Decoherence of temporal quantum correlation in electrically controllable quantum-dots molecules
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2022-0025
-
摘要:
本文以与光腔耦合的电控量子点分子为研究对象,分析了量子点的时域量子关联退相干特性。基于可测量的Leggett-Garg不等式,研究光电混合系统的时域量子关联。测量不等式的违背性可以作为动态演化过程中时域量子关联的存在证据。调控电子隧穿强度和光腔频率失谐有利于增强时域量子关联。发现,在空间量子关联值为零的区域内,不存在时域量子关联。当空间量子关联值较高时,量子点动力学演化存在Leggett-Garg不等式测量的最大程度违背现象。与之相反,在时域量子关联为零的时间段内,空间量子关联仍然存在。本文采用开放量子系统动力学方法研究环境效应对时域量子关联的影响。量子点的自发衰变和光腔泄漏抑制了时域量子关联。这些结果可用于混合量子系统的量子信息处理技术。
-
关键词:
- 时域量子关联 /
- 量子点分子 /
- Leggett-Garg不等式 /
- 混合量子系统
Abstract:The decoherence of temporal quantum correlation is explored in a voltage-controlled quantum dots molecule coupled to a cavity. The temporal correlation in the optoelectronic hybrid system is studied based on Leggett-Garg inequalities. The inequality violations can be interpreted as the existence of temporal quantum correlation during dynamical evolution. The temporal quantum correlation is enhanced by its electron tunnel’s strength and cavity frequency detuning. It is found that there is no temporal quantum correlation in the regions where the values of spatial quantum correlation are zero and the maximal violations occur in conditions with high values of quantum correlation. In contrast, the spatial quantum coherence can still exsit when the value of temporal quantum correlation is zero. The method of open quantum system dynamic is used to study the effect of reservoir memory on temporal quantum correlation. The temporal quantum correlation can be suppressed due to the spontaneous decay of the quantum dots and cavity leakage. These results are helpful for quantum information processing technology in hybrid quantum systems.
-
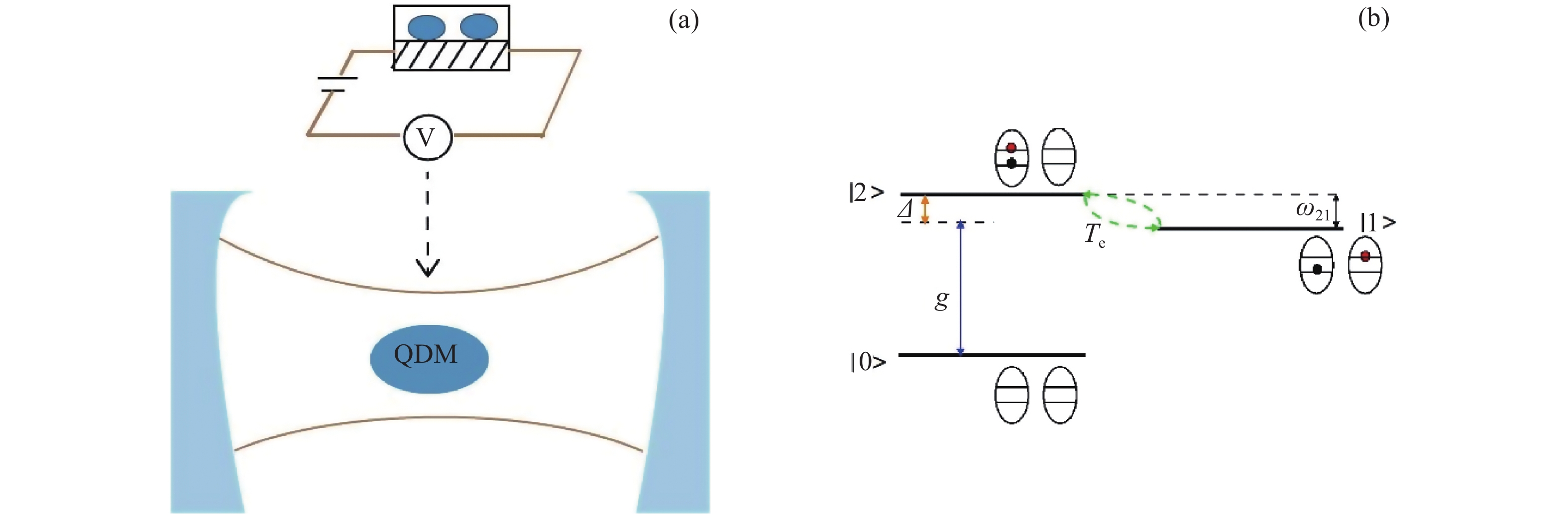
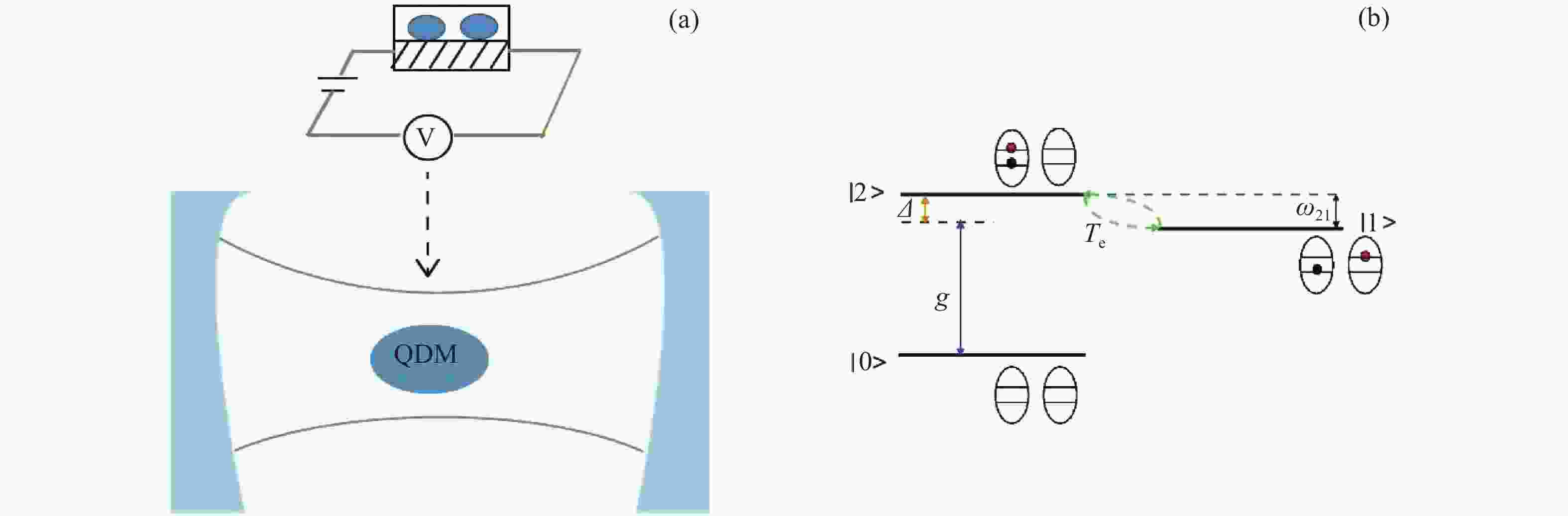
Figure 1. (a) A quantum dots molecule is coupled to a cavity. The symbol V denotes an electrical voltage which is used to control the electron tunnel. (b) Schematic diagram of band structure and level configuration of a quantum dots molecule. The system of the quantum dots molecule consists of two dots with lateral couplings. The electron and hole are represented by the red circle and black circle, respectively
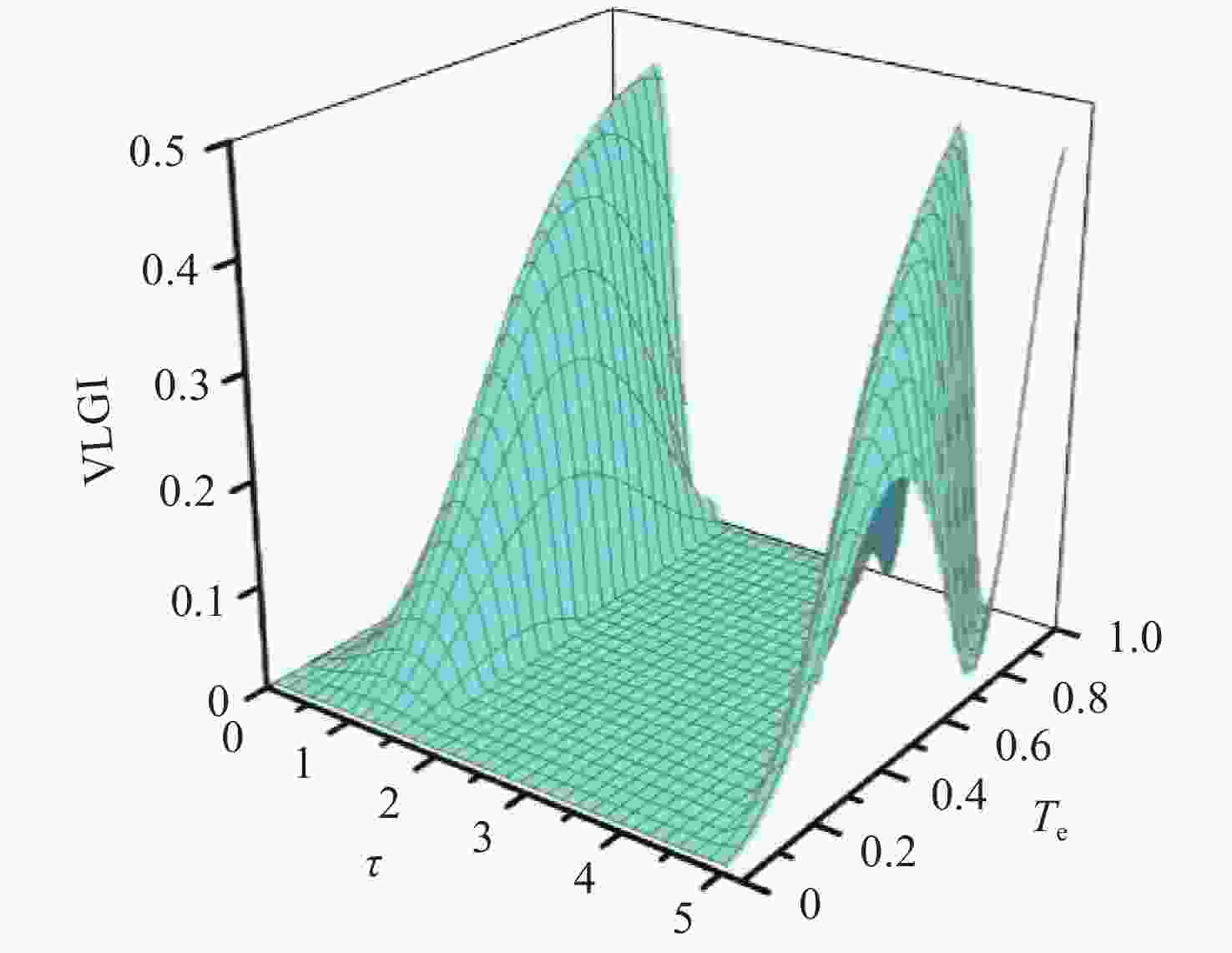
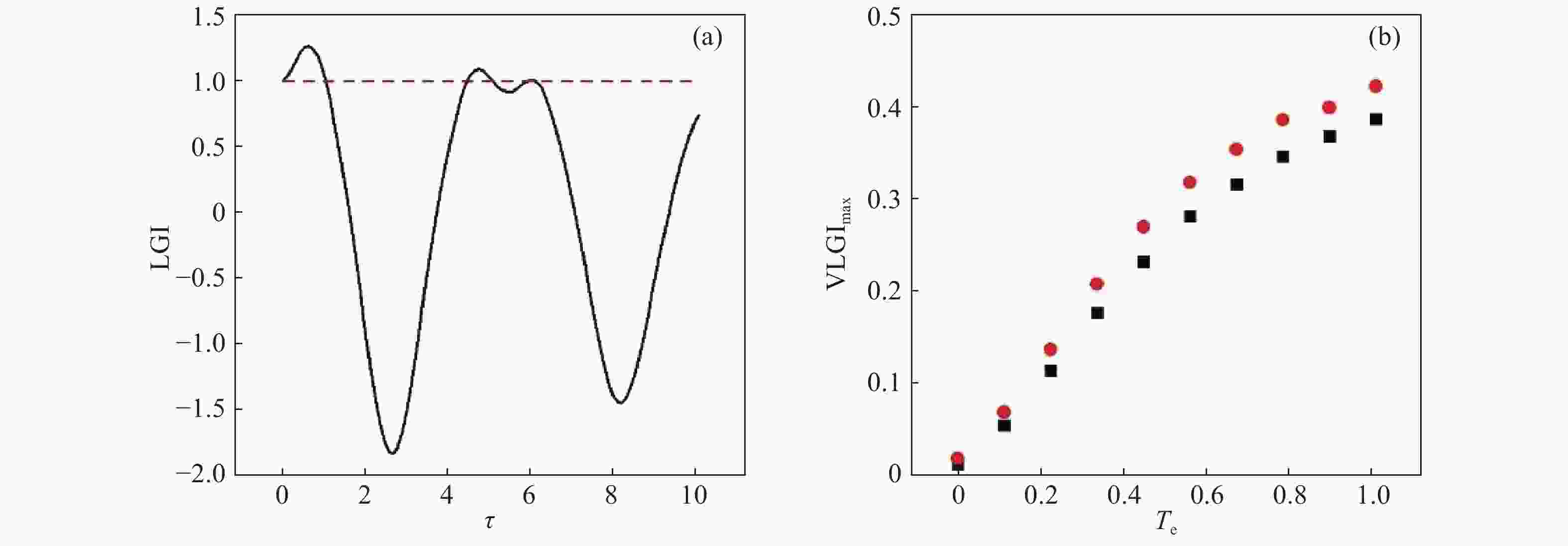
Figure 4. The evolution of the spatial and temporal correlation is shown when the parameters
$g = 1$ ,${T_e} = 0.5g$ ,$\Delta = 0$ and${\omega _{21}} = 0$ are chosen. The red dashed line denotes the spatial quantum correlation evaluated by${l_1}$ -norm quantum coherence. The black solid line describes the behavior of temporal correlation given by the${\text{LGI}}$ violationFigure 5. The effects of environmental noise on the temporal correlation are considered when the parameters are
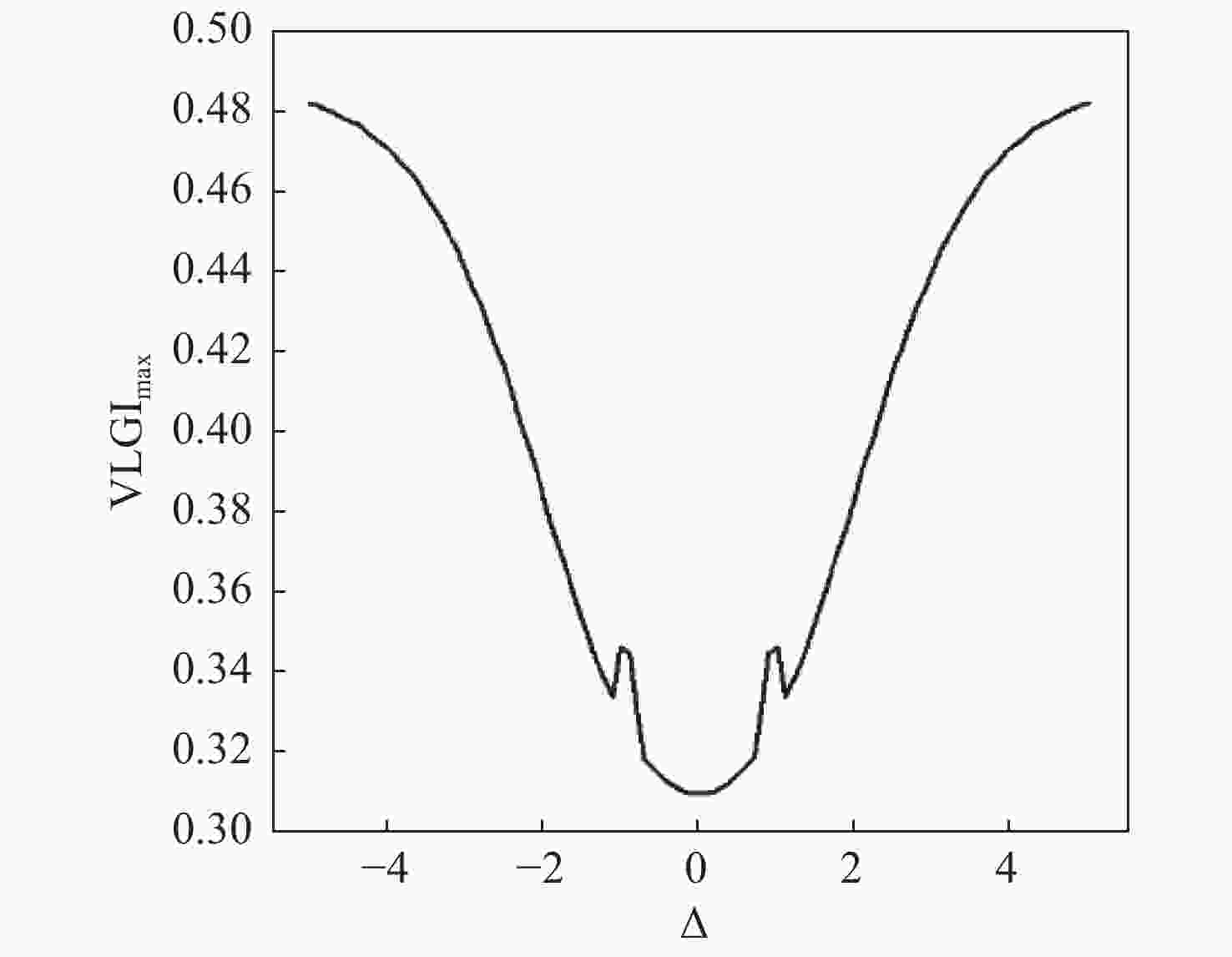
$g = 1$ ,${T_e} = 0.6g$ ,$\Delta = 0$ and${\omega _{21}} = 0$ . (a) The decreased oscillation of the${\text{LGI}}$ violation is plotted when the spontaneous decay$\gamma = 0.02g$ and the cavity leakage$\kappa = 0.01g$ ; (b) The maximal${\text{LGI}}$ violations are plotted as a function of the tunneling coupling for the different decaying parameters of$\gamma = 0.02g,\;0.01g$ which are represented by the red circles and black squares, respectively -
[1] HORODECKI R, HORODECKI P, HORODECKI M, et al. Quantum entanglement[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2009, 81(2): 865-942. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.81.865 [2] NIELSEN M A, CHUANG I L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010. [3] ALICKI R, FANNES M. Entanglement boost for extractable work from ensembles of quantum batteries[J]. Physical Review E, 2013, 87(4): 042123. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.87.042123 [4] PRESKILL J. Quantum computing in the NISQ era and beyond. quantum: the open journal for quantum science[J]. Quantum, 2018, 2: 79. doi: 10.22331/q-2018-08-06-79 [5] PEREIRA E. Perfect thermal rectification in a many-body quantum Ising model[J]. Physical Review E, 2019, 99(3): 032116. [6] MODI K, BRODUTCH A, CABLE H, et al. The classical-quantum boundary for correlations: discord and related measures[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2012, 84: 1655-1707. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.84.1655 [7] BRUNNER N, CAVALCANTI D, PIRONIO S, et al. Bell nonlocality[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2014, 86(2): 419-478. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.86.419 [8] CLEMENTE L, KOFLER J. No fine theorem for macrorealism: limitations of the Leggett-Garg inequality[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2016, 116(15): 150401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.150401 [9] BELL J S. On the Einstein Podolsky Rosen paradox[J]. Physics Physique Fizika, 1964, 1(3): 195-200. doi: 10.1103/PhysicsPhysiqueFizika.1.195 [10] CLAUSER J F, SHIMONY A. Bell's theorem. Experimental tests and implications[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 1978, 41(12): 1881-1927. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/41/12/002 [11] HILL S A, WOOTTERS W K. Entanglement of a pair of quantum bits[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1997, 78(26): 5022-5025. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.78.5022 [12] WOOTTERS W K. Entanglement of formation of an arbitrary state of two qubits[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1998, 80(10): 2245-2248. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.2245 [13] OLLIVIER H, ZUREK W H. Quantum discord: a measure of the quantumness of correlations[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2001, 88(1): 017901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.017901 [14] HENDERSON L, VEDRAL V. Classical, quantum and total correlations[J]. Journal of Physics A:Mathematical and General, 2001, 34(35): 6899-6905. doi: 10.1088/0305-4470/34/35/315 [15] BAUMGRATZ T, CRAMER M, PLENIO M B. Quantifying coherence[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2014, 113(14): 140401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.140401 [16] SINGH U, BERA M N, DHAR H S, et al. Maximally coherent mixed states: complementarity between maximal coherence and mixedness[J]. Physical Review A, 2015, 91(5): 052115. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.91.052115 [17] ZHAO M J, MA T, QUAN Q, et al. ${l_1}$ -norm coherence of assistance[J]. Physical Review A, 2019, 100(1): 012315. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.100.012315[18] BEYER K, UOLA R, LUOMA K, et al. Joint measurability in nonequilibrium quantum thermodynamics[J]. Physical Review E, 2022, 106(2): L022101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.106.L022101 [19] LUO SH L. Quantum discord for two-qubit systems[J]. Physical Review A, 2008, 77(4): 042303. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.77.042303 [20] LEGGETT A J, GARG A. Quantum mechanics versus macroscopic realism: is the flux there when nobody looks?[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1985, 54(9): 857-860. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.54.857 [21] EMARY C, LAMBERT N, NORI F. Leggett–Garg inequalities[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2014, 77(1): 016001. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/77/1/016001 [22] HUELGA S F, MARSHALL T W, SANTOS E. Proposed test for realist theories using Rydberg atoms coupled to a high-Q resonator[J]. Physical Review A, 1995, 52(4): R2497-R2500. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.52.R2497 [23] GOGGIN M E, ALMEIDA M P, BARBIERI M, et al. Violation of the Leggett–Garg inequality with weak measurements of photons[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(4): 1256-1261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005774108 [24] GROEN J P, RISTÈ D, TORNBERG L, et al. Partial-measurement backaction and nonclassical weak values in a superconducting circuit[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 111(9): 090506. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.090506 [25] SANTINI A, VITALE V. Experimental violations of Leggett-Garg inequalities on a quantum computer[J]. Physical Review A, 2022, 105(3): 032610. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.105.032610 [26] BUDRONI C, EMARY C. Temporal quantum correlations and Leggett-Garg inequalities in multilevel systems[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2014, 113(5): 050401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.050401 [27] KATIYAR H, BRODUTCH A, LU D W, et al. Experimental violation of the Leggett–Garg inequality in a three-level system[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2017, 19: 023033. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/aa5c51 [28] WANG K K, EMARY C, ZHAN X, et al. Enhanced violations of Leggett-Garg inequalities in an experimental three-level system[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(25): 31462-31470. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.031462 [29] VILLAS-BÔAS J M, GOVOROV A O, ULLOA S E. Coherent control of tunneling in a quantum dot molecule[J]. Physical Review B, 2004, 69(12): 125342. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.69.125342 [30] MÜLLER K, BECHTOLD A, RUPPERT C, et al. Electrical control of interdot electron tunneling in a double InGaAs quantum-dot nanostructure[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 108(19): 197402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.197402 [31] BEIRNE G J, HERMANNSTÄDTER C, WANG L, et al. Quantum light emission of two lateral tunnel-coupled (In, Ga)As/GaAs quantum dots controlled by a tunable static electric field[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 96(13): 137401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.137401 [32] BEIRNE G J, HERMANNSTÄDTER C, WANG L J, et al. Tunable lateral tunnel coupling between two self-assembled InGaAs quantum dots[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6471: 647104. doi: 10.1117/12.697165 [33] MAHDAVI M, SABEGH Z A, MOHAMMADI M, et al. Manipulation and exchange of light with orbital angular momentum in quantum-dot molecules[J]. Physical Review A, 2020, 101(6): 063811. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.101.063811 [34] LÜ X Y, WU J, ZHENG L L, et al. Voltage-controlled entanglement and quantum-information transfer between spatially separated quantum-dot molecules[J]. Physical Review A, 2011, 83(4): 042302. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.83.042302 [35] ZHENG A SH, CHENG Y J, LIU J B. Voltage-controlled multipartite entanglement with distant quantum dot molecules via adiabatic-varying tunnel coupling[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2013, 30(12): 3168-3173. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.30.003168 [36] HUA M, TAO M J, ALSAEDI A, et al. Universal distributed quantum computing on superconducting qutrits with dark photons[J]. Annalen der Physik, 2018, 530(4): 1700402. doi: 10.1002/andp.201700402 [37] SCHALL J, DECONINCK M, BART N, et al. Bright electrically controllable quantum-dot-molecule devices fabricated by in situ electron-beam lithography[J]. Advanced Quantum Technologies, 2021, 4(6): 2100002. doi: 10.1002/qute.202100002 -





 下载:
下载: