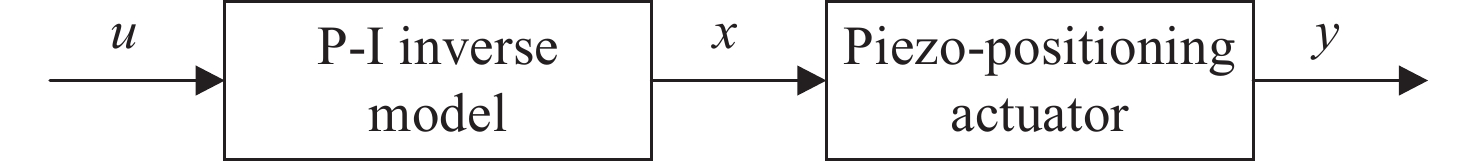
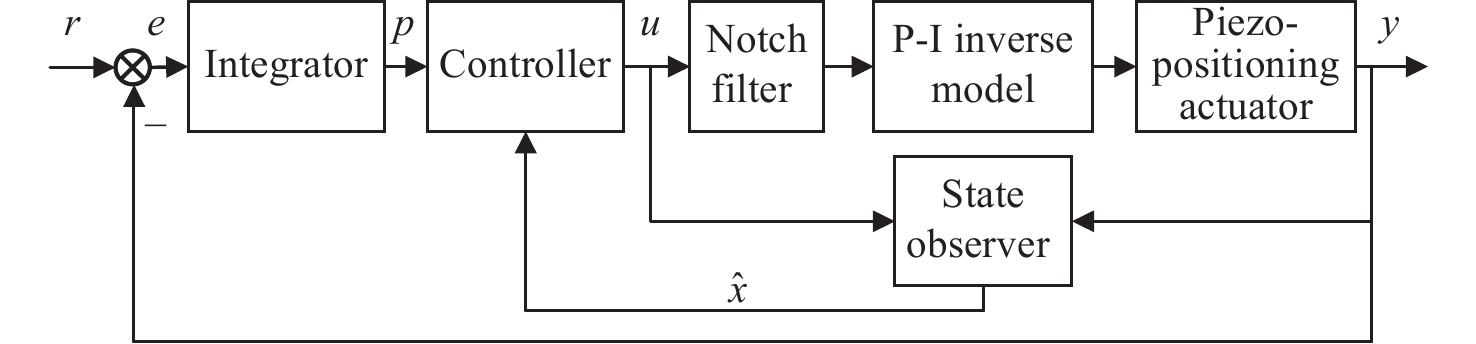
Modeling and sliding mode control based on inverse compensation of piezo-positioning system
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2024-0012
-
摘要:
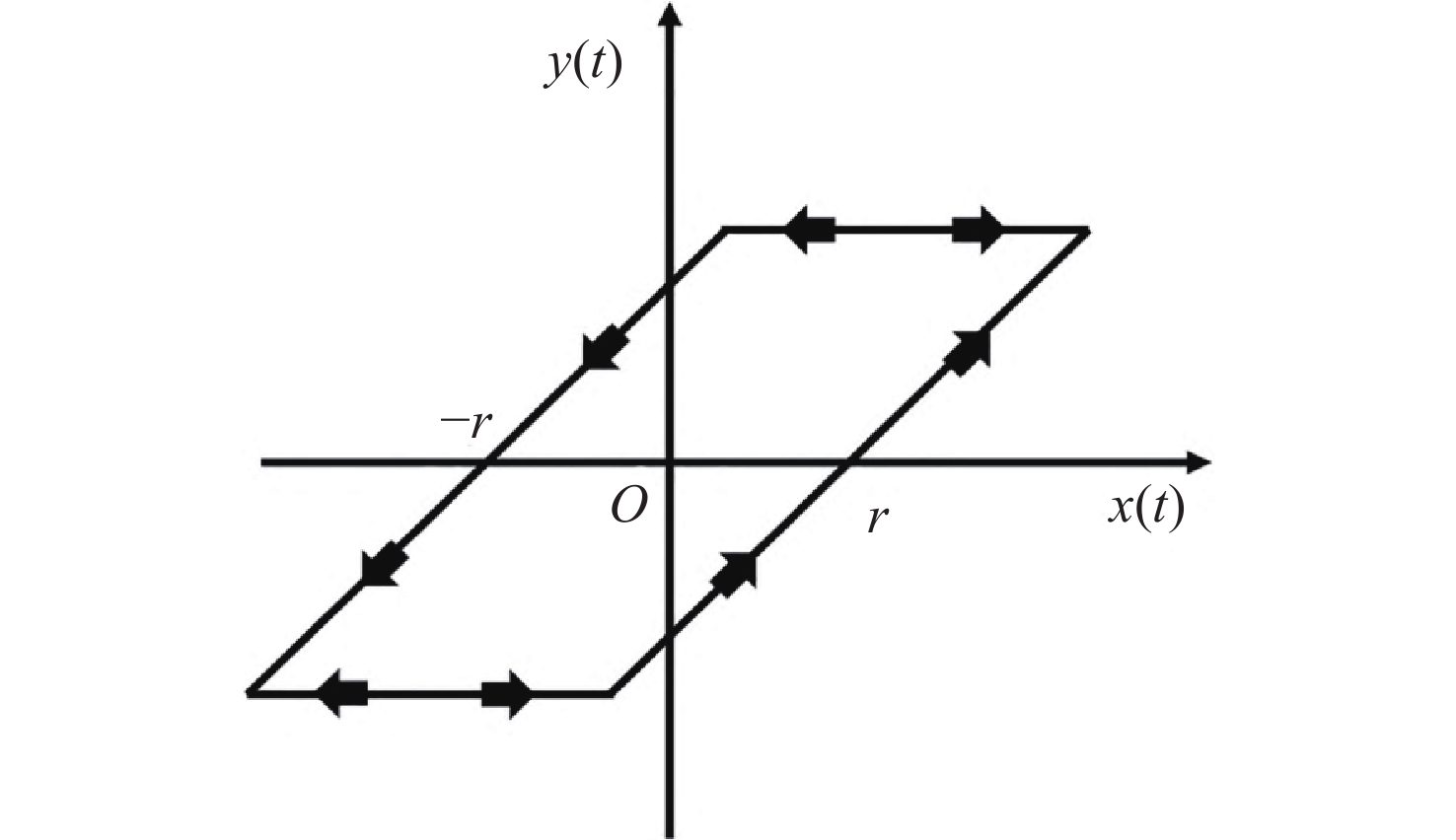
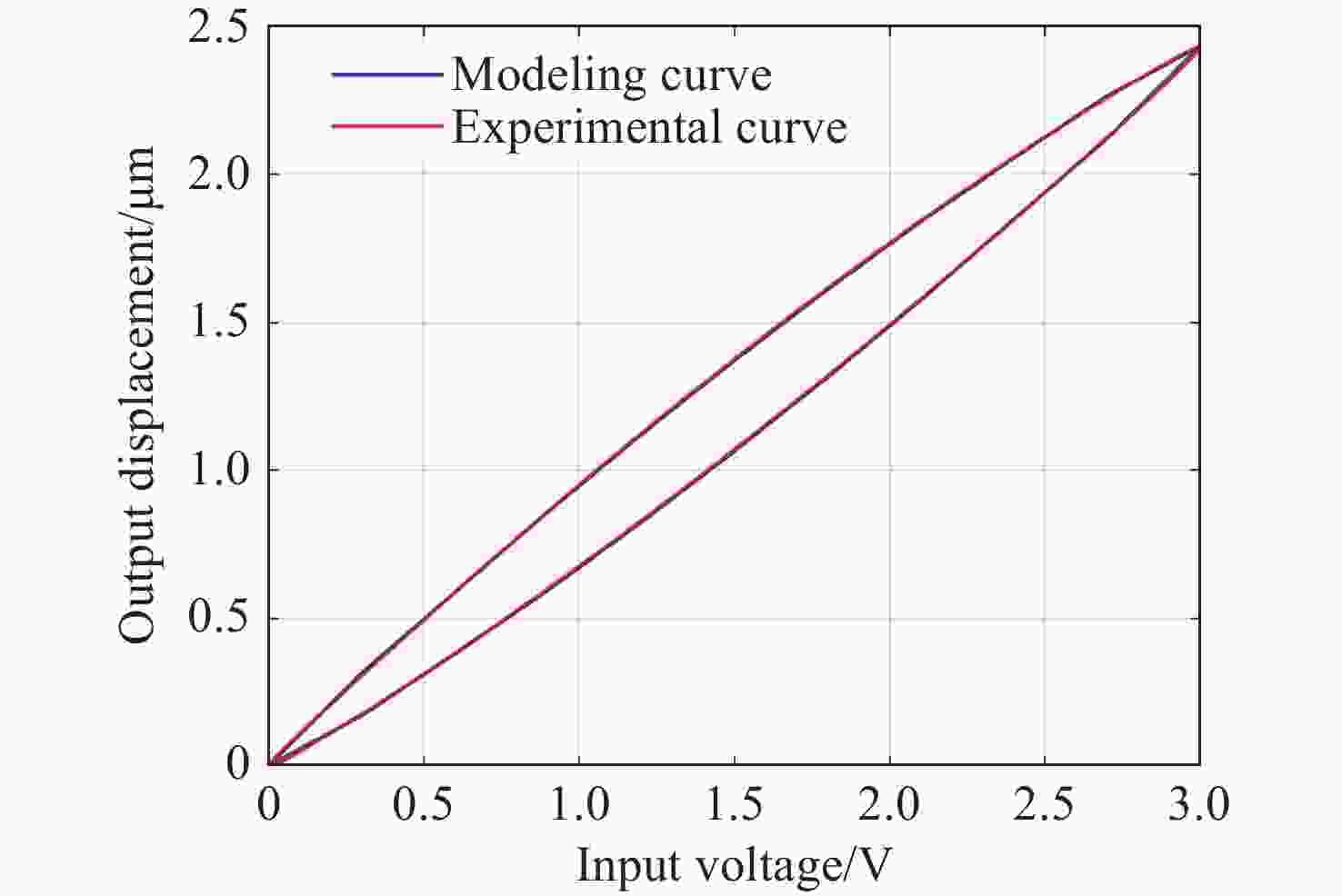
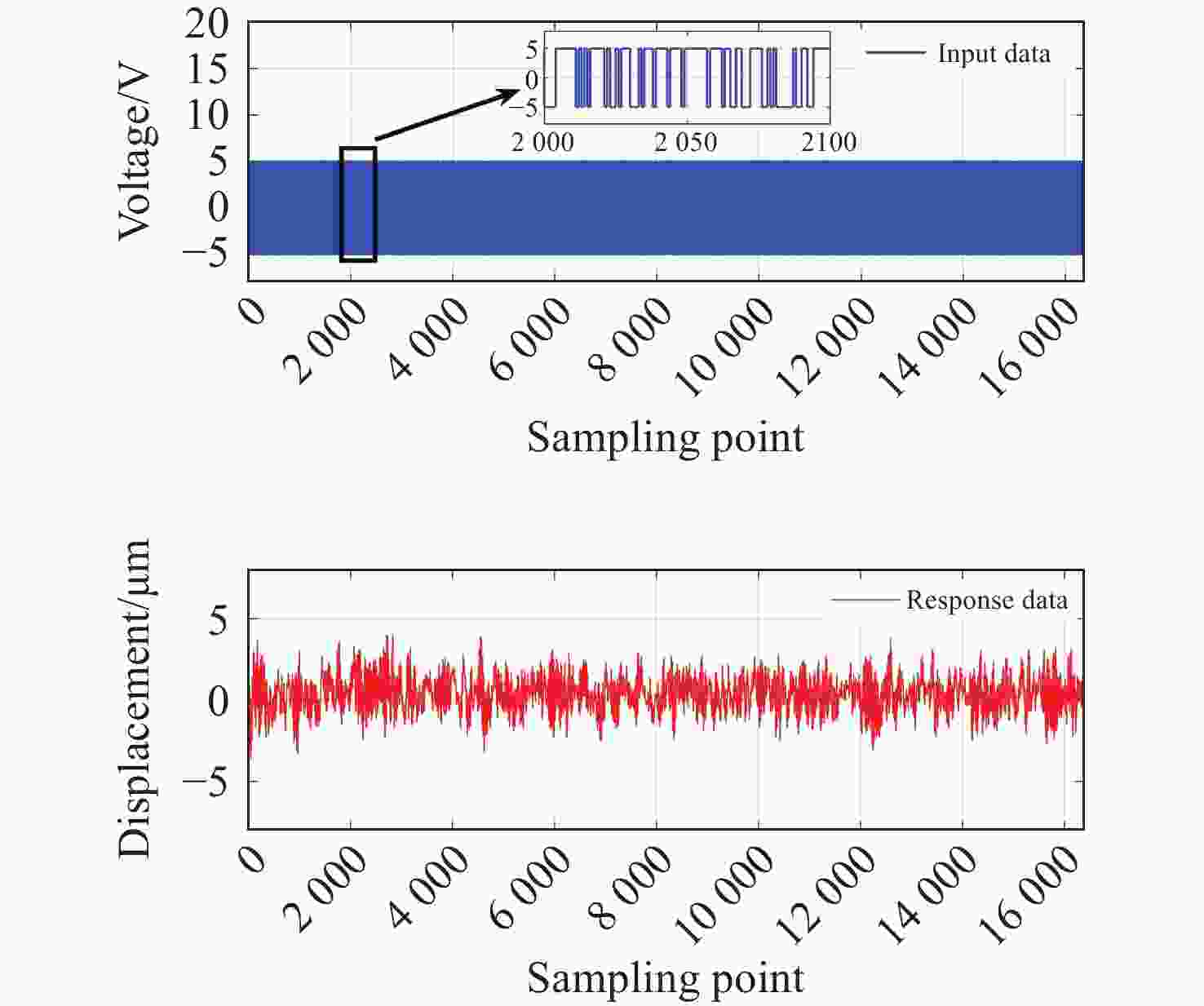
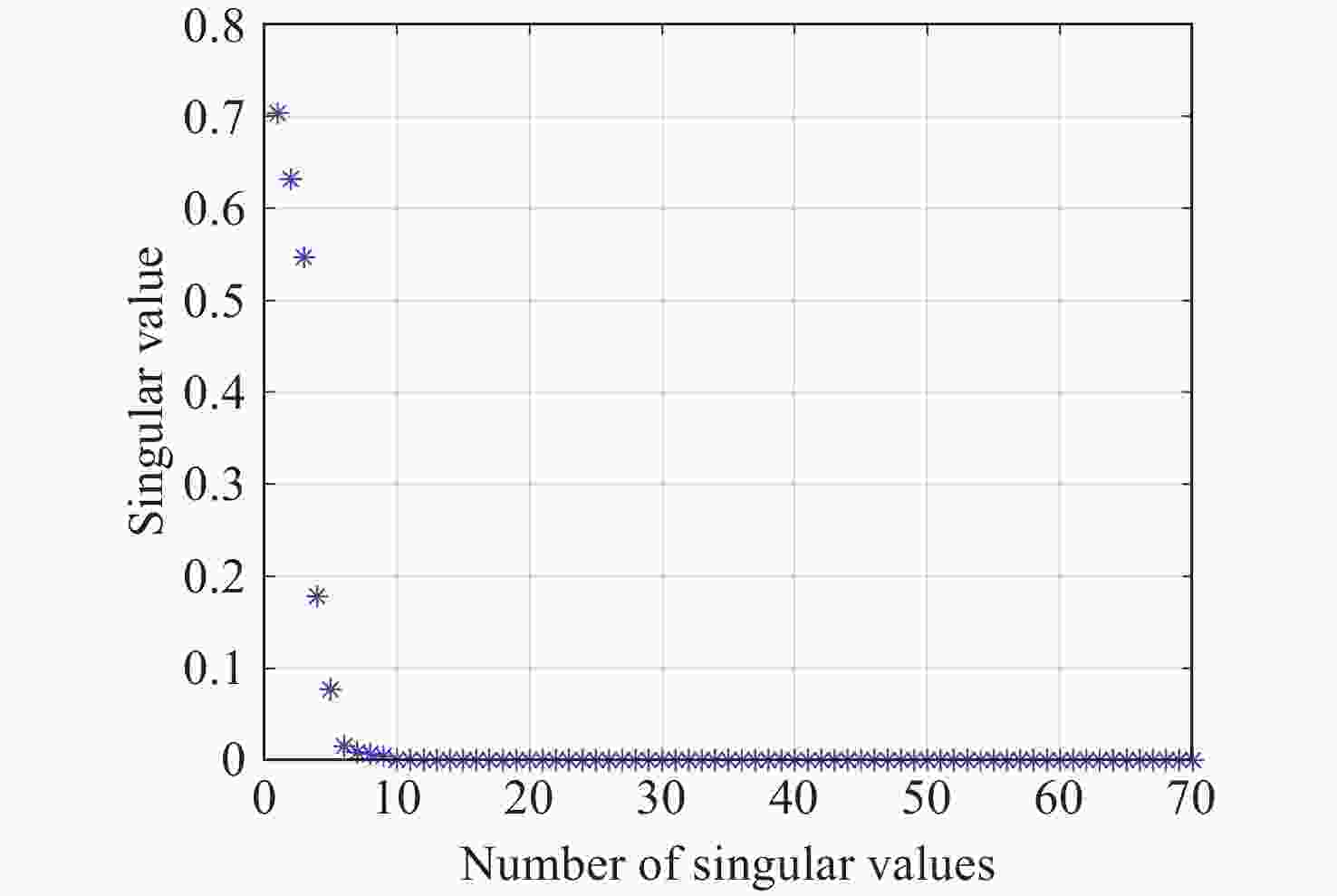
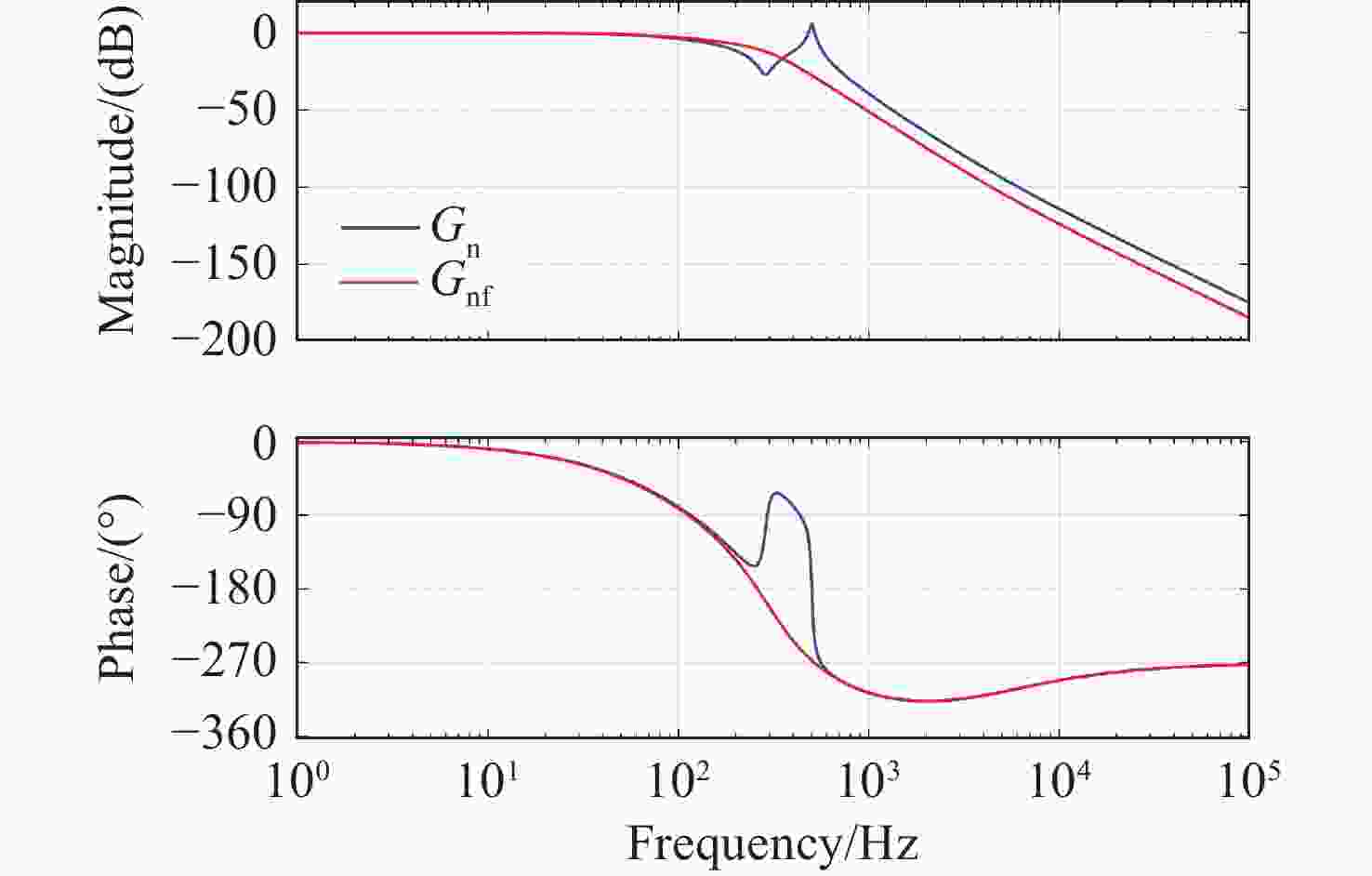
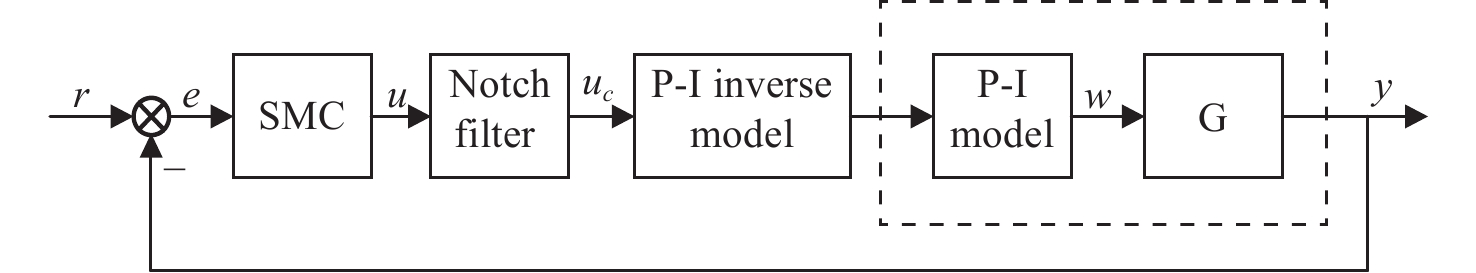
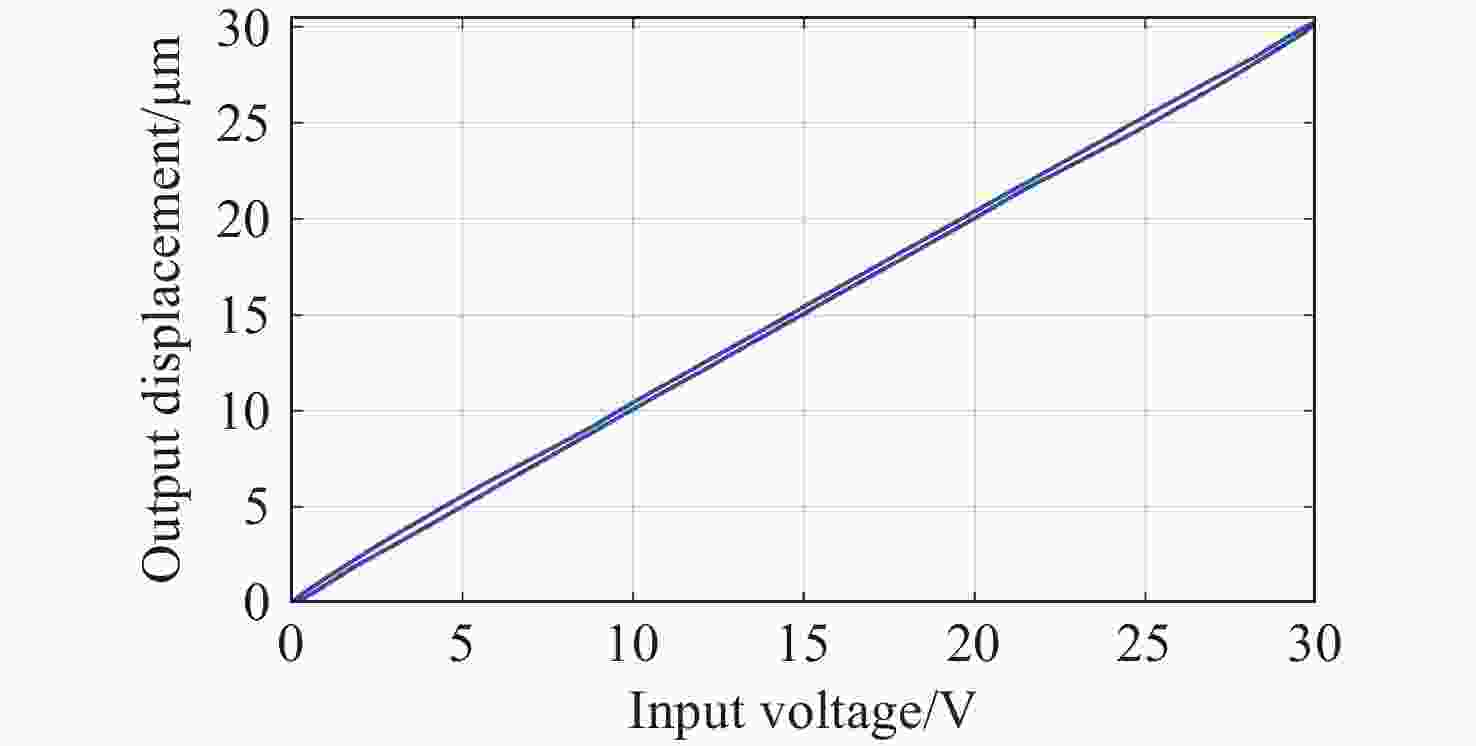
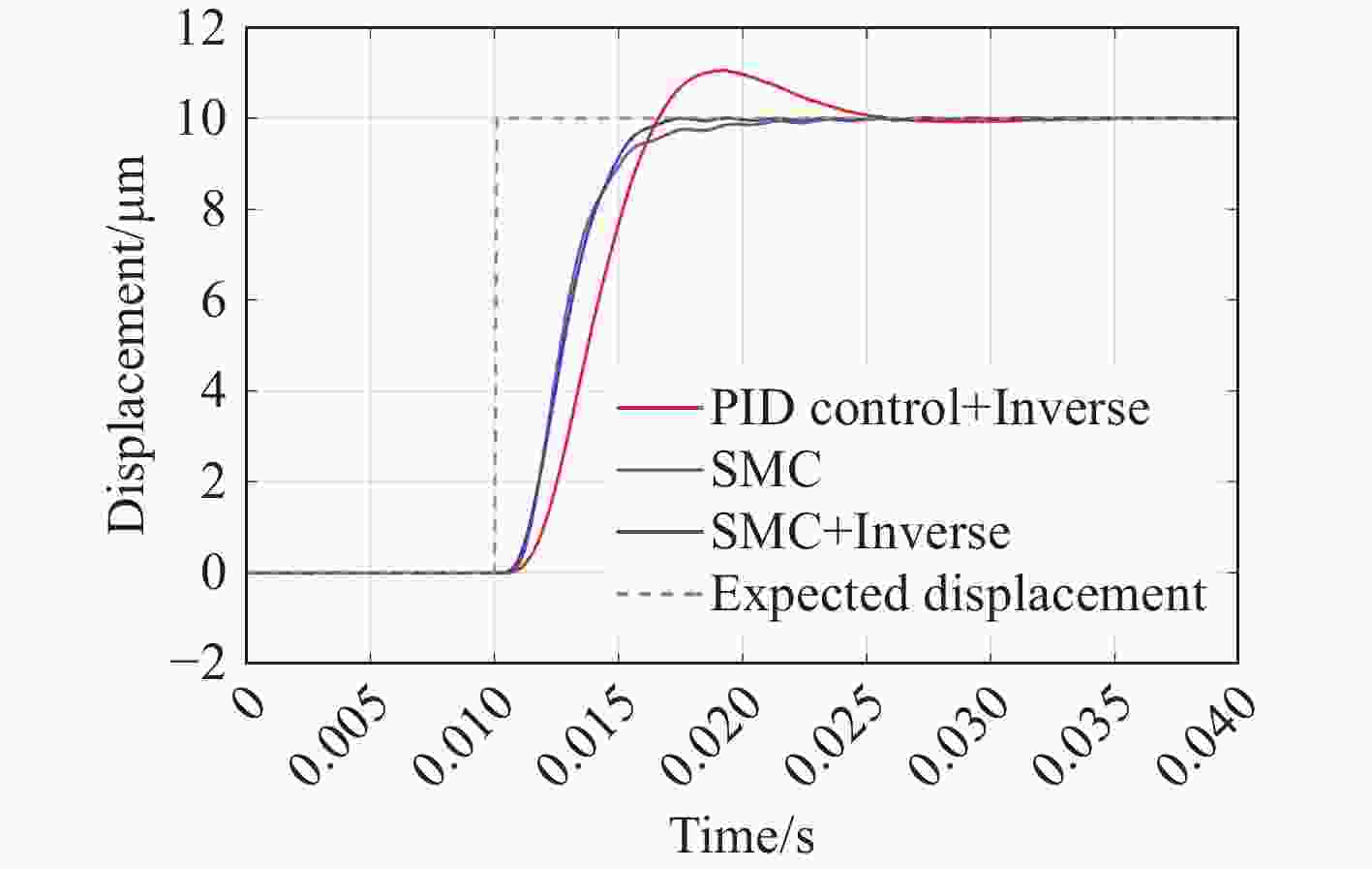
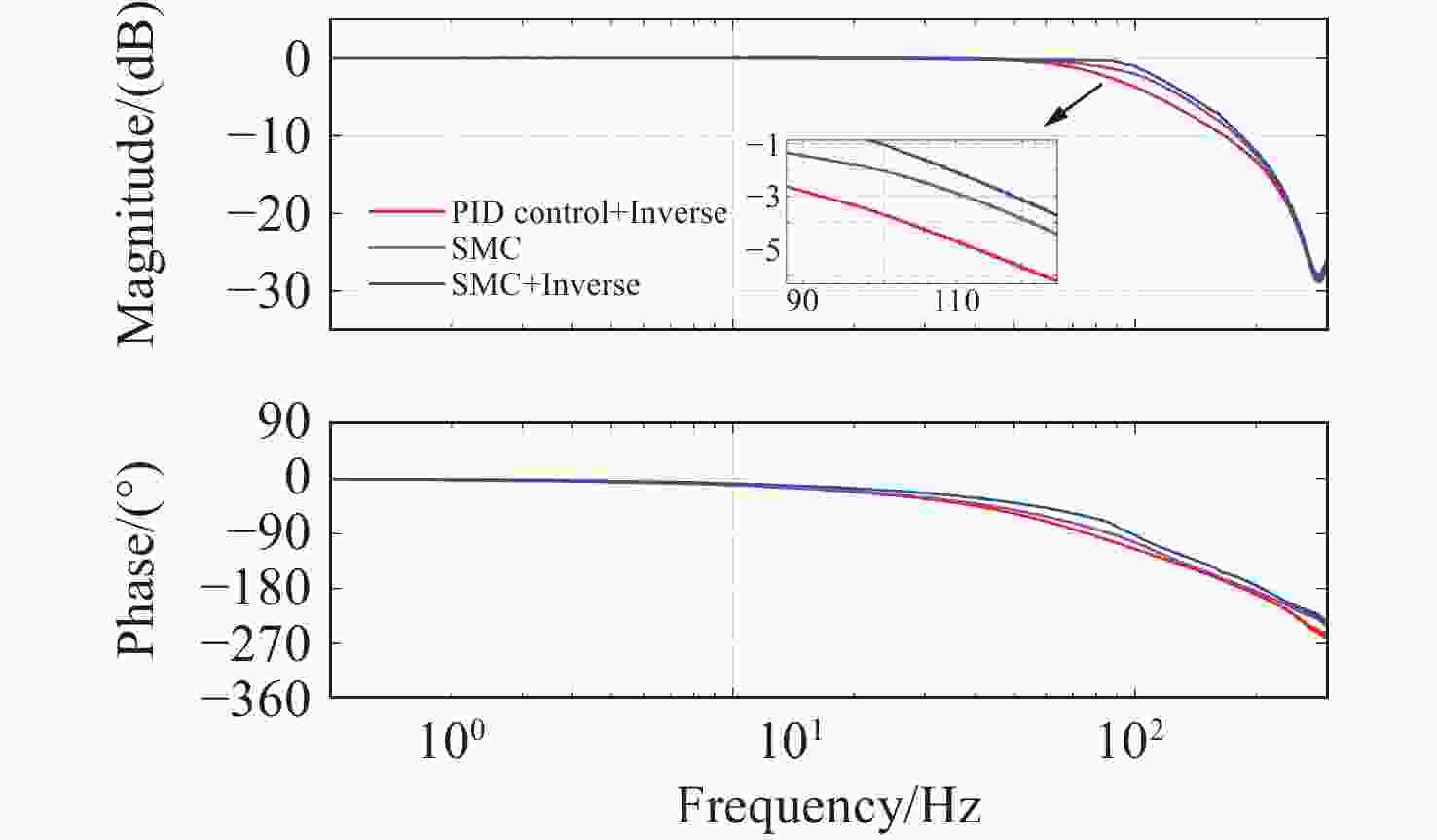
为了提高压电定位系统(Piezo-positioning system)的控制性能,对迟滞特性产生的影响及其补偿控制方法进行了研究。利用Hammerstein模型表征压电陶瓷定位器的动态迟滞非线性特性,分别以Prandtl-Ishlinskii(P-I)模型和Hankel矩阵系统辨识法求得的模型表示Hammerstein模型的静态非线性部分和动态线性部分。此模型对于200 Hz以内的典型输入频率具有较好的泛化能力。在此基础上,还提出了基于P-I逆模型与积分增广的滑模逆补偿跟踪控制策略。实验结果表明,相较于PID逆补偿控制和无逆补偿的滑模控制,滑模逆补偿控制具有更加理想的阶跃响应,无超调且调节时间仅为6.2 ms,在频域内系统闭环跟踪带宽达到119.9 Hz,且扰动抑制带宽达到86.2 Hz。所提控制策略实现了迟滞非线性的有效补偿,提高了压电定位系统的跟踪精度与抗扰性能。
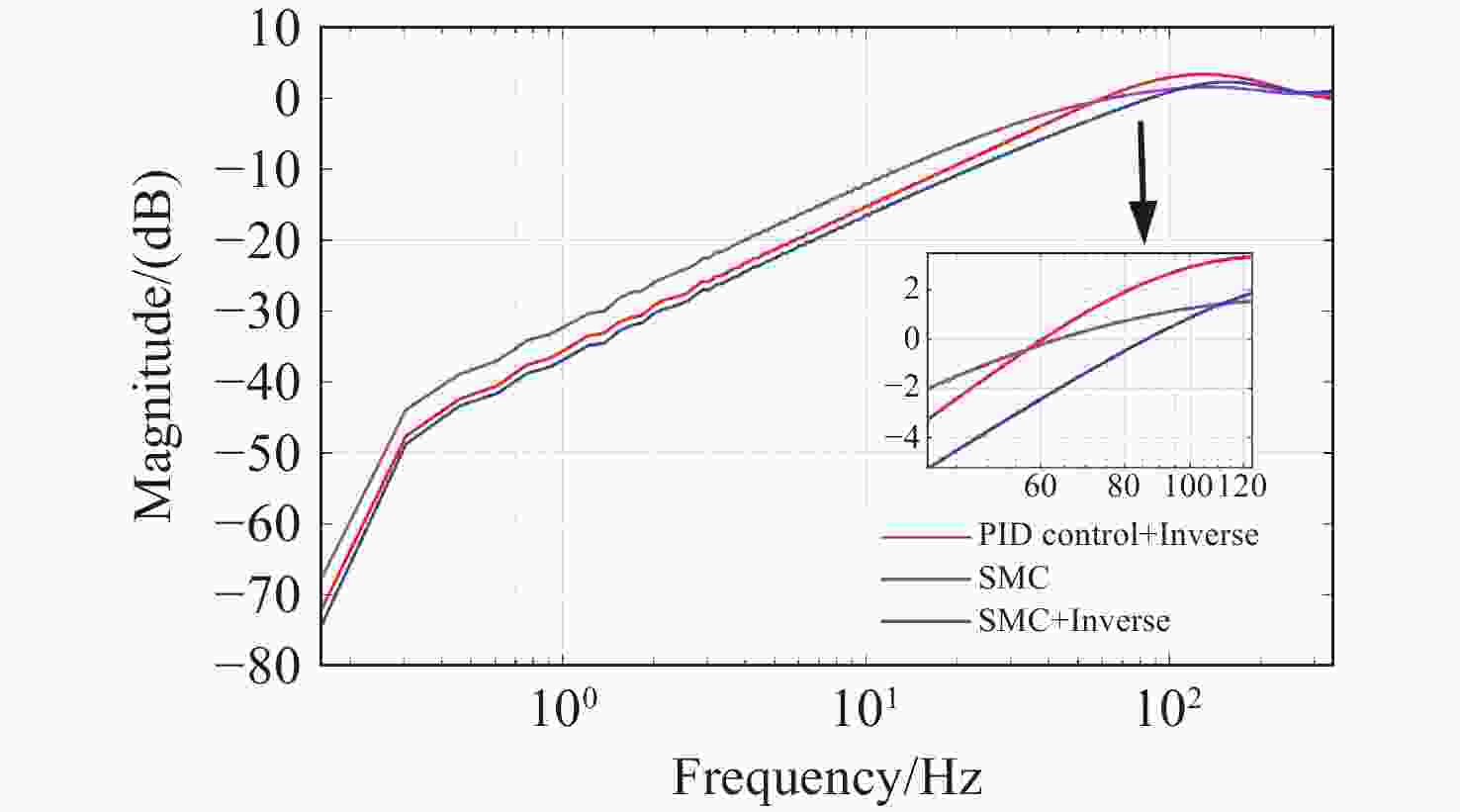
Abstract:In order to enhance the control performance of piezo-positioning system, the influence of hysteresis characteristics and its compensation method are studied. Hammerstein model is used to represent the dynamic hysteresis nonlinear characteristics of piezo-positioning actuator. The static nonlinear part and dynamic linear part of the Hammerstein model are represented by models obtained through the Prandtl-Ishlinskii (P-I) model and Hankel matrix system identification method, respectively. This model demonstrates good generalization capability for typical input frequencies below 200 Hz. A sliding mode inverse compensation tracking control strategy based on P-I inverse model and integral augmentation is proposed. Experimental results show that compared with PID inverse compensation control and sliding mode control without inverse compensation, the sliding mode inverse compensation control has a more ideal step response and no overshoot, moreover, the settling time is only 6.2 ms. In the frequency domain, the system closed-loop tracking bandwidth reaches 119.9 Hz, and the disturbance rejection bandwidth reaches 86.2 Hz. The proposed control strategy can effectively compensate the hysteresis nonlinearity, and improve the tracking accuracy and anti-disturbance capability of piezo-positioning system.
-
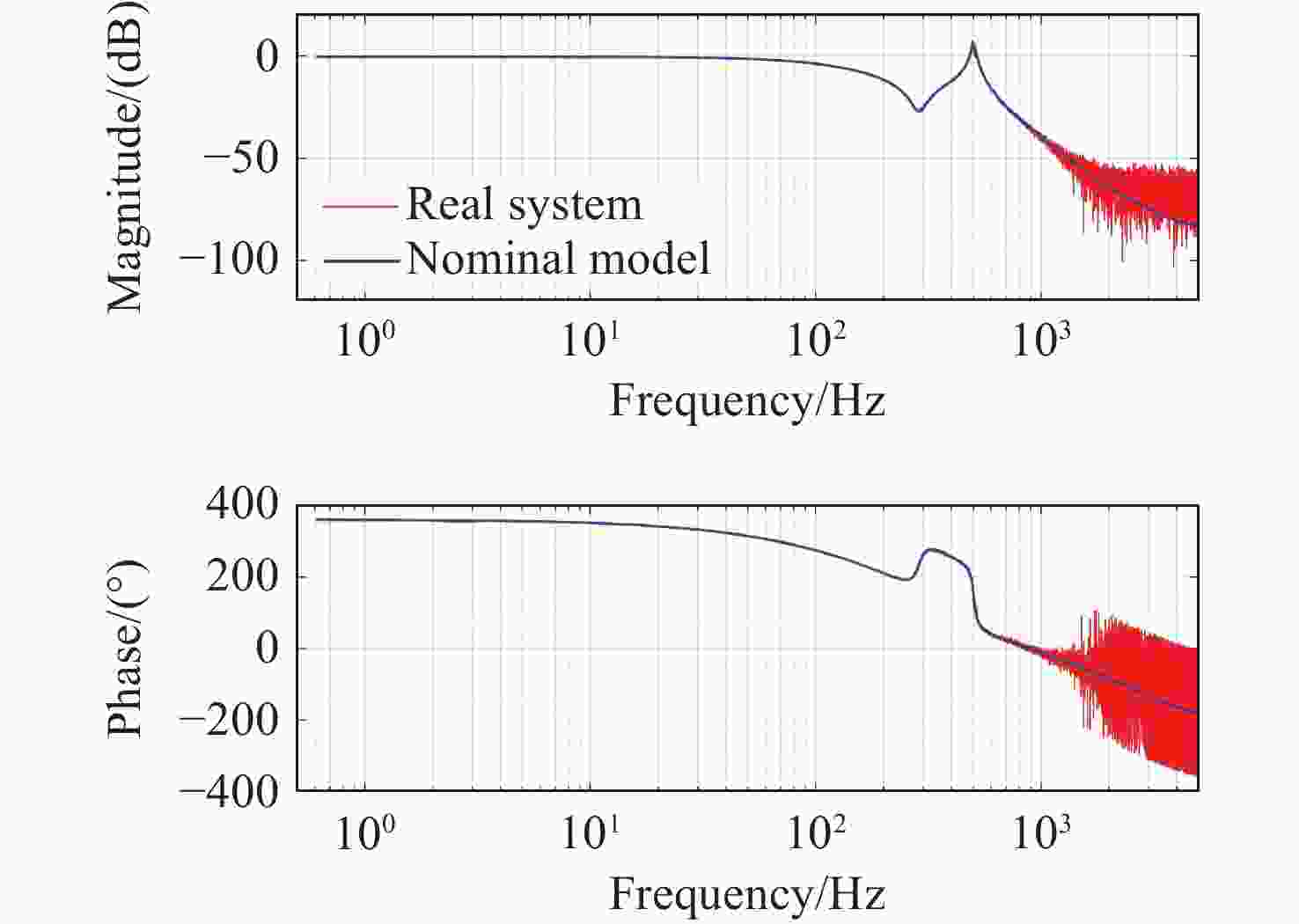
Table 1. Model test errors at different frequencies
Frequency (Hz) RMSE (μm) RE 1 0.1835 0.0121 10 0.3141 0.0214 30 0.3538 0.0244 50 0.3106 0.0219 70 0.2557 0.0185 100 0.2289 0.0173 130 0.2572 0.0201 160 0.3717 0.0297 200 0.4345 0.0365 -
[1] VASILJEV P, MAZEIKA D, KULVIETIS G. Modelling and analysis of omni-directional piezoelectric actuator[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2007, 308(3-5): 867-878. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2007.03.074 [2] BROKATE M, SPREKELS J. Hysteresis and Phase Transitions[M]. New York: Springer, 1996. [3] LEE S H, ROYSTON T J, FRIEDMAN G. Modeling and compensation of hysteresis in piezoceramic transducers for vibration control[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2000, 11(10): 781-790. doi: 10.1106/GQLJ-JGEU-MHG1-7JDF [4] JILES D, ATHERTON D. Ferromagnetic hysteresis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1983, 19(5): 2183-2185. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.1983.1062594 [5] AL JANAIDEH M, RAKHEJA S, SU CH Y. An analytical generalized Prandtl-Ishlinskii model inversion for hysteresis compensation in micropositioning control[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2011, 16(4): 734-744. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2010.2052366 [6] LI ZH, SHAN J J, GABBERT U. Inverse compensation of hysteresis using Krasnoselskii-Pokrovskii model[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2018, 23(2): 966-971. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2018.2805761 [7] WANG X H, SUN T. Preisach modeling of hysteresis for fast tool servo system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2009, 17(6): 1421-1425. [8] WONG P K, XU Q S, VONG CH M, et al. Rate-dependent hysteresis modeling and control of a piezostage using online support vector machine and relevance vector machine[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(4): 1988-2001. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2011.2166235 [9] DONG R L, TAN Y H, CHEN H, et al. A neural networks based model for rate-dependent hysteresis for piezoceramic actuators[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2008, 143(2): 370-376. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2007.11.023 [10] MAO J Q, DING H SH. Intelligent modeling and control for nonlinear systems with rate-dependent hysteresis[J]. Science in China Series F: Information Sciences, 2009, 52(4): 656-673. doi: 10.1007/s11432-009-0026-8 [11] QIN Y X, HU D J. Nonlinear modeling for piezoelectric actuators[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2004, 38(8): 1334-1336,1341. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-2467.2004.08.027 [12] HAN T P, LI G P, SHEN J. Study on accurate positioning technology of piezoelectric ceramics micro-displacement actuator[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2010, 29(2): 51-53. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9787.2010.02.016 [13] SUN T, LI G P, SUN H Y. Accurate positioning and control of piezoelectric actuator based on Duhem model and inverse model[J]. Journal of Ningbo University (NSEE), 2017, 30(1): 13-17. (in Chinese). [14] LI L, LIU X D, WANG W, et al. Generalized nonlinear Preisach model for hysteresis nonlinearity of piezoceramic actuator and its numerical implementation[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2007, 15(5): 706-712. (in Chinese). [15] AL JANAIDEH M, SU CH Y, RAKHEJA S. Development of the rate-dependent Prandtl-Ishlinskii model for smart actuators[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2008, 17(3): 035026. doi: 10.1088/0964-1726/17/3/035026 [16] XIAO SH L, LI Y M. Modeling and high dynamic compensating the rate-dependent hysteresis of piezoelectric actuators via a novel modified inverse Preisach model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2013, 21(5): 1549-1557. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2012.2206029 [17] LIU Y K, LÜ F R, GAO SH J, et al. Compensation of hysteresis effect of piezoelectric fast steering mirror in dynamic target tracking of ground-based large aperture telescope system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(23): 3081-3089. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223023.3081 [18] AL JANAIDEH M, RAKOTONDRABE M, AL-DARABSAH I, et al. Internal model-based feedback control design for inversion-free feedforward rate-dependent hysteresis compensation of piezoelectric cantilever actuator[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2018, 72: 29-41. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2017.11.001 [19] WANG Q Q, SU CH Y, TAN Y H. On the control of plants with hysteresis: overview and a Prandtl-Ishlinskii hysteresis based control approach[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2005, 31(1): 92-104. [20] ZHANG J Q, SUN CH SH, WU J B, et al. System identification and balanced truncation of fast steering mirror for laser communication[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2024, 41(12): 2315-2324. (in Chinese). [21] LI ZH B, LI L, ZHANG J Q, et al. System modeling and sliding mode control of dual-axis voice coil actuator fast steering mirror[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2023, 31(24): 3580-3594. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20233124.3580 -






 下载:
下载: