-
摘要:
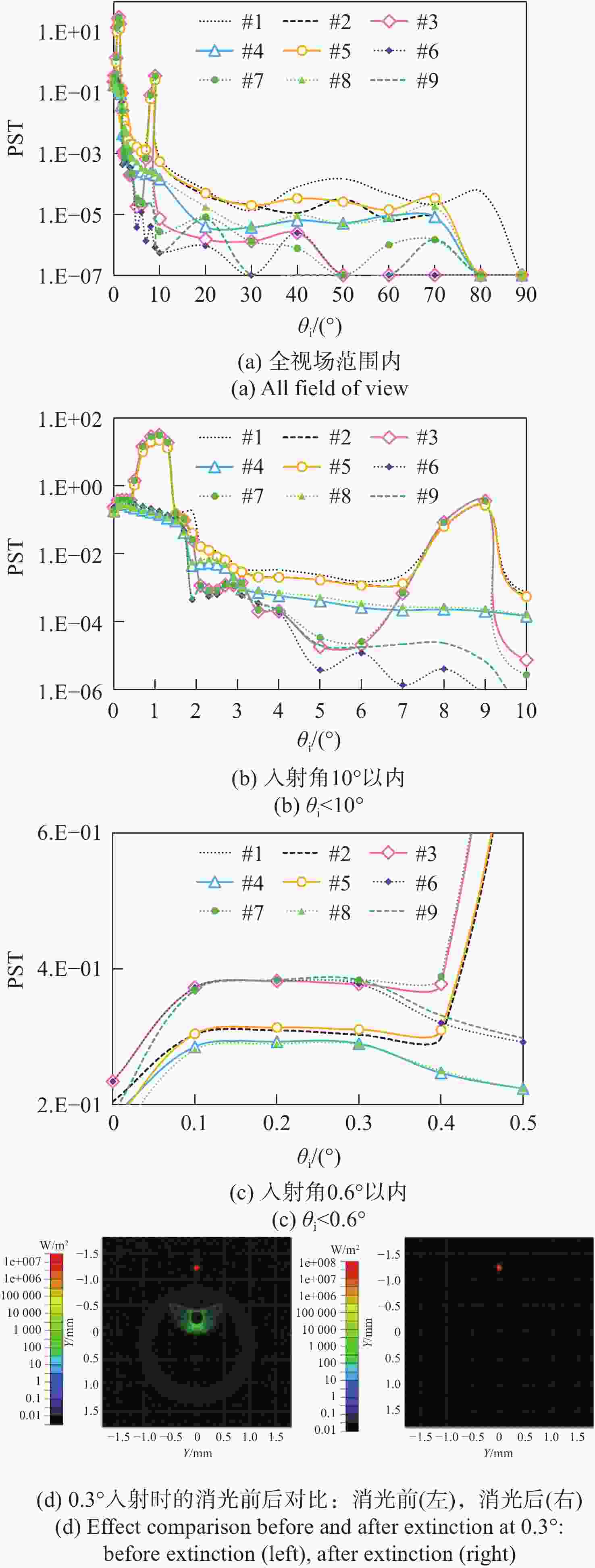
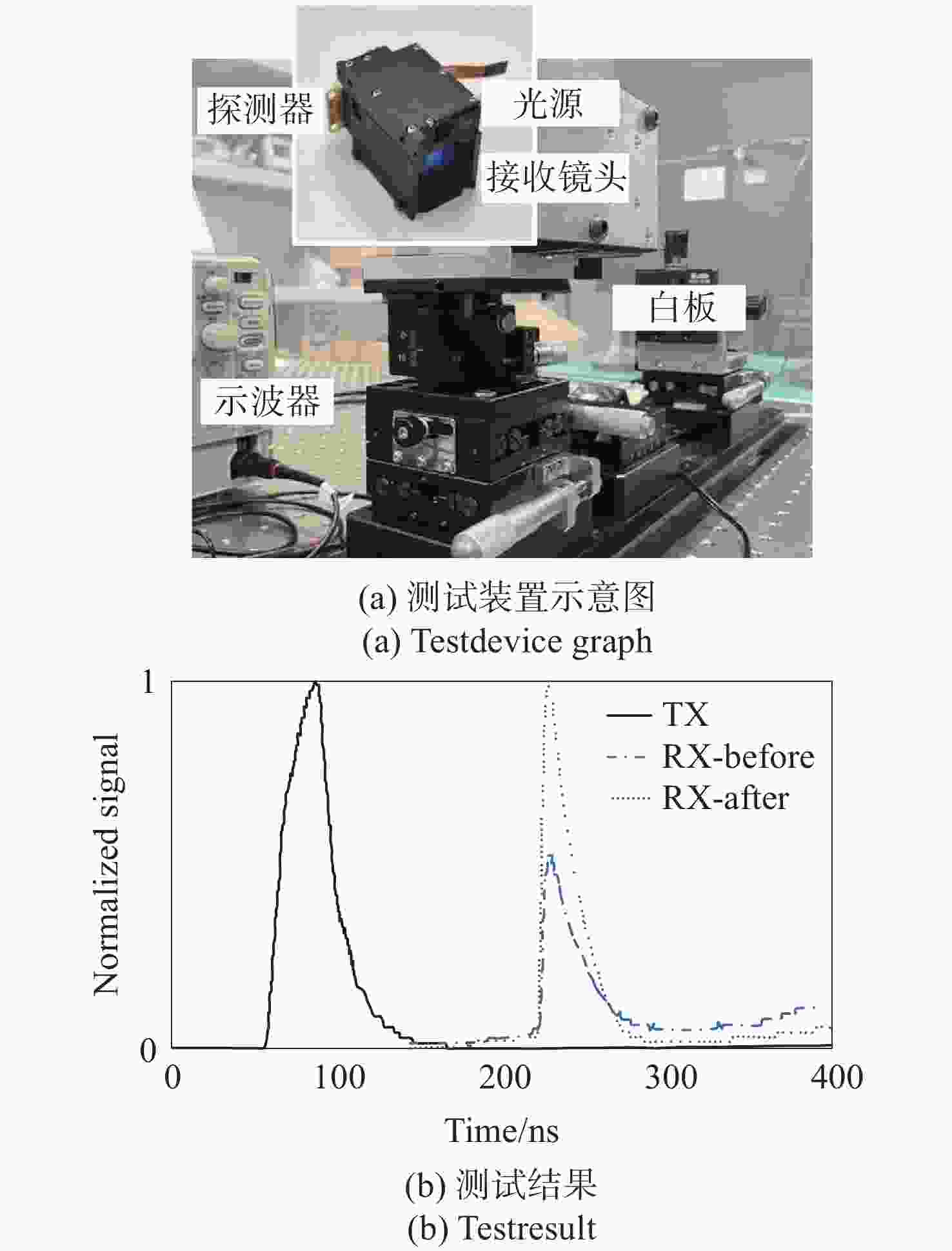
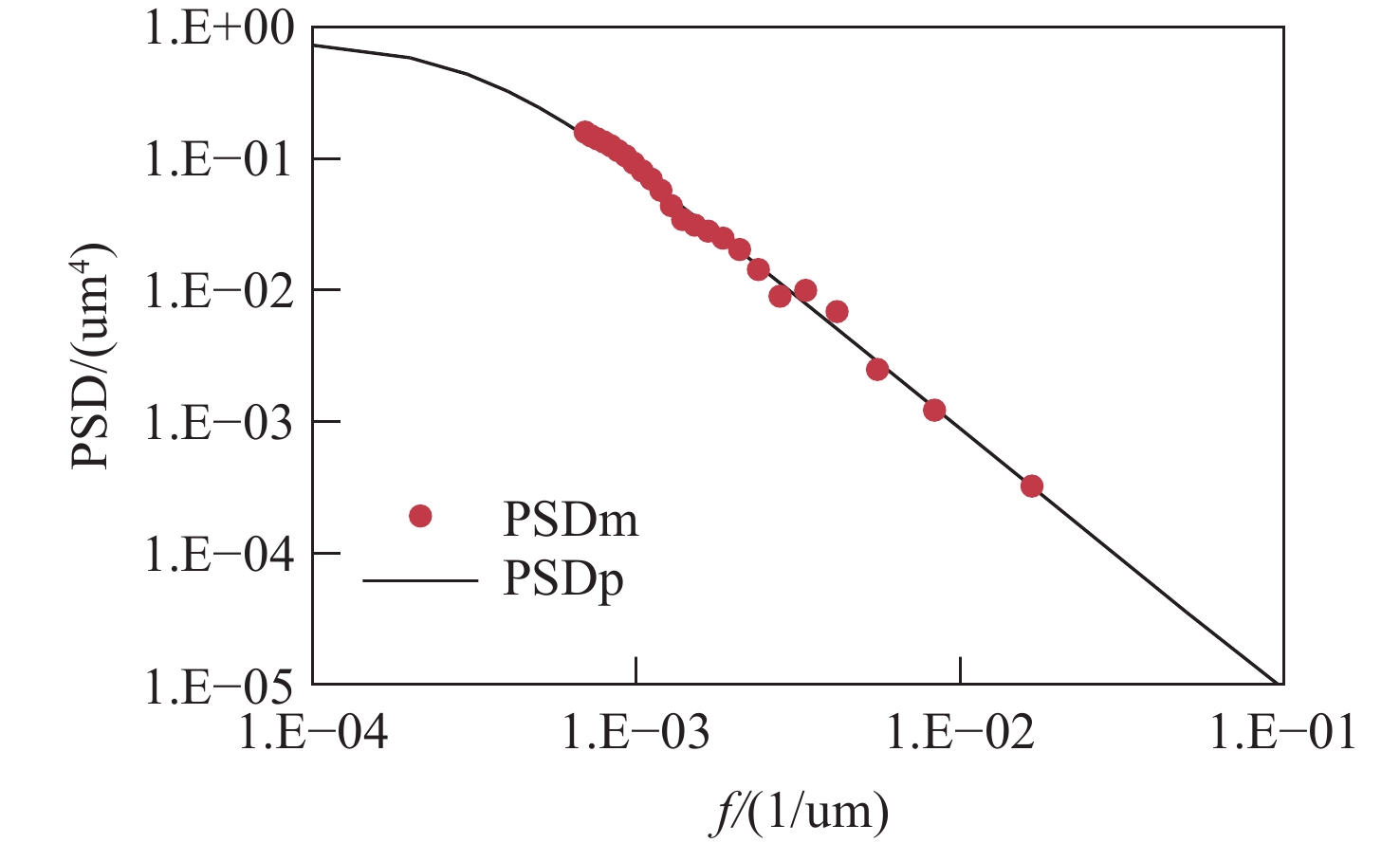
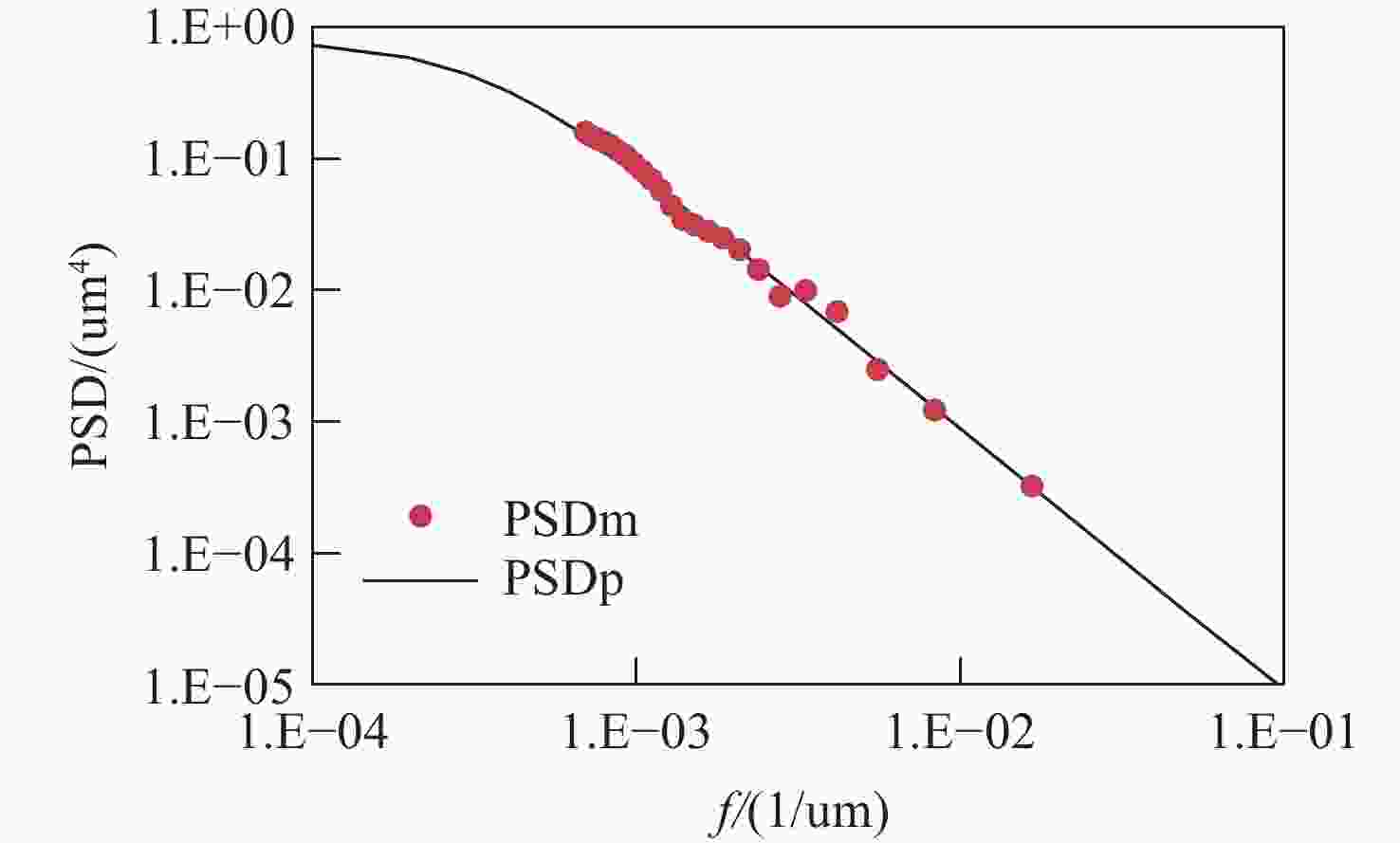
车载激光雷达受杂散光干扰会导致信噪比降低和探测效率下降。因此,本文提出了一种基于光谱功率密度函数和总积分散射的表面散射建模方法,拟合了不同材料表面的双向反射分布函数(BRDF)。模型计算结果与实测BRDF数据高度吻合,验证了该方法的有效性。基于此模型,本文系统分析了车载激光雷达长焦接收镜头的杂散光来源及传播路径,包括机盒内壁、镜片边缘、隔圈表面散射等。根据仿真结果,本文提出了多项杂光抑制措施,如采用低散射材料结构件、镜片表面镀增透膜、透镜非工作区涂覆消光油墨等,并且从光学设计、信号处理及工程优化等多维度评估了该激光雷达接收光学系统的杂光抑制水平。实验结果显示,优化后系统杂散辐射水平显著降低:成像视场外的点源透过率(PST)从1e+0降至1e-5,视场内PST从1e+2降至1e-1,杂散光与目标信号对比度控制在10e-4以下。此外,探测回波信号强度提升显著,有效提高了激光雷达的探测性能。本研究为车载激光雷达的杂散光抑制提供了理论模型和实用解决方案,对高灵敏度光学系统的设计与优化具有一定的参考价值。
Abstract:Stray light interference in vehicular LiDAR systems can reduce the signal-to-noise ratio and degrade detection efficiency. To mitigate this issue, this paper proposed a surface scattering modeling method based on the spectral power density function and total integrated scattering, which fits the bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) for various material surfaces. The model calculation results were highly consistent with the measured BRDF data, verifying the effectiveness of the method. Based on this model, the study systematically analyzed the sources and propagation paths of stray light in the long-focal-length receiving optics of vehicular LiDAR, with specific attention to scattering from the housing's inner walls, lens edges, and spacer ring surfaces. According to the simulation results, this paper put forward a number of stray light suppression measures, such as using structural components made of low-scattering materials, coating anti-reflection films on lens surfaces, and applying light-absorbing ink to the non-optical areas of lenses, etc. Furthermore, from optical design, signal processing and engineering optimization, the stray light suppression level of this LiDAR receiving optical system was evaluated in multiple dimensions. The results of the experiment showed that the level of stray radiation in the optimized system was significantly reduced: the point source transmittance (PST) outside the imaging field of view was reduced from 1e+0 to 1e-5, the PST in the field of view was reduced from 1e+2 to 1e-1, and the stray light contrast with the target signal was controlled below 10e-4. Additionally, the intensity of the detected echo signal is significantly improved, thereby effectively enhancing the detection performance of the LiDAR. This study provides a theoretical model and practical solutions for stray light suppression in vehicle-mounted LiDAR, offering valuable references for the design and optimization of high-sensitivity optical systems.
-
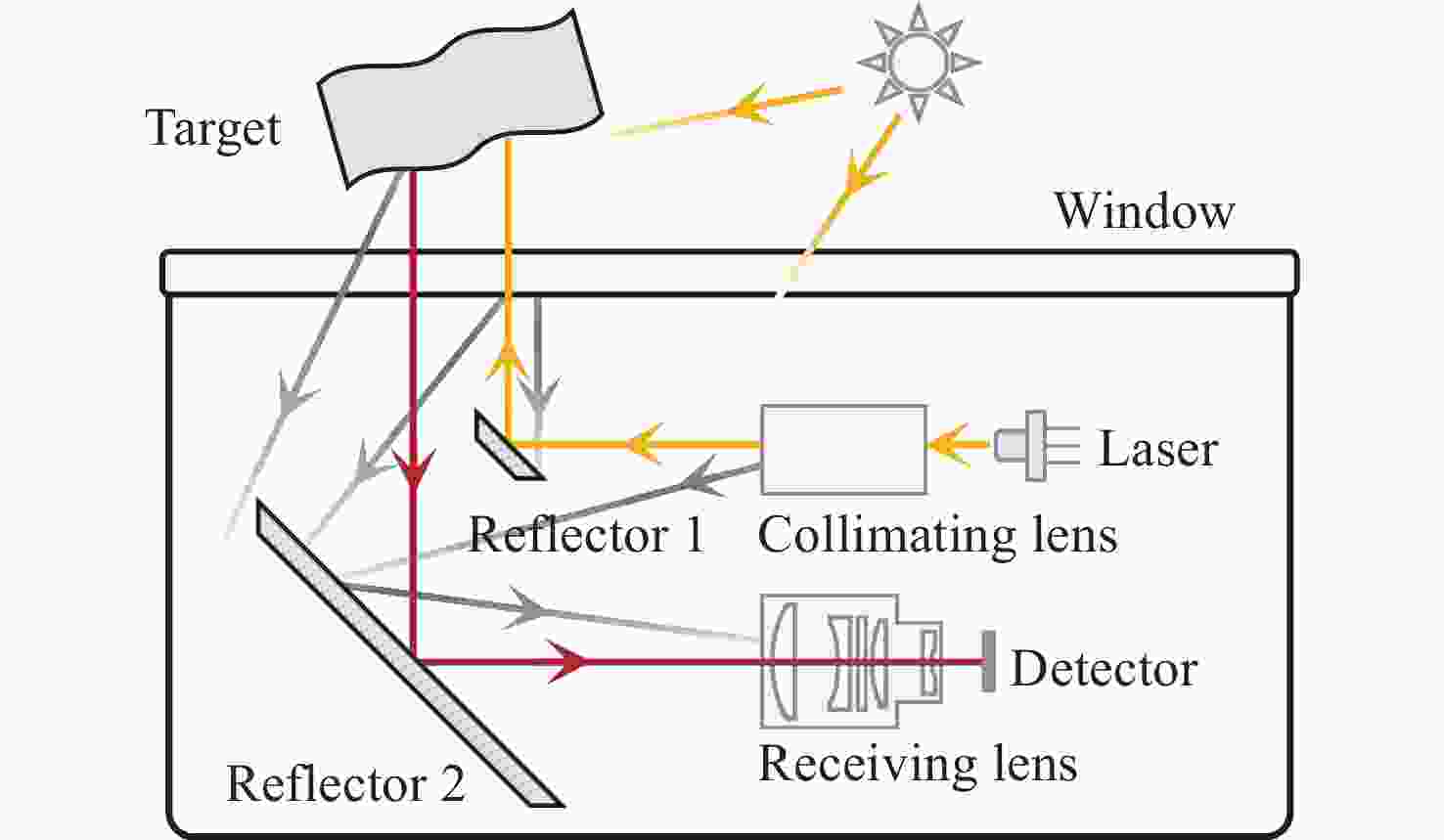
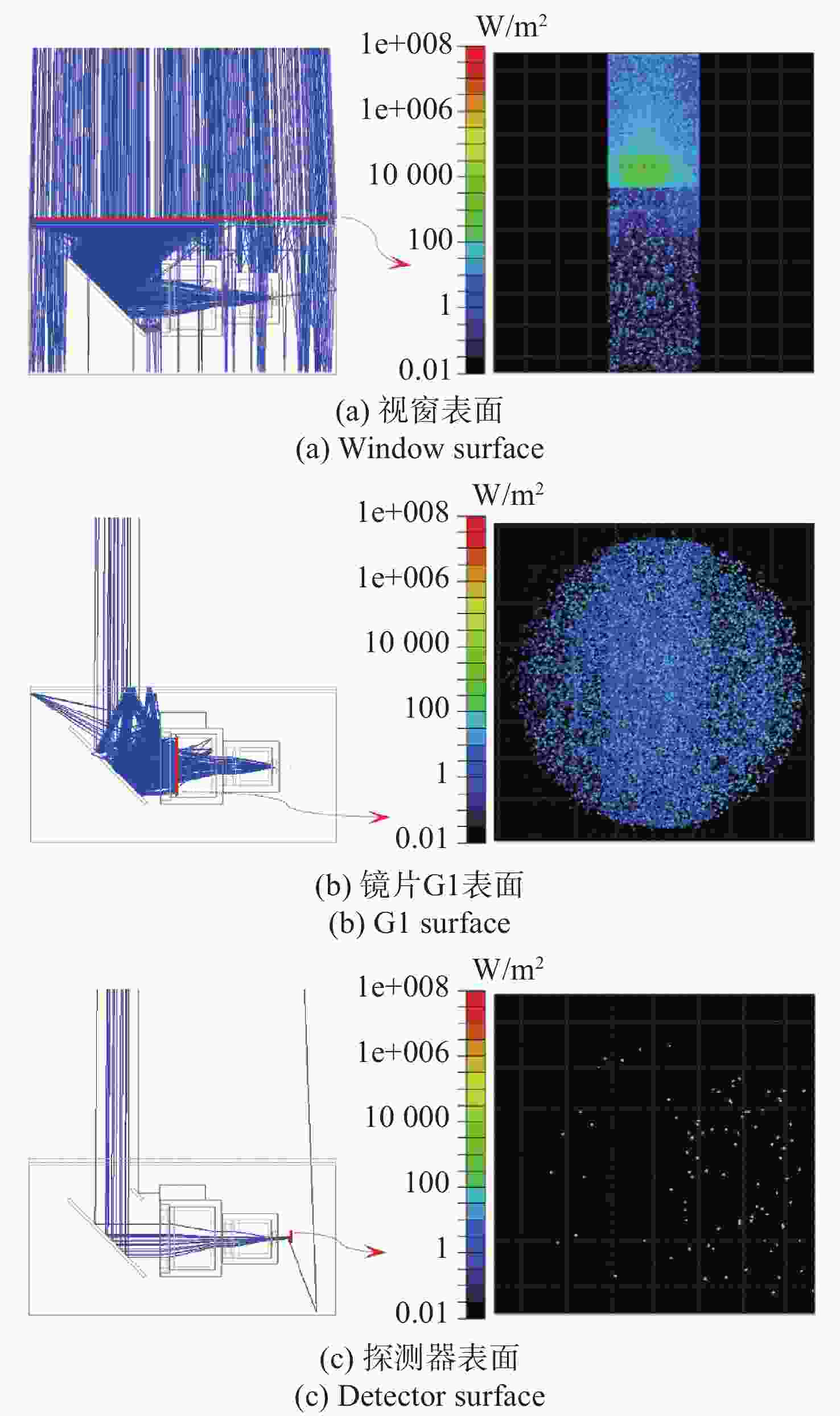
表 1 机盒内主要光线路径
Table 1. Primary ray propagation paths within housing
序号 光线路径 入射光通量与
光源之比/%在其接收面的
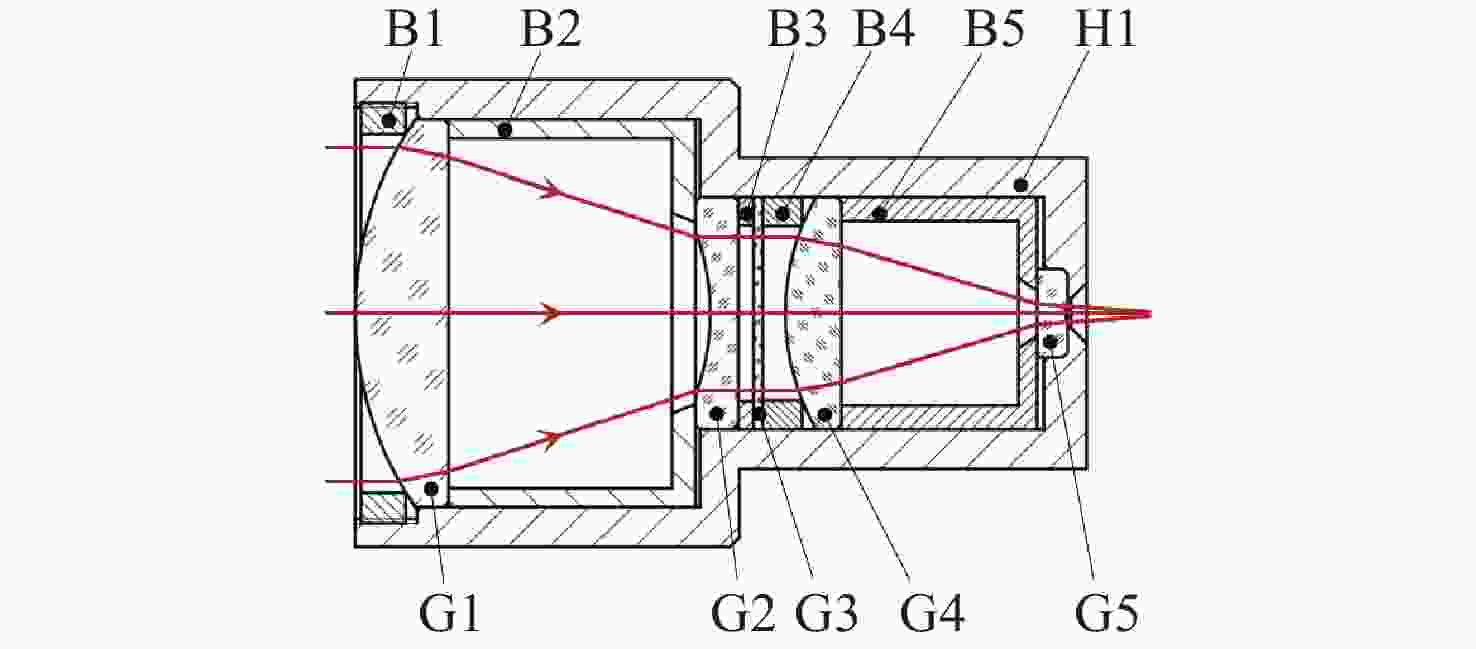
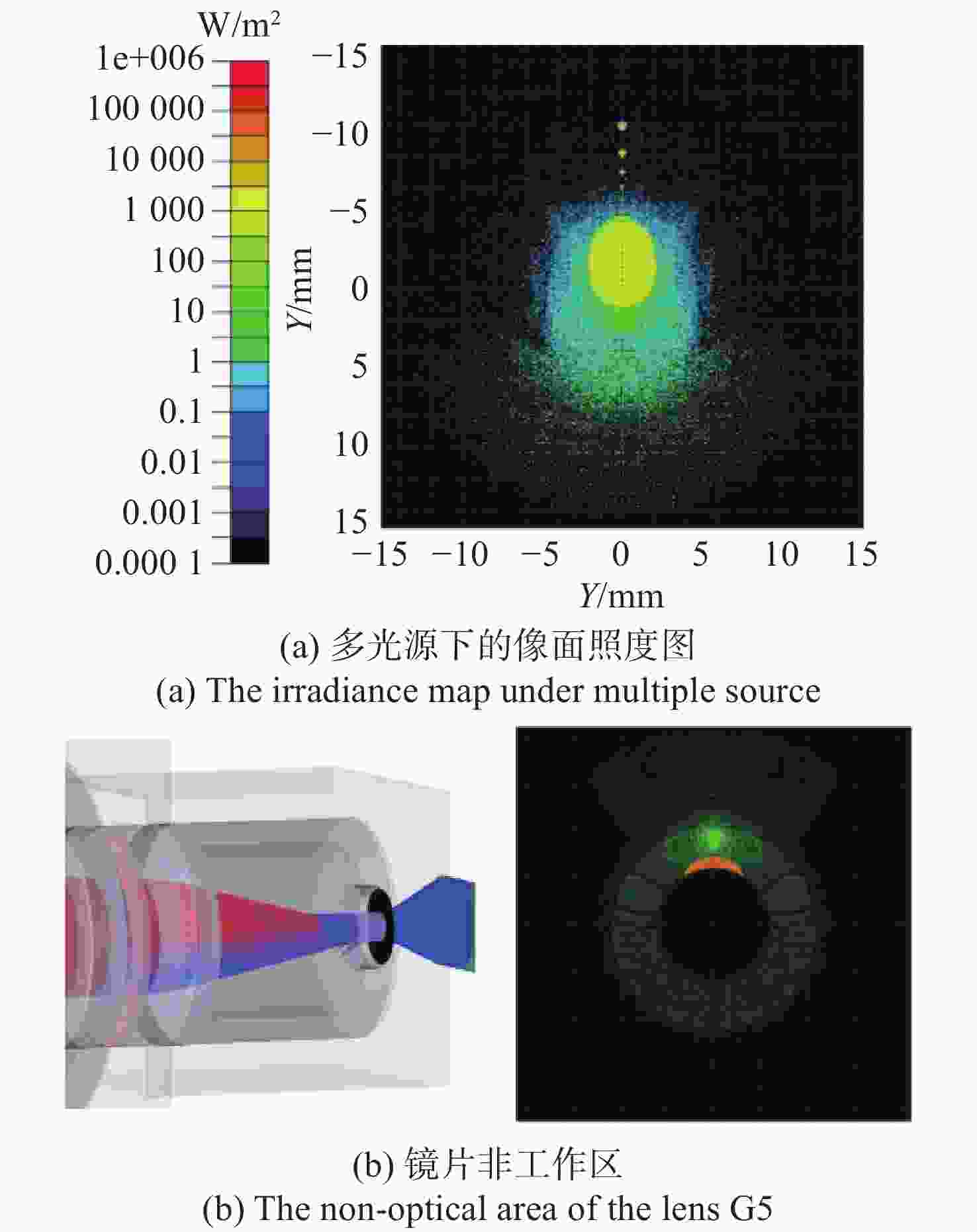
占比/%光线数/根 1 光源-反射镜1-视窗 94.9240 98.90 119401 2 光源-反射镜1-视窗-目标-视窗 0.0426 0.01 1129 3 光源-反射镜1-视窗-目标-视窗-反射镜2-G1 0.0035 29.75 107 4 光源-反射镜1-视窗-反射镜1-光源-反射镜2-G1 0.0027 22.54 1326 5 光源-反射镜1-视窗内部反射-反射镜1-光源-反射镜2-G1 0.0024 20.56 1342 6 光源-反射镜1-视窗-目标-视窗-反射镜2-G1-G2-G3-G4-G5-探测器 0.0019 86.44 77 7 光源-反射镜1-视窗-目标-视窗-反射镜2-G1-G2-G3-G4-G5非工作区-探测器 0.0003 13.47 12 表 2 镜头内主要光线路径
Table 2. Dominant optical paths through lens system
序号 光线路径 入射光通量与光源之比/% 在接收面的占比/% 光线数/根 1 目标-G1-G2-G3-G4-G5-探测器 11.3395 68.3153 17924 2 目标-G1-G2-G3-G4-G5非工作区-探测器 3.9552 23.8282 6252 3 目标-G1-G2-G3-G4-B5-G5-探测器 0.0602 0.3627 1910 4 目标-G1-G2非工作区-G3-G4-G5非工作区-探测器 0.0112 0.0673 18 5 目标-G1-G2非工作区-G3-G4-G5-探测器 0.0099 0.0599 16 6 目标-G1-G2-G3S1-G2S2-G3-G4-G5-探测器 0.0077 0.0464 16535 7 目标-G1-G2-G3-G4-G5非工作区-H1-探测器 0.0075 0.0450 236 8 目标-G1-G2-G3内部反射一次-G4-G5-探测器 0.0074 0.0448 15974 9 目标-G1-G2-G3S2-G2S2-G3-G4-G5-探测器 0.0069 0.0417 15792 表 3 分析与抑制方案设计
Table 3. Design of analysis and inhibition protocol
方案
序号结构件表面 光学件表面 其它 黑漆 黑漆喷涂 普通镀膜 增透膜 镜片非工作区
涂墨消光螺纹 #1 √ - √ - - - #2 - √ √ - - - #3 - √ - √ - - #4 - √ √ - √ - #5 - √ √ - - √ #6 - √ - √ √ - #7 - √ - √ - √ #8 - √ √ - √ √ #9 - √ - √ √ √ -
[1] HE Y X, WANG Q, HAN X, et al. Integrated solid-state lidar employing orthogonal polarizations and counterpropagation [Invited][J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2024, 22(9): 090011. doi: 10.3788/COL202422.090011 [2] YANG L, NIU H Q, WU SH X, et al. Single-photon frequency-modulated continuous-wave Lidar based on quantum compressed sensing[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2024, 22(7): 072602. doi: 10.3788/COL202422.072602 [3] 肖鹏益, 刘铭鑫, 闫磊, 等. 鬼像影响下的调制传递函数计算模型[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(5):1183-1191.XIAO P Y, LIU M X, YAN L, et al. An MTF calculation model under the influence of ghost images[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(5): 1183-1191. (in Chinese). [4] 马博伦, 田爱玲, 王红军, 等. 卫星光通信系统中金属结构件的表面散射特性研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2023,60(1):0106006.MA B L, TIAN A L, WANG H J, et al. Research of surface scattering characteristics of metal structures in satellite optical communication system[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(1): 0106006. (in Chinese). [5] 冷荣宽, 王上, 王智, 等. 空间引力波探测前向杂散光测量和抑制[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(5):1081-1088. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0251LENG R K, WANG SH, WANG ZH, et al. Measurement and suppression of forward stray light for spaceborne gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 1081-1088. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0251 [6] 孙红胜, 梁新刚, 马维刚, 等. 空间探测用真空紫外光谱辐射计的校准[J]. 光学 精密工程,2022,30(7):765-772. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223007.0765SUN H SH, LIANG X G, MA W G, et al. Calibration of VUV spectroradiometers for space exploration[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(7): 765-772. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223007.0765 [7] 王虎, 陈钦芳, 马占鹏, 等. 杂散光抑制与评估技术发展与展望(特邀)[J]. 光子学报,2022,51(7):0751406. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20225107.0751406WANG H, CHEN Q F, MA ZH P, et al. Development and prospect of stray light suppression and evaluation technology (Invited)[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2022, 51(7): 0751406. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20225107.0751406 [8] MA ZH P, HANSEN P E, WANG H, et al. Harvey-Shack theory for a converging-diverging Gaussian beam[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2023, 40(5): 1162-1169. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.478801 [9] 沈正祥, 余俊, 王晓强, 等. 面向激光探测的精密光机系统研制及应用[J]. 光学 精密工程,2022,30(21):2737-2751. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223021.2737SHEN ZH X, YU J, WANG X Q, et al. Development and application of precision optical system for laser detection[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(21): 2737-2751. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223021.2737 [10] GÜNÖVEN M, NASSER H, ÜNAL M, et al. Implementation of generalized Harvey-Shack theory in light scattering from rough surfaces[J]. Physical Review A, 2020, 102(6): 063521. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.102.063521 [11] 张丽芝, 陆秋萍, 段帆琳, 等. 长焦镜头光学系统设计及无热化研究[J]. 光学学报,2024,44(8):0822004. doi: 10.3788/AOS231926ZHANG L ZH, LU Q P, DUAN F L, et al. Optical system design and athermalization of telephoto lens[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2024, 44(8): 0822004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS231926 [12] FEST E C. Stray Light Analysis and Control[M]. Bellingham: SPIE Press, 2013. [13] ZENG CH L, XIA G Q, ZHONG X, et al. Fast stray light performance evaluation based on BSDF and radiative transfer theory[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(22): 9182. doi: 10.3390/s23229182 [14] DURY M R, THEOCHAROUS T, HARRISON N, et al. Common black coatings-reflectance and ageing characteristics in the 0.32-14.3 μm wavelength range[J]. Optics Communications, 2007, 270(2): 262-272. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2006.08.038 [15] 徐亮. 大口径光学系统杂散光测试关键技术研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所), 2019.XU L. Research on key technologies of stray light measurement for large aperture optical system[D]. Xi’an: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Xi’an Institute of Optics & Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2019. (in Chinese). [16] BUTLER S D, NAUYOKS S E, MARCINIAK M A. Comparison of microfacet BRDF model to modified Beckmann-Kirchhoff BRDF model for rough and smooth surfaces[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(22): 29100-29112. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.029100 [17] 宋延松, 杨建峰, 李福, 等. 基于杂散光抑制要求的光学表面粗糙度控制方法研究[J]. 物理学报,2017,66(19):194201. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.194201SONG Y S, YANG J F, LI F, et al. Method of controlling optical surface roughness based on stray light requirements[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(19): 194201. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.66.194201 [18] 张运方, 朱飞虎, 郑岩, 等. 小行星地形探测激光雷达接收光学系统设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2025,33(4):521-531. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20253304.0521ZHANG Y F, ZHU F H, ZHENG Y, et al. Design of receiving optical system for asteroid terrain detection LiDAR[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2025, 33(4): 521-531. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20253304.0521 [19] 周星宇, 孙亮, 潘俏, 等. 大相对孔径激光测距接收光学系统及杂散光抑制[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2024,61(5):0528001.ZHOU X Y, SUN L, PAN Q, et al. Large relative aperture receiving optical system and stray light suppression for laser ranging[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(5): 0528001. (in Chinese). [20] 梅超. 大口径多光谱变焦光学系统杂散光分析与抑制技术研究[D]. 中国科学院大学(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所), 2014.MEI CH. The study of stray light analysis and suppressing technology in large pupil mulit-spectal zoom optical system[D]. Xi’an: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Xi’an Institute of Optics & Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2014. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: