Spectral calibration based on echelle
-
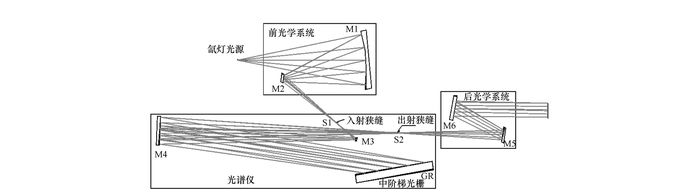
摘要: 波长定标是仪器遥感数据定量化的前提和基础。针对星载大气微量成分探测仪视场大、波长宽、空间分辨率和波长分辨率高的特点,建立了基于中阶梯衍射光栅的波长定标装置。中阶梯光栅因其较少的线密度和较大的闪耀角工作在较高的闪耀级次,光谱范围宽且具有较高的分辨率,可在工作波段内一次性输出多条分布较为均匀的谱线,克服了传统定标方式的缺点,提高了定标精度。本文首先介绍了波长定标装置的工作原理,接着利用该装置对高光谱大气微量成份探测仪进行波长定标,通过寻峰和回归分析给出载荷的波长定标方程,并利用标准汞灯谱线对定标结果进行检验。结果表明:高光谱大气微量成份探测仪的像元和波长近似满足线性分布规律,定标不确定度为0.025 8 nm,汞灯特征谱线的定标值和标准值偏差最大不超过0.043 5 nm,证明了定标结果的准确性。
-
关键词:
- 波长定标 /
- 中阶梯光栅 /
- 星载大气微量成分探测仪 /
- 光栅衍射方程
Abstract: Spectral calibration is the premise of remote sensing data inversion. Considering the advantages of a large field, wide wavelength range, high spatial and spectral resolution, the spectral calibration equipment based on echelle is built. Working at a higher blazed order with a large blaze angle, the echelle is characterized by a wide spectrum range and high spectral resolution. It can output multiple spectral lines with uniform distribution in the detection band, which overcomes the shortcomings of the traditional calibration methods and improves the calibration accuracy. In our study, the working principle of the spectral calibration equipment is given first. Then using this equipment, the spectral calibration equation of the hyperspectral imaging spectrometer is given accurately by peak-searching and regression analysis. Finally, the calibration results are verified by using the unique characteristics of mercury spectral lines. The experiment results show that there is a approximate linear distribution between pixel and wavelength. The uncertainty of the wavelength calibration is 0.025 8 nm, and the maximum deviation of calibration values and standard deviation values of mercury spectral lines is less than 0.043 5 nm, which can prove the accuracy of the calibration results. -
表 1 L2479的主要辐射特性
Table 1. Radiation characteristic of L2479
型号 功率/W 弧长/mm 光强μW/cm2.nm@50 cm
λ 440 nmL2479 300 3.0 5.06 表 2 定标装置的中心波长及分辨率
Table 2. Central wavelength and spectral resolution of the equipment
衍射级次 中心波长/nm 光谱分辨率/nm 64 375.798 38 0.045 321 30 63 381.749 51 0.048 817 80 62 387.895 80 0.049 600 35 61 394.273 75 0.049 250 70 60 400.854 40 0.049 650 30 59 407.637 76 0.049 716 90 58 414.654 17 0.049 567 05 57 421.945 58 0.050 366 25 56 429.456 20 0.053 846 10 55 437.251 77 0.050 932 35 54 445.359 62 0.055 927 35 53 453.745 17 0.053 246 70 52 462.462 39 0.057 459 15 51 471.542 92 0.056 809 80 50 480.961 76 0.056 443 50 49 490.780 22 0.057 559 05 48 500.994 20 0.058 424 85 表 3 波长定标不确定度分析
Table 3. Uncertainty analysis of spectral calibration
σ1/nm σ2/nm σ3/nm σ/nm 0.01 0.017 2 0.016 5 0.025 84 表 4 定标波长与标准波长的对比
Table 4. Comparison of the calculated value and standard values
标准波长/nm 定标波长/nm 偏差绝对值/nm 435.833 5 435.794 8 0.038 7 407.783 7 407.774 9 0.008 7 404.656 5 404.613 0 0.043 5 -
[1] 周斌, 刘文清, 齐峰, 等.差分吸收光谱法测量大气污染中数据处理方法研究[J].物理学报, 2001, 9(50):1818-1823. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXB200109035.htmZHOU B, LIU W Q, QI F, et al.. Study of concentration method in differential optical absorption spectroscopy for measuring air pollutants[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2001, 9(50):1818-1823.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXB200109035.htm [2] 郑玉权.温室气体遥感探测仪器发展现状[J].中国光学, 2011, 4(6):546-561. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8743.shtmlZHENG Y Q. Development status of remote sensing Instruments for greenhouse gases[J]. Chinese Optics, 2011, 4(6):546-561.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8743.shtml [3] 赵敏杰, 司福祺, 江宇, 等.星载大气痕量气体差分吸收光谱仪的实验室定标[J].光学精密工程, 2013, 3(21):567-573. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201211000.htmZHAO M J, SI F Q, JIANG Y, et al.. In-lab calibration of space-borne differential optical absorption spectrometer[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2013, 3(21):567-573.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201211000.htm [4] 郑玉权.超光谱成像仪的精细光谱定标[J].光学精密工程, 2010, 18(11):2347-2354. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201011006.htmZHENG Y Q. Precise spectral calibration for hyperspectral imager[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2010, 18(11):2347-2354.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201011006.htm [5] 刘倩倩, 郑玉权.超高分辨率光谱定标技术发展概况[J].中国光学, 2012, 5(6):566-577. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8906.shtmlLIU Q Q, ZHENG Y Q. Development of spectral calibration technologies with ultra-high resolutions[J]. Chinese Optics, 2012, 5(6):566-577.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8906.shtml [6] 周海金, 刘文清, 司福祺, 等.星载大气痕量气体差分吸收光谱仪光谱定标技术研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 11(32):2881-2885. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201211000.htmZHOU H J, LIU W Q, SI F Q, et al.. Spectral calibration for space-borne differential optical absorption spectrometer[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 11(32):2881-2885.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201211000.htm [7] 李聪, 王咏梅.用PtNe灯对大气紫外成像光谱仪进行光谱定标[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2010, 30(12):3302-3305. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2010)12-3302-04LI C, WANG Y M. Spectral calibration of the atmosphere ultraviolet imaging spectrograph using a PtNe lamp[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2010, 30(12):3302-3305.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2010)12-3302-04 [8] 裴舒.成像光谱仪光谱定标[J].光机电信息, 2011, 28(11):48-51. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80139-1012296958.htmPEI SH. Spectral calibration of imaging spectrometor[J]. OME Information, 2011, 28(11):48-51.(in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80139-1012296958.htm [9] DOBBER M R, DIRKSEN R J, LEVELT P F, et al.. Ozone monitoring instrument calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(5):1209-1238. https://aura.gsfc.nasa.gov/science/publications/Dobber_Dirksen_Levelt_IEEE2006.pdf [10] DIRKSEN R, DOBBER M, VOORS R, et al.. Prelaunch characterization of the ozone monitoring instrument transfer function in the spectral domain[J]. Appl. Opt., 2006, 45(17):3972-3981. doi: 10.1364/AO.45.003972 [11] DIRKSEN R, DOBBER M, LEVELT P, et al.. The on-ground calibration of the ozone monitoring instrument from a scientific point of view[J]. SPIE, 2004, 5234:400-410. http://projects.knmi.nl/omi/documents/publications/proceedings/SPIE2003_Barcelona_OMI_calibration.pdf [12] ZHANG R, BAYANHESHIG, YIN L, LI X T, et al.. Wavelength calibration model for prism-type echelle spectrometer by reversely solving prism's refractive index in real time[J]. Appl. Opt., 2016, 55:4153-4158. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.004153 [13] KIM J H, HAN J H, JEONG J CH. Accurate wavelength calibration method for spectrometer using low coherence interferometry[J]. J. Lightwave Technol., 2015, 33:3413-3418. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2015.2393881 [14] PEARLMAN A, POGORZALA D, CAO CH Y. GOES-R advanced baseline imager:spectral response functions and radiometric biases with the NPP Visible Infrared Imaging radiometer Suite evaluated for desert calibration sites[J]. Appl. Opt., 2013, 52:7660-7668. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.007660 [15] WANG K, DING ZH H. Spectral calibration in spectral domain optical coherence tomography[J]. Chin. Opt. Lett., 2008, 6:902-904. doi: 10.3788/COL -






 下载:
下载: