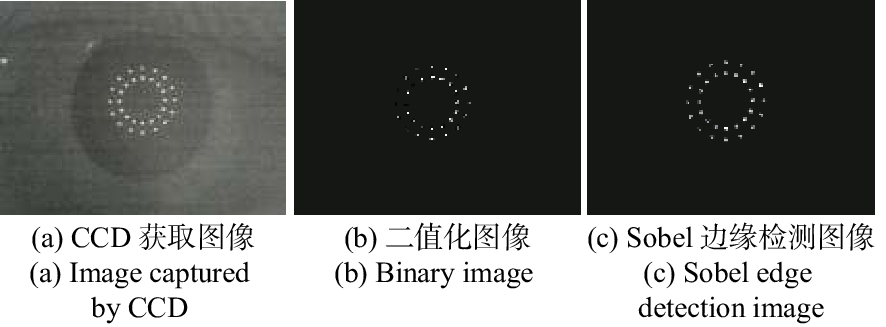
-
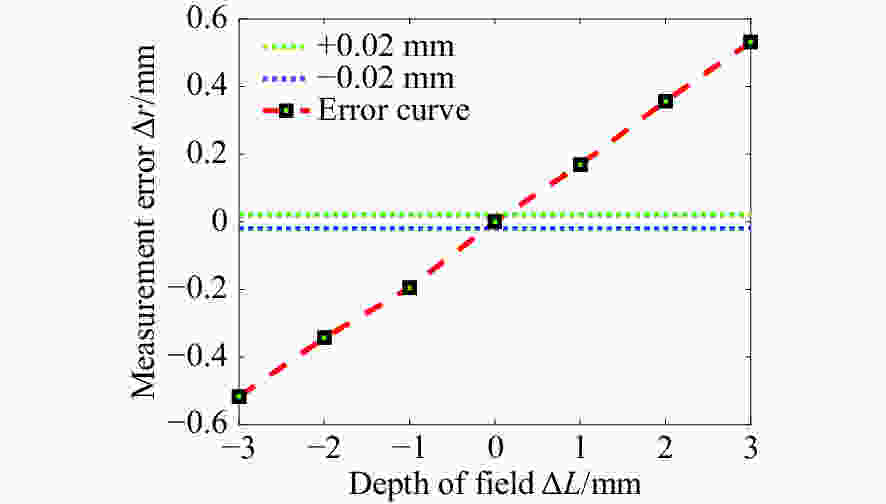
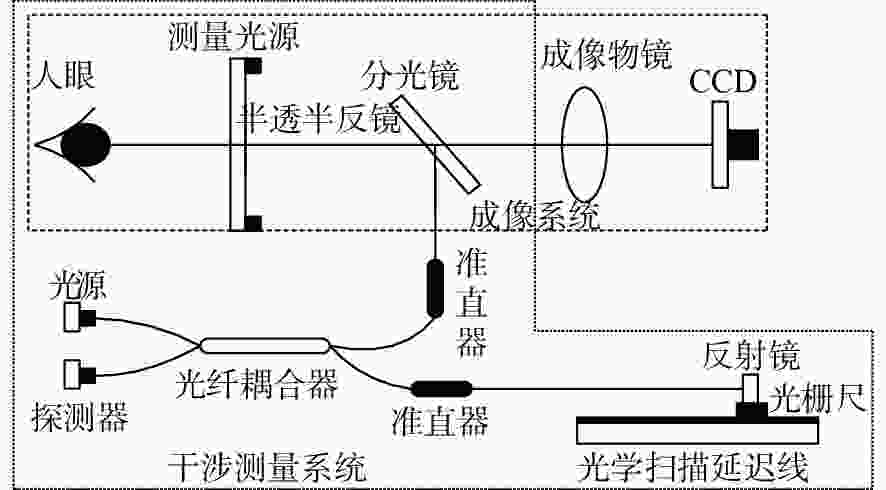
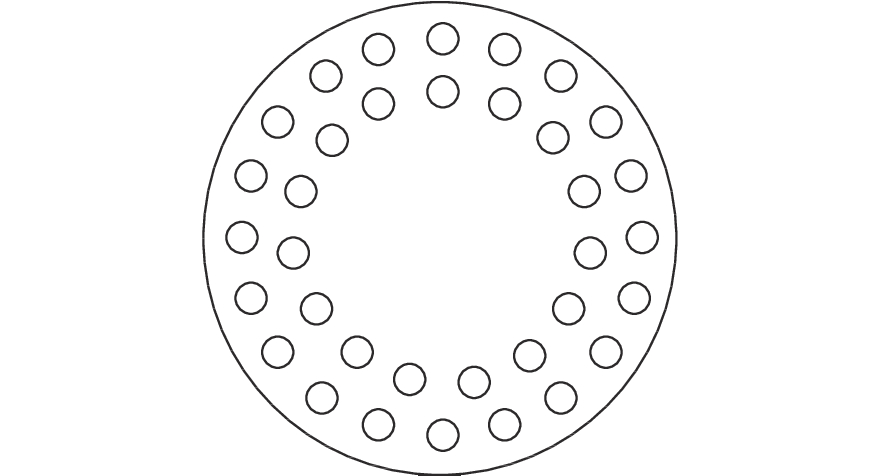
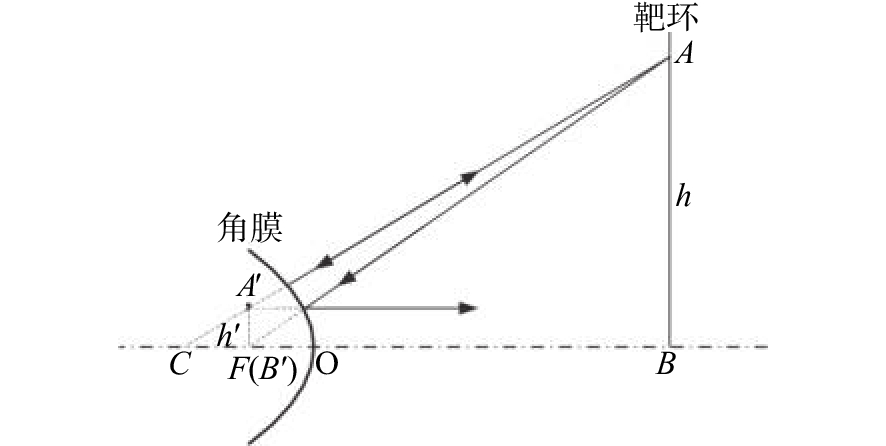
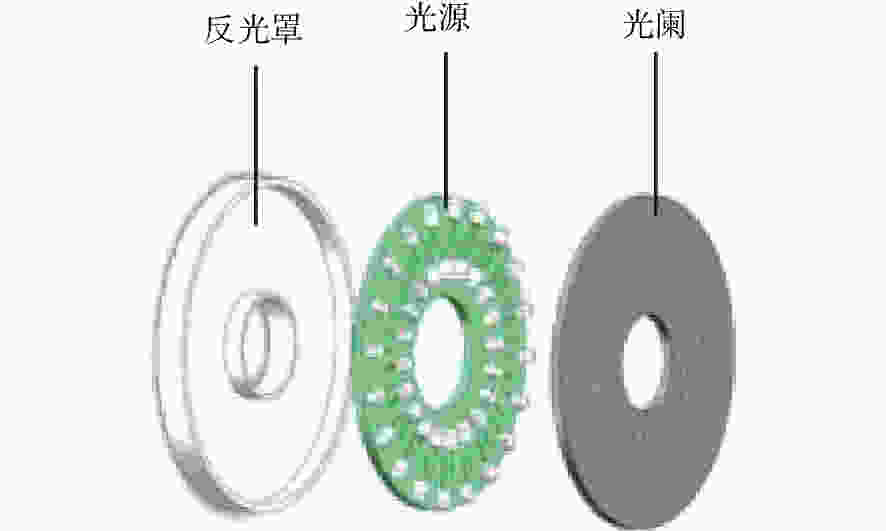
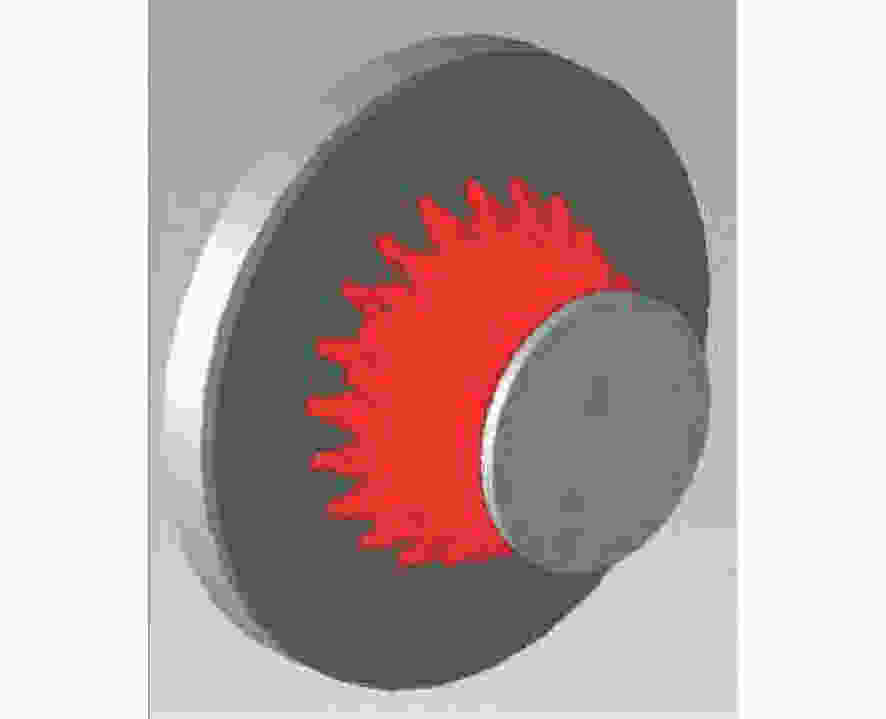
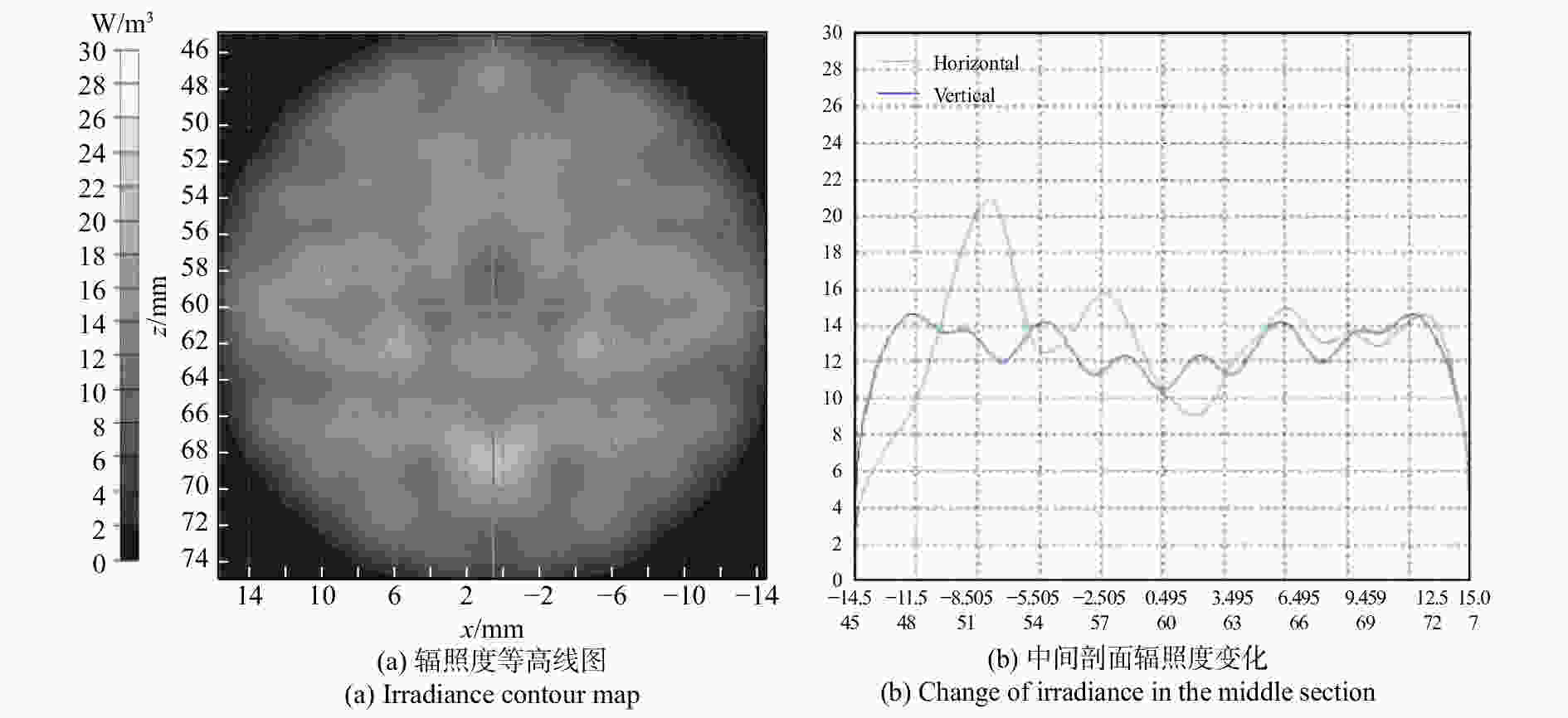
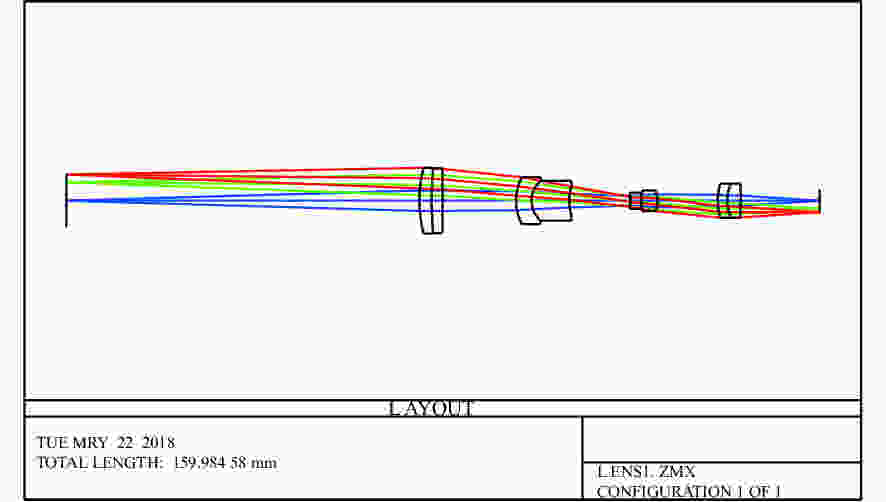
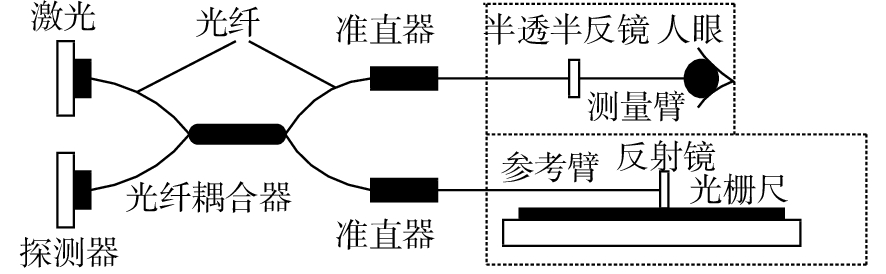
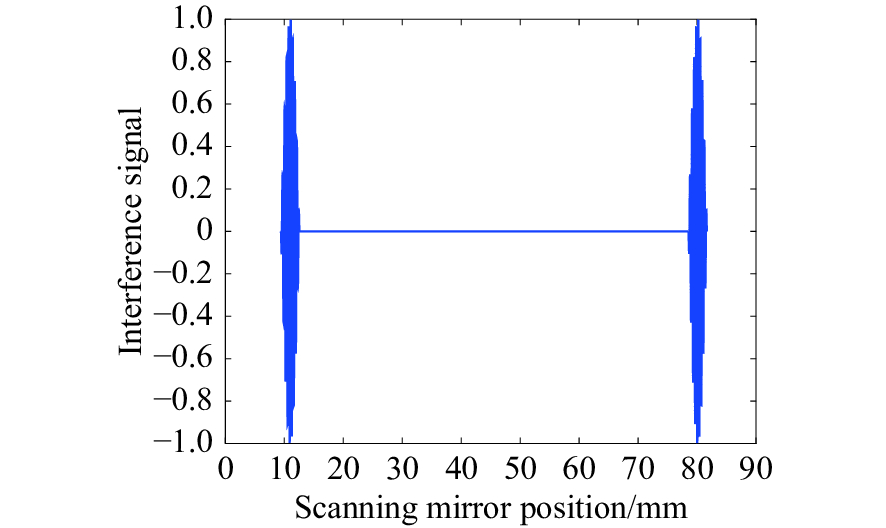
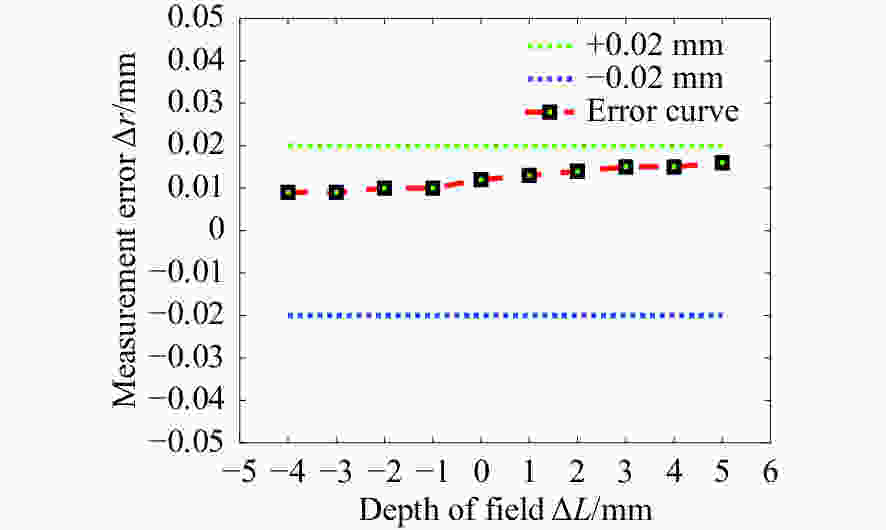
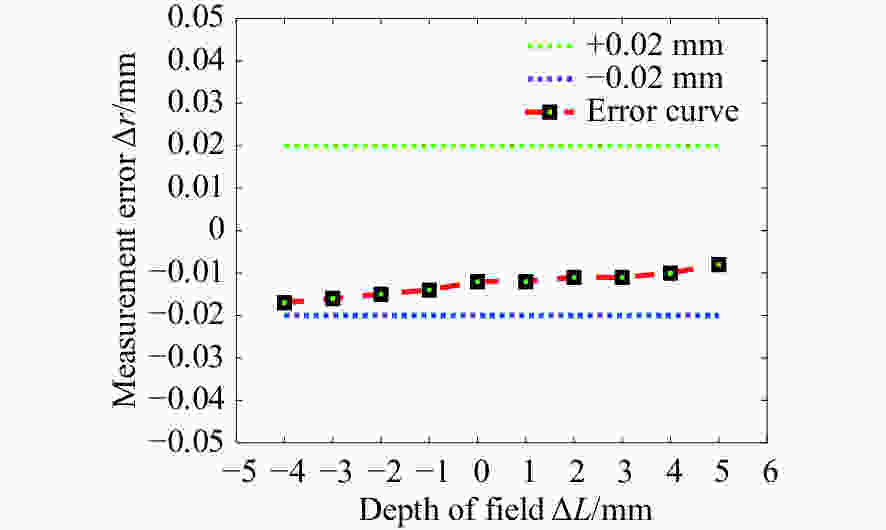
摘要: 为了实现成像角膜曲率计沿光轴方向的精确对准,提高角膜曲率的测量精度,设计了一种高精度成像角膜曲率测量系统。对该系统的成像光源、成像光学系统、干涉测量系统等进行研究。通过LED阵列均匀照射靶环形成光源;成像物镜采用双远心镜头,使景深变大,有利于对准测量,同时保证成像物镜的放大率不会受景深的影响;引用低相干干涉测量技术,利用低相干干涉信号定位角膜顶点和测量光源的位置,利用光栅尺监测扫描反射镜的位置,实现了角膜顶点到测量光源距离的精确测量。最后,分析了该系统成像物镜放大率的稳定性和角膜曲率测量误差,在理论基础上,做出了实验样机,用所设计的样机对标准角膜模拟眼进行测试,系统精度达到±0.02 mm,基本满足角膜曲率的测量要求。Abstract: To achieve accurate alignment of the imaging keratometer along the optical axis and improve the measurement accuracy of corneal curvature, we design a high precision imaging corneal curvature measurement system. The imaging light source, imaging optical system and interferometry system of the measurement system are studied. A light source is formed using uniform irradiation of the target ring with an LED array; The imaging objective lens adopts a double telephoto lens to enlarge the depth of its field, which is conducive to the measurement of alignment. Meanwhile, the magnification of the imaging objective lens are not affected by the depth of field. By using low coherent interferometry, the distance between the corneal vertex and the measured light source is accurately measured using a grating ruler to monitor the position of the scanning mirror. In this paper, the stability of the imaging objective magnification and the error of the corneal curvature measurement of the system are analyzed, and an experimental prototype is made based on the theory. The designed prototype is used to test the standard corneal simulators and the measurement accuracy of the system is up to ±0.02 mm, which basically meets the requirements of corneal curvature measurement.
-
表 1 景深对应的
$b$ 和$\beta $ 值Table 1. The
$b$ and$\beta $ values corresponding to different depthes of field景深/mm $b$/mm $\beta $/mm −3 67 −0.464 −2 68 −0.459 −1 69 −0.456 0 70 −0.450 1 71 −0.446 2 72 −0.441 3 73 −0.437 表 2 双远心镜头参数
Table 2. Double telecentric lens parameters
参数 数值 物距/mm 100 前景深/mm 4.68 后景深/mm 5.47 放大率 –0.45 表 3 不同物距的放大率
Table 3. Magnifications corresponding to different object distances
物距/mm 放大率 97 −0.450 19 98 −0.450 15 99 −0.450 12 100 −0.450 00 101 −0.449 92 102 −0.449 86 103 −0.449 82 104 −0.449 78 表 4 实验结果
Table 4. Experimental results
标准值 测量值/mm 误差/mm 标准值 测量值/mm 误差/mm 6.656 ${r_{\max }}$ 6.675 ﹢0.019 7.988 ${r_{\max}}$ 7.997 0.009 ${r_{\min }}$ 6.641 −0.015 ${r_{\min}}$ 7.975 −0.013 6.656 ${r_{\max}}$ 6.673 +0.017 9.458 ${r_{\max}}$ 9.466 +0.008 ${r_{\min }}$ 6.637 −0.019 ${r_{\min }}$ 9.443 −0.015 6.656 ${r_{\max}}$ 6.669 +0.013 9.458 ${r_{\max}}$ 9.473 +0.015 ${r_{\min }}$ 6.647 +0.011 ${r_{\min }}$ 9.455 −0.003 7.988 ${r_{\max}}$ 7.999 +0.011 9.458 ${r_{\max}}$ 9.477 +0.019 ${r_{\min }}$ 7.974 −0.014 ${r_{\min }}$ 9.459 +0.001 7.988 ${r_{\max}}$ 7.998 +0.010 ${r_{\min }}$ 7.980 −0.008 -
[1] HOWLAND H C, HOWLAND B. Photorefraction: a technique for study of refractive state at a distance[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1974, 64(2): 240-249. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.64.000240 [2] CHOI M, WEISS S, SCHAEFFEL F, et al. Laboratory, clinical, and kindergarten test of a new eccentric infrared photorefractor (Power Refractor)[J]. Optometry and Vision Science, 2000, 77(10): 537-548. doi: 10.1097/00006324-200010000-00008 [3] MOUROULIS P. Visual Instrumentation: Optical Design and Engineering Principles[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional, 1999. [4] 闫洁, 孟鹏花, 赵俊奇. 人眼角膜曲率测量系统的研究[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报,2011,19(S1):254-261.YAN J, MENG P H, ZHAO J Q. Research of curvature measuring system of eyes cornea[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2011, 19(S1): 254-261. (in Chinese) [5] 潘兵, 俞立平, 吴大方. 使用双远心镜头的高精度二维数字图像相关测量系统[J]. 光学学报,2013,33(4):0412004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201333.0412004PAN B, YU L P, WU D F. High-accuracy two-dimensional digital image correlation measurement system using a bilateral telecentric lens[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2013, 33(4): 0412004. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201333.0412004 [6] 李明东. 基于机器视觉的高分辨率双远心物镜的设计[D]. 桂林: 桂林电子科技大学, 2016: 226-232.LI M D. The design of high resolution double telecentric lens based on machine vision[D]. Guilin: Guilin University of Electronic Technology, 2016: 226-232. (in Chinese) [7] 马森, 谢芳, 刘义秦, 等. 光纤双干涉在线绝对测量技术研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2013,34(2):268-274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2013.02.005MA S, XIE F, LIU Y Q, et al. Research on optical fiber dual-interferometry for on-line and absolute measurement[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2013, 34(2): 268-274. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2013.02.005 [8] 刘富国, 查学军, 杨波, 等. 基于光纤低相干干涉技术的透镜中心厚度测量方法研究[J]. 应用激光,2016,36(5):605-610.LIU F G, ZHA X J, YANG B, et al. Study on the method of measuring the center thickness of the lenses based on low coherence interferometry of optical fiber[J]. Applied Laser, 2016, 36(5): 605-610. (in Chinese) [9] SEIDEMANN A, SCHAEFFEL F, GUIRAO A, et al. Peripheral refractive errors in myopic, emmetropic, and hyperopic young subjects[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2002, 19(12): 2363-2373. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.19.002363 [10] SCHAEFFEL F, FARKAS L, HOWLAND H C. Infrared photoretinoscope[J]. Applied Optics, 1987, 26(8): 1505-1509. doi: 10.1364/AO.26.001505 [11] 闫蓓, 王斌, 李媛. 基于最小二乘法的椭圆拟合改进算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报,2008,34(3):295-298.YAN B, WANG B, LI Y. Optimal ellipse fitting method based on least-square principle[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2008, 34(3): 295-298. (in Chinese) -





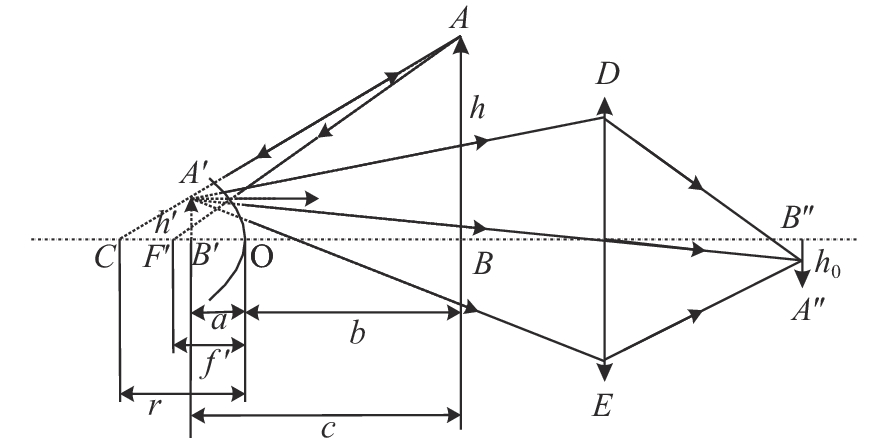
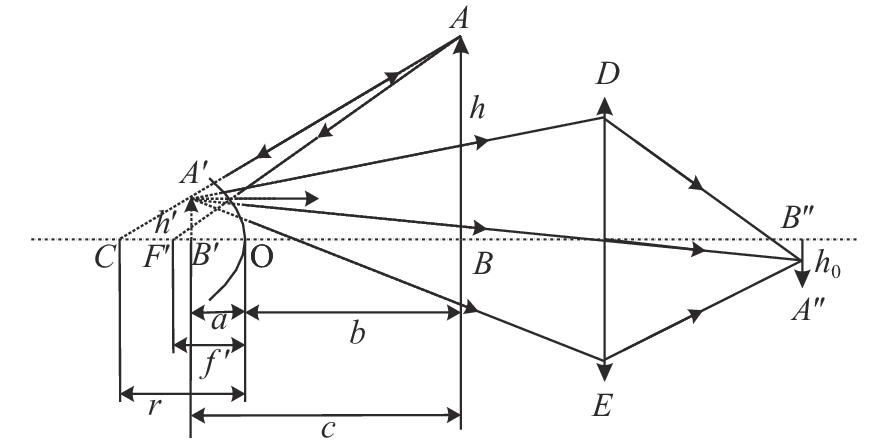
 下载:
下载: