基于改进互相关算法的游标效应光纤应变传感器解调方法
Demodulation of Vernier-effect-based optical fiber strain sensor by using improved cross-correlation algorithm
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2025-0024
-
摘要:
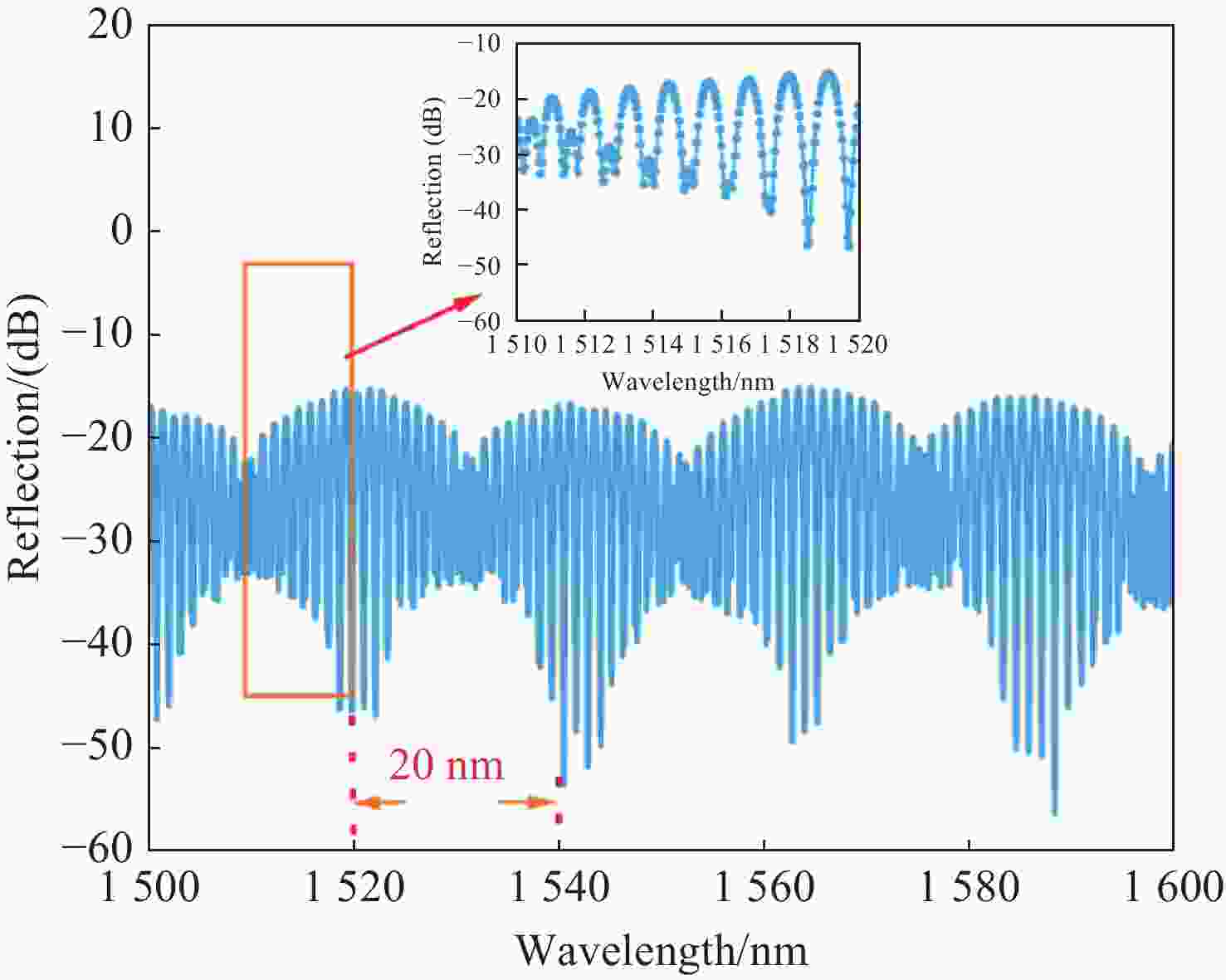
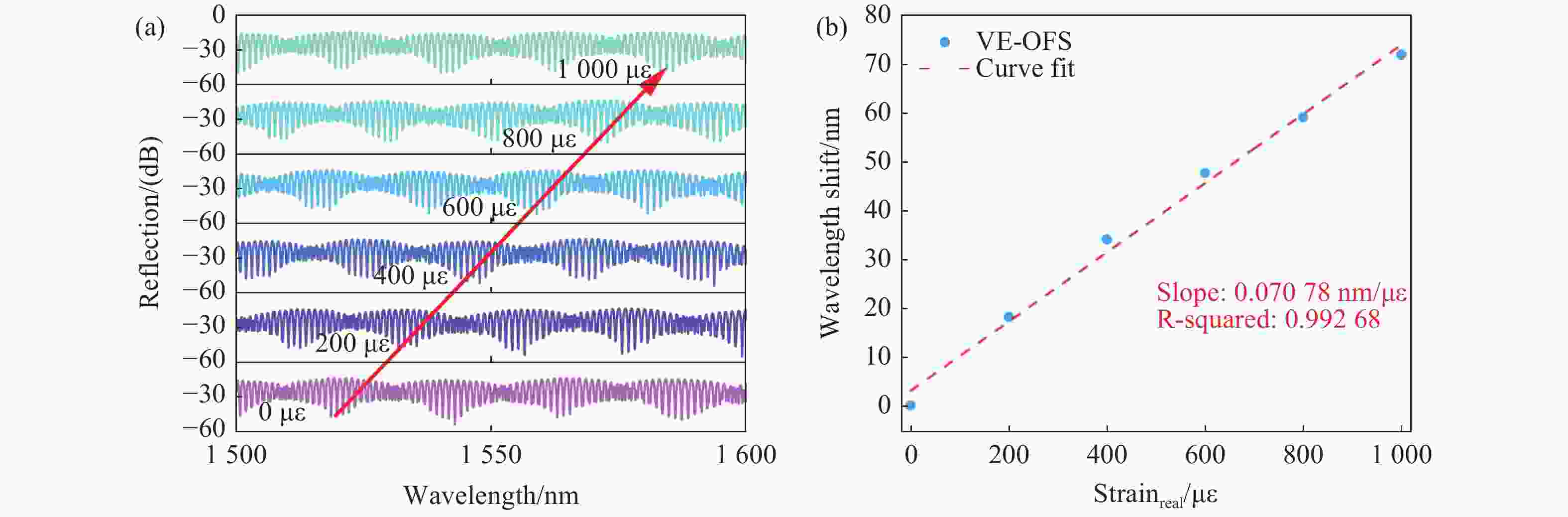
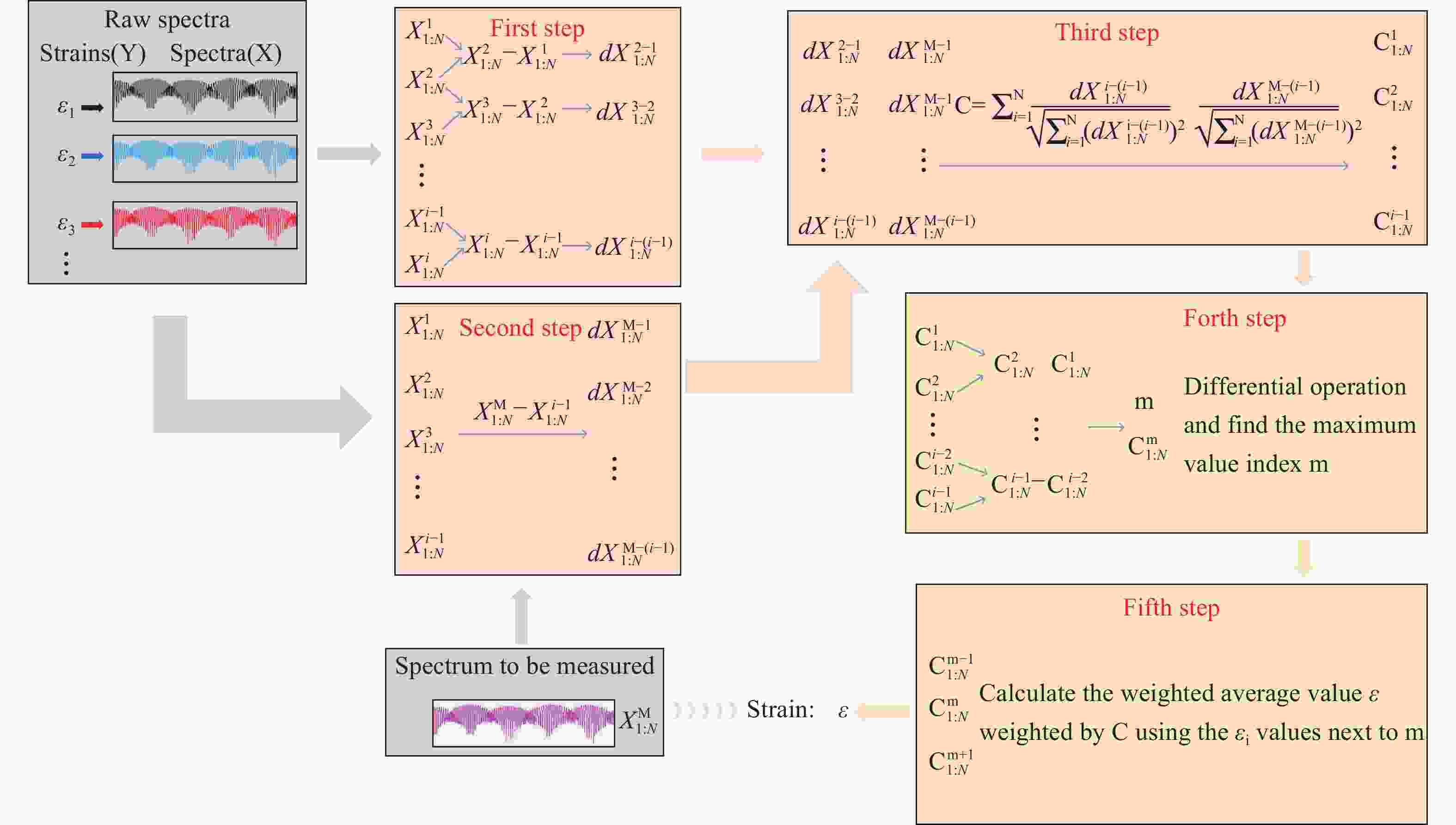
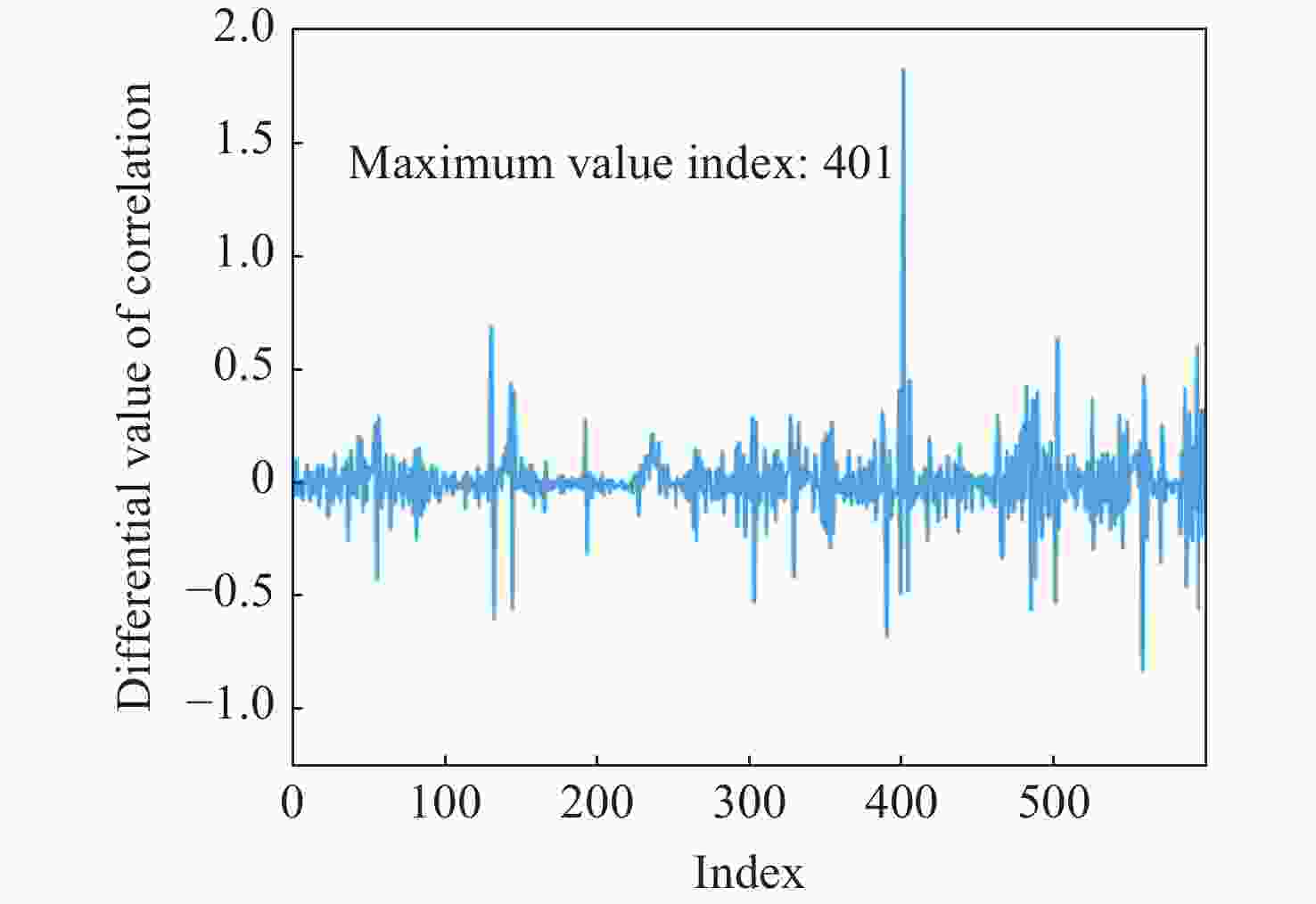
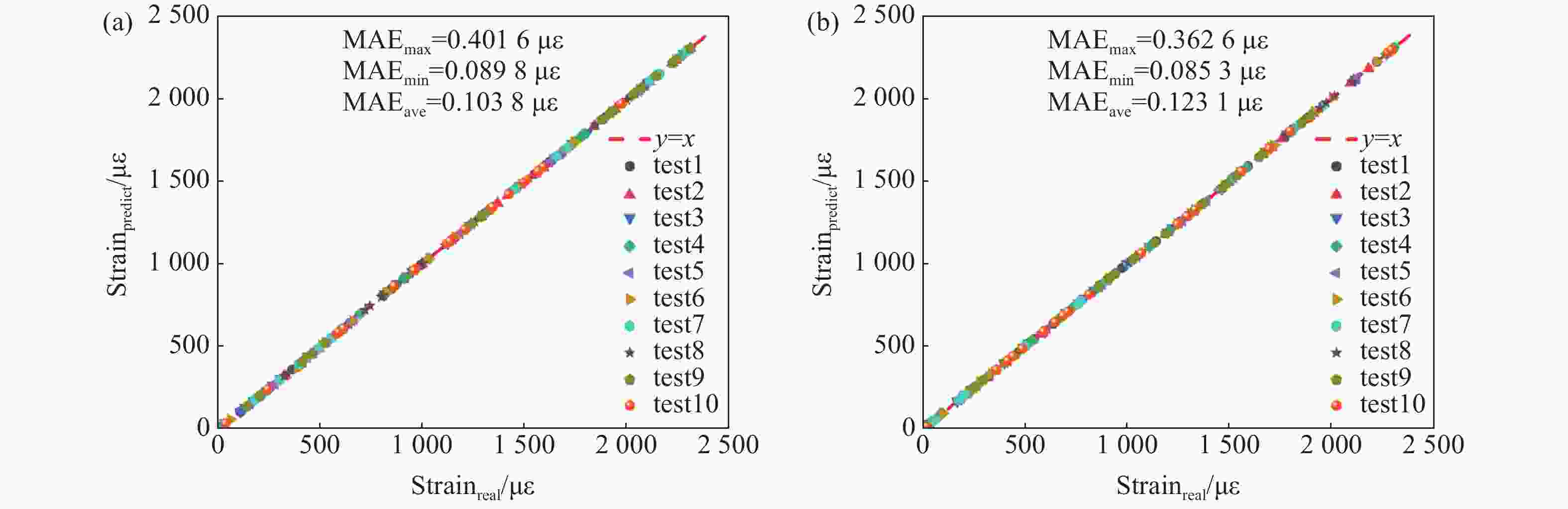
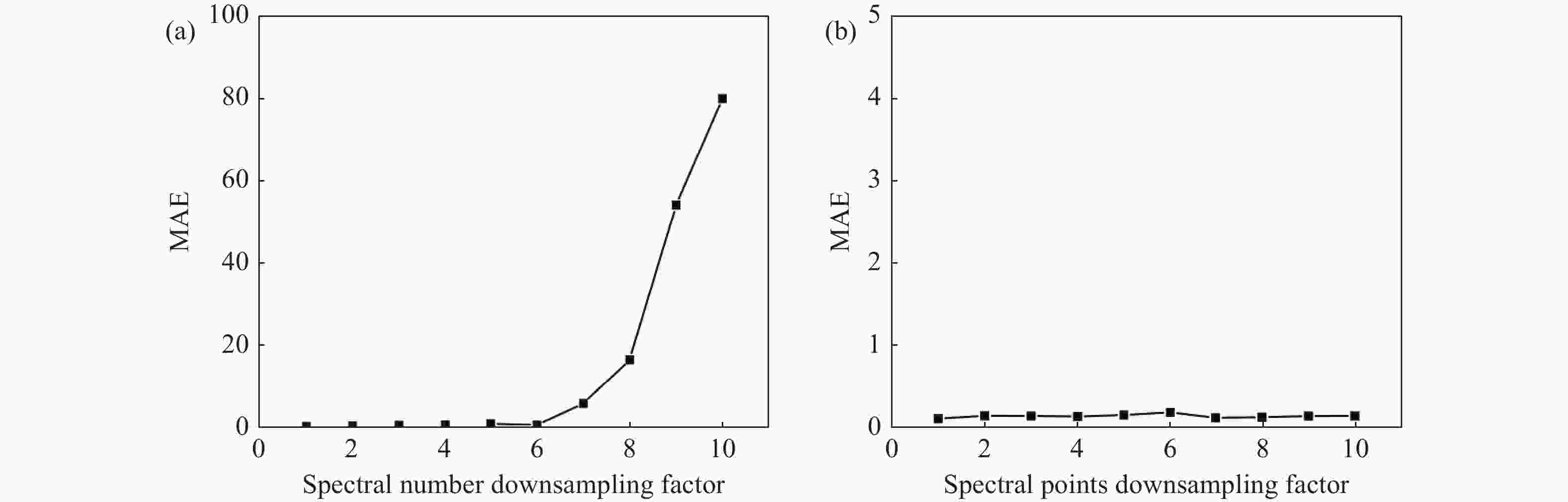
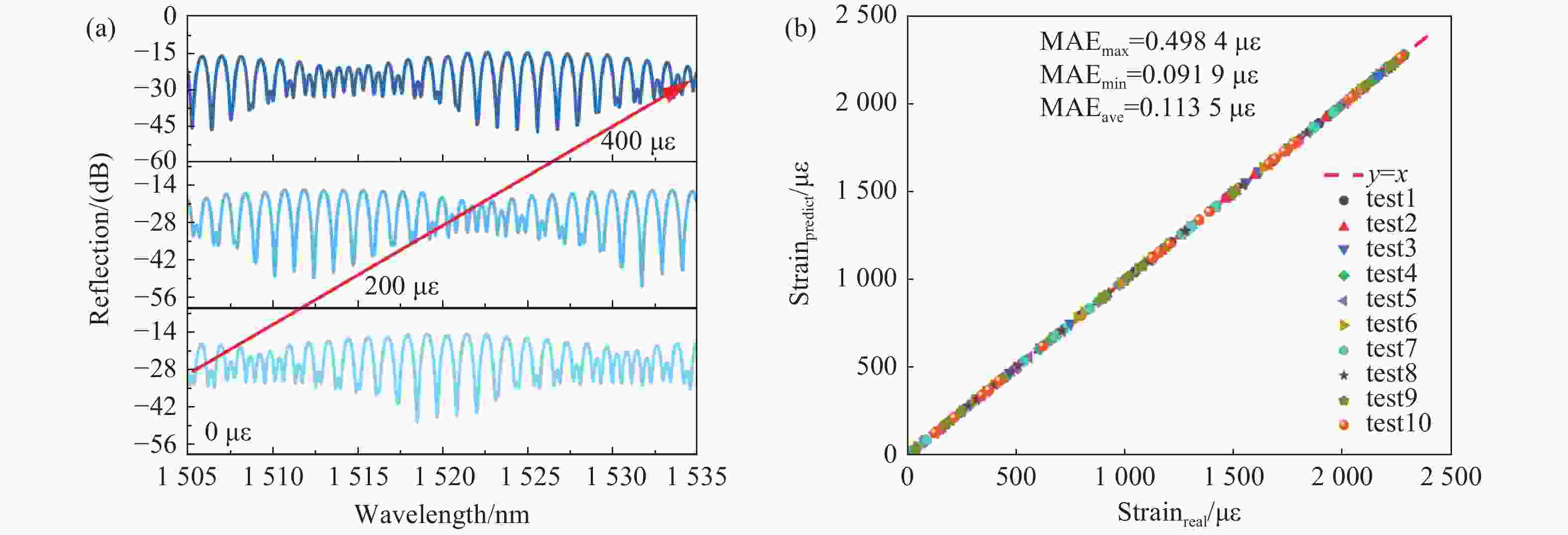
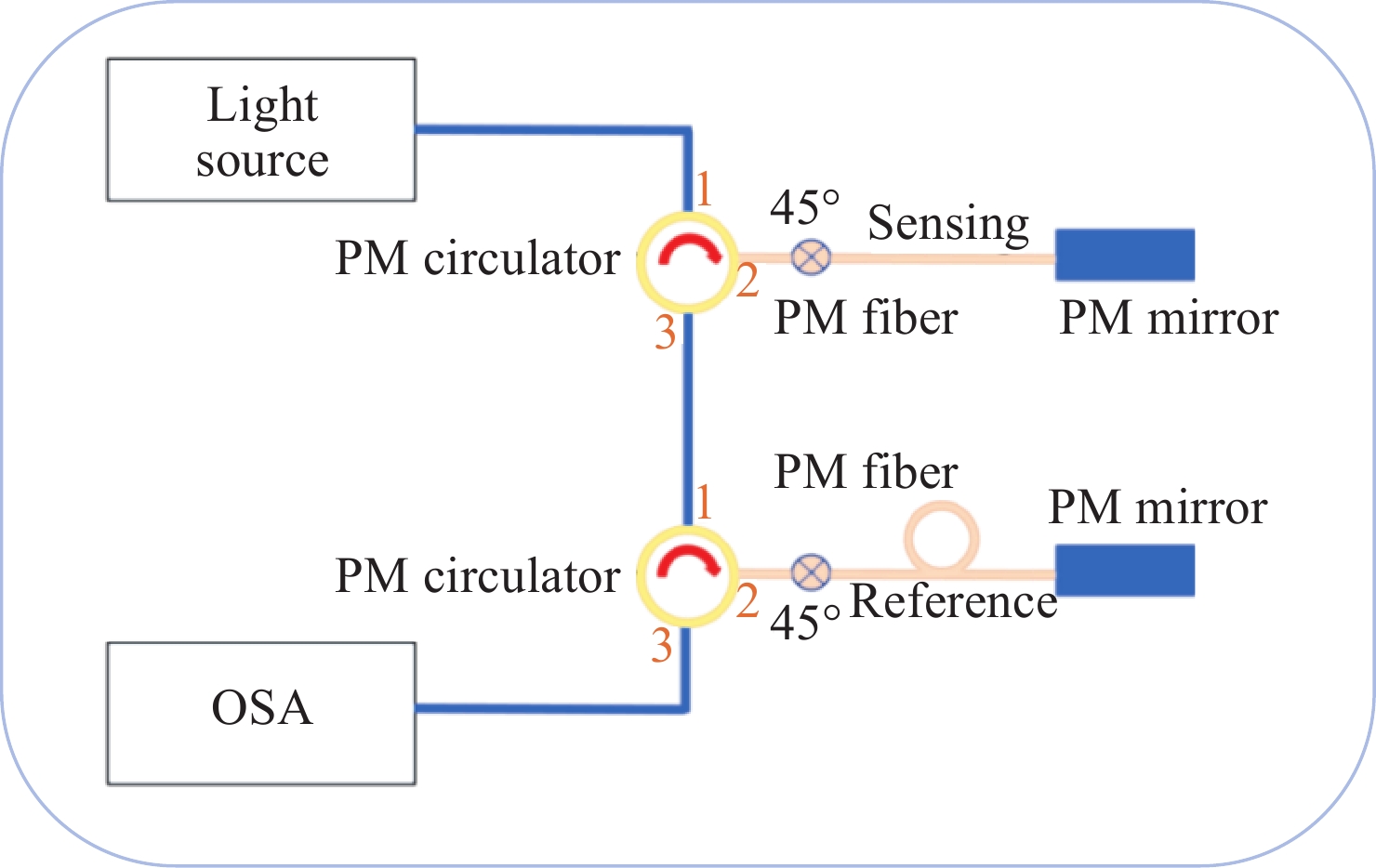
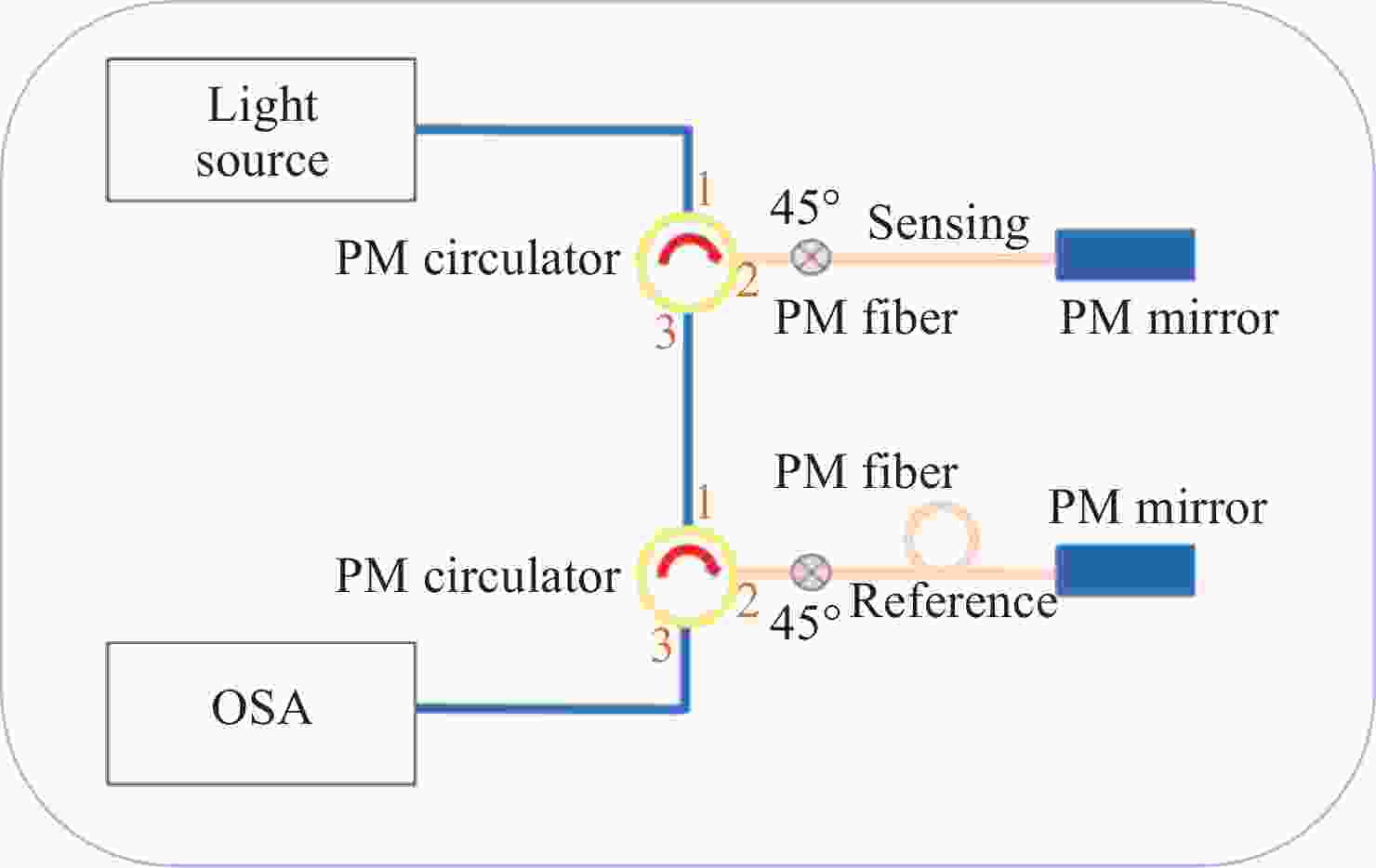
为了解决基于光学游标效应的光纤应变传感器中传统光谱跟踪解调方式测量精度不足、测量范围小的问题,本文提出了一种改进型互相关算法并将其应用于游标型光纤应变传感器信号解调。该算法通过互相关操作从采集的光谱数据中识别出与待测光谱最为相似的光谱,然后通过加权计算得到预测应变值。由于该算法使用了被测量光谱中包含的全部信息,因此可以得到更准确的结果和更大的测量范围,经过实验验证,获得了
0.1038 $ \mu \varepsilon $ 的低平均绝对误差,并且消除了光谱范围对测量范围的限制。此外,与光谱跟踪技术相比,由于其可以使用低分辨率光谱进行解调,该改进互相关算法还具有提高测量速度的能力,因此该算法进一步提高了基于游标效应的光纤应变传感器解调性能。Abstract:The improved cross-correlation algorithm for the strain demodulation of Vernier-effect-based optical fiber sensor (VE-OFS) is proposed in this article. The algorithm identifies the most similar spectrum to the measured one from the database of the collected spectra by employing the cross-correlation operation, subsequently deriving the predicted value via weighted calculation. As the algorithm uses the complete information in the measured raw spectrum, more accurate results and larger measurement range can be obtained. Additionally, the improved cross-correlation algorithm also has the potential to improve the measurement speed compared to current standards due to the possibility for the collection using low sampling rate. This work presents an important algorithm towards a simpler, faster way to improve the demodulation performance of VE-OFS.
-
Key words:
- improved cross-correlation algorithm /
- fiber sensor /
- vernier effect /
- machine learning.
-
Table 1. Comparison of the predicted results.
Algorithm MAE_0 MAE_1 MAE_2 Improved cross-correlation
algorithm0.1038 $ \mu \varepsilon $80.1957 $ \mu \varepsilon $0.1361 $ \mu \varepsilon $GPR 4.2784 $ \mu \varepsilon $512.909 $ \mu \varepsilon $ 4.5726 $ \mu \varepsilon $CNN 8.3923 $ \mu \varepsilon $579.633 $ \mu \varepsilon $ 8.9753 $ \mu \varepsilon $LSTM 6.9757 $ \mu \varepsilon $346.147 $ \mu \varepsilon $ 6.1725 $ \mu \varepsilon $FNN 12.9246 $ \mu \varepsilon $512.358 $ \mu \varepsilon $ 13.5166 $ \mu \varepsilon $Linear curve fitting 26.7467 $ \mu \varepsilon $/ / Table 2. Demodulation on different intensity fluctuations.
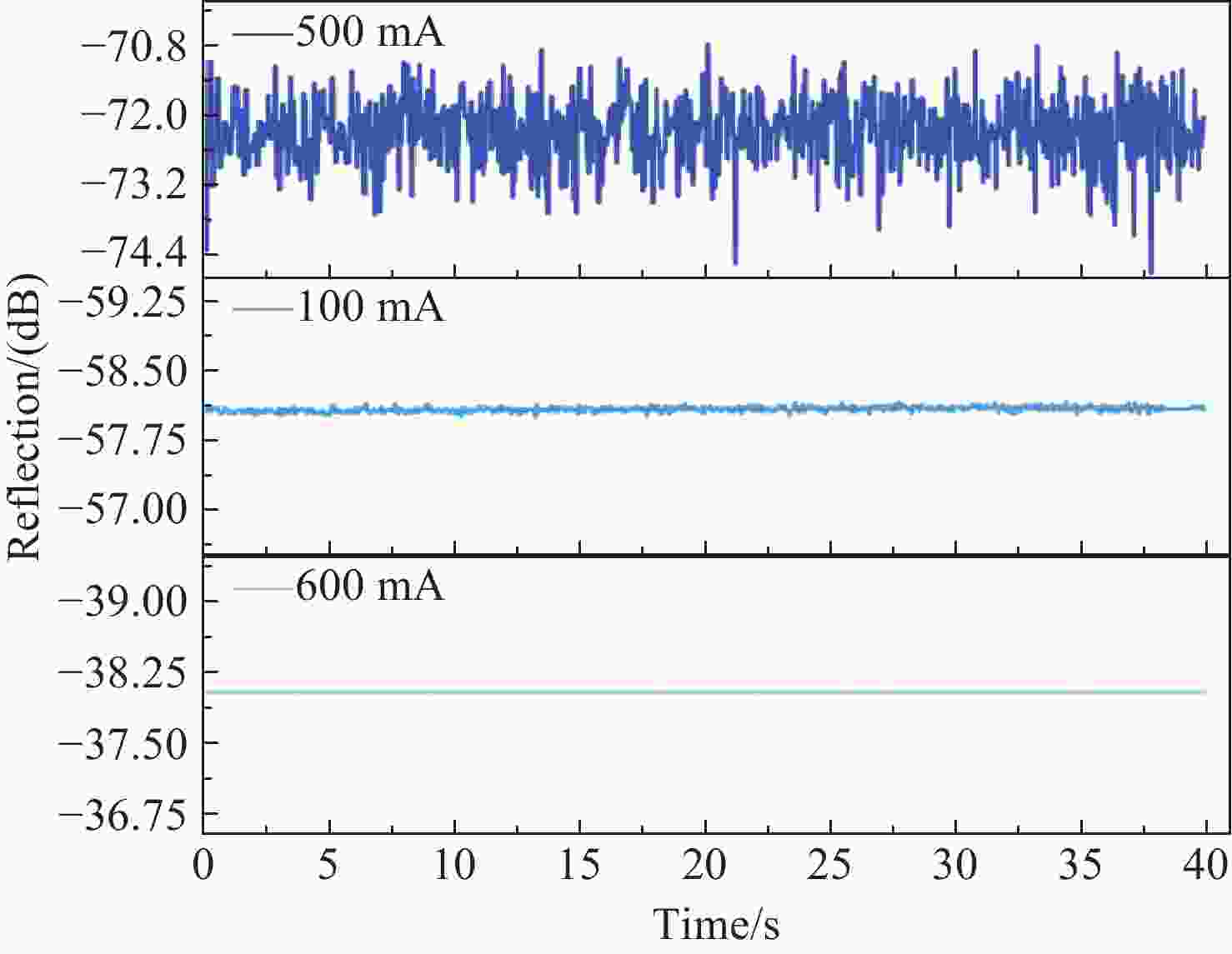
MAE/drive current 600 mA 100 mA 50 mA MAEmax 0.4016 $ \mu \varepsilon $0.2306 $ \mu \varepsilon $0.6835 $ \mu \varepsilon $MAEmin 0.0898 $ \mu \varepsilon $0.1137 $ \mu \varepsilon $0.5037 $ \mu \varepsilon $MAEave 0.1038 $ \mu \varepsilon $0.18 $ \mu \varepsilon $ 0.59 $ \mu \varepsilon $ -
[1] XU R R, LIU S, SUN Q ZH, et al. Experimental characterization of a Vernier strain sensor using cascaded fiber rings[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2012, 24(23): 2125-2128. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2012.2222369 [2] LIU Y X, LI X G, ZHANG Y N, et al. Fiber-optic sensors based on Vernier effect[J]. Measurement, 2021, 167: 108451. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108451 [3] GOMES A D, BARTELT H, FRAZÃO O. Optical Vernier effect: recent advances and developments[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2021, 15(7): 2000588. [4] ZHANG P, TANG M, GAO F, et al. Cascaded fiber-optic Fabry-Perot interferometers with Vernier effect for highly sensitive measurement of axial strain and magnetic field[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(16): 19581-19588. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.019581 [5] ZHAO Y F, DAI M L, CHEN ZH M, et al. Ultrasensitive temperature sensor with Vernier-effect improved fiber Michelson interferometer[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(2): 1090-1101. doi: 10.1364/OE.415857 [6] ZHANG P, TANG M, GAO F, et al. Simplified hollow-core fiber-based Fabry–Perot interferometer with modified Vernier effect for highly sensitive high-temperature measurement[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2015, 7(1): 7100210. [7] GOMES A D, BECKER M, DELLITH J, et al. Multimode Fabry–Perot interferometer probe based on Vernier effect for enhanced temperature sensing[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(3): 453. doi: 10.3390/s19030453 [8] ROBALINHO P M R, GOMES A D, FRAZÃO O. High enhancement strain sensor based on Vernier effect using 2-fiber loop mirrors[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2020, 32(18): 1139-1142. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2020.3014695 [9] TIAN J J, LI ZH G, SUN Y X, et al. High-sensitivity fiber-optic strain sensor based on the Vernier effect and separated Fabry–Perot interferometers[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2019, 37(21): 5609-5618. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2019.2936174 [10] ABBAS L G. Vernier effect-based strain sensor with cascaded Fabry–Pérot interferometers[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(16): 9196-9201. [11] YANG Y, ZHANG X B, YANG L, et al. Ultrahigh-sensitivity displacement sensing enabled by the Vernier effect with inhibited antiresonance[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(5): 1053-1056. doi: 10.1364/OL.419203 [12] ZHOU CH, ZHOU Q, WANG B, et al. High-sensitivity relative humidity fiber-optic sensor based on an internal–external Fabry–Perot cavity Vernier effect[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(8): 11854-11868. doi: 10.1364/OE.421060 [13] ZHOU CH, SONG Y J, ZHOU Q, et al. Ultra-high-sensitivity humidity fiber sensor based on harmonic Vernier effect in cascaded FPI[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(13): 4816. doi: 10.3390/s22134816 [14] QUAN M R, TIAN J J, YAO Y. Ultra-high sensitivity Fabry–Perot interferometer gas refractive index fiber sensor based on photonic crystal fiber and Vernier effect[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(21): 4891-4894. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.004891 [15] LI J W, ZHANG M, WAN M G, et al. Ultrasensitive refractive index sensor based on enhanced Vernier effect through cascaded fiber core-offset pairs[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(3): 4145-4155. doi: 10.1364/OE.384815 [16] LIU CH Y, CHEN H L, GU M Q, et al. Experimental study on a parallel optical fiber Sagnac loops-based sensor with the advantages of both high sensitivity and ultra-wide measurement range[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2024, 137: 105174. [17] ZHANG Y F, YU L, HU ZH L, et al. Ultrafast and accurate temperature extraction via kernel extreme learning machine for BOTDA sensors[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2021, 39(5): 1537-1543. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2020.3035810 [18] ESQUIVEL-HERNÁNDEZ J, MARTÍNEZ-MANUEL R, VALENTÍN-CORONADO L M, et al. Pattern-recognition-based dual-point fiber temperature sensor using a reliable synthetic database[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(6): 7850-7857. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3355394 [19] JIANG H, TANG R, WANG CH Y, et al. Recognition and localization of FBG temperature sensing based on combined CDAE and 1-DCNN[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(7): 10125-10137. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3365995 [20] NAKU W, ALSALMAN O, ZHU CH. High-sensitivity and large-range displacement sensor based on a balloon-shaped optical fiber and machine learning analysis[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2024, 42(15): 5399-5406. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2024.3388458 [21] PEDRAZA A, DEL RÍO D, BAUTISTA-JUZGADO V, et al. Study of the feasibility of decoupling temperature and strain from a ϕ-PA-OFDR over an SMF using neural networks[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23: 5515. doi: 10.3390/s23125515 [22] CHOI B K, KIM J S, AHN S, et al. Simultaneous temperature and strain measurement in fiber Bragg grating via wavelength-swept laser and machine learning[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(17): 27516-27524. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3429366 [23] CHEN Y R, LI N, YU Y, et al. Dual-parametric simultaneous demodulation of fiber optic seawater temperature and pressure sensors based on machine learning methods[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(22): 28294-28303. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3308079 [24] ZHU CH, ALSALMAN O, NAKU W. Machine learning for a Vernier-effect-based optical fiber sensor[J]. Optics Letters, 2023, 48(9): 2488-2491. doi: 10.1364/OL.489471 [25] ZHU CH, ALSALMAN O. Vernier effect-based optical fiber sensor for dynamic sensing using a coarsely resolved spectrometer[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(13): 22250-22259. doi: 10.1364/OE.493302 [26] MEI Y CH, XIA T T, CAI H E, et al. Deep learning improved spectral demodulation of interferometry Vernier effect for pressure sensing[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2024, 42(1): 430-440. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2023.3307812 [27] ZUO G M, HU H L, LI SH Y, et al. Iterative normalized cross-correlation method for absolute optical path difference demodulation of dual interferometers[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(11): 16595-16610. doi: 10.1364/OE.423326 [28] DAI M L, CHEN ZH M, ZHAO Y F, et al. Fiber optic temperature sensor with online controllable sensitivity based on Vernier effect[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(19): 21555-21563. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3101572 -






 下载:
下载: