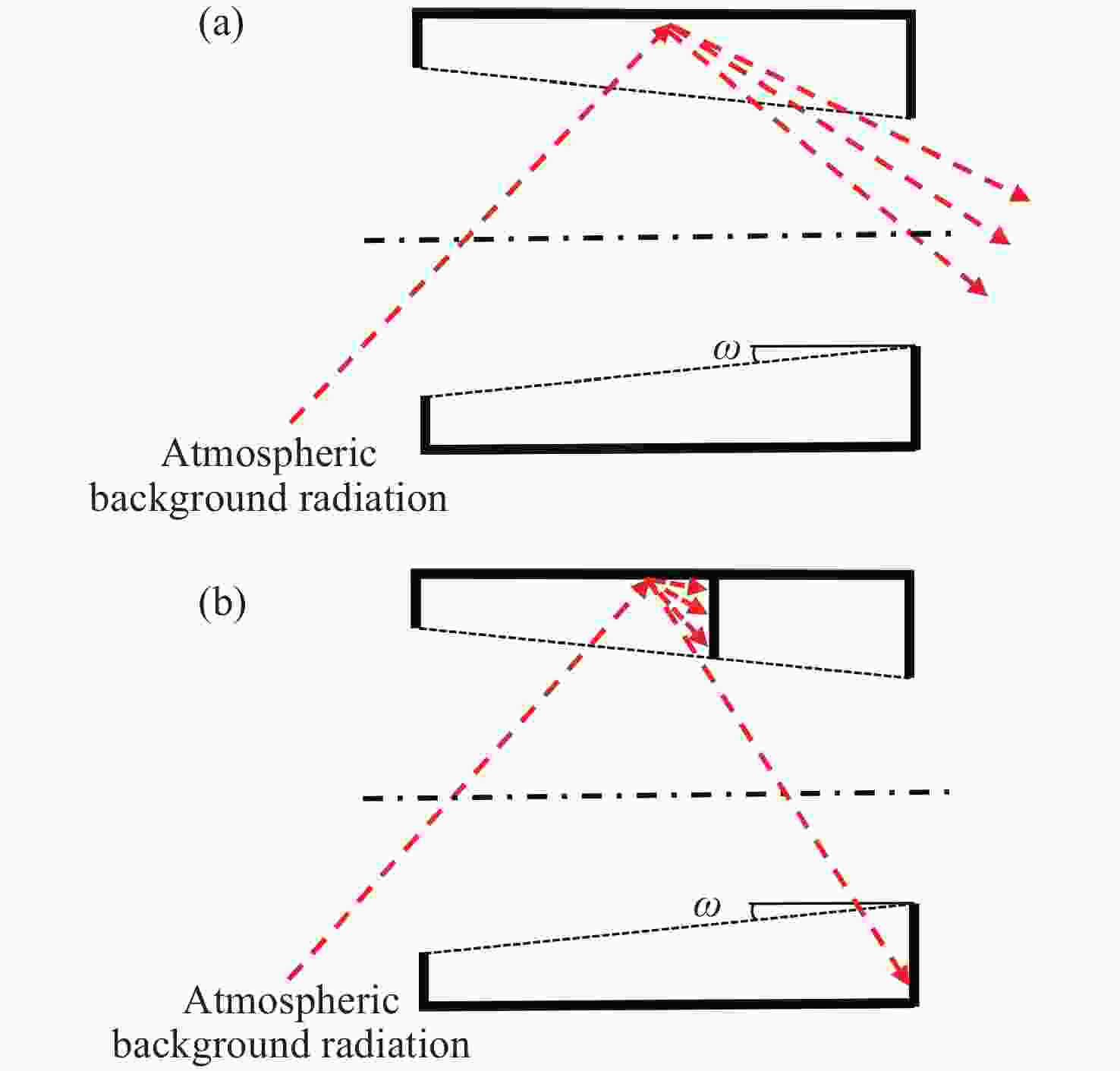
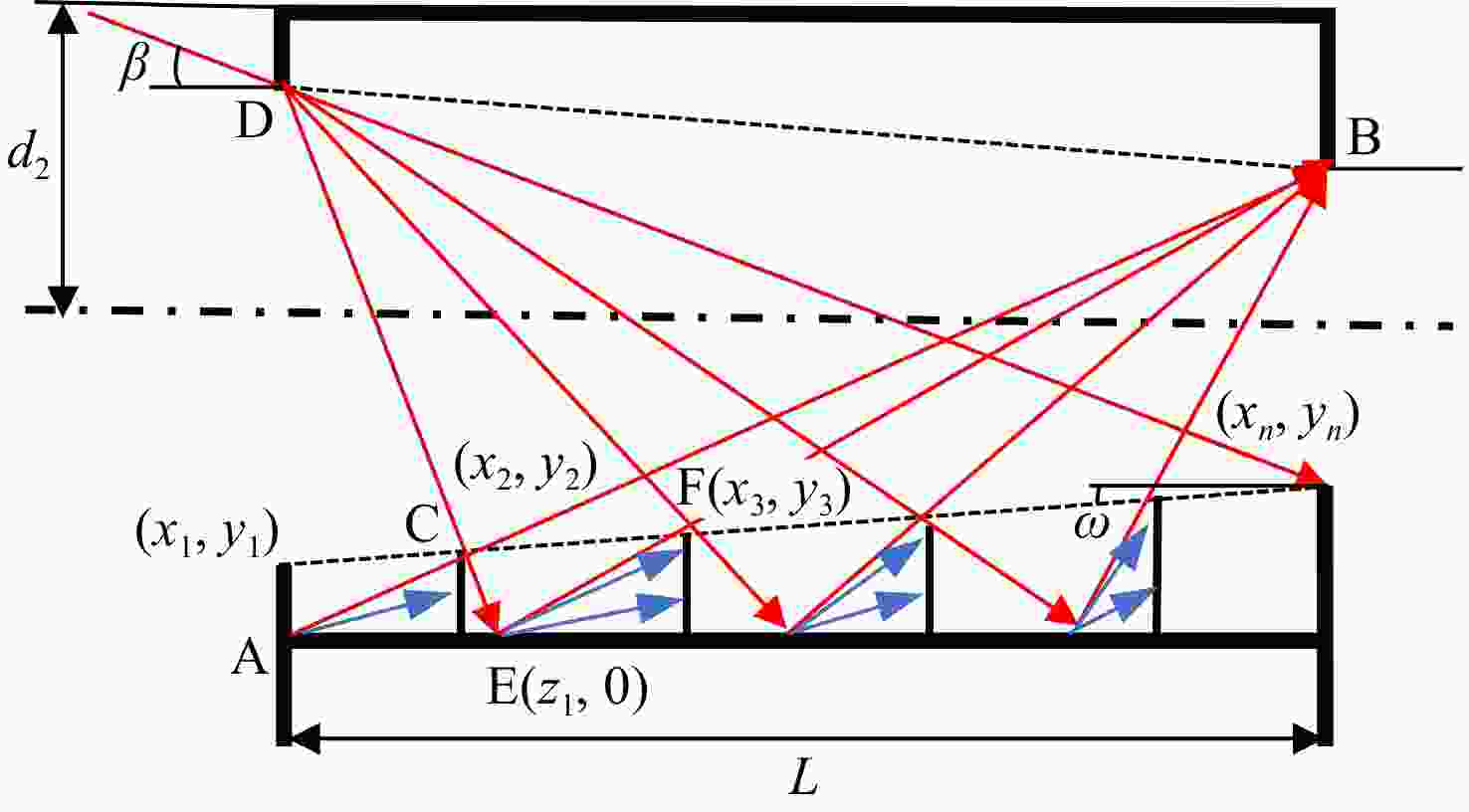
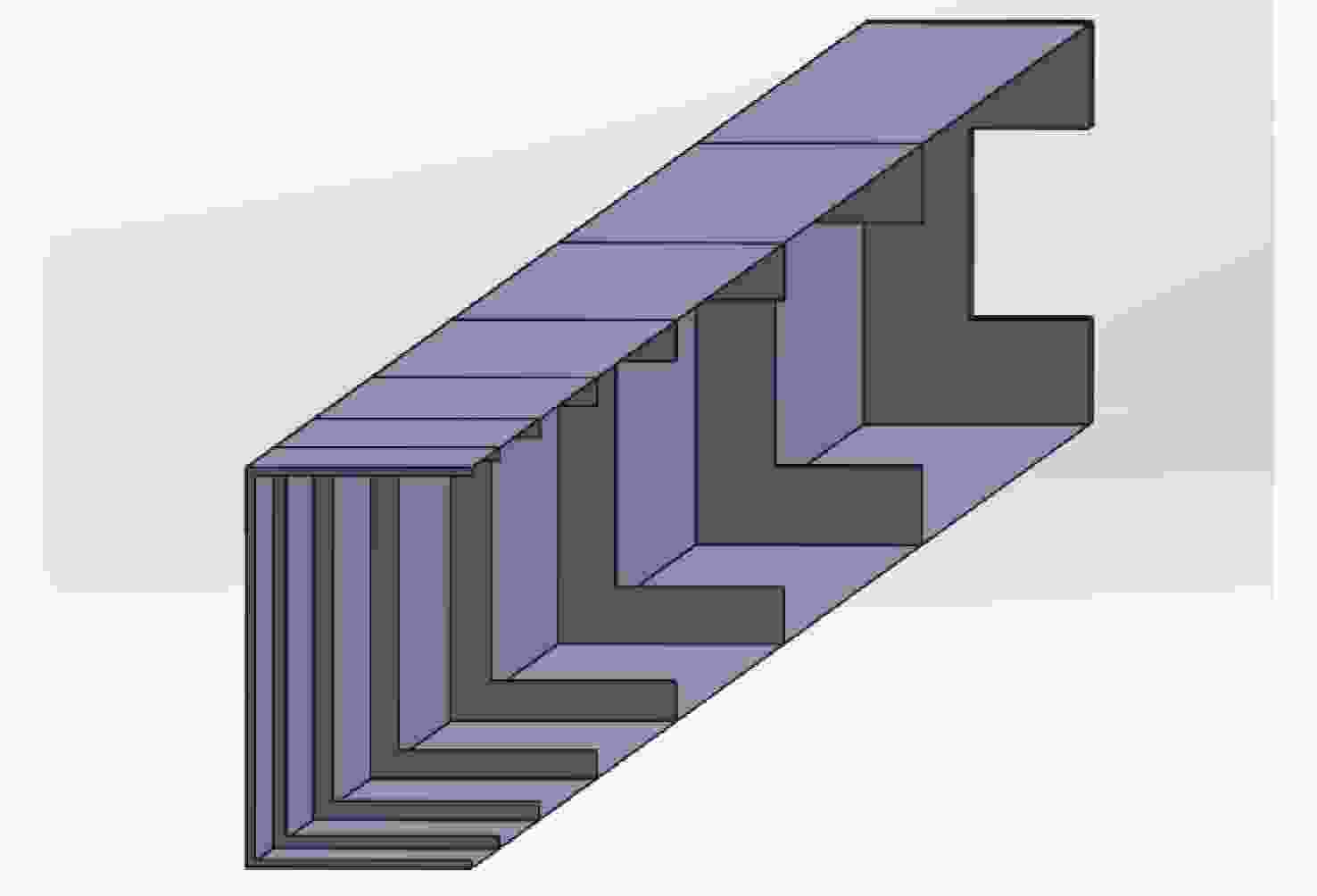
Analysis and suppression of stray light in the 557.7 nm band spaceborne doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne interferometer for wind field detection
-
摘要:
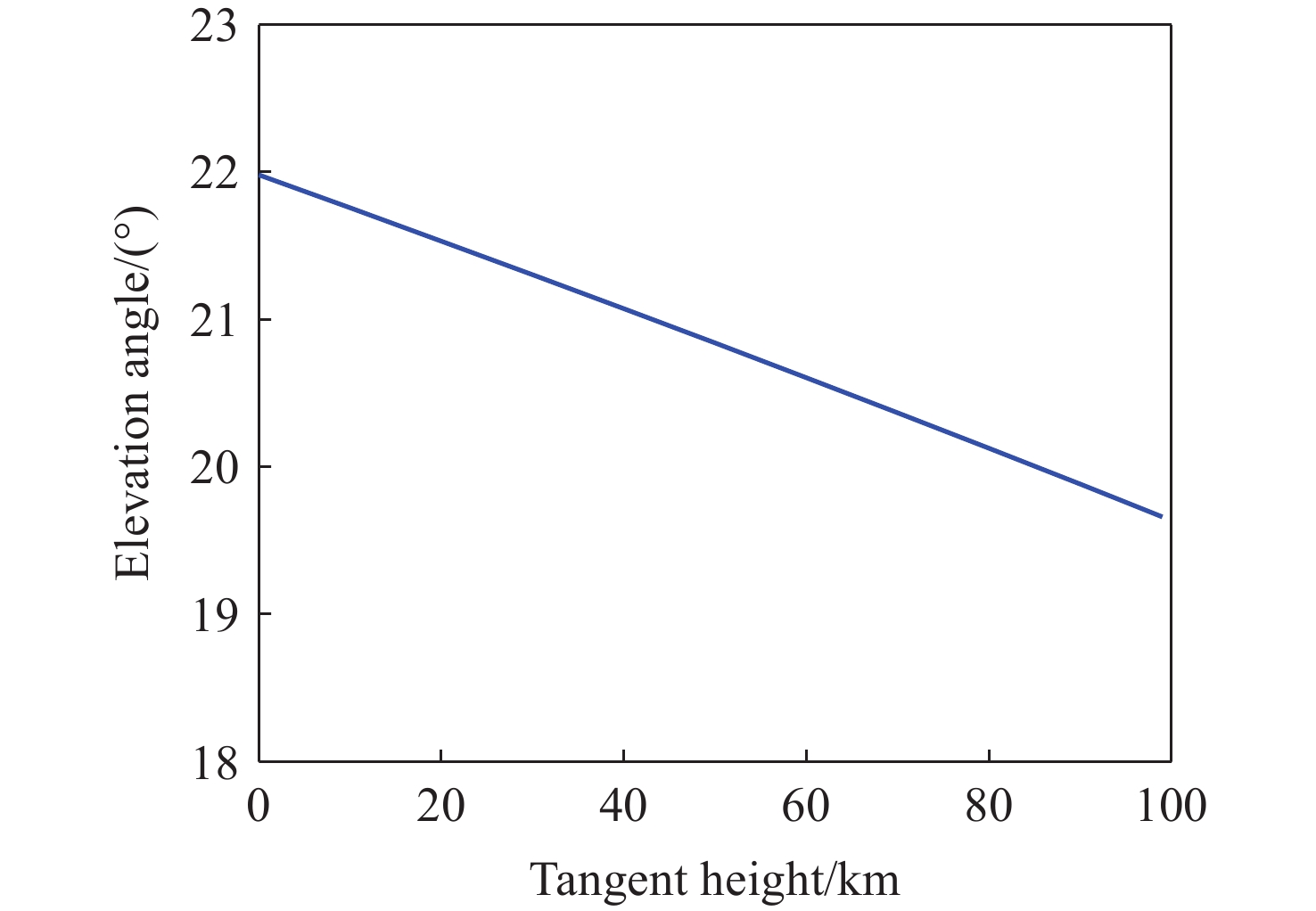
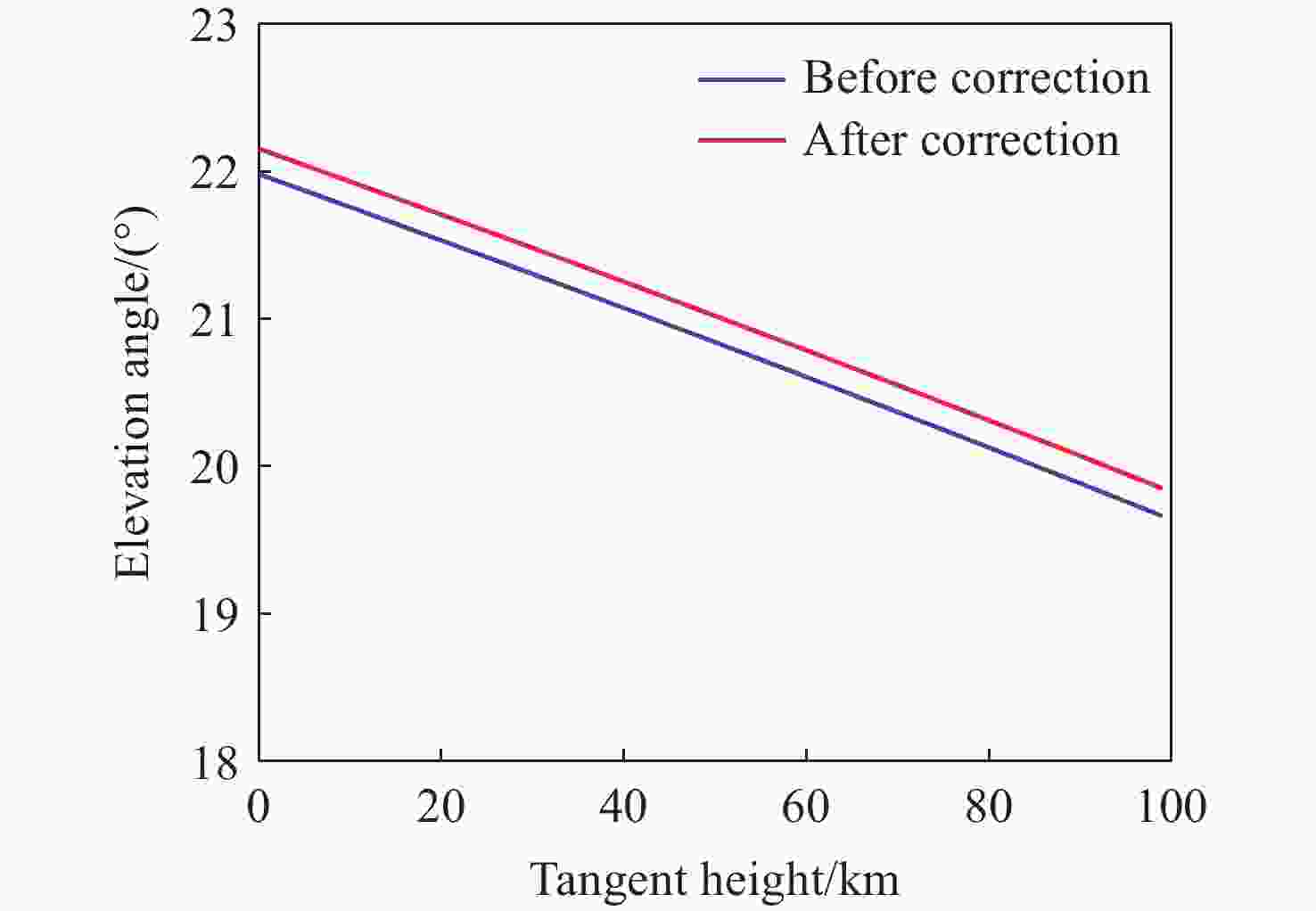
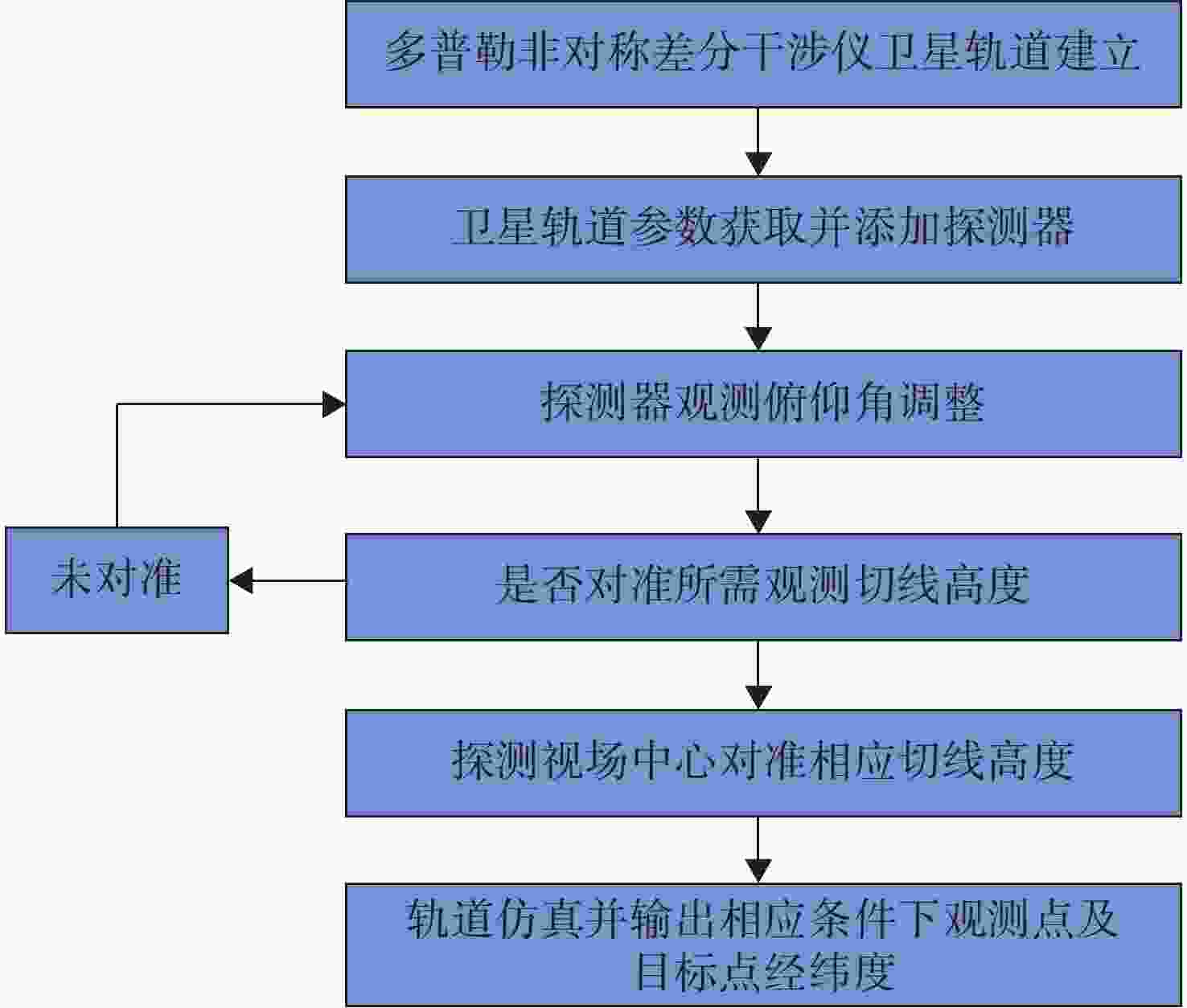
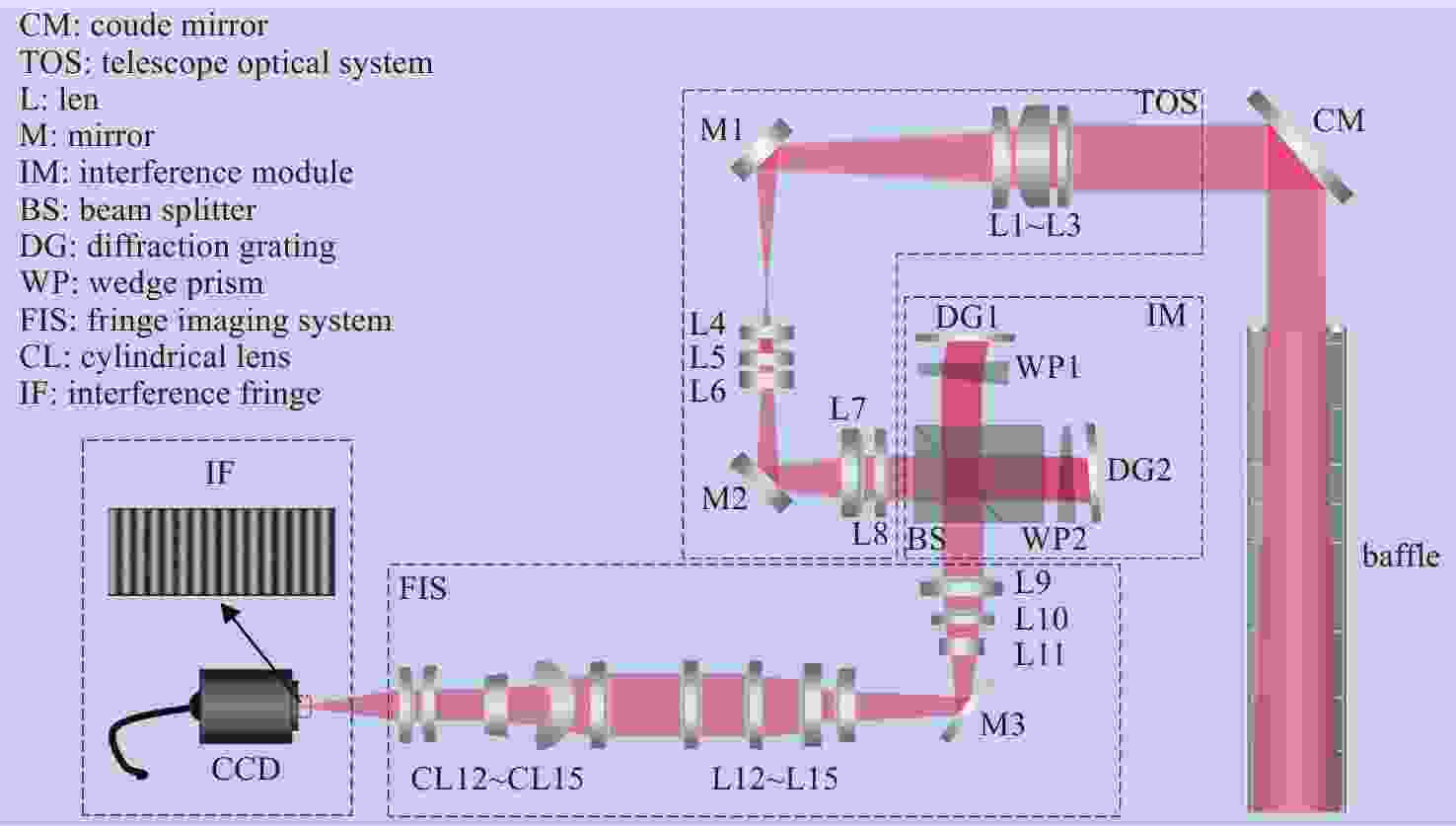
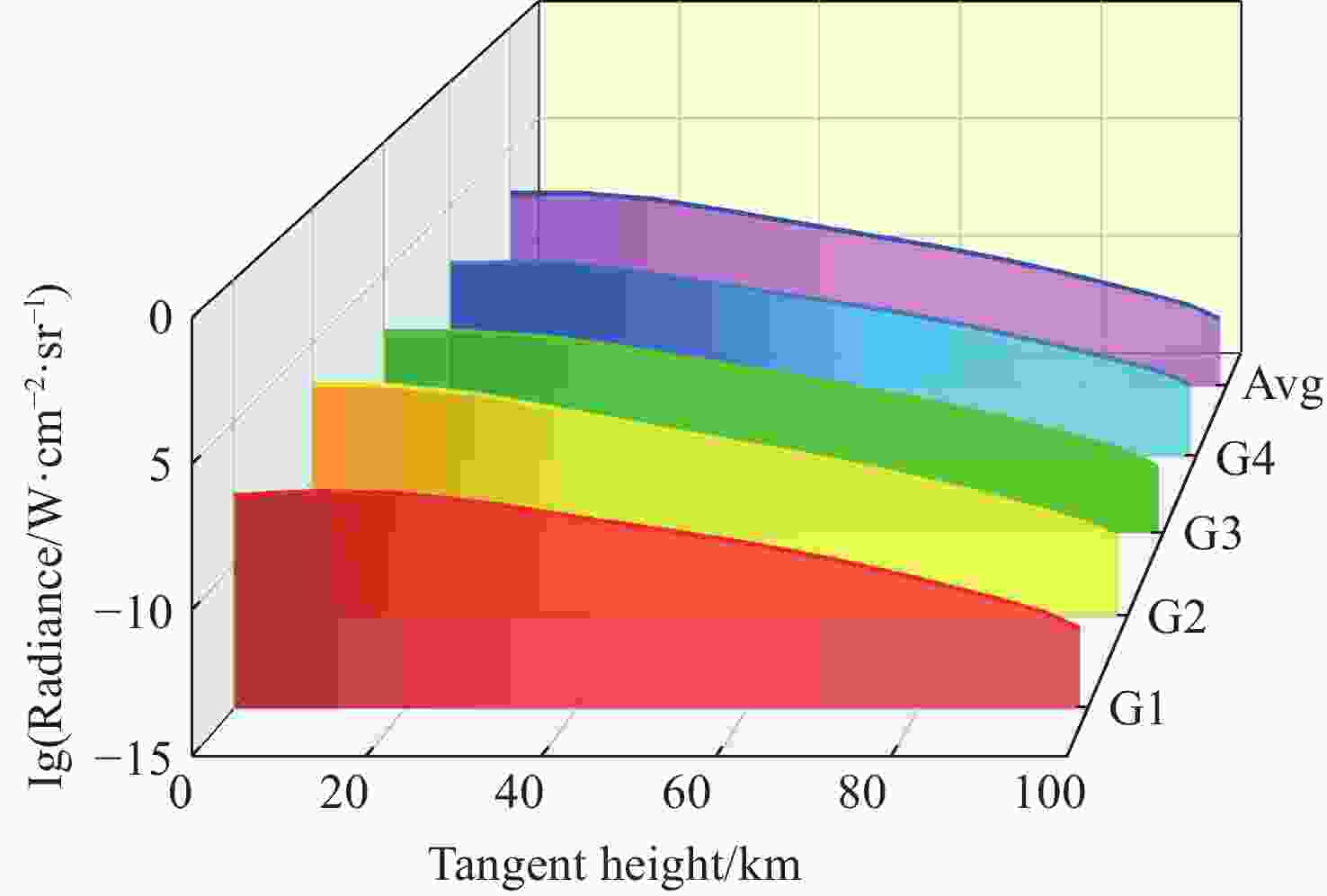
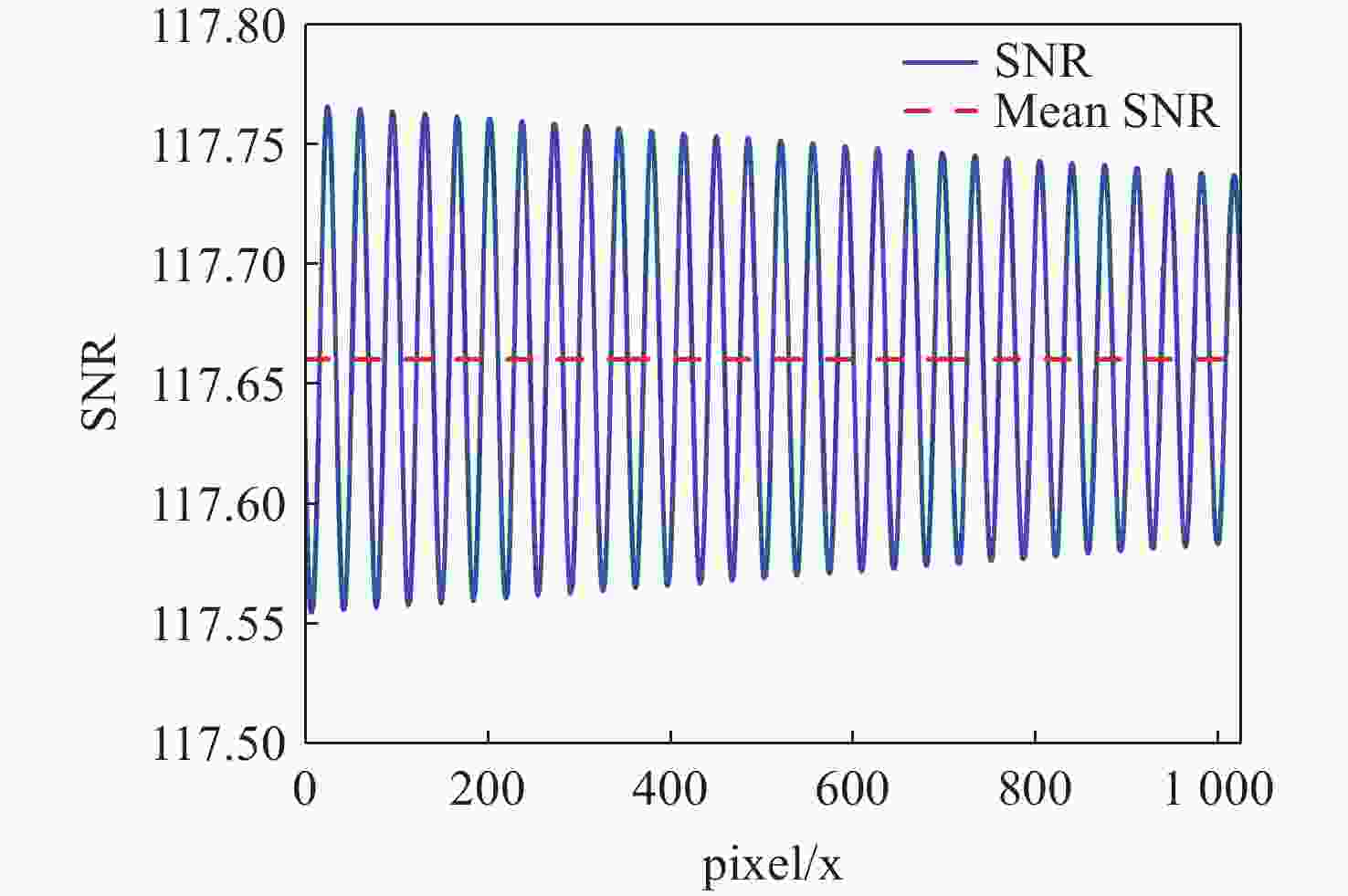
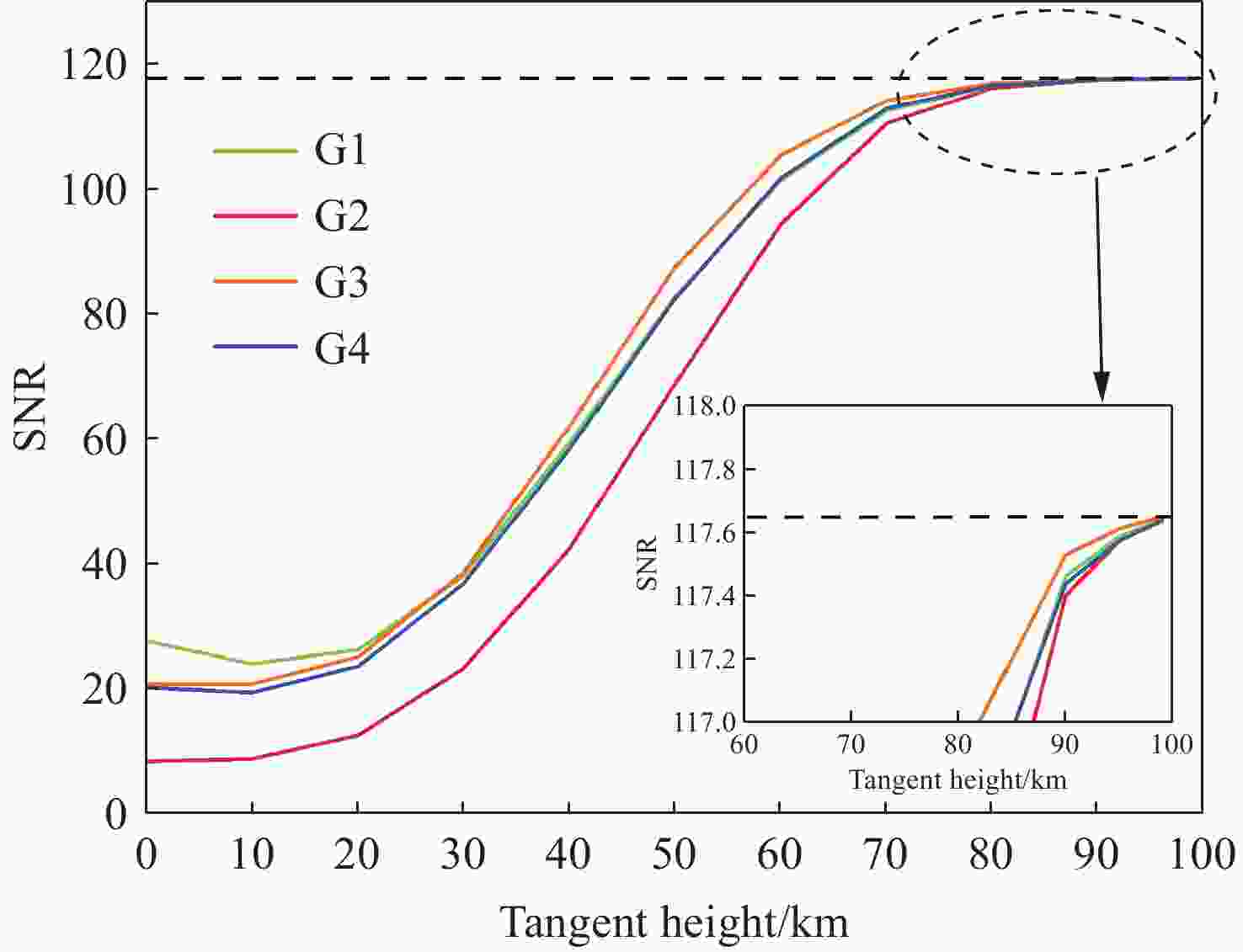
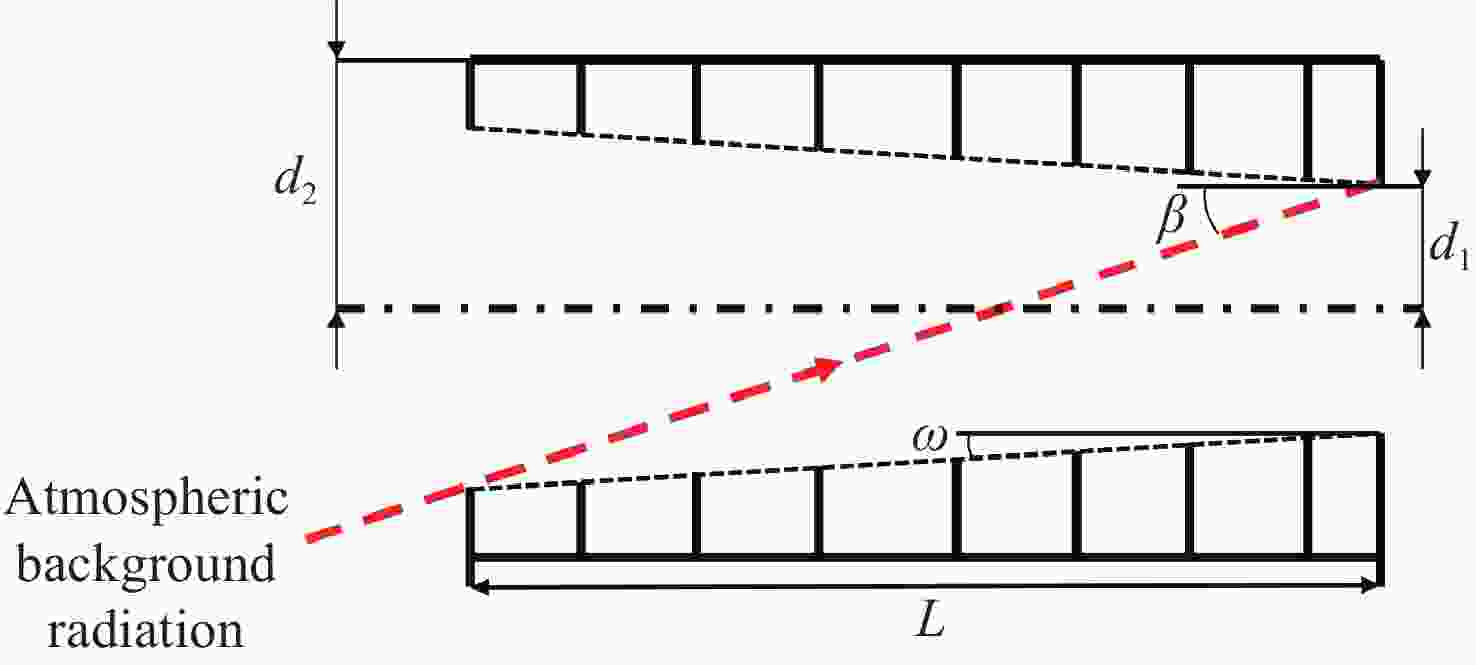
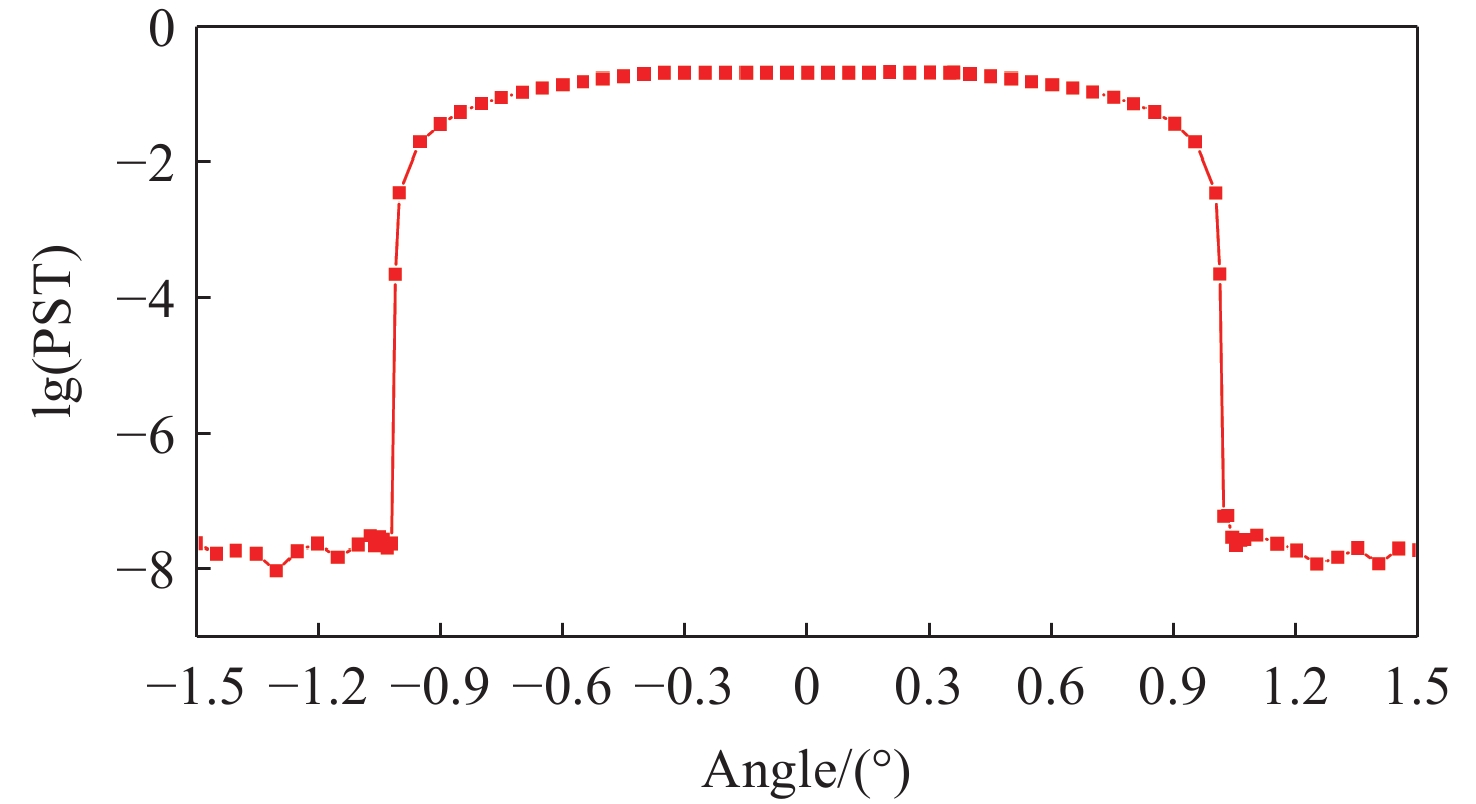
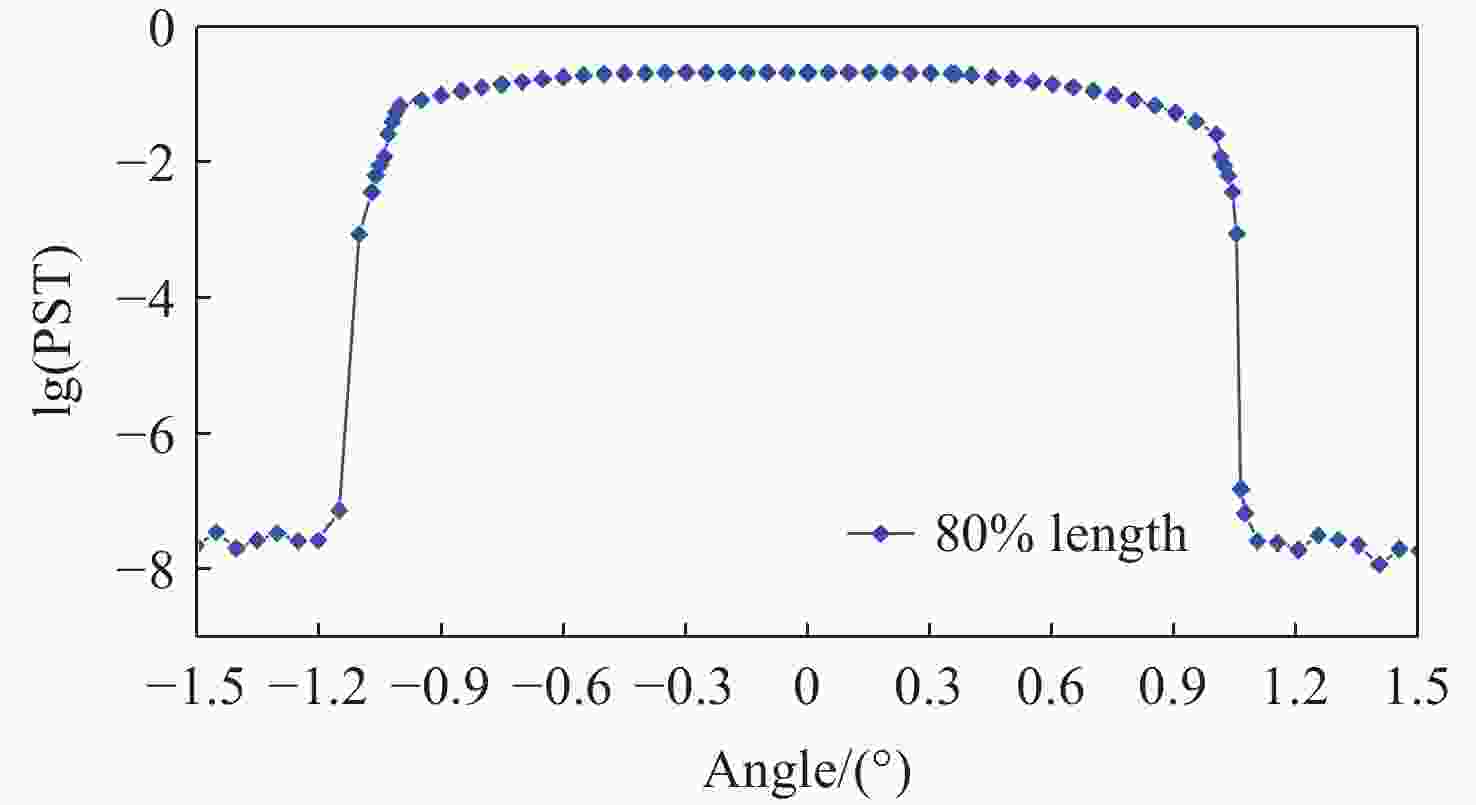
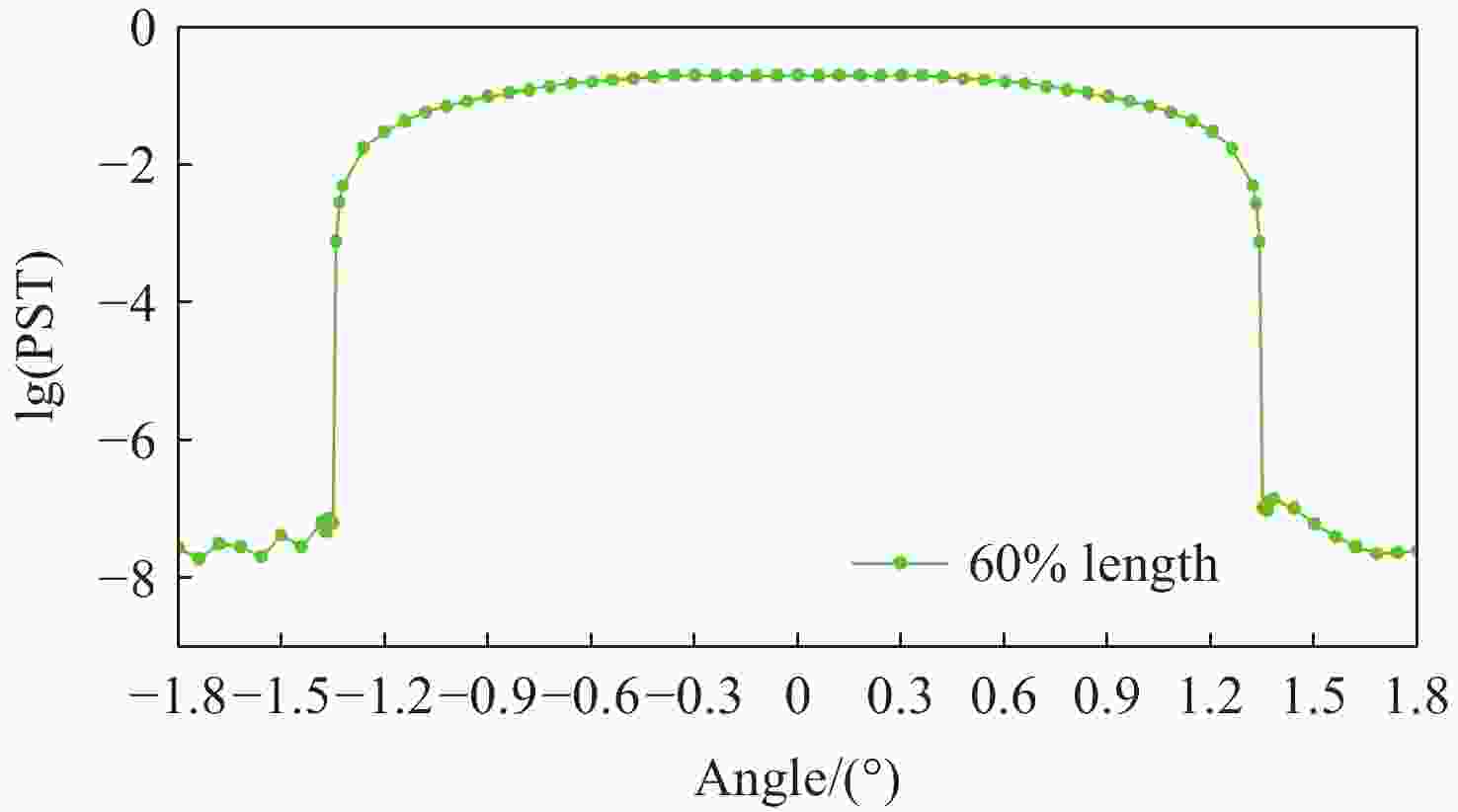
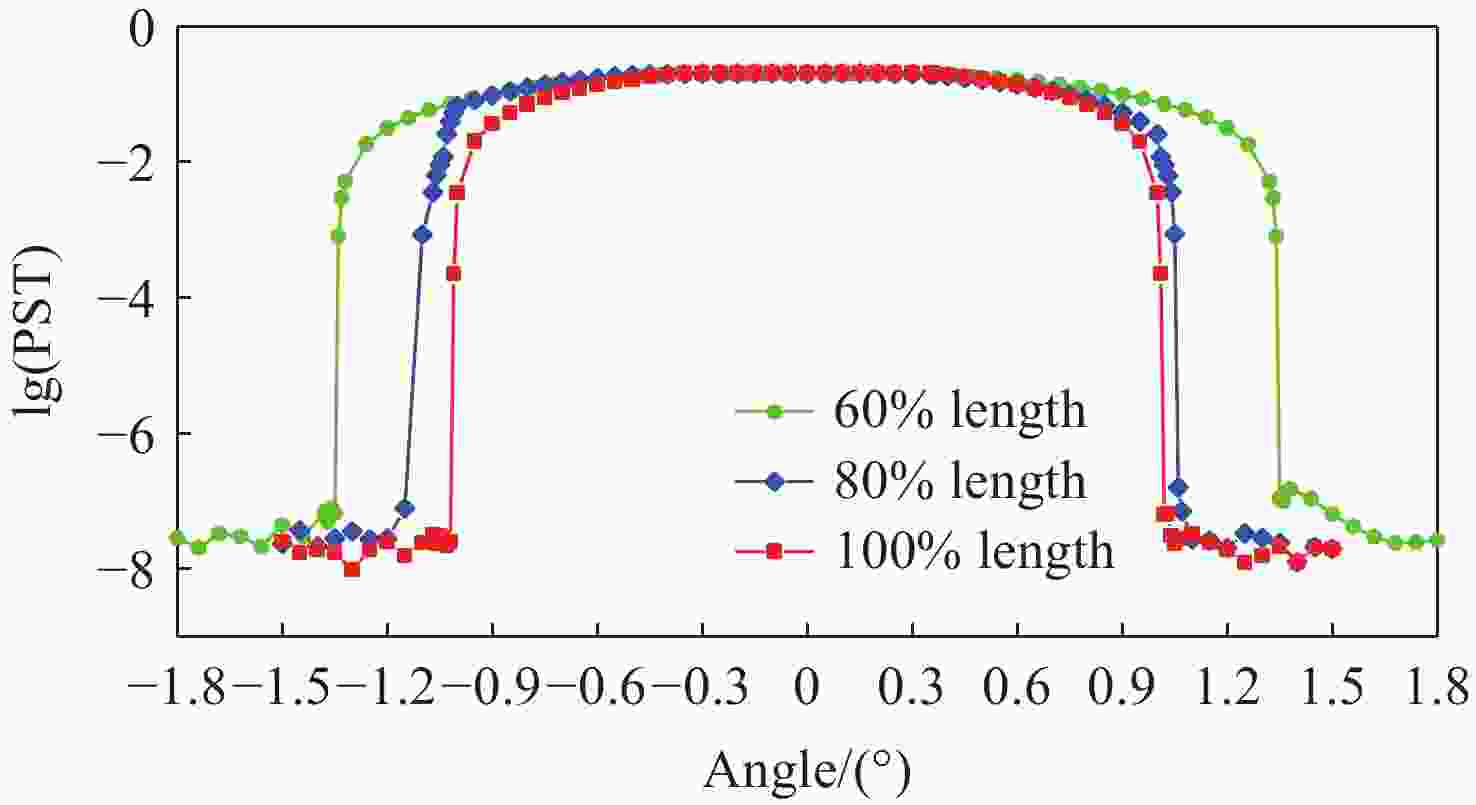
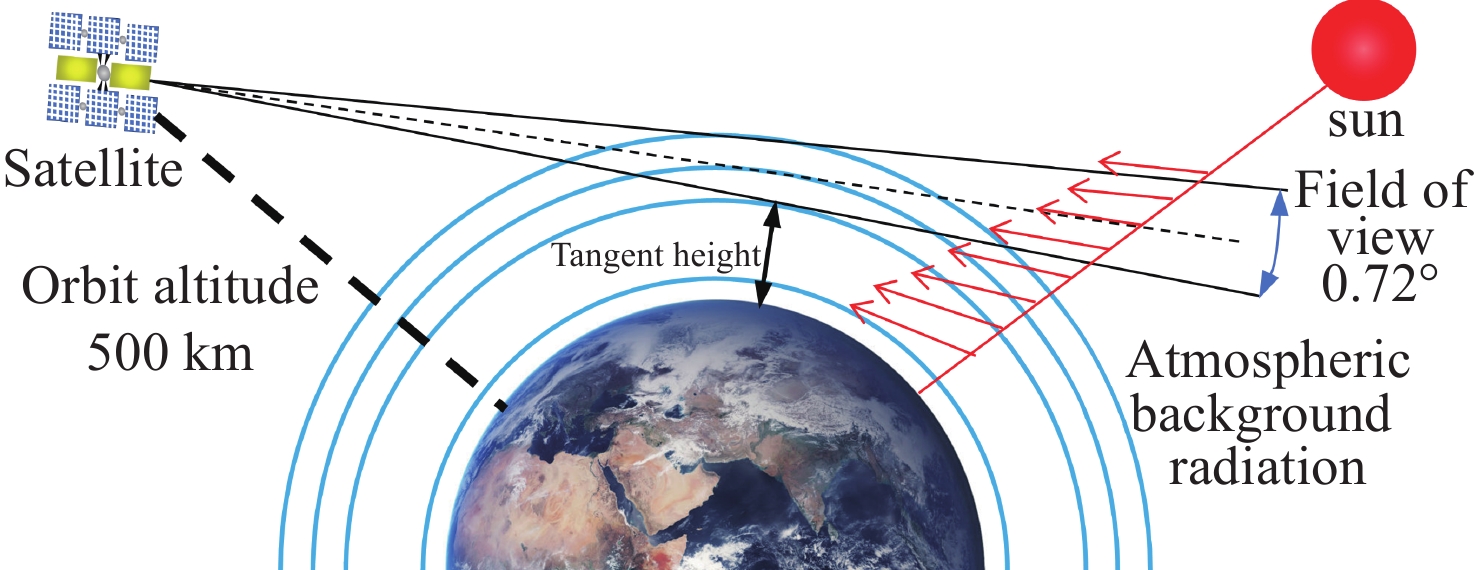
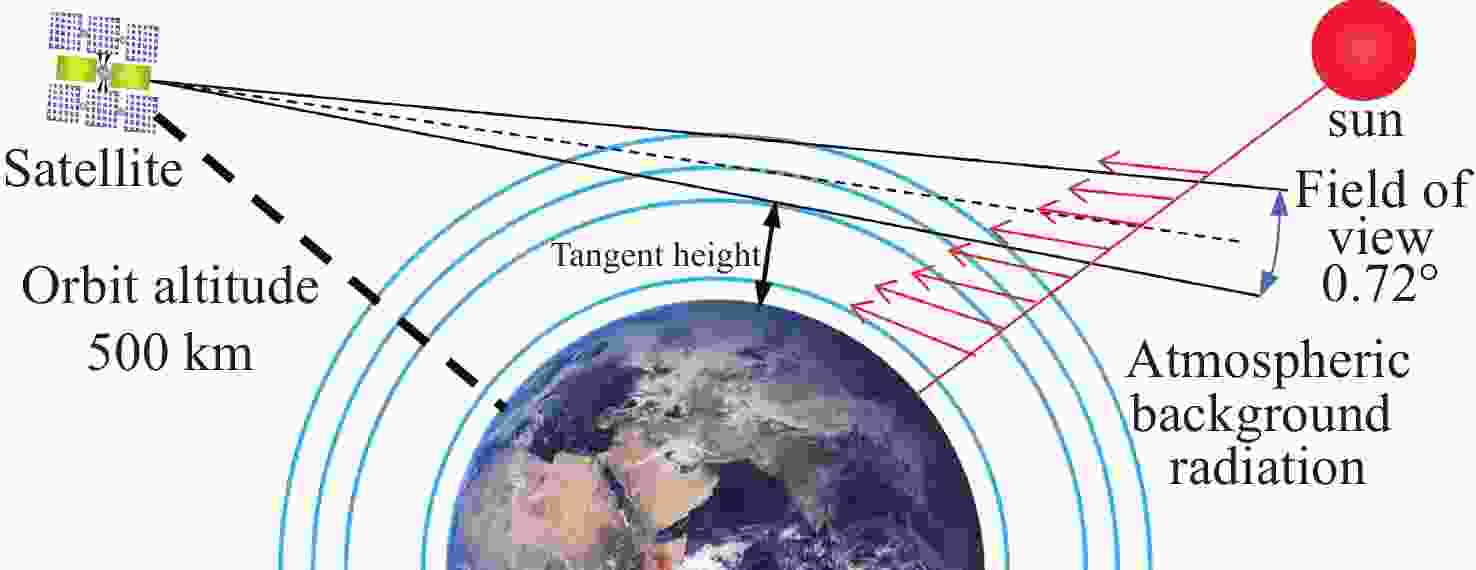
由于大气背景辐射对多普勒非对称差分(DASH)干涉仪风场探测成像质量产生影响,本文对其进行研究并设计杂散光抑制结构。基于轨道参数和观测几何,分析不同高度下大气背景辐射对系统信噪比(SNR)影响。随后,结合系统参数和信噪比变化规律设计遮光罩,并通过点源透过率(PST)评估抑制效果。结果表明,随着高度降低,大气背景辐射逐渐增强,从而导致信噪比逐渐下降。从PST曲线可知,系统视场内PST保持稳定,遮光罩未影响对目标光线的探测;视场外PST随离轴角增加而降低,在杂散光抑制角1.07°附近降至10−8以下,所提抑制设计满足系统对大气背景辐射的抑制要求。
Abstract:The impact of atmospheric background radiation on imaging quality in Doppler Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne (DASH) interferometers for wind field detection is investigated, and a stray light suppression structure is designed. Utilizing orbital parameters and observation geometry, the influence of atmospheric background radiation on the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) at varying altitudes is analyzed. Subsequently, a baffle is designed considering system parameters and SNR variation patterns, with its suppression efficacy evaluated via point source transmittance (PST). Results demonstrate that atmospheric background radiation intensifies with decreasing altitude, leading to progressive SNR degradation. PST curves indicate stable in-field PST unaffected by the baffle, preserving target light detection capability. Out-of-field PST decreases with increasing off-axis angle, dropping below 10−8 near the critical stray light suppression angle of 1.07°. The proposed suppression design fulfills system requirements for atmospheric background radiation mitigation.
-
表 1 轨道参数
Table 1. Orbital parameters
参数 数值 轨道高度/km 500.0 偏心率 0.0010489 升交点赤经/(°) 242.086 近地点幅角/(°) 187.310 观测目标波长/nm 557.7 观测范围/km 80.0~110.0 表 2 观测线60 km轨道参数
Table 2. Orbital parameters of the 60 km observation
时间 观测点经度 观测点纬度 目标点经度 目标点纬度 06:38 295.996 71.470 280.831 67.889 06:40 271.592 72.149 261.391 66.883 06:42 249.234 69.815 245.056 63.681 06:44 233.076 65.304 232.825 58.95 06:46 222.216 59.562 223.939 53.271 06:48 214.748 53.153 217.391 47.01 06:50 209.354 46.363 212.42 40.383 06:52 205.263 39.338 208.528 33.512 06:54 202.026 32.158 205.395 26.473 06:56 199.375 24.871 202.816 19.315 表 3 测风仪系统参数
Table 3. Parameters of the wind measurement system
参数 数值 视场/(°) 0.72 系统透过率 0.12 光学系统F数 8.38 探测器规格 1024 ×1024 @13 μm探测器量子效率/% 90 制冷温度/(°C) −40 探测器暗电流/(e−/pixel/s) 0.0004 积分时间/(s) 120 表 4 模型参数设置
Table 4. Property setting in the mode unit:%
表面类型 透过率 吸收率 反射率 BRDF 透镜表面 97.880 0.100 1.900 0.120 反射镜表面 0 2.000 97.880 0.120 机械结构表面 0 90.000 0.001 9.999 分束镜表面 47.44 5 47.44 0.12 -
[1] 韩斌, 冯玉涛, 王劲松, 等. 中高层大气风场探测光学干涉仪载荷发展综述(特邀)[J]. 光学学报,2024,44(18):1800008. doi: 10.3788/AOS240679HAN B, FENG Y T, WANG J S, et al. Overview of optical interferometer payloads for detecting wind fields in middle and upper atmosphere (invited)[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2024, 44(18): 1800008. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS240679 [2] SHEPHERD G G. Development of wind measurement systems for future space missions[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2015, 115: 206-217. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2015.05.015 [3] SHEPHERD G G, THUILLIER G, CHO Y M, et al. The wind imaging interferometer (WINDII) on the upper atmosphere research satellite: a 20 year perspective[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2012, 50(2): RG2007. [4] GAULT W A, BRUN J F, DESAULNIERS M D L, et al. Design and on-orbit performance of the WINDII baffle system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1993, 1753: 189-195. doi: 10.1117/12.140701 [5] ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, BROWN C M, et al. Michelson Interferometer for Global High-resolution Thermospheric Imaging (MIGHTI): instrument design and calibration[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2017, 212(1-2): 553-584. doi: 10.1007/s11214-017-0358-4 [6] BLAMONT J E, LUTON J M. Geomagnetic effect on the neutral temperature of the F region during the magnetic storm of September 1969[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1972, 77(19): 3534-3556. doi: 10.1029/JA077i019p03534 [7] HAYS P B, KILLEEN T L, KENNEDY B C. The Fabry-Perot interferometer on dynamics explorer[J]. Space Science Instrumentation, 1981, 5(4): 395-416. [8] HAYS P B, ABREU V J, DOBBS M E, et al. The high-resolution doppler imager on the upper atmosphere research satellite[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1993, 98(D6): 10713-10723. doi: 10.1029/93JD00409 [9] 王道琦, 王后茂, 何微微, 等. 1.27 ${\text{μm}}$ ${{\text{O}}_2}\;( {{{\text{a}}^1}{\Delta _{\text{g}}}} )$ 气辉临边观测辐射传输特性[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2024,44(4):1088-1097. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2024)04-1088-10WANG D Q, WANG H M, HE W W, et al. Radiative transfer characteristics of the 1.27${\text{μm}}$ ${{\text{O}}_2}\;( {{{\text{a}}^1}{\Delta _{\text{g}}}})$ airglow in limb-viewing[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2024, 44(4): 1088-1097. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2024)04-1088-10[10] 刘欢, 江伦, 张晓菲, 等. 557.7 nm波段地基探测风场的多普勒非对称空间外差干涉仪研制(英文)[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2023, 16(5): 1226-1242.LIU H, JIANG L, ZHANG X F, et al. Development of a doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne interferometer for ground-based wind field detection at the 557.7 nm wavelength[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 1226-1242. . [11] 陈洁婧. 多普勒差分干涉光谱仪风速反演技术研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所), 2017.CHEN J J. Study on Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectrometer in wind velocity retrieval[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Institute of Optics & Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. (in Chinese). [12] 王锦疆. 星载实条纹空间外差干涉测风技术研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2024.WANG J J. Research on spaceborne real-fringe spatial heterodyne interferometry wind measurement technology[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2024. (in Chinese). [13] 段维铮. 极光的辐射特性与图像压缩编码[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2014.DUAN W Z. Radiance characters of aurora and image compression encoding[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2014. (in Chinese). [14] 陈醒, 胡春晖, 彦昌翔, 等. 大视场空间可见光相机的杂散光分析与抑制[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(3):678-685. doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0678CHEN X, HU CH H, YAN CH X, et al. Analysis and suppression of space stray light of visible cameras with wide field of view[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 678-685. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0678 [15] 周星宇, 孙亮, 潘俏, 等. 大相对孔径激光测距接收光学系统及杂散光抑制[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2024,61(5):0528001.ZHOU X Y, SUN L, PAN Q, et al. Large relative aperture receiving optical system and stray light suppression for laser ranging[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(5): 0528001. (in Chinese). [16] 刘琳岚. 临边观测条件下的杂散光抑制方法研究[D]. 西安: 西安工业大学, 2024.LIU L L. Research on the suppression method of stray light under limb-viewing conditions[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Technological University, 2024. (in Chinese). [17] 王虎, 陈钦芳, 马占鹏, 等. 杂散光抑制与评估技术发展与展望(特邀)[J]. 光子学报,2022,51(7):0751406. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20225107.0751406WANG H, CHEN Q F, MA ZH P, et al. Development and prospect of stray light suppression and evaluation technology (invited)[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2022, 51(7): 0751406. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20225107.0751406 -





 下载:
下载: