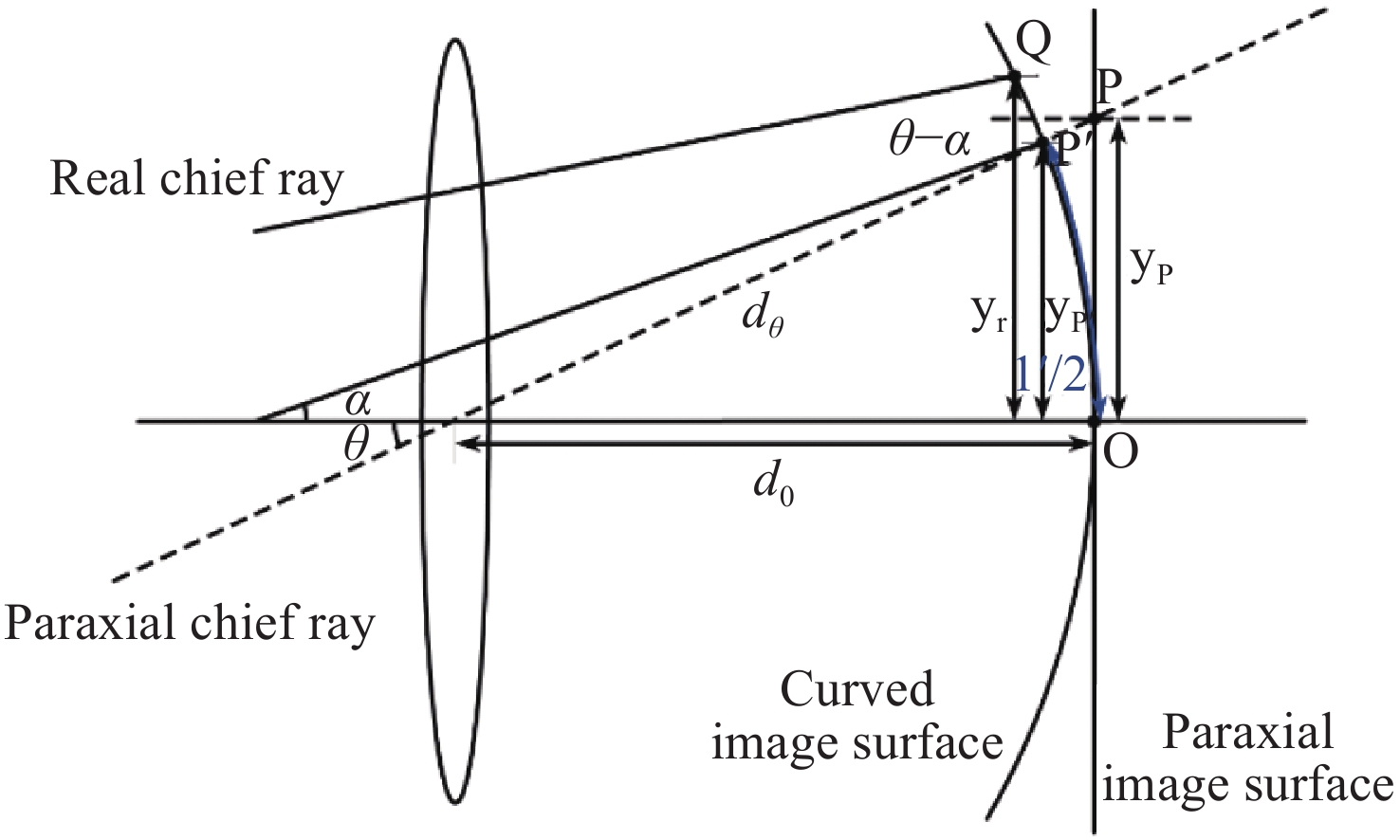
-
摘要:
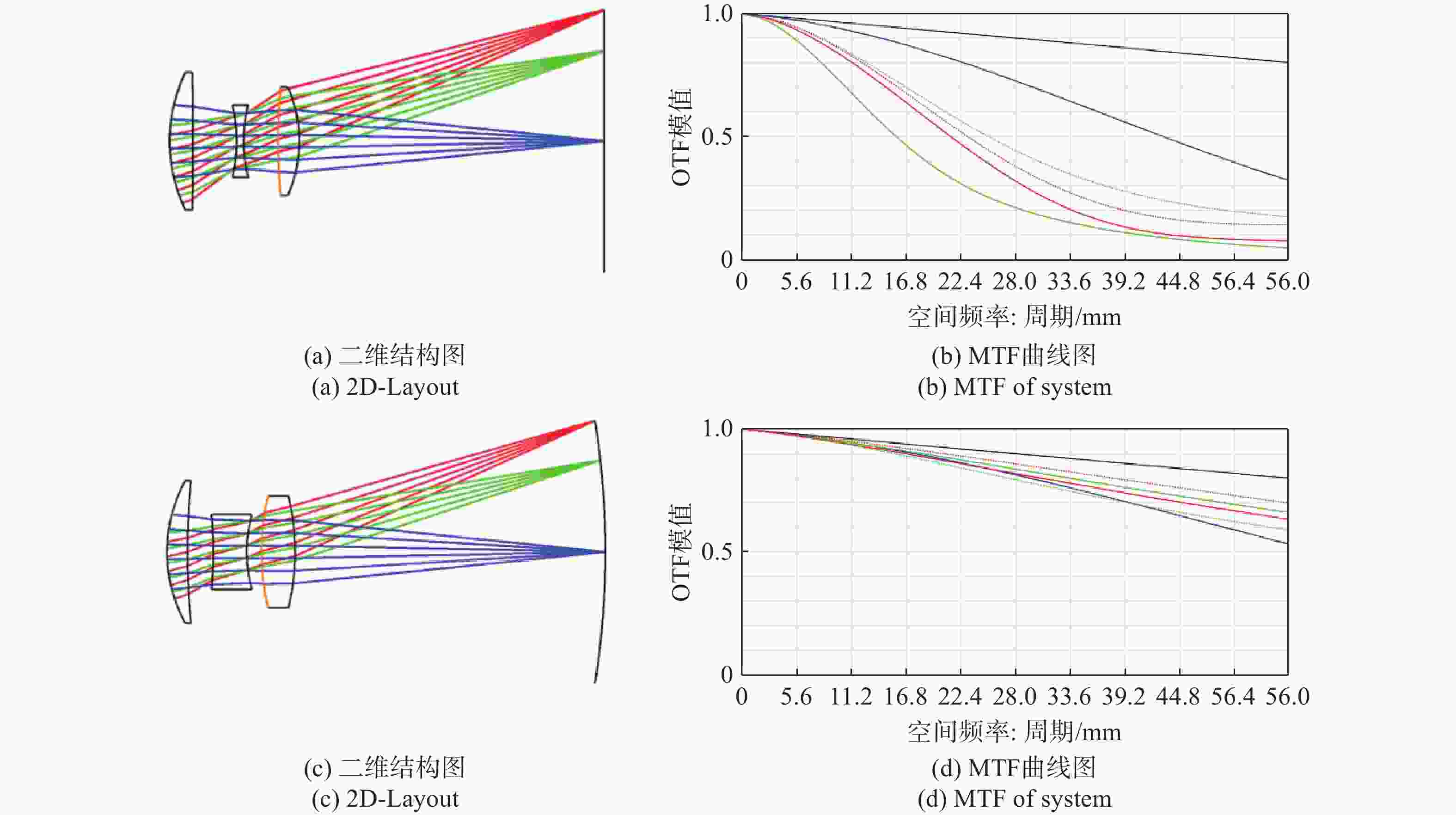
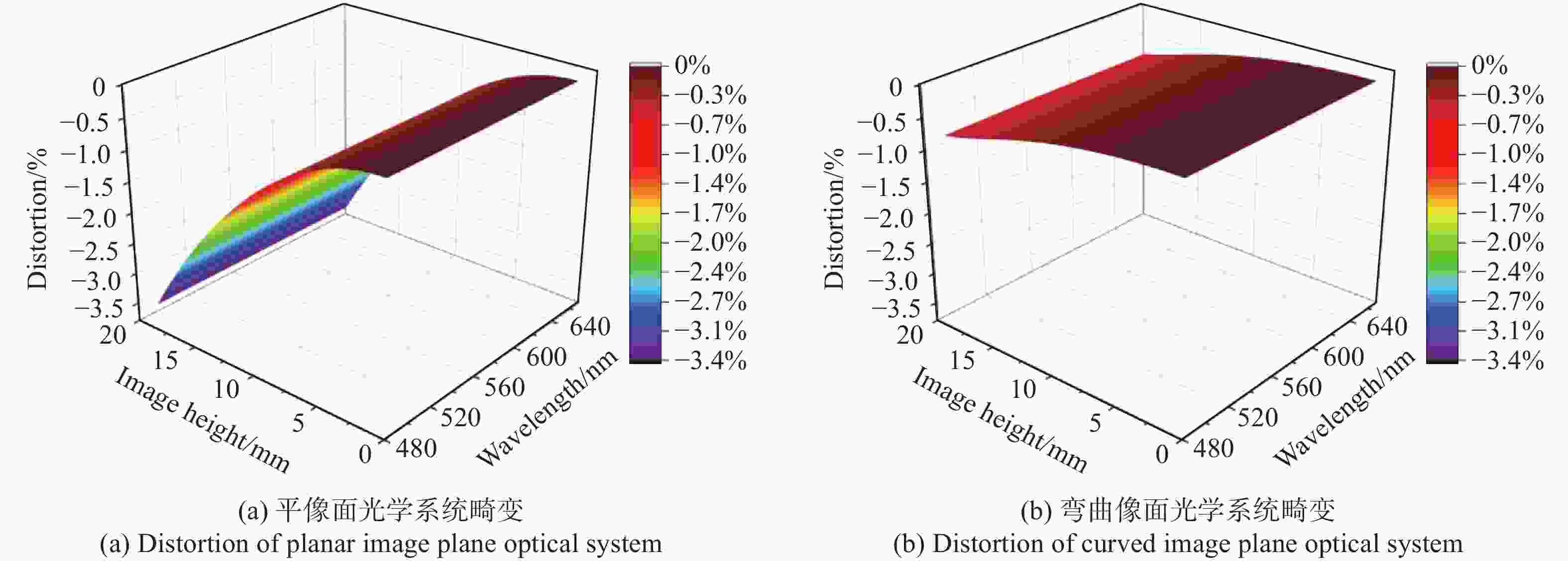
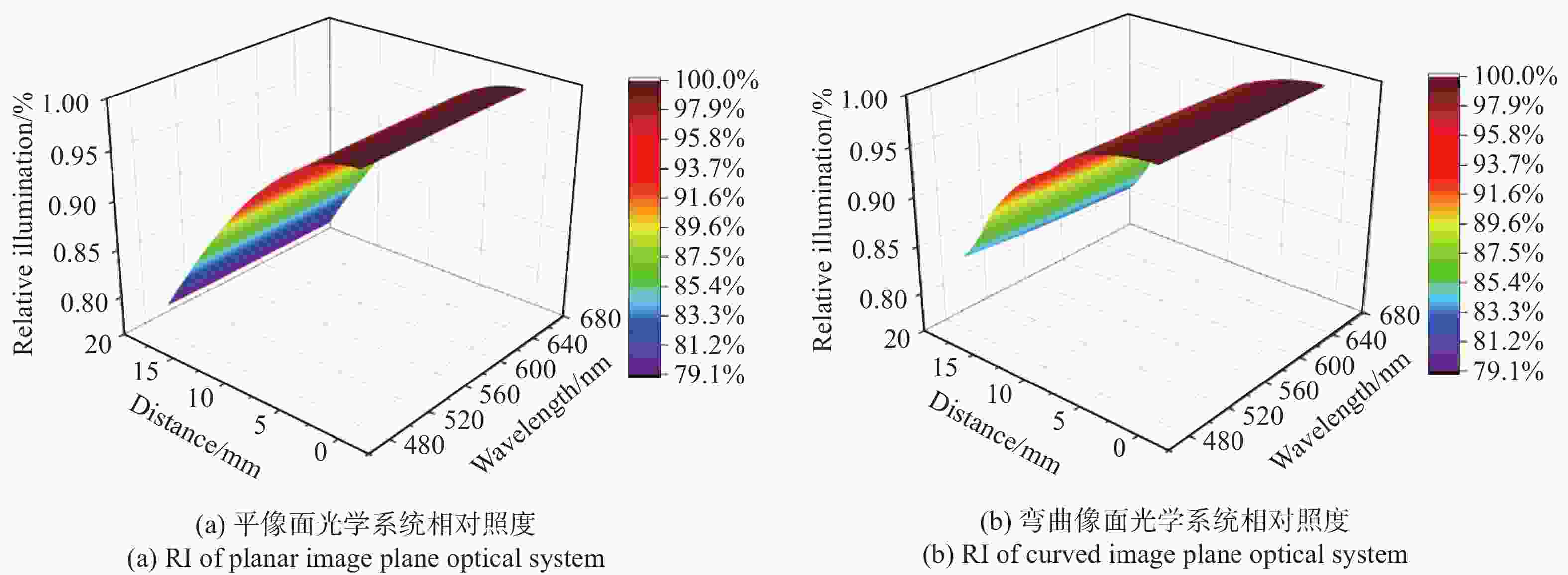
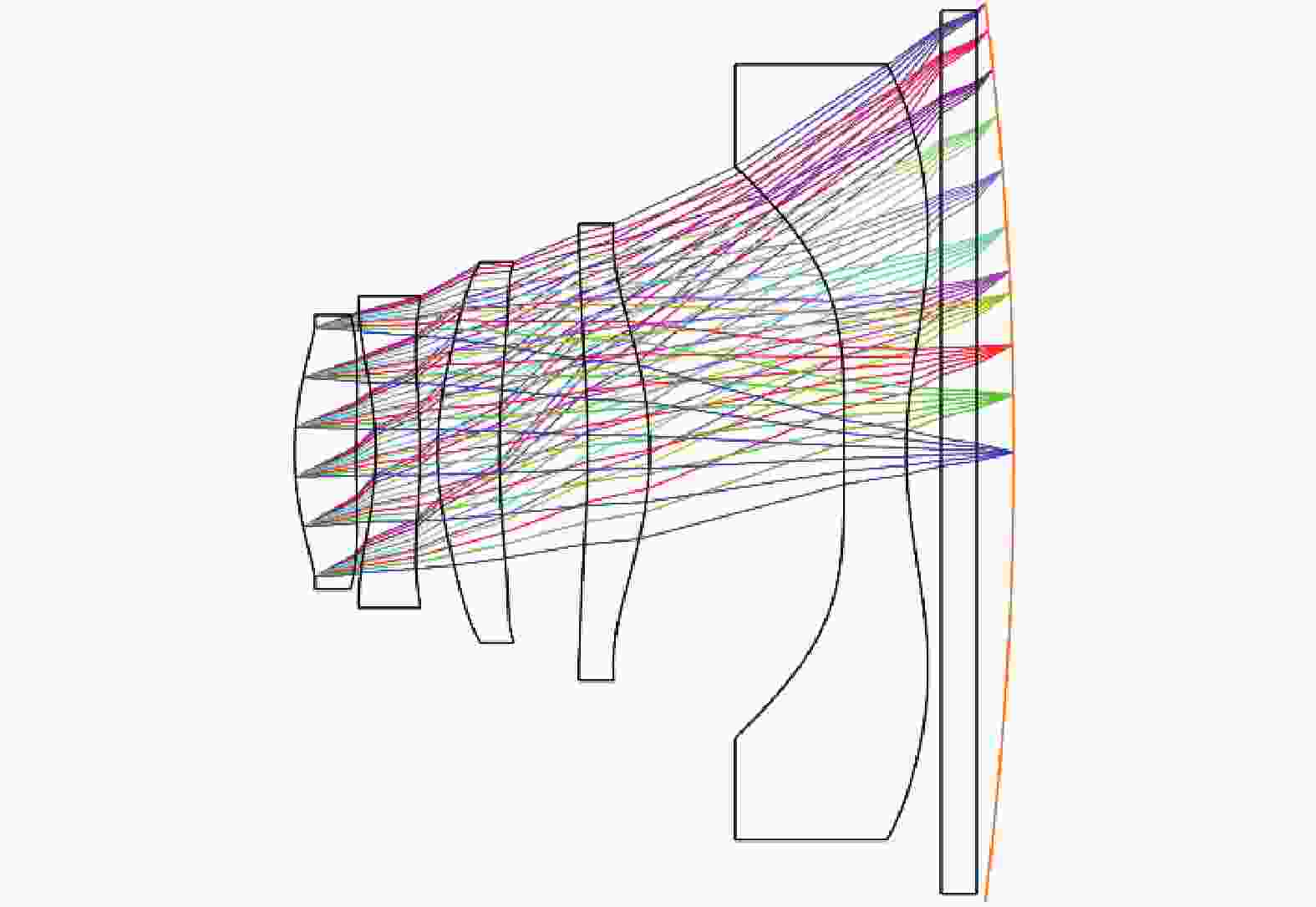
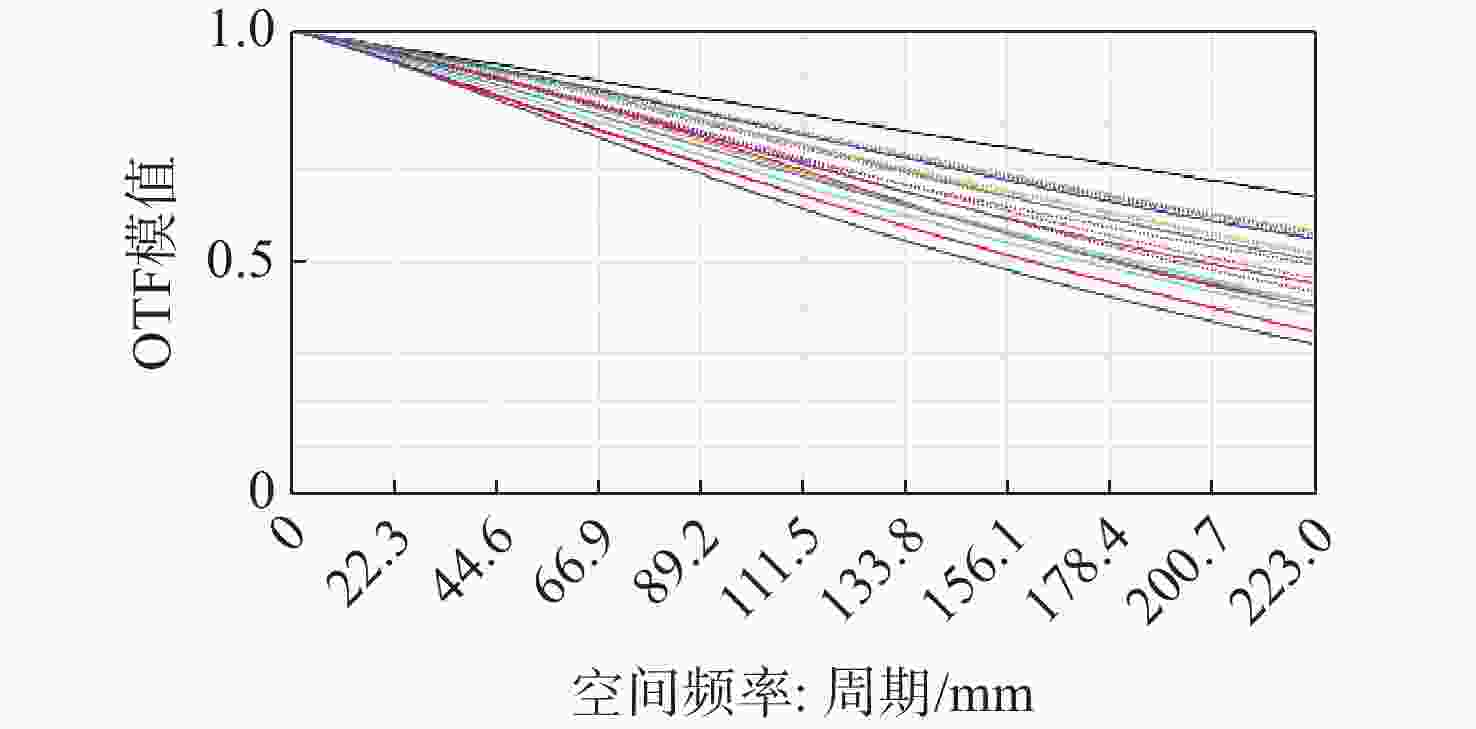
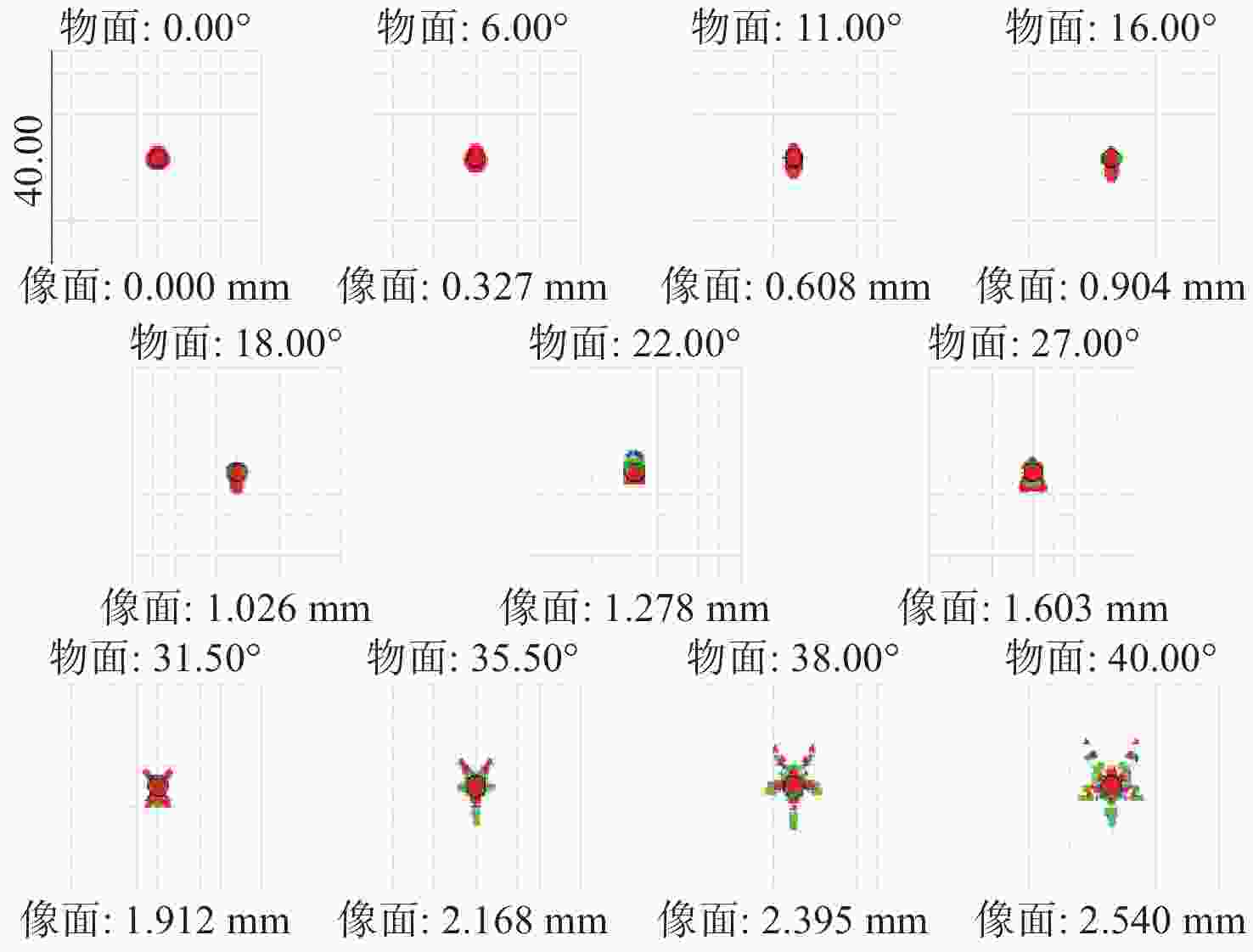
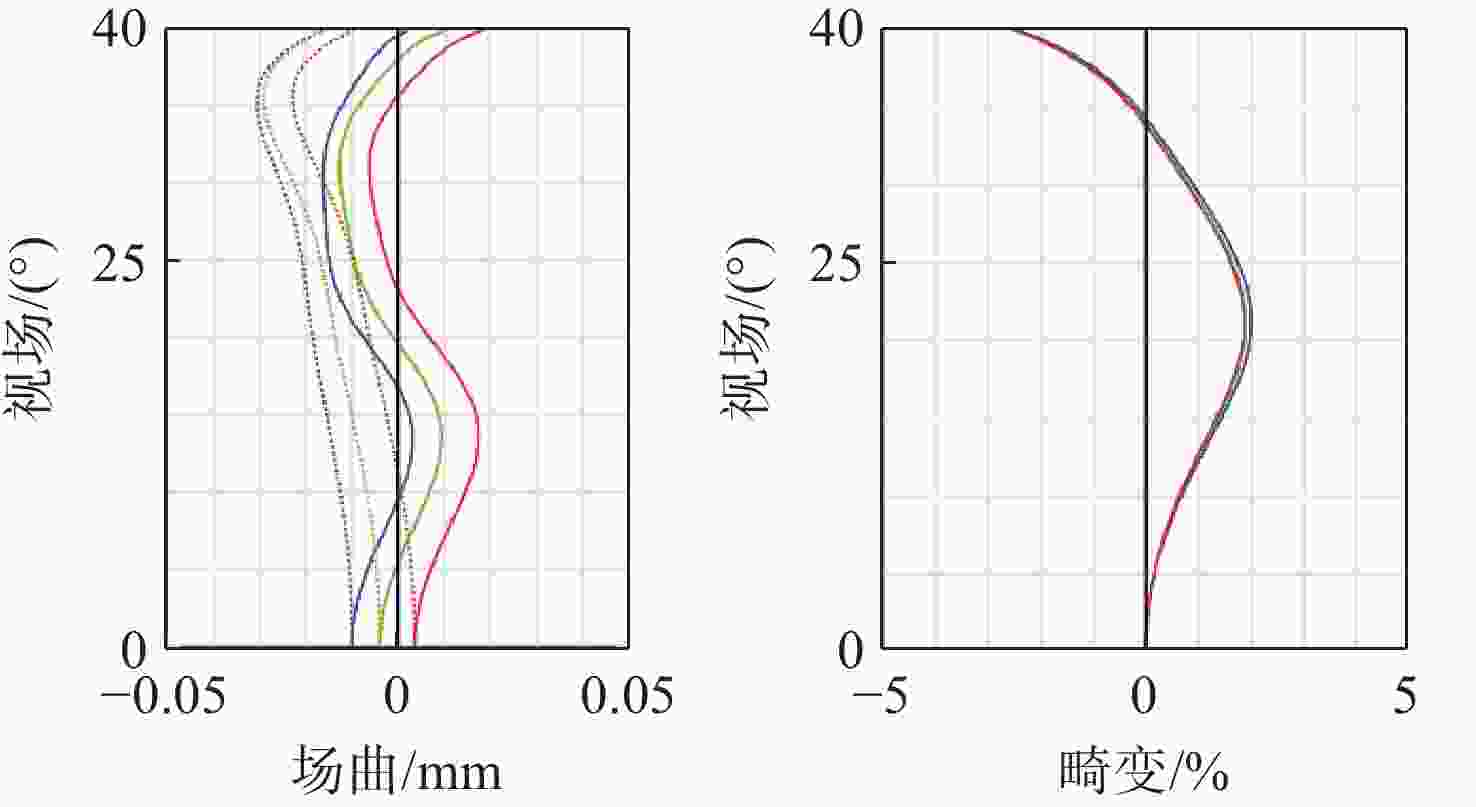
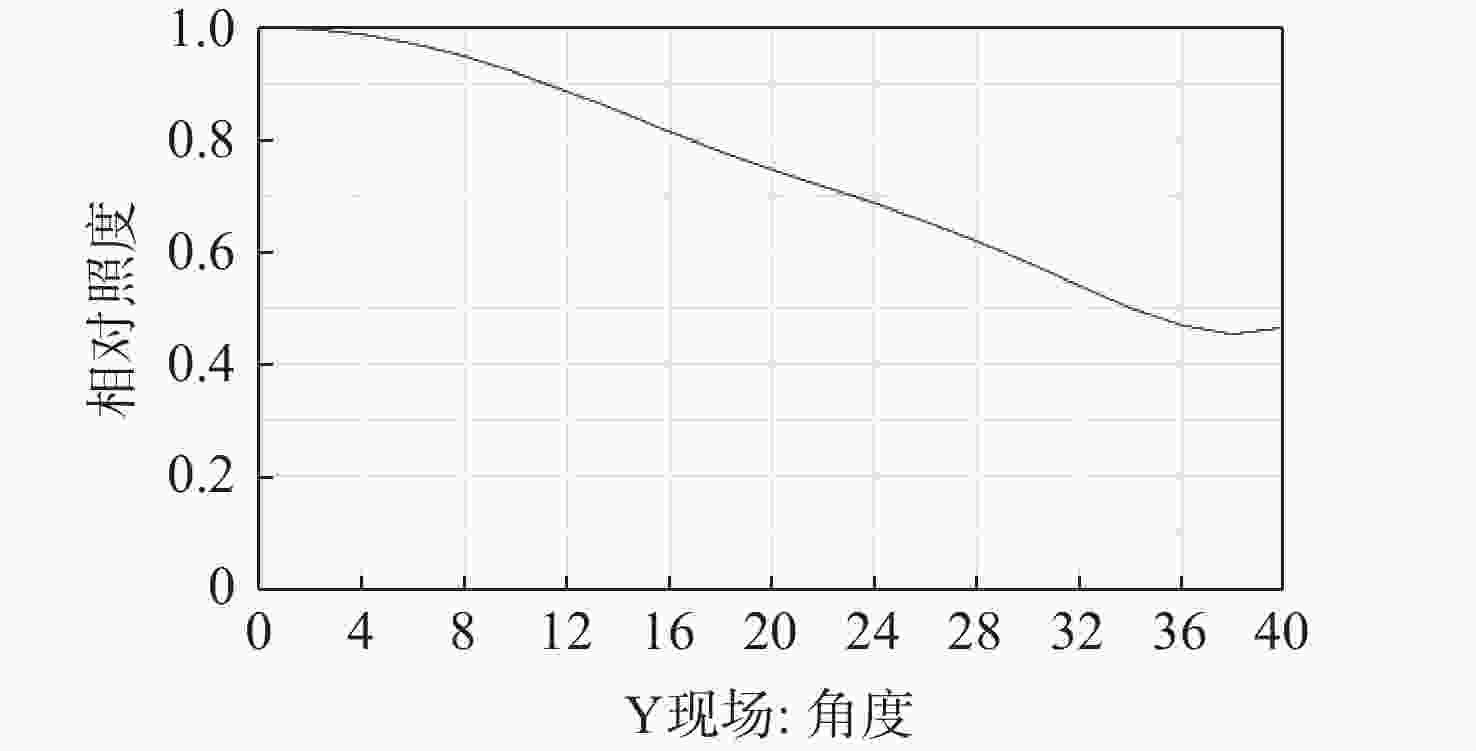
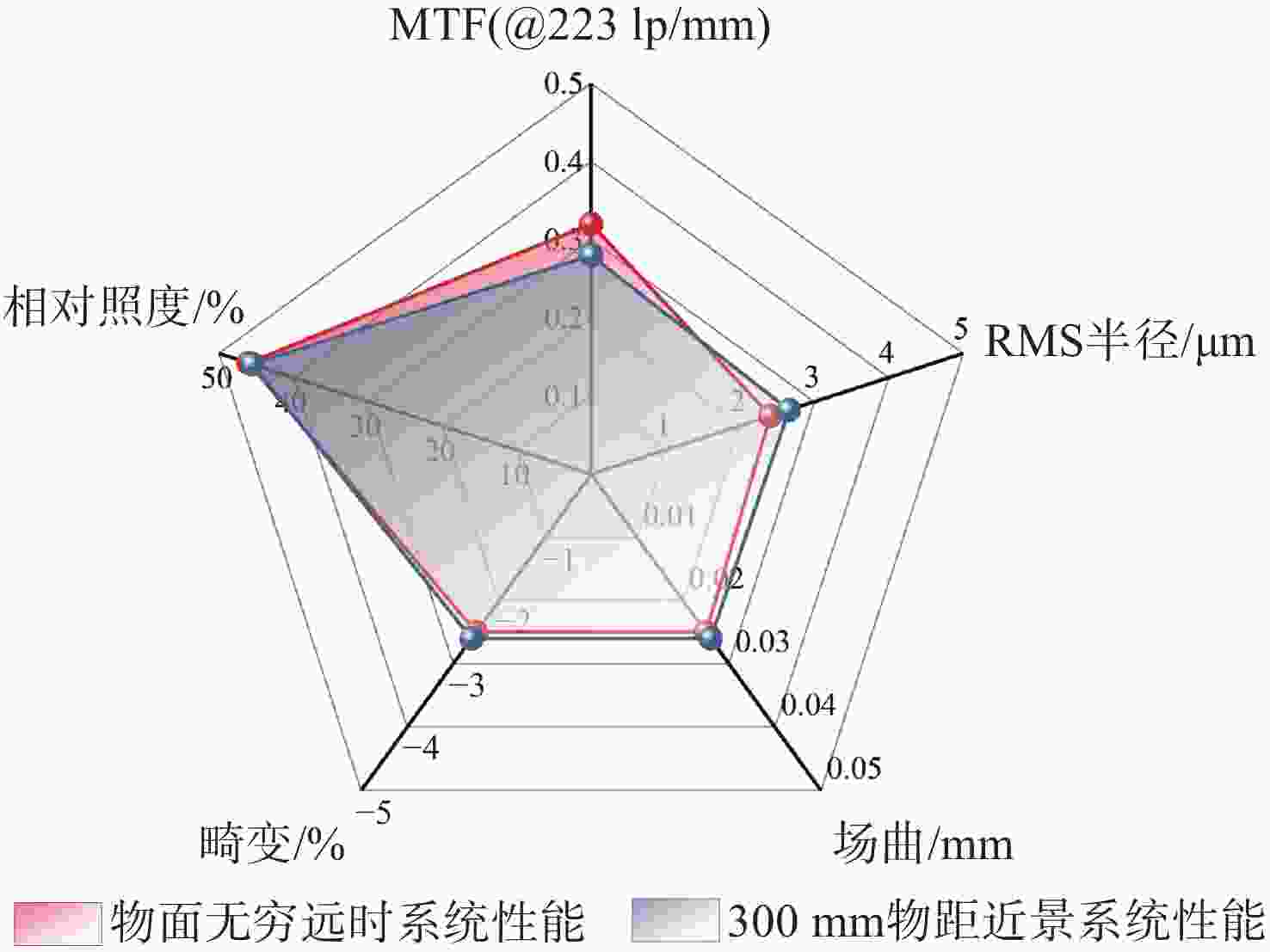
针对轻量化AR眼镜对搭载摄像头的大视场与高紧凑性的需求,本文提出了结合弯曲像面的设计方法。首先,由高斯光学理论对弯曲像面成像系统进行理论分析,推导各光学系统Petzval像面曲率特性,并通过双系统仿真对比,重点分析弯曲像面的性能优势。然后,采用分段多目标优化策略,设计了一款大视场紧凑性的光学系统。最后,对光学系统进行像质评价和公差分析。该光学系统由5片非球面塑料透镜和一片后置滤光片组成,系统焦距为3.1 mm,视场角可达80°,系统总长仅4.07 mm。设计结果表明:在223 lp/mm处,各视场的调制传递函数均优于0.32,全视场最大RMS光斑半径为2.41 μm,最大畸变为2.5%,相对照度均优于45%。研究成果可为曲面传感器的应用奠定基础,并为大视场紧凑型镜头的设计提供技术参考。
Abstract:To address the demand for large field-of-view and high compactness in lightweight AR glasses equipped with cameras, this study proposes an optical design method incorporating a curved image plane. First, based on Gaussian optics theory, the curved image plane imaging system is theoretically analyzed. The Petzval surface curvature characteristics of various optical configurations are derived, and the performance advantages of the curved image plane are highlighted through comparative simulations of dual systems. Then, a wide-angle and compact optical system is designed using a segmented multi-objective optimization strategy. Finally, image quality evaluation and tolerance analysis are performed on the designed system. The compact optical system comprises five aspheric plastic lenses and a rear-mounted filter. It features a focal length of 3.1 mm, a field of view (FOV) up to 80°, and a total system length of only 4.07 mm. The design results show that at 223 lp/mm, the modulation transfer function (MTF) exceeds 0.32 across all fields. The maximum RMS spot radius is 2.41 μm, with a distortion of only 2.5%, and the relative illumination remains above 45% across the entire field. This work lays a foundation for the application of curved sensors and offers a technical reference for the design of wide-angle compact lenses.
-
Key words:
- optical design /
- compact lens /
- curved CMOS /
- wide field-of-view /
- chief ray angle
-
表 1 光学系统的Petzval像面曲率特性
Table 1. Petzval curvature characteristics of optical systems.
系统类型 透镜组合 屈光度特点 Rp 像面形状 显微系统 多正透镜 短焦距,高屈光度 正 凹向透镜 标准摄影 正负透镜组 正透镜主导 正 凹向透镜 鱼眼摄影 多负透镜 负透镜高屈光度 负 凸向透镜 开普勒望远 双正透镜 目镜短焦距主导 正 凹向透镜 伽利略望远 正负透镜组 负目镜高屈光度 负 凸向透镜 表 2 设计指标
Table 2. Design Specifications
项目 参数 焦距/mm 3.0~3.3 F数 2.2 视场角/(°) 2ω=80 光学畸变/% ≤2.5 系统总长/mm ≤4.5 MTF/(lp/mm) ≥0.3@233(0-0.7Y) 表 3 镜片参数
Table 3. Lens Parameters
序号 面型 曲率半径/mm 厚度/mm 材料 折射率 阿贝数 物面 标准面 无限 无限 — — — 光阑 偶次非球面 1.777 0.350 6015S-04 1.533 54.975 2 偶次非球面 9.877 0.110 — — — 3 偶次非球面 −1.763 0.250 OKP-4HT 1.631 23.415 4 偶次非球面 −3.625 0.100 — — — 5 偶次非球面 1.850 0.350 ARTON_FX4727 1.523 52.125 6 偶次非球面 5.162 0.500 — — — 7 偶次非球面 −5.604 0.350 PMMA 1.492 57.441 8 偶次非球面 −1.908 1.100 — — — 9 偶次非球面 135.235 0.350 OKP-4HT 1.631 23.415 10 偶次非球面 2.529 0.200 — — — 11 标准面 无限 0.200 H-K9L 1.517 64.212 12 标准面 无限 0.210 — — — 13 标准面 −20.000 0.000 — — — 表 4 非球面系数
Table 4. Aspheric Coefficients
序号 k A4 A6 A8 A10 A12 1 0.00000E+00 −7.02848E-02 −8.04067E-03 −1.76041E-01 −1.60913E-02 −4.84484E-02 2 2.08083E-01 −1.36408E-01 −3.30294E-02 −1.84115E-01 3.69911E-01 −3.12379E-01 3 0.00000E+00 2.79638E-01 −1.56058E-01 1.31685E-01 1.57258E-01 −2.49223E-01 4 1.29397E-02 2.02942E-01 −5.50542E-02 2.31616E-01 −3.01072E-01 6.48883E-02 5 0.00000E+00 −1.38136E-01 4.35390E-02 −6.98809E-02 1.06082E-01 −3.35713E-02 6 −1.30823E-02 1.28664E-02 −1.21648E-01 6.18287E-02 −2.44867E-02 3.36290E-02 7 −6.27958E-02 6.50400E-02 −4.97805E-03 −1.91219E-02 3.37033E-03 2.25369E-03 8 0.00000E+00 7.67427E-02 1.05464E-02 1.79650E-02 −8.40372E-03 4.07342E-04 9 2.53734E+01 −1.41854E-01 3.27186E-03 1.08393E-02 −1.66595E-03 −5.59933E-05 10 0.00000E+00 −1.13567E-01 2.48152E-02 −5.09814E-03 7.67813E-04 −6.13429E-05 表 5 近景调焦性能参数变化率
Table 5. Near-field Focus Adjustment Performance Parameter Variation Rates
参数 物距 变化率 无穷远 300 mm MTF(@223 lp/mm) 0.32 0.29 −9.38% RMS半径(μm) 2.41 2.64 +9.54% 场曲(mm) 0.025 0.026 +4.00% 畸变(%) −2.5 −2.6 +4.00% 相对照度(%) 46 45.5 −1.09% 表 6 公差分配
Table 6. Tolerance Allocation
公差类型 参数 曲率半径 ±1.5 fringes 厚度 ± 0.0015 mm偏心 ± 0.0015 mm倾斜 ±3' 表 7 系统公差分析结果
Table 7. Tolerance Analysis Results
蒙特卡洛分析 MTF 90% 0.23129849 80% 0.24933111 50% 0.28139853 20% 0.31265427 10% 0.32439743 -
[1] 陈露, 刘辉, 封志明, 等. 基于局部焦距追迹计算优化的广角镜头设计方法[J]. 光子学报,2024,53(3):0322002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20245303.0322002CHEN L, LIU H, FENG ZH M, et al. Design method of wide angle lens based on optimization of local focal length through ray tracing[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2024, 53(3): 0322002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20245303.0322002 [2] 张越, 张宁, 徐熙平. 改进AO优化算法的折反射全景镜头畸变参数估计[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2025,18(1):89-104. doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0118ZHANG Y, ZHANG N, XU X P. Improved AO optimization algorithm for distortion parameter estimation of catadioptric omnidirectional lens[J]. Chinese Optics, 2025, 18(1): 89-104. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0118 [3] 熊玉朋, 陈适宇, 黄铖, 等. 基于自由曲面光学元件的大视场光学成像系统[J]. 光学 精密工程,2024,32(9):1261-1272. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20243209.1261XIONG Y P, CHEN SH Y, HUANG CH, et al. Large field optical imaging system based on freeform surface optics[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2024, 32(9): 1261-1272. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20243209.1261 [4] WU J M, GUO Y D, DENG CH, et al. An integrated imaging sensor for aberration-corrected 3D photography[J]. Nature, 2022, 612(7938): 62-71. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05306-8 [5] 韩耀辉, 王鹍, 朱友强, 等. 光子集成干涉阵列视场拼接子孔径光路设计[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(6):1458-1466. doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0030HAN Y H, WANG K, ZHU Y Q, et al. Photonic-integrated interferometric array field-of-view splicing subaperture optical path design[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(6): 1458-1466. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0030 [6] LOMBARDO S, BEHAGHEL T, CHAMBION B, et al. Curved CMOS sensor: characterization of the first fully functional prototype[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10679: 1067910. [7] ITONAGA K, ARIMURA T, MATSUMOTO K, et al. A novel curved CMOS image sensor integrated with imaging system[C]. 2014 Symposium on VLSI Technology (VLSI-Technology): Digest of Technical Papers, IEEE, 2014: 1-2. [8] GUENTER B, JOSHI N, STOAKLEY R, et al. Highly curved image sensors: a practical approach for improved optical performance[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(12): 13010-13023. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.013010 [9] DUMAS D, FENDLER M, BAIER N, et al. Curved focal plane detector array for wide field cameras[J]. Applied Optics, 2012, 51(22): 5419-5424. doi: 10.1364/AO.51.005419 [10] JOAQUINA K, CALVINHAC L, STRUSS Q, et al. Curved cmos imaging sensors for enhanced astronomical optical instruments[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2022, 12191: 121910H. [11] JOAQUINA K, JAHN W, STRUSS Q, et al. Curved CMOS imaging sensor: development and reliability test results[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2023, 12777: 127776S. [12] XUE G, ZHANG CH X, ZHANG ZH X, et al. Analysis of the impact of temperature on the performance of curved surface CMOS image sensors[J]. AIP Advances, 2025, 15(2): 025101. doi: 10.1063/5.0252687 [13] RESHIDKO D, SASIAN J. Optical analysis of miniature lenses with curved imaging surfaces[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(28): E216-E223. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.00E216 [14] ZUBER F, CHAMBION B, GASCHET C, et al. Tolerancing and characterization of curved image sensor systems[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(28): 8814-8821. doi: 10.1364/AO.400950 [15] HUGOT E, LOMBARDO S, BEHAGHEL T, et al. Curved sensors: experimental performance of CMOS prototypes and wide field related imagers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11180: 111802Y. [16] Image Sensors World. Review of 3D Cameras for AR Glasses[EB/OL]. Image Sensors World, (2018-04-26)[2025-06-15]. https://image-sensors-world.blogspot.com/search?q=Review+of+3D+cameras+for+AR+glasses. [17] 李航, 颜昌翔. 800万像素手机广角镜头设计[J]. 中国光学,2014,7(3):456-461.LI H, YAN CH X. Design of wide-angle lens for 8 mega-pixel mobile phone camera[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(3): 456-461. (in Chinese). [18] 李延伟, 伍雁雄, 陈太喜, 等. 超薄超短物像距高分辨率检测成像系统设计与试验[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(1):61-68. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0099LI Y W, WU Y X, CHEN T X, et al. Design and experiment of high-resolution detection imaging system with ultra-thin and ultra-short object-image distance[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(1): 61-68. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0099 [19] 史晓刚, 薛正辉, 李会会, 等. 增强现实显示技术综述[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(5):1146-1161. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0032SHI X G, XUE ZH H, LI H H, et al. Review of augmented reality display technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(5): 1146-1161. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0032 [20] 张以谟. 现代应用光学[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2018.ZHANG Y M. Contemporary Applied Optics[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2018. (in Chinese). [21] 李晓彤, 岑兆丰. 几何光学·像差·光学设计[M]. 杭州: 浙江大学出版社, 2003.LI X T, CEN ZH F. Geometrical Optics, Aberrations and Optical Design[M]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Press, 2003. (in Chinese) (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献英文信息, 请确认). [22] 李升辉. 大相对孔径高分辨率手机镜头设计[J]. 激光技术,2022,46(1):139-142.LI SH H. Large numerical aperture and high resolution mobile phone lens[J]. Laser Technology, 2022, 46(1): 139-142. (in Chinese). [23] 玉晶光电(厦门)有限公司. 光学成像镜头: 中国, 108627958B[P]. 2020-03-20.Largan Precision (Xiamen) Co. , Ltd. Optical imaging lens: CN, 108627958B[P]. 2020-03-20. (in Chinese). [24] 大立光电股份有限公司. 光学影像撷取镜片组、取像装置及电子装置: 中国, 108931845B[P]. 2020-05-15.Largan Precision Co. , Ltd. Optical imaging lens assembly, image capturing unit and electronic device: CN, 108931845B[P]. 2020-05-15. (in Chinese). [25] MOSS S, ZHANG Z, BEVAN A J, et al. Large area curved silicon modules for future trackers[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2025, 1075: 170388. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2025.170388 [26] 师途, 杨甬英, 张磊, 等. 非球面光学元件的面形检测技术[J]. 中国光学,2014,7(1):26-46.SHI T, YANG Y Y, ZHANG L, et al. Surface testing methods of aspheric optical elements[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(1): 26-46. (in Chinese). [27] 张旭, 李世杰, 刘丙才, 等. 凹非球面的非零位干涉检测技术[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(1):140-149. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0042ZHANG X, LI SH J, LIU B C, et al. A non-null interferometry for concave aspheric surface[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(1): 140-149. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0042 [28] 勾治践, 樊仲维, 卢锷, 等. 光学塑料透镜注射成型关键技术的研究[J]. 光学 精密工程,2000,8(6):526-531.GOU ZH J, FAN ZH W, LU E, et al. Injection molding method for optical plastics lens[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2000, 8(6): 526-531. (in Chinese). [29] MALACARA-HERNÁNDEZ D, MALACARA-HERNÁNDEZ Z. Handbook of Optical Design[M]. 3rd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017. -





 下载:
下载: