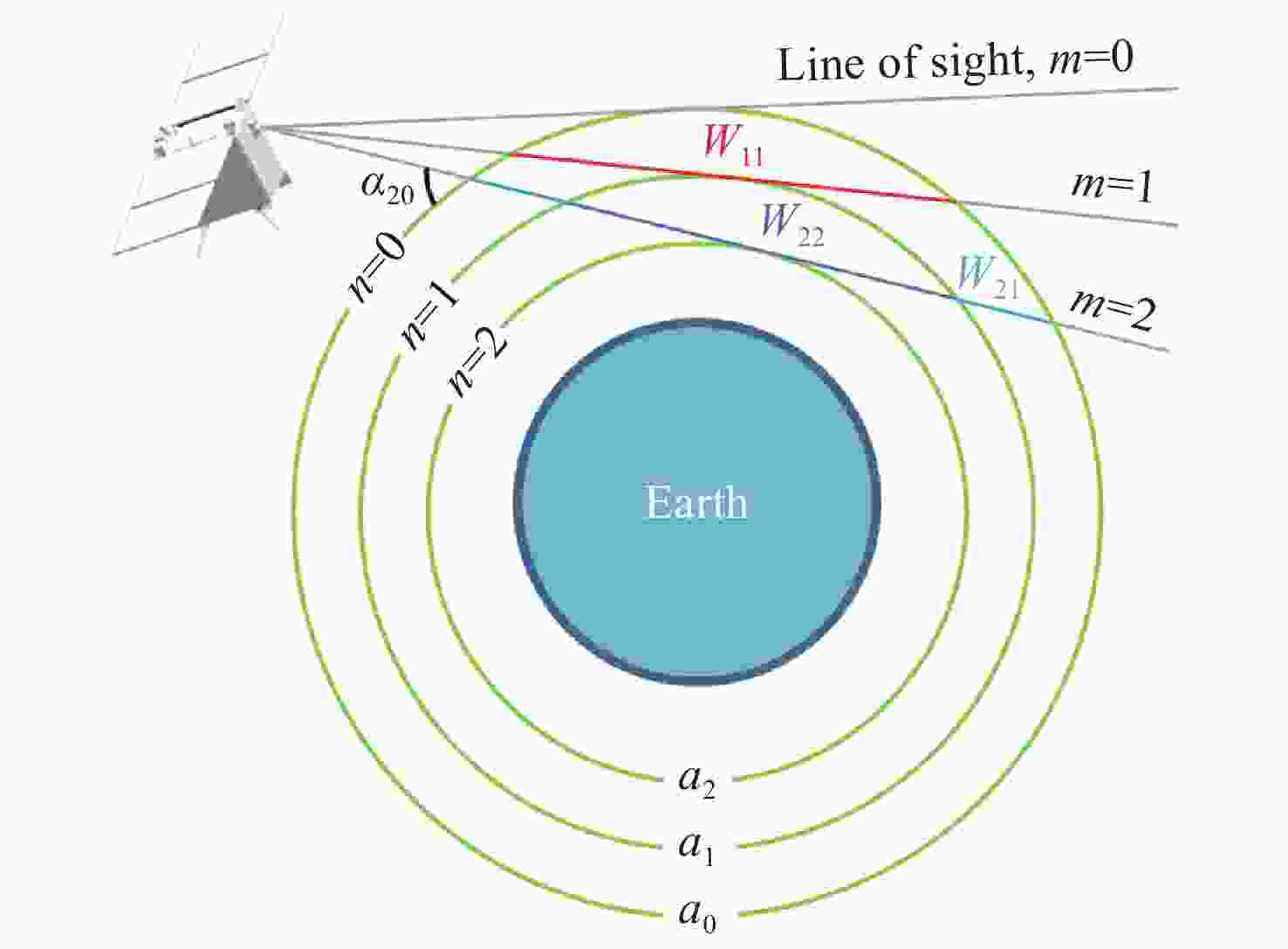
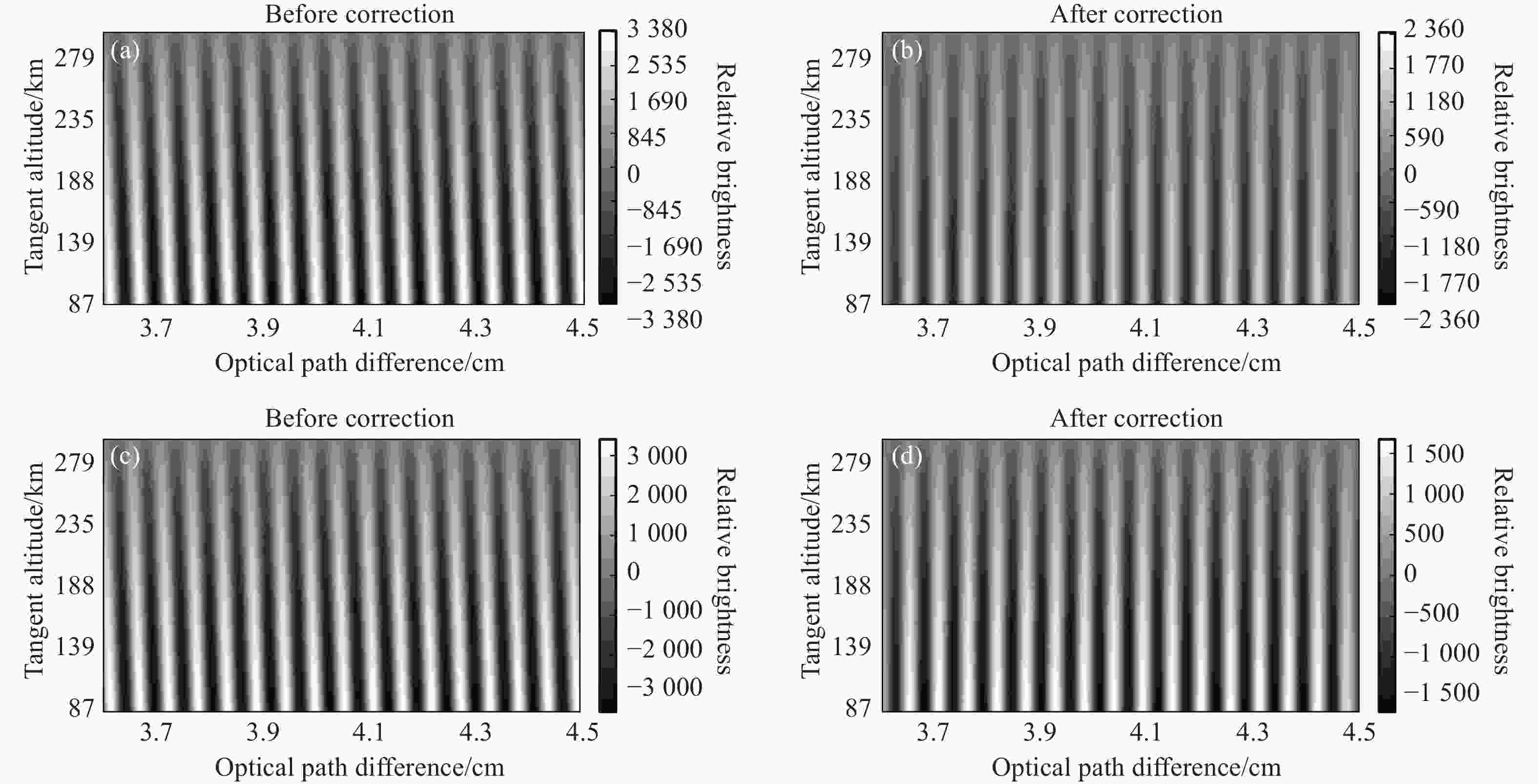
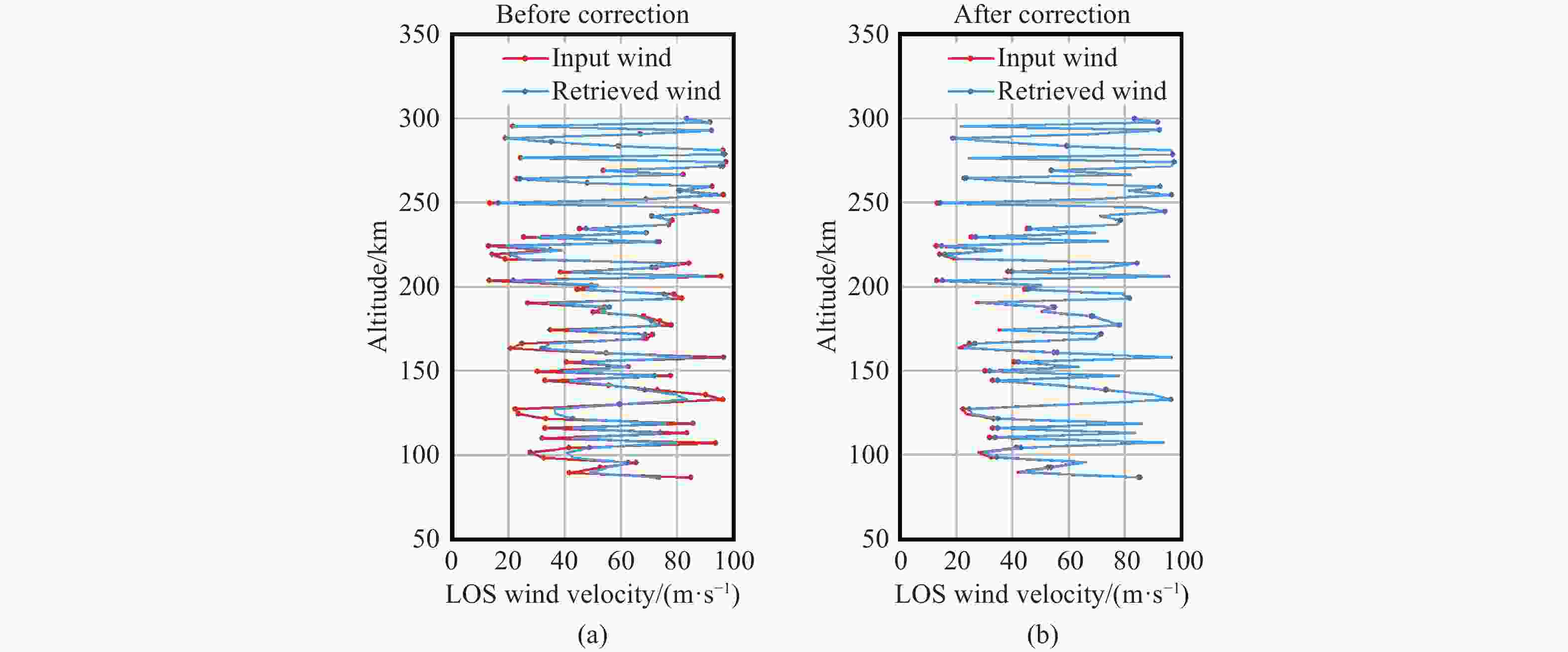
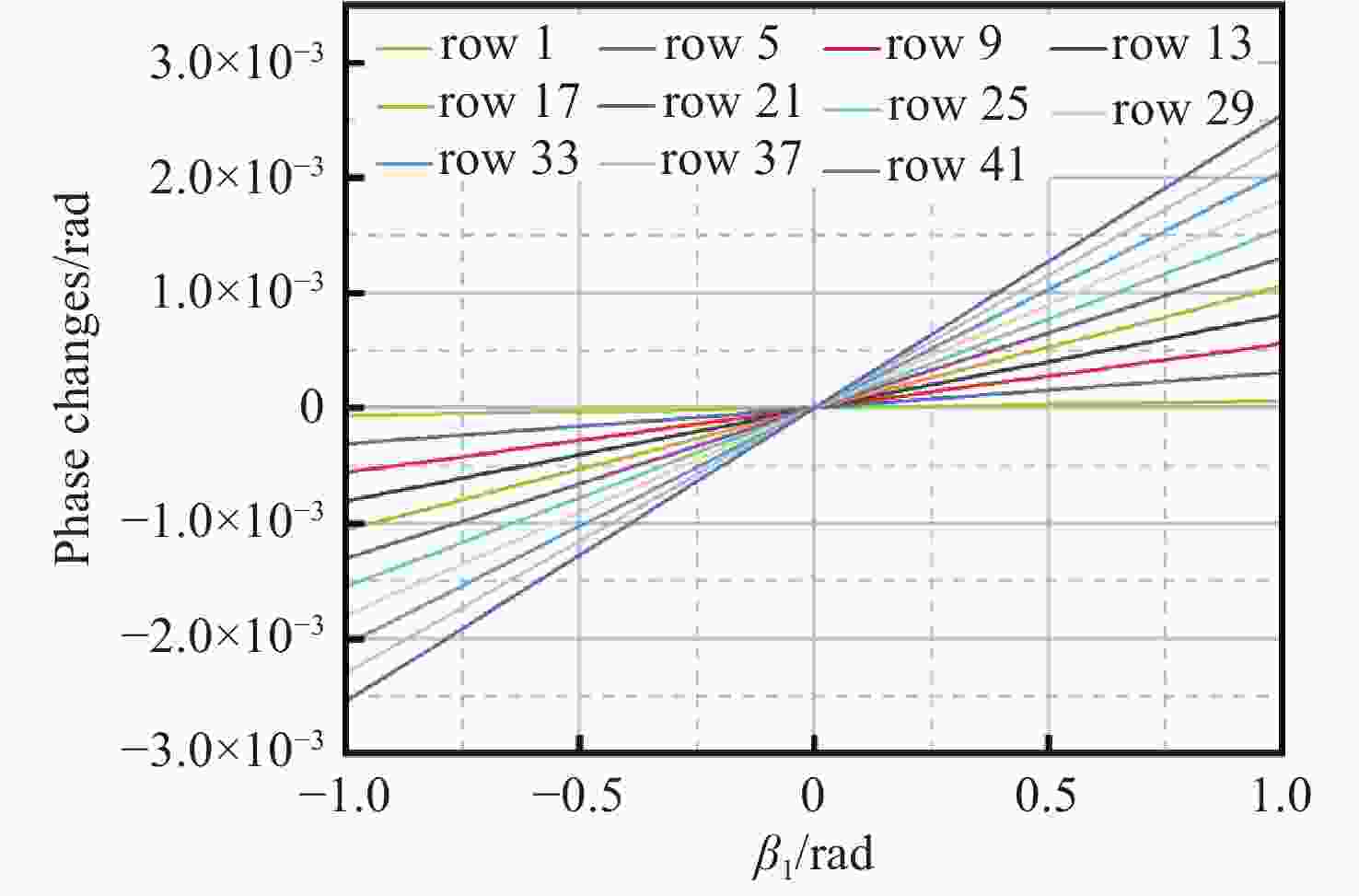
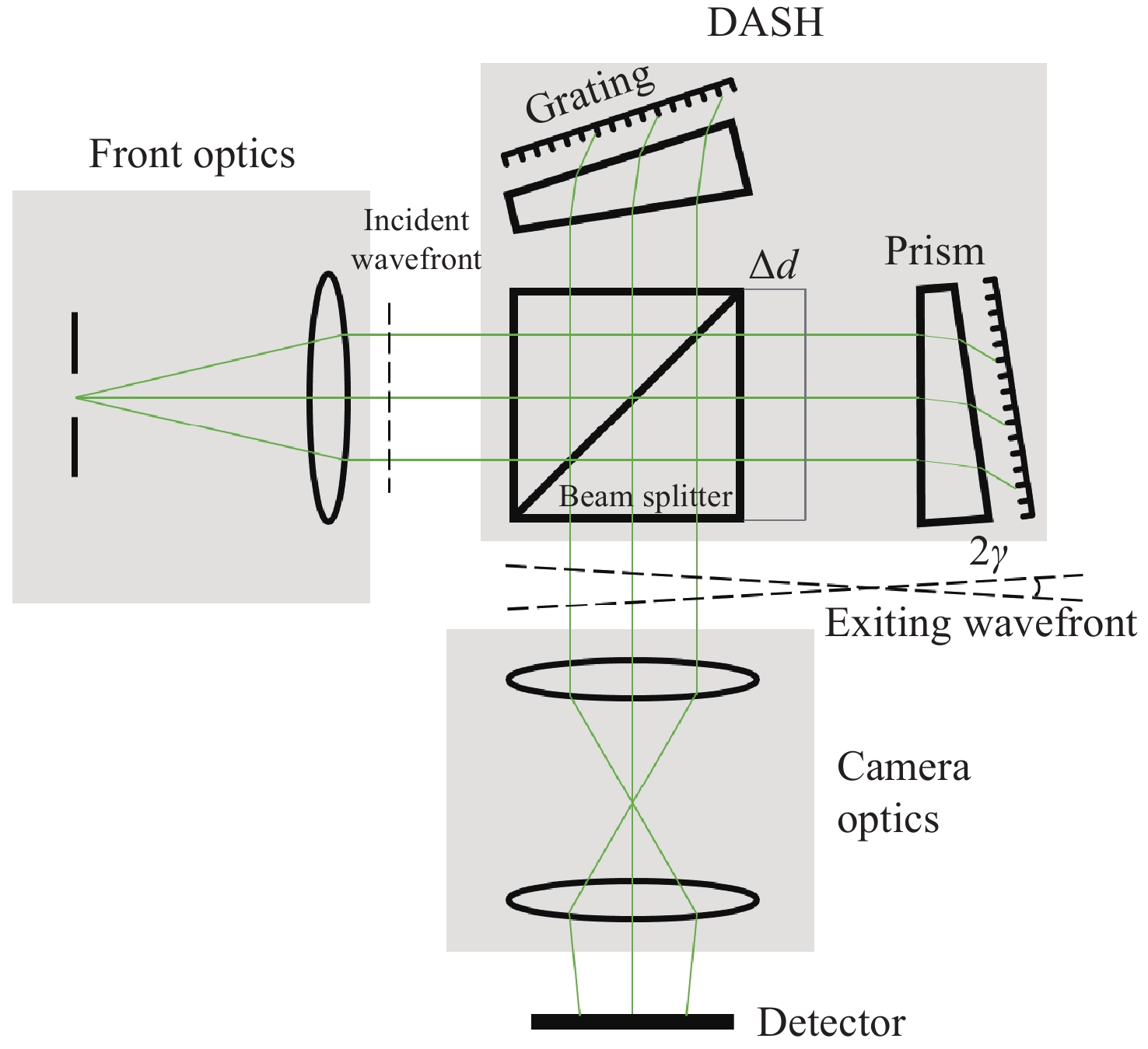
Phase distortion correction of fringe patterns in spaceborne Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne interferometry
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2024-0007
-
摘要:
作为观测大气风的先进设备,星载多普勒非对称空间外差(DASH)干涉仪也面临着与相位畸变相关的挑战,特别是在临边探测场景中。本文讨论了星载DASH干涉仪的干涉图建模和相位畸变校正技术。对临边观测中有与无多普勒频移的相位畸变干涉图进行了建模,并通过数值模拟验证了解析表达式的有效性。仿真结果表明,在使用洋葱皮反演算法处理相位失真干涉图时,误差会逐层传播。相比之下,相位畸变校正算法可以实现有效的校正。该相位校正方法可成功应用于星载DASH干涉仪干涉图中的相位畸变校正,为提高其测量精度提供了可行的解决方案。
-
关键词:
- 多普勒非对称空间外差光谱 /
- 相位畸变 /
- 相位反演 /
- 大气风测量
Abstract:As an advanced device for observing atmospheric winds, the spaceborne Doppler Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne (DASH) interferometer also encounters challenges associated with phase distortion, particularly in limb sounding scenarios. This paper discusses interferogram modeling and phase distortion correction techniques for spaceborne DASH interferometers. The modeling of phase distortion interferograms with and without Doppler shift for limb observation was conducted, and the effectiveness of the analytical expression was verified through numerical simulation. The simulation results indicate that errors propagate layer by layer while using the onion-peeling inversion algorithm to handle phase-distorted interferograms. In contrast, the phase distortion correction algorithm can achieve effective correction. This phase correction method can be successfully applied to correct phase distortions in the interferograms of the spaceborne DASH interferometer, providing a feasible solution to enhance its measurement accuracy.
-
Table 1. Parameters for simulation
Parameters Values Wavelengths/nm 557.7 Littrow wavelengths/nm 557.137 OPD offset/mm 20.363 Detector resolution 82× 1024 Grating groove density/(grooves·mm−1) 600 Diffraction order 1 Pixel pitch/µm 13 -
[1] GIRAUD A, PETIT M. Ionospheric Techniques and Phenomena[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 1978. [2] VADAS S L, LIU H L. Generation of large-scale gravity waves and neutral winds in the thermosphere from the dissipation of convectively generated gravity waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2009, 114(A10): A10310. [3] WANG W B, BURNS A G, LIU J. Upper thermospheric winds: forcing, variability, and effects[M]//WANG W B, ZHANG Y L, PAXTON L J. Upper Atmosphere Dynamics and Energetics. Hoboken: American Geophysical Union, 2021: 41-63. [4] MERIWETHER J W. Studies of thermospheric dynamics with a Fabry–Perot interferometer network: a review[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2006, 68(13): 1576-1589. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2005.11.014 [5] MAKELA J J, BAUGHMAN M, NAVARRO L A, et al. Validation of ICON-MIGHTI thermospheric wind observations: 1. Nighttime red-line ground-based fabry-perot interferometers[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2021, 126(2): e2020JA028726. doi: 10.1029/2020JA028726 [6] WEI D K. Development of an optical instrument for the observation of neutral winds in Earth's upper atmosphere[D]. Wuppertal: Bergische Universität, 2020. [7] ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, BABCOCK D D, et al. Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectroscopy (DASH): an innovative concept for measuring winds in planetary atmospheres[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6303: 63030T. doi: 10.1117/12.681704 [8] ENGLERT C R, BABCOCK D D, HARLANDER J M. Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectroscopy (DASH): concept and experimental demonstration[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(29): 7297-7307. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.007297 [9] WEI D K, ZHU Y J, LIU J L, et al. Thermally stable monolithic Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne interferometer: optical design and laboratory performance[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(14): 19887-19900. doi: 10.1364/OE.394101 [10] ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, MARR K D, et al. Michelson interferometer for global high-resolution thermospheric imaging (MIGHTI) on-orbit wind observations: data analysis and instrument performance[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2023, 219(3): 27. doi: 10.1007/s11214-023-00971-1 [11] ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, CARDON J G, et al. Correction of phase distortion in spatial heterodyne spectroscopy[J]. Applied Optics, 2004, 43(36): 6680-6687. doi: 10.1364/AO.43.006680 [12] ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, EMMERT J T, et al. Initial ground-based thermospheric wind measurements using Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectroscopy (DASH)[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(26): 27416-27430. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.027416 [13] HARLANDER J M, ENGLERT C R, MARR K D, et al. On the uncertainties in determining fringe phase in Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectroscopy[J]. Applied Optics, 2019, 58(13): 3613-3619. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.003613 [14] WEI D K, GONG Q CH, CHEN Q Y, et al. Modeling and correction of fringe patterns in Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne interferometry[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(35): 10528-10537. doi: 10.1364/AO.473147 [15] HARDING B J, MAKELA J J, ENGLERT C R, et al. The MIGHTI wind retrieval algorithm: description and verification[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2017, 212(1): 585-600. [16] WU Y J J, HARDING B J, TRIPLETT C C, et al. Errors from asymmetric emission rate in spaceborne, limb sounding doppler interferometry: a correction algorithm with application to ICON/MIGHTI[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2020, 7(10): e2020EA001164. doi: 10.1029/2020EA001164 [17] HARLANDER J, REYNOLDS R J, ROESLER F L. Spatial heterodyne spectroscopy for the exploration of diffuse interstellar emission lines at far-ultraviolet wavelengths[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 1992, 396(2): 730-740. [18] ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, BROWN C M, et al. Michelson Interferometer for Global High-Resolution Thermospheric Imaging (MIGHTI): instrument design and calibration[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2017, 212(1-2): 553-584. doi: 10.1007/s11214-017-0358-4 -





 下载:
下载: