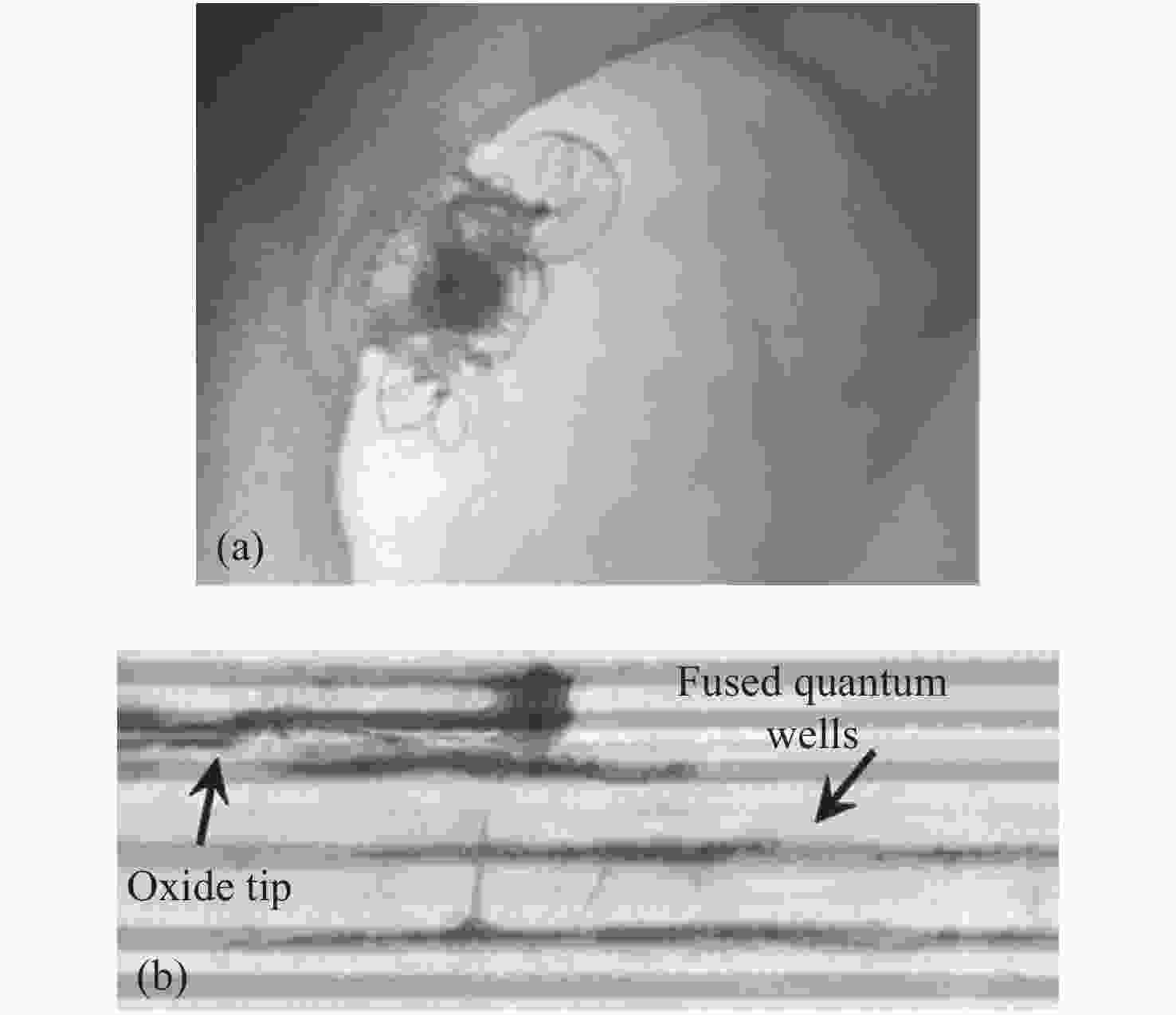
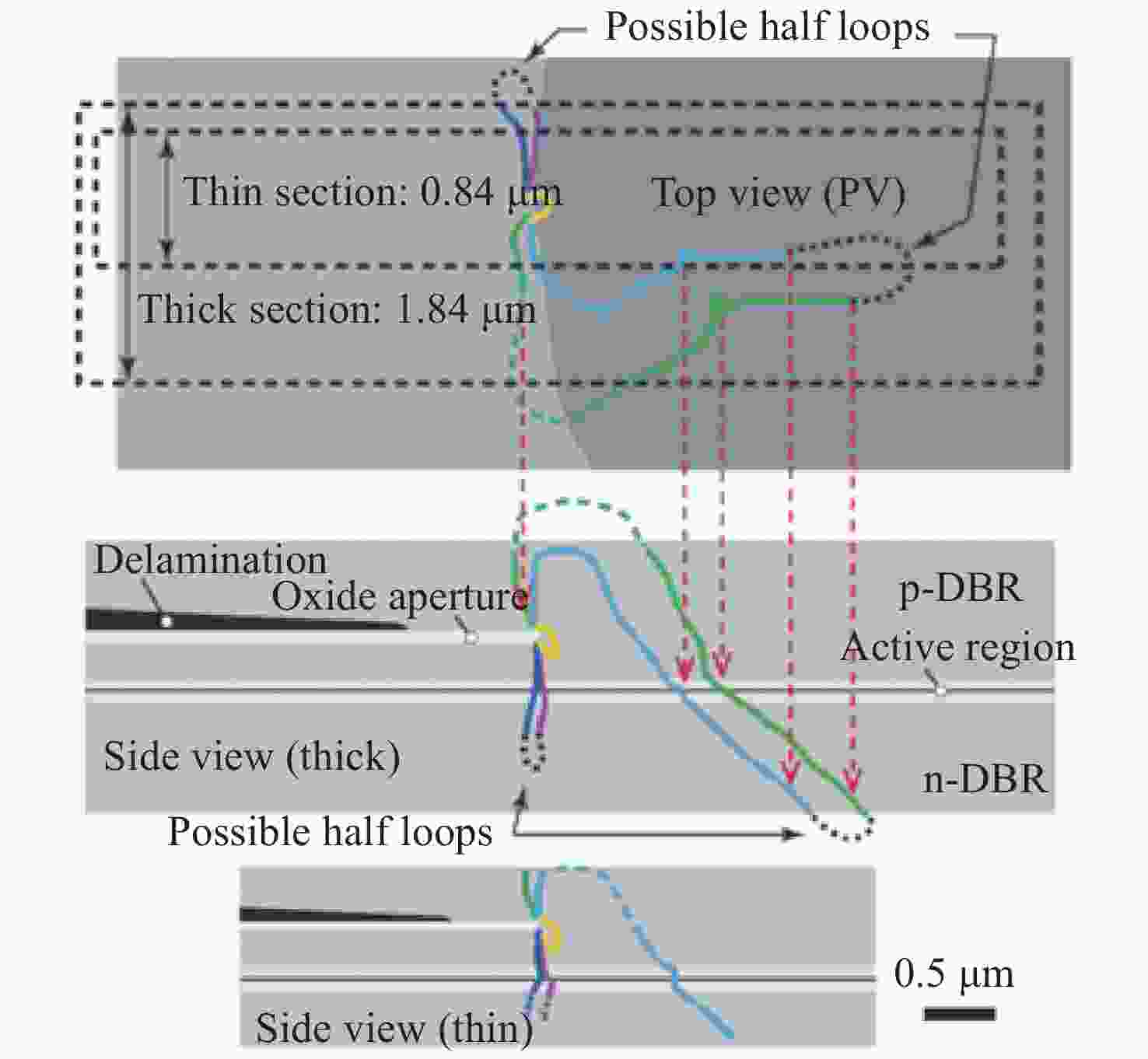
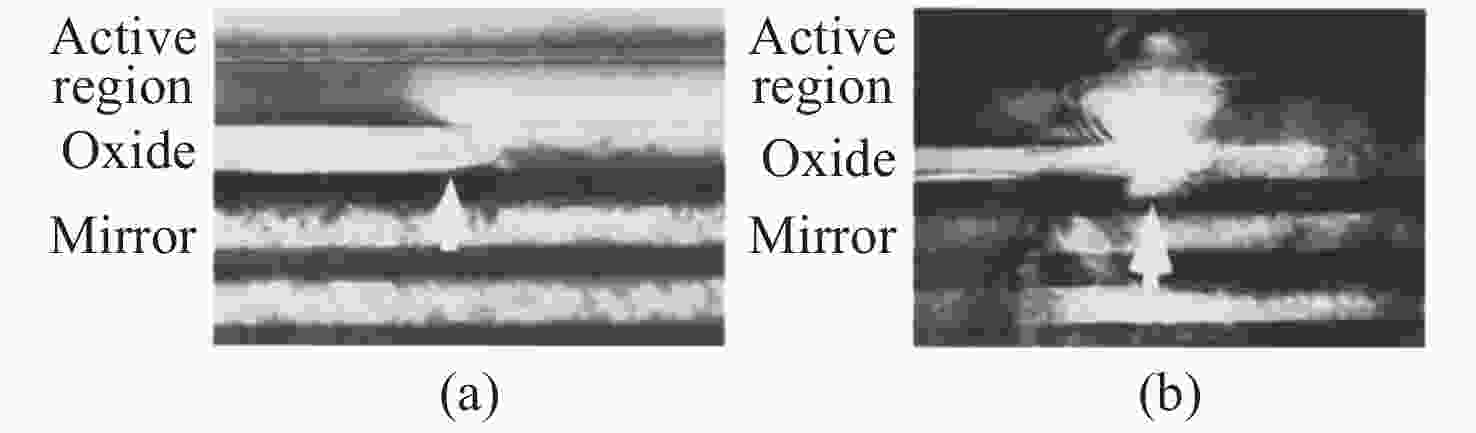
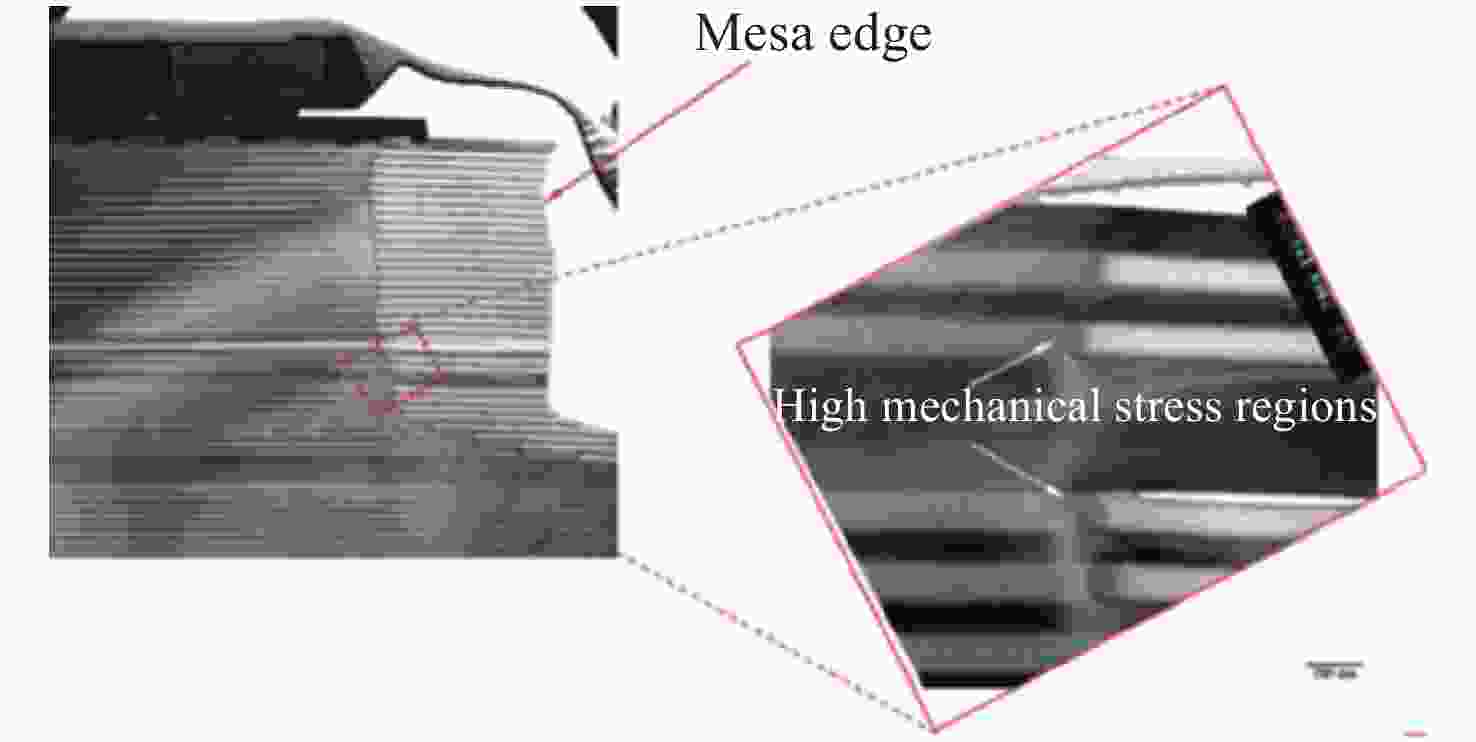
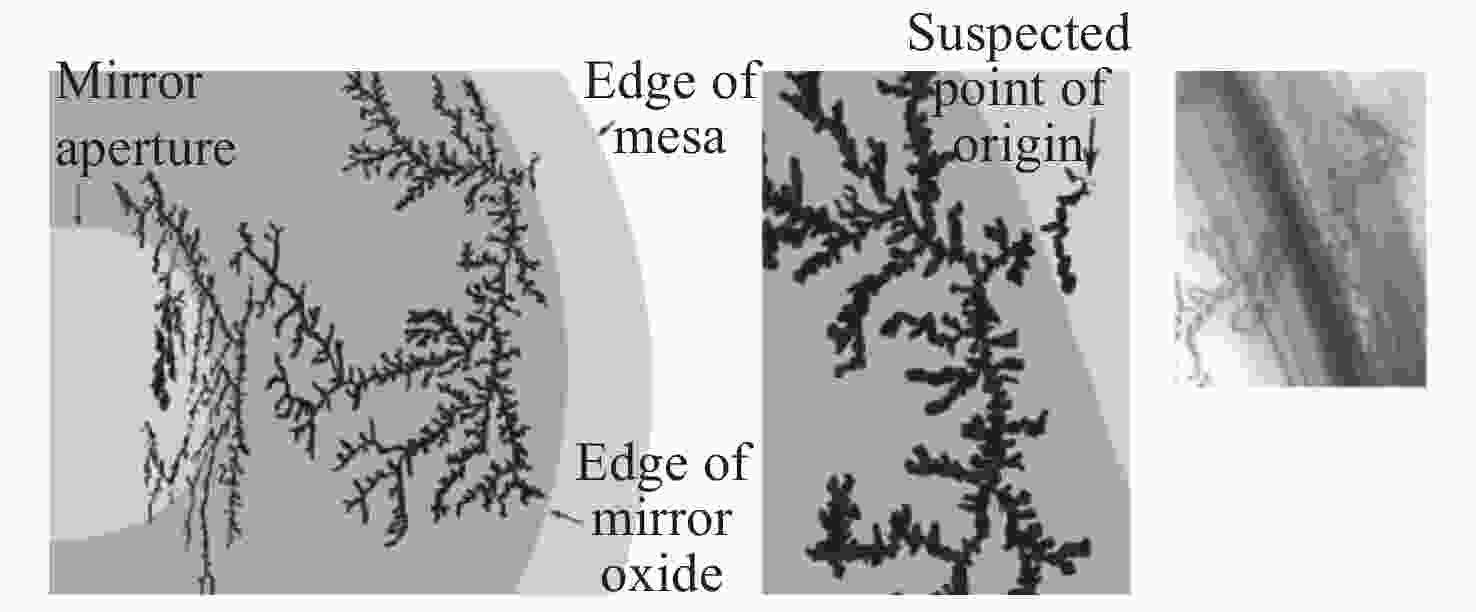
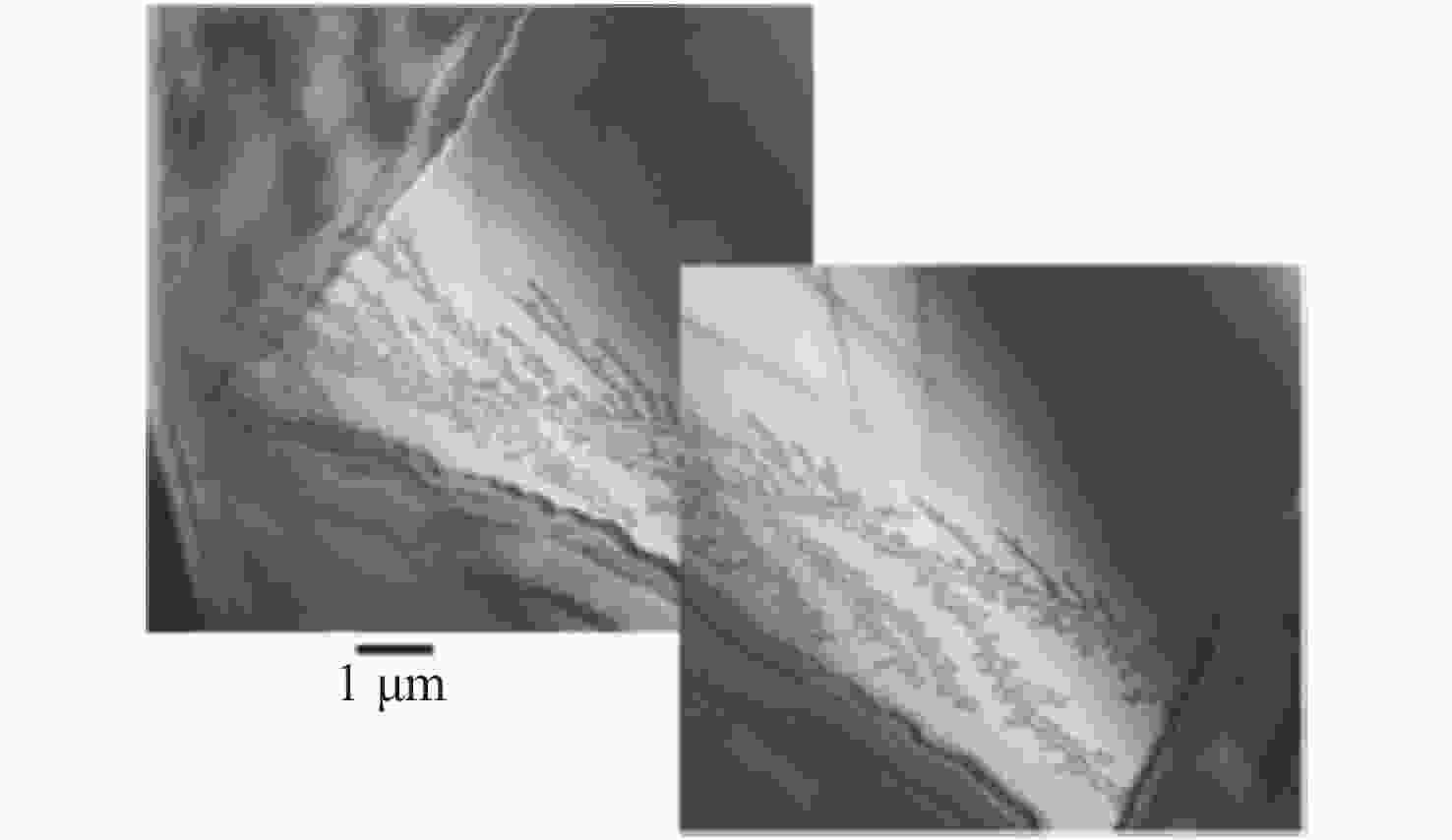
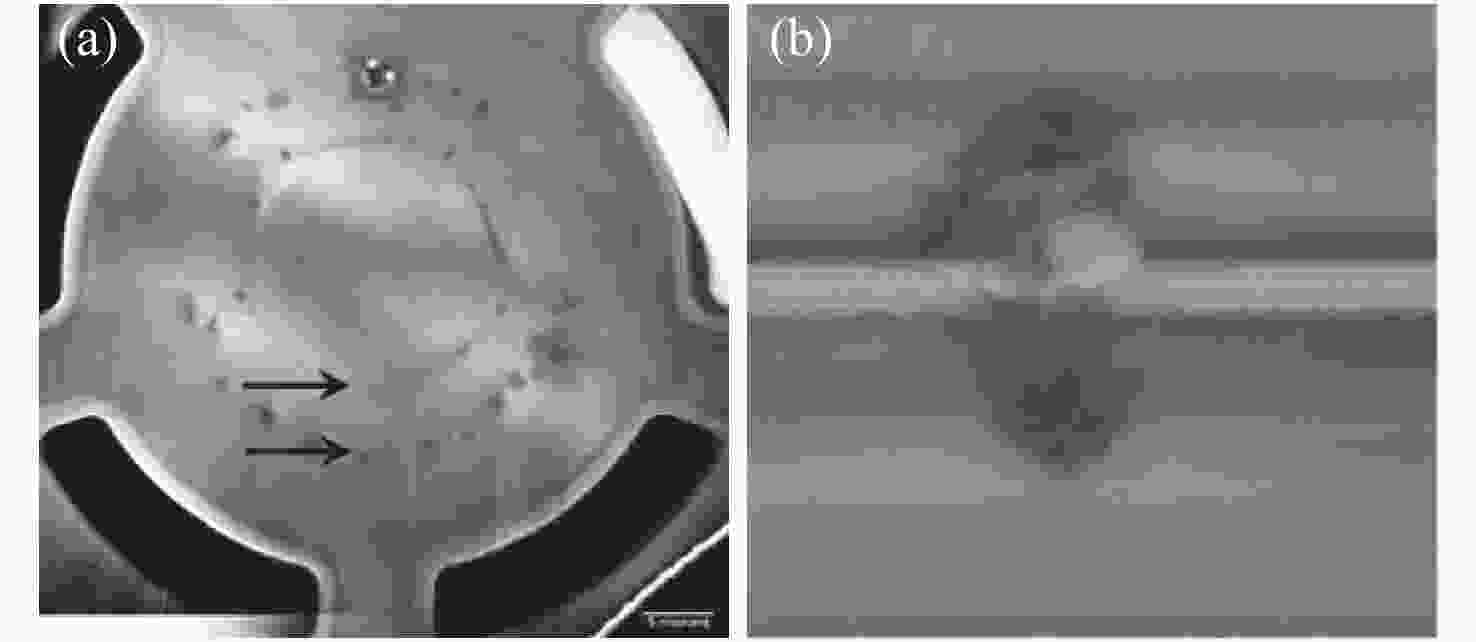
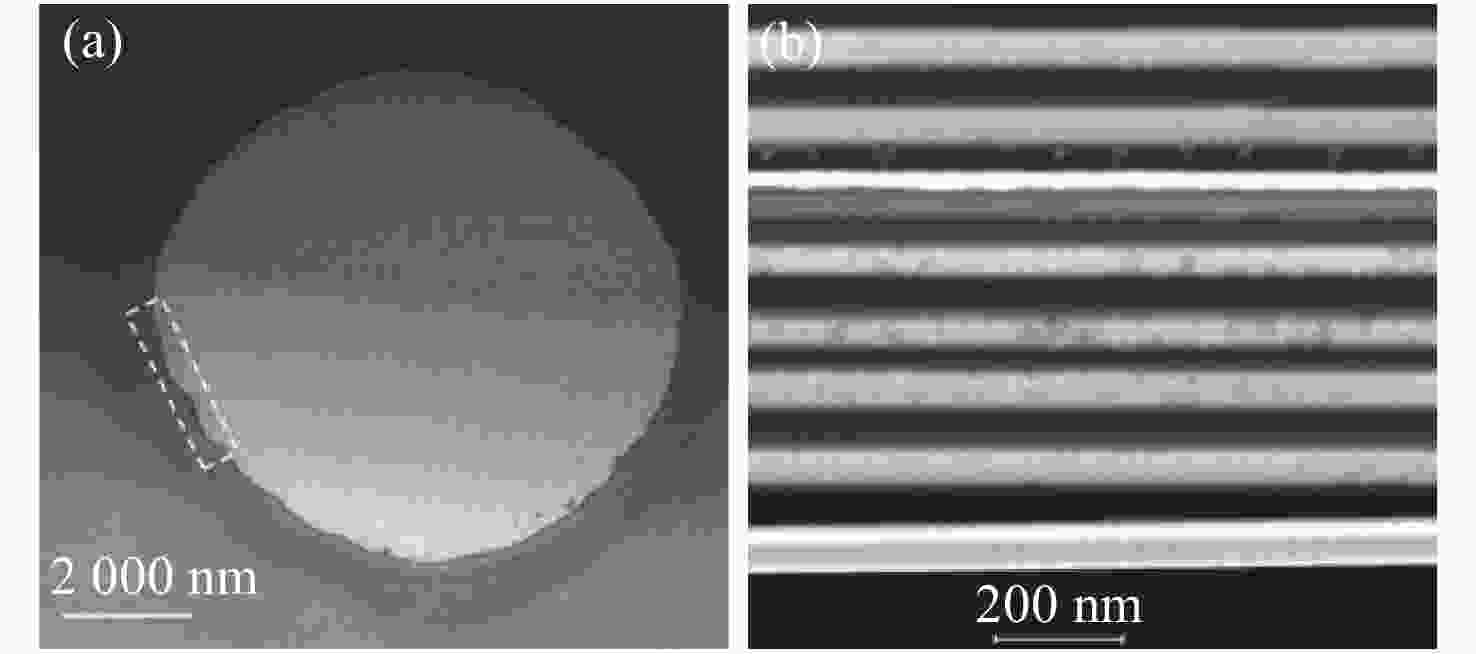
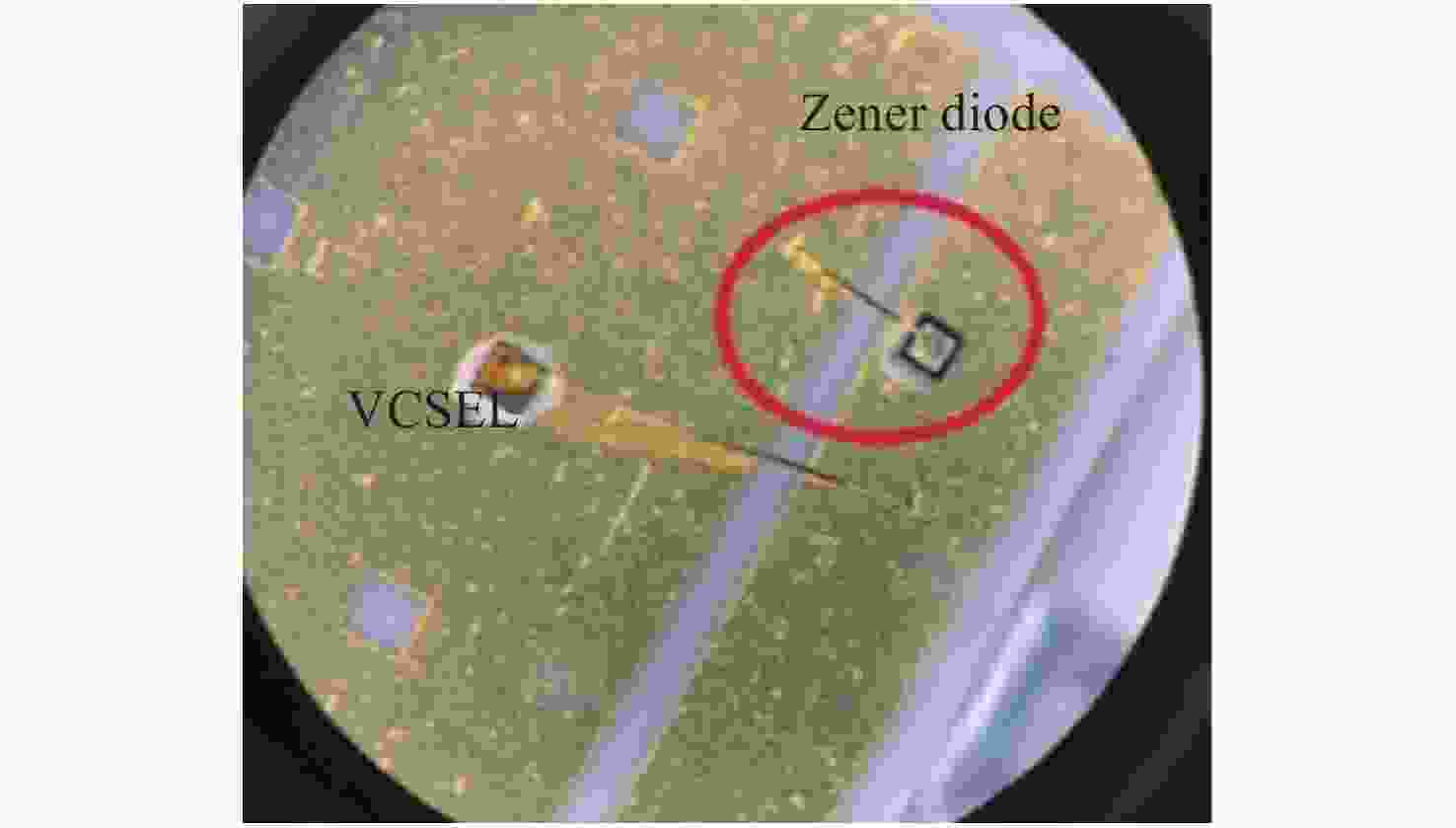
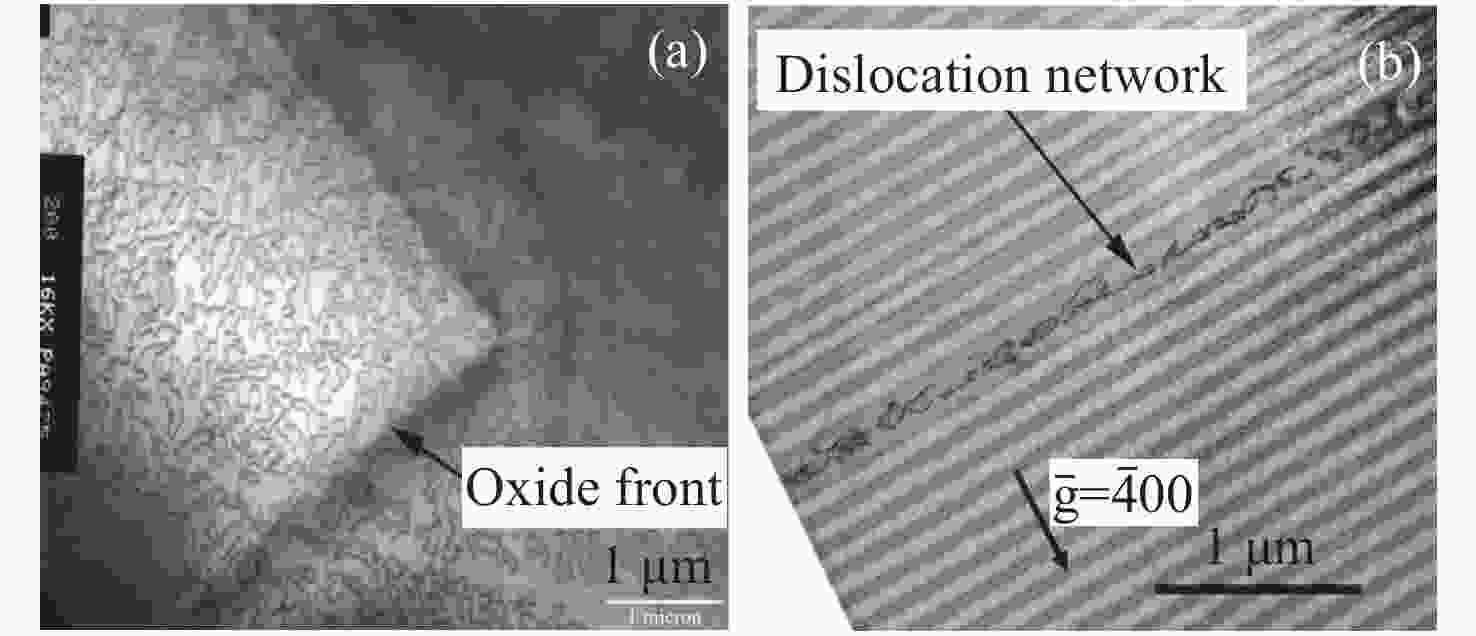
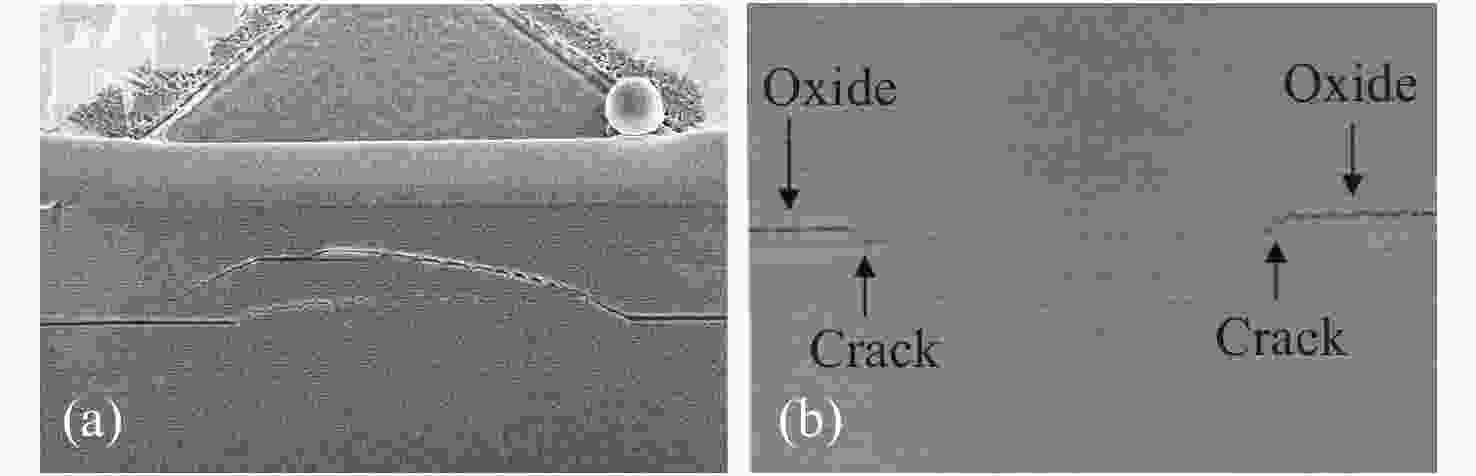
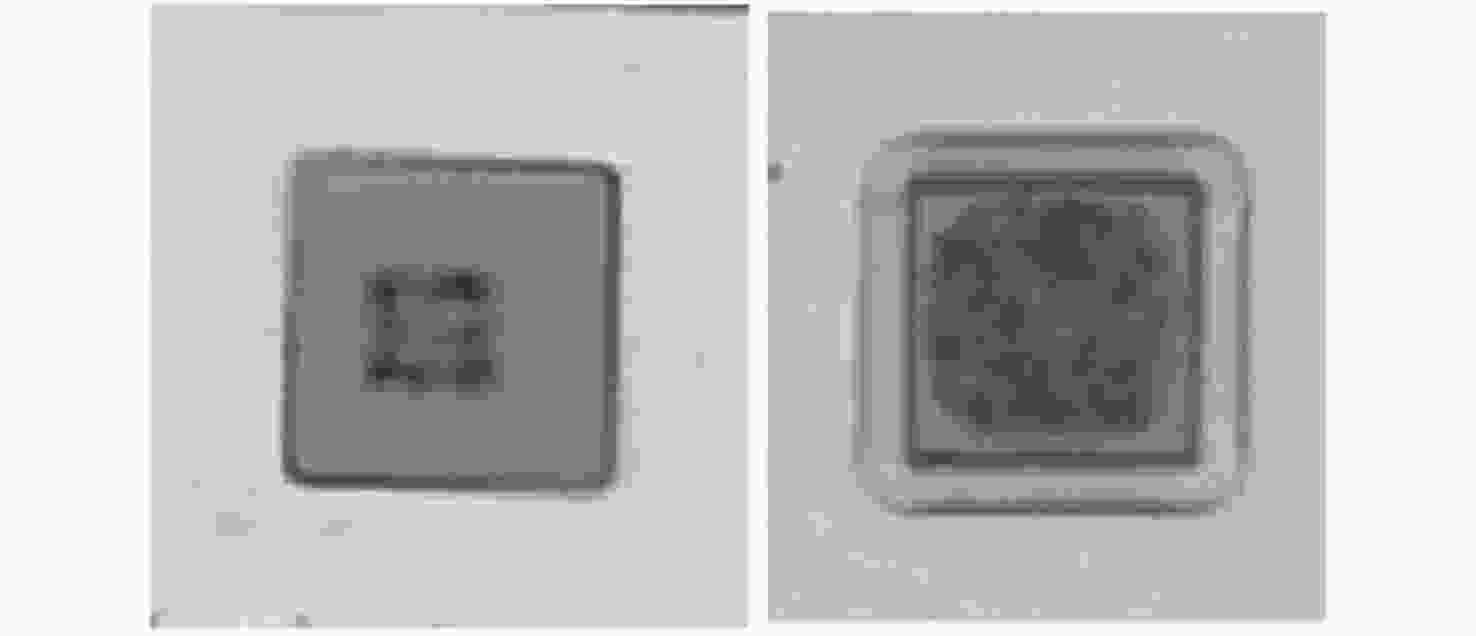
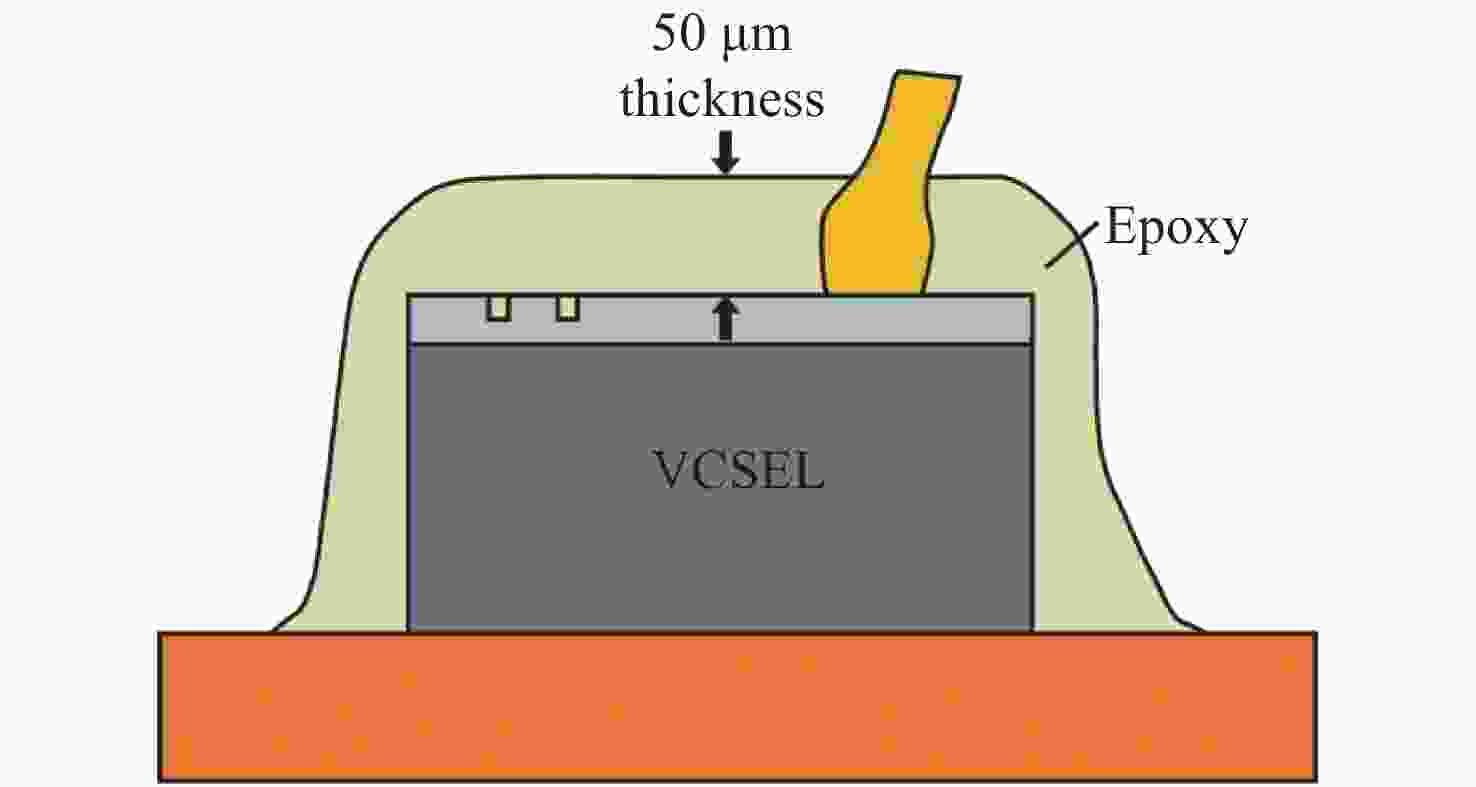
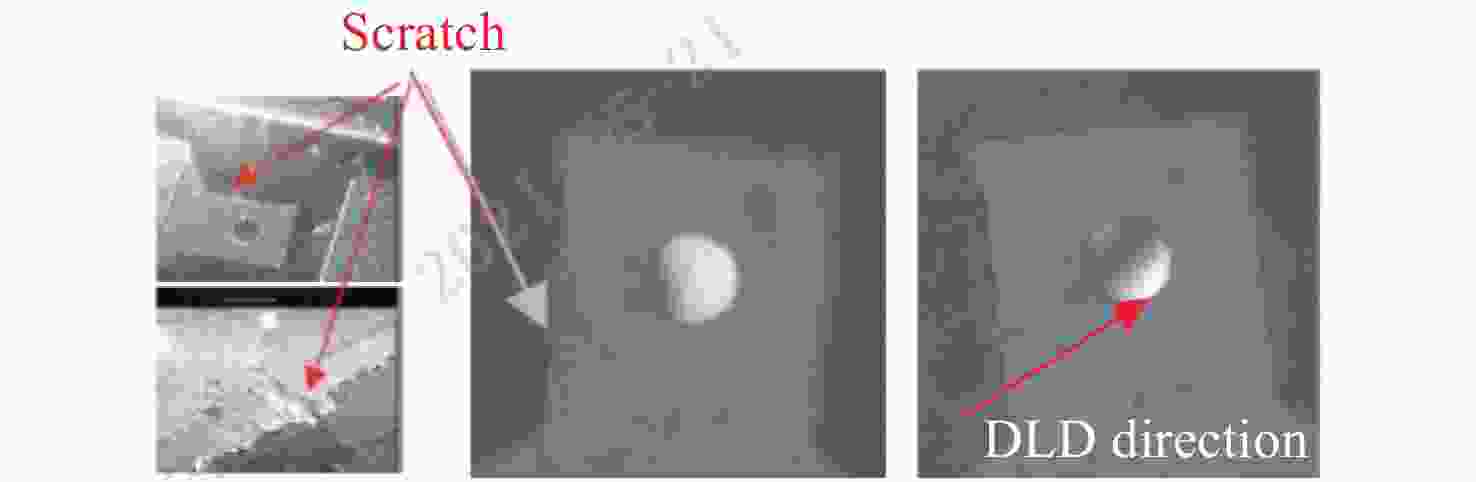
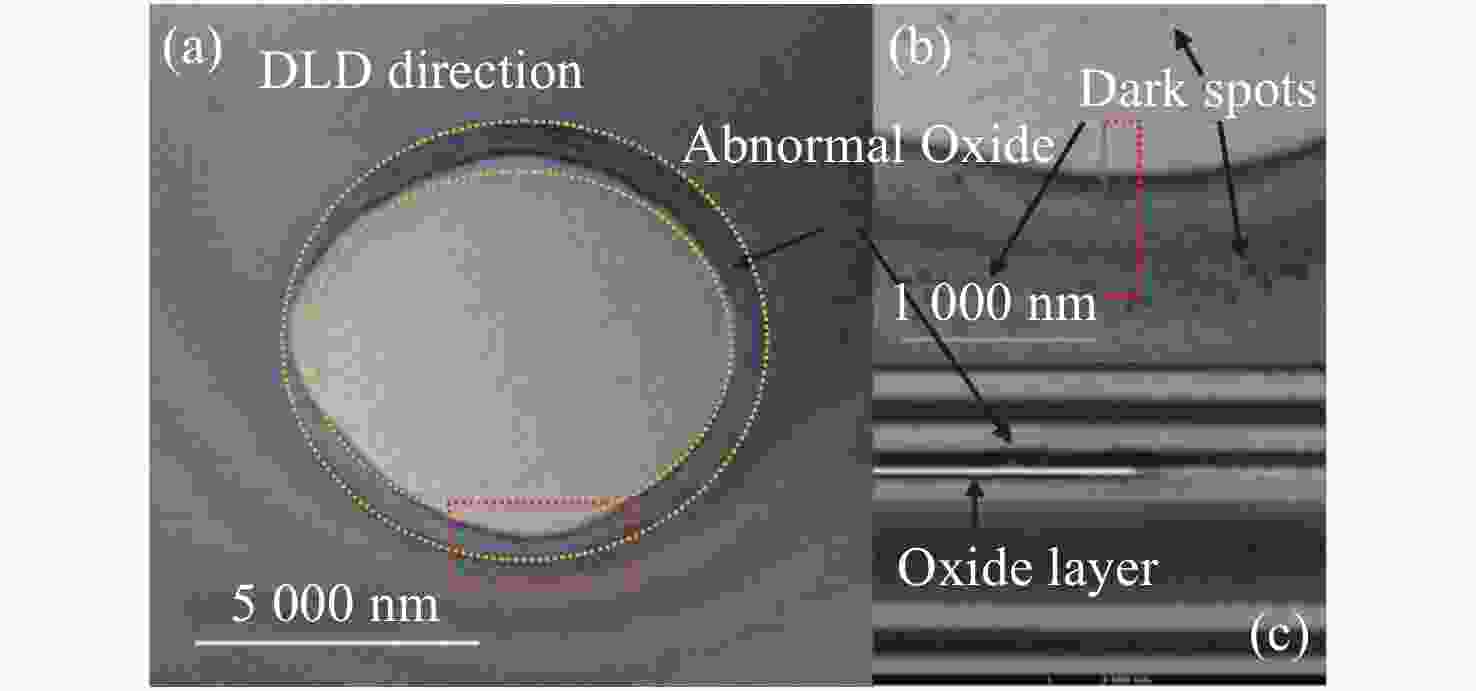
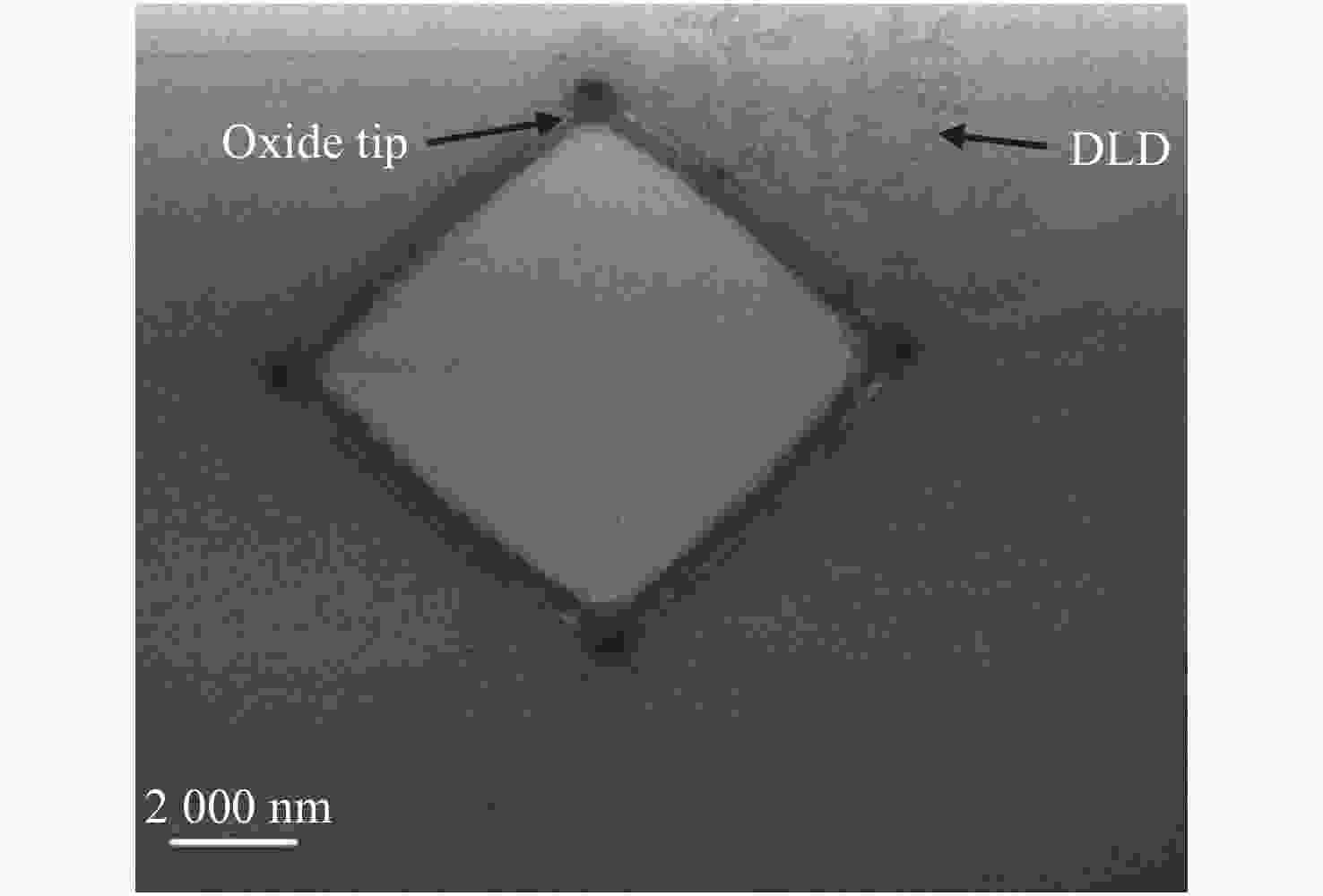
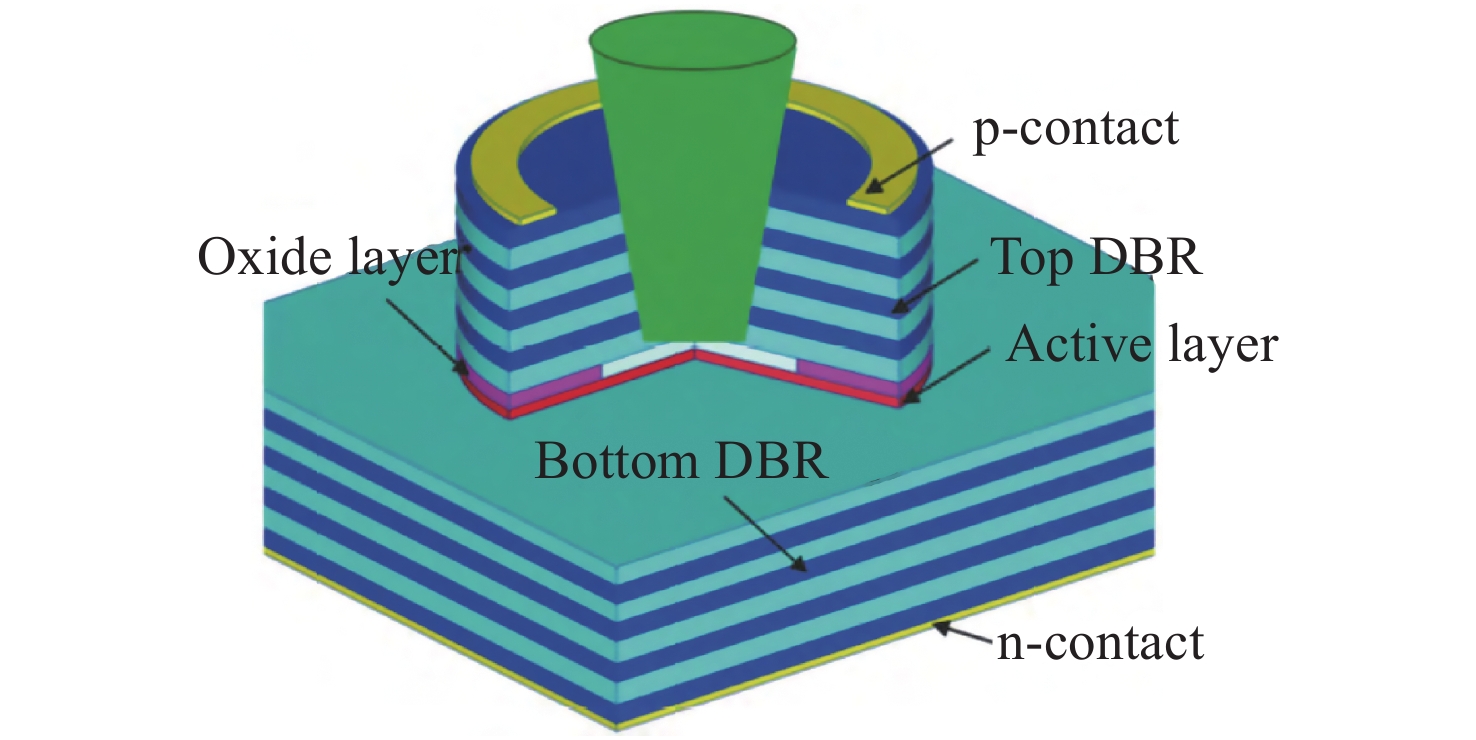
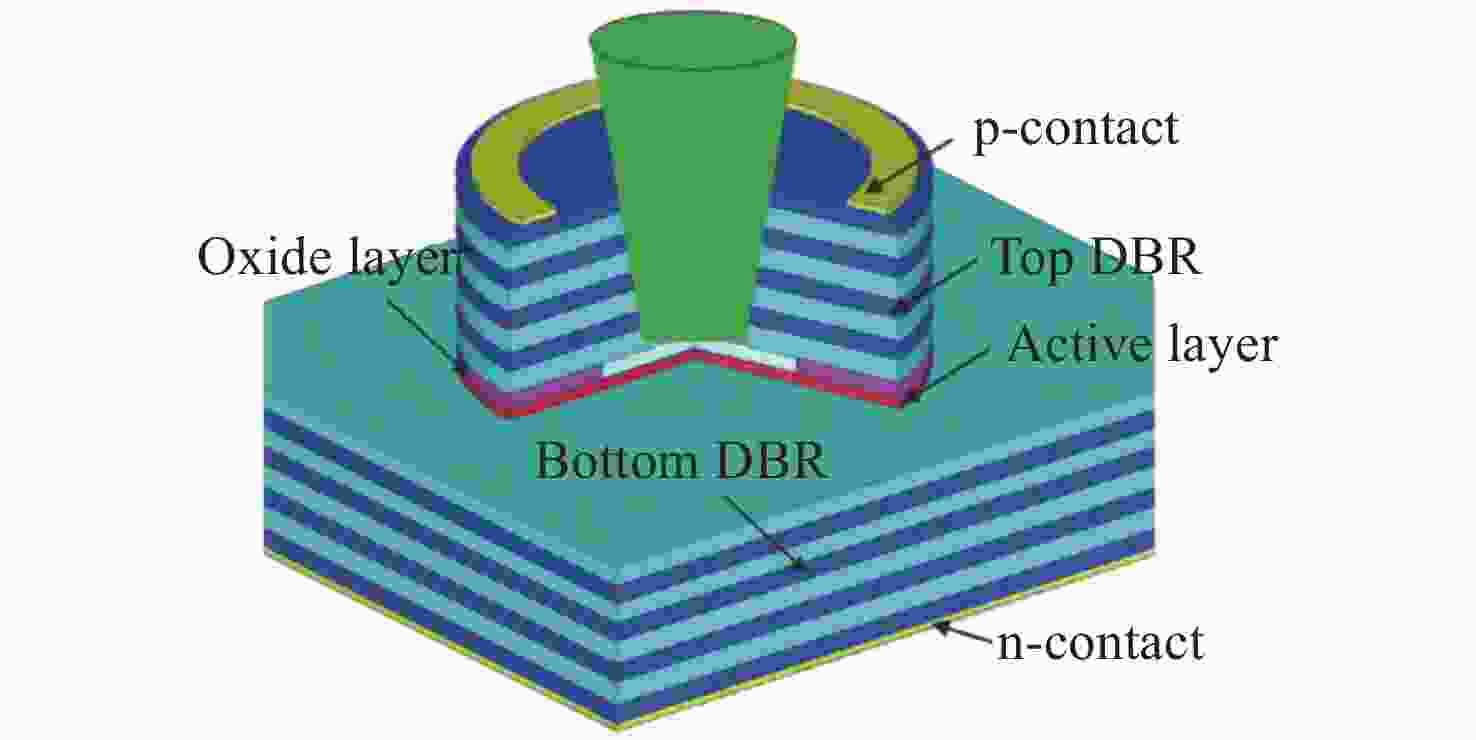
Common failure modes and mechanisms in oxide vertical cavity surface emitting lasers
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN.2021-0012
-
摘要: 氧化型垂直腔面发射激光器(VCSEL)在高速光通信中有着广泛的应用,应用过程中的可靠性是一个非常重要的指标,要求有高寿命和低失效率。为了更好地了解VCSEL在应用过程中的失效模式和机理,提升器件的可靠性,本文从器件设计、加工制造和应用过程等3个环节总结分析了氧化型VCSEL的常见失效模式、产生原因和机理,并提出了适当的改善措施和建议。其中,对氧化应力、静电放电和湿气腐蚀这3个主要失效因素进行了更为详细的分析。基于以上对业界研究工作的总结和分析,最后对实际工作中遇到的VCSEL失效案例进行简单的介绍,为VCSEL学者、研发设计、制造和使用人员提供一个较为全面的失效分析案例库。Abstract: Oxide Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers(VCSELs) are widely used in high-speed optical communications. The reliability of VCSELs is a very important index that requires a high lifetime and low failure rate in the application process. Understanding the root causes and mechanisms of VCSEL failure is necessary and helpful to improve device reliability. In this paper, we summarize and analyze the most common failure modes, causes and mechanisms observed in oxide VCSELs from the perspective of design, manufacturing and application, then apply some appropriate measures and suggestions to prevent or improve them. Moreover, the three dominating factors leading to the failure of VCSELs including oxide layer stress, Electronic Static Discharge (ESD) and humidity corrosion are introduced in more detail. At last, we simply introduce the VCSEL failure cases encountered in the actual accelerated aging verification process. This article can be used as a good VCSEL failure analysis library for chip development and production researchers.
-
Key words:
- VCSEL /
- oxide /
- failure modes and mechanisms /
- reliability
-
表 1 A summary of the easiness of formation of dislocation loops in some III-V compound semiconductors[20]
Table 1. A summary of the easiness of formation of dislocation loops in some III-V compound semiconductors[20]
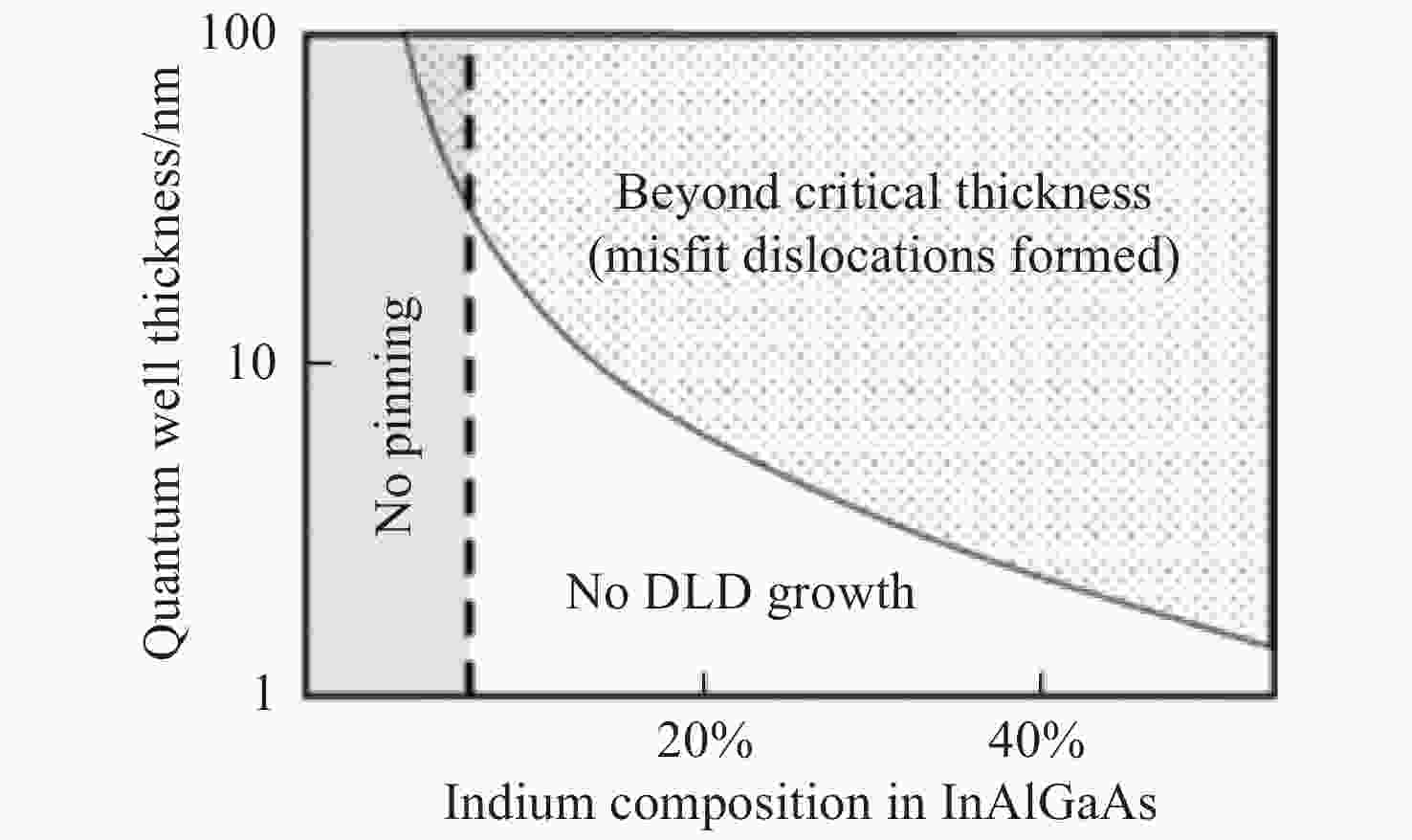
Material Band gap energy/eV@300K Formation of dislocation loops GaAs 1.42 Yes AlGaAs 1.42~2.15 Yes GaP 2.27 Yes GaAsP 1.42~2.27 Yes InP 1.34 No InGaAsP on InP 0.75~1.34 No InGaP on GaAs 1.42~1.91 Yes InGaAsP on GaAs 1.42~1.76 Yes -
[1] TONG H X, TONG C ZH, WANG Z Y, et al. Advances in the technology of 850 nm high-speed vertical cavity surface emitting lasers (invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(12): 20201077. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA20201077 [2] ZHANG J Y, LI X, ZHANG J W, et al. Research progress of vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2020, 41(12): 1443-1459. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJL.20200339 [3] IGA K. Forty years of vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser: invention and innovation[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 57(8S2): 08PA01. doi: 10.7567/JJAP.57.08PA01 [4] HE X Y, DONG J, HU SH, et al. High-speed 850 nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers with BCB planarization technique[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(2): 190-197. doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0190 [5] CHEN L H, YANG G W, LIU Y X. Development of semiconductor lasers[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(5): 0500001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0500001 [6] SUN T Y, XIA M J, QIAO L. Failure mechanism and detection analysis of semiconductor laser[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(19): 1900003. (in Chinese) [7] UEDA O, PEARTON S J. Materials and Reliability Handbook for Semiconductor Optical and Electron Devices[M]. New York: Springer, 2013. [8] MATHES D, GUENTER J, TATUM J, et al. AOC moving forward: the impact of materials behavior[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6132: 613203. doi: 10.1117/12.646447 [9] TATUM J A. Evolution of VCSELs[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9001: 90010C. [10] LOWES T D. VCSEL reliability research at gore photonics[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2002, 4649: 121-129. doi: 10.1117/12.469226 [11] HERRICK R W. Oxide VCSEL reliability qualification at agilent technologies[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2002, 4649: 130-141. doi: 10.1117/12.469227 [12] AEBY I, COLLINS D, GIBSON B, et al. Highly reliable oxide VCSELs for datacom applications[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 4994: 152-161. doi: 10.1117/12.482633 [13] TATUM J A, GUENTER J A. The VCSELS are coming[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 4994: 1-11. doi: 10.1117/12.475724 [14] LIU A J, WOLF P, LOTT J A, et al. Vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers for data communication and sensing[J]. Photonics Research, 2019, 7(2): 121-136. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.7.000121 [15] CAO Y X. Development of vertical cavity surface emitting laser modulation for data communication[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2020, 1653(1): 012001. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1653/1/012001 [16] LIU A J. Progress in single-mode and directly modulated vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(7): 0701005. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0701005 [17] JIMÉNEZ J. Laser diode reliability: crystal defects and degradation modes[J]. Comptes Rendus Physique, 2003, 4(6): 663-673. doi: 10.1016/S1631-0705(03)00097-5 [18] HERRICK R W. Design for reliability and common failure mechanisms in vertical cavity surface emitting lasers[J]. MRS Online Proceedings Library, 2012, 1432: 9-20. [19] MUKHERJEE K. Materials Science of Defects in GaAs-based Semiconductor Lasers[M]. HERRICK R W, UEDA O. Reliability of Semiconductor Lasers and Optoelectronic Devices. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2021: 113-176. [20] UEDA O. Reliability and Degradation of III-V Optical Devices Focusing on Gradual Degradation[M]. UEDA O, PEARTON S J. Materials and Reliability Handbook for Semiconductor Optical and Electron Devices. New York, NY: Springer, 2013: 87-122. [21] JONES R. Do we really understand dislocations in semiconductors?[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:B, 2000, 71(1-3): 24-29. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5107(99)00344-X [22] KIRKBY P. Dislocation pinning in GaAs by the deliberate introduction of impurities[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1975, 11(7): 562-568. doi: 10.1109/JQE.1975.1068634 [23] TWESTEN R D, FOLLSTAEDT D M, CHOQUETTE K D, et al. Microstructure of laterally oxidized AlxGa1−xAs layers in vertical‐cavity lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1996, 69(1): 19-21. doi: 10.1063/1.118103 [24] CHOQUETTE K D, GEIB K M, CHUI H C, et al. Selective oxidation of buried AlGaAs versus AlAs layers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1996, 69(10): 1385-1387. doi: 10.1063/1.117589 [25] HERRICK R W, DAFINCA A, FARTHOUAT P, et al. Corrosion-based failure of oxide-aperture VCSELs[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2013, 49(12): 1045-1052. doi: 10.1109/JQE.2013.2285572 [26] STARK T J, RUSSELL P E, NEVERS C. 3-D defect characterization using plan view and cross-sectional TEM/STEM analysis[C]. ISTFA 2005: Conference Proceedings from the 31st International Symposium for Testing and Failure Analysis, ISTFA, 2005: 344-349. [27] CHENG Y M, HERRICK R W, PETROFF P M, et al.. Degradation mechanisms of vertical cavity surface emitting lasers[C]. Proceedings of International Reliability Physics Symposium, IEEE, 1996: 211-213. [28] PAO J J, WU T C, KYI W, et al. Reliability and manufacturability of 25G VCSELs with oxide apertures formed by in-situ monitoring[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10115: 1011519. doi: 10.1117/12.2253565 [29] HERRICK R W. Reliability and Degradation of Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers[M]. UEDA O, PEARTON S J. Materials and Reliability Handbook for Semiconductor Optical and Electron Devices. New York, NY: Springer, 2013: 147-205. [30] HELMS C J, AEBY I, LUO W L, et al. Reliability of oxide VCSELs at Emcore[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5364: 183-189. doi: 10.1117/12.539282 [31] JOHNSON R H. Passivation of VCSEL sidewalls: US, 9997892B2[P]. 2018-06-12. [32] ITAKURA T, SEYAMA Y, TERADA T, et al. Transmission-electron-microscopy observation of dislocation networks of oxide vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. Optical Engineering, 2006, 45(1): 014201. doi: 10.1117/1.2150232 [33] MATHES D T, GUENTER J, HAWKINS B, et al.. An atlas of ESD failure signatures in vertical cavity surface emitting lasers[C]. ISTFA, 2005: Conference Proceedings from the 31st International Symposium for Testing and Failure Analysis, ISTFA, 2005: 336-343. [34] GUENTER J, MATHES D, HAWKINS B, et al. Developments at finisar AOC[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 6908: 690805. doi: 10.1117/12.771311 [35] MCHUGO S A, KRISHNAN A, KRUEGER J J, et al. Characterization of failure mechanisms for oxide VCSELs[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 4994: 55-66. doi: 10.1117/12.482637 [36] KRUEGER J J, SABHARWAL R, MCHUGO S A, et al. Studies of ESD-related failure patterns of Agilent oxide VCSELs[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 4994: 162-172. doi: 10.1117/12.482632 [37] VANZI M, MURA G, MARCELLO G, et al. ESD tests on 850 nm GaAs-based VCSELs[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2016, 64: 617-622. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2016.07.023 [38] GUENTER J K, TATUM J A, HAWTHORNE III R A, et al. VCSELs at Honeywell: the story continues[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5364: 34-46. doi: 10.1117/12.540129 [39] PETROFF P, HARTMAN R L. Rapid degradation phenomenon in heterojunction GaAlAs–GaAs lasers[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1974, 45(9): 3899-3903. doi: 10.1063/1.1663883 [40] MATHES D T, HULL R, CHOQUETTE K D, et al. Nanoscale materials characterization of degradation in VCSELs[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 4994: 67-82. doi: 10.1117/12.482858 [41] KIM T, KIM T, KIM S, et al. Degradation behavior of 850 nm AlGaAs/GaAs oxide VCSELs suffered from electrostatic discharge[J]. ETRI Journal, 2008, 30(6): 833-843. doi: 10.4218/etrij.08.0108.0148 [42] HO K T, CHAN C H. Failure case studies of GaAs-based oxide-confined VCSELs[C]. ISTFA 2020: Papers Accepted for the Planned 46th International Symposium for Testing and Failure Analysis, ISTFA, 2020: 317-321. [43] HAWKINS B M, HAWTHORNE R A, GUENTER J K, et al.. Reliability of various size oxide aperture VCSELs[C]. 52nd Electronic Components and Technology Conference 2002, IEEE, 2002: 540-550. [44] LEI C, LI N, CHUAN X. Emcore VCSEL failure mechanism and resolution[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7615: 761504. doi: 10.1117/12.845968 [45] HUANG J SH, OLSON T, ISIP E. Human-body-model electrostatic-discharge and electrical-overstress studies of buried-heterostructure semiconductor lasers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Device and Materials Reliability, 2007, 7(3): 453-461. doi: 10.1109/TDMR.2007.907425 [46] MATHES D T. Materials issues for VCSEL operation and reliability[D]. Charlattesville, Virginia: University of Virginia, 2002. [47] FURUKAWA Y, KOBAYASHI T, WAKITA K, et al. Accelerated life test of AlGaAs–GaAs DH lasers[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1977, 16(8): 1495-1496. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.16.1495 [48] NANNICHI Y, MATSUI J, ISHIDA K. Rapid degradation in double-heterostructure Lasers. II. semiquantitative analyses on the propagation of dark line defects[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1975, 14(10): 1561-1568. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.14.1561 [49] KAMEJIMA T, ISHIDA K, MATSUI J. Injection-enhanced dislocation glide under uniaxial stress in GaAs–(GaAl)As double heterostructure laser[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1977, 16(2): 233-240. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.16.233 [50] MAEDA K, SATO M, KUBO A, et al. Quantitative measurements of recombination enhanced dislocation glide in gallium arsenide[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1983, 54(1): 161-168. doi: 10.1063/1.331725 [51] YONENAGA I, SUMINO K. Dislocation velocity in GeSi alloy[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1996, 69(9): 1264-1266. doi: 10.1063/1.117386 [52] DAFINCA A, WEIDBERG A R, MCMAHON S J, et al. Reliability and degradation of oxide VCSELs due to reaction to atmospheric water vapor[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2013, 8639: 86390L. doi: 10.1117/12.2001195 [53] HERRICK R W. Reliability of vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 51(11S): 11PC01. doi: 10.7567/JJAP.51.11PC01 [54] XIE S N, HERRICK R W, CHAMBERLIN D, et al. Failure mode analysis of oxide VCSELs in high humidity and high temperature[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2003, 21(4): 1013-1019. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2003.809546 [55] XIE S N, HERRICK R W, DE BRABANDER G N, et al. Reliability and failure mechanisms of oxide VCSELs in non-hermetic enviroments[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 4994: 173-180. doi: 10.1117/12.480281 [56] XIE S N, DE BRABANDER G, WIDJAJA W, et al.. Reliability of oxide VCSELs in non-hermetic environments[C]. The 15th Annual Meeting of the IEEE Lasers and Electro-optics Society, IEEE, 2002: 544-545. [57] DREYBRODT J, MALACARNE F. Failure mechanism of VCSELs in optical mouse applications at non-hermitic conditions[C]. 2015 IEEE 22nd International Symposium on the Physical and Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits, IEEE, 2015. [58] WEIDBERG A R. VCSEL reliability in ATLAS and development of robust arrays[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2012, 7(1): C01098. [59] COOKE M S. Studies of VCSEL failures in the optical readout systems of the ATLAS silicon trackers and liquid argon calorimeters[J]. arXiv: , 1109, 6679: 2011. [60] SIEGELIN F. Failure analysis of vertical cavity surface emission laser diodes[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2004, 44(9-11): 1593-1597. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2004.07.075 [61] WATERS R G. Diode laser degradation mechanisms: a review[J]. Progress in Quantum Electronics, 1991, 15(3): 153-174. doi: 10.1016/0079-6727(91)90004-2 -





 下载:
下载: