Error correction of complex texture objects based on bidirectional fringe projection point cloud matching
-
摘要:
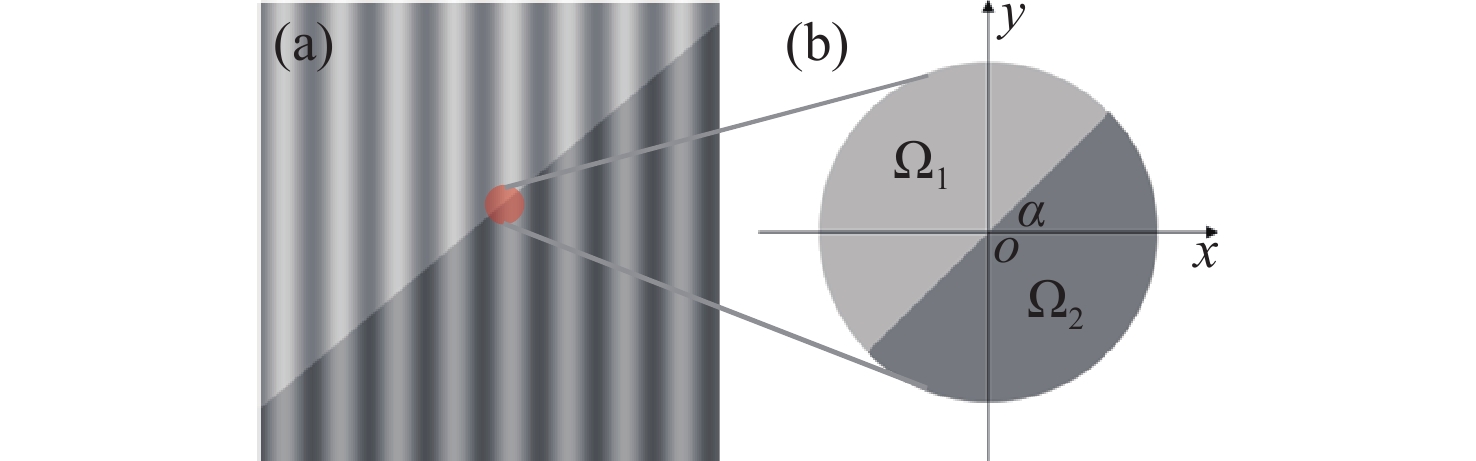
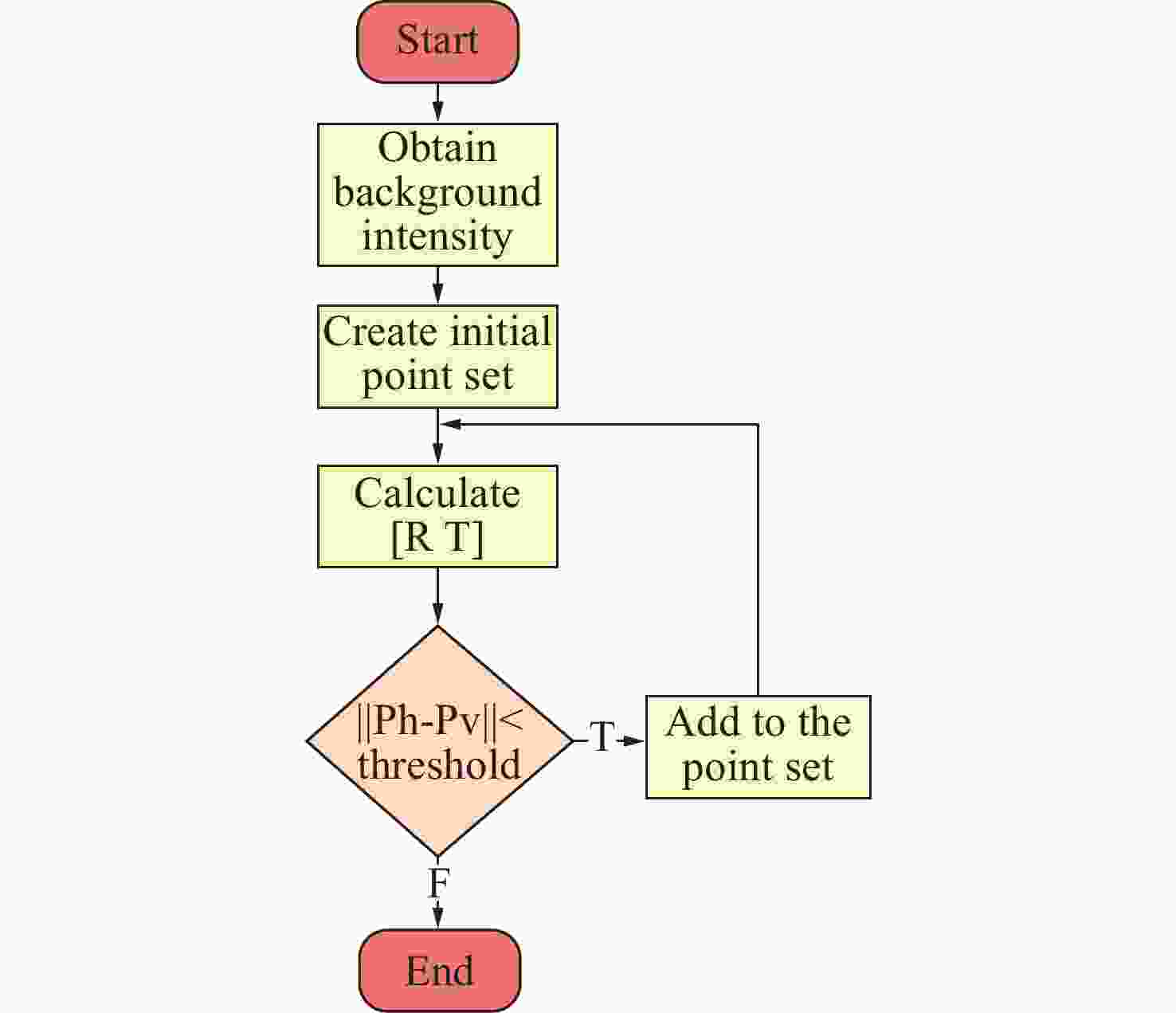
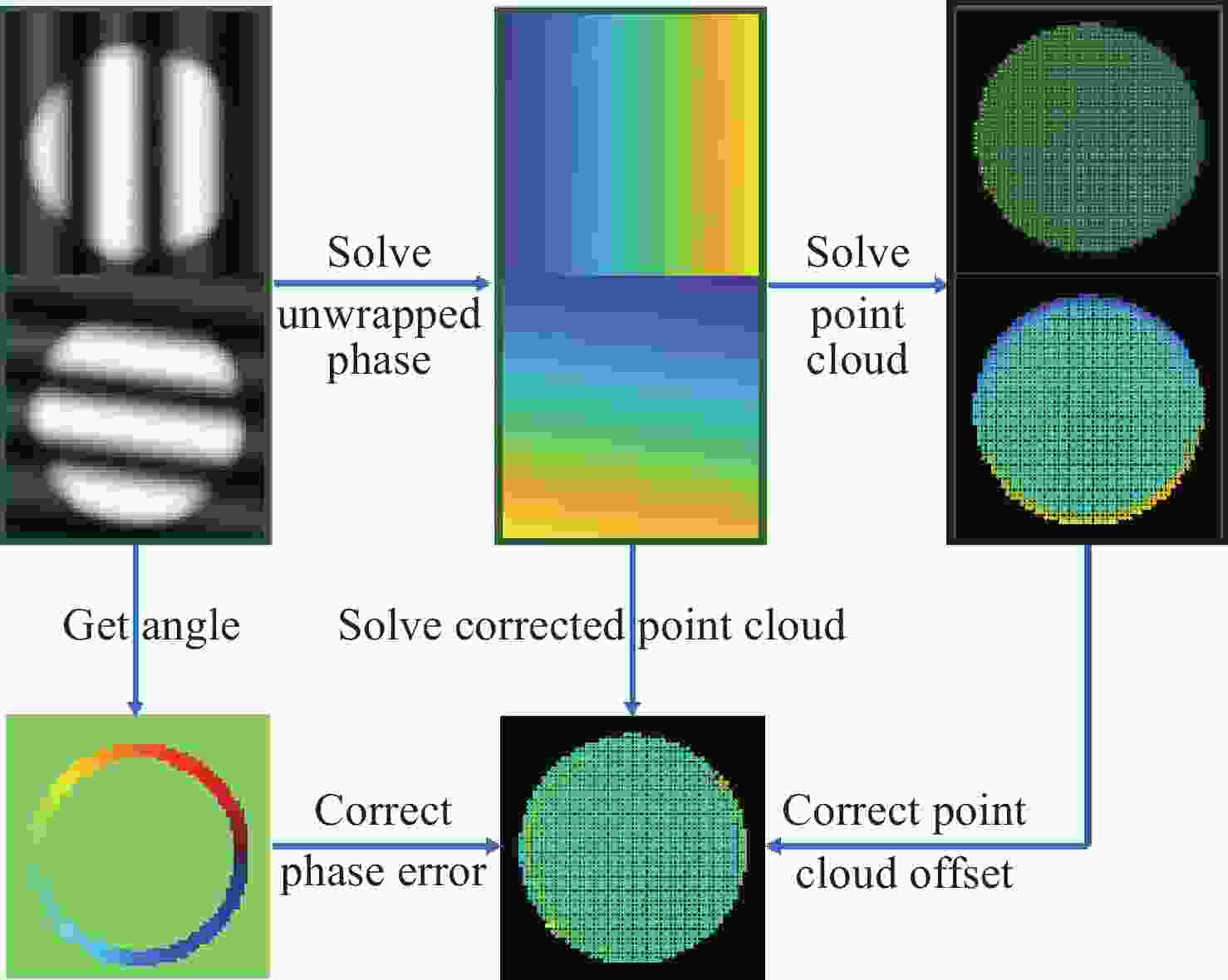
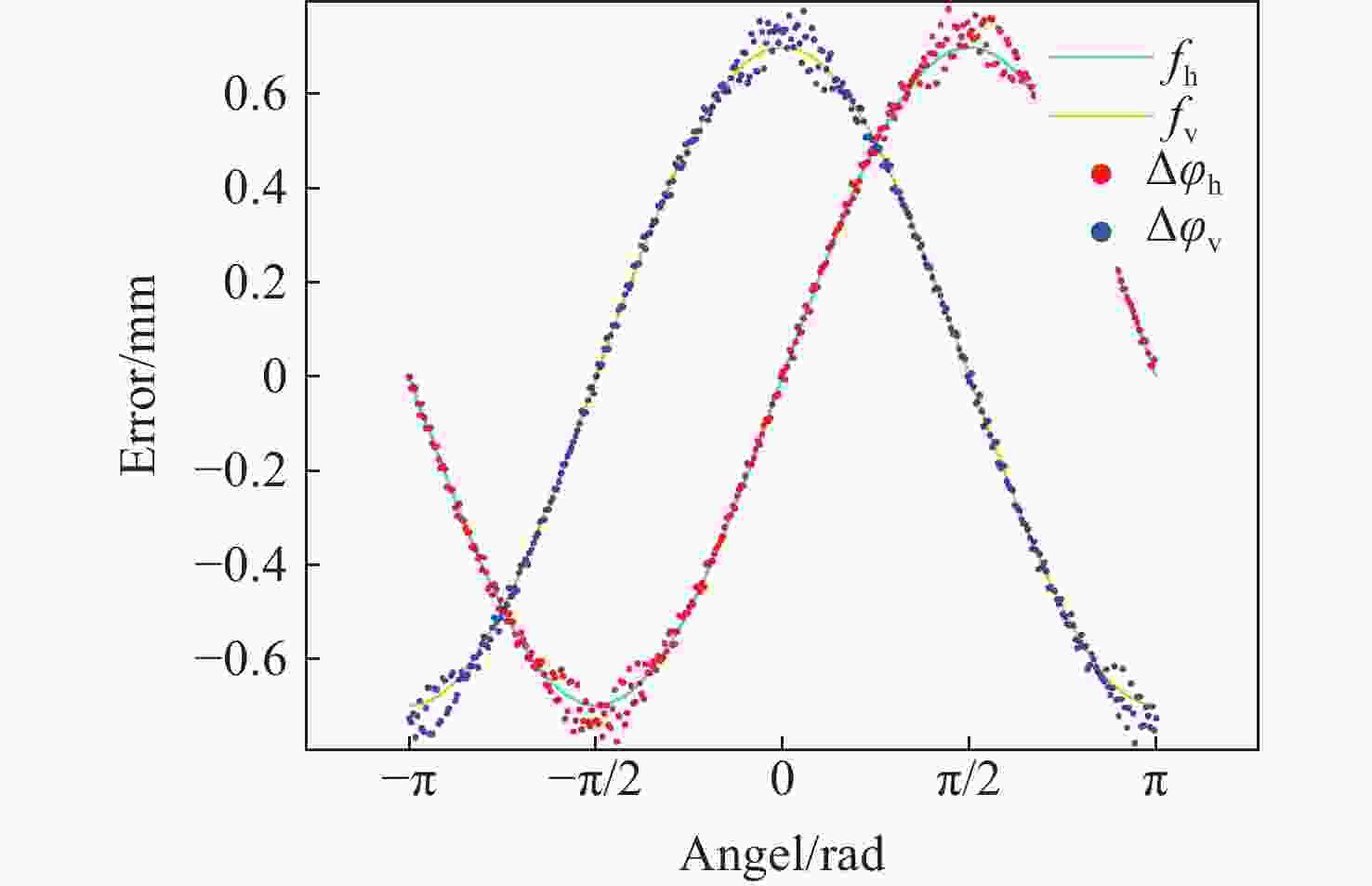
在结构光三维测量系统中,相机离焦现象不可避免。在离焦的影响下,物体表面的复杂纹理会引入显著的相位误差,影响测量精度。本文针对该问题,分析并构建了该相位误差的理论模型,指出了其与纹理变化方向的关系,并由此提出了一种基于双向条纹点云匹配的复杂纹理误差校正方法。理论上,通过投影横纵条纹图案获得的双向相位信息应解出完全一致的点云。基于这一原理,本文提出以最小化横纵点云对应点距离为目标,修正每个点对应的相位,最终得到校正后的点云。为了消除标定参数误差导致的点云整体偏移,本文通过点云匹配进行了预校正。对比实验结果表明:对实际物体,相较传统方法,本文方法的平均绝对误差(MAE)和均方根误差(RMSE)最高可分别降低33.6%和39.1%。本文方法能够以更高的精度重建具有复杂纹理的物体。
Abstract:In structured light 3D measurement systems, defocusing of the camera is inevitable. Because of camera defocus, the object’s complex surface texture introduces substantial phase errors, degrading measurement accuracy. To address this issue, this paper analyzes and formulates an error model for phase distortions arising from complex textures, and elucidates the relationship between the phase error and the direction of texture edge. Thus, a correction method for complex texture errors based on bidirectional fringe projection point cloud fitting is proposed. Theoretically, the bidirectional phase information obtained by projecting horizontal and vertical fringe patterns should yield perfect consistent point clouds. Thus, the method corrects the phase by minimizing the Euclidean distance between the corresponding points in the horizontal and vertical point clouds, ultimately obtain the corrected point cloud. To remove global shifts from calibration parameter errors, a pre-correction process is applied through point cloud matching. In comparative experiments, our method achieves up to 33.6% reduction in the mean absolute error (MAE) and 39.1% reduction in the root mean square error (RMSE) versus conventional approaches. These results demonstrate its superior accuracy for reconstructing objects with complex texture.
-
Key words:
- 3D measurement /
- structured light /
- phase shifting method /
- complex texture /
- phase map correction
-
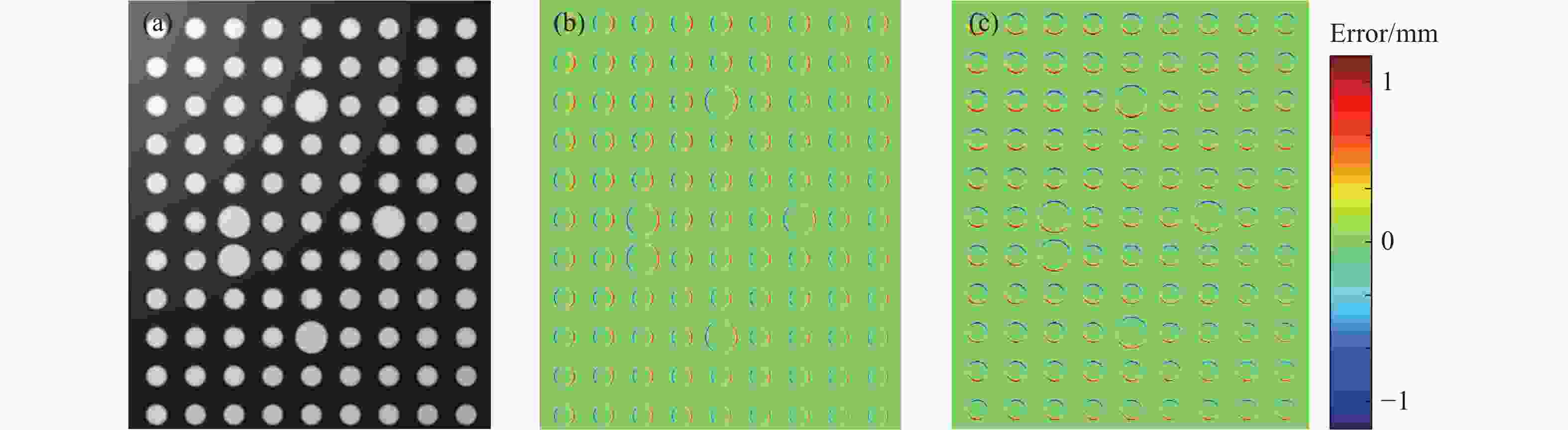
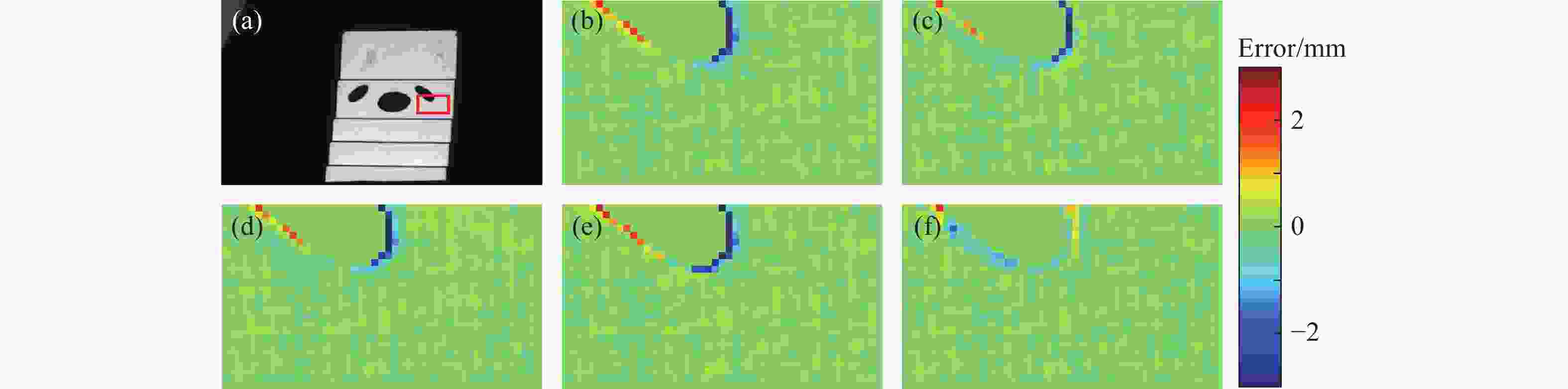
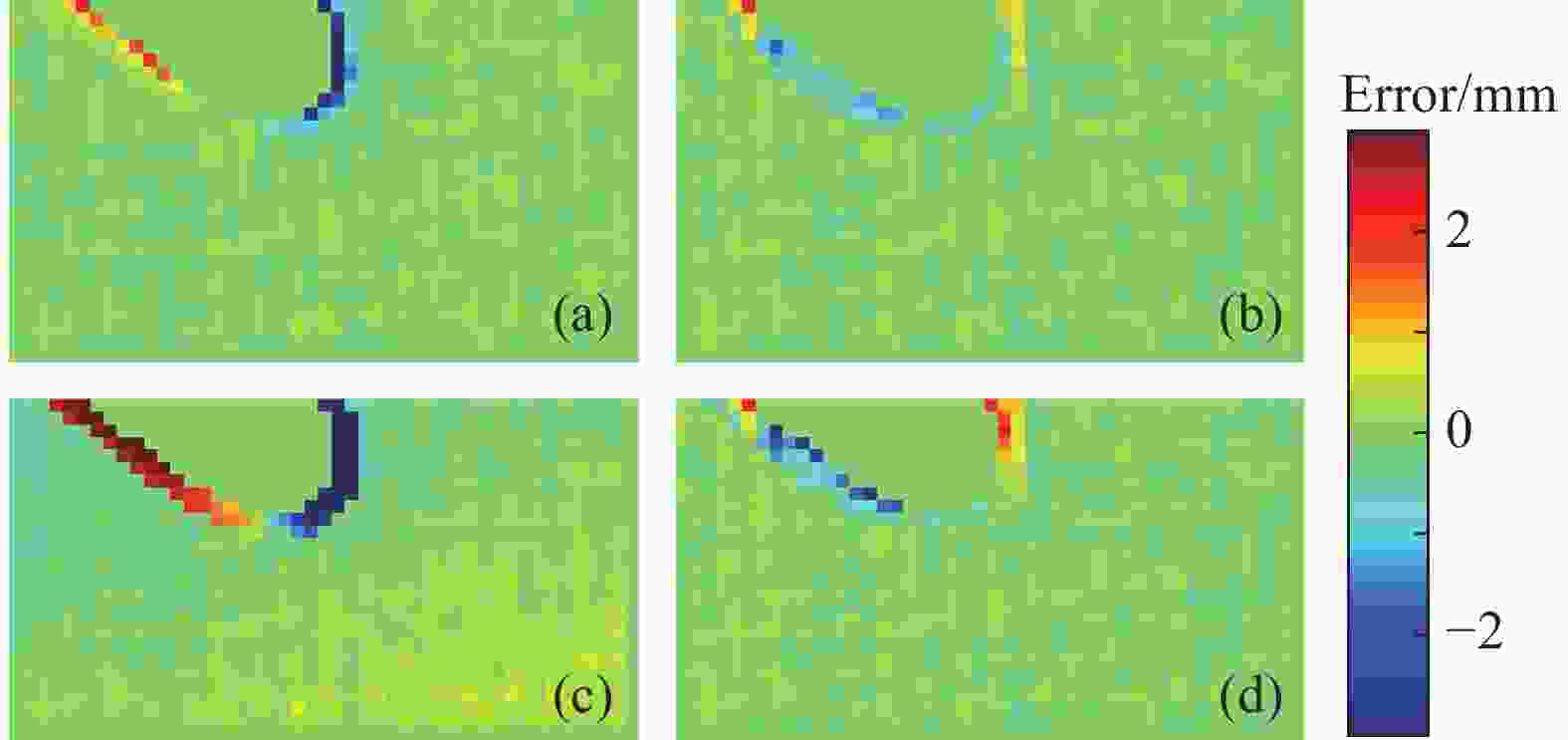
表 1 模拟标定板重建误差对比
Table 1. Comparison of reconstruction errors of the simulated calibration board
(mm) Methods HFP TEM PC KE IFT BPF MAE 0.1083 0.0859 0.0808 0.2623 0.1065 0.0612 RMSE 0.1470 0.1176 0.1106 1.1835 0.1441 0.0868 表 2 模拟物体模型重建误差对比
Table 2. Comparison of reconstruction errors of the simulated object model using different algorithms
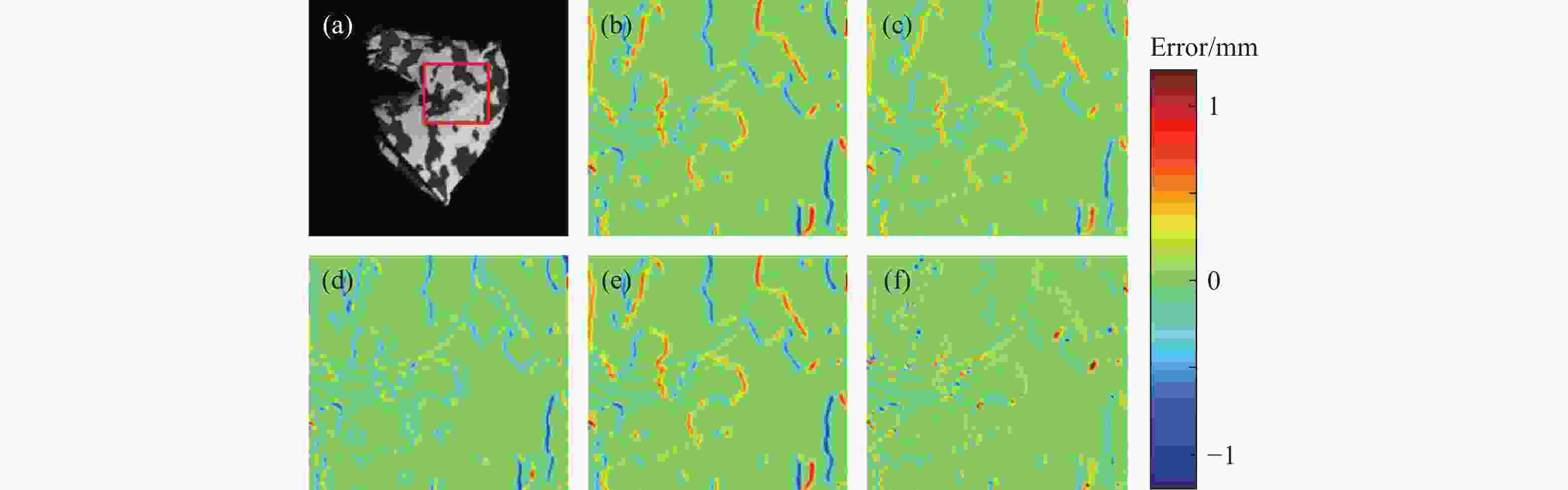
(mm) HFP TEM PC IFT BPF MAE 0.0763 0.0625 0.0683 0.0738 0.0512 RMSE 0.1679 0.1335 0.1382 0.1613 0.1147 表 3 梯形块重建误差对比
Table 3. Comparison of reconstruction errors of the trapezoidal block using different algorithms
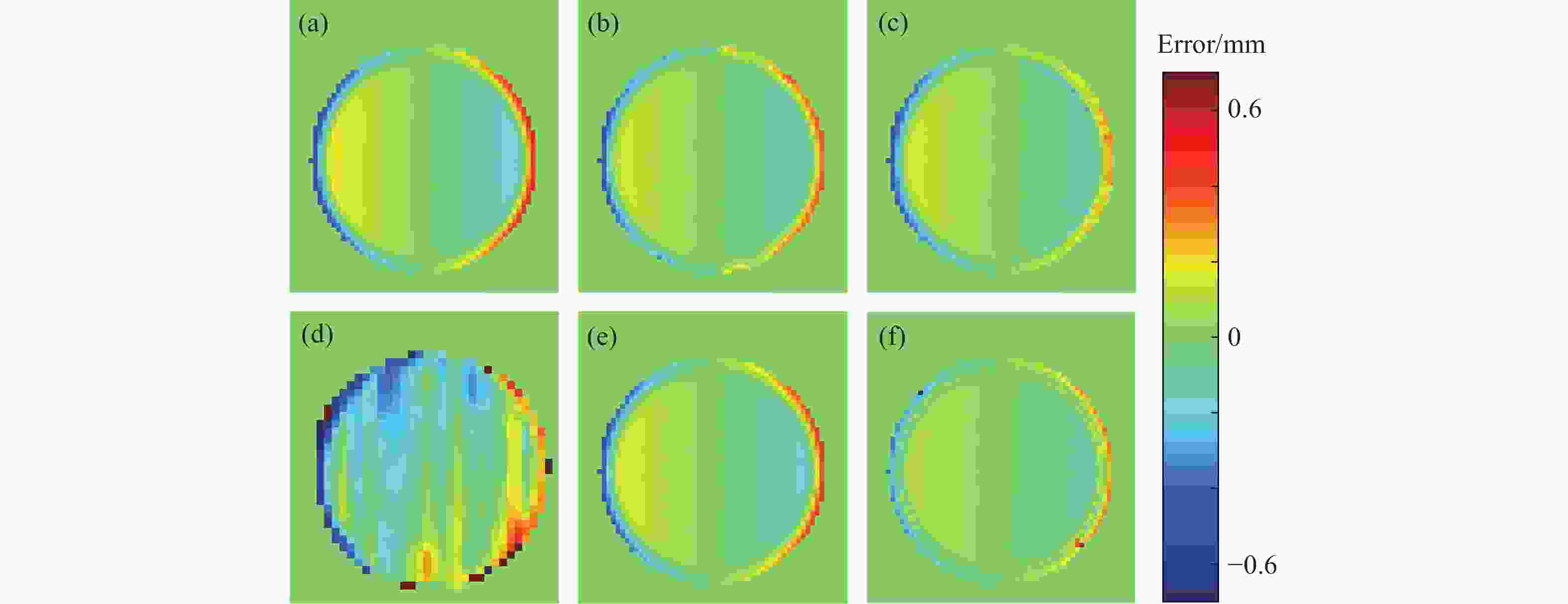
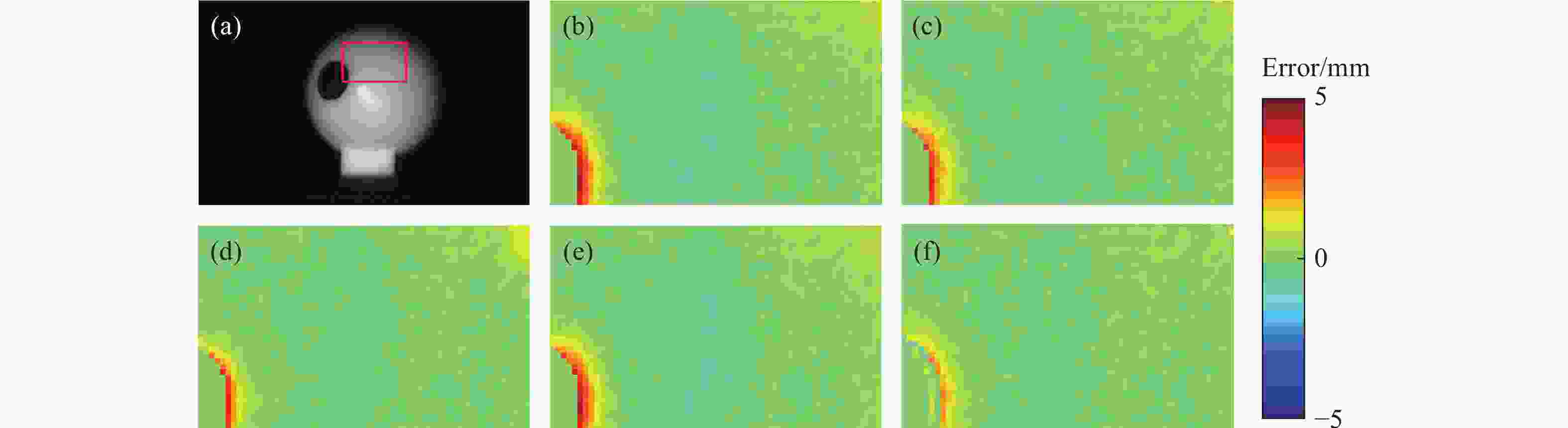
(mm) HFP TEM PC IFT BPF MAE 0.1631 0.1482 0.1540 0.1612 0.1377 RMSE 0.3660 0.2970 0.3511 0.3238 0.2199 表 4 标准球重建误差对比
Table 4. Comparison of reconstruction errors of the standard sphere using different algorithms
(mm) HFP TEM PC IFT BPF MAE 0.3271 0.2805 0.2382 0.3265 0.2173 RMSE 0.5414 0.4531 0.4176 0.5378 0.3296 Diameter 45.2 47.1 47.7 46.0 49.6 -
[1] XU J, ZHANG S. Status, challenges, and future perspectives of fringe projection profilometry[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 135: 106193. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106193 [2] ZUO CH, FENG SH J, HUANG L, et al. Phase shifting algorithms for fringe projection profilometry: a review[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2018, 109: 23-59. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2018.04.019 [3] 余佳杰, 周建平, 薛瑞雷, 等. 基于结构光视觉和光照模型的焊缝表面质量检测[J]. 中国激光,2022,49(16):1602019. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1602019YU J J, ZHOU J P, XUE R X, et al. Weld Surface quality detection based on structured light and illumination model[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(16): 1602019. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1602019 [4] 李勇, 张广汇, 马利红, 等. 条纹投影动态三维表面成像技术综述[J]. 红外与激光工程,2020,49(3):0303005. doi: 10.3788/IRLA202049.0303005LI Y, ZHANG G H, MA L H, et al. Review of dynamic three-dimensional surface imaging based on fringe projection[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(3): 0303005. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA202049.0303005 [5] LIU ZH CH, LIU X L, CAO ZH Q, et al. High precision calibration for three-dimensional vision-guided robot system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(1): 624-634. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3152026 [6] WANG Q, KIM M K. Applications of 3D point cloud data in the construction industry: a fifteen-year review from 2004 to 2018[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2019, 39: 306-319. doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2019.02.007 [7] 李茂月, 蔡东辰, 赵伟翔, 等. 航空叶片形貌高精度结构光扫描视点规划[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(4):802-815. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0221LI M Y, CAI D CH, ZHAO W X, et al. High precision structural light scanning viewpoint planning for aircraft blade morphology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(4): 802-815. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0221 [8] 沈春梅, 刘凡, 朱佳乐. 基于结构光和CT的背部点云配准算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2023,60(22):2210007.SHEN CH M, LIU F, ZHU J L. Back point cloud registration algorithm based on structured light and CT[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(22): 2210007. (in Chinese). [9] 汪运, 郭建英, 梁浚哲, 等. 面向高反光表面的结构光面形测量方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2025,18(1):42-52. doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0087WANG Y, GUO J Y, LIANG J ZH, et al. Structured light surface shape measurement method for highly reflective surfaces[J]. Chinese Optics, 2025, 18(1): 42-52. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0087 [10] 刘泽隆, 李茂月, 卢新元, 等. 高动态范围条纹结构光在机检测技术及应用进展[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(1):1-18. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0068LIU Z L, LI M Y, LU X Y, et al. On-machine detection technology and application progress of high dynamic range fringe structured light[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(1): 1-18. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0068 [11] 曹智睿. 基于相移条纹投影的动态3D测量误差补偿技术(英文)[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(1):184-192. doi: 10.37188/CO.EN.2022-0004CAO ZH R. Dynamic 3D measurement error compensation technology based on phase-shifting and fringe projection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(1): 184-192. doi: 10.37188/CO.EN.2022-0004 [12] BLANCHARD C, ZHANG S. Removal of phase artifacts from high-contrast texture for 3D fringe projection system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2022, 12098: 1209805. [13] CHEN ZH D, LI X R, WANG H R, et al. Multi-dimensional information sensing of complex surfaces based on fringe projection profilometry[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(25): 41374-41390. doi: 10.1364/OE.509447 [14] RAO L, DA F P. Local blur analysis and phase error correction method for fringe projection profilometry systems[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(15): 4267-4276. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.004267 [15] WU Y X, CAI X J, ZHU J J, et al. Analysis and reduction of the phase error caused by the non-impulse system psf in fringe projection profilometry[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 127: 105987. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2019.105987 [16] HU CH P, LIU SH T, WU D, et al. Phase error model and compensation method for reflectivity and distance discontinuities in fringe projection profilometry[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(3): 4405-4422. doi: 10.1364/OE.482158 [17] YAO P CH, CHEN Y CH, GAI SH Y, et al. Accurate 3D measurement of complex texture objects by height compensation using a dual-projector structure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2024, 33: 3021-3030. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2024.3389609 [18] JUAREZ-SALAZAR R, RODRIGUEZ-REVELES G A, ESQUIVEL-HERNANDEZ S, et al. Three-dimensional spatial point computation in fringe projection profilometry[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2023, 164: 107482. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2023.107482 [19] GUO B J, XU Y P, ZHANG CH L, et al. An optimized error compensation method for phase measurement profilometry[J]. Photonics, 2023, 10(9): 1036. doi: 10.3390/photonics10091036 [20] EGGERT D W, LORUSSO A, FISHER R B. Estimating 3-D rigid body transformations: a comparison of four major algorithms[J]. Machine Vision and Applications, 1997, 9(5-6): 272-290. doi: 10.1007/s001380050048 [21] WANG B, ZHAO ZH SH, CHEN Y, et al. A novel robust point cloud fitting algorithm based on nonlinear gauss-helmert model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 1002012. [22] WU Y, MA W P, GONG M G, et al. A novel point-matching algorithm based on fast sample consensus for image registration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(1): 43-47. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2325970 [23] 季宇航, 宋爱国. 基于点线特征的通风管道建模与管内定位方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2024,45(2):272-279.JI Y H, SONG A G. Modeling and localization method for ventilation ducts based on point and line features[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2024, 45(2): 272-279. (in Chinese). [24] ZHANG ZH Y. A flexible new technique for camera calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000, 22(11): 1330-1334. doi: 10.1109/34.888718 [25] XU L, JIA J Y. Two-phase kernel estimation for robust motion deblurring[C]. Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2010: 157-170. [26] ZHUO SH J, SIM T. Defocus map estimation from a single image[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2011, 44(9): 1852-1858. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2011.03.009 -





 下载:
下载: