-
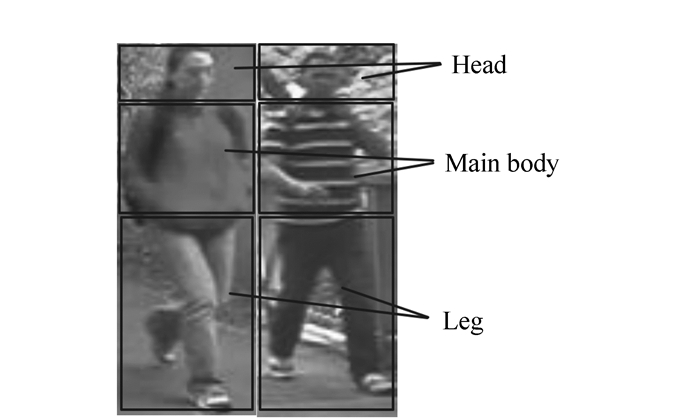
摘要: 针对当前行人重识别方法采用单一底层特征识别率较低的问题,提出一种融合底层和中层特征的识别方法,由粗到精对人体目标进行匹配识别。首先提取目标的颜色直方图和纹理直方图进行粗分类;然后将人体目标分为头部、躯干和腿部3个部分。忽略包含信息量较少的头部,对躯干和腿部,提出一种中层图像块字典提取方法,并对照该字典生成中层特征,进行精确分类。底层特征结合中层特征使算法既具有较好的区分度,又具有良好的泛化能力。实验结果表明本文算法在VIPeR数据库上的nAUC比已有方法提高6.3%,对遮挡和背景粘连的鲁棒性更好。Abstract: Aiming at the problem of low recognition rate in the existing pedestrian re-identification algorithm using single low-level feature, a new method by fusing low-level and mid-level features is proposed, which identifies person in a coarse to fine strategy. First, the pedestrian is recognized roughly by color and texture features. Then, the human body is divided into three parts, including head, main body and leg. Head is ignored for its few useful information. A mid-level dictionary method is proposed and the dictionary is trained using patches from main body and leg, and then mid-level feature is computed for fine recognition. Fusing mid-level and low-level features can be not only discriminative but also representative. The experimental results indicate that the proposed method can increase nAUC by 6.3% compared with the existing methods, which is more robust to occlusion and background adhesion.
-
Key words:
- pedestrian re-identification /
- color histogram /
- texture features /
- mid-level features /
- clustering
-
表 1 算法排名等级和nAUC对比
Table 1. Comparation of ranking matching rate and nAUC
Method Rank-1 Rank-10 Rank-20 Rank-30 nAUC SDALF 21.8 51.4 65.7 76.8 83.5 ELF 19.4 45.6 60.5 70.9 79.6 SCEAF 24.6 57.3 70.4 81.5 85.4 Proposed method 37.8 70.9 77.2 86.7 91.7 -
[1] GONG S, CRISTANI M, YAN S, et al..Person Re-identification[M].London:Springer, 2014. [2] WANG X, DORETTO G, SEBASTIAN T B, et al..Shape and appearance context modeling[J].IEEE, 2007, 1(1):1-8. http://www.docin.com/p-1479988732.html [3] ARENZENA M, BAZZANI L, PERINA A, et al..Person re-identification by symmetry-driven accumulation of local features[C].IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010:2360-2367. [4] CHENG D, CRISTANI M, STOPPA M, et al..Custom pictorial structures for re-identification[C].British Machine Vision Conference, Dundee, UK, 2011:749-760. [5] KOSTINGER M, HIRZER M, WOHLHART P, et al..Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints[C].IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2012:2288-2295. [6] MA B, SU Y, JURIE F.Local descriptors encoded by fisher vectors for person re-identification[C].European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012:413-422. [7] ZHENG W, GONG S, XIANG T.Re-identification by Relative Distance Comparison[J].IEEE, 2013, 35(3):653-668. [8] 王睿, 朱正丹.融合全局-颜色信息的尺度不变特征变换[J].光学精密工程, 2015, 23(1): 295-301. doi: 10.3788/OPE.WANG R, ZHU ZH D.SIFT matching with color invariant characteristics and global context[J].Opt.Precision Eng., 2015, 23(1):295-301.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE. [9] 王飞宇, 邸男, 贾平.结合尺度空间FAST角点检测器和SURF描绘器的图像特征[J].液晶与显示, 2014, 29(4):598-604. doi: 10.3788/YJYXSWANG F Y, DI N, JIA P.Image features using scale-space FAST corner detector and SURF descriptor[J].Chinese J.Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2014, 29(4):598-604.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS [10] 王晓华, 孙小姣.联合Gabor降维特征与奇异值特征的人脸识别[J].光学精密工程, 2015, 23(10):553-558. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-GXJM201507001084.htmWANG X H, SUN X J.Face recognition based on Gabor reduction dimensionality features and singular value decomposition features[J].Opt.Precision Eng., 2015, 23(10):553-558.(in Chinese) http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-GXJM201507001084.htm [11] 邓丹, 吴谨, 朱磊, 等.基于纹理抑制和连续分布估计的显著性目标检测方法[J].液晶与显示, 2015, 30(1):120-125. doi: 10.3788/YJYXSDENG D, WU J, ZHU L, et al.Significant target detection method based on texture inhibition and continuous distribution estimation[J].Chinese J.Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2015, 30(1):120-125.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS [12] BIRCHFIELD S T, RANGARAJAN S.Spatiograms versus histograms for region-based tracking[J].IEEE, 2005(2):1158-1163. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.73.3012 [13] SINGH S, GUPTA A, EFROS A A.Unsupervised discovery of mid-level discriminative patches[C].European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012:73-86. [14] JAIN A, GUPTA A, RODRIGUEZ M, et al..Representing videos using mid-level discriminative patches[C].IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2013:571-2578. [15] 陈莹, 朱明, 刘剑, 等.高斯混合模型自适应微光图像增强[J].液晶与显示, 2015, 30(2):300-309. doi: 10.3788/YJYXSCHEN Y, ZHU M, LIU J, et al..Automatic low light level image enhancement using Gaussian mixture modeling[J].Chinese J.Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2015, 30(2):300-309.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS [16] GRAY D, TAO H.Viewpoint invariant pedestrian recognition with an ensemble of localized features[C].European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Marseille, Italy, 2008:262-275. [17] HU Y, LIAO S, LEI Z, et al..Exploring structural information and fusing multiple features for person re-identification[C].IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013:794-799. [18] SCHWARTZ W, DAVIS L.Learning discriminative appearance based models using partial least squares[C].Computer Graphics and Image Processing, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2009:322-329. -






 下载:
下载: