Resistive plasmonic absorbing structures for stability enhancement of broadband absorption
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2023-0022
-
摘要:
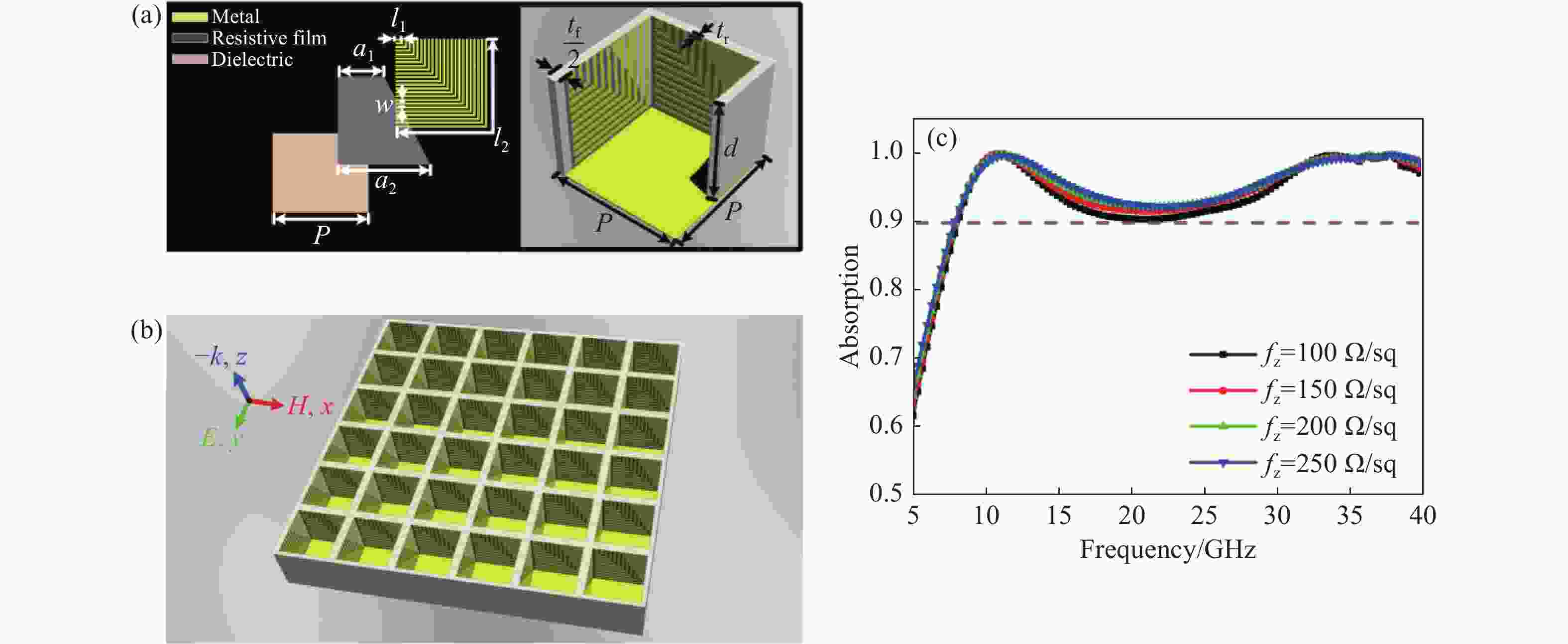
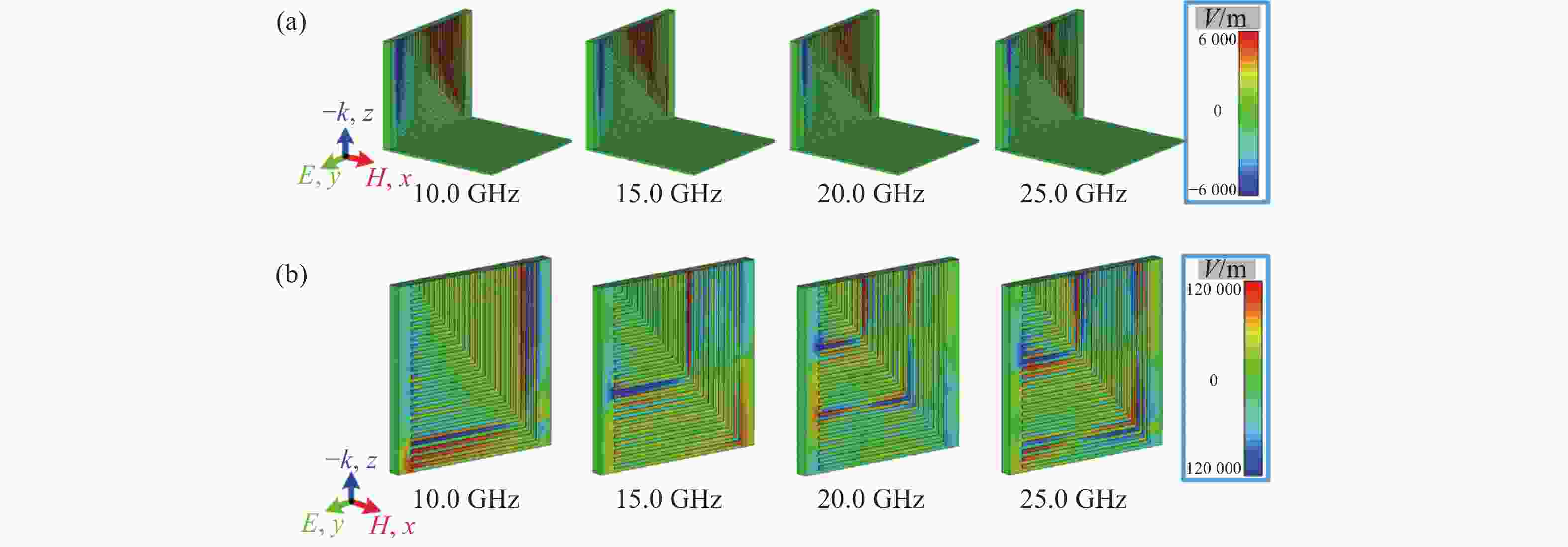
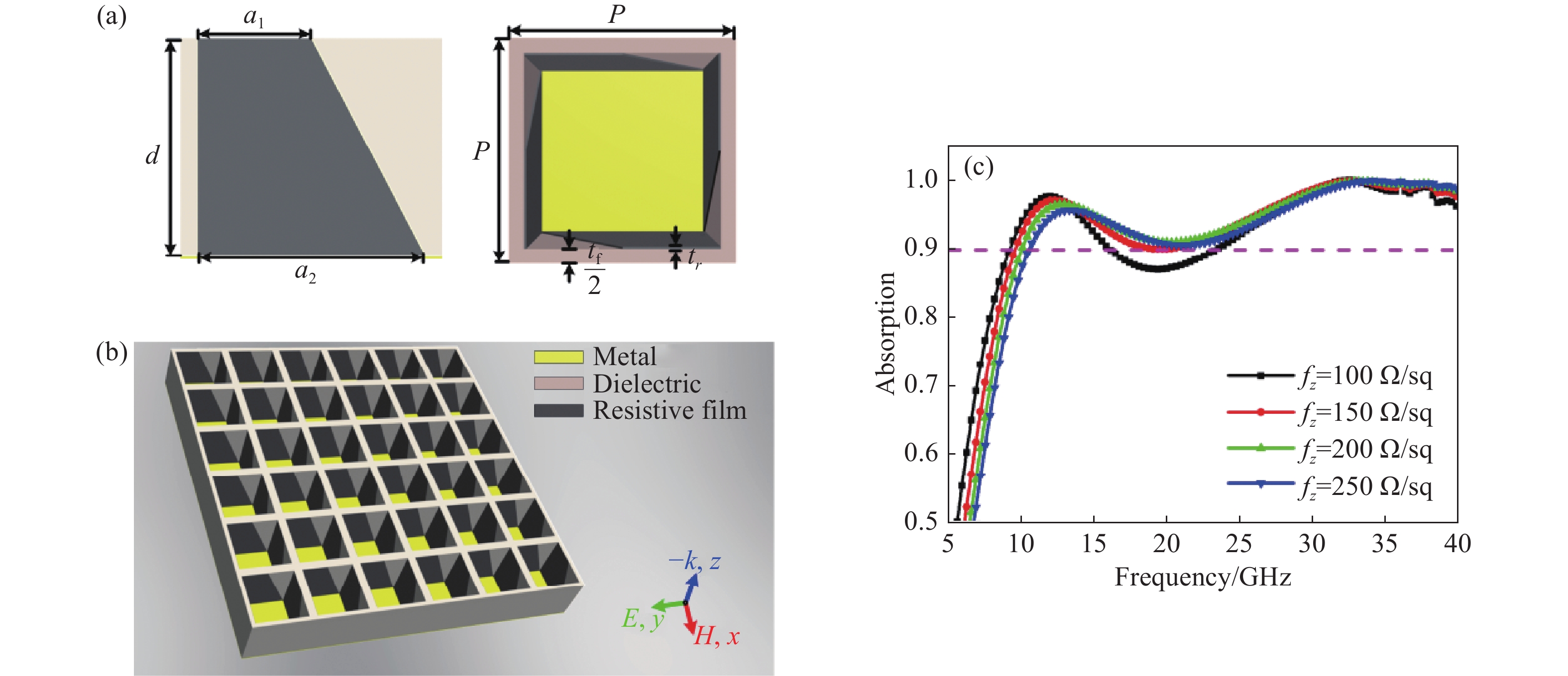
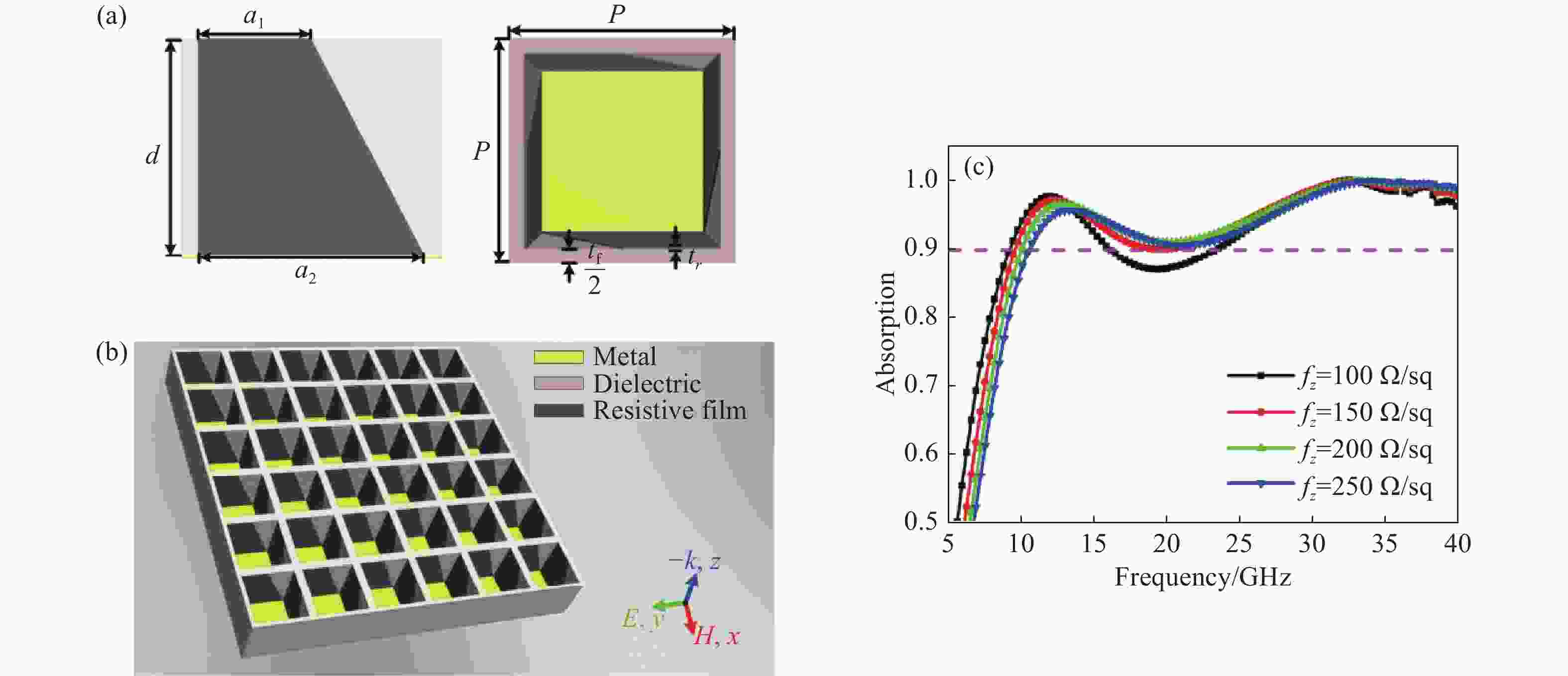
电阻型吸波结构具有优异的宽带电磁吸波性能,但电阻片方阻值对吸波结构宽带电磁吸波性能影响较大,且在样品制备过程中较难精确控制。本文通过在电阻型吸波结构表面加载周期性人工等离子结构,利用宽频带内激发的多重等离子谐振,实现高效宽带色散调控,进而获得电阻型吸波材料表面局域场增强效应,提升宽带电磁吸波的稳定性。仿真与试验结果表明,当电阻片方阻值在100~250 Ω/sq内变化时,该电阻型等离子吸波结构在7.8~40.0 GHz频段内的吸收效率高于90%以上,具有连续宽带电磁吸波能力。该设计方案提供了一种加载人工等离子结构用于强化吸波超材料综合性能的设计思路,对复合型吸波超材料设计具有一定的启发。
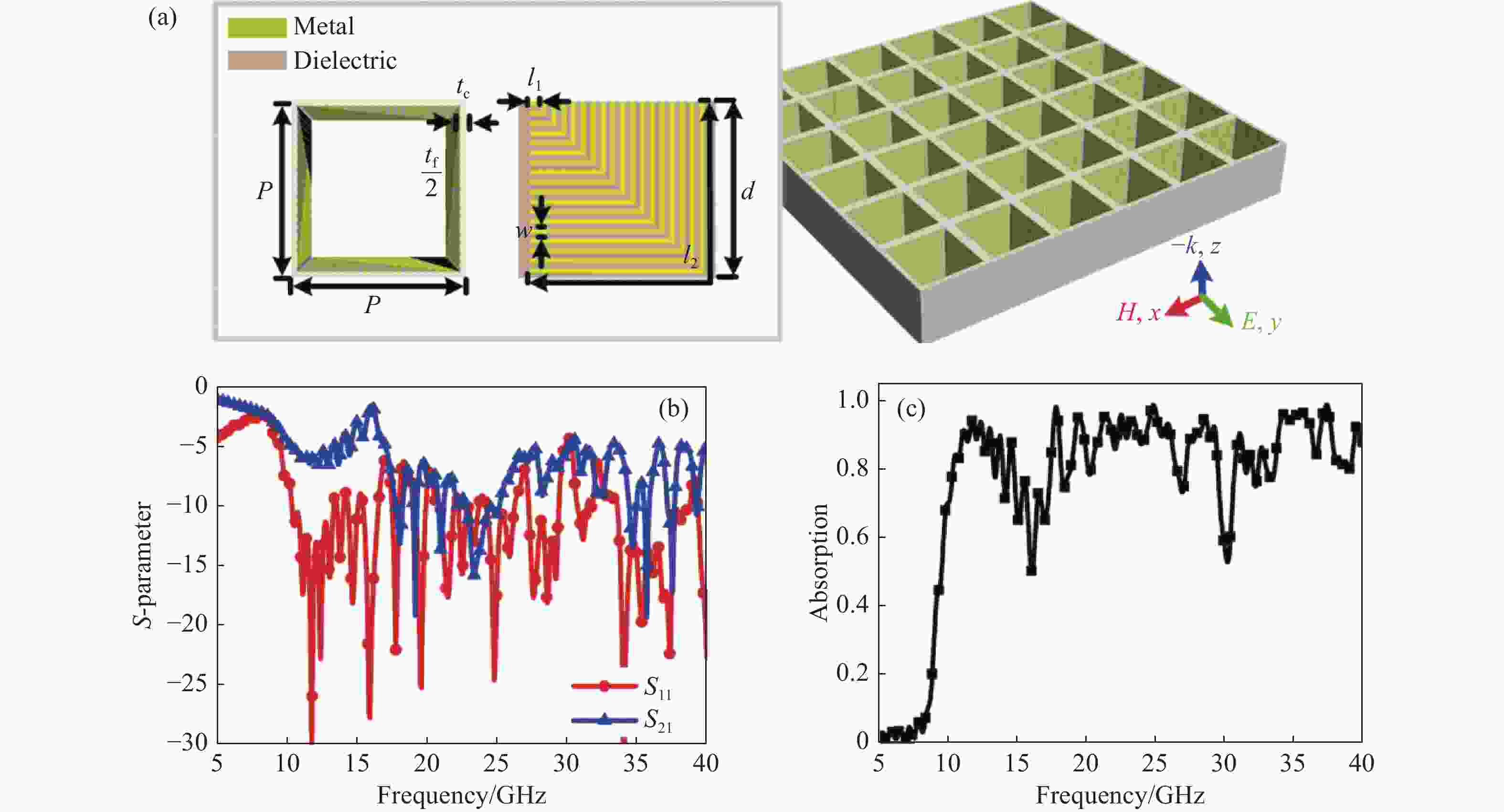
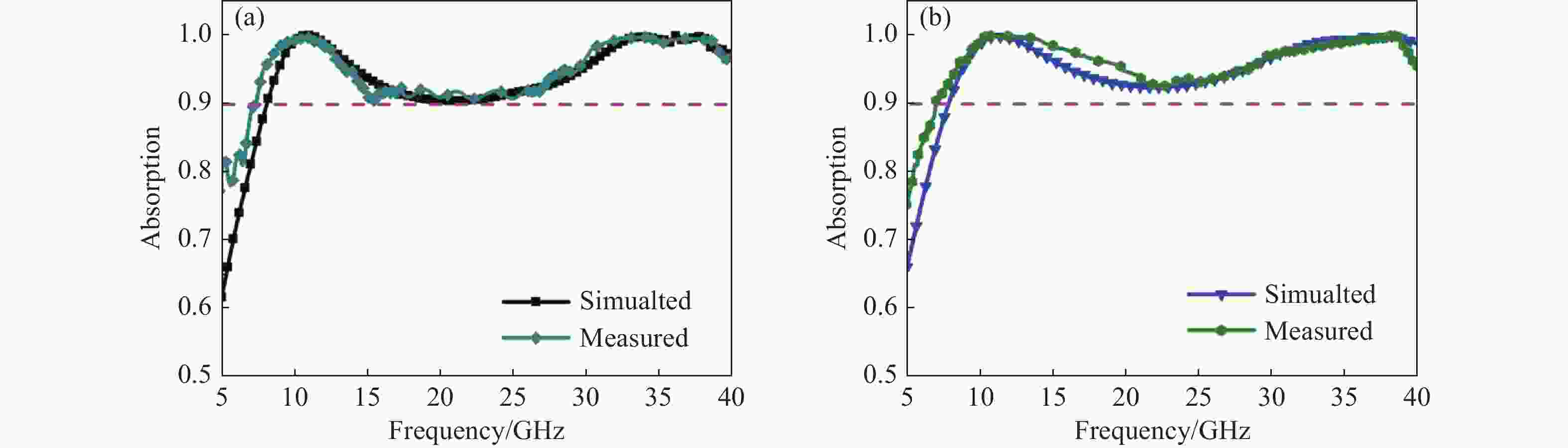
Abstract:Broadband absorption performance in resistive metamaterial absorbers (MA) has always been disturbed by its ohmic sheet element. We propose a comprehensive scheme based on integrating resistive MA and plasmonic structure (PS) to enhance the stable absorption performance. Theoretical investigation indicated that the PS can inspire multi-resonance based on dispersion engineering, and that the localized electric field takes effect on the surface of the ohmic sheet accordingly. Simulation and experimental measurement demonstrated that the proposed resistive plasmonic absorbing structures (PAS) can achieve stable and highly efficient absorption within the frequency band from 7.8 to 40.0 GHz with the ohmic sheet ranging from 100 to 250 Ω/sq. In conclusion, the proposed integration of PS and resistive MA provides an efficient pathway to optimize performance for various applications.
-
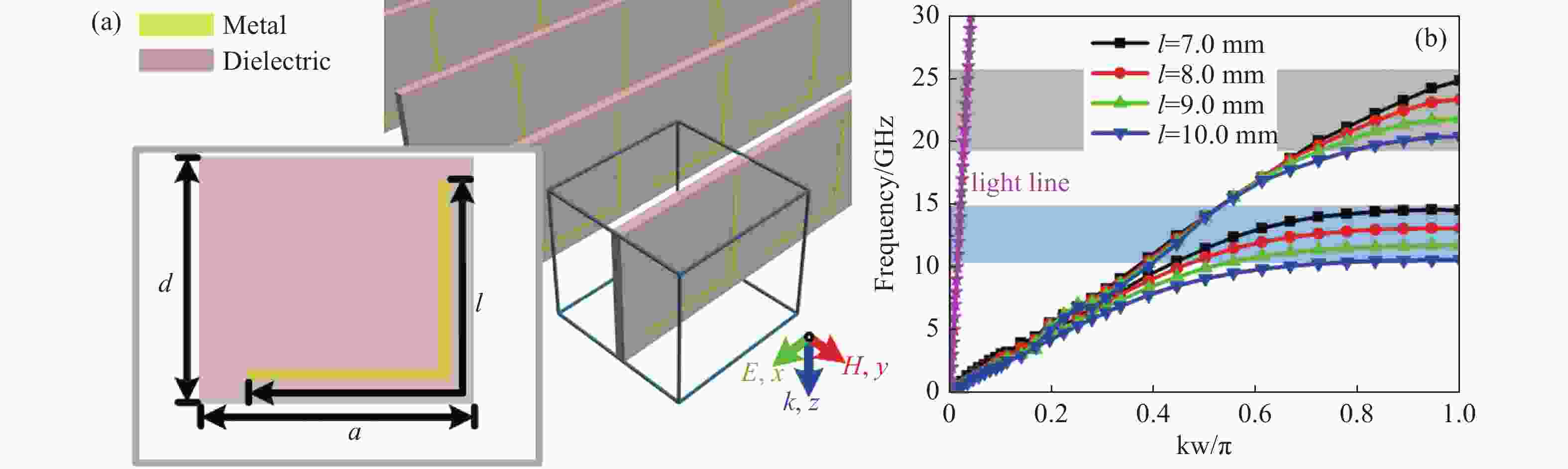
Table 1. Cut-off frequencies of the bent-wire-shaped structure with different lengths
${\boldsymbol{l }}$ l=7.0 mm l=8.0 mm l=9.0 mm l=10.0 mm The first cut-off
frequency/GHz14.5 13.1 11.8 10.6 The second cut-off
frequency/GHz24.9 23.4 21.8 20.4 -
[1] WATTS C M, LIU X L, PADILLA W J. Metamaterial electromagnetic wave absorbers[J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(23): OP98-OP120. [2] GLYBOVSKI S B, TRETYAKOV S A, BELOV P A, et al. Metasurfaces: from microwaves to visible[J]. Physics Reports, 2016, 634: 1-72. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2016.04.004 [3] TONG J K, HSU W C, HUANG Y, et al. Thin-film ‘thermal well’ emitters and absorbers for high-efficiency thermophotovoltaics[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 10661. doi: 10.1038/srep10661 [4] ATALLA M R M, ATTIA M T. On the broadband continuous polarization-independent excitation of surface-plasmon-polariton waves for energy-harvesting applications[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2017, 34(2): 270-278. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.34.000270 [5] WANG ZH Y, TONG ZH, YE Q X, et al. Dynamic tuning of optical absorbers for accelerated solar-thermal energy storage[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 1478. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01618-w [6] DIEM M, KOSCHNY T, SOUKOULIS C M. Wide-angle perfect absorber/thermal emitter in the terahertz regime[J]. Physical Review B, 2008, 79(3): 033101. [7] MASON J A, SMITH S, WASSERMAN D. Strong absorption and selective thermal emission from a midinfrared metamaterial[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 98(24): 241105. doi: 10.1063/1.3600779 [8] SHEN Y, ZHANG J Q, PANG Y Q, et al. Transparent broadband metamaterial absorber enhanced by water-substrate incorporation[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(12): 15665-15674. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.015665 [9] LANDY N I, BINGHAM C M, TYLER T, et al. Design, theory, and measurement of a polarization-insensitive absorber for terahertz imaging[J]. Physical Review B, 2009, 79(12): 125104. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.79.125104 [10] BAKIR M, KARAASLAN M, UNAL E, et al. Microwave metamaterial absorber for sensing applications[J]. Opto-Electronics Review, 2017, 25(4): 318-325. doi: 10.1016/j.opelre.2017.10.002 [11] LIU N, MESCH M, WEISS T, et al. Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor[J]. Nano Letters, 2010, 10(7): 2342-2348. doi: 10.1021/nl9041033 [12] LANDY N I, SAJUYIGBE S, MOCK J J, et al. Perfect metamaterial absorber[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100(20): 207402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.207402 [13] TAO H, BINGHAM C M, PILON D, et al. A dual band terahertz metamaterial absorber[J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 2010, 43(22): 225102. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/43/22/225102 [14] CUI Y X, XU J, HUNG FUNG K, et al. A thin film broadband absorber based on multi-sized nanoantennas[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(25): 253101. doi: 10.1063/1.3672002 [15] HUANG L, CHOWDHURY D R, RAMANI S, et al. Experimental demonstration of terahertz metamaterial absorbers with a broad and flat high absorption band[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(2): 154-156. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.000154 [16] TUNG B S, KHUYEN B X, VAN DUNG N, et al. Multi-band near-perfect absorption via the resonance excitation of dark meta-molecules[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 356: 362-367. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2015.08.022 [17] CHENG Y ZH, CHENG ZH Z, MAO X S, et al. Ultra-thin multi-band polarization-insensitive microwave metamaterial absorber based on multiple-order responses using a single resonator structure[J]. Materials, 2017, 10(11): 1241. doi: 10.3390/ma10111241 [18] ZHAO L, LIU H, HE ZH H, et al. Design of multi-narrowband metamaterial perfect absorbers in near-infrared band based on resonators asymmetric method and modified resonators stacked method[J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 420: 95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.03.051 [19] LI SH Y, AI X CH, WU R H, et al. Enhancement of multi-band absorption based on compound structure metamaterials[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2019, 115: 239-245. [20] MAO Q J, FENG CH Z, YANG Y ZH. Design of tunable multi-band metamaterial perfect absorbers based on magnetic polaritons[J]. Plasmonics, 2019, 14(2): 389-396. doi: 10.1007/s11468-018-0816-1 [21] HANNAN S, ISLAM M T, SAHAR N M, et al. Modified-segmented split-ring based polarization and angle-insensitive multi-band metamaterial absorber for X, Ku and K band applications[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 144051-144063. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3013011 [22] GOMON D, SEDYKH E, RODRÍGUEZ S, et al. Influence of the geometric parameters of the electrical ring resonator metasurface on the performance of metamaterial absorbers for terahertz applications[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(1): 47-59. [23] SHEN Y, PEI ZH B, PANG Y Q, et al. Phase random metasurfaces for broadband wide-angle radar cross section reduction[J]. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 2015, 57(12): 2813-2819. doi: 10.1002/mop.29444 [24] TRAN M C, PHAM V H, HO T H, et al. Broadband microwave coding metamaterial absorbers[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 1810. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58774-1 [25] MUDACHATHI R, TANAKA T. 3D conical helix metamaterial–based isotropic broadband perfect light absorber[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(19): 26369-26376. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.026369 [26] CUI Y X, FUNG K H, XU J, et al. Ultrabroadband light absorption by a sawtooth anisotropic metamaterial slab[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(3): 1443-1447. doi: 10.1021/nl204118h [27] DING F, CUI Y X, GE X CH, et al. Ultra-broadband microwave metamaterial absorber[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 100(10): 103506. doi: 10.1063/1.3692178 [28] LIU SH, CHEN H B, CUI T J. A broadband terahertz absorber using multi-layer stacked bars[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2015, 106(15): 151601. doi: 10.1063/1.4918289 [29] JI SH J, JIANG CH X, ZHAO J, et al. An ultra-broadband metamaterial absorber with high absorption rate throughout the X-band[J]. Physica Status Solidi (B), 2019, 256(11): 1900069. doi: 10.1002/pssb.201900069 [30] SHEN Y, PEI ZH B, PANG Y Q, et al. An extremely wideband and lightweight metamaterial absorber[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 117(22): 224503. doi: 10.1063/1.4922421 [31] TANG J Y, XIAO ZH Y, XU K K, et al. Polarization-controlled metamaterial absorber with extremely bandwidth and wide incidence angle[J]. Plasmonics, 2016, 11(5): 1393-1399. doi: 10.1007/s11468-016-0189-2 [32] HU D W, CAO J, LI W, et al. Optically transparent broadband microwave absorption metamaterial by standing-up closed-ring resonators[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2017, 5(13): 1700109. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700109 [33] YE D X, WANG ZH Y, XU K W, et al. Ultrawideband dispersion control of a metamaterial surface for perfectly-matched-layer-like absorption[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 111(18): 187402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.187402 [34] ZHANG H F, JING Y, ZHANG H, et al. Design of an ultra-broadband absorber based on plasma metamaterial and lumped resistors[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2018, 8(8): 2103-2113. doi: 10.1364/OME.8.002103 [35] MA X, TIAN F, LI X Y, et al. Broadband with enhanced oblique incidence metamaterial absorber[J]. Materials Research Express, 2020, 7(9): 095803. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/abba9e [36] PANG Y Q, WANG J F, MA H, et al. Spatial k-dispersion engineering of spoof surface plasmon polaritons for customized absorption[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 29429. doi: 10.1038/srep29429 [37] SHEN Y, ZHANG J Q, MENG Y Y, et al. Merging absorption bands of plasmonic structures via dispersion engineering[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2018, 112(25): 254103. doi: 10.1063/1.5040067 [38] SHEN Y, ZHANG J Q, WANG J F, et al. Multistage dispersion engineering in a three-dimensional plasmonic structure for outstanding broadband absorption[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2019, 9(3): 1539-1550. doi: 10.1364/OME.9.001539 [39] SHEN Y, ZHANG J Q, WANG W J, et al. Overcoming the pixel-density limit in plasmonic absorbing structure for broadband absorption enhancement[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2019, 18(4): 674-678. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2019.2900846 [40] ROZANOV K N, STAROSTENKO S N. Numerical study of bandwidth of radar absorbers[J]. The European Physical Journal Applied Physics, 1999, 8(2): 147-151. doi: 10.1051/epjap:1999240 [41] ROZANOV K N. Ultimate thickness to bandwidth ratio of radar absorbers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2000, 48(8): 1230-1234. doi: 10.1109/8.884491 -





 下载:
下载: