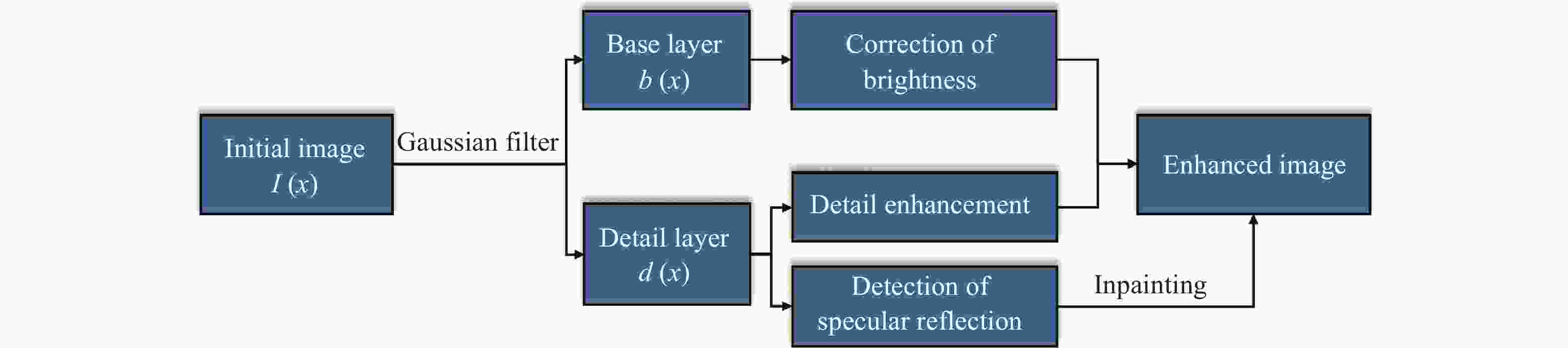
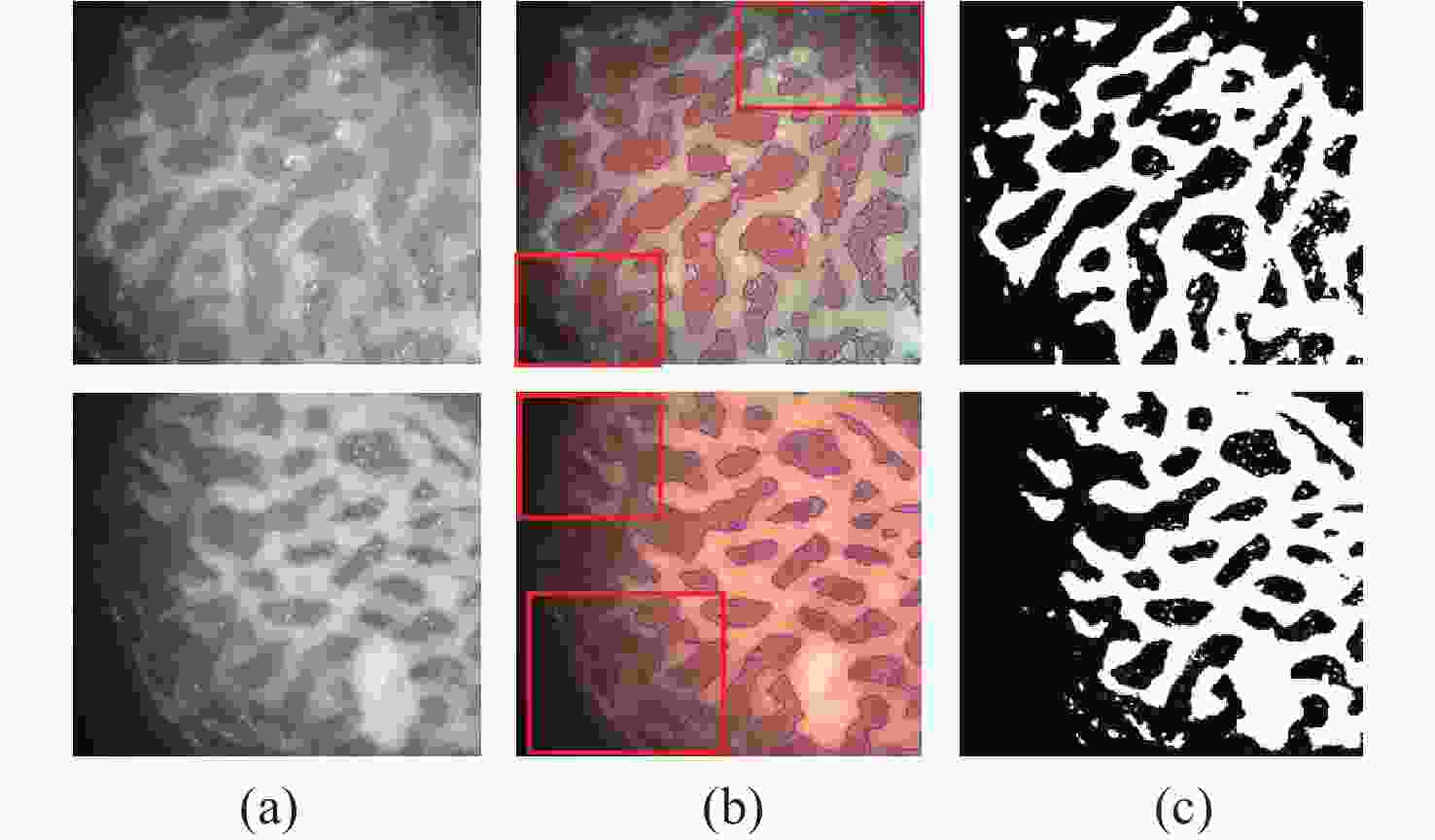
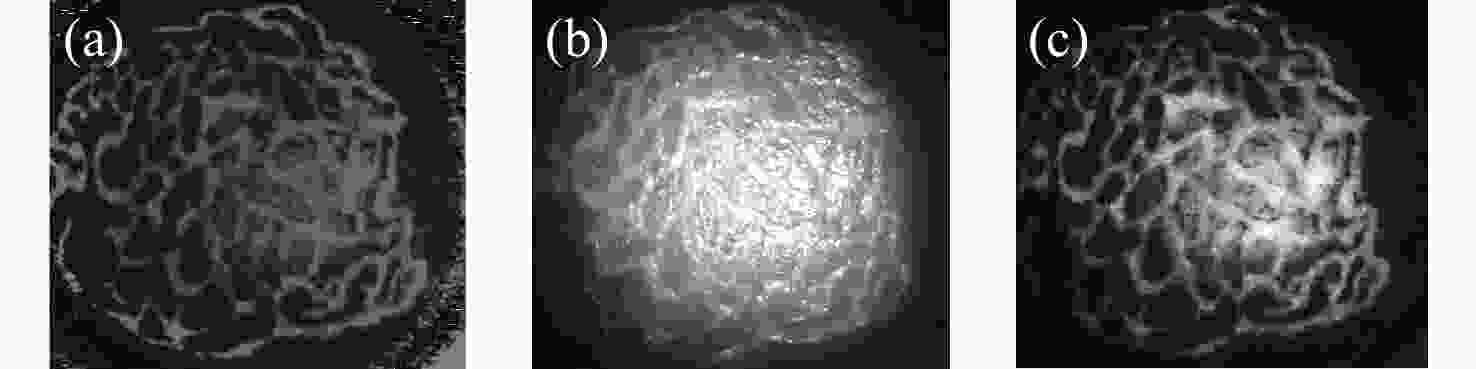
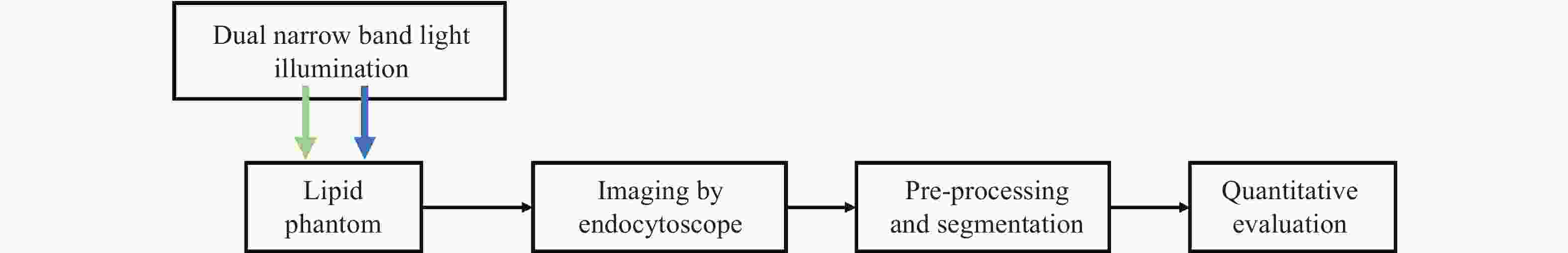
Lipid segmentation method based on magnification endoscopy with narrow-band imaging
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2023-0024
-
摘要:
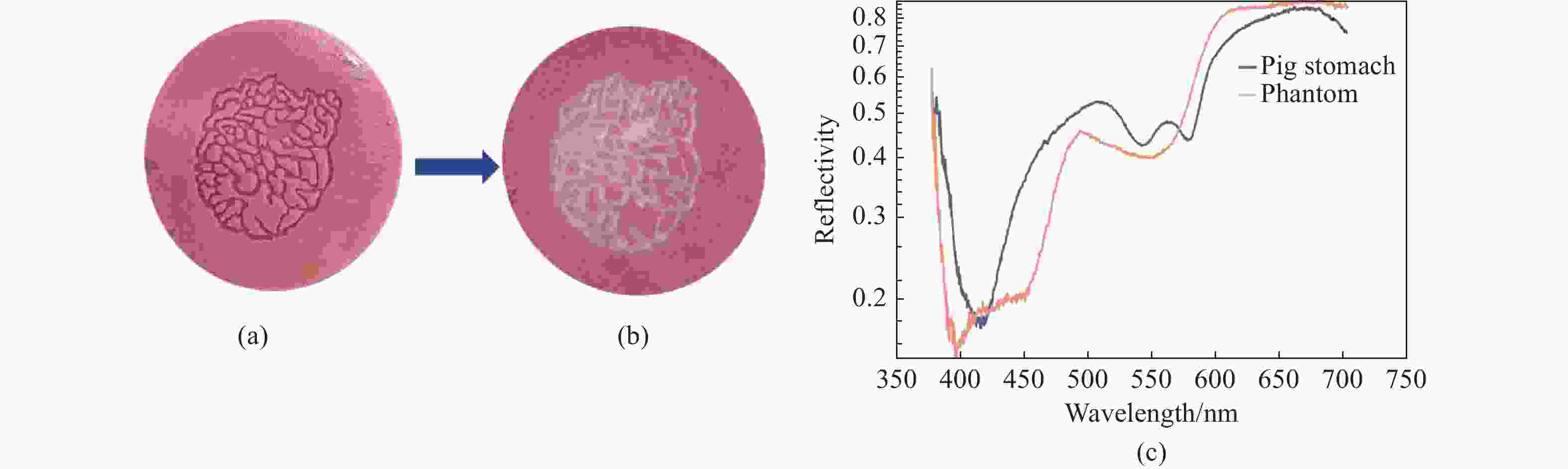
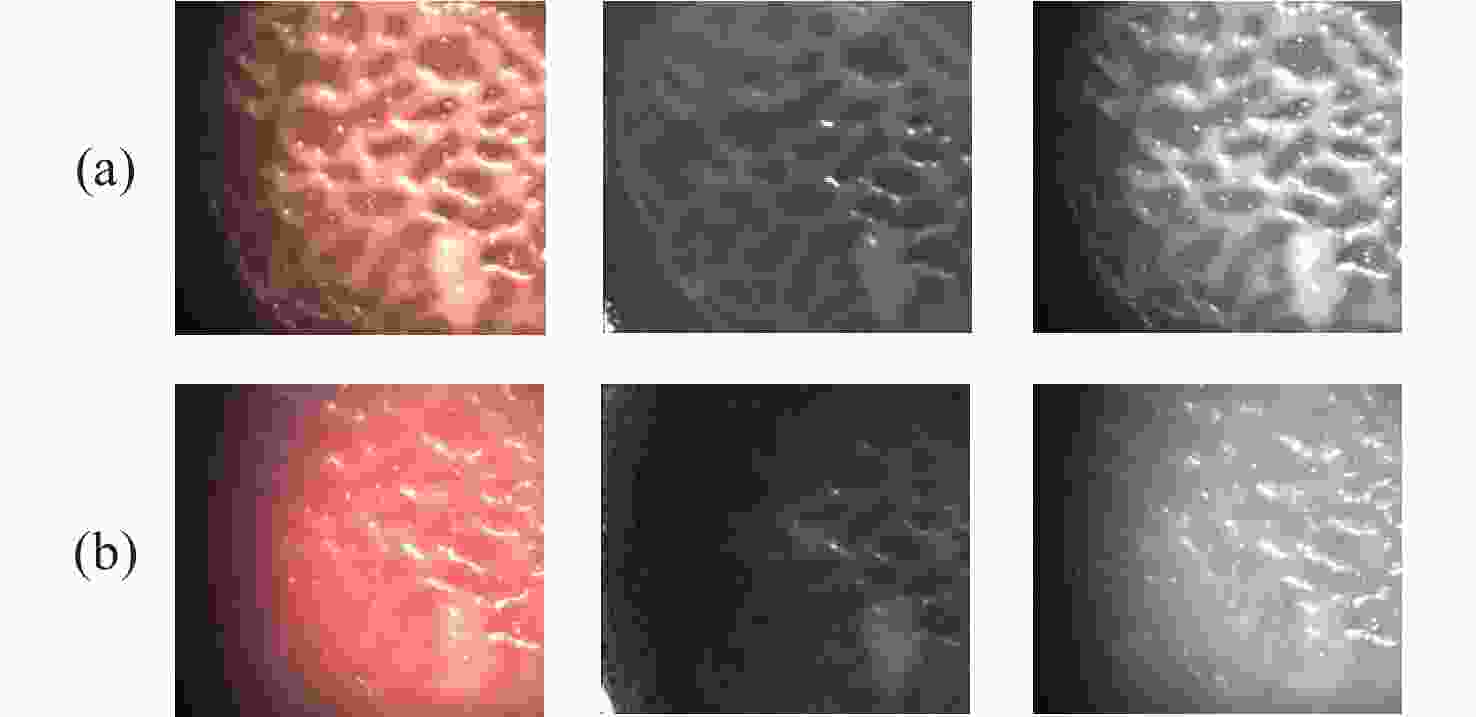
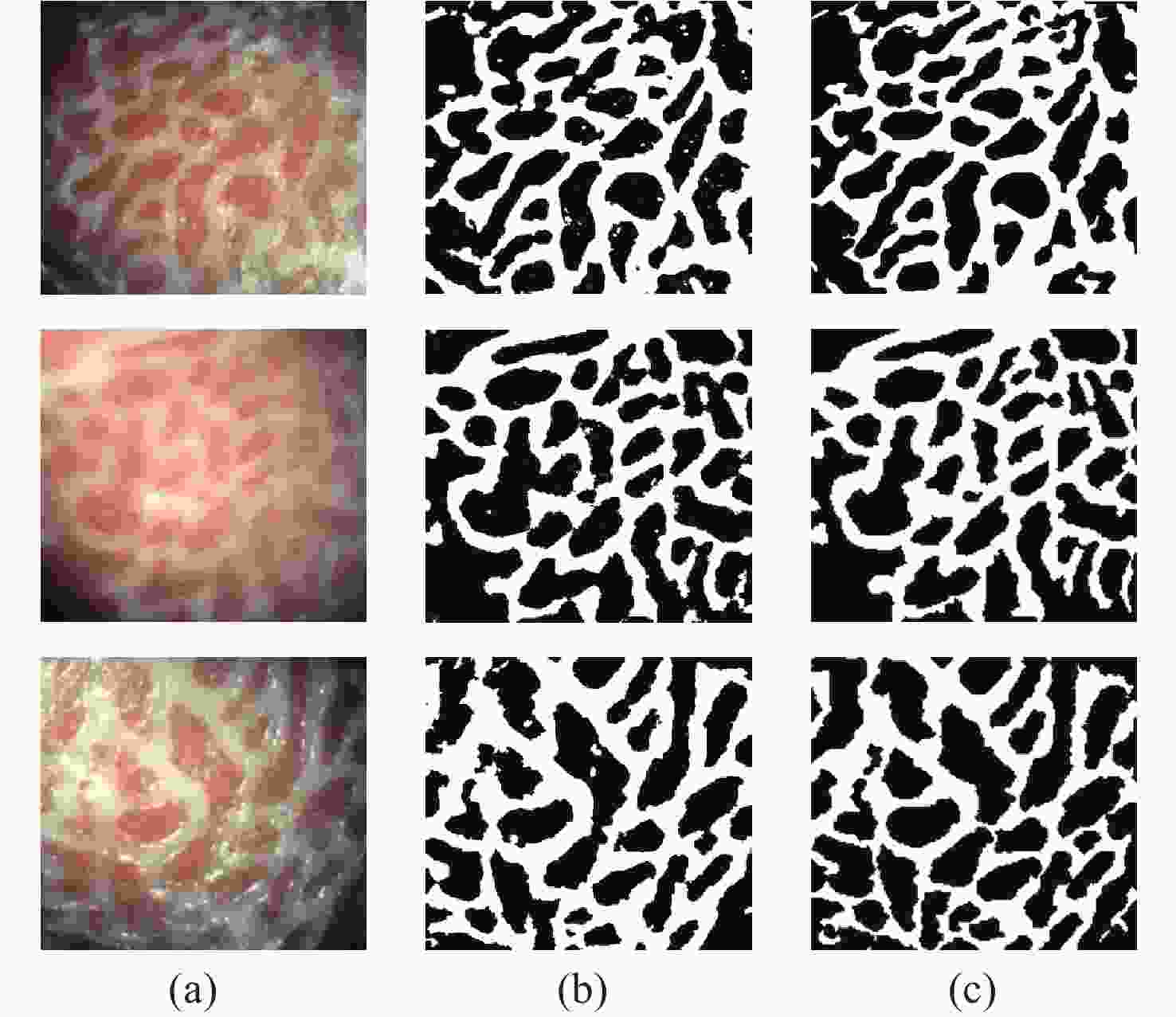
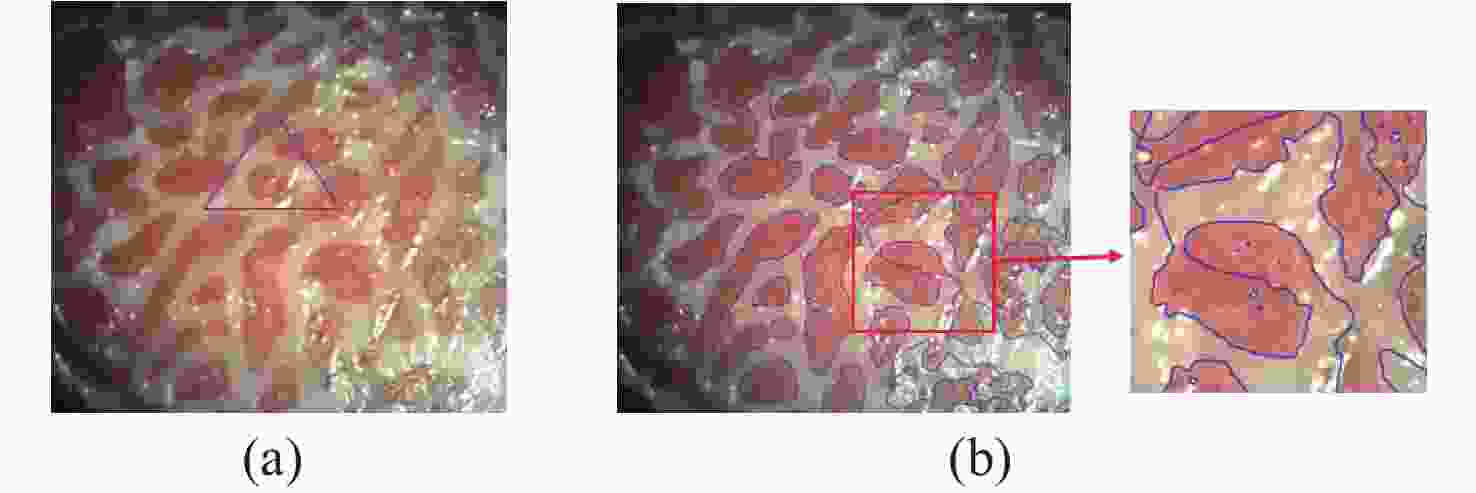
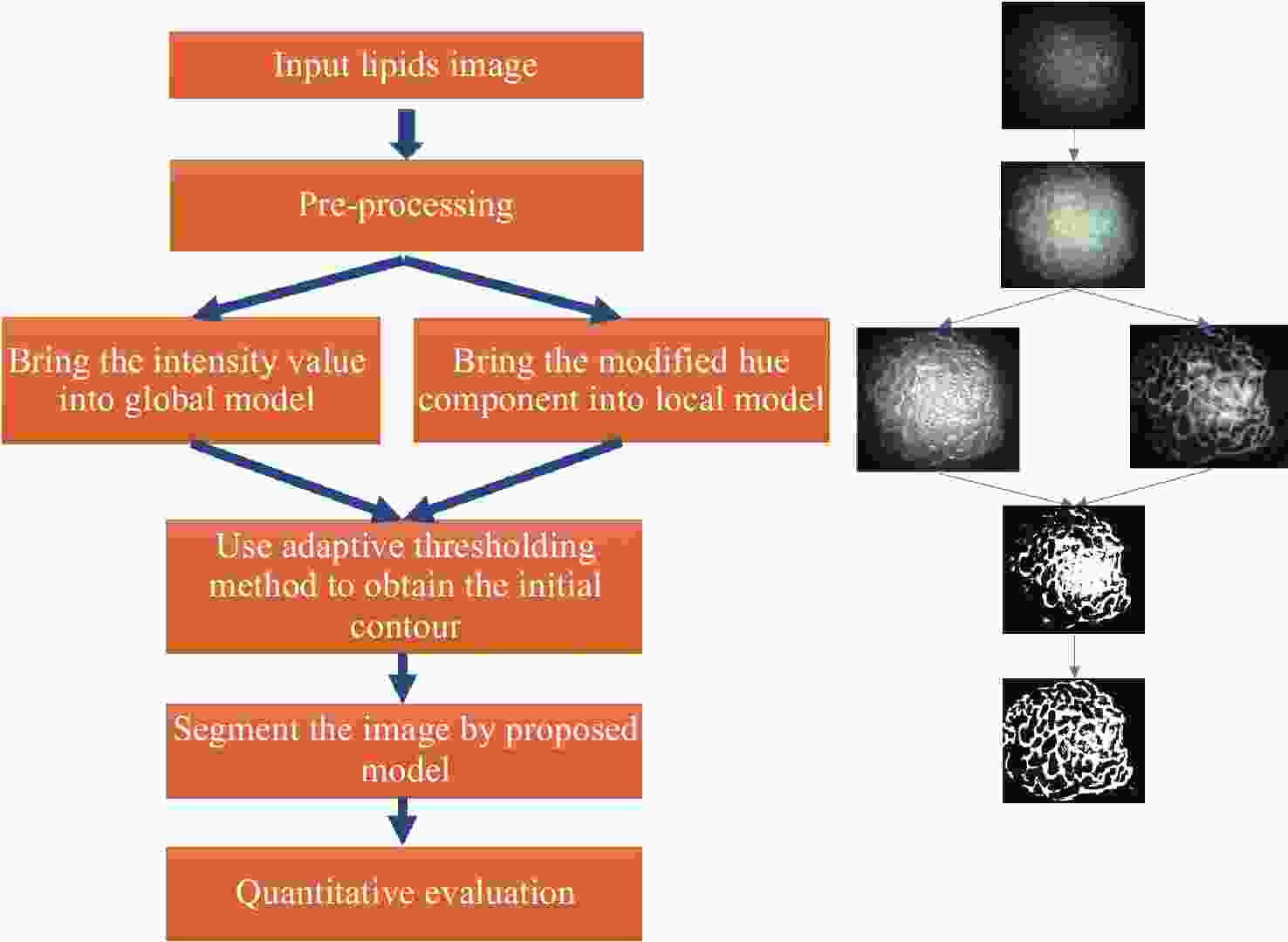
一种主要成分是脂质的白色不透明物质(WOS)会覆盖与癌症诊断有关的微观结构,但WOS的形态特征又与肿瘤分级有密切关系。为了给医生提供更多与脂质相关的可用信息,本文对脂质图像的分割方法进行了研究。首先,介绍了基于Retinex框架的脂质图像增强算法,并介绍了反光去除算法。然后,介绍了基于活动轮廓模型的脂质分割方法,该方法从校正后的色调值中提取局部信息,从强度值中提取全局信息,自适应地获得权重因子,并基于初始轮廓来分割脂质区域。最后,基于自研细胞内镜成像系统,设计了仿体实验来验证了该方法的有效性。实验结果表明,该分割方法的像素准确度、灵敏度、Dice系数均高于90%。该方法能够克服照明不均匀、反光等的影响,很好地反映脂质的形状,为医生提供可用的信息。
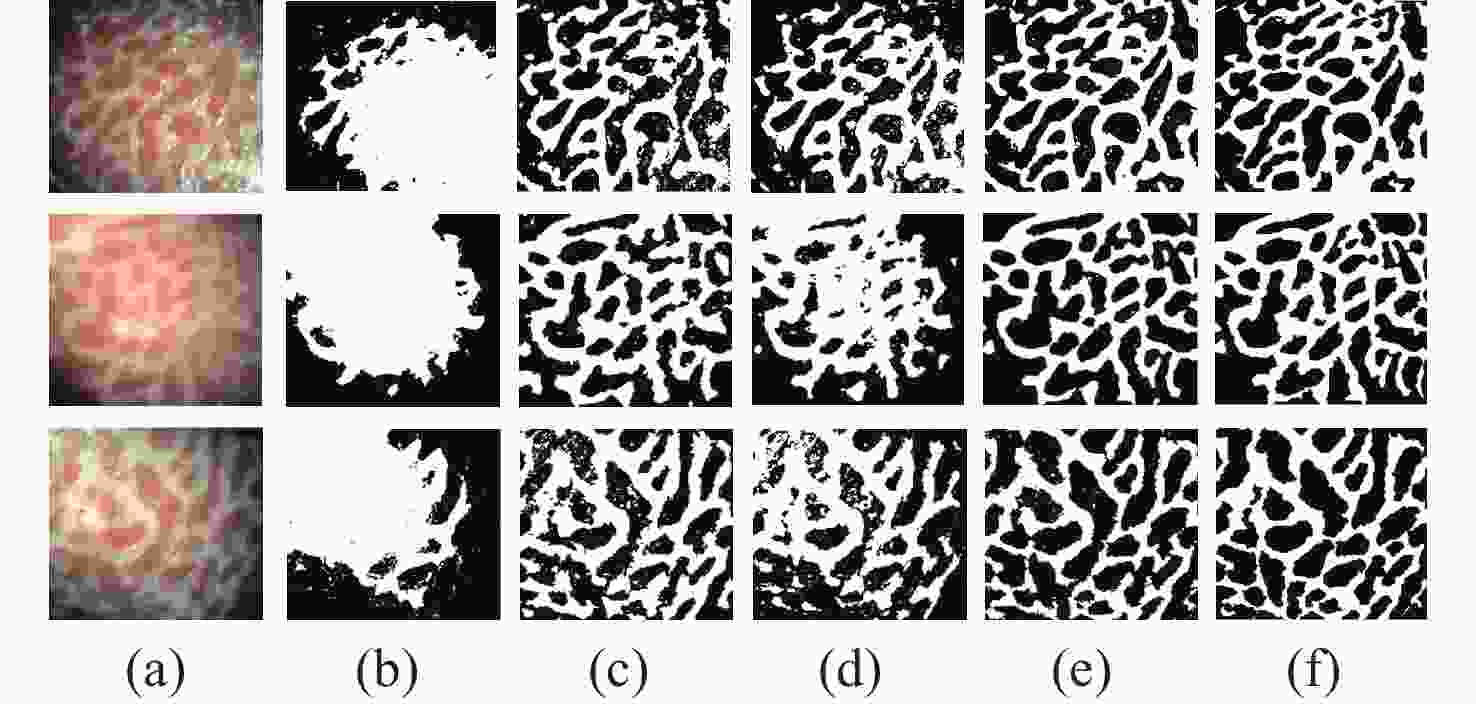
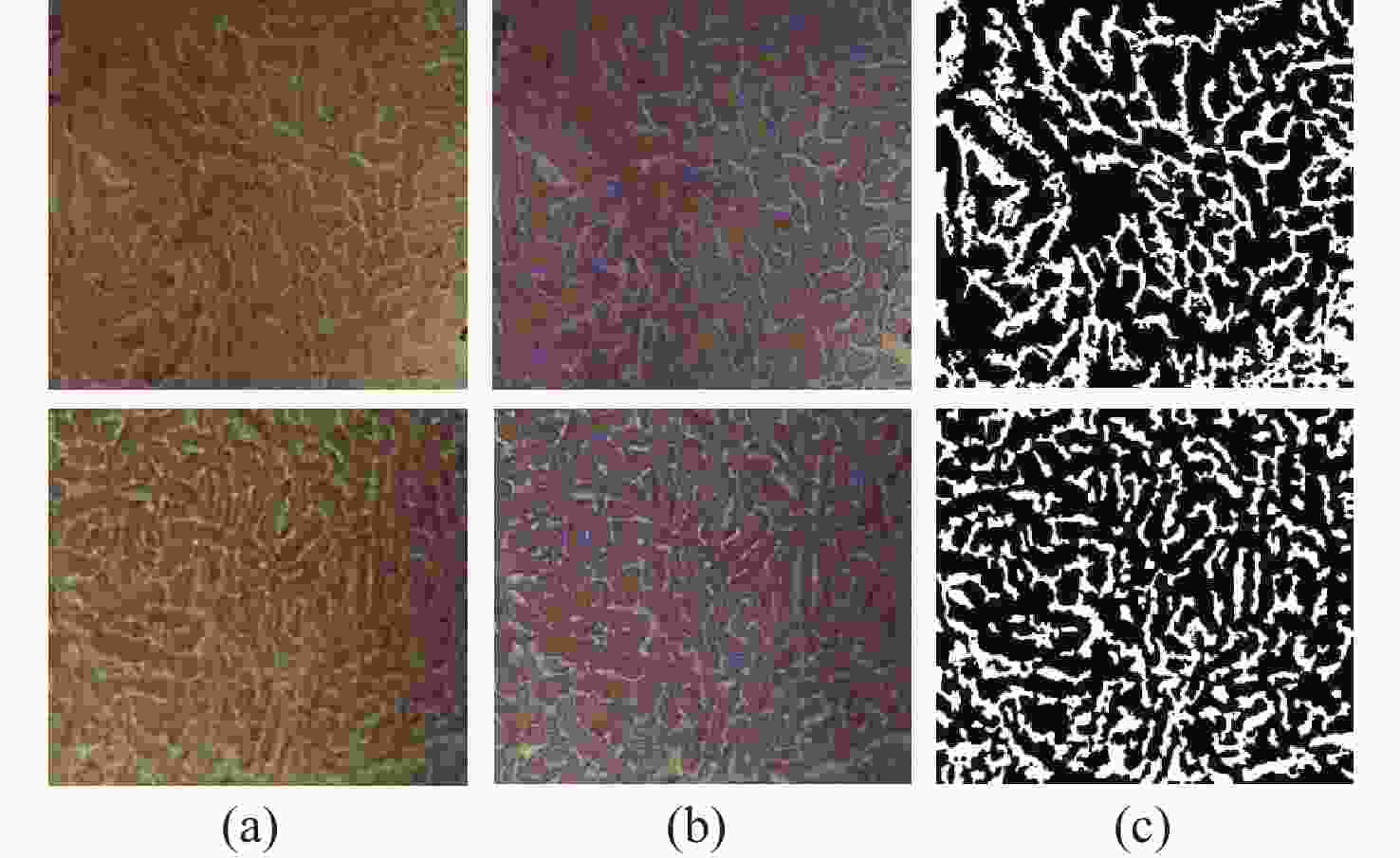
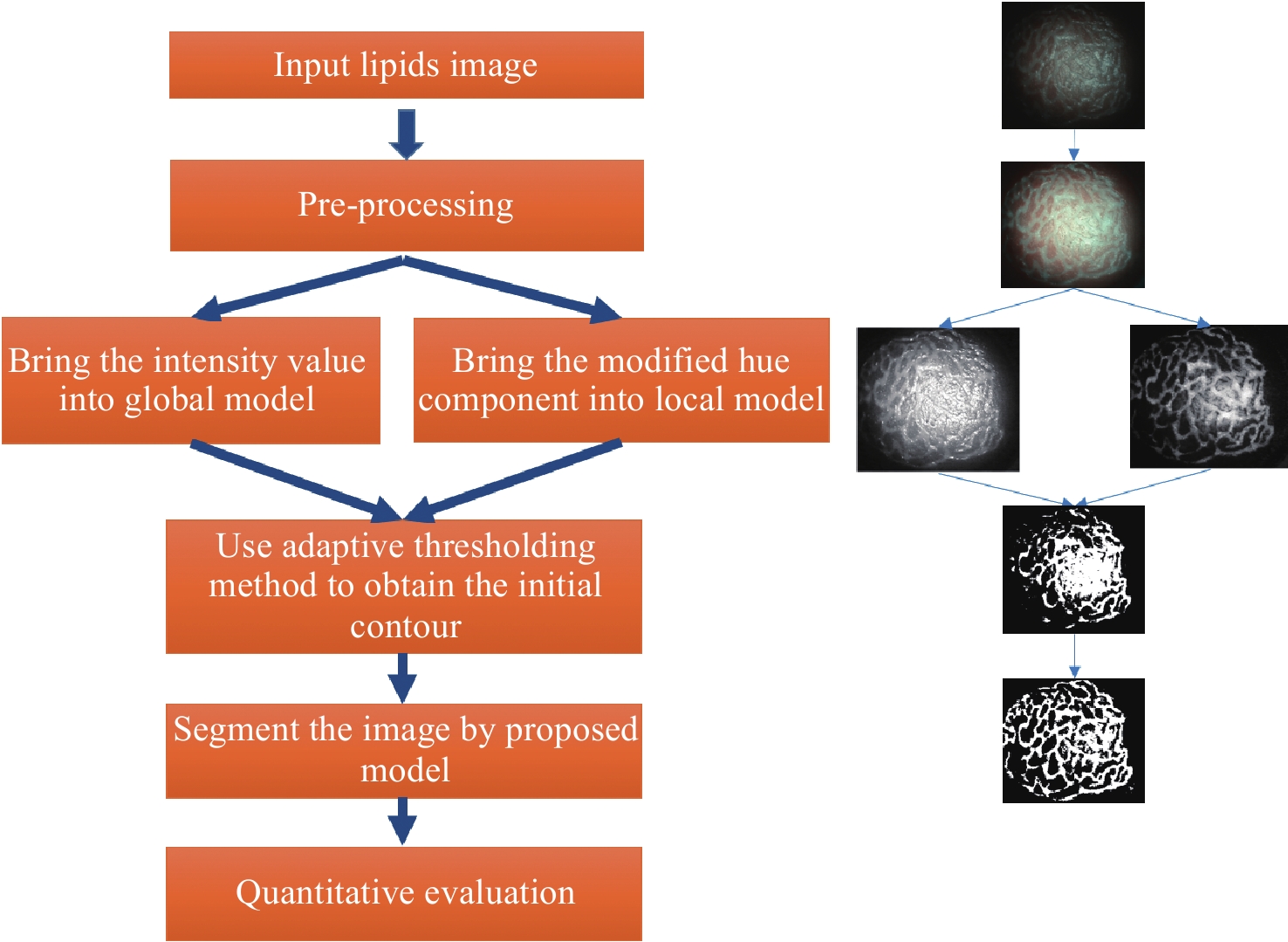
Abstract:Magnification endoscopy with narrow-band imaging (ME-NBI) has been widely used for cancer diagnosis. However, some microstructures are rendered invisible by a white opaque substance (WOS) composed mainly of lipids. In such lesions, the morphological structure of lipids becomes another marker of tumor grade. We propose a lipid segmentation method. First, the lipid image enhancement algorithm and the specular reflection correction algorithm are introduced. Then, in the framework of the active contour model, the proposed segmentation method extracts local information from modified hue value and global information from intensity value and adaptively obtains the weight factor to segment the lipid region based on the initial contour. This method’s effectiveness is verified by a phantom experiment, which shows that it attained higher than 90% in several key measures: pixel accuracy, sensitivity, and Dice coefficient. The proposed method can accurately reflect the shape of lipids to provide available information for doctors.
-
Key words:
- narrow-band imaging /
- lipids /
- segmentation /
- active contour model /
- phantom
-
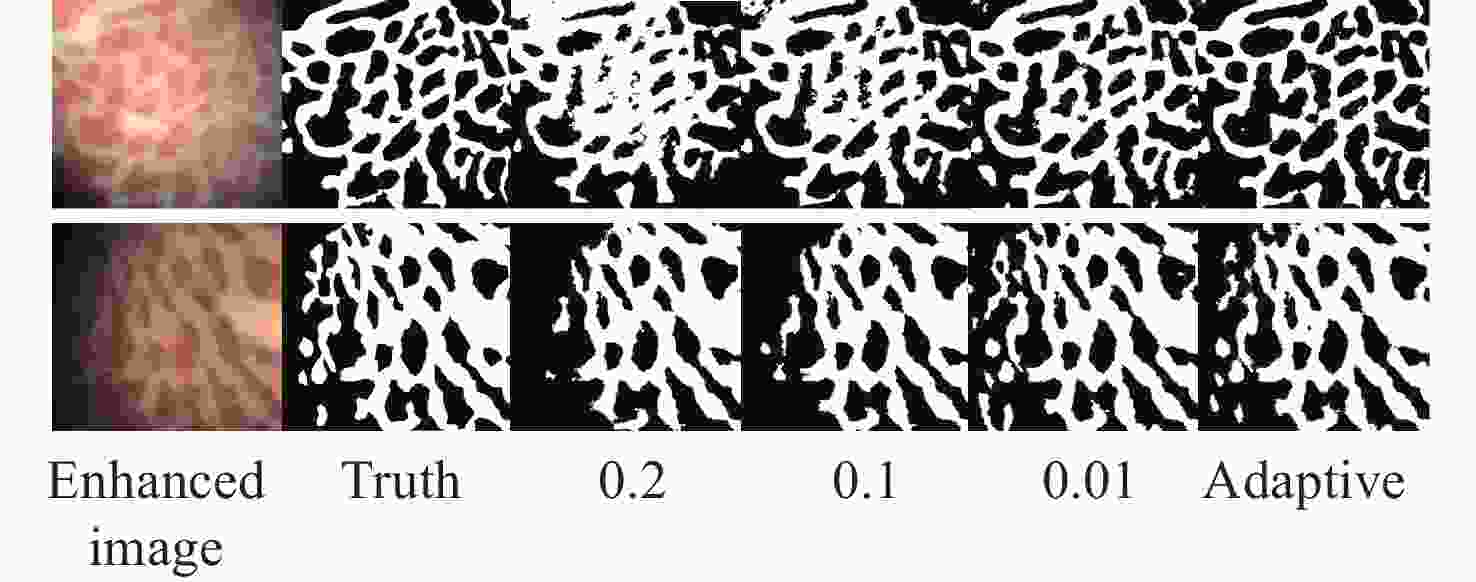
Table 1. The accuracy, sensitivity, and Dice values of the proposed method
Test image A/% Se/% D Test_1 91.23 90.47 0.9029 Test_2 93.23 91.65 0.9234 Test_3 91.61 93.33 0.9169 Table 2. The segmentation time and iteration numbers
C-V LBF LGIF proposed iterations Time(s) iterations Time(s) iterations Time(s) iterations Time(s) Image1 33 2.6089 19 1.4171 18 1.3352 9 0.8359 Image2 47 3.7690 48 3.6305 64 5.0240 6 0.6095 Image3 27 2.5913 45 4.5998 19 1.7729 9 0.8001 -
[1] SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590 [2] MIYAOKA M, YAO K, TANABE H, et al. Diagnosis of early gastric cancer using image enhanced endoscopy: a systematic approach[J]. Translational Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2020, 5: 50. doi: 10.21037/tgh.2019.12.16 [3] KODASHIMA S, FUJISHIRO M, KOIKE K. Image-enhanced endoscopy-NBI, FICE, i-scan[J]. Gastroenterological Endoscopy, 2010, 52(9): 2665-2677. [4] YAMADA S, DOYAMA H, YAO K, et al. An efficient diagnostic strategy for small, depressed early gastric cancer with magnifying narrow-band imaging: a post-hoc analysis of a prospective randomized controlled trial[J]. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 2014, 79(1): 55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2013.07.008 [5] ANG T L, FOCK K M, TEO E K, et al. The diagnostic utility of narrow band imaging magnifying endoscopy in clinical practice in a population with intermediate gastric cancer risk[J]. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2012, 24(4): 362-367. [6] YAO K, ANAGNOSTOPOULOS G K, RAGUNATH K. Magnifying endoscopy for diagnosing and delineating early gastric cancer[J]. Endoscopy, 2009, 41(5): 462-467. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1214594 [7] YAO K, TAKAKI Y, MATSUI T, et al. Clinical application of magnification endoscopy and narrow-band imaging in the upper gastrointestinal tract: new imaging techniques for detecting and characterizing gastrointestinal neoplasia[J]. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Clinics of North America, 2008, 18(3): 415-433. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2008.05.011 [8] MUTO M, YAO K, KAISE M, et al. Magnifying endoscopy simple diagnostic algorithm for early gastric cancer (MESDA-G)[J]. Digestive Endoscopy, 2016, 28(4): 379-393. doi: 10.1111/den.12638 [9] YAO K, IWASHITA A, NAMBU M, et al. Nature of white opaque substance in gastric epithelial neoplasia as visualized by magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging[J]. Digestive Endoscopy, 2012, 24(6): 419-425. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01314.x [10] YAO K, IWASHITA A, TANABE H, et al. White opaque substance within superficial elevated gastric neoplasia as visualized by magnification endoscopy with narrow-band imaging: a new optical sign for differentiating between adenoma and carcinoma[J]. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 2008, 68(3): 574-580. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2008.04.011 [11] NAKAYAMA A, KATO M, TAKATORI Y, et al. How I do it: Endoscopic diagnosis for superficial non-ampullary duodenal epithelial tumors[J]. Digestive Endoscopy, 2020, 32(3): 417-424. doi: 10.1111/den.13538 [12] HISABE T, YAO K, IMAMURA K, et al. White opaque substance visualized using magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging in colorectal epithelial neoplasms[J]. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 2014, 59(10): 2544-2549. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3204-5 [13] KAWASAKI K, KURAHARA K, YANAI S, et al. Significance of a white opaque substance under magnifying narrow-band imaging colonoscopy for the diagnosis of colorectal epithelial neoplasms[J]. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 2015, 82(6): 1097-1104. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2015.06.023 [14] HARA Y, GODA K, HIROOKA S, et al. Association between endoscopic milk-white mucosa, epithelial intracellular lipid droplets, and histological grade of superficial non-ampullary duodenal epithelial tumors[J]. Diagnostics, 2021, 11(5): 769. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11050769 [15] YAMASAKI K, HISABE T, YAO K, et al. White opaque substance, a new optical marker on magnifying endoscopy: usefulness in diagnosing colorectal epithelial neoplasms[J]. Clinical Endoscopy, 2021, 54(4): 570-577. doi: 10.5946/ce.2020.205 [16] UEO T, YONEMASU H, YAO K, et al. Histologic differentiation and mucin phenotype in white opaque substance-positive gastric neoplasias[J]. Endoscopy International Open, 2015, 3(6): E597-E604. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1393177 [17] OHTSU K, YAO K, MATSUNAGA K, et al. Lipid is absorbed in the stomach by epithelial neoplasms (adenomas and early cancers): a novel functional endoscopy technique[J]. Endoscopy International Open, 2015, 3(4): E318-E322. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1392095 [18] LIU X Q, WANG CH L, BAI J Y, et al. Hue-texture-embedded region-based model for magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging image segmentation based on visual features[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2017, 145: 53-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.04.010 [19] GANZ M, YANG X Y, SLABAUGH G. Automatic segmentation of polyps in colonoscopic narrow-band imaging data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2012, 59(8): 2144-2151. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2012.2195314 [20] FIGUEIREDO I N, PINTO L, FIGUEIREDO P N, et al. Unsupervised segmentation of colonic polyps in narrow-band imaging data based on manifold representation of images and Wasserstein distance[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2019, 53: 101577. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101577 [21] KASS M, WITKIN A, TERZOPOULOS D. Snakes: Active contour models[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1988, 1(4): 321-331. doi: 10.1007/BF00133570 [22] BRADLEY D, ROTH G. Adaptive thresholding using the integral image[J]. Journal of Graphics Tools, 2007, 12(2): 13-21. doi: 10.1080/2151237X.2007.10129236 [23] WANG L, LI CH M, SUN Q S, et al. Active contours driven by local and global intensity fitting energy with application to brain MR image segmentation[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2009, 33(7): 520-531. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2009.04.010 [24] CHAN T F, VESE L A. Active contours without edges[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(2): 266-277. doi: 10.1109/83.902291 [25] LI CH M, KAO C Y, GORE J C, et al. Implicit active contours driven by local binary fitting energy[C]. 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2007: 1-7. [26] JIANG X L, WU X L, XIONG Y, et al. Active contours driven by local and global intensity fitting energies based on local entropy[J]. Optik, 2015, 126(24): 5672-5677. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.09.021 [27] LI CH M, XU CH Y, GUI CH F, et al. Level set evolution without re-initialization: a new variational formulation[C]. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'05), IEEE, 2005: 430-436. [28] ZHANG L, PENG X G, LI G, et al. A novel active contour model for image segmentation using local and global region-based information[J]. Machine Vision and Applications, 2017, 28(1-2): 75-89. doi: 10.1007/s00138-016-0805-3 [29] ZHANG W, NIU CH Y, YOU X H, et al. Endocytoscopic imaging system with high magnification and large field of view[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(17): 1717001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1717001 [30] POGUE B W, PATTERSON M S. Review of tissue simulating phantoms for optical spectroscopy, imaging and dosimetry[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2006, 11(4): 041102. doi: 10.1117/1.2335429 [31] RUSSELL B C, TORRALBA A, MURPHY K P, et al. LabelMe: A database and web-based tool for image annotation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2008, 77(1): 157-173. -





 下载:
下载: