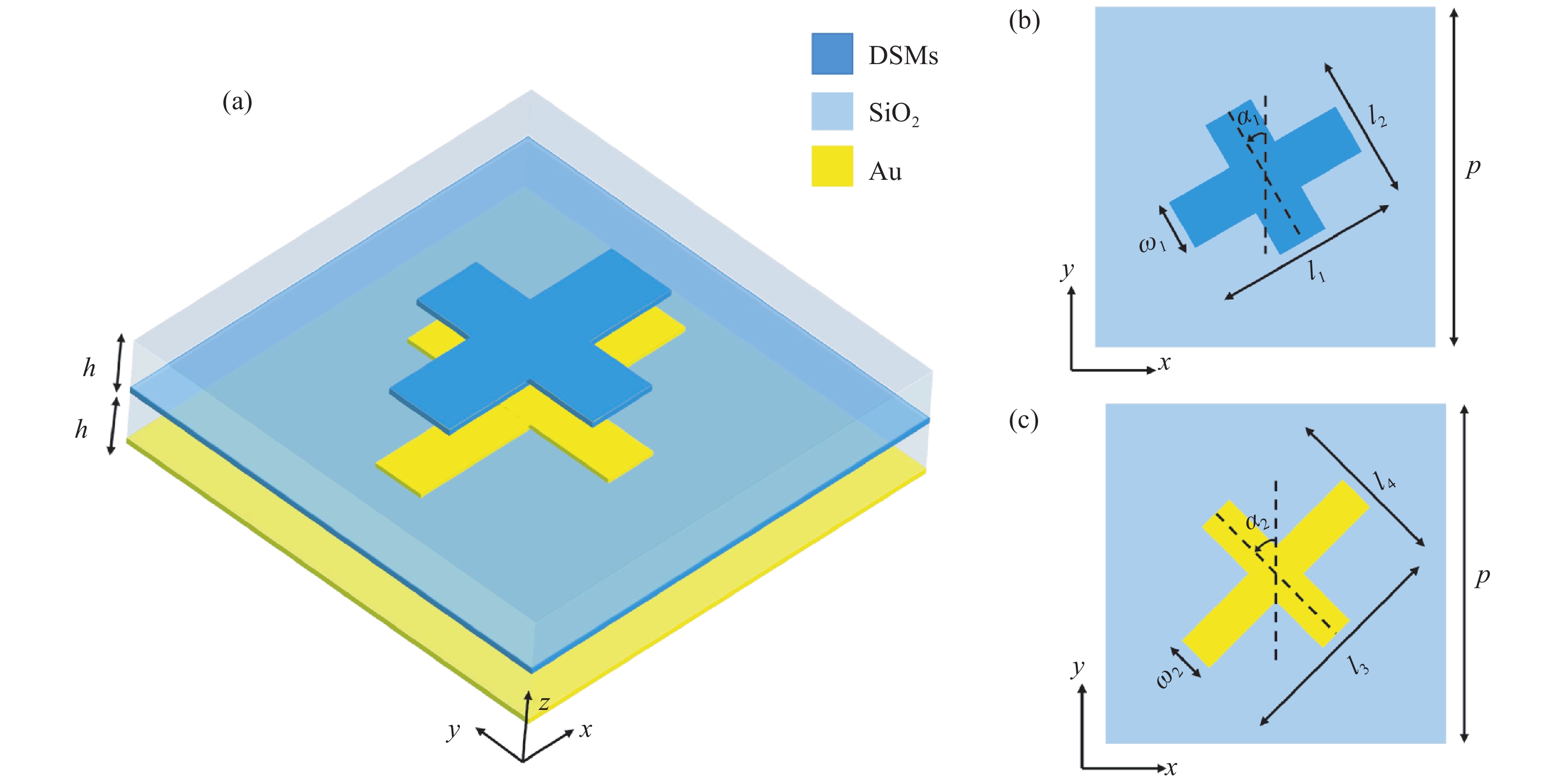
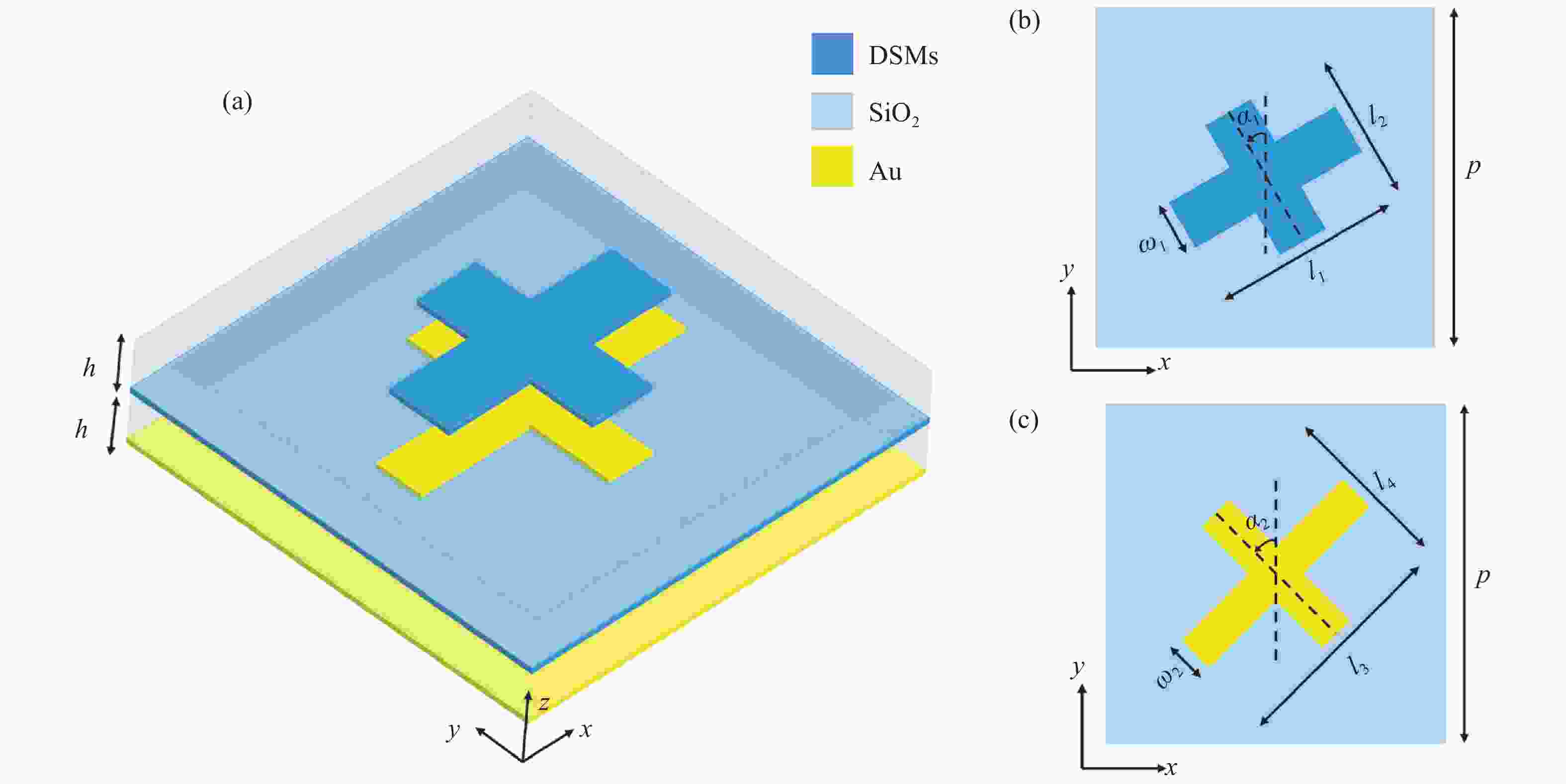
Tunable reflective spin-decoupled encoding metasurface based on Dirac semimetals
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2024-0037
-
摘要:
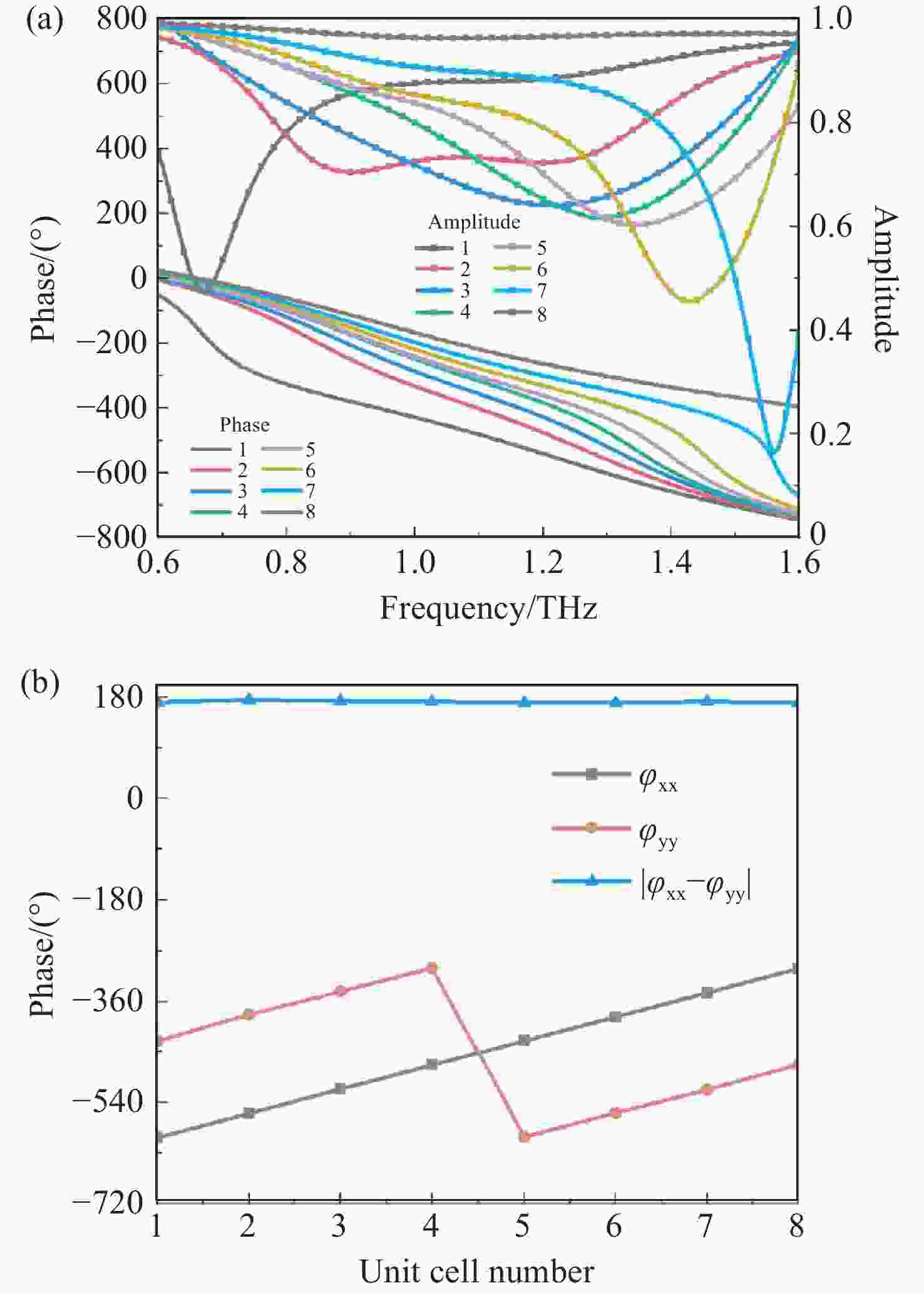
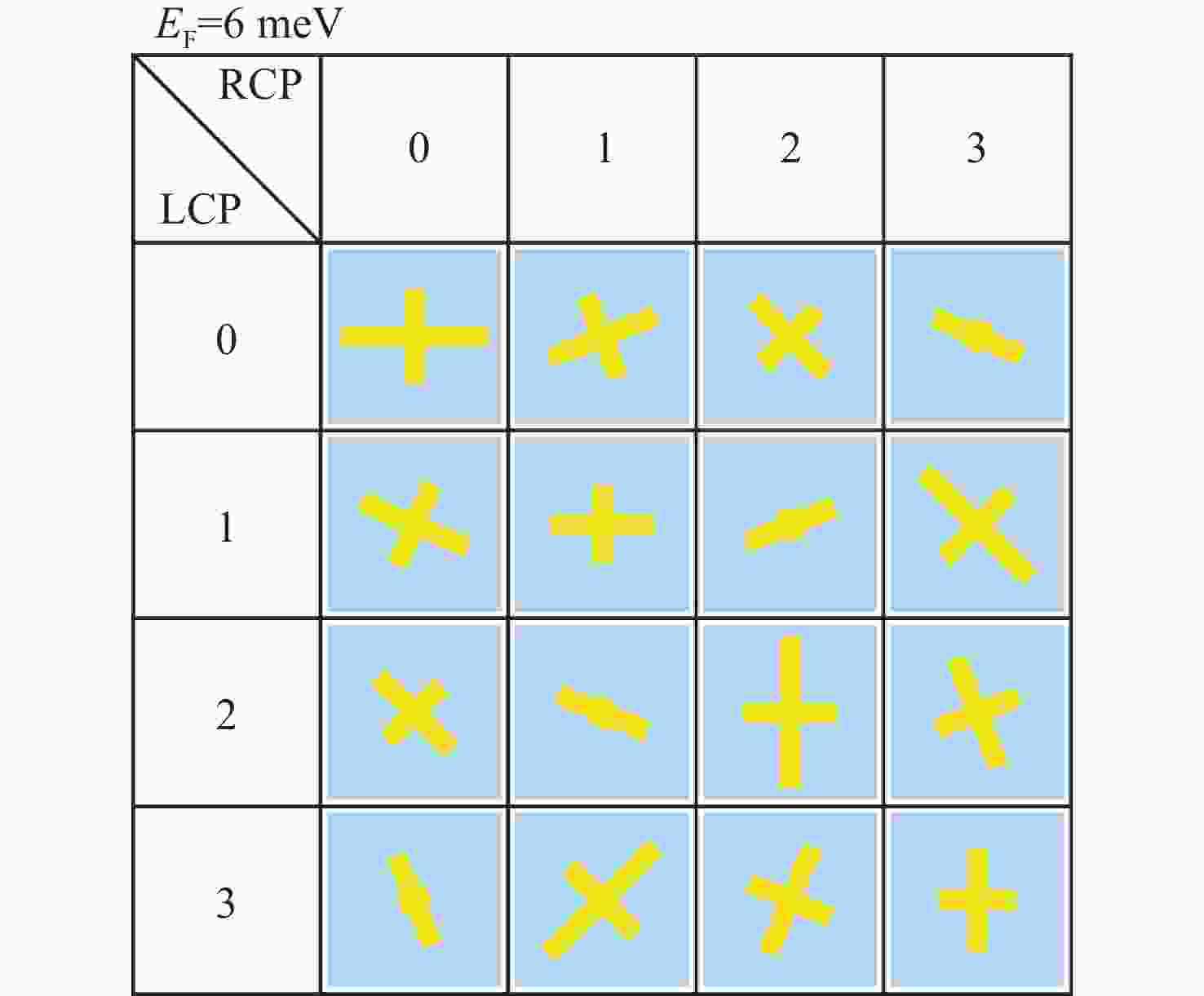
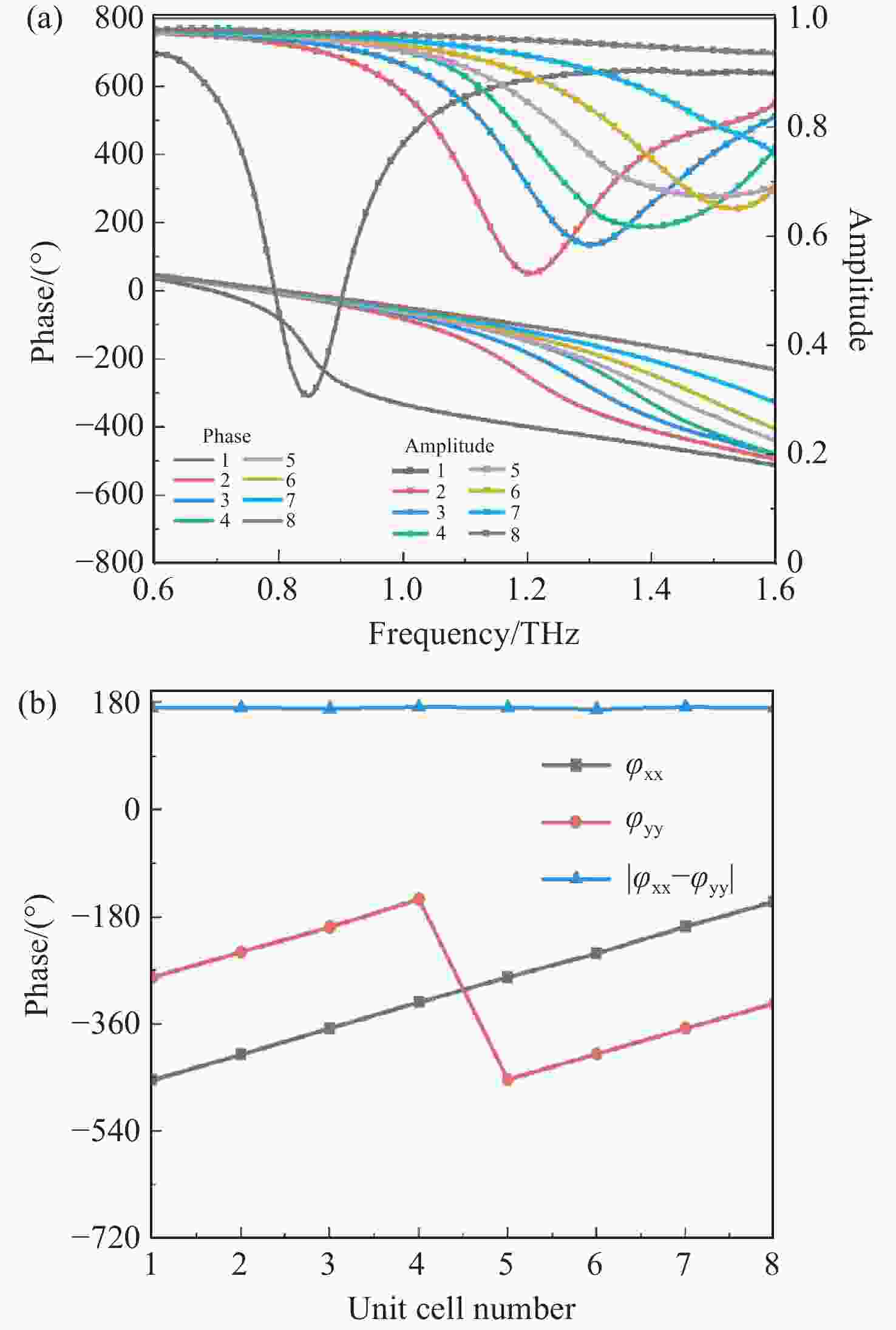
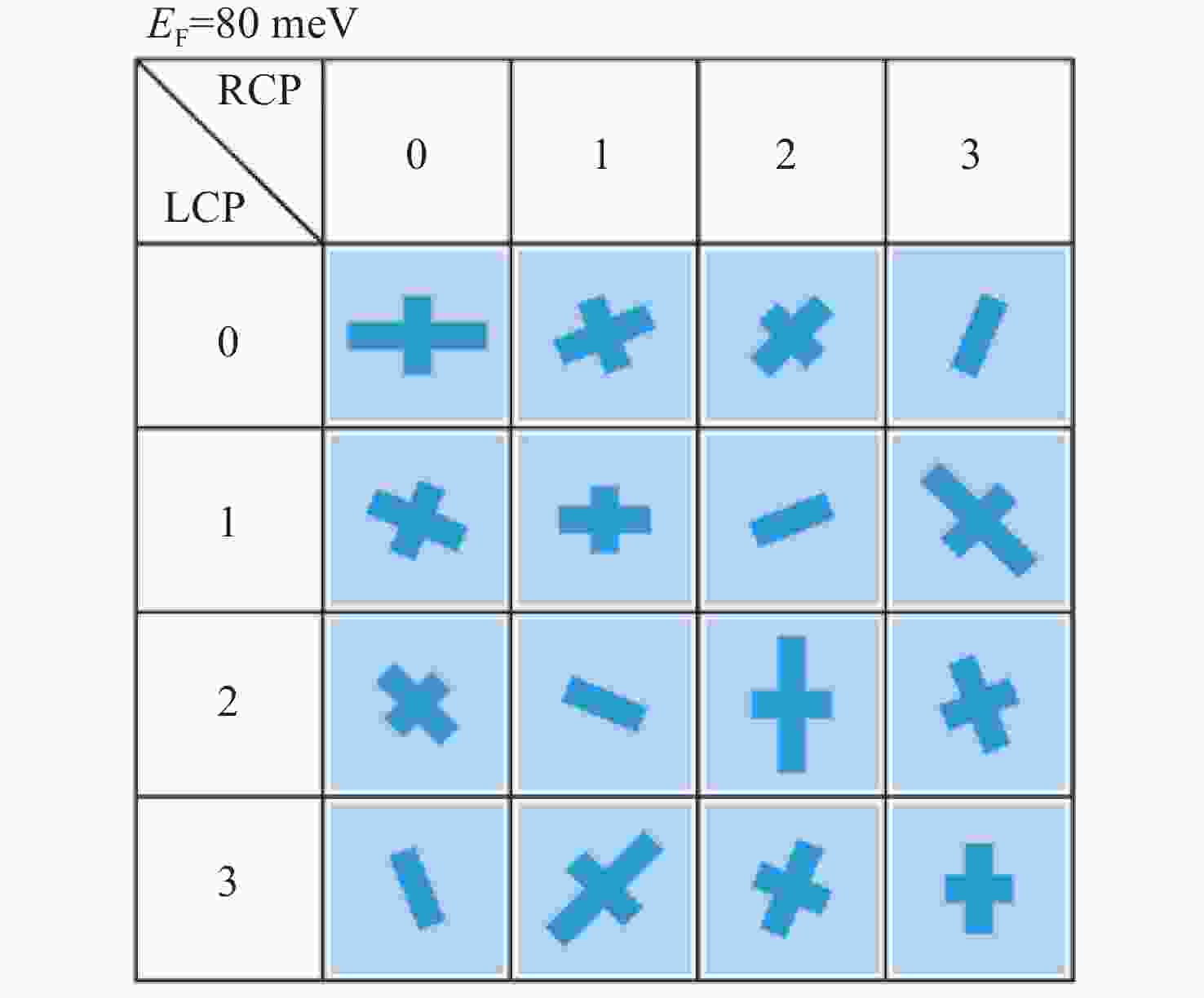
具有较高信息容量的多功能超表面受到研究者的广泛关注。本文提出了一种基于太赫兹波段的2位可调谐自旋解耦编码超表面,利用狄拉克半金属(DSM)的可调谐特性设计了一种新的多层结构,在超表面结构中引入几何相位和传播相位,可以有效地调控电磁波。当DSM的费米能级(
E F)为6 meV时,电磁波由嵌在DSM薄膜上的金贴片控制,在1.3 THz这一频点工作;当DSM的费米能级为80 meV时,电磁波由DSM贴片控制,在1.4 THz这一频点工作。这两种模式都可以在左旋圆极化(LCP)波和右旋圆极化(RCP)波激励下实现轨道角动量(OAM)模式不同的涡旋波束的独立控制。这项工作为提高信息容量和无线通信中极化复用技术带来巨大潜力。Abstract:Multiple functional metasurfaces with high information capacity have attracted considerable attention from researchers. This study proposes a 2-bit tunable spin-decoupled coded metasurface designed for the terahertz band, which utilizes the tunable properties of Dirac semimetals (DSM) to create a novel multilayer structure. By incorporating both geometric and propagating phases into the metasurface design, we can effectively control the electromagnetic wave. When the Fermi level (
E F) of the DSM is set at 6 meV, the electromagnetic wave is manipulated by the gold patch embedded in the DSM film, operating at a frequency of 1.3 THz. When theE F of the DSM is set at 80 meV, the electromagnetic wave is manipulated by the DSM patch, operating at a frequency of 1.4 THz. Both modes enable independent control of beam splitting under left-rotating circularly polarized (LCP) and right-rotating circularly polarized (RCP) wave excitation, resulting in the generation of vortex beams with distinct orbital angular momentum (OAM) modes. The findings of this study hold significant potential for enhancing information capacity and polarization multiplexing techniques in wireless communications.-
Key words:
- coding metasurface /
- dirac semimetal /
- spin decoupling /
- circular polarization /
- tunable
-
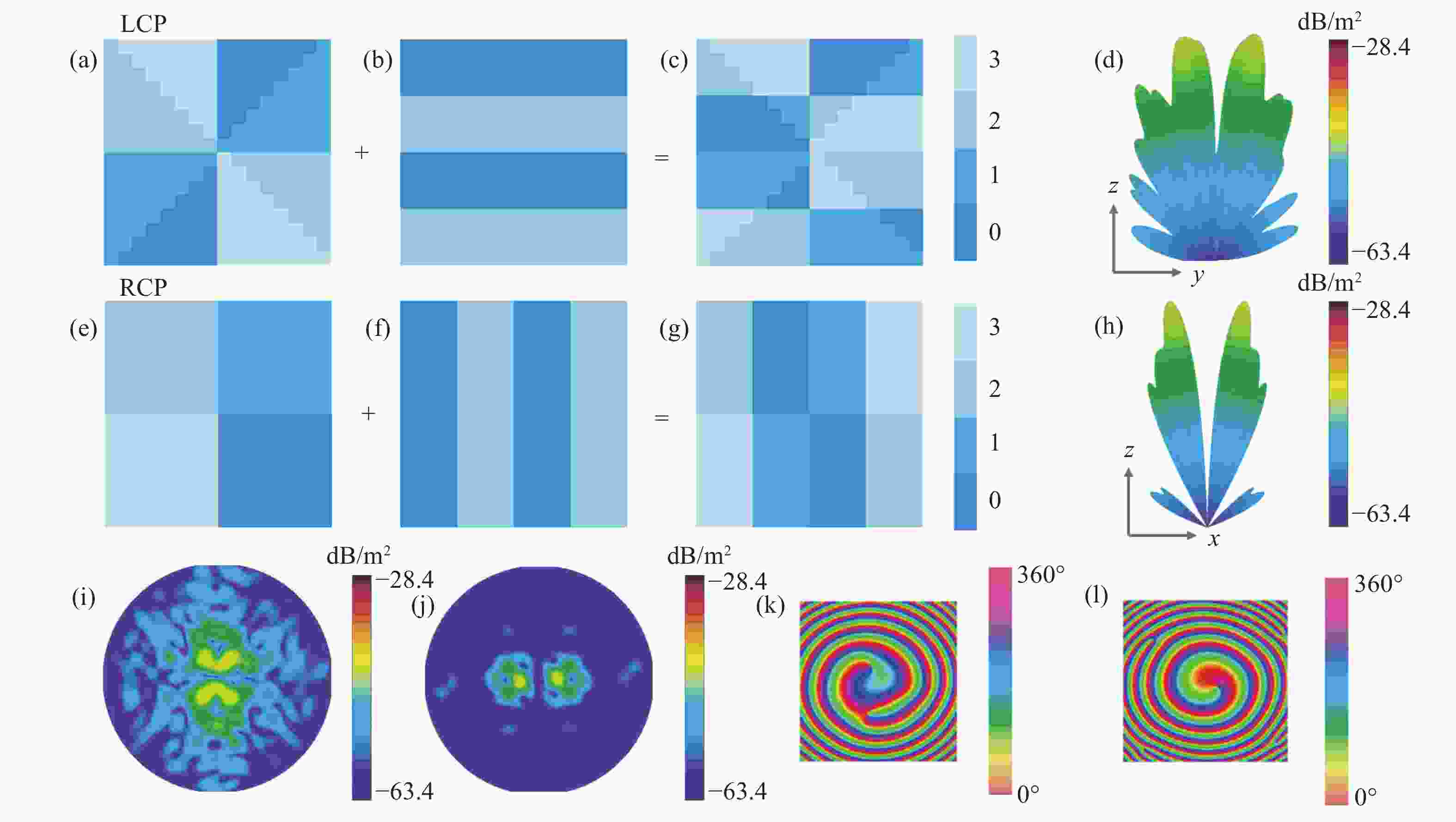
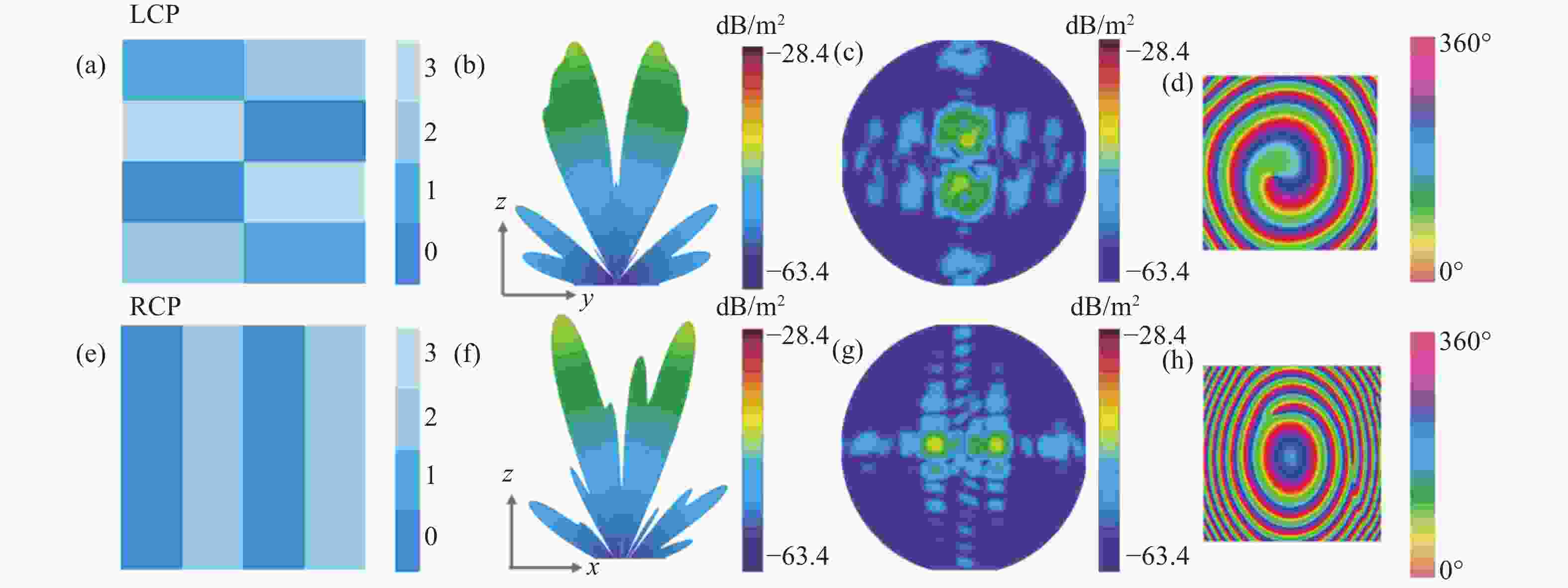
Figure 6. (a, e) Vortex phase distributions for l = −2 with l = 1. (b, f) Phase distribution of gradients varying along the y-axis as well as the x-axis. (c, g) Reflection coding map under LCP wave and RCP wave incidence. (d, h) 3D far-field map under LCP wave and RCP wave incidence. (i, j) 2D maps under the incidence of LCP wave and RCP wave. (k, l) Vortex phases under incidence of LCP wave and RCP wave. (EF = 6 meV)
-
[1] WANG M, LIAO D, DAI J Y, et al. Dual-polarized reconfigurable metasurface for multifunctional control of electromagnetic waves[J]. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, 2022, 70(6): 4539-4548. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2022.3140506 [2] LUO X. Principles of electromagnetic waves in metasurfaces[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2015, 58(9): 594201. [3] LI L, CUI T J, JI W, et al. Electromagnetic reprogrammable coding-metasurface holograms[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 197. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00164-9 [4] HUANG C, PAN W, MA X, et al. Multi-spectral metasurface for different functional control of reflection waves[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 23291. doi: 10.1038/srep23291 [5] LI Z Y, LI S J, HAN B W, et al. Quad-band transmissive metasurface with Linear to dual-circular polarization conversion simultaneously[J]. Advanced Theory and Simulations, 2021, 4(8): 2100117. doi: 10.1002/adts.202100117 [6] XING W, SI L, DONG L, et al. Rapid design of hybrid mechanism metasurface with random coding for terahertz dual-band RCS reduction[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(17): 28444-28458. doi: 10.1364/OE.496423 [7] CHEN P, Ma L L, HU W, et al. Chirality invertible superstructure mediated active planar optics[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 2518. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10538-w [8] LI S J, LI Z Y, HUANG G S, et al. Digital coding transmissive metasurface for multi-OAM-beam[J]. Frontiers of Physics, 2022, 17(6): 62501. doi: 10.1007/s11467-022-1179-9 [9] YUAN Y, ZHANG K, RATNI B, et al. Independent phase modulation for quadruplex polarization channels enabled by chirality-assisted geometric-phase metasurfaces[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 4186. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17773-6 [10] ZHANG Z, GAO L. 2-bit coding metasurface with a double layer random flip structure for wide band diffuse reflection and reciprocity protected transmission[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(20): 32253-32262. doi: 10.1364/OE.501272 [11] CUI T J, QI M Q, WAN X, et al. Coding metamaterials, digital metamaterials and programmable metamaterials[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2014, 3(10): e218-e218. [12] LIU S, CUI T J, XU Q, et al. Anisotropic coding metamaterials and their powerful manipulation of differently polarized terahertz waves[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2016, 5(5): e16076-e16076. [13] ZHANG L, LIU S, LI L, et al. Spin-controlled multiple pencil beams and vortex beams with different polarizations generated by pancharatnam-berry coding metasurfaces[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(41): 36447-36455. [14] CHENG G, SI L, SHEN Q, et al. Transmissive pancharatnam-berry metasurfaces with stable amplitude and precise phase modulations using dartboard discretization configuration[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(19): 30815-30831. doi: 10.1364/OE.501702 [15] CHONG A, WAN C, CHEN J, et al. Generation of spatiotemporal optical vortices with controllable transverse orbital angular momentum[J]. Nature Photonics, 2020, 14(6): 350-354. doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-0587-z [16] GUO Y, ZHANG S, PU M, et al. Spin-decoupled metasurface for simultaneous detection of spin and orbital angular momenta via momentum transformation[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2021, 10(1): 63. [17] ZHANG K, YUAN Y, DING X, et al. High-efficiency metalenses with switchable functionalities in microwave region[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(31): 28423-28430. [18] LI J S, CHEN J Z. Simultaneous and independent regulation of circularly polarized terahertz wave based on metasurface[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(12): 20298-20310. doi: 10.1364/OE.458810 [19] WANG F, ZHANG Y, TIAN C, et al. Gate-variable optical transitions in graphene[J]. Science, 2008, 320(5873): 206-209. doi: 10.1126/science.1152793 [20] Iyer PP, Pendharkar M, Schuller JA. Electrically reconfigurable metasurfaces using heterojunction resonators[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2016, 4(10): 1582-1588. doi: 10.1002/adom.201600297 [21] DU Z, HE C, XIN J, et al. Terahertz dynamic multichannel holograms generated by spin-multiplexing reflective metasurface[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(1): 248-259. doi: 10.1364/OE.510046 [22] ZHANG Y, JIANG C, LI Z, et al. Circularly polarized terahertz wave independently controlled tunable spin-decoupled metasurface[J]. Results in Physics, 2024, 56: 107287. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2023.107287 [23] CUI T J, LI L, LIU S, et al. Information metamaterial systems[J]. iScience, 2020, 23(8). [24] XU J, LIU W, SONG Z. Terahertz dynamic beam steering based on graphene coding metasurfaces[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2021, 13(4): 4600409. [25] MA H, YANG J, CHEN T, et al. Tunable metasurface for independent controlling radar stealth properties via geometric and propagation phase modulation[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(7): 11760-11774. doi: 10.1364/OE.485132 [26] DING G, CHEN K, LUO X, et al. Dual-helicity decoupled coding metasurface for independent spin-to-orbital Angular momentum conversion[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2019, 11(4): 044043. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.11.044043 [27] JIANG C, LI Z, LV X, et al. Active modulation of terahertz vortex beams by Dirac semimetals-based space-time-coding metasurface[J]. OPTICS COMMUNICATIONS, 2023, 540: 129506. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2023.129506 [28] KOTOV O. V, LOZOVIK Y E. Dielectric response and novel electromagnetic modes in three-dimensional Dirac semimetal films[J]. PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 2016, 93(23): 235417. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.93.235417 [29] HE C, PAN Z, SONG Z. Manipulating spin-dependent wavefronts of vortex beams via plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. Annalen der Physik, 2023, 535(10): 2300235. doi: 10.1002/andp.202300235 [30] XIN J, DU Z, ZHOU Z, et al. Optical reflective metasurfaces enable spin-decoupled OAM and focusing[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2023, 25(40): 27008-27016. doi: 10.1039/D3CP02321D -





 下载:
下载: