-
摘要:
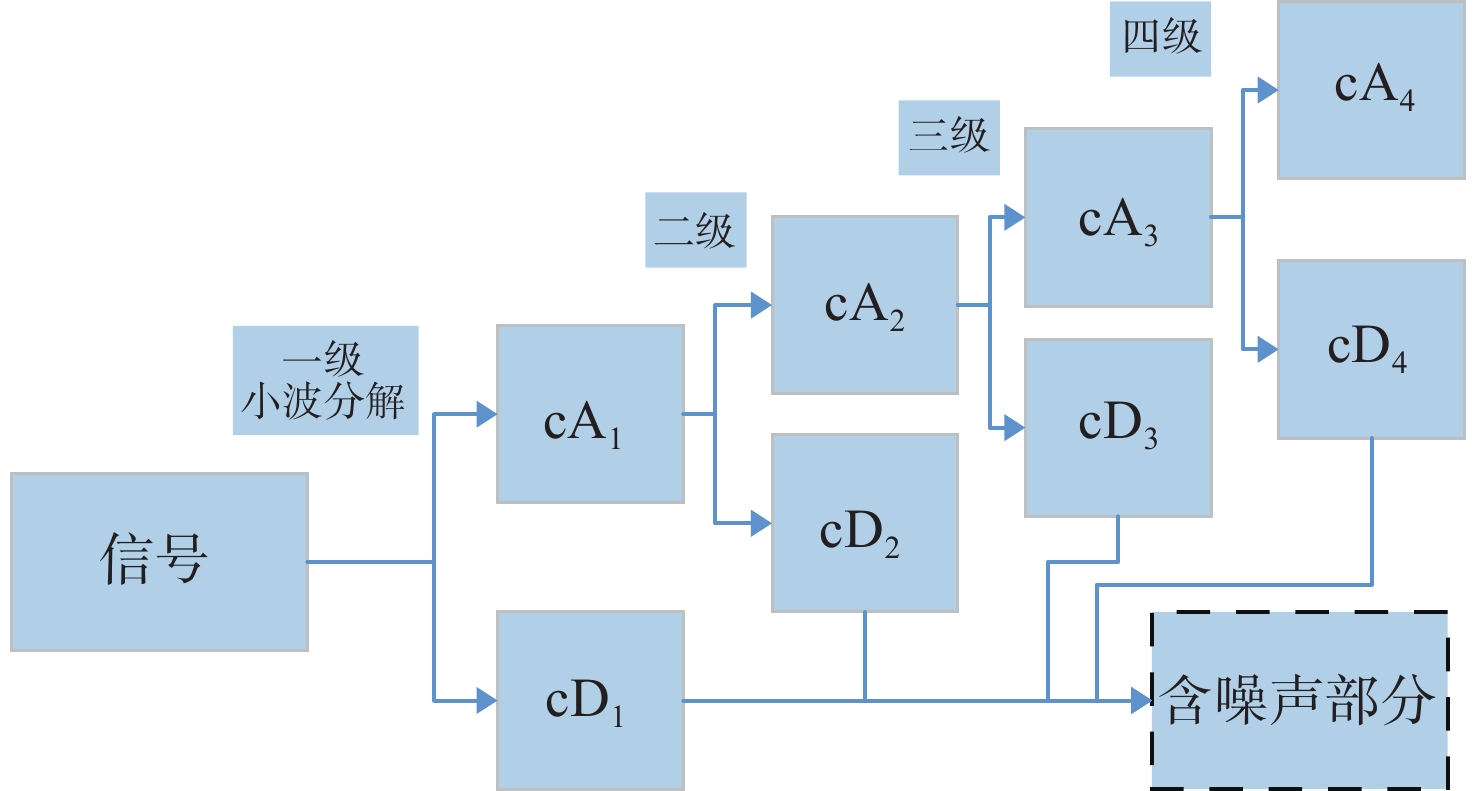
光谱技术可以从大量原始信号中提取有用的特征信息,直接用来分析和识别被观测样品的物质成分,在生物医药、食品安全、军事侦察中具有极高的应用价值。由于预处理目的与效果不同,目前存在多种光谱预处理方法。针对目前光谱预处理方法使用时存在的问题,本文提出了一种基于多尺度小波变换的光谱数据预处理方法,并利用仿真光谱和实测光谱对提出算法和设计软件的性能进行了测试。信噪比为0.5 dB的仿真信号经本文算法处理后,信噪比可达8.978 dB。仿真中加入5种不同类型的基线,包括线型、高斯型、多项式型、e指数型、sigmoidal函数型,使用本文算法进行基线估计,估计值的均方根误差RMSE分别为
0.3759 、0.2883 、0.6631 、0.3489 、0.4520 。使用共聚焦显微拉曼光谱仪测量了聚四氟乙烯光谱,并用本文算法进行了预处理。结果表明该算法具有良好的可操作性,能够有效去除噪声和校正基线,并完整保留谱峰信息,该算法为光谱数据预处理提供了新思路。Abstract:Spectral technology can extract useful characteristic information from a large number of raw signals, which can be directly utilized for analyzing and identitying the material components of the observed samples. It has high application value in fields such as biomedicine, food safety and military reconnaissance. Due to the varying objectives and effects of the pretreatment, there are currently multiple spectral pre-processing methods available. We propose a spectrum signal pre-processing algorithm based on multi-scale wavelet transform, and the performance of the proposed algorithm and the designed softwere are evaluated through tests using both simulated and experimental spectra. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the simulated signal is 0.5 dB. After processing with the algorithm proposed in this paper, the SNR can reach to 8.978 dB. In the simulation, five different types of baselines are introduced, including linear, Gaussian, polynomial, exponential, and sigmoidal function types. Baseline estimation is performed using the algorithm proposed in this paper. The root mean square errors (RMSE) of the estimated values are
0.3759 ,0.2883 ,0.6631 ,0.3489 ,0.4520 , respectively. The spectrum of Polytetrafluoroethylene was measured using a confocal micro-Raman spectrometer and preprocessed with the algorithm proposed in this paper. The results demonstrate that the algorithm is capable of fast and accurate processing of the spectra. The algorithm can be used to reduce noise and correct baseline. This study put on a set of new ideas on spectrum signal processing. -
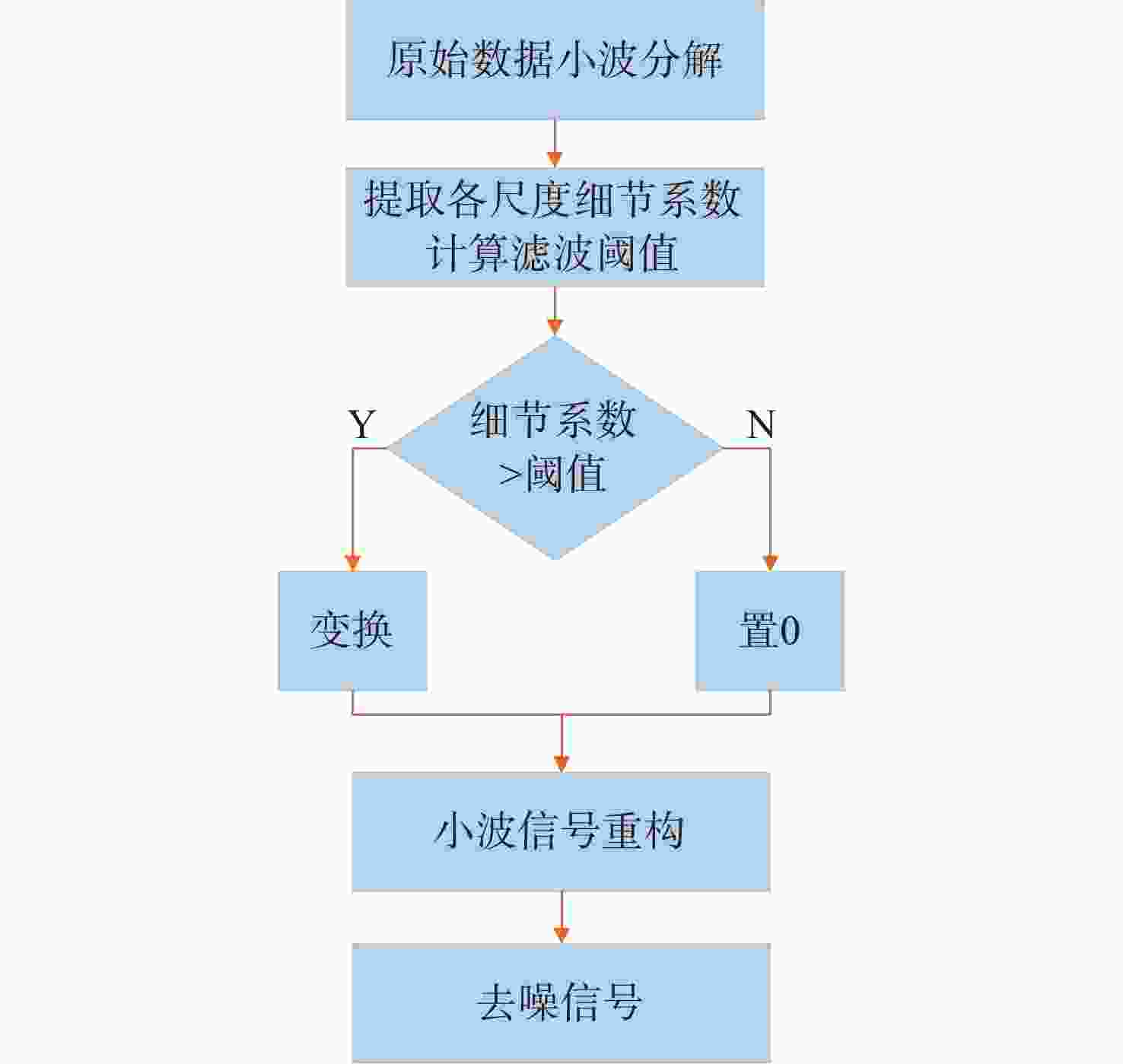
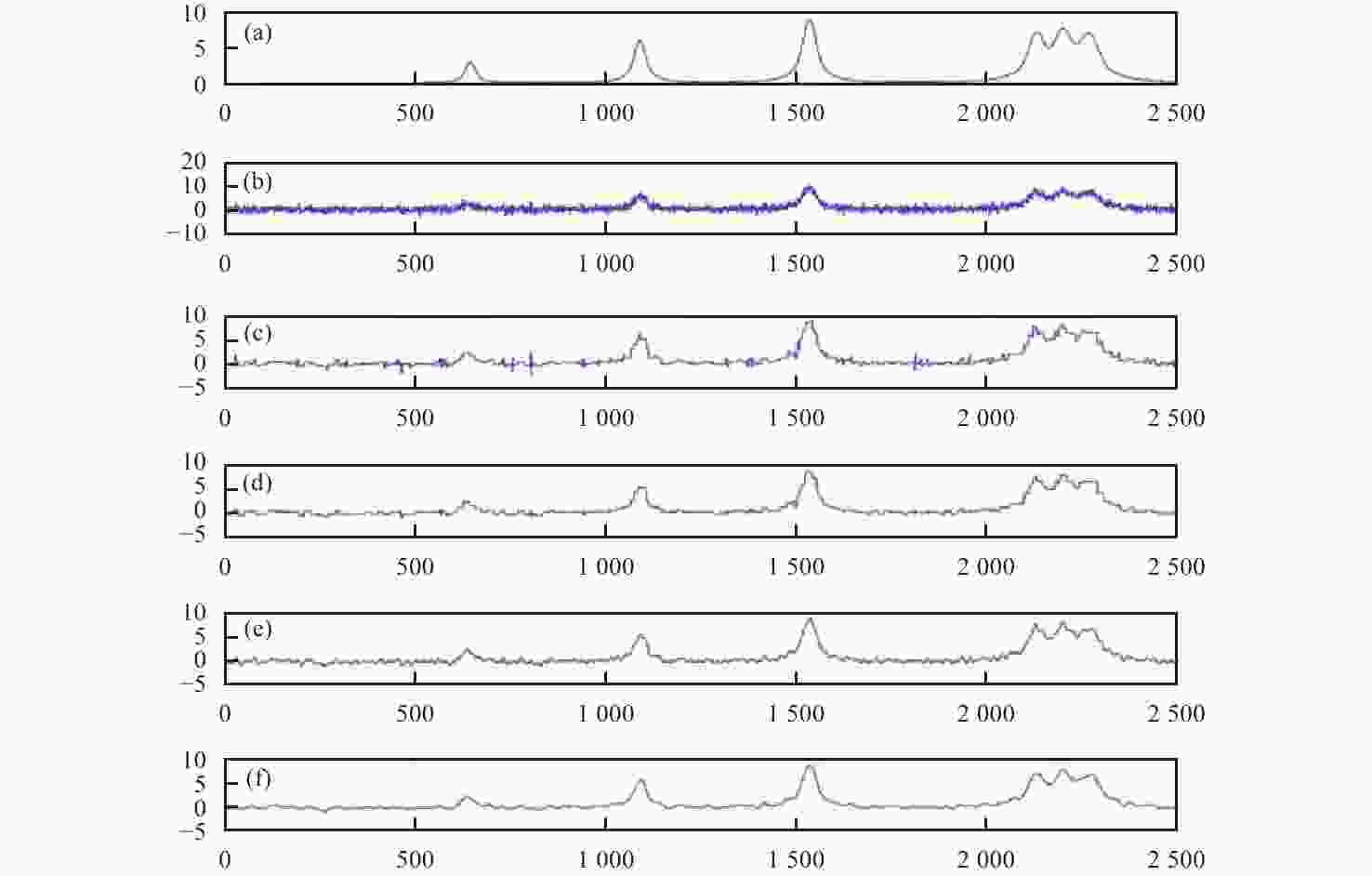
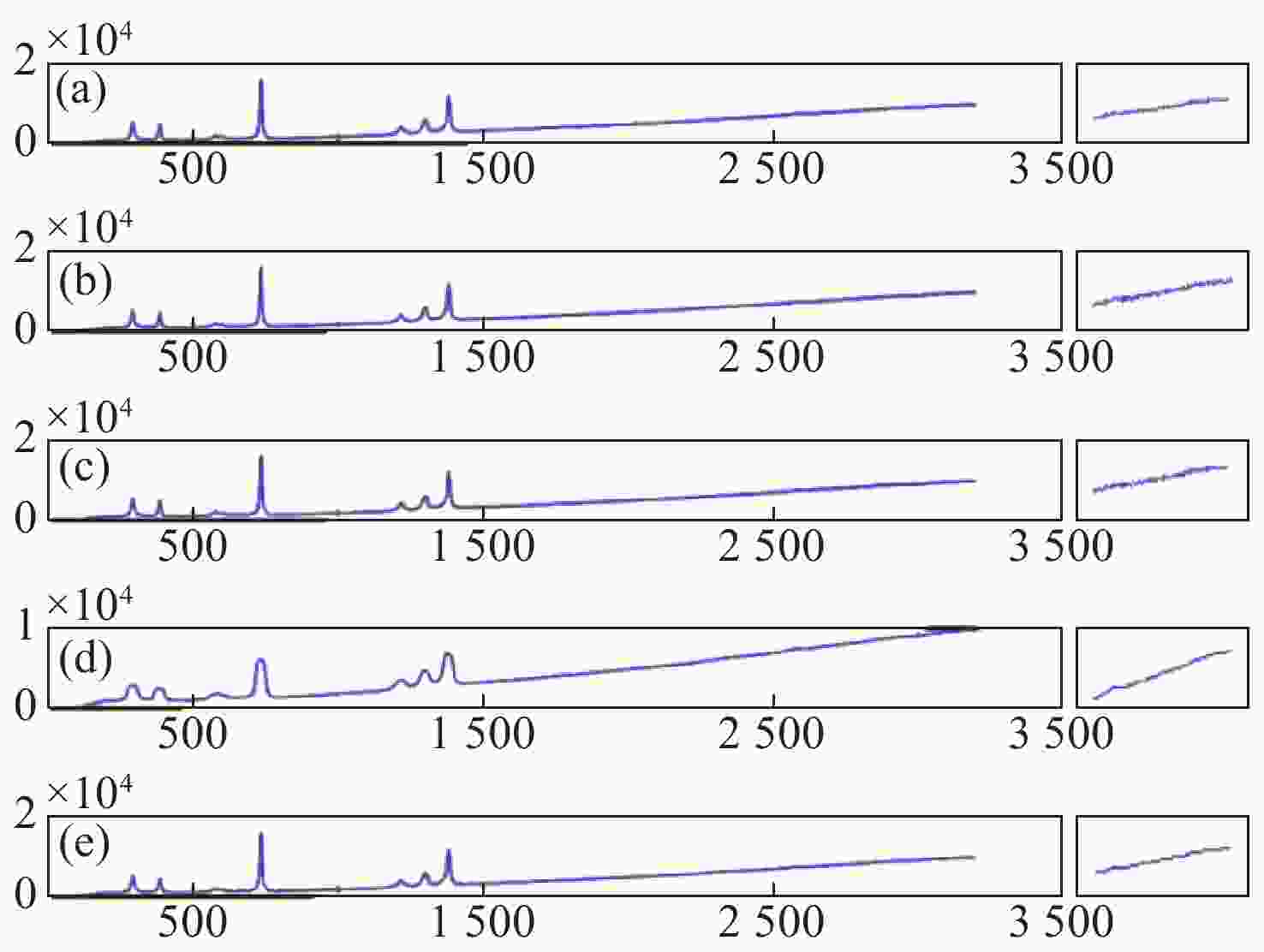
图 7 仿真数据去噪效果对比图。(a)原始信号;(b)加噪声信号;(c)硬阈值去噪;(d)软阈值去噪;(e) Savitzky-Golay去噪;(f)本文算法去噪
Figure 7. Contrast map of simulated de-noising spectral signal. (a) Initial signal; (b) signal with noise; (c) hard thresholding denoising; (d) soft thresholding denoising; (e) Savitzky-Golay denoising; (f) DTD denoising
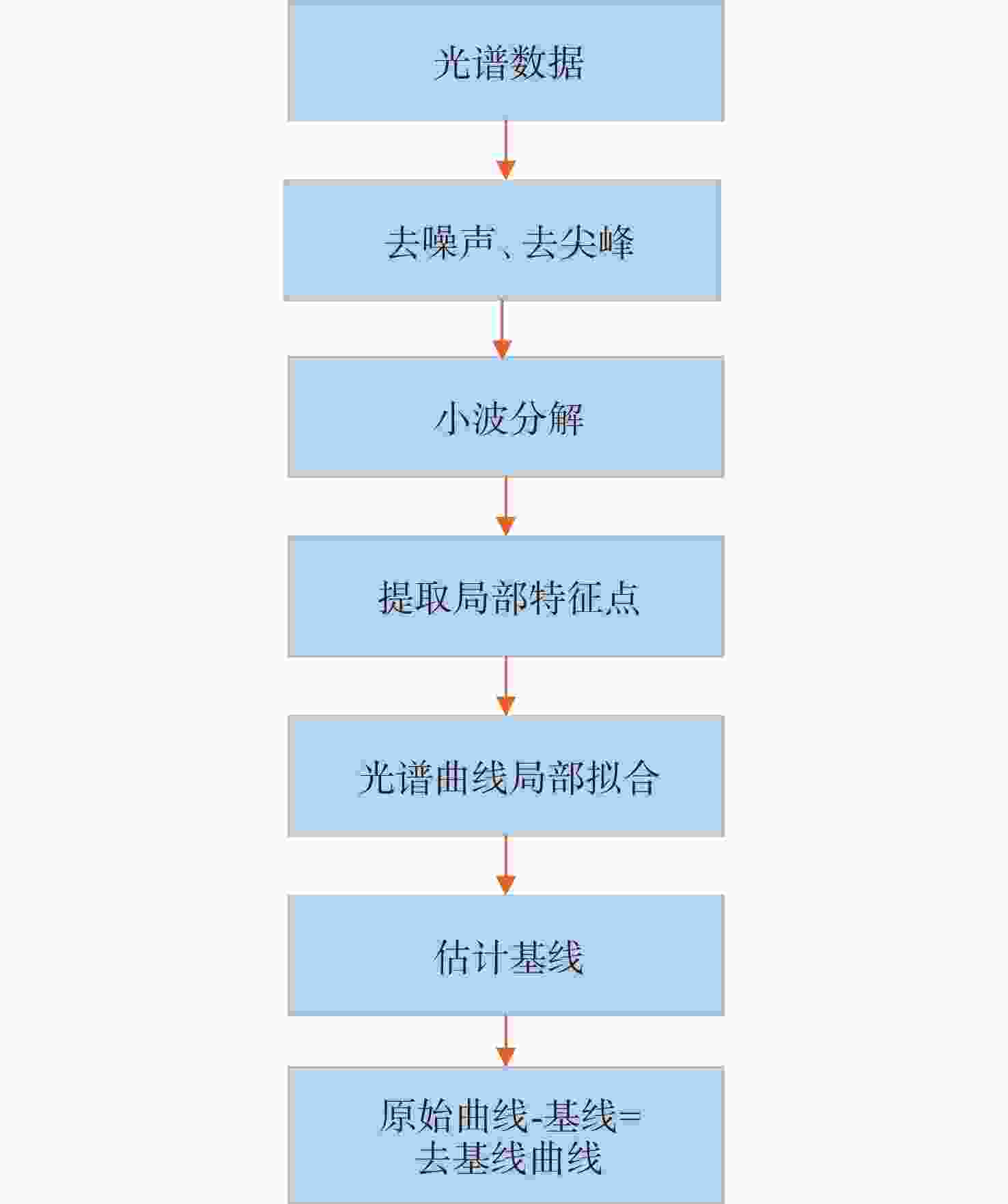
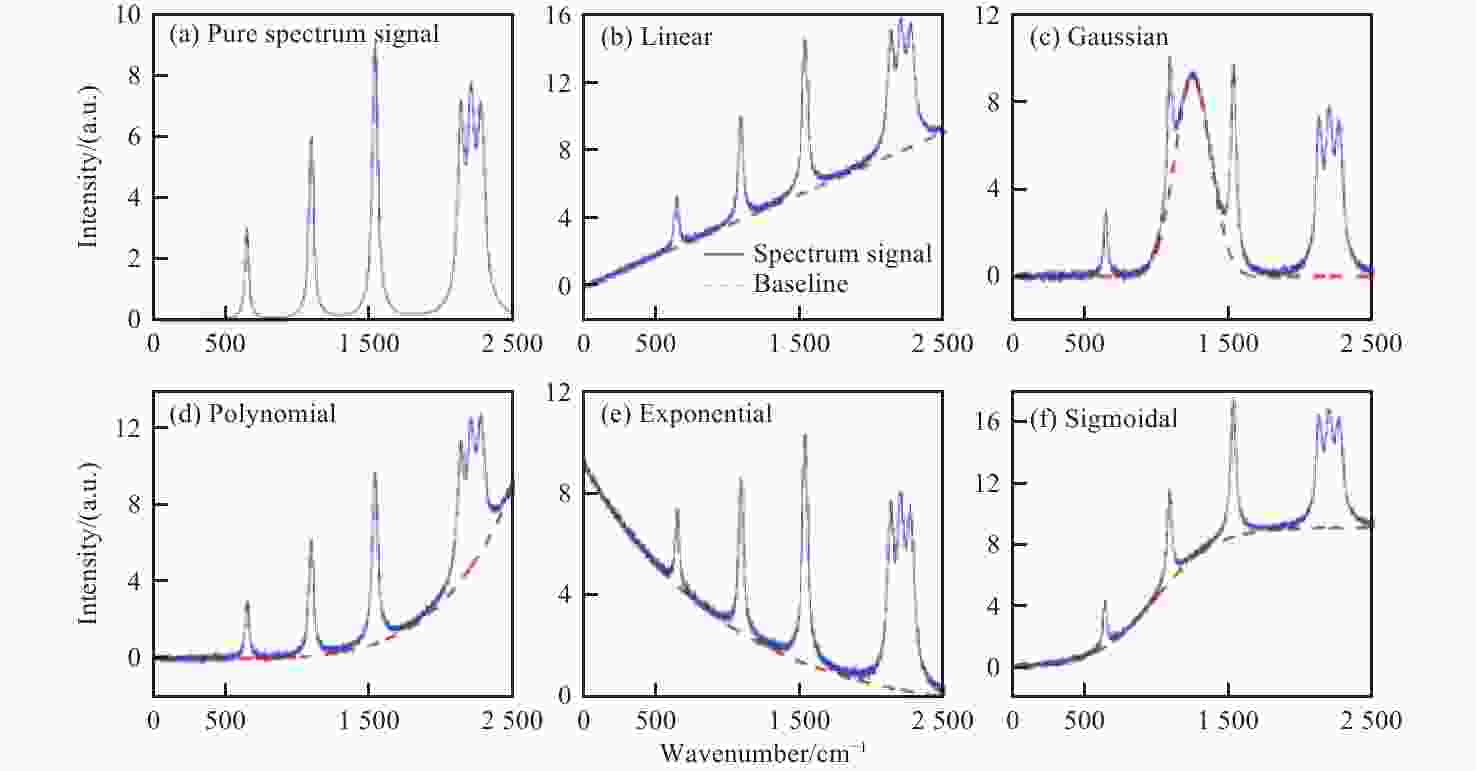
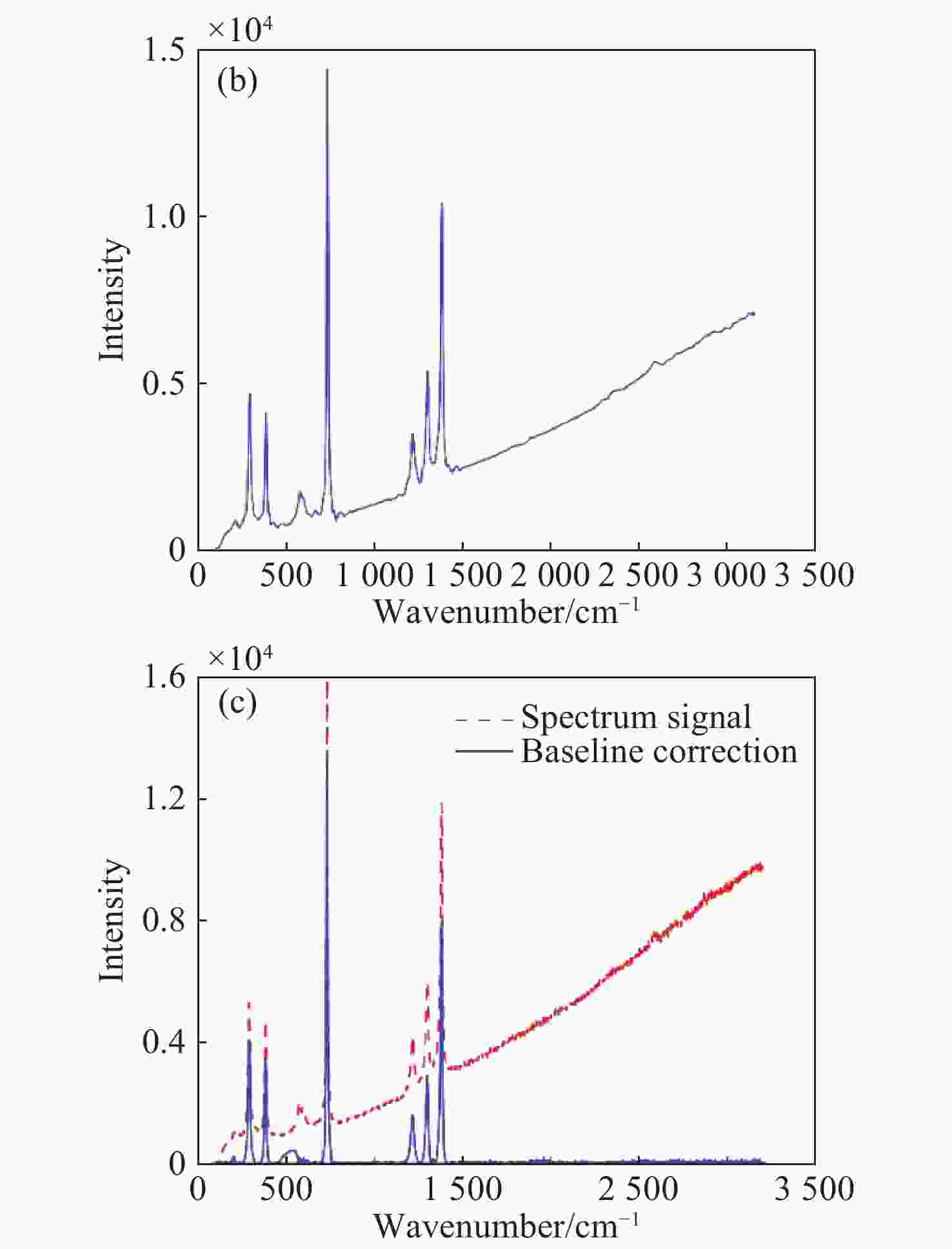
图 8 加入基线的光谱图。(a)原始信号;(b)加入线型基线;(c)加入高斯型基线;(d)加入多项式型基线;(e)加入e指数型基线;(f)加入sigmoidal函数型基线
Figure 8. Map of spectral signal with baseline. (a) Initial signal; (b) signal with linear baseline; (c) signal with Gaussian baseline; (d) signal with polynomial baseline; (e) signal with exponential baseline; (f) signal with sigmoidal baseline
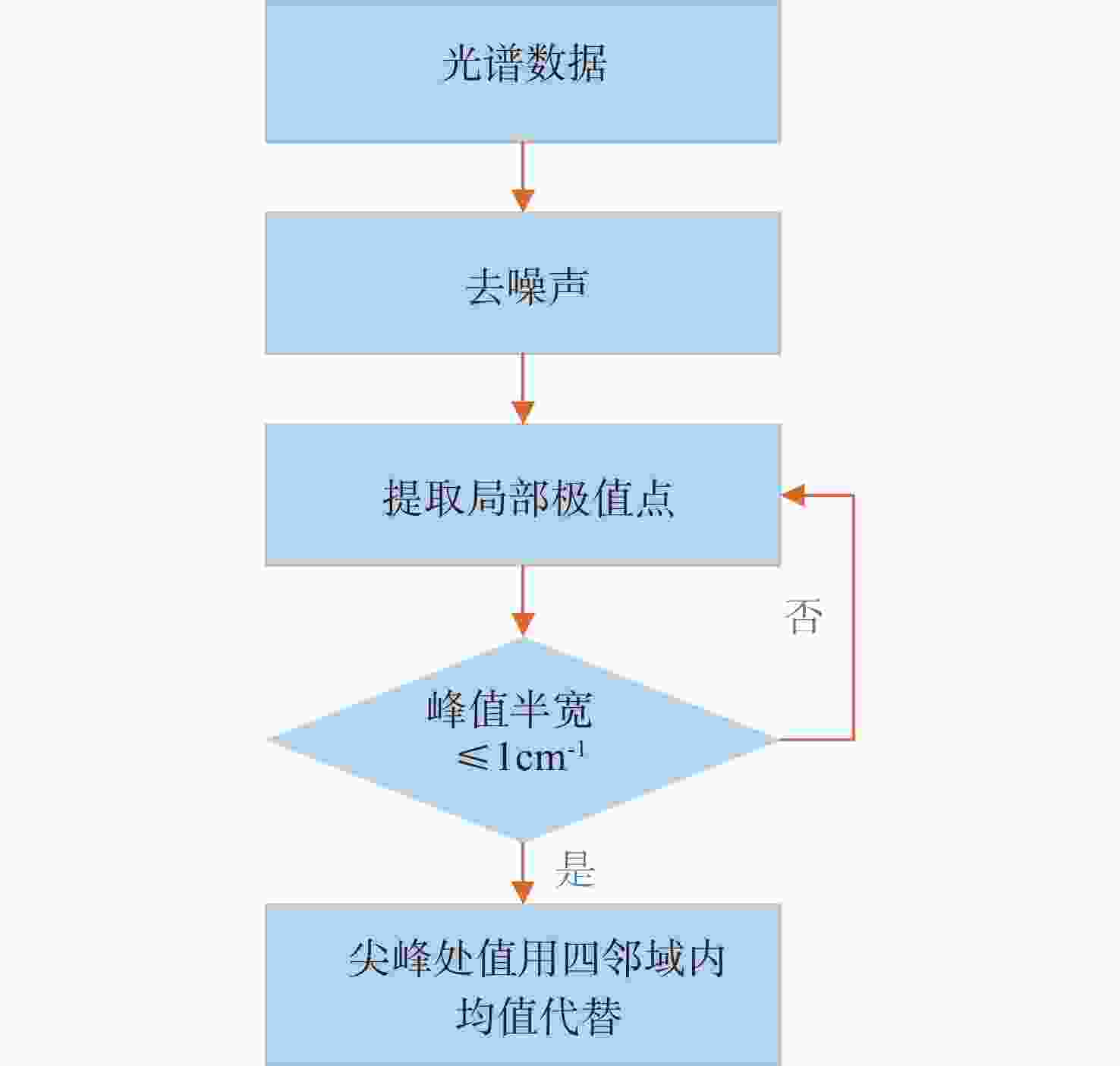
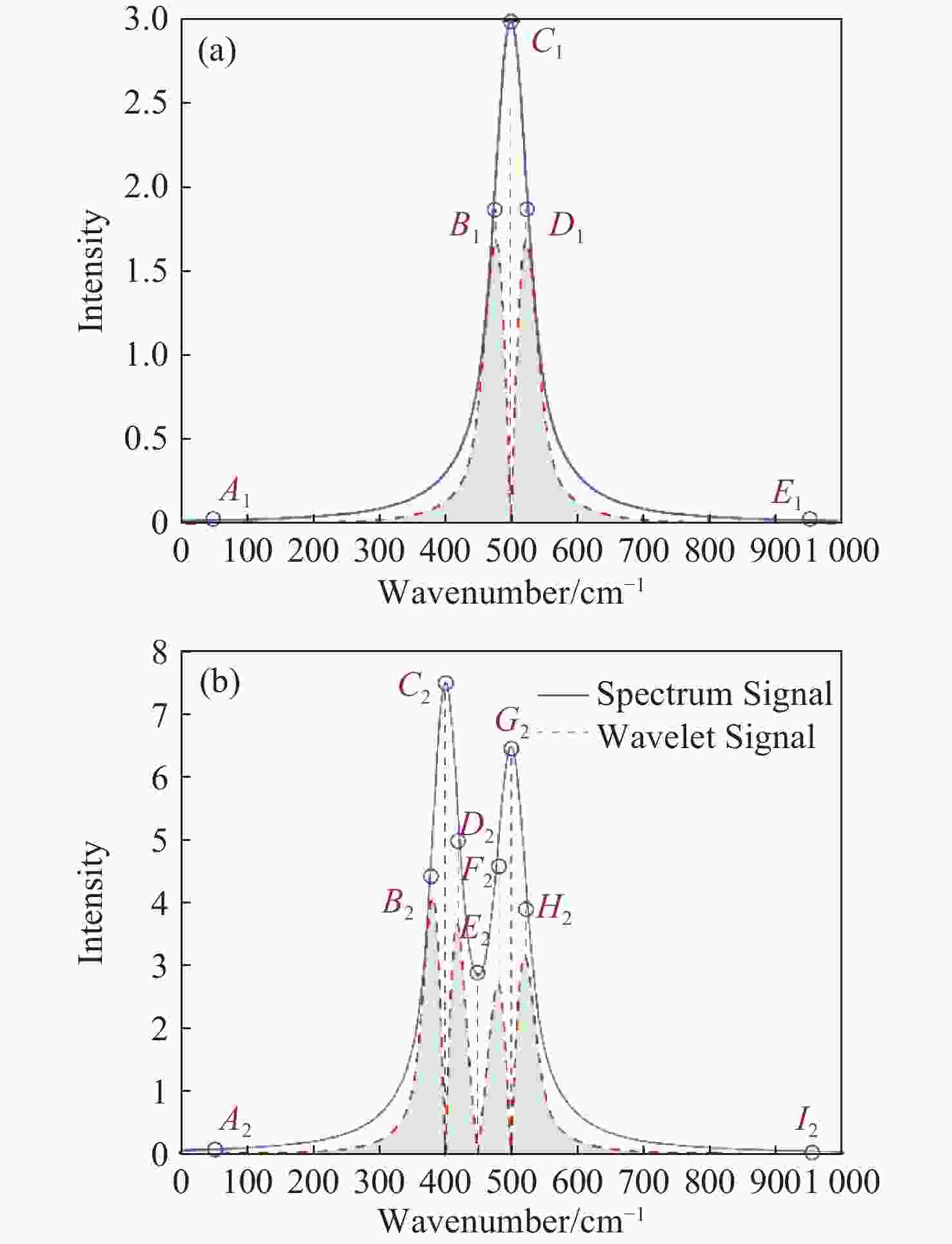
表 1 光谱特征点属性
Table 1. Attribute of spectral characteristic
谱峰类型 单峰 多峰 光谱值 小波变换值 一阶导数是否
通过零点起始点 A1 A2 最小值 最小值 × 左拐点 B1 B2, F2 上升沿 最大值 × 谱峰 C1 C2, G2 最大值 最小值 ∨ 右拐点 D1 D2, H2 下降沿 最大值 × 波谷 -- E2 最小值 最小值 ∨ 结束点 E1 I2 最小值 最小值 × 表 2 仿真光谱信号
Table 2. Simulated spectral signal
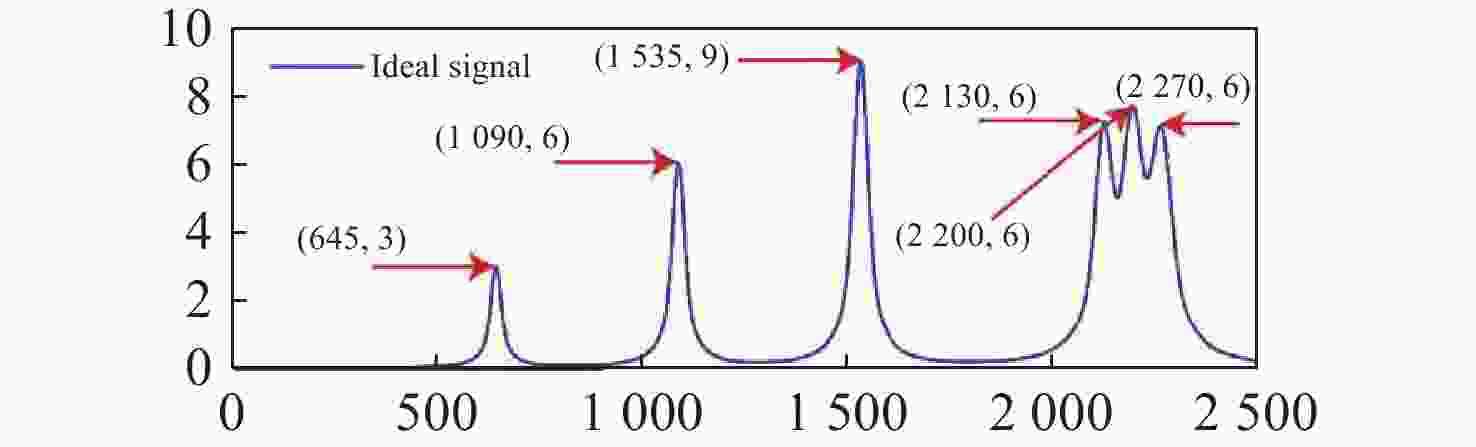
谱峰位置(cm−1) 645 1090 1535 2130 2200 2270 谱峰高度 3 6 9 6 6 6 半峰全宽 25 30 35 40 45 50 表 3 不同方法去噪后信号的信噪比
Table 3. SNR of signals after denoising using different methods
原始
信号硬阈值
算法软阈值
算法Savitzky-Golay
滤波算法本文算法
DTDSNR(dB) 0.5 8.0621 8.3231 8.4106 8.9775 表 4 不同算法的去基线性能比较
Table 4. Comparison of baseline removal performance among different algorithms
基线类型 PF算法 AIRPLS算法 SWMA算法 本文算法
WFPSI线型 1.2629 0.3141 0.4751 0.3759 高斯函数型 1.0733 0.3290 0.4881 0.2883 多项式型 1.2986 0.6501 0.7076 0.6631 e指数型 1.2755 0.3953 0.4729 0.3489 sigmoidal函数型 1.2562 1.2178 1.2330 0.4520 表 5 光谱数据基线校正后凸包面积减小百分比
Table 5. Percentage reduction in area of convex hull
算法 凸包面积减小百分比 PF算法 54.69% AIRPLS算法 64.76% SWMA算法 58.51% WFPSI算法 66.21% -
[1] 孙嘉豪, 张伟, 施鉴芩, 等. 光谱数据预处理策略选择及应用[J]. 计量学报,2023,44(8):1284-1292. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158.2023.08.20SUN J H, ZHANG W, SHI J Q, et al. Selection and application of spectral data preprocessing strategy[J]. Acta Metrologica Sinica, 2023, 44(8): 1284-1292. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158.2023.08.20 [2] 周粲入, 王哲涛, 杨思危, 等. 化学计量学和深度学习方法在拉曼光谱处理方面的应用研究进展[J]. 分析化学,2023,51(8):1232-1242.ZHOU C R, WANG ZH T, YANG S W, et al. Application progress of chemometrics and deep learning methods in Raman spectroscopy signal processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(8): 1232-1242. (in Chinese). [3] 张雪容, 梁维新, 杨玉敏, 等. 顶空固相萃取-纸基表面增强拉曼光谱法快速测定水中痕量汞[J]. 分析化学,2023,51(9):1536-1544.ZHANG X R, LIANG W X, YANG Y M, et al. Determination of trace mercury in water by headspace solid phase extraction combining paper-based surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(9): 1536-1544. (in Chinese). [4] 刘成员, 于江玉, 李奉翠, 等. 拉曼光谱测试技术在可充电铝离子电池储能机理的研究进展[J]. 应用化学,2023,40(10):1347-1358.LIU CH Y, YU J Y, LI F C, et al. Research progress of Raman spectroscopy technique in energy storage mechanism of rechargeable aluminum-ion batteries[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2023, 40(10): 1347-1358. (in Chinese). [5] 李艳坤, 董汝南, 张进, 等. 光谱数据解析中的变量筛选方法[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2021,41(11):3331-3338.LI Y K, DONG R N, ZHANG J, et al. Variable selection methods in spectral data analysis[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2021, 41(11): 3331-3338. (in Chinese). [6] ESTEVES C S M, DE REDROJO E M M, MANJÓN J L G, et al. Combining FTIR-ATR and OPLS-DA methods for magic mushrooms discrimination[J]. Forensic Chemistry, 2022, 29: 100421. doi: 10.1016/j.forc.2022.100421 [7] CAMPOS M P, REIS M S. Data preprocessing for multiblock modelling-a systematization with new methods[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2020, 199: 103959. doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2020.103959 [8] YANG W Y, XIONG Y R, XU ZH ZH, et al. Piecewise preprocessing of near-infrared spectra for improving prediction ability of a PLS model[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2022, 126: 104359. [9] SCHULZE H G, FOIST R B, IVANOV A, et al. Fully automated high-performance signal-to-noise ratio enhancement based on an iterative three-point zero-order Savitzky–Golay filter[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2008, 62(10): 1160-1166. doi: 10.1366/000370208786049079 [10] DONOHO D L. De-noising by soft-thresholding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1995, 41(3): 613-627. doi: 10.1109/18.382009 [11] ZHAO R ZH, LIU X Y, LI C C, et al. Wavelet denoising via sparse representation[J]. Science in China Series F: Information Sciences, 2009, 52(8): 1371-1377. doi: 10.1007/s11432-009-0116-7 [12] 刘帅奇, 胡绍海, 肖扬. 基于小波-Contourlet变换与Cycle Spinning相结合的SAR图像去噪[J]. 信号处理,2011,27(6):837-842. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2011.06.006LIU SH Q, HU SH H, XIAO Y. SAR image de-noised based on wavelet-Contourlet transform with Cycle Spinning[J]. Signal Processing, 2011, 27(6): 837-842. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2011.06.006 [13] PHILLIPS G R, HARRIS J M. Polynomial filters for data sets with outlying or missing observations: application to charge-coupled-device-detected Raman spectra contaminated by cosmic rays[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1990, 62(21): 2351-2357. doi: 10.1021/ac00220a017 [14] LIU H C, SHAH S, Jiang W. On-line outlier detection and data cleaning[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2004, 28(9): 1635-1647. [15] GAN F, RUAN G H, MO J Y. Baseline correction by improved iterative polynomial fitting with automatic threshold[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2006, 82(1-2): 59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2005.08.009 [16] SCHULZE H G, FOIST R B, OKUDA K, et al. A small-window moving average-based fully automated baseline estimation method for Raman spectra[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2012, 66(7): 757-764. doi: 10.1366/11-06550 [17] ZHANG ZH M, CHEN SH, LIANG Y Z. Baseline correction using adaptive iteratively reweighted penalized least squares[J]. Analyst, 2010, 135(5): 1138-1146. doi: 10.1039/b922045c [18] ALI F, KABIR M, ARIF M. DBPPred-PDSD: Machine learning approach for prediction of DNA-binding proteins using discrete wavelet transform and optimized integrated features space[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2018, 182: 21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2018.08.013 -





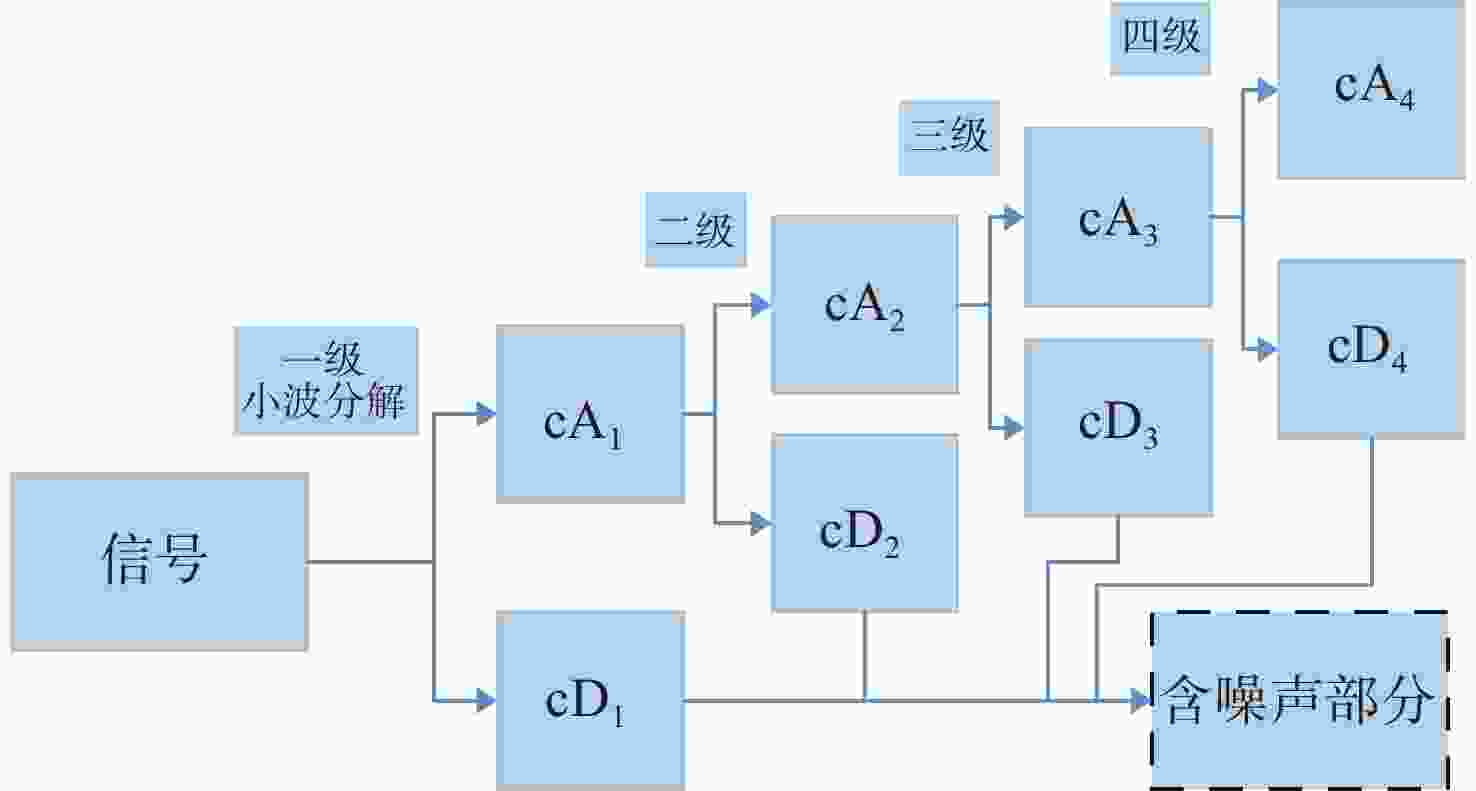
 下载:
下载: