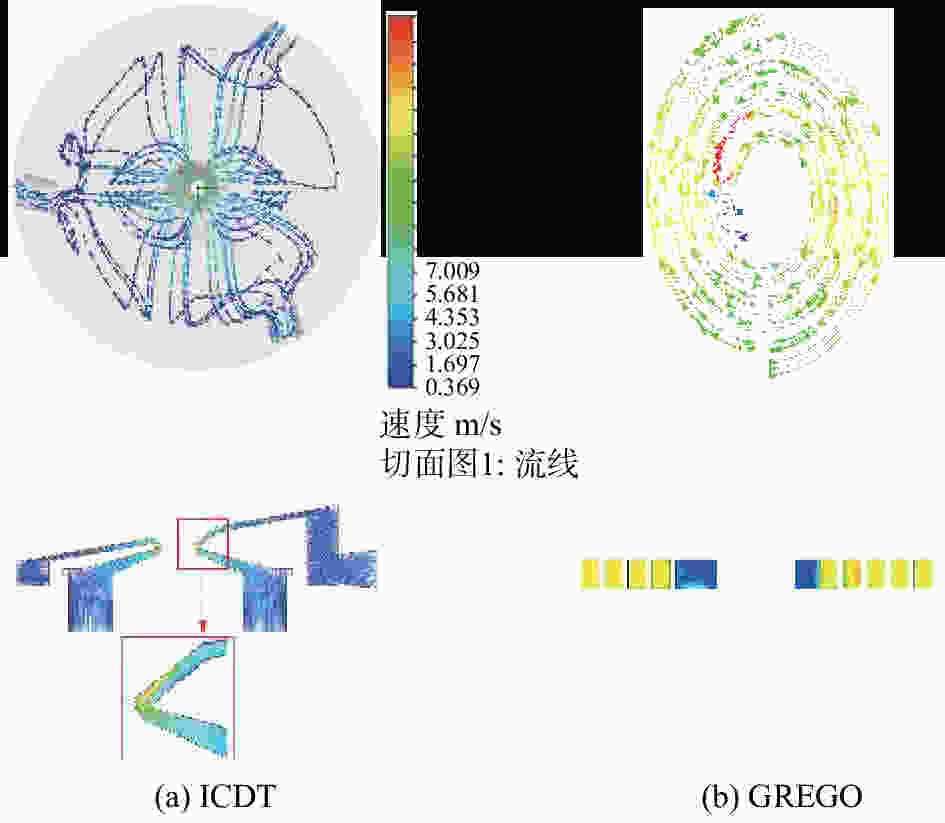
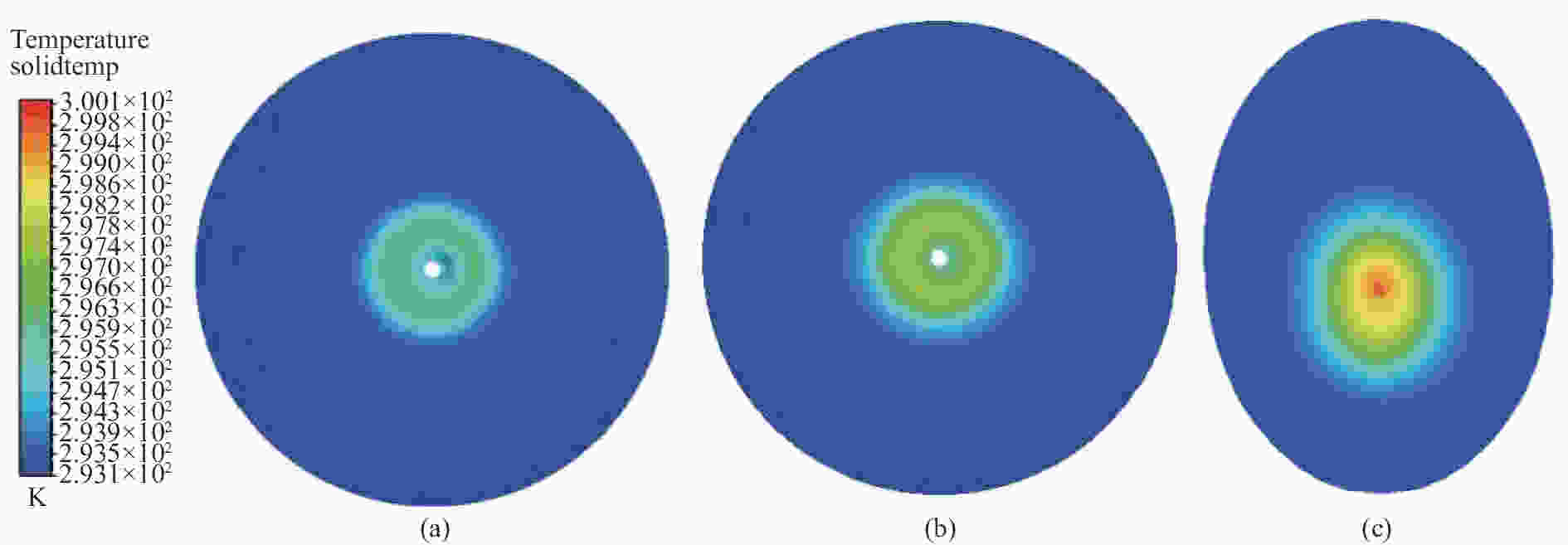
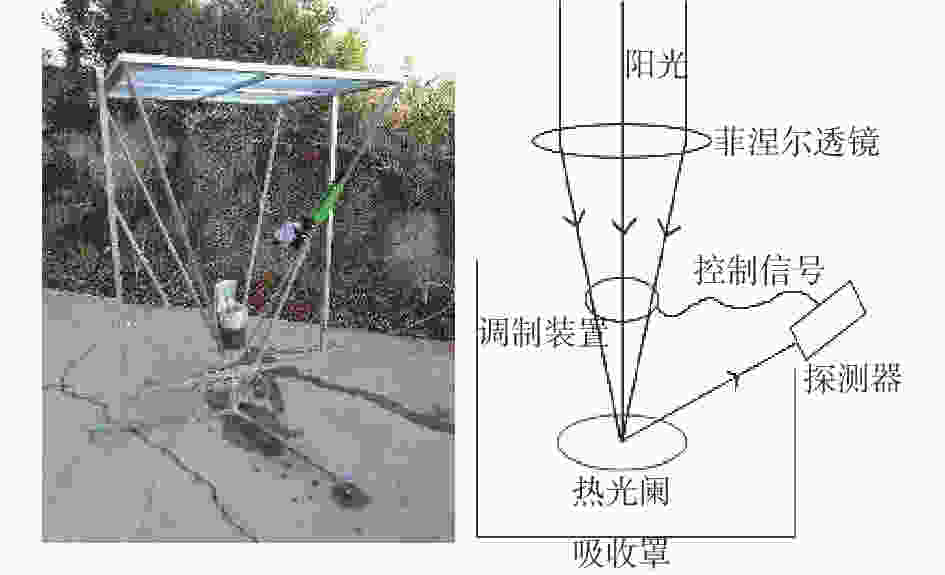
-
摘要: 对于大口径地基开放式太阳望远镜,热光阑温升将导致其像质劣化。尤其是,热光阑通光孔紧挨成像光束,其与环境的温度差对像质影响很大。这是中国巨型太阳望远镜(Chinese Giant Solar Telescope, CGST)计划面临的诸多问题之一。解决热光阑温控问题的具体方法是设计整体冷却效率高且在关键位置得到进一步强化的热光阑结构,以达到温控均匀的目的。本文提出倒锥导流式热光阑设计方案,该方案有利于降低通光孔位置温度,使温度极高点离开通光孔。对流换热系数和光阑温度场仿真结果证明此方案明显优于目前常用的方法。倒锥导流式热光阑的极限温升为3 ℃,优于GREGO的极限温升(7 ℃);实测温度场与仿真温度场进行对照,结果在误差范围内。结果证明导流式倒锥结构具有较好的温控效果。Abstract: For large-aperture ground-based open-structure solar telescopes, an increase in heat-stop temperature will result in deterioration of image quality. In particular, heat-stop, located closely to the light-passing hole, has a great influence on image quality. This is one of the problems for the Chinese Giant Solar Telescope (CGST) development plan. For solving the heat-stop temperature control problem, the overall cooling efficiency should be high and further strengthen is implemented at key locations to achieve uniform temperature control. According to the above problem, an Inverted-Cone Diversion Type (ICDT) heat-stop design is proposed, which can reduce the temperature of the light-passing hole and make the hottest area away from the light-passing hole. The simulation results of cooling efficiency and heat-stop temperature field show that this scheme is obviously superior to its predecessor. The temperature of ICDT′s heat-stop is up to 3 ℃ above ambient, which is better than GREGO′s temperature difference of 7 ℃. The research team also carried out the heat-stop temperature field measurement experiment and verified the accuracy of the temperature field simulation′s results showing that ICDT heat-stop design has good temperature control capability.
-
Key words:
- heat-stop /
- infrared temperature measurement /
- CGST pre-research /
- diversion type /
- jet impact
-
表 1 模型求解参数设置
Table 1. Solution parameter setting for the model
设置类型 参数 入口边界 20 ℃冷却水,流量15 L/min 外表面边界 20 ℃空气、15 W·m−2k−1对流 热流 105 W、直径2 cm光斑 表 2 拟合结果
Table 2. Fitting results
拟合参数 结果 ΔT0/℃ 17.6(17.14,18.02) τ/s 0.38(0.35,0.41) Ta/℃ 24.6(24.2,24.99) 表 3 实测温升和数值模拟温升结果
Table 3. Measured and numerical simulation temperature rises
流量L/min 点1实测T/(℃) 点1模拟T/(℃) 点2实测T/(℃) 点2模拟T/(℃) 点3实测T/(℃) 点3模拟T/(℃) 0.15 40.9 41.6 33.2 33.4 16.0 16.7 0.42 32.8 33.7 27.3 27.0 13.5 13.2 0.64 27.0 27.7 22.0 22.0 10.3 10.5 0.86 21.9 22.5 18.0 18.2 8.9 8.9 1.125 17.6 17.8 14.3 14.6 7.3 7.2 -
[1] 刘忠, 邓元勇, 季海生, 等. 中国地基大太阳望远镜[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学,2012,42(12):1282-1291.LIU ZH, DENG Y Y, JI H SH, et al. Ground-based giant solar telescope of China[J]. Scientia Sinica Physica,Mechanica &Astronomica, 2012, 42(12): 1282-1291. (in Chinese) [2] LIU Y Y, GU N T, RAO CH H. Quantitative evaluation on internal seeing induced by heat-stop of solar telescope[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(15): 19980-19995. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.019980 [3] DENKER C, GOODE P R, REN D, et al. Progress on the 1.6-meter new solar telescope at big bear solar observatory[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6267: 62670A. [4] DIDKOVSKY L V, KUHN J R, GOODE P R. Optical design for a new off-axis 1.7-m solar telescope (NST) at big bear[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5171: 333-343. doi: 10.1117/12.518671 [5] RIMMELE T R, KEIL S L, KELLER C U, et al. Technical challenges of the advanced technology solar telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 4837: 94-109. doi: 10.1117/12.456707 [6] WAGNER J, RIMMELE T R, KEIL S, et al. Advanced technology solar telescope: a progress report[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7012: 70120I. [7] BERRILLI F, EGIDI A, DEL MORO D, et al. The heat stop for the 4-m European Solar Telescope EST[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7733: 77332Z. [8] LIU Y Y, GU N T, RAO CH H, et al. Heat-stop structure design with high cooling efficiency for large ground-based solar telescope[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(21): 6441-6447. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.006441 [9] 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所. 基于双通道冷却的大口径太阳望远镜全吸收式热光阑: 中国, CN109164567A[P]. 2019-01-08.Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, CAS. Large-caliber solar telescope full absorption thermal diaphragm based on dual-channel cooling: CN, CN109164567A[P]. 2019-01-08. (in Chinese) [10] VOLKMER R, EISENTRÄGER P, EMDE P, et al. Mechanical design of the solar telescope GREGOR[J]. Astronomische Nachrichten, 2012, 333(9): 816-822. doi: 10.1002/asna.201211740 [11] VOLKMER R, VON DER LUHE O, SOLTAU D, et al. Optical and thermal design of the main optic of the solar telescope GREGOR[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 5179: 270-281. doi: 10.1117/12.506710 [12] COLLADOS M, BETTONVIL F, CAVALLER L, et al. European Solar Telescope: project status[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7733: 77330H. doi: 10.1117/12.856994 [13] 杨世铭, 陶文铨. 传热学[M]. 4版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006.YANG SH M, TAO W Q. Heat Transfer[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. (in Chinese) [14] GNIELINSKI V. New equations for heat and mass transfer in the turbulent flow in pipes and channels[R]. Berlin: NASA, 1975: 8-16. [15] 董韶峰, 李荫堂. 常热流密度矩形管内层流对流换热系数的数值计算[J]. 能源技术,2010,31(2):70-72.DONG SH F, LI Y T. Numerical simulation about convection of laminar flow through rectangular pipe under constant heat flux[J]. Energy Technology, 2010, 31(2): 70-72. (in Chinese) -





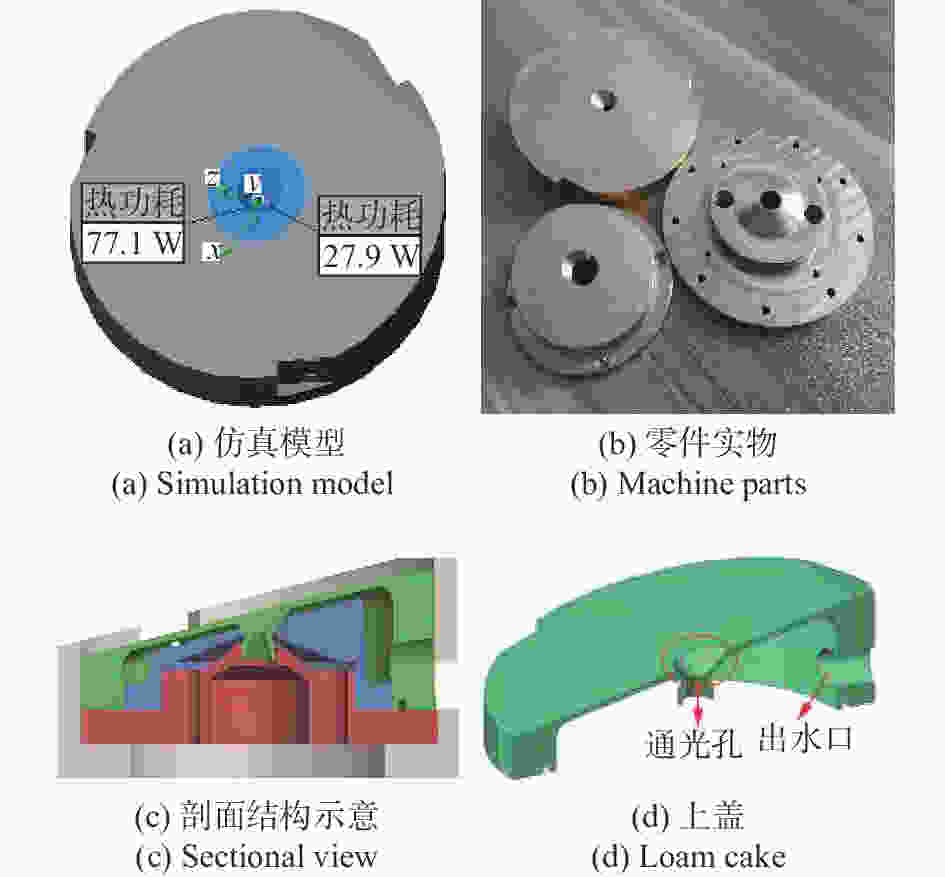
 下载:
下载: