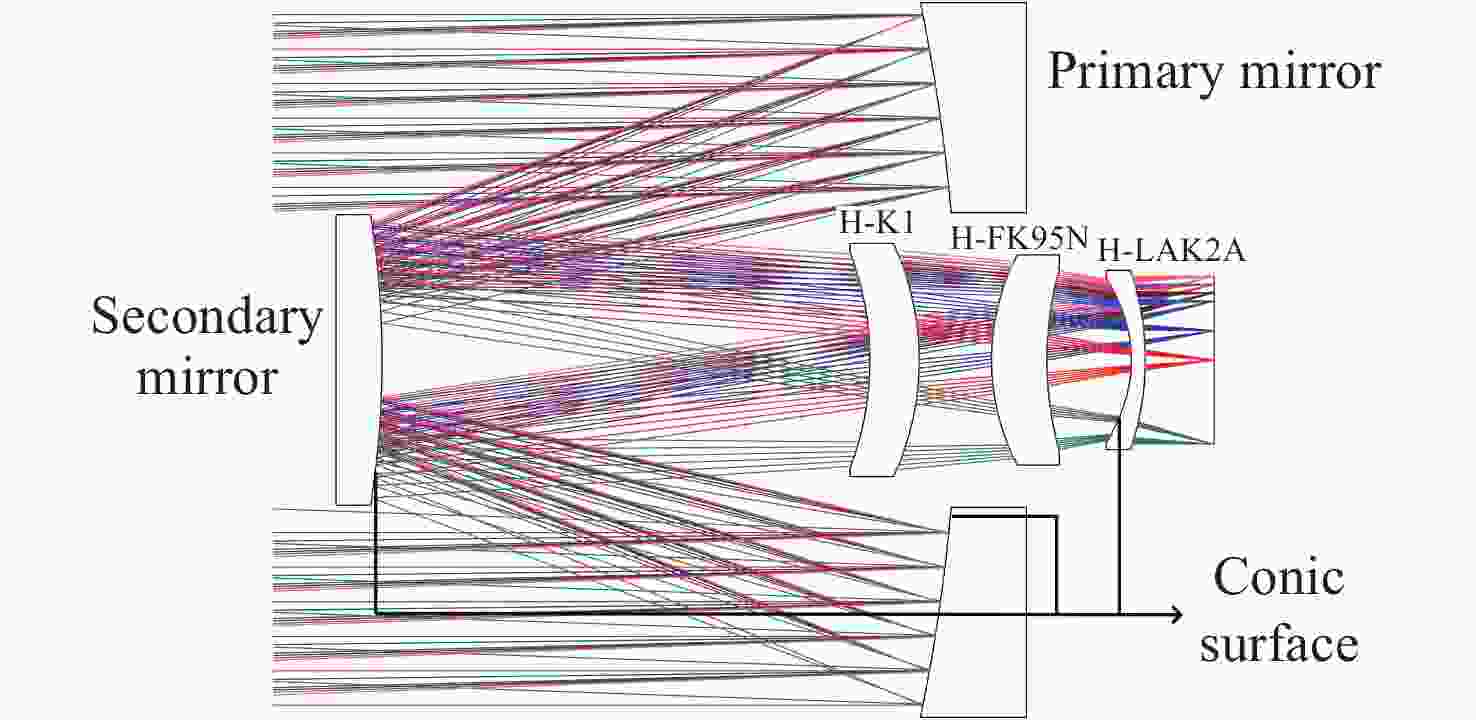
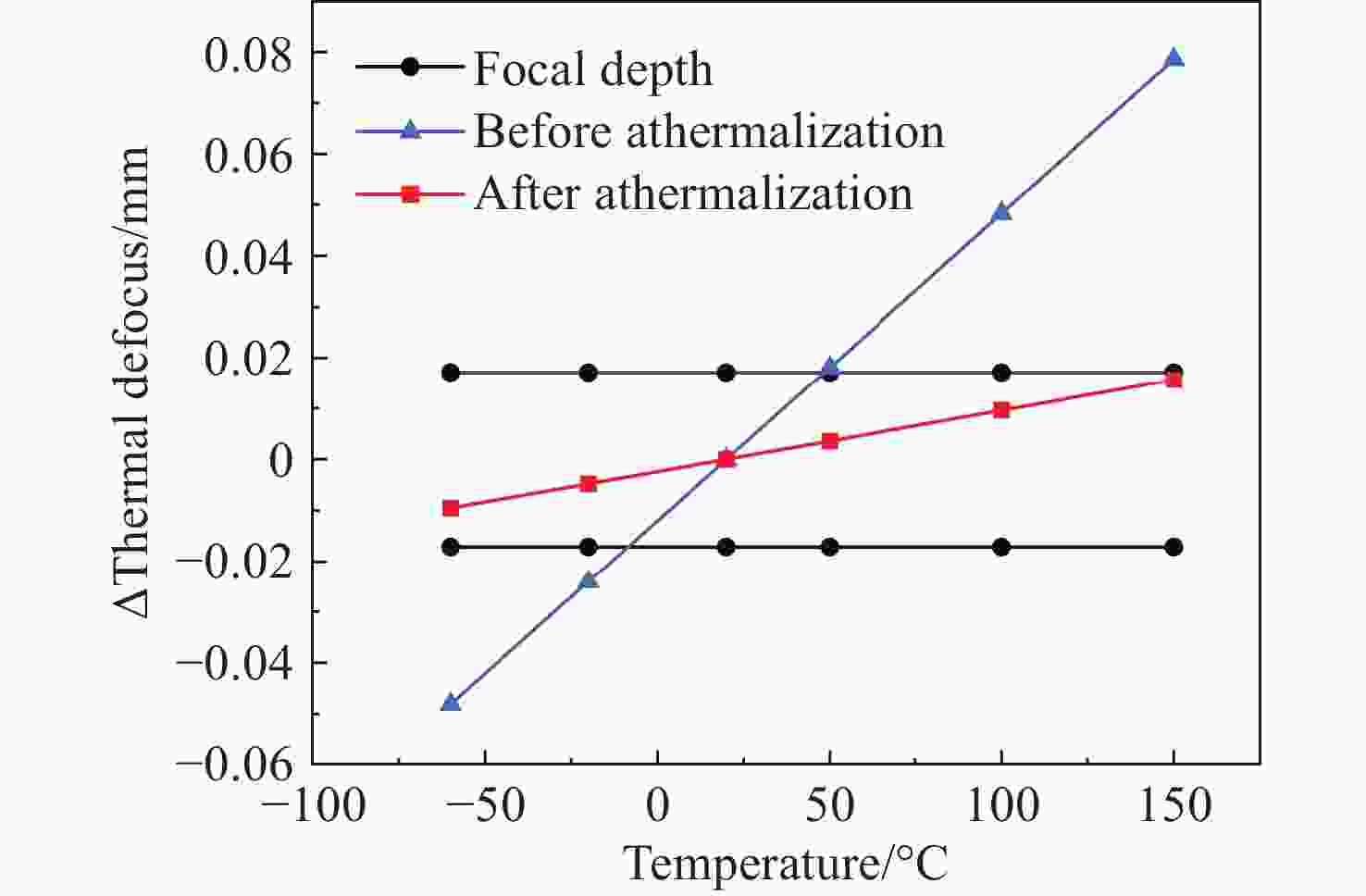
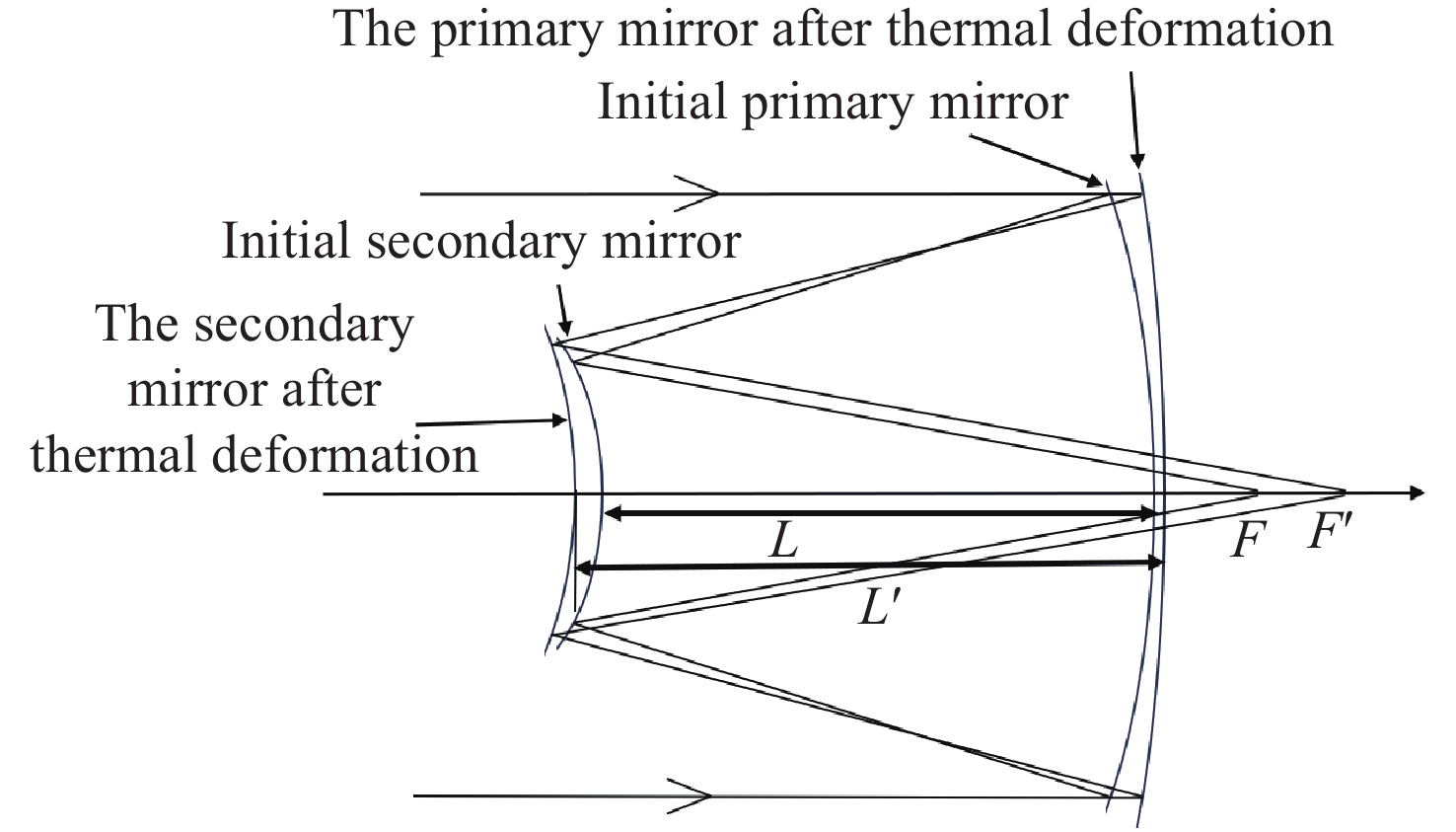
Athermal design of a space camera using a single lens material over a wide temperature range
-
摘要:
折反式空间相机广泛应用于空间探测领域,但温度变化将会导致成像质量下降。针对该问题,本文对折反式空间相机进行了宽温度范围的无热化设计。首先对相关的光学元件、机械结构等部件进行了温度影响分析,并总结消热差的便捷方法。接着以工作在400 nm~
1000 nm波段,焦距为525 mm,F数为3.5的空间相机为设计对象,通过选择合适的反射镜基底材料和支撑结构材料,只使用熔融石英一种透镜材料校正像差,从而确保折反式光学系统在空间环境运行的性能稳定性并实现宽温度范围无热化。最终仿真结果表明空间相机经过设计优化后可在−60 °C~150 °C温度范围内奈奎斯特频率77 lp/mm处的调制传递函数值优于0.4。该相机的材料物理性能稳定、成像质量好、高低温环境内成像质量稳定,在空间探测等领域具有广泛的应用前景。Abstract:Catadioptric space cameras are widely used in space exploration, However, temperature variations can degrade their imaging performance. To address this issue, this paper presents an athermal design for a catadioptric space camera operating over a wide temperature range. Initially, the temperature effects on optical elements, mechanical structures, and other components were analyzed, and convenient methods for thermal aberration compensation are summarized. Subsequently, taking a camera with a spectral range of 400–
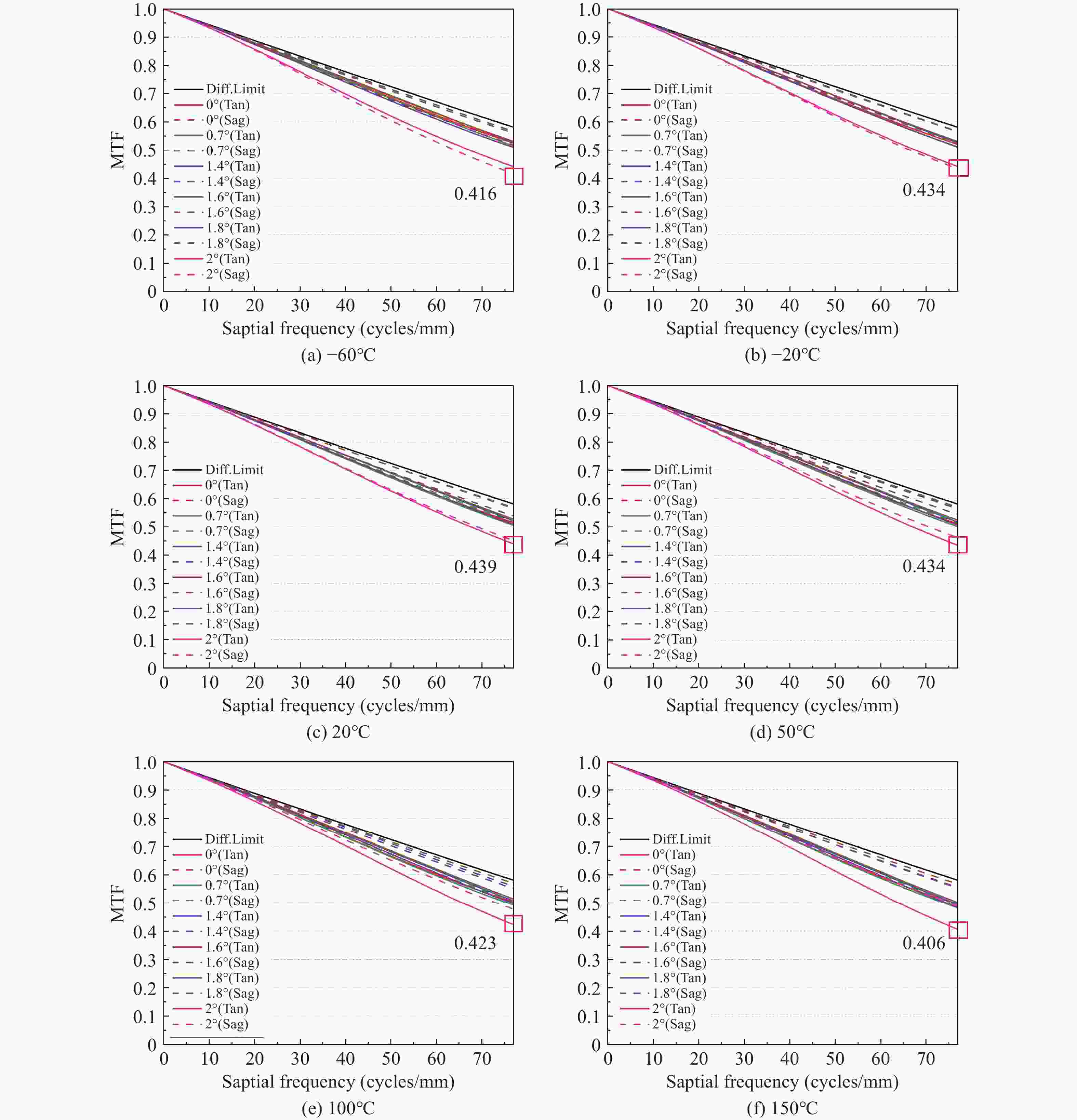
1000 nm, a focal length of 525 mm, and an F-number of 3.5 as the design case, an athermal solution is developed. By selecting appropriate materials for the mirror substrates and support structures, and using fused silica as the single lens material to correct aberrations, the optical system maintains stable performance in space environments. Final simulation results confirm that the optimized camera maintains a Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) value above 0.4 at 77 lp/mm (Nyquist frequency) over a temperature range of –60°C to 150°C. The camera exhibits stable material properties, excellent imaging quality, and consistent performance under extreme temperatures. This design demonstrates significant potential for applications in space exploration and related fields. -
表 1 空间相机部分常用材料参数
Table 1. Some commonly used material parameters of space cameras
Reflector
materialCoefficient of
thermal expansion
α(10−6/ °C)Mechanical
structural
materialCoefficient of
thermal expansion
α(10−6/ °C)glass-ceramics 0.05 4J36 Invar 1.8 Fused quartz 0.5 Titanium alloy 8.8 Silicon carbide 2.5 Aluminium alloy 23.6 表 2 设计指标
Table 2. Design indexes
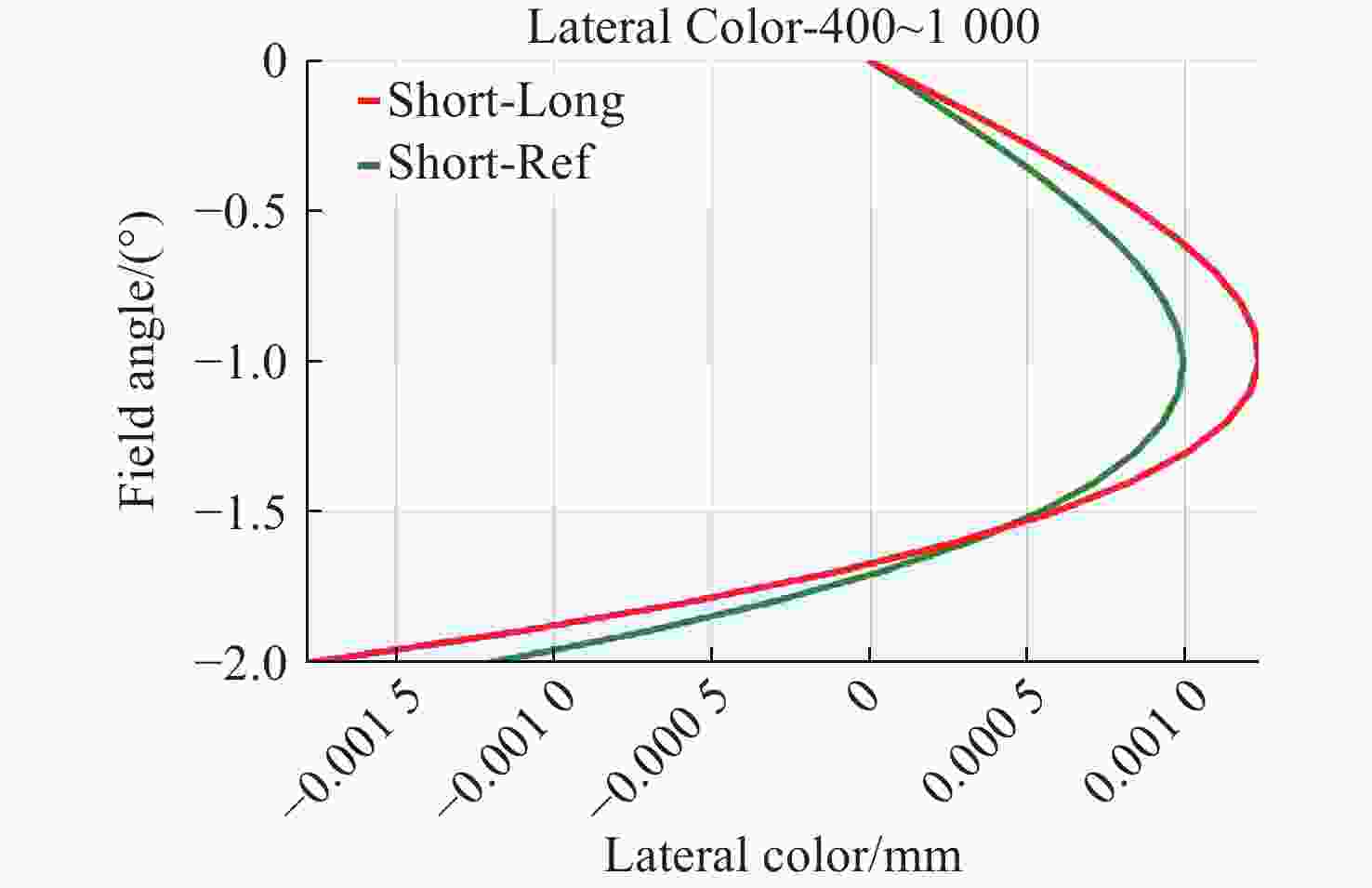
Index Value Wavelength range 400 nm~ 1000 nmField of view 4° F 3.5 Focal length 525 mm Pixel size 6.5 μm×6.5 μm Temperature range −60 °C~150 °C 表 3 初始光学系统结构参数
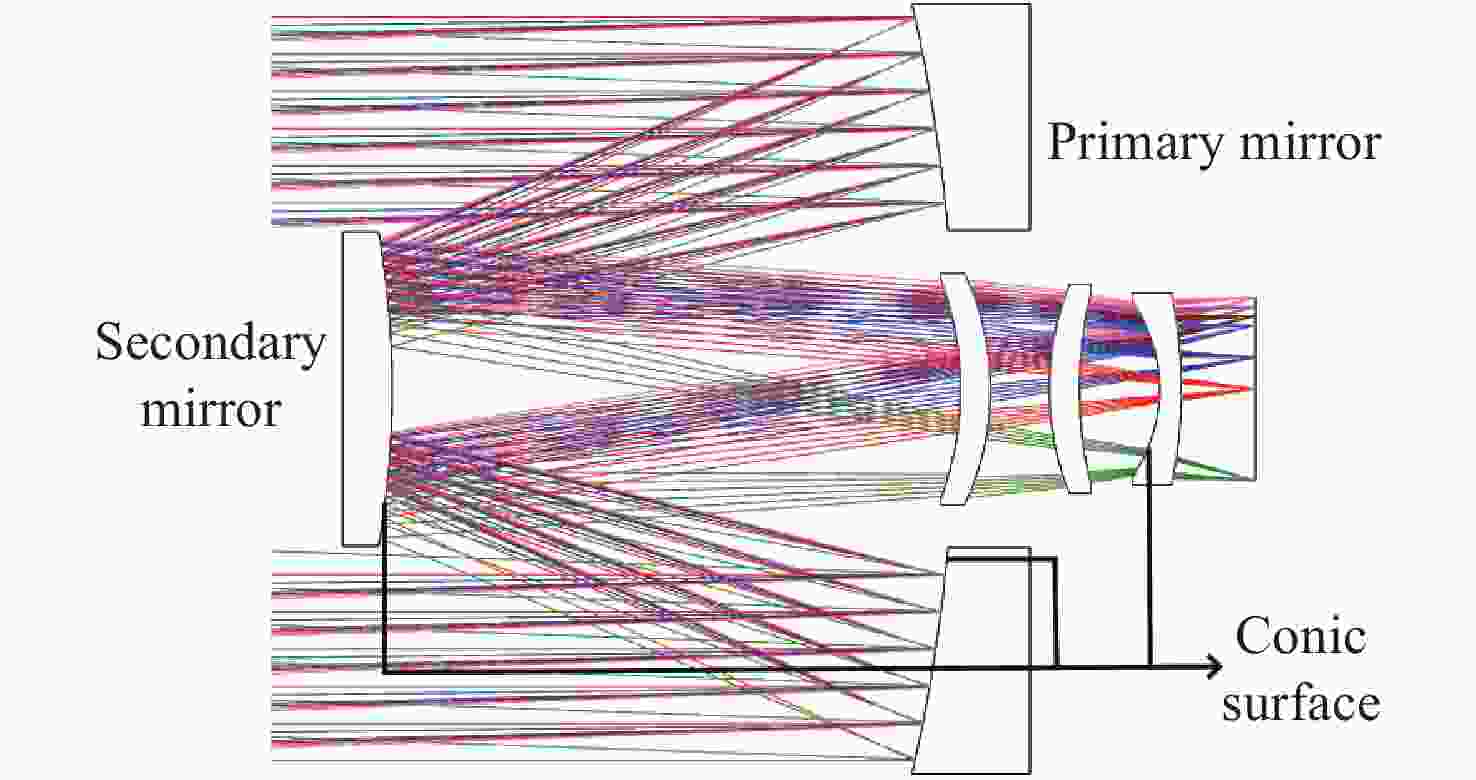
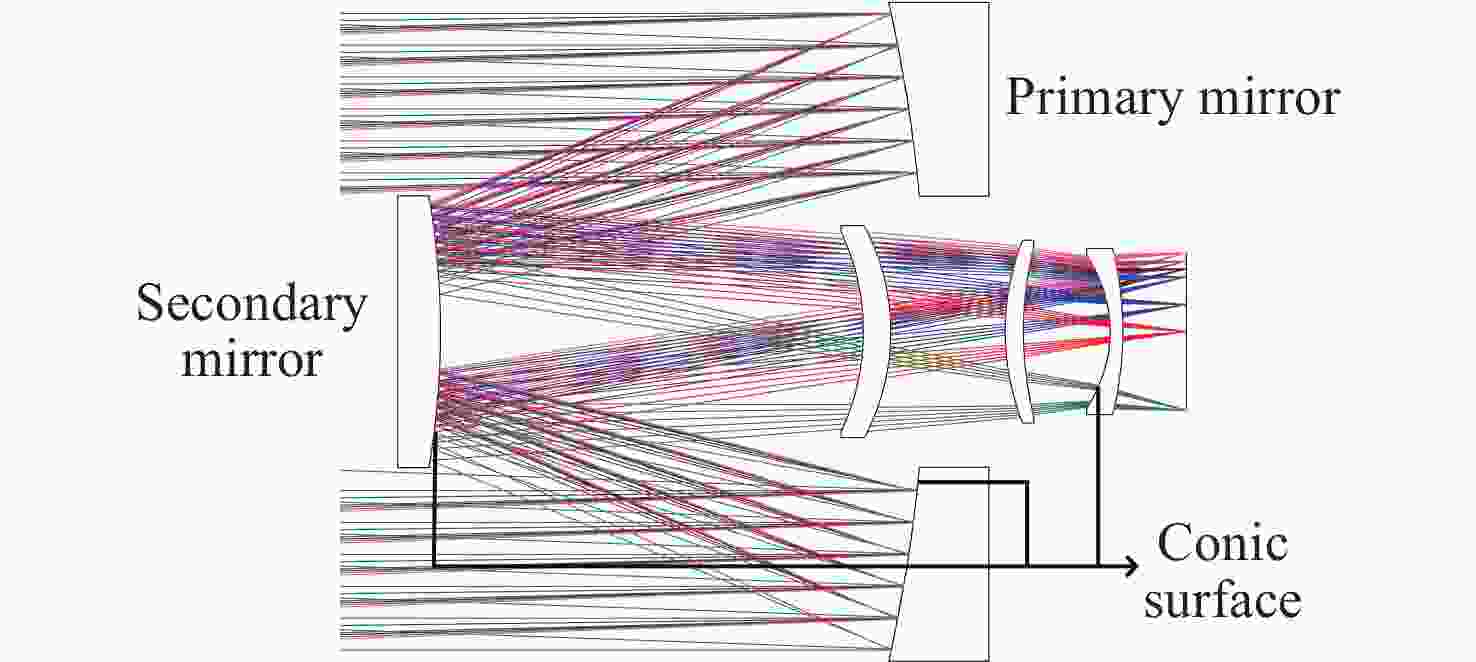
Table 3. Parameters of initial optical system configuration
Element Materials Coefficient of
thermal expansion
α(10−6/ °C)Radius
(mm)Constant of the
quadric surfaceThickness
(mm)Focal
(mm)Focal power
(mm−1)Paraxial ray
height
(mm)Primary mirror Silicon Carbide 2.5 −342.72 −1.18 −113.62 −171.36 − 0.00584 75 Secondary mirror Silicon Carbide 2.5 −174.08 −5.94 114.62 −87.04 − 0.01149 25.2725 Lens 1 Silica 0.5 −64.04 \ 6.06 735.35 0.00136 8.3877 Air \ −55.35 \ 11.86 Lens 2 Silica 0.5 57.48 \ 6.06 393.72 0.00254 6.2007 Air \ 81.82 \ 16.24 Lens 3 Silica 0.5 −28.65 −1.11 4.35 -92.14 - 0.01085 2.5471 Air \ −94.60 \ 15.00 表 4 优化后光学系统结构参数
Table 4. Parameters of optimized optical system configuration
Materials Radius/mm Constant of the
quadric surfaceThickness/mm Silicon Carbide −347.98 −1.20 −114.55 Silicon Carbide −181.49 −6.33 99.97 Silica −55.15 \ 6.42 Air −53.20 \ 27.02 Silica 58.42 \ 4.29 Air 83.45 \ 20.47 Silica −29.45 −1.11 3.00 Air −78.77 \ 15.00 表 5 各个温度下各个视场点列图的RMS直径
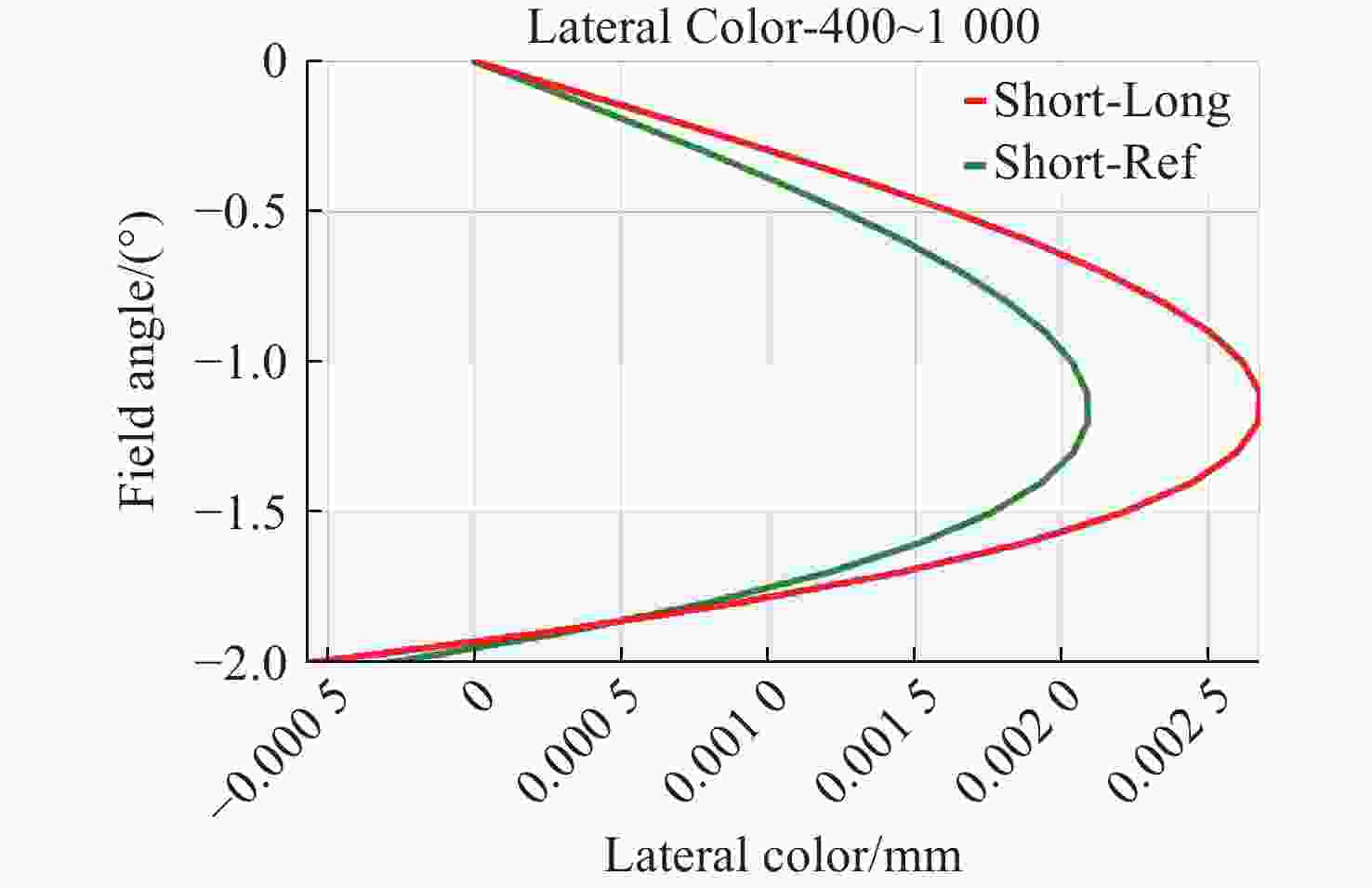
Table 5. RMS diameter of spot diagrams at various field points and temperatures
Temperatures/
°CRMS diameter /μm Field
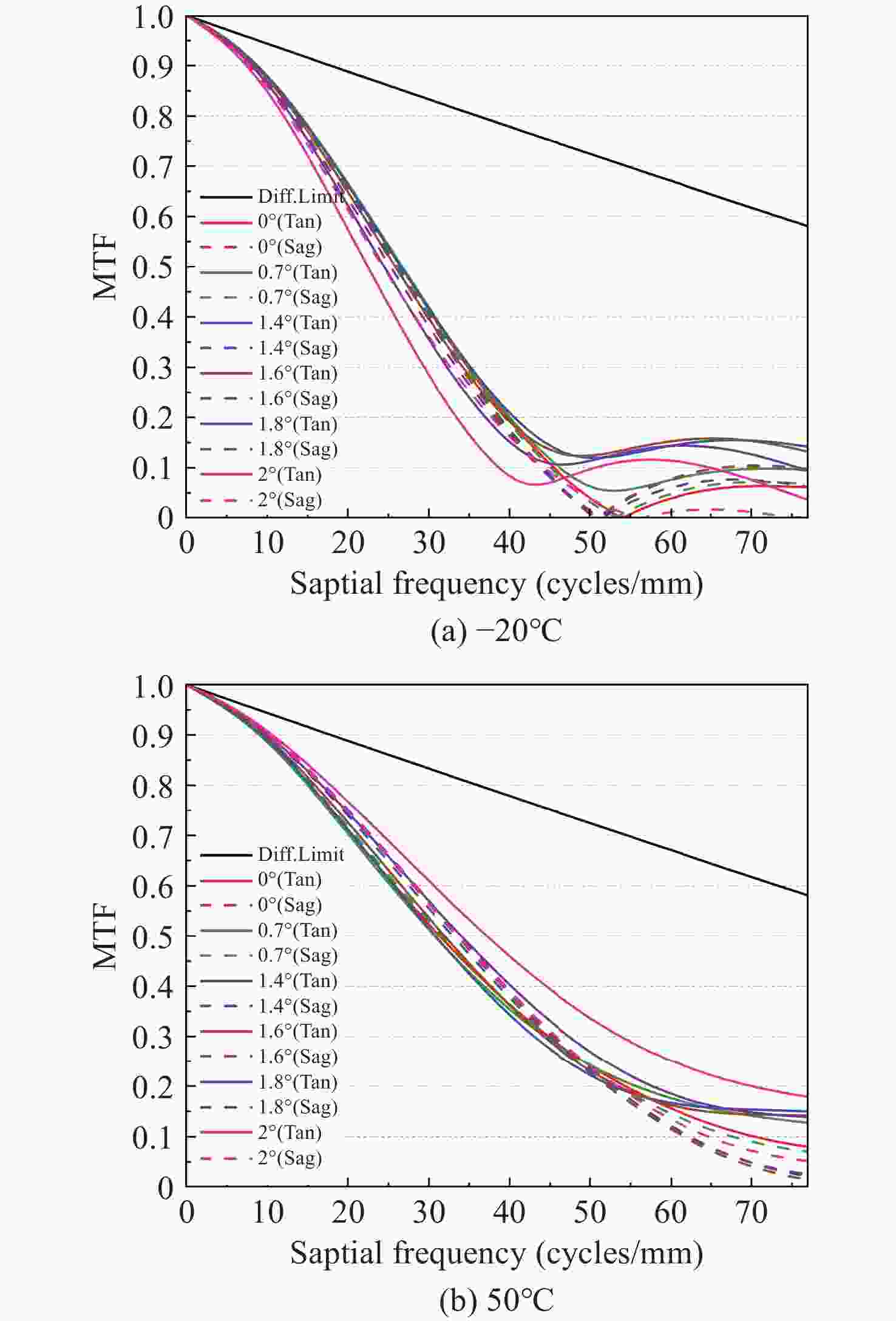
angle0° 0.7° 1.4° 1.6° 1.8° 2° −60 4.294 5.5 4.314 3.784 4.518 7.252 −20 4.592 5.782 4.558 3.868 4.242 6.82 20 4.9 6.08 4.846 4.032 4.044 6.428 50 5.136 6.31 5.084 4.202 3.95 6.164 100 5.538 6.706 5.522 4.56 3.912 5.788 150 5.948 7.116 5.996 4.994 4.018 5.504 表 6 对照组2各个温度下在奈奎斯特频率处的最低MTF值
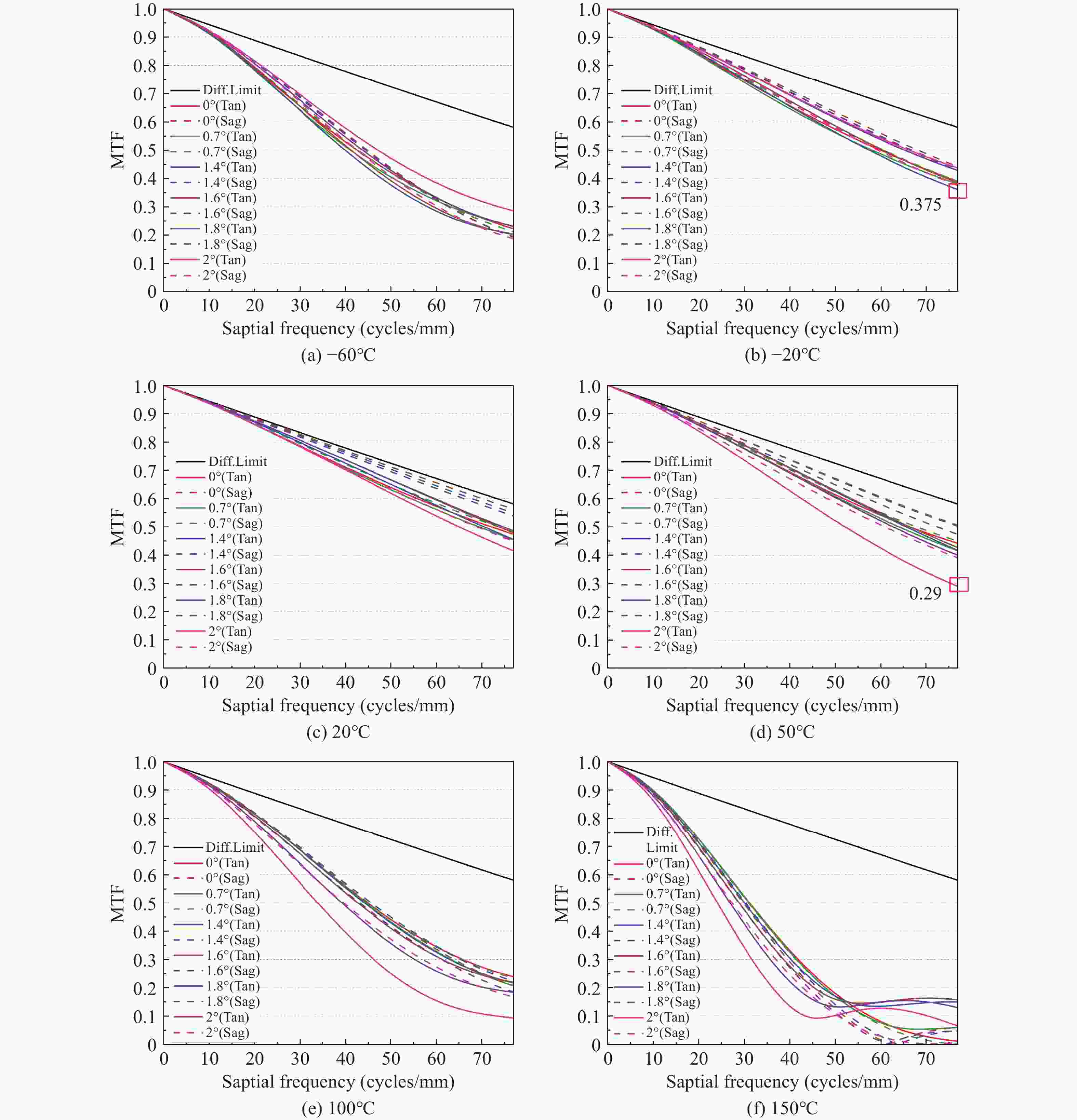
Table 6. The lowest MTF value at the nyquist frequency for each temperature in the control group 2
Temperatures/ °C −60 −20 20 50 100 150 The lowest MTF value 0.452 0.473 0.475 0.475 0.483 0.481 -
[1] 曹一青, 沈志娟. 长波红外大孔径长焦距无热化光学系统设计[J]. 光子学报,2024,53(3):0322004. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20245303.0322004CAO Y Q, SHEN ZH J. Design of long-wave infrared athermalized optical system with large aperture and long focal length[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2024, 53(3): 0322004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20245303.0322004 [2] PAN G T, LI B, GU G CH, et al. Analysis of the impact of temperature on the spectral shift in ultraviolet hyperspectral imaging spectrometers[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(7): 11774-11793. doi: 10.1364/OE.517945 [3] 张卓, 蔡猛. 双波段红外光学系统无热化设计[J]. 电光与控制,2015,22(5):63-67.ZHANG ZH, CAI M. Athermalization design of dual-wavelength infrared optical system[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2015, 22(5): 63-67. (in Chinese). [4] 孙宏宇. 紧凑型折/衍混合中波红外无热化成像光学系统[J]. 光电技术应用,2016,31(3):20-24.SUN H Y. Compact refractive and diffractive hybrid MWIR athermalizing optical imaging system[J]. Electro-Optic Technology Application, 2016, 31(3): 20-24. (in Chinese). [5] TAMAGAWA Y, WAKABAYASHI S, TAJIME T. New design method for athermalized optical systems[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1992, 1752: 232-238. doi: 10.1117/12.130734 [6] 胡玉禧, 周绍祥, 相里斌, 等. 消热差光学系统设计[J]. 光学学报,2000,20(10):1386-1391.HU Y X, ZHOU SH X, XIANG L B, et al. Design of athermal optical system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2000, 20(10): 1386-1391. (in Chinese). [7] LI R G. Passively athermalized broadband optical design using doublet combinations[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(18): 3903-3907. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.003903 [8] 解娜, 崔庆丰. 基于权重分组的可见光光学系统无热化设计[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(12):1222001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.1222001XIE N, CUI Q F. Athermalization design of visible light optical system based on grouping by weight[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(12): 1222001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.1222001 [9] XIE N, CUI Q F, SUN L, et al. Optical athermalization in the visible waveband using the 1+∑method[J]. Applied Optics, 2019, 58(3): 635-641. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.000635 [10] LI J, DING Y L, LIU X J, et al. Achromatic and athermal design of aerial catadioptric optical systems by efficient optimization of materials[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(4): 1754. doi: 10.3390/s23041754 [11] ZHANG X, FANG X, LI T, et al. Design method for eliminating spectral line tilt in a multiple sub-pupil ultra-spectral imager (MSPUI)[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(7): 11583-11599. doi: 10.1364/OE.514538 [12] ZHANG X, LI B, ZHI D D, et al. Stray light analysis and suppression of a UV multiple sub-pupil ultra-spectral imager[J]. Applied Optics, 2024, 63(23): 6112-6120. doi: 10.1364/AO.531177 [13] ZHANG L, LI B, LI H SH, et al. Method for designing a grid-slit spectrometer with low spectral-line bending[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2024, 183: 108514. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2024.108514 [14] 徐思华, 彭小强, 铁贵鹏, 等. 同质材料反射系统热特性研究[J]. 应用光学,2020,41(1):60-66. doi: 10.5768/JAO202041.0101009XU S H, PENG X Q, TIE G P, et al. Study on thermal characteristic of homogeneous material reflective system[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 41(1): 60-66. (in Chinese). doi: 10.5768/JAO202041.0101009 [15] LIM T Y, PARK S C. Achromatic and athermal lens design by redistributing the element powers on an athermal glass map[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(16): 18049. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.018049 [16] 孙景浩, 杨照华, 吴云, 等. 基于消色差透镜的单像素与计算关联光谱成像[J]. 光学 精密工程,2023,31(16):2333-2342. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20233116.2333SUN J H, YANG ZH H, WU Y, et al. A single-pixel and computational ghost spectral imaging system based on achromatic lens[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2023, 31(16): 2333-2342. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20233116.2333 [17] 张洪伟, 丁亚林, 马迎军, 等. 红外双波段双视场成像告警系统设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(6):1283-1294. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202806.1283ZHANG H W, DING Y L, MA Y J, et al. Design of infrared dual-band/dual-FOV imaging early warning system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(6): 1283-1294. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202806.1283 [18] 叶卉, 李晓峰, 崔壮壮, 等. 熔石英玻璃高效低缺陷磁辅助抛光[J]. 光学 精密工程,2022,30(15):1857-1867. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223015.1857YE H, LI X F, CUI ZH ZH, et al. Magnetic-assisted polishing of fused silica optics with high efficiency and low defects[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(15): 1857-1867. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223015.1857 [19] 李寒霜, 李博, 李昊晨, 等. 基于一种透镜材料的宽谱段紫外成像仪光学设计[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(1):65-71. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0127LI H SH, LI B, LI H CH, et al. Optical design of a wide spectrum UV imager based on a lens material[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(1): 65-71. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0127 [20] 叶井飞, 朱润徽, 马梦聪, 等. 紫外宽光谱大相对孔径光学系统设计[J]. 应用光学,2021,42(5):761-766. doi: 10.5768/JAO202142.0501001YE J F, ZHU R H, MA M C, et al. Design of UV optical system with wide ultraviolet spectrum and large relative aperture[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 42(5): 761-766. doi: 10.5768/JAO202142.0501001 [21] FAN J Z, WANG Y W, GU G CH, et al. Development of an imaging spectrometer with a high signal-to-noise ratio based on high energy transmission efficiency for soil organic matter detection[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(13): 4385. doi: 10.3390/s24134385 -





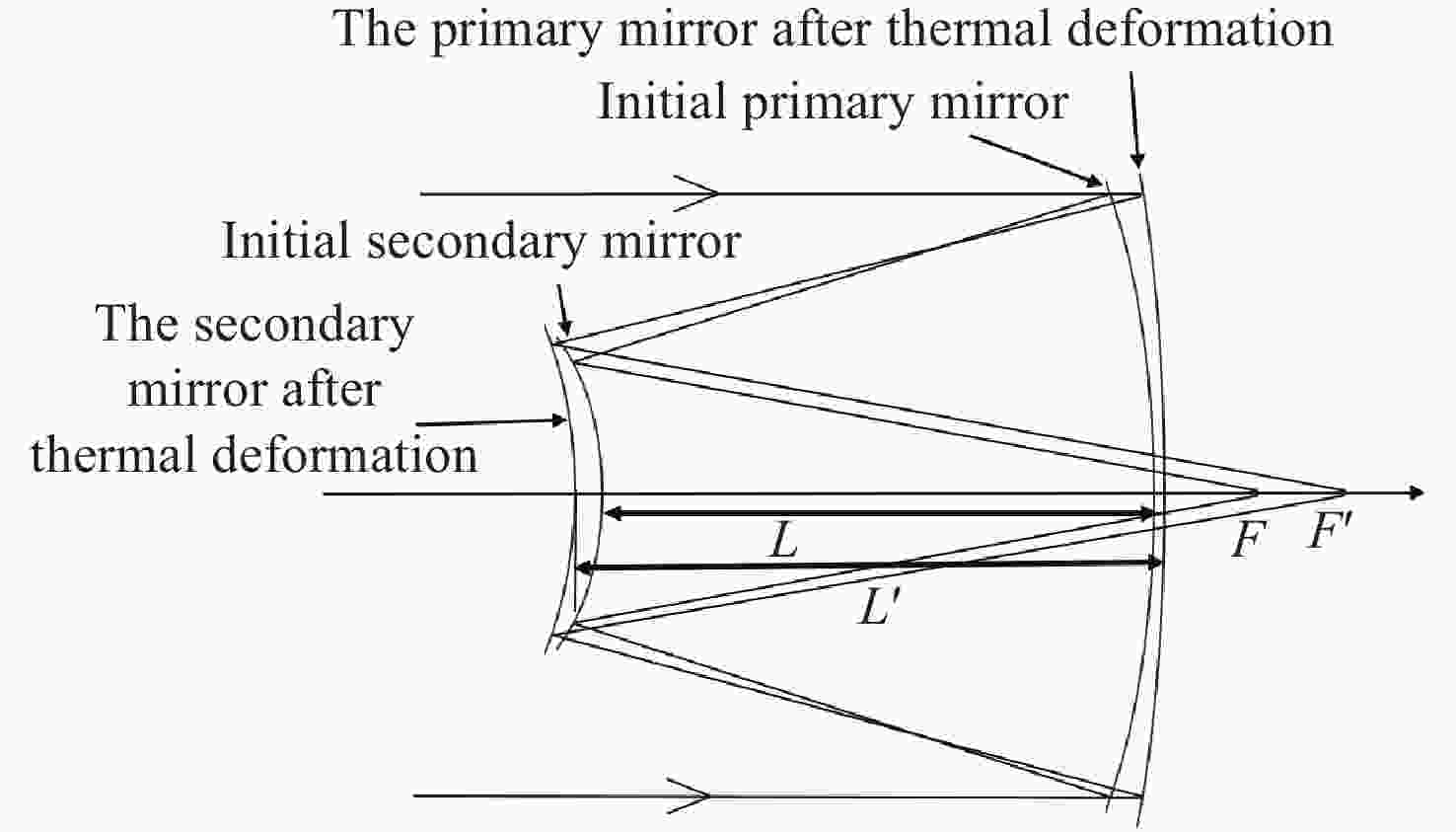
 下载:
下载: