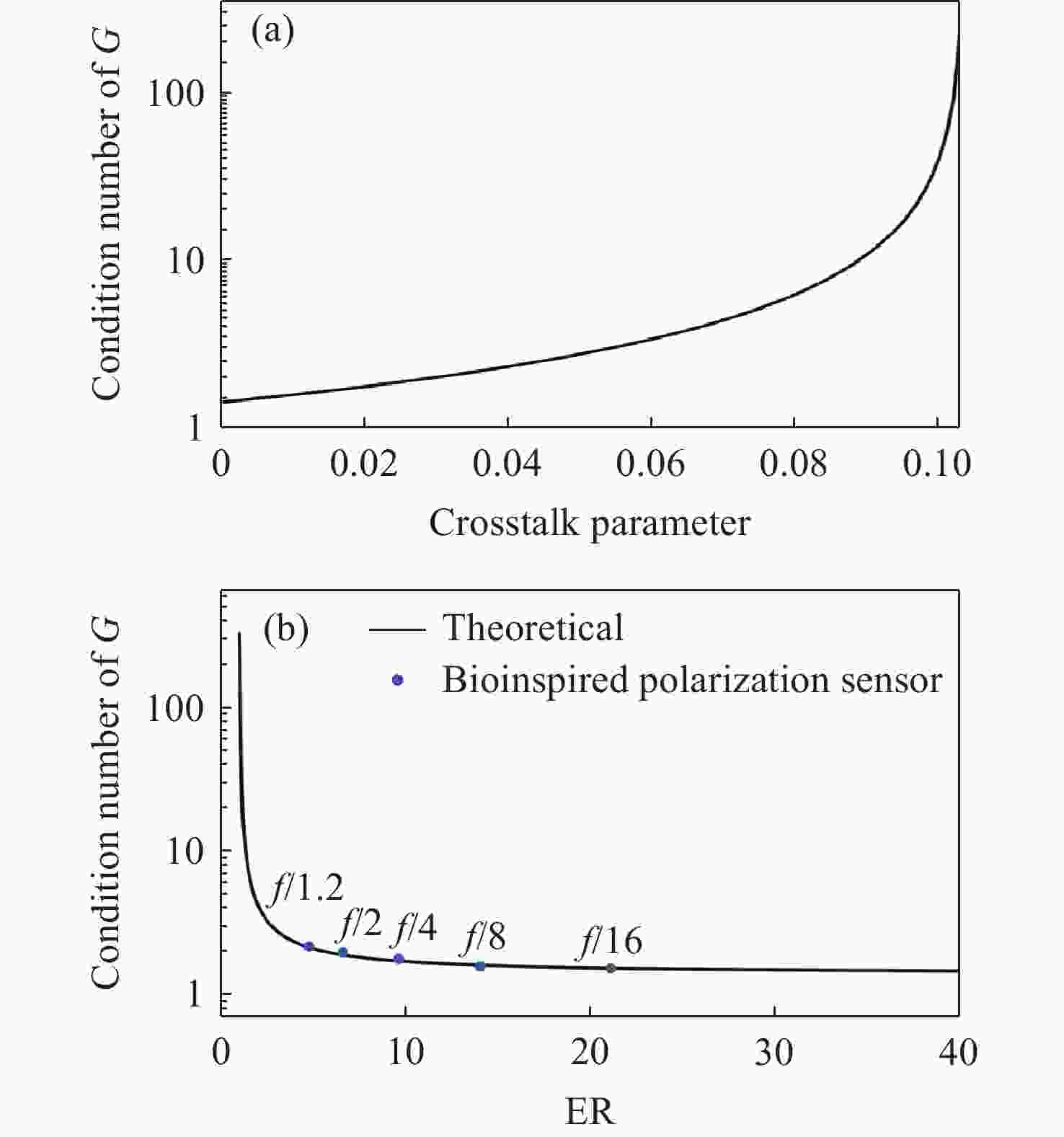
表 2 各传感器样机最佳消光比测量结果
Table 2. Optimal extinction ratio measurement results of each sensor prototype
-
[1] JONES M W, PERSONS C M. Performance predictions for micro-polarizer array imaging polarimeters[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6682: 668208. doi: 10.1117/12.736225 [2] CRUZ-CABRERA A A, KEMME S A, WENDT J R, et al. Polarimetric imaging cross talk effects from glue separation between FPA and micropolarizer arrays at the MWIR[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6478: 64780Q. doi: 10.1117/12.702084 [3] KEMME S A, CRUZ-CABRERA A A, NANDY P, et al. Micropolarizer arrays in the MWIR for snapshot polarimetric imaging[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6556: 655604. doi: 10.1117/12.720036 [4] GRUEV V, PERKINS R, YORK T. CCD polarization imaging sensor with aluminum nanowire optical filters[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(18): 19087-19094. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.019087 [5] YORK T, GRUEV V. Optical characterization of a polarization imager[C]. IEEE International Symposium of Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), IEEE, 2011: 1576-1579. [6] YORK T, GRUEV V. Characterization of a visible spectrum division-of-focal-plane polarimeter[J]. Applied Optics, 2012, 51(22): 5392-5400. doi: 10.1364/AO.51.005392 [7] POWELL S B, GRUEV V. Calibration methods for division-of-focal-plane polarimeters[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(18): 21039-21055. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.021040 [8] MYHRE G, HSU W L, PEINADO A, et al. Liquid crystal polymer full-stokes division of focal plane polarimeter[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(25): 27393-27409. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.027393 [9] FOURSPRING K, NINKOV Z. Optical characterization of a micro-grid polarimeter[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8364: 83640M. doi: 10.1117/12.919301 [10] VOROBIEV D, NINKOV Z, GARTLEY M. Polarization in a snap: imaging polarimetry with micropolarizer arrays[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9099: 909904. [11] MARUYAMA Y, TERADA T, YAMAZAKI T, et al. 3.2-MP back-illuminated polarization image sensor with four-directional air-gap wire grid and 2.5-μm pixels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2018, 65(6): 2544-2551. doi: 10.1109/TED.2018.2829190 [12] SUN H, WANG D J, CHEN CH, et al. Effect of sensor SNR and extinction ratio on polarimetric imaging error for nanowire-based systems[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(25): 7344-7351. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.007344 [13] 王德江, 孙翯, 孙雪倩. 消光比与探测器噪声对基于纳米线栅偏振成像系统偏振精度的影响[J]. 光学 精密工程,2018,26(10):2371-2379. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182610.2371WANG D J, SUN H, SUN X Q. Effect of extinction ratio and detector noise on polarization accuracy of nanometer wire grid polarization imaging system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(10): 2371-2379. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182610.2371 [14] 孙翯. 纳米线栅偏振成像系统应用研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2021.SUN H. Application research of nanowire polarization imaging system[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese). [15] SUN X Q, SUN H, WANG D J, et al. Extinction ratio and image accuracy of relayed-microgrid polarimetric imaging systems: theory and experiment[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(8): 2298-2307. doi: 10.1364/AO.386216 [16] 孙雪倩. 灵巧型偏振/强度共口径光学成像系统的研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2021.SUN X Q. Research on smart polarization/intensity common aperture optical imaging system[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese). [17] HAGEN N, SHIBATA S, OTANI Y. Calibration and performance assessment of microgrid polarization cameras[J]. Optical Engineering, 2019, 58(8): 082408. [18] DELIWALA A. Crosstalk and noise in division-of-focal-plane polarimeters and polarization imaging applications[D]. Urbana: University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2019. [19] DELIWALA A, GRUEV V. Optical crosstalk in division of focal plane imagers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2020, 11412: 114120F. [20] ZHOU J, ZHOU Y, SHI Y, et al. The light crosstalk suppression between adjacent pixels in polarization-integrated infrared detectors[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2020, 11427: 1142738. [21] LANE C, RODE D, RÖSGEN T. Calibration of a polarization image sensor and investigation of influencing factors[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(6): C37-C45. doi: 10.1364/AO.437391 [22] GIMÉNEZ-HENRÍQUEZ Y C. Characterization and calibration of polarizer filter array stokes imaging systems[D]. Mulhouse: Université de Haute Alsace, 2022. [23] KIM Y, CHOI W, PARK D, et al. A 1/2.8-inch 24 Mpixel CMOS image sensor with 0.9 μm unit pixels separated by full-depth deep-trench isolation[C]. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), IEEE, 2018: 84-86. [24] NIE A R, QIU ZH W, SUN X B, et al. Numerical study of a high-extinction-ratio micro-polarizer array with a metal grid substrate[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(33): 9795-9800. doi: 10.1364/AO.472707 [25] LIU J Y, ZHANG R, LI Y H, et al. A bio-inspired polarization navigation sensor based on artificial compound eyes[J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2022, 17(4): 046017. [26] CHEN ZH Y, WANG X, LIANG R G. Calibration method of microgrid polarimeters with image interpolation[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(5): 995-1001. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.000995 [27] FEI H, LI F M, CHEN W C, et al. Calibration method for division of focal plane polarimeters[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(18): 4992-4996. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.004992 [28] YANG J, QIU S, JIN W Q, et al. Temporal and spatial error model for estimating the measurement precision of the division of focal plane polarimeters[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(13): 20808-20828. doi: 10.1364/OE.428202 [29] 罗海波, 张俊超, 盖兴琴, 等. 偏振成像技术的发展现状与展望(特邀)[J]. 红外与激光工程,2022,51(1):20210987.LUO H B, ZHANG J CH, GAI X Q, et al. Development status and prospects of polarization imaging technology (invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(1): 20210987. (in Chinese). -





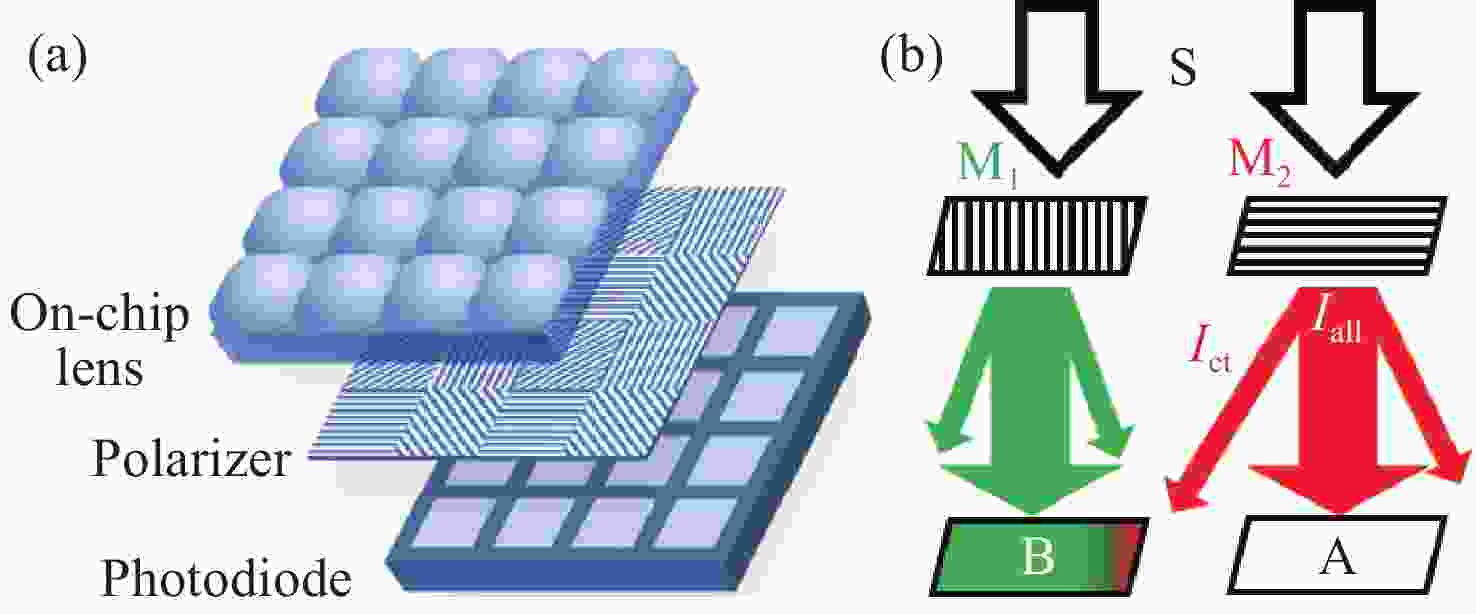
 下载:
下载: