Distortion correcting method when testing large-departure asphere
-
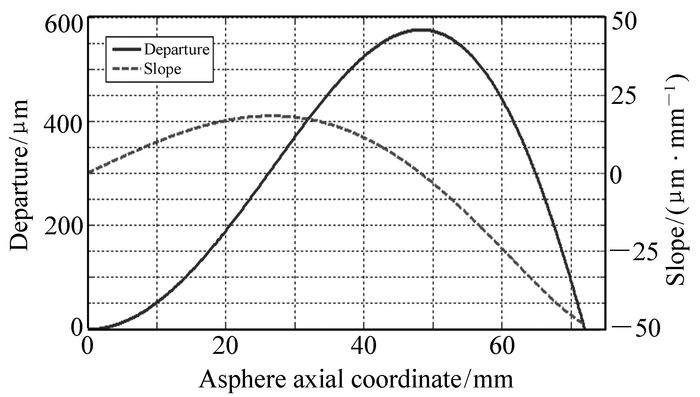
摘要: 在高数值孔径(NA)投影光刻物镜中,随着数值孔径的增加,非球面的偏离度越来越大。对这种大偏离度非球面进行亚纳米量级的检测,一直是光学检测的一大难题。本文首先对一偏离度超过500 μm的偶次高次非球面进行了计算全息图(Computer-Generated Hologram,CGH)设计,设计出了满足高精度面形检测和刻蚀加工要求的CGH。然后,针对此设计方案,定量分析了CGH的成像畸变及畸变对像差分析的影响。分析结果表明,不同径向位置的成像倍率偏差(畸变)最大达到了2.7:1,并且由于畸变的存在,低阶像差衍生出了明显的高阶像差。最后,针对用CGH检测大偏离度非球面时出现的成像畸变,提出了采用光线追迹与最小二乘法相结合的成像畸变的校正方法,并通过实验验证了此方法的准确性。实验结果表明,畸变校正之后相对剩余残差小于0.2%,可以满足高精度非球面检测加工的要求。Abstract: With the increase in numerical aperture, the aspheric departure is also increasing in the high-NA projection objective. It is a problem to test the large-departure asphere in nanometers in the optical metrology. For an asphere with aspheric departure exceeding 500 micrometers, firstly, we design a CGH to satisfy the demands of high precise testing and etching fabrication. Secondly, the imaging distortion and the effect of distortion on aberration are analyzed quantitatively. The analysis results show that the maximum magnification deviation is 2.7:1 for the different radial positions, and the low order aberrations will generate high order aberrations obviously. Lastly, we propose the ray trace and least square method to correct the imaging distortion when testing large-departure asphere with CGH, and verify the precision of the method through the experiments. The results show that the relative residue is less than 0.2% after correcting, and the precision will satisfy the demands of high precise optical testing and fabrication.
-
Key words:
- computer-generated hologram /
- CGH /
- distortion /
- asphere testing
-
图 5 非球面倾斜0.001度时,分别以非球面和参考面为光阑,仿真获得的干涉图与Zernike系数;(a)以非球面为光阑时的干涉图;(b)以参考面为光阑时的干涉图;(c)以非球面为光阑时的Zernike系数;(d)以参考面为光阑时的Zernike系数
Figure 5. Interferograms and Zernike coefficients generated by simulation when the asphere and reference surface are set as stop respectively, and the tilt of asphere is set 0.001 degree; (a) Interferogram when the asphere is set as stop. (b) Interferogram when the reference surface is set as stop. (c) Zernike coefficients when the asphere is set as stop. (d) Zernike coefficients when the reference surface is set as stop
表 1 非球面参数
Table 1. Parameters of asphere
D R K A4 A6 A8 144 297.510 0 -1.363×10-7 6.488×10-12 -7.002×10-16 A10 A12 A14 A16 A18 4.057×10-19 -1.505×10-22 3.533×10-26 -4.479×10-30 2.358×10-34 -
[1] IKEZAWA H, OHMURA Y, MATSUYAMA T, et al.. A hyper-NA projection lens for ArF immersion exposure tool[J]. SPIE, 2006, 6154:615421. http://proceedings.spiedigitallibrary.org/proceeding.aspx?articleid=1279410 [2] KNEER B, GRÄUPNER P, GARREIS R, et al.. Catadioptric lens design:the breakthrough to hyper-NA optics[J]. SPIE, 2006, 6154:615420. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2006SPIE.6154..692K [3] ROSTALSKI H J, DODOC A, ULRICH W, et al.. Projection optical system:US, 0258152 A1[P]. 2007-11-08. [4] DODOC A. High-NA projection objective:US, 7848016 B2[P]. 2010-12-07. [5] 师途, 杨甬英, 张磊, 等.非球面光学元件的面形检测技术[J].中国光学, 2014, 7(1):26-46. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9094.shtmlSHI T, YANG Y Y, ZHANG L, et al.. Surface testing methods of aspheric optical elements[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(1):26-46.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9094.shtml [6] OFFNER A. A null corrector for paraboloidal mirrors[J]. Applied Optics, 1963, 2(2):153-155. doi: 10.1364/AO.2.000153 [7] KIM Y S, KIM B Y, LEE Y W. Design of null lenses for testing of elliptical surfaces[J]. Applied Optics, 2001, 40(19):3215-3219. doi: 10.1364/AO.40.003215 [8] WYANT J C, BENNETT V P. Using computer generated holograms to test aspheric wavefronts[J]. Applied Optics, 1972, 11(12):2833-2839. doi: 10.1364/AO.11.002833 [9] BURGE J. A null test for null correctors-error analysis[J]. Quality and Reliability for Optical Systems, 1993, 1993:86-97. doi: 10.1117/12.164976 ZHAO C Y, BURGE J. Orthonormal vector polynomials in a unit circle, application:fitting mapping distortions in a null test[J]. SPIE, 2009, 7426:74260V1-74260V8. http://www.loft.optics.arizona.edu/documents/journal_articles/Chunyu_Zhao_Orthonormal_Vector_Polynomials_in_a_Unit_Circle.pdf [12] NOVAK M, ZHAO C Y, BURGE J. Distortion mapping correction in aspheric null testing[J]. SPIE, 2008, 7063:7063131-7063138. http://www.loft.optics.arizona.edu/ [13] 王会峰.一种成像测量图像径向几何畸变的校正方法[J].应用光学, 2010, 31(1):55-59. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYGX201001014.htmWANG H F. Radial geometrical distortion correction in imaging measurement system[J]. J. Applied Optics, 2010, 31(1):55-59.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYGX201001014.htm [14] 高松涛, 王高文, 张健, 等.用计算全息图校正非球面的畸变[J].光学精密工程, 2013, 21(8):1929-1935. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201308003.htmGAO S T, WANG G W, ZHANG J, et al.. The distortion correction of asphere testing with computer-generated hologram[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2013, 21(8):1929-1935.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201308003.htm [15] 高松涛, 隋永新, 杨怀江.用计算全息图对非球面的高精度检测与误差评估[J].光学学报, 2013, 33(6):0612003. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201306018.htmGAO S T, SUI Y X, YANG H J. High precise testing of asphere with computer-generated hologram and error evaluation[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2013, 33(6):0612003.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201306018.htm [16] XIE Y, CHEN Q, WU F. Design of twin computer-generated holograms used for testing concave conic mirrors[J]. SPIE, 1995, 6723:67235S. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2007SPIE.6723E.208X [17] QI Y J, WANG P, JIANG Y. Design of CGH wavefront generator for aspheric testing with wavefront tracing method[J]. SPIE, 2007, 6723:672362. [18] 许英朝, 张新, 周平.一种三次非旋转对称的相位板的检测系统设计[J].光学学报, 2008, 28(5):971-975. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB200805033.htmXU Y CH, ZHANG X, ZHOU P. Optical design for unsymmetrical aspherical cubic phase plate testing system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2008, 28(5):971-975.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB200805033.htm [19] 谢意, 陈强, 伍凡, 等.用双计算全息图检测凹非球面[J].光学学报, 28(7):1313-1317. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB200807017.htmXIE Y, CHEN Q, WU F, et al.. Concave asphereical surface testing with computer-generated holograms[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2008, 28(7):1313-1317.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB200807017.htm [20] 高松涛, 武东城, 彭石军, 等.用计算全息图检测非球面时的自补偿效应分析[J].光学学报, 2015, 35(11):1112002. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201511015.htmGAO S T, WU D CH, PENG SH J, et al.. Self-compensating effect analysis in testing asphere with computer-generated hologram[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2015, 35(11):1112002.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201511015.htm [21] 黄亚, 马俊, 朱日宏, 等.基于计算全息的光学自由曲面测量不确定度分析[J].光学学报, 2015, 35(11):1112007. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201511020.htmHUANG Y, MA J, ZHU R H, et al.. Investigation of measurement uncertainty of optical freeform surface based on Compurter-Generated Hologram[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2015, 35(11):1112007.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201511020.htm -






 下载:
下载: