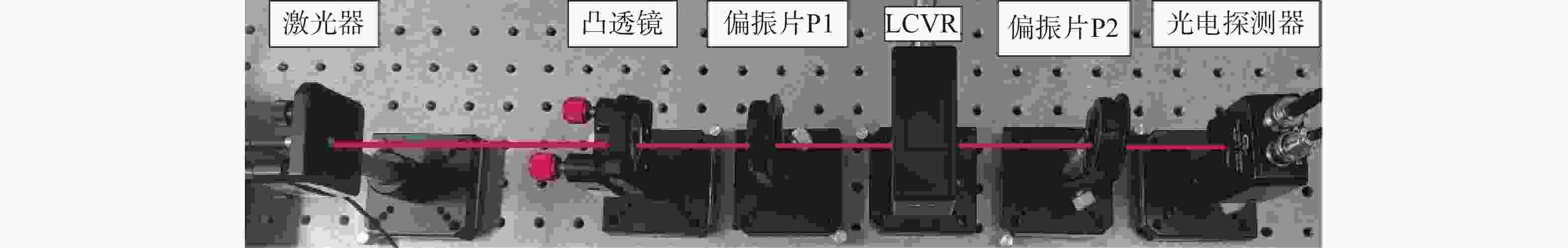
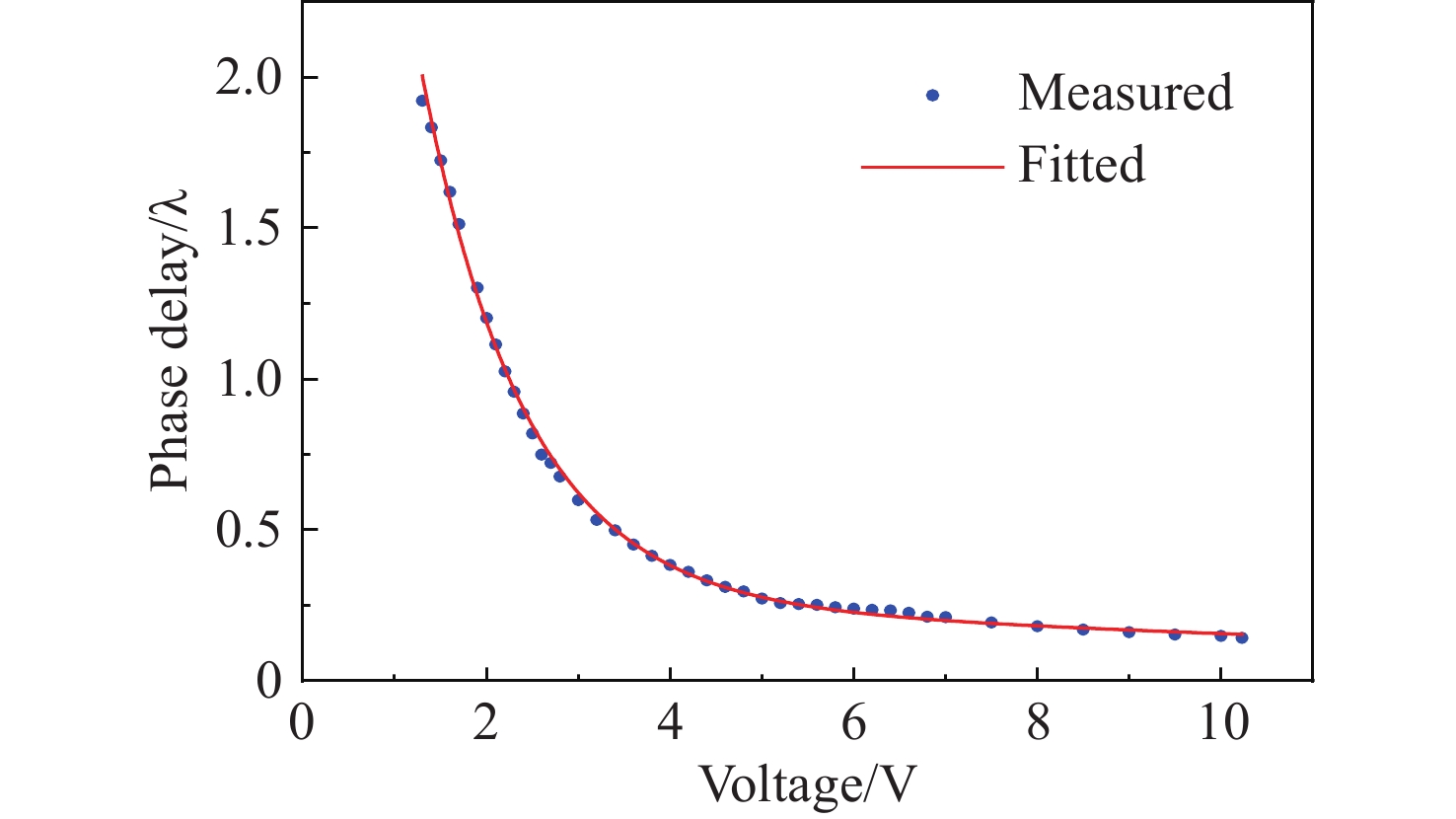
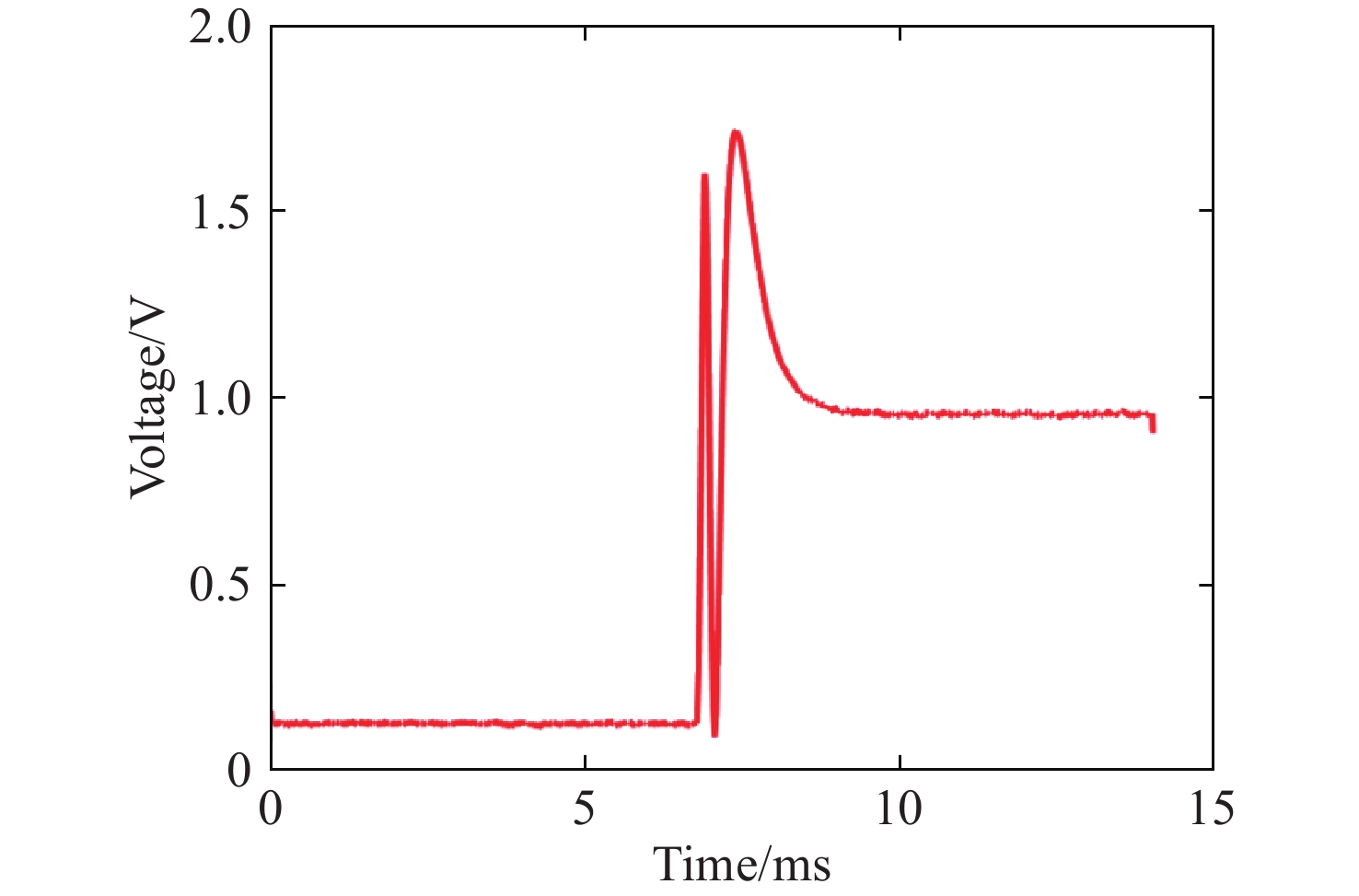
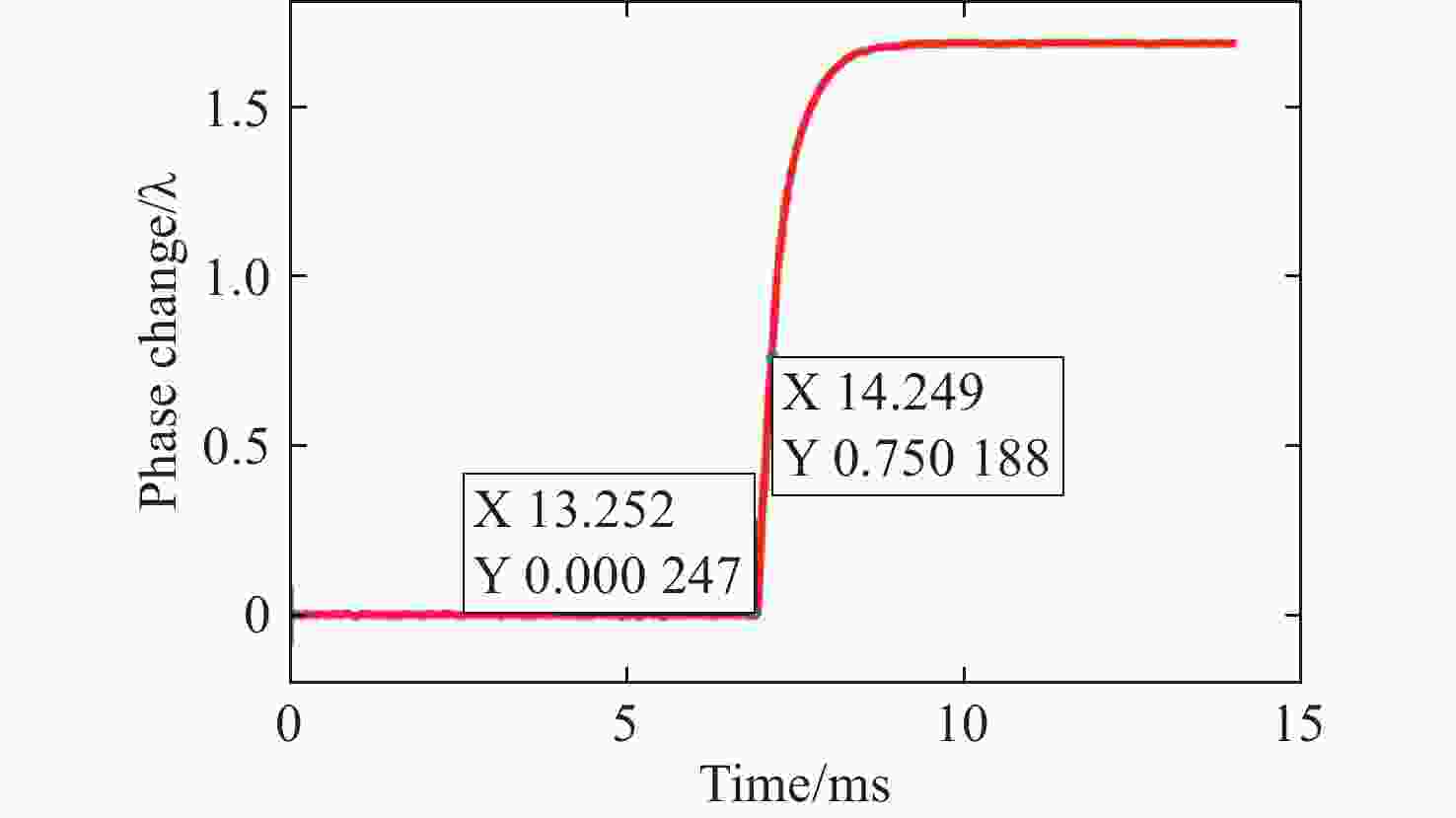
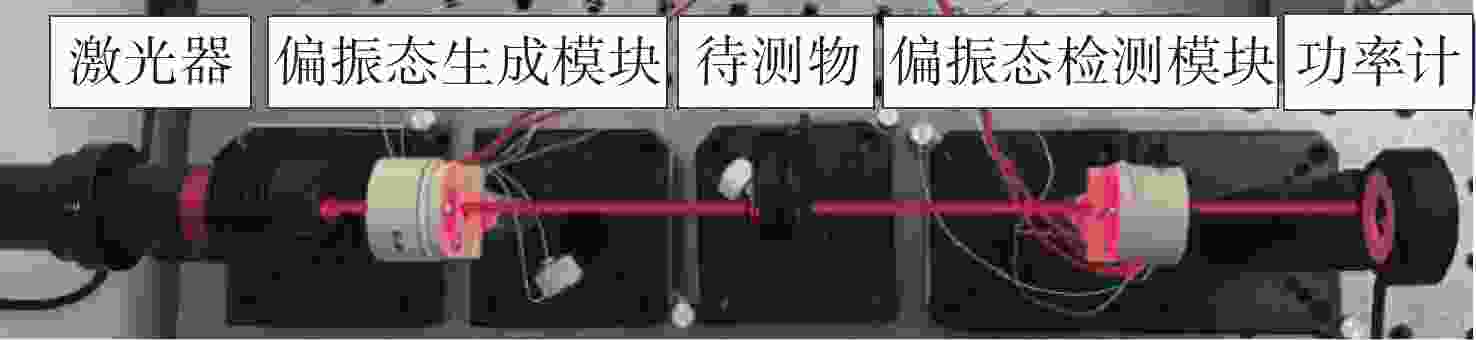
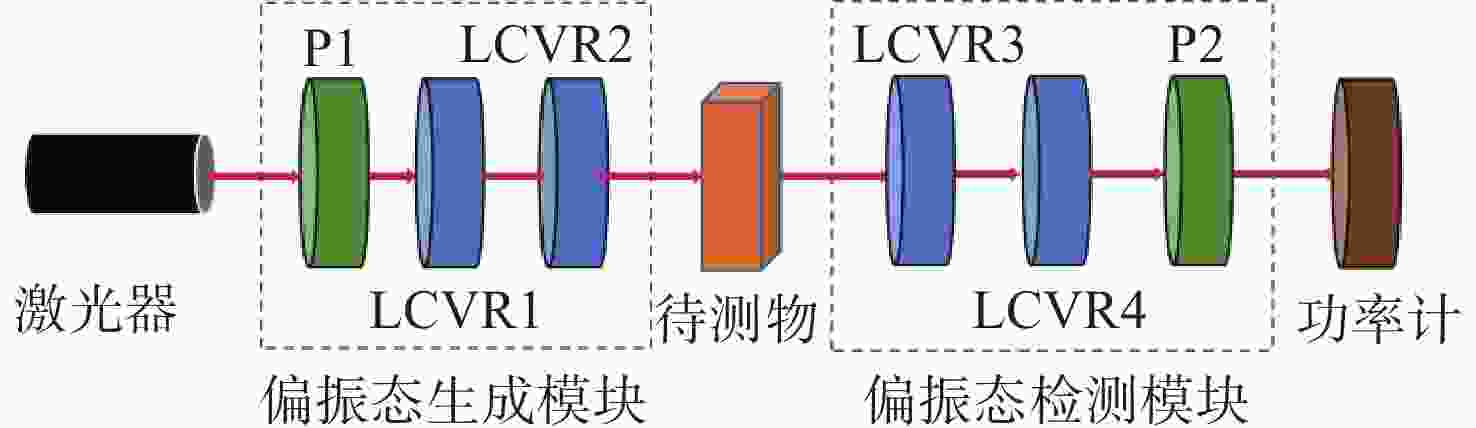
Research on high-speed measurement of Mueller matrix based on overdriving technique
-
摘要:
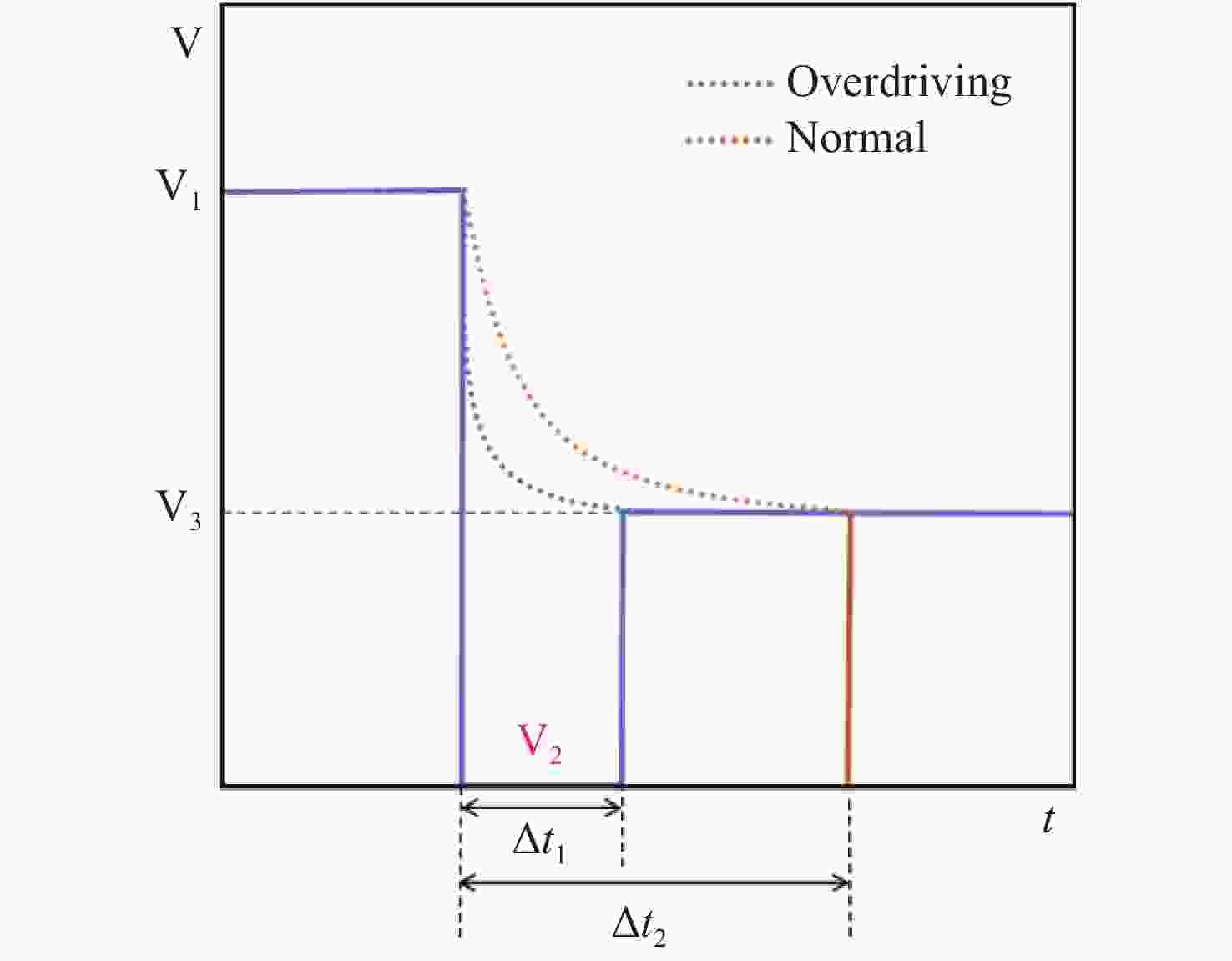
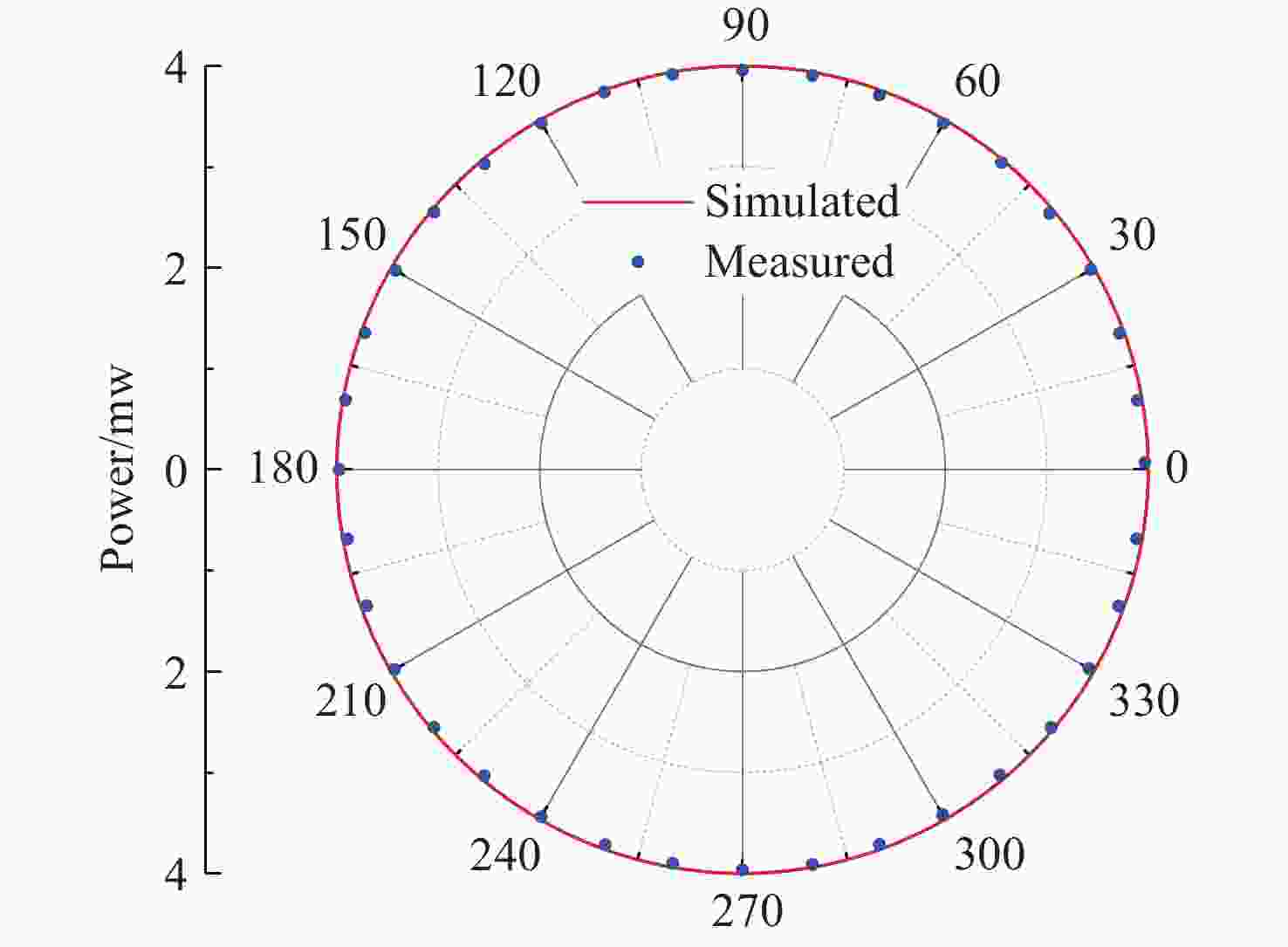
为实现穆勒矩阵的高速测量,本文提出一种基于过压驱动的穆勒矩阵高速测量方法。首先,建立基于液晶的穆勒矩阵仿真模型,仿真分析了待测物穆勒矩阵测量的可行性。其次,给出液晶相位延迟器的过压驱动方法,并利用过压驱动技术缩短了偏振态的切换时间。最后,实验测量了空气、偏振片及1/4波片的穆勒矩阵。实验结果表明:6个偏振态的生成频率从71 Hz提升到417 Hz,穆勒矩阵的测量频率从10 Hz提升到60 Hz,提升约6倍;同时,穆勒矩阵测量均方误差(MSE)优于
0.0004 ,消光比优于750∶1,椭偏度低于1.06%。因此,过压驱动方法能够实现穆勒矩阵的高速测量,进一步推动其在动态偏振分析、光学元件在线质检、生物医学成像等实时检测领域的应用。Abstract:This paper proposes a high-speed Mueller matrix measurement method based on an overdriving technique exerted on a liquid crystal variable retarder. First, a liquid crystal-based simulation model of the Mueller matrix measurement system is established, which helps to confirm the feasibility of the system. Next, an overdriving scheme for the liquid crystal variable retarder is introduced to shorten the polarization-state switching time. Finally, the Mueller matrices of air, a polarizer, and a quarter-wave plate are measured experimentally. The results show that the generation frequency of six polarization states increases from 71 Hz to 417 Hz, and the Mueller matrix measurement frequency increases from 10 Hz to 60 Hz, representing approximately a sixfold improvement. Furthermore, the mean squared error (MSE) of the measurements is below 0.0004. The extinction ratio exceeds 750:1. And the ellipsometric error is below 1.06%. These results demonstrate that the overdriving method enables high-speed Mueller matrix measurements, thereby facilitating applications in real-time inspection fields such as dynamic polarization analysis, online quality inspection of optical components, and biomedical imaging.
-
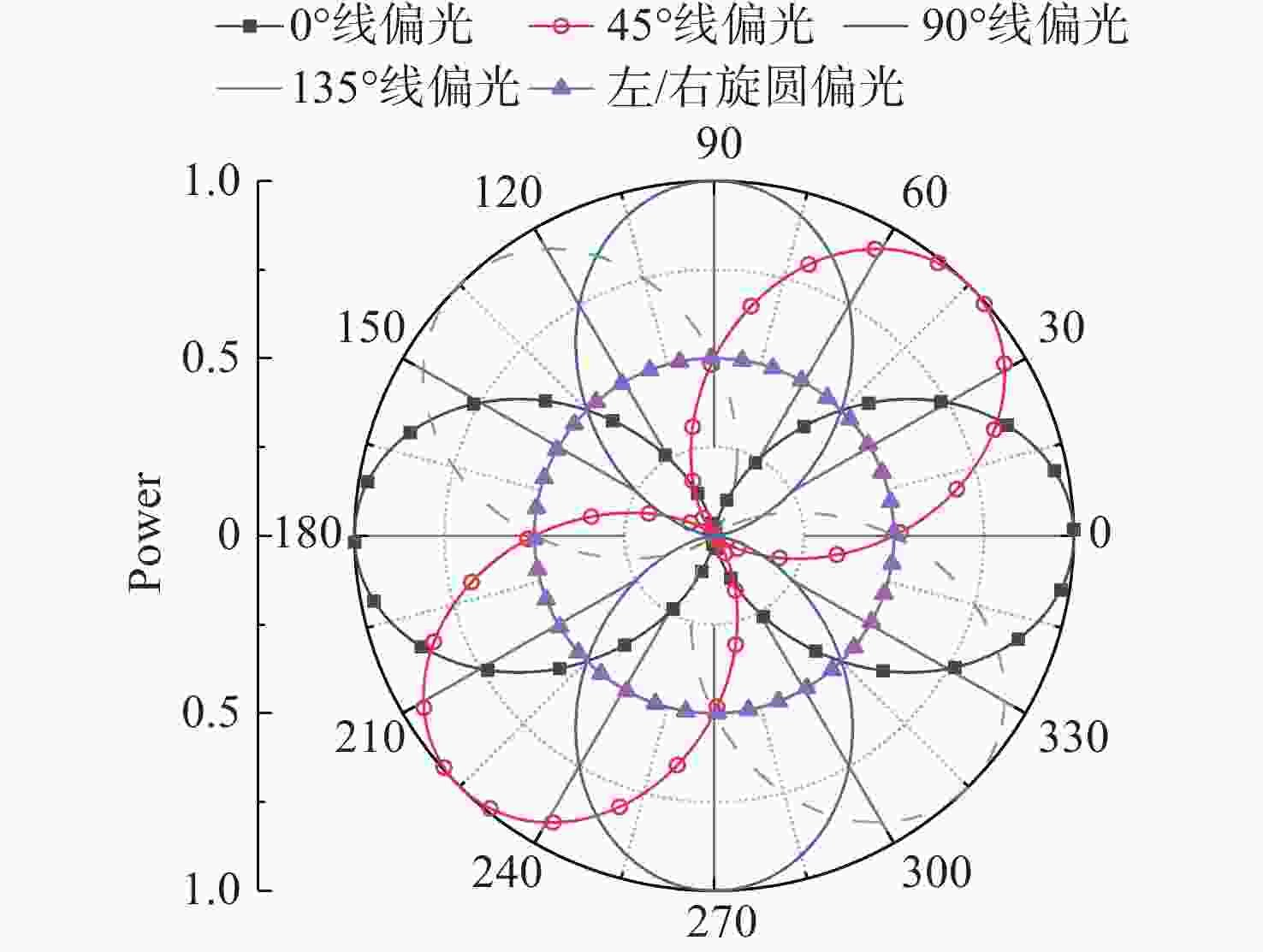
表 1 偏振态与液晶相位延迟量对应关系
Table 1. Relation between polarization state and liquid crystal phase delay
δ1/λ δ2/λ Stokes矢量 偏振态 0.5 1 (1 1 0 0) 0°线偏振(H) 0.25 0.25 (1 0 1 0) 45°线偏振(P) 1 1 (1 −1 0 0) 90°线偏振(V) 0.25 0.75 (1 0 −1 0) 135°线偏振(M) 0.75 0.5 (1 0 0 1) 左旋圆偏振(L) 0.25 0.5 (1 0 0 −1) 右旋圆偏振(R) 表 2 穆勒矩阵仿真测量的光强
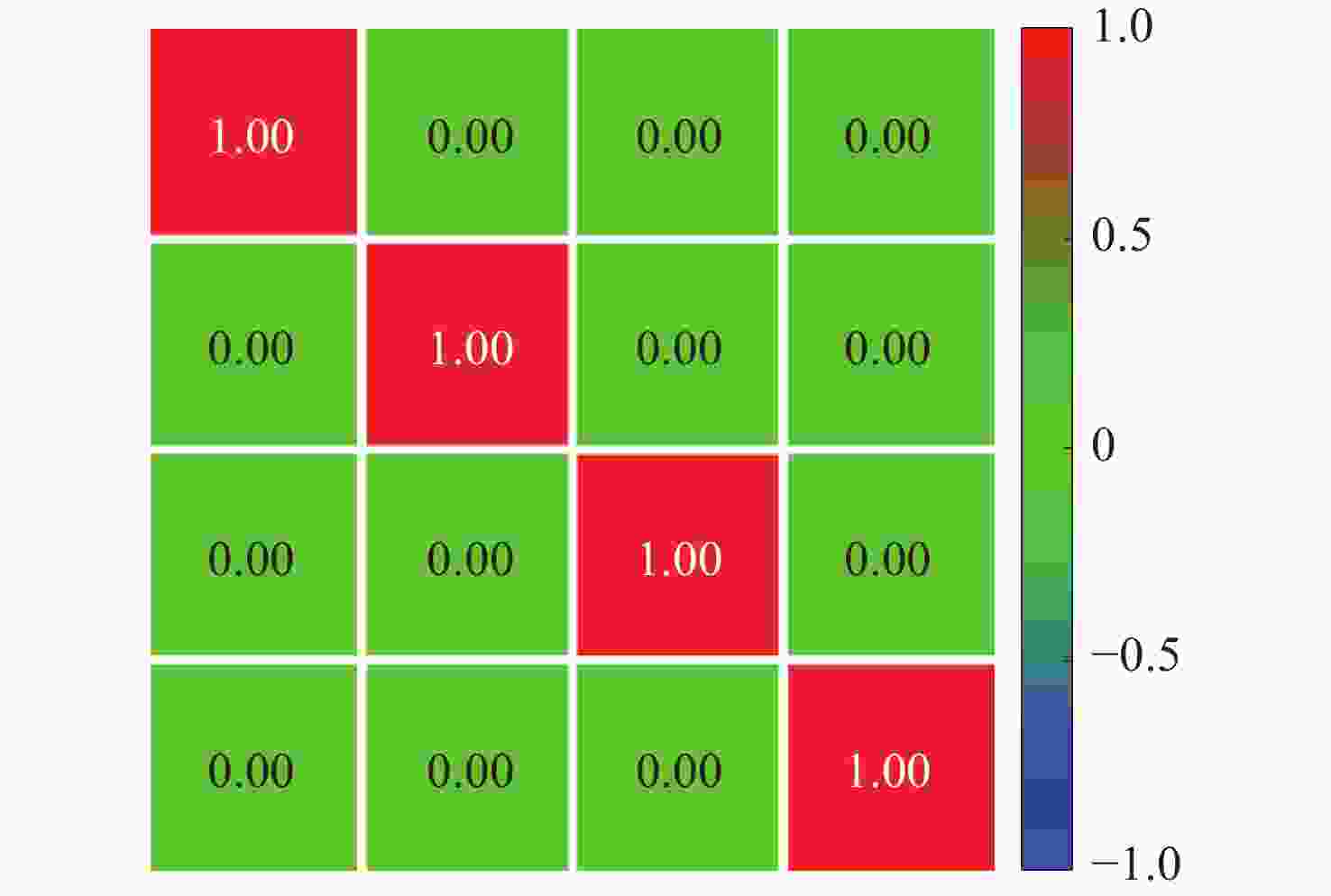
Table 2. Simulated light intensity for Mueller matrix test
H P V M L R H 1 0.5 0 1 0.5 0.5 P 0.5 1 0.5 0 0.5 0.5 V 0 0.5 1 0.5 0.5 0.5 M 0.5 0 0.5 1 0.5 0.5 L 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 1 0 R 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0 1 表 3 偏振态切换时间
Table 3. Switch time of polarization state
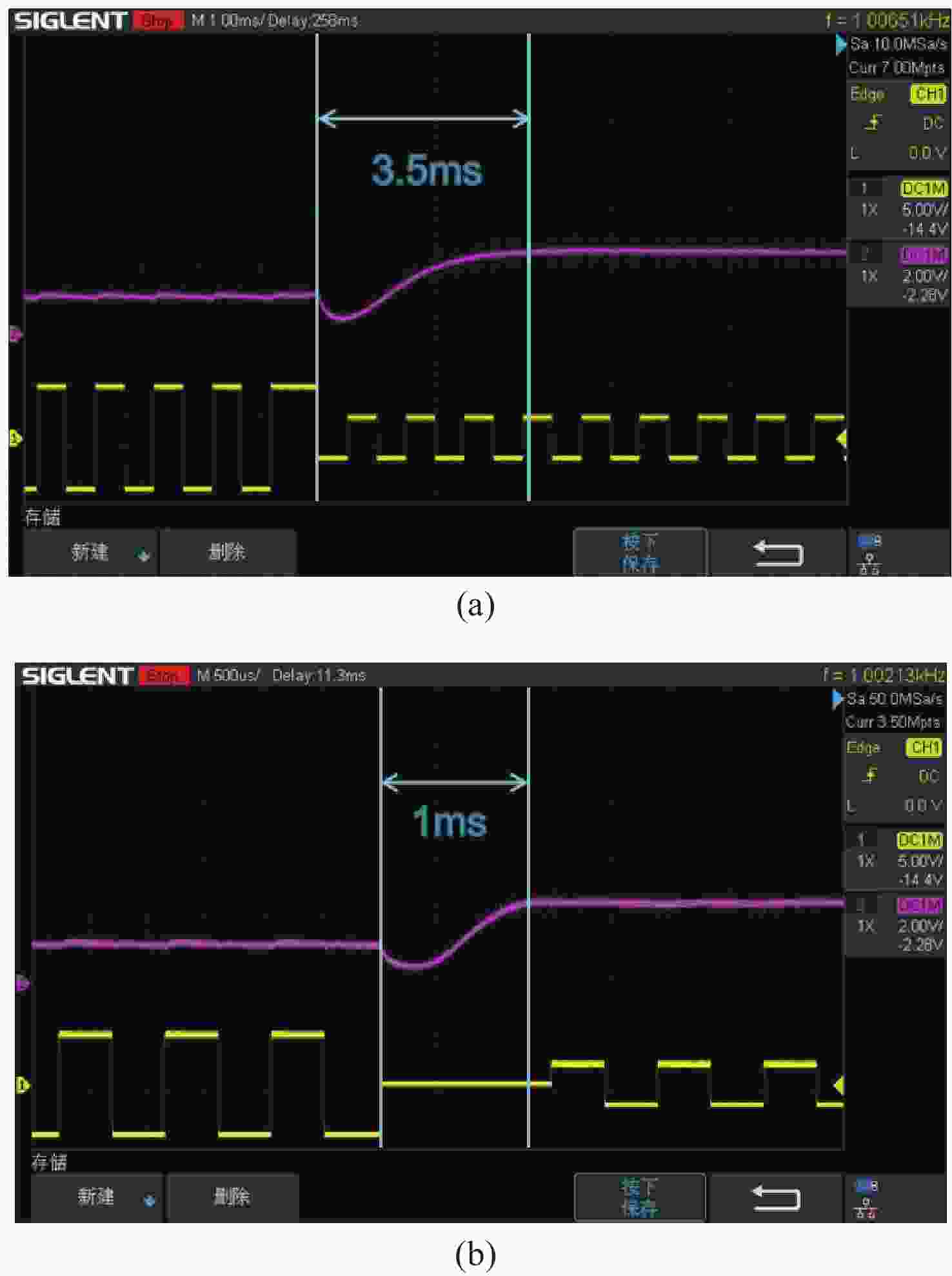
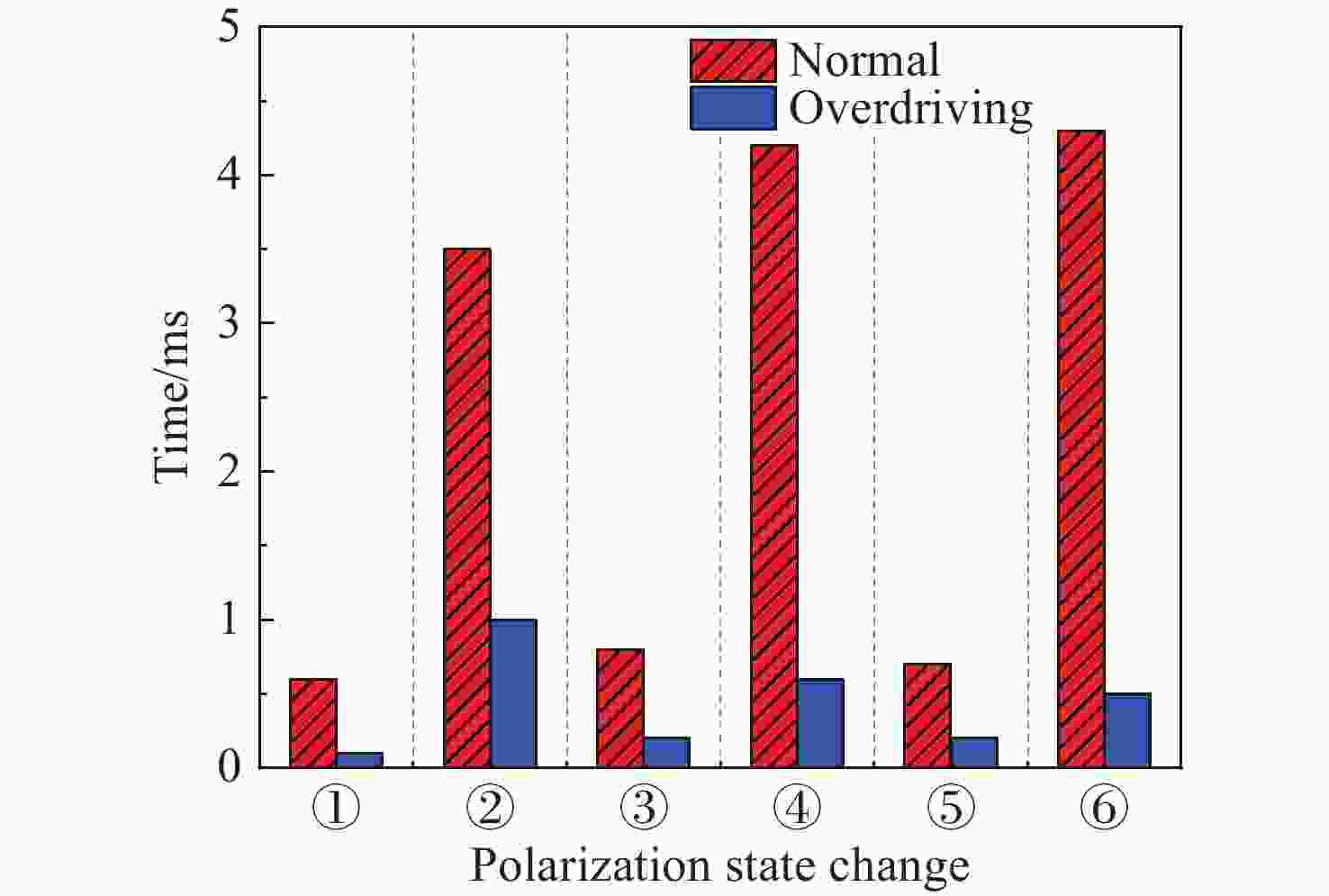
偏振态 LCVR-1/λ 时间/ms LCVR-2/λ 时间/ms ①H→P 0.5→0.25 0.6 1→0.25 0.6 ②P→V 0.25→1 3.5 0.25→1 3.5 ③V→M 1→0.25 0.6 1→0.75 0.8 ④M→L 0.25→0.75 4.2 0.75→0.5 0.7 ⑤L→R 0.75→0.25 0.7 0.5→0.5 0 ⑥R→H 0.25→0.5 3.8 0.5→1 4.3 表 4 偏振态产生实验结果
Table 4. Experimental results for Polarization generation
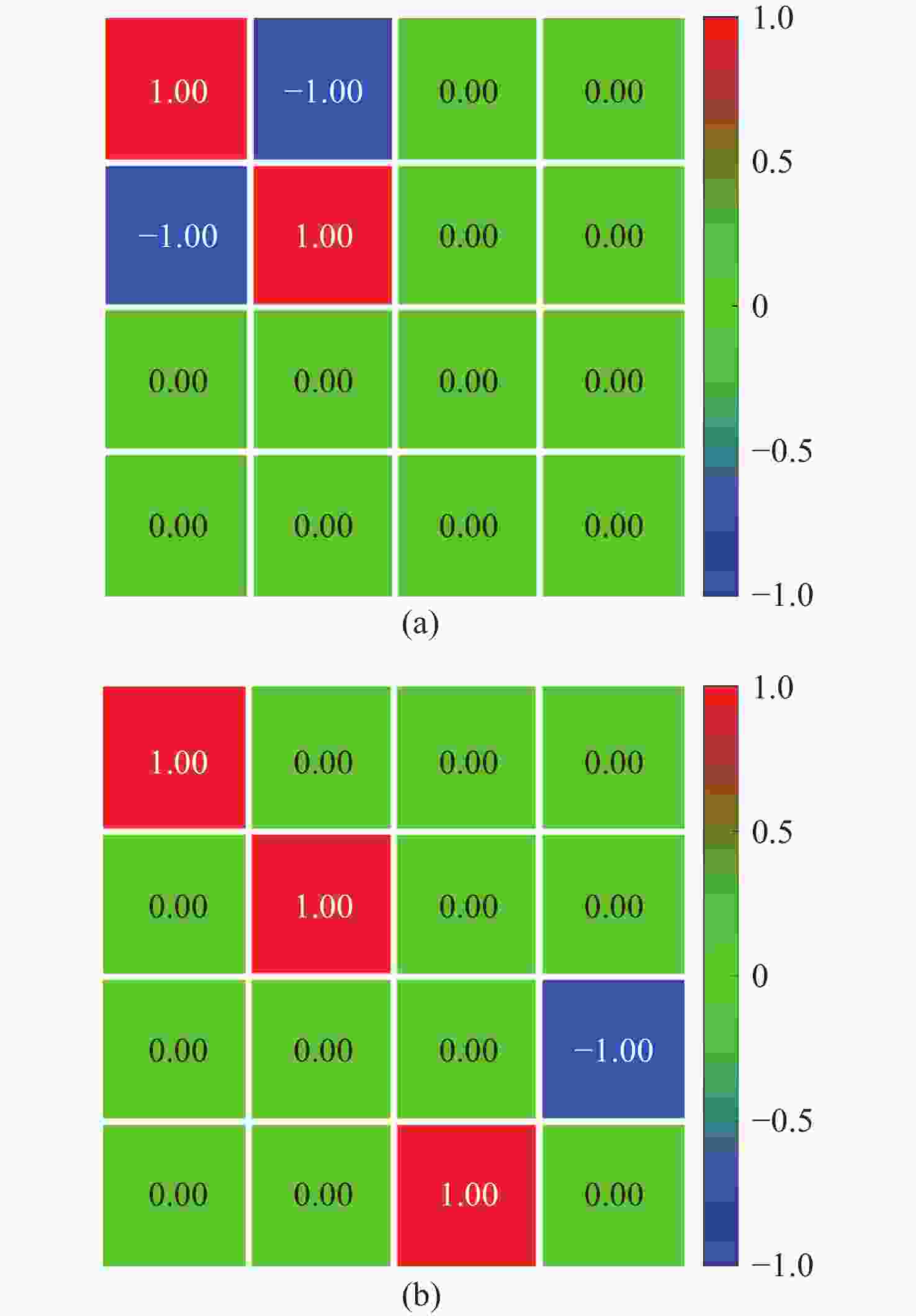
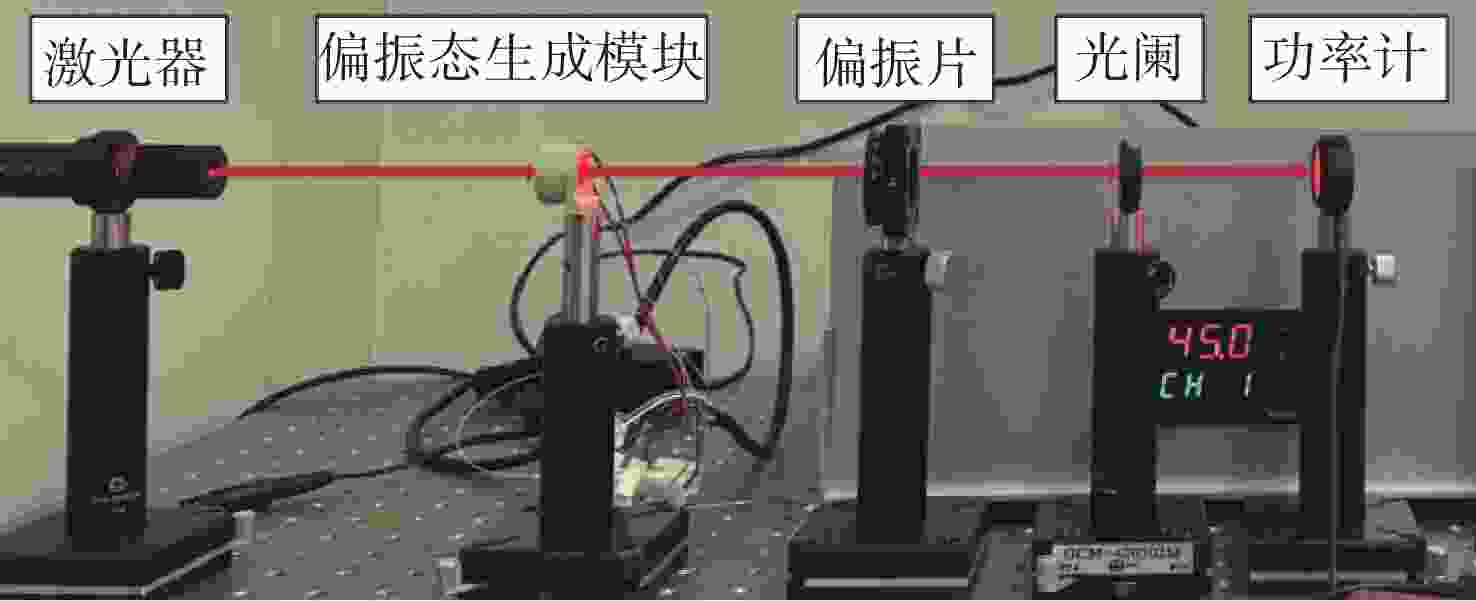
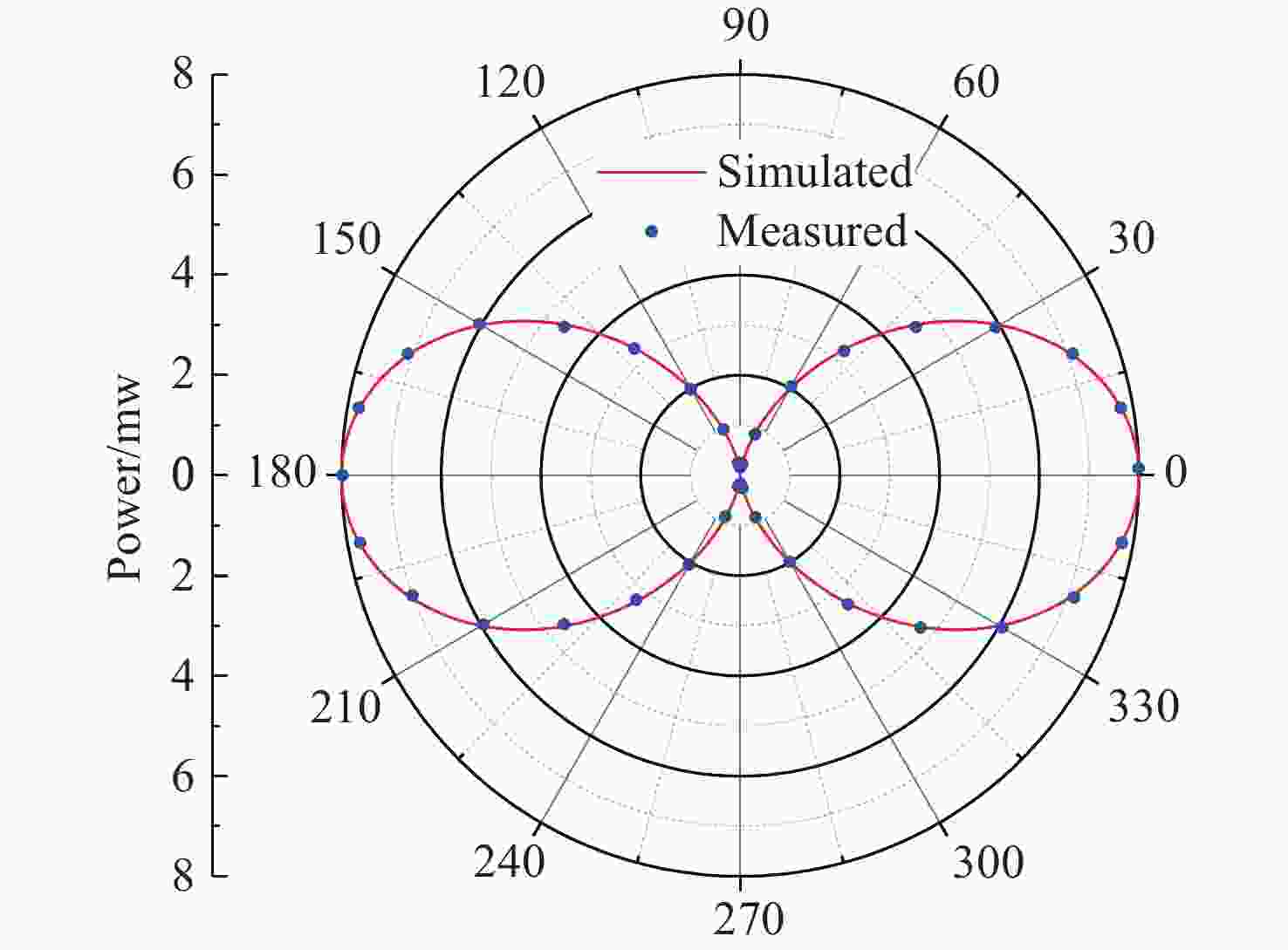
偏振态 最小值(μw) 最大值(mw) 消光比 椭偏度 H 10.1 7.987 790∶1 P 10.5 7.975 759∶1 V 10.4 7.962 765∶1 M 10.2 7.976 781∶1 L 3.941 3.982 1.03% R 3.936 3.978 1.06% 表 5 穆勒矩阵的测量光强
Table 5. Measured intensity for Mueller matrix
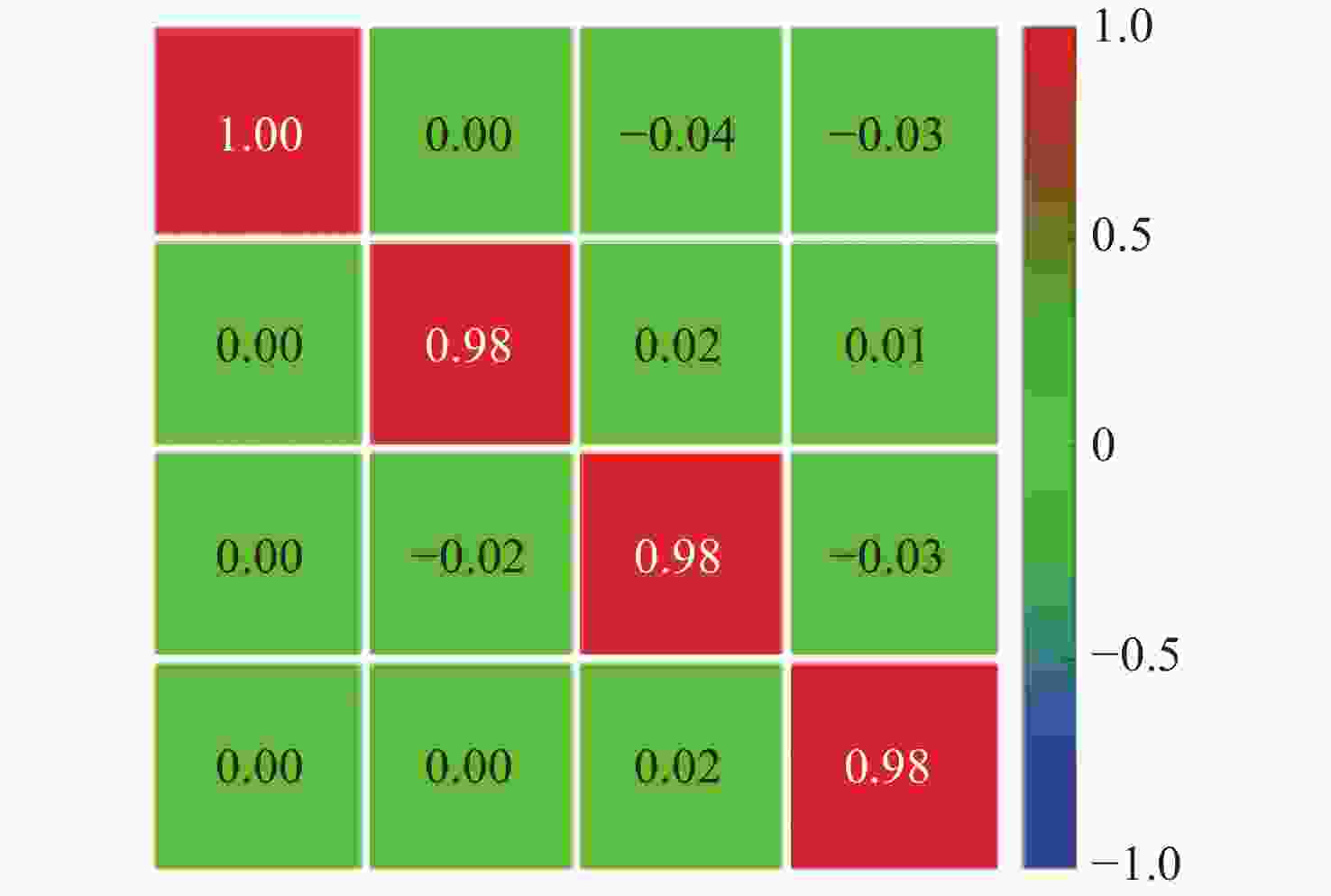
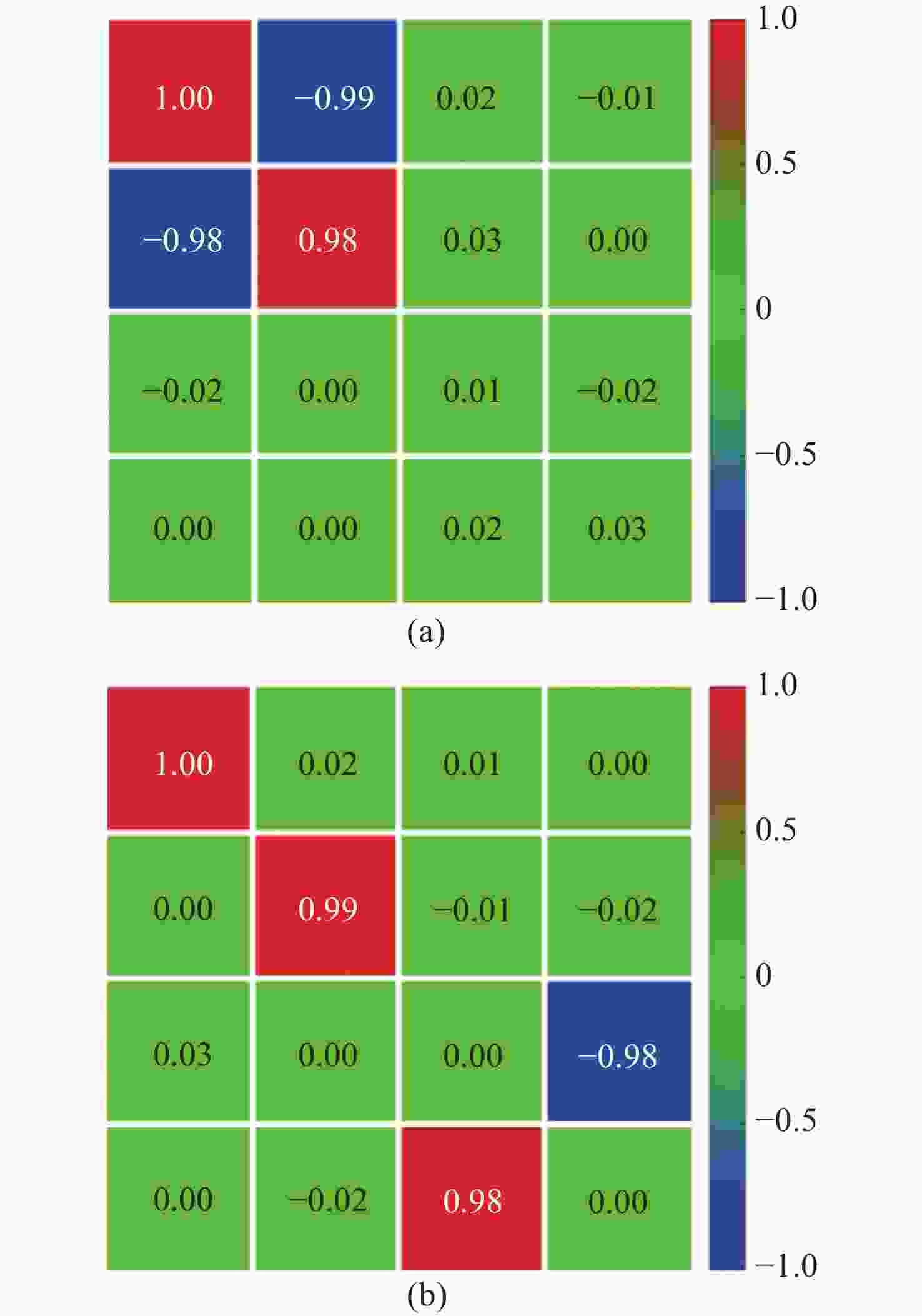
H P V M L R H 5.52 2.55 0.055 2.68 2.65 2.78 P 2.66 5.49 2.53 0.063 2.62 2.74 V 0.056 2.58 5.51 2.45 2.62 2.73 M 2.54 0.058 2.61 5.57 2.79 2.65 L 2.75 2.83 2.94 2.64 5.48 0.069 R 2.69 2.65 2.72 2.74 0.058 5.51 -
[1] SI L, HUANG T Y, WANG X J. Deep learning Mueller matrix feature retrieval from a snapshot Stokes image[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(6): 8676-8689. doi: 10.1364/OE.451612 [2] DONG H, ZHANG H L, HU D J J. Polar decomposition of Jones matrix and Mueller matrix of coherent Rayleigh backscattering in single-mode fibers[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(6): 1760. doi: 10.3390/s24061760 [3] SINGH M D, GHOSH N, VITKIN I A. Mueller matrix polarimetry in biomedicine: enabling technology, biomedical applications, and future prospects[M]//RAMELLA-ROMAN J C, NOVIKOVA T. Polarized Light in Biomedical Imaging and Sensing: Clinical and Preclinical Applications. Cham: Springer, 2022: 61-103. [4] ZHANG Y N, WU J Y, JIA L N, et al. Advanced optical polarizers based on 2D materials[J]. npj Nanophotonics, 2024, 1(1): 28. doi: 10.1038/s44310-024-00028-3 [5] GE J G, YUAN B, CHEN H J, et al. Anisotropy in microstructural features and tensile performance of laser powder bed fusion NiTi alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 24: 8656-8668. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.05.046 [6] SOLEILLET P. Sur les paramètres caractérisant la polarisation partielle de la lumière dans les phénomènes de fluorescence[J]. Annales De Physique, 1929, 10(12): 23-97. doi: 10.1051/anphys/192910120023 [7] MUELLER H. The foundation of optics[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1948, 38(7): 661-669. [8] BICKEL W S, BAILEY W M. Stokes vectors, Mueller matrices, and polarized scattered light[J]. American Journal of Physics, 1985, 53(5): 468-478. doi: 10.1119/1.14202 [9] GOLDSTEIN D H, CHIPMAN R A. Error analysis of a Mueller matrix polarimeter[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1990, 7(4): 693-700. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.7.000693 [10] LU S Y, CHIPMAN R A. Interpretation of Mueller matrices based on polar decomposition[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1996, 13(5): 1106-1113. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.13.001106 [11] FUJIWARA H. Spectroscopic Ellipsometry: Principles and Applications[M]. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 2007. [12] GU H G, CHEN X G, ZHANG CH W, et al. Study of the retardance of a birefringent waveplate at tilt incidence by Mueller matrix ellipsometer[J]. Journal of Optics, 2018, 20(1): 015401. doi: 10.1088/2040-8986/aa9b05 [13] 赵鑫鑫, 宋茂新, 许智龙, 等. 离轴三反望远物镜的穆勒矩阵测量[J]. 光学学报,2023,43(12):1212004. doi: 10.3788/AOS221873ZHAO X X, SONG M X, XU ZH L, et al. Mueller matrix measurement of off-axis three-mirror telescope objective[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2023, 43(12): 1212004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS221873 [14] LAUDE-BOULESTEIX B, DE MARTINO A, DRÉVILLON B, et al. Mueller polarimetric imaging system with liquid crystals[J]. Applied Optics, 2004, 43(14): 2824-2832. doi: 10.1364/AO.43.002824 [15] AAS L M S, ELLINGSEN P G, KILDEMO M. Near infra-red Mueller matrix imaging system and application to retardance imaging of strain[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(9): 2737-2741. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2010.12.093 [16] SHENG SH, CHEN X G, CHEN CH, et al. Design and calibration of a Mueller matrix microscope based on liquid crystal variable retarders[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2023, 770: 139779. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2023.139779 [17] 陈冬静, 崔宏青, 冯亚云, 等. 一种新的测量扭曲向列相液晶盒盒厚和扭曲角的Stokes矢量法[J]. 液晶与显示,2007,22(6):662-667. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2780.2007.06.004CHEN D J, CUI H Q, FENG Y Y, et al. Novel Stokes parameter method for determination of cell thickness and twist angle of twisted nematic liquid crystal cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2007, 22(6): 662-667. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2780.2007.06.004 [18] 李作恩, 鞠学平, 胡春晖, 等. 通道型偏振光谱仪望远镜组偏振效应分析与优化[J]. 液晶与显示,2023,38(12):1728-1735. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2023-0049LI Z E, JU X P, HU CH H, et al. Analysis and optimization of polarization effect of telescope group of channel polarization spectrometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2023, 38(12): 1728-1735. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2023-0049 [19] 杨志勇, 张志伟, 蔡伟, 等. 基于Mueller矩阵的目标偏振特性分析[J]. 光学学报,2023,43(1):0112005. doi: 10.3788/AOS221004YANG ZH Y, ZHANG ZH W, CAI W, et al. Analysis of polarization characteristics of targets based on Mueller matrix[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2023, 43(1): 0112005. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS221004 [20] 史文雄, 卢绮涵, 梁如标, 等. 用于液晶调控器件的过压驱动技术进展[J]. 液晶与显示,2024,39(3):384-392. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2024-0049SHI W X, LU Q H, LIANG R B, et al. Development of overdriving technology for liquid crystal modulatory devices[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2024, 39(3): 384-392. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2024-0049 [21] GUO H Y, LI Q, XU Y J, et al. Line of sight correction of high-speed liquid crystal using overdriving technology[J]. Electronics, 2020, 9(9): 1477. doi: 10.3390/electronics9091477 [22] 芦永军, 曹召良, 曲艳玲, 等. 液晶波前校正器动态位相响应特性研究[J]. 液晶与显示,2012,27(6):730-735. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20122706.0730LU Y J, CAO ZH L, QU Y L, et al. Dynamic phase response of liquid crystal wavefront corrector[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2012, 27(6): 730-735. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20122706.0730 [23] 杜莹, 陈梅蕊, 刘禹彤, 等. 基于掩模光刻的液晶波前校正器设计与制备[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(2):324-333. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0137DU Y, CHEN M R, LIU Y T, et al. Design and fabrication of liquid crystal wavefront corrector based on mask lithography[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(2): 324-333. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0137 [24] GAMEL O, JAMES D F V. Measures of quantum state purity and classical degree of polarization[J]. Physical Review A, 2012, 86(3): 033830. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.86.033830 [25] 张郁文, 刘丙才, 王红军, 等. 同步相移横向剪切干涉中偏振器件的误差建模[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(3):640-647. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0152ZHANG Y W, LIU B C, WANG H J, et al. Error modeling of polarization devices in simultaneous phase-shifted lateral shearing interferometry[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(3): 640-647. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0152 [26] 王启东, 穆全全, 刘璐璐, 等. 宽波段大视角液晶偏振转换器研究进展[J]. 液晶与显示,2024,39(5):683-696. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2024-0063WANG Q D, MU Q Q, LIU L L, et al. Research progress on liquid crystal polarization converter with a large field of view and broadband[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2024, 39(5): 683-696. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2024-0063 [27] 史浩东, 卢琦, 赵义武, 等. 基于阵列光学的快速多维度成像制导光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(6):1418-1430. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0206SHI H D, LU Q, ZHAO Y W, et al. Design of a fast multi-dimensional imaging guidance optical system based on array optics[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(6): 1418-1430. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0206 -





 下载:
下载: