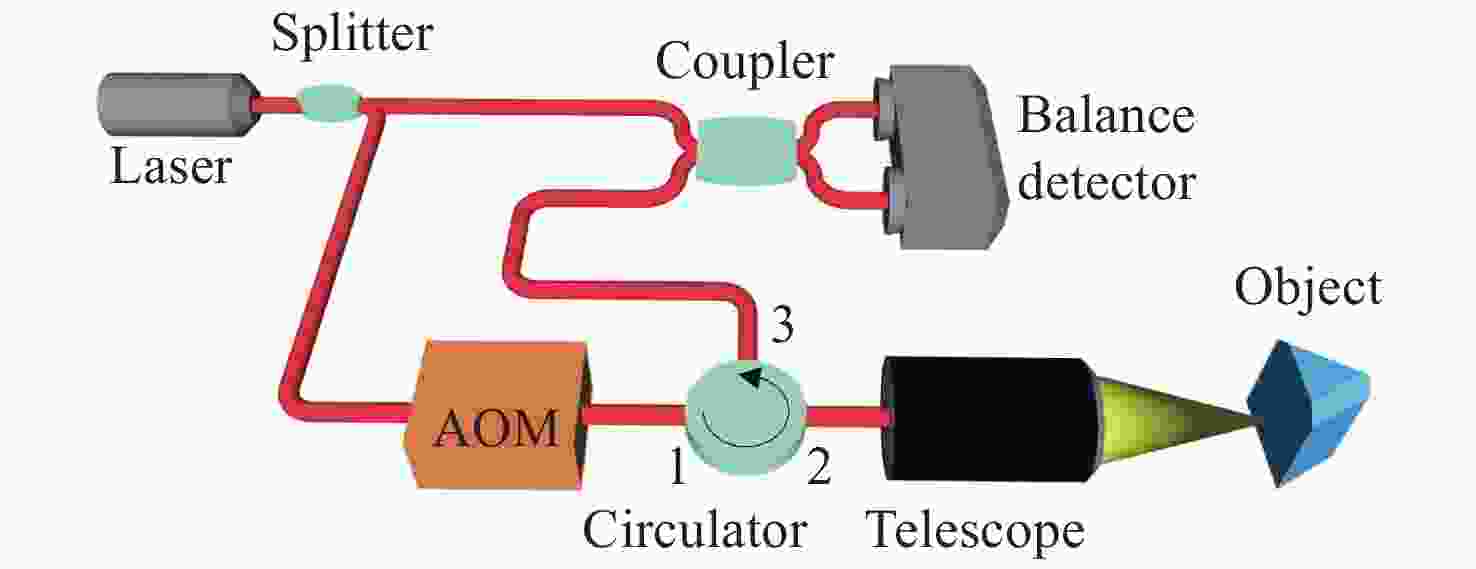
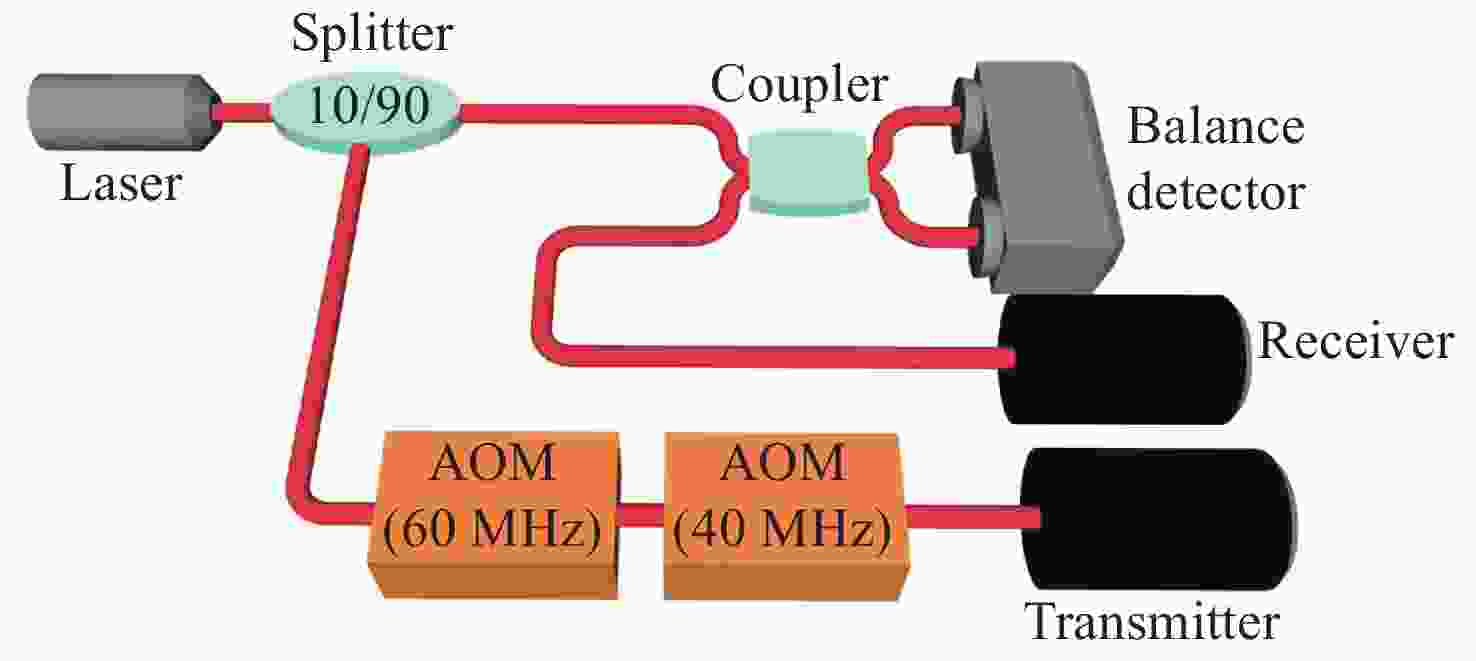
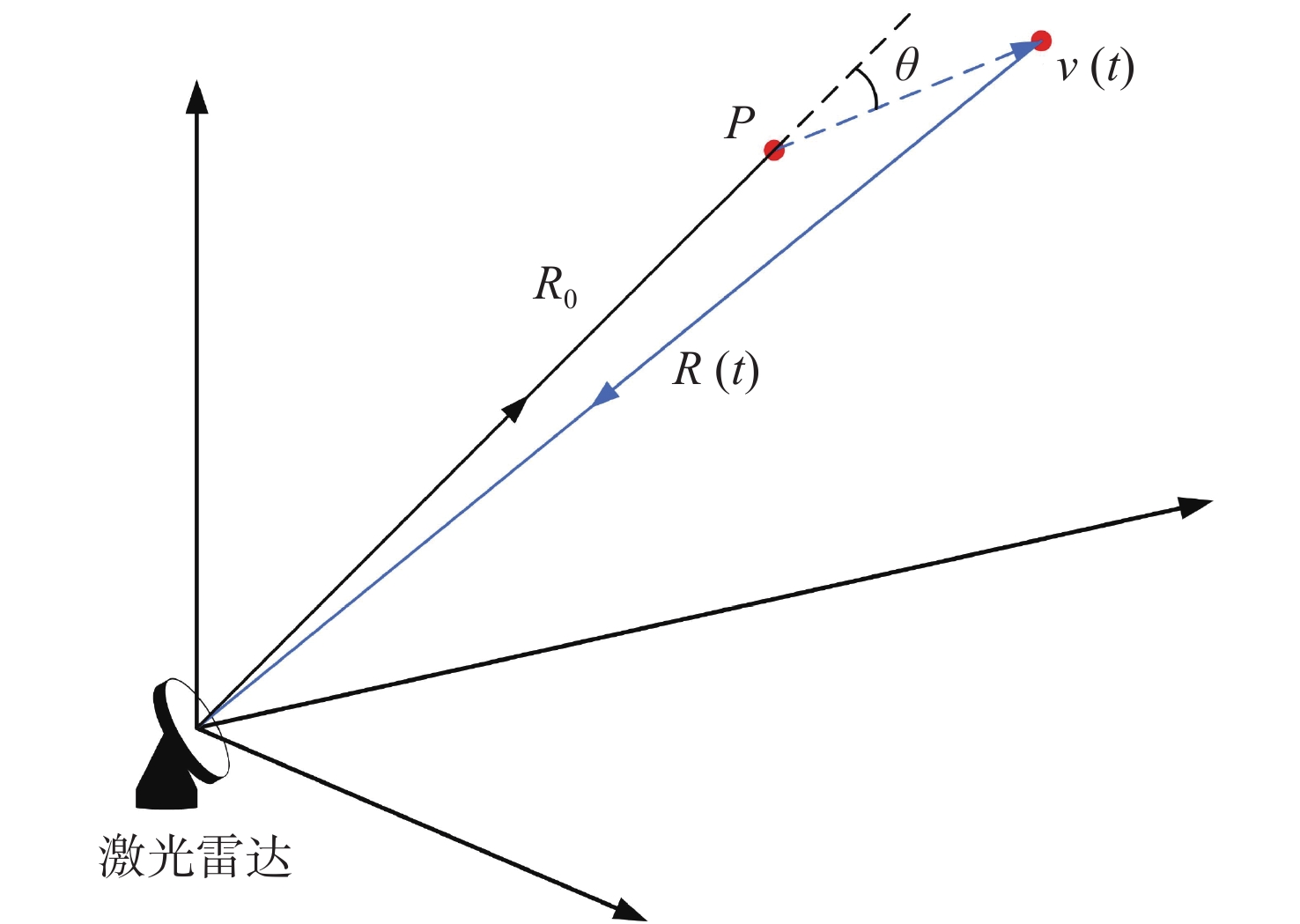
-
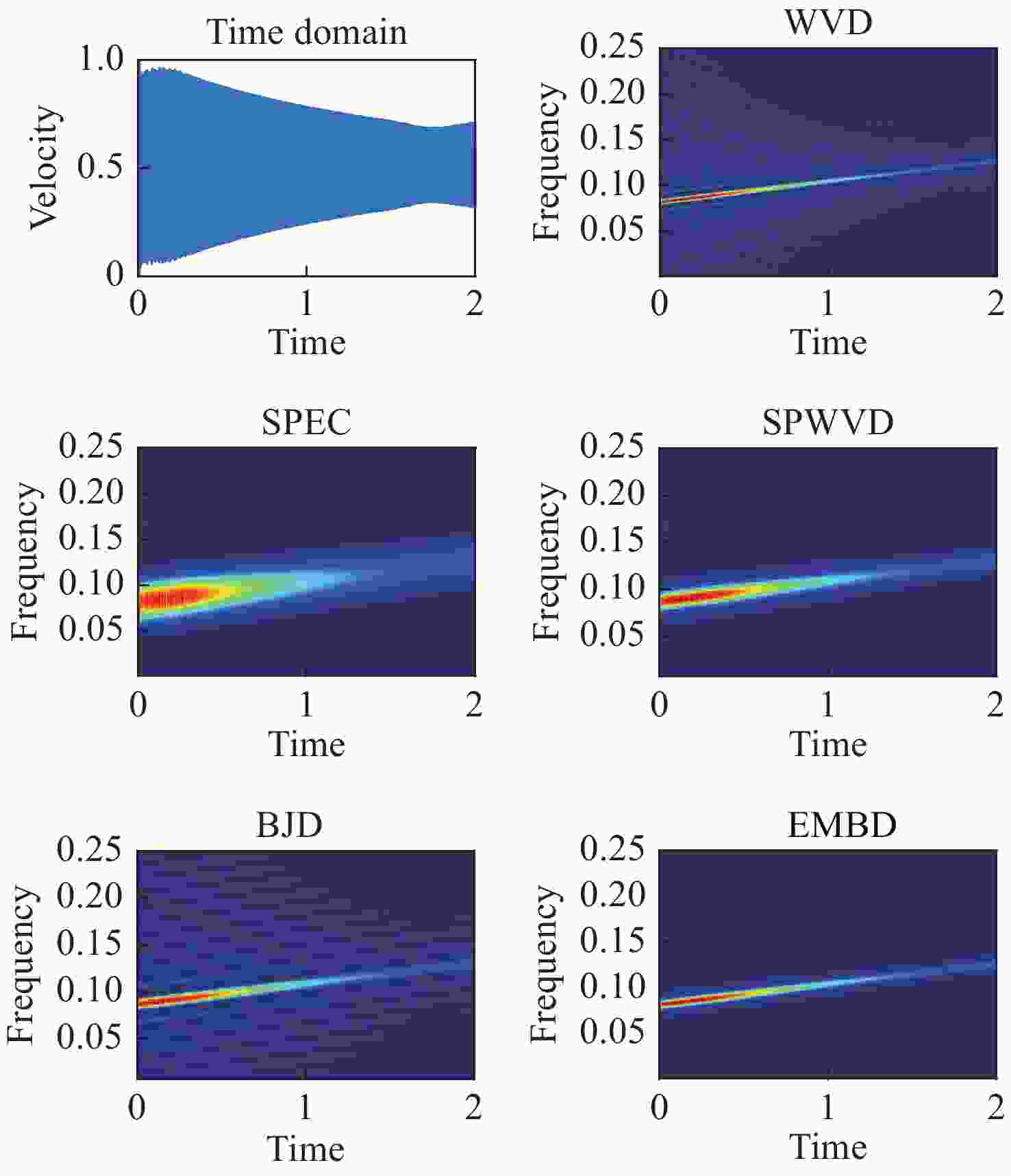
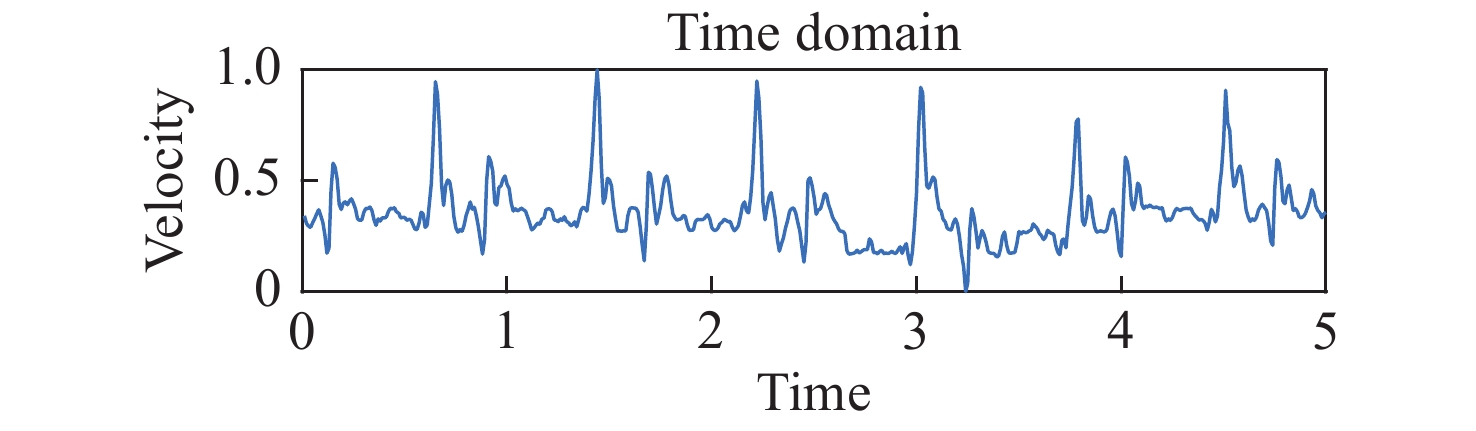
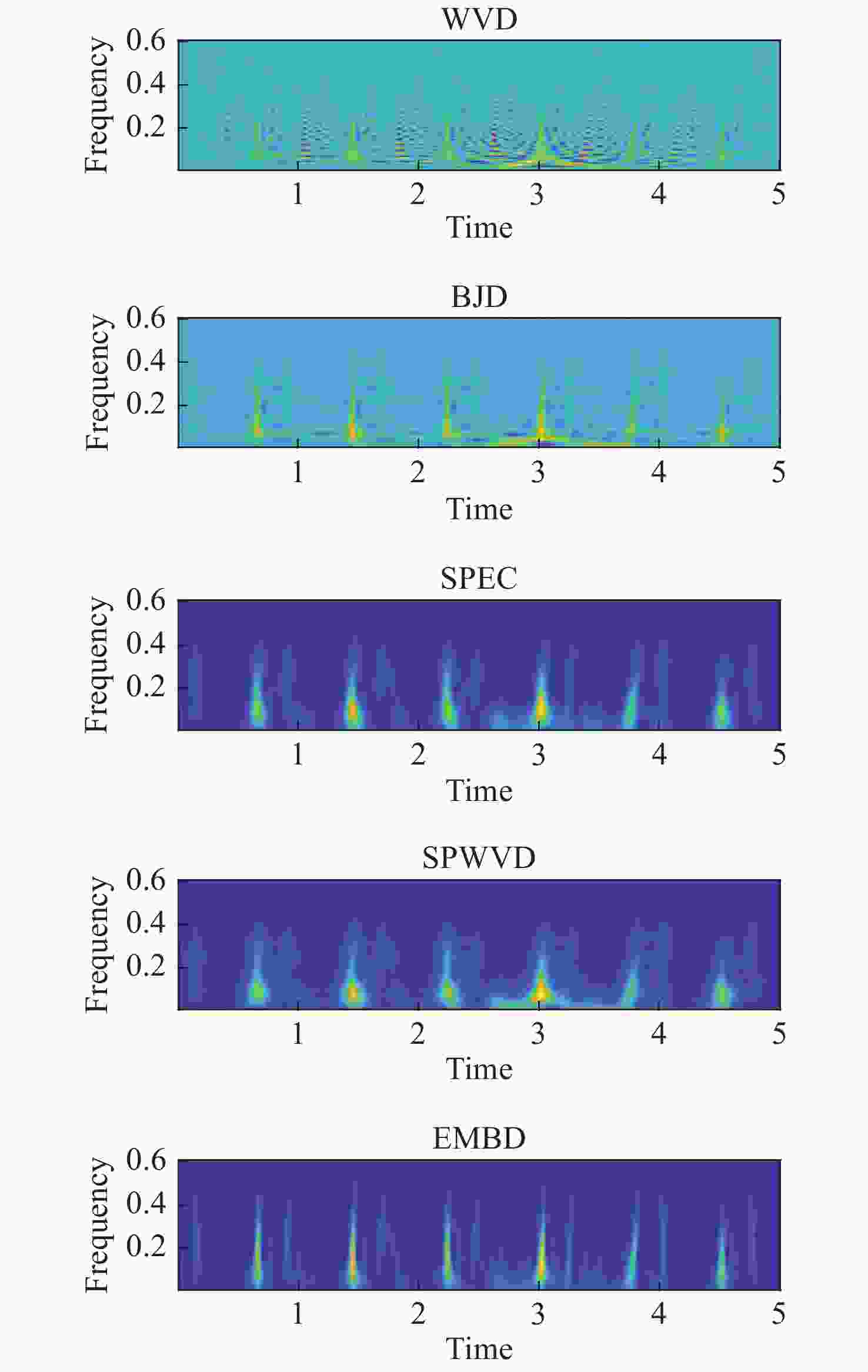
摘要: 激光多普勒雷达实际测得的振动信号绝大多数都是时变信号,而基于傅立叶变换的时频分析方法是处理时变信号的有利工具。本文针对激光多普勒雷达测得的实际振动信号,比较了魏格纳-维利分布、平滑伪魏格纳-维利分布、频谱图、波恩-约旦分布和扩展修正B分布5种形式的时频分析性能。利用激光多普勒雷达测量实际单音响产生的啁啾信号振动、双音响产生的二分量啁啾信号振动、以及成年男性心跳振动3种振动,分析了时频图的分辨率和交叉项抑制情况,并通过计算时频聚集度指数,比较了5种分布情况下振动的分析性能。实验证明,扩展修正B分布的性能优于其他4种时频分布,扩展修正B分布更适合应用于激光多普勒雷达材料共振频率探测和心跳检测领域。Abstract: Most actual vibration signals measured by lidar are time-varying signals. Methods of time-frequency analysis based on Fourier transforms are effective tools for processing time-varying signals. In this paper, the properties of the Wigner-Wiley distribution, the smooth pseudo-Wigner-Wiley distribution, the spectrogram, the Bonn-Jordan distribution, and the extended modified B distribution are compared and analyzed with actual vibration signals measured by laser Doppler radar. Three kinds of vibrations are measured with a laser Doppler radar: chirps generated by a single loudspeaker, two-component chirps generated by two loudspeakers, and adult male heartbeat vibrations. Their time-frequency distribution resolution and the suppression of cross-terms are analyzed. By calculating the time-frequency concentration index, the analysis capacites of the five distributions for three vibrations are compared. Experimental results indicate that the performance of the extended modified B distribution is better than that of the other four time-frequency distributions. Therefore, the extended modified B distribution is more suitable for the detection of material resonance frequency of laser Doppler radar and the detection of heartbeat.
-
表 1 单分量啁啾信号的振动时频聚集度评价
Table 1. Evaluation of time frequency concentration of single component chirps vibration
时频分布 WVD SPWVD SPEC BJD EMBD 评价指数 1.89×10−4 5.05×10−5 2.88×10−5 1.97×10−4 2.12×10−4 表 2 二分量啁啾信号振动时频聚集度评价
Table 2. Evaluation of time frequency concentration of two component chirp vibration
时频分布 WVD SPWVD SPEC BJD EMBD 评价指数 8.88×10−5 7.12×10−5 1.04×10−5 9.16×10−5 1.08×10−4 表 3 成年男性心跳振动时频聚集度评价
Table 3. Evaluation of time frequency concentration of adult male heatbeat vibration
时频分布 WVD SPWVD SPEC BJD EMBD 评价指数 2.67×10−4 3.07×10−4 4.00×10−4 4.94×10−4 5.56×10−4 -
WAZ A T, KACZMAREK P R, ABRAMSKI K M. Laser–fibre vibrometry at 1550 nm[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2009, 20(10): 105301. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/20/10/105301 甄佳奇, 仲维丹, 布音嘎日迪, 等. 正弦调制多光束激光外差测量压电材料电致伸缩系数[J]. 发光学报,2017,38(12):1661-1667. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20173812.1661ZHEN J Q, ZHONG W D, BU Y, et al. Piezoelectric material electrostriction coefficient measurement method combined sinusoidal modulation with multi-beam laser heterodyne[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2017, 38(12): 1661-1667. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20173812.1661 陈家键, 胡慧珠, 缪立军, 等. 双频激光干涉三自由度微振动测量系统[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(7):1435-1443. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192707.1435CHEN J J, HU H ZH, MIAO L J, et al. Three-degree-of-freedom micro-vibration measurement system based on dual-frequency laser interference[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(7): 1435-1443. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192707.1435 GABOR D. Theory of communication. Part 1: the analysis of information[J]. Journal of the Institution of Electrical Engineers - Part III:Radio and Communication Engineering, 1946, 93(26): 429-441. doi: 10.1049/ji-3-2.1946.0074 ALMEIDA L B. The fractional Fourier transform and time-frequency representations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(11): 3084-3091. doi: 10.1109/78.330368 COHEN L. Generalized phase-space distribution functions[J]. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 1966, 7(5): 781-786. doi: 10.1063/1.1931206 BOASHASH B. Time Frequency Signal Analysis and Processing: A Comprehensive Reference[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2003. BOASHASH B, BEN-JABEUR T. Design of a high-resolution separable-kernel quadratic TFD for improving newborn health outcomes using fetal movement detection[C]. Proceedings of the 2012 11th International Conference on Information Science, Signal Processing and Their Applications, IEEE, 2012: 354-359. VAN EEDEN W D, DE VILLIERS J P, BERNDT R J, et al. Micro-Doppler radar classification of humans and animals in an operational environment[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2018, 102: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.02.019 GAO Y Q, CHEN W H, YANG B, et al. Identifying users based on time-frequency characteristics[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2019, 1302(4): 042035. LIU J L, WANG S F, ZHENG J Y, et al. Time-frequency signal processing for integrity assessment and damage localization of concrete piles[J]. International Journal of Structural Stability and Dynamics, 2020, 20(2): 2050020. doi: 10.1142/S0219455420500200 MAJHI S, MUKHERJEE A, GEORGE N V, et al. Corrosion detection in steel bar: a time-frequency approach[J]. NDT &E International, 2019, 107: 102150. QI P F, WANG Y C. Seismic time–frequency spectrum analysis based on local polynomial Fourier transform[J]. Acta Geophysica, 2020, 68(1): 1-17. doi: 10.1007/s11600-019-00377-0 IMADUDDIN S M, LAROVERE K L, KUSSMAN B D, et al. A time-frequency approach for cerebral embolic load monitoring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 67(4): 1007-1018. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2019.2927709 谢斌, 夏立新. 伪Wigner-Ville分布在心电信号时频分析中的应用[J]. 现代信息科技,2019,3(12):56-57, 60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4706.2019.12.021XIE B, XIA L X. Application of pseudo Wigner-Ville distribution in time-frequency analysis of ECG signals[J]. Modern Information Technology, 2019, 3(12): 56-57, 60. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4706.2019.12.021 饶震红, 王明安, 陈蓁蓁, 等. 柠檬黄与玉米醇溶蛋白的相互作用研究[J]. 发光学报,2019,40(4):511-519. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20194004.0511RAO ZH H, WANG M A, CHEN ZH ZH, et al. Interaction between tartrazine and zein[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2019, 40(4): 511-519. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20194004.0511 王云鹏, 胡以华, 雷武虎, 等. 基于激光回波时频图纹理特征的飞机目标分类方法[J]. 光学学报,2017,37(11):1128004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.1128004WANG Y P, HU Y H, LEI W H, et al. Aircraft target classification method based on texture feature of laser echo time-frequency image[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(11): 1128004. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.1128004 王云鹏, 胡以华, 雷武虎, 等. 典型旋翼形状参数微多普勒激光探测计算方法[J]. 红外与激光工程,2018,47(9):0906003. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.0906003WANG Y P, HU Y H, LEI W H, et al. Algorithm of typical rotor shape parameters by micro-Doppler laser detection[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(9): 0906003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.0906003 LÜ T, GUO J, ZHANG H Y, et al. Acquirement and enhancement of remote speech signals[J]. Optoelectronics Letters, 2017, 13(4): 275-278. doi: 10.1007/s11801-017-7059-9 KURVINEN E, JOHN M, MIKKOLA A. Measurement and evaluation of natural frequencies of bulk ice plate using scanning laser Doppler vibrometer[J]. Measurement, 2020, 150: 107091. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.107091 李晴棉, 李也凡, 何大伟, 等. 光外差电信号接收机[J]. 发光学报,1998,19(1):82-84. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7032.1998.01.017LI Q M, LI Y F, HE D W, et al. Optic heterodyning electronic signals receiving device[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 1998, 19(1): 82-84. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7032.1998.01.017 张晓琳, 唐文彦, 孙和义. 水下声信号的激光干涉测量[J]. 光学 精密工程,2010,18(4):809-815.ZHANG X L, TANG W Y, SUN H Y. Laser interferometry of underwater acoustic signals[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2010, 18(4): 809-815. (in Chinese) 刘立生, 张合勇, 王挺峰, 等. 激光外差探测对振动目标多普勒频谱成像[J]. 光学 精密工程,2015,23(6):1508-1515. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152306.1508LIU L SH, ZHANG H Y, WANG T F, et al. Doppler spectrum imaging of vibrating target using laser heterodyne detection[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(6): 1508-1515. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152306.1508 JONES D L, PARKS T W. A high resolution data-adaptive time-frequency representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics,Speech,and Signal Processing, 1990, 38(12): 2127-2135. doi: 10.1109/29.61539 -





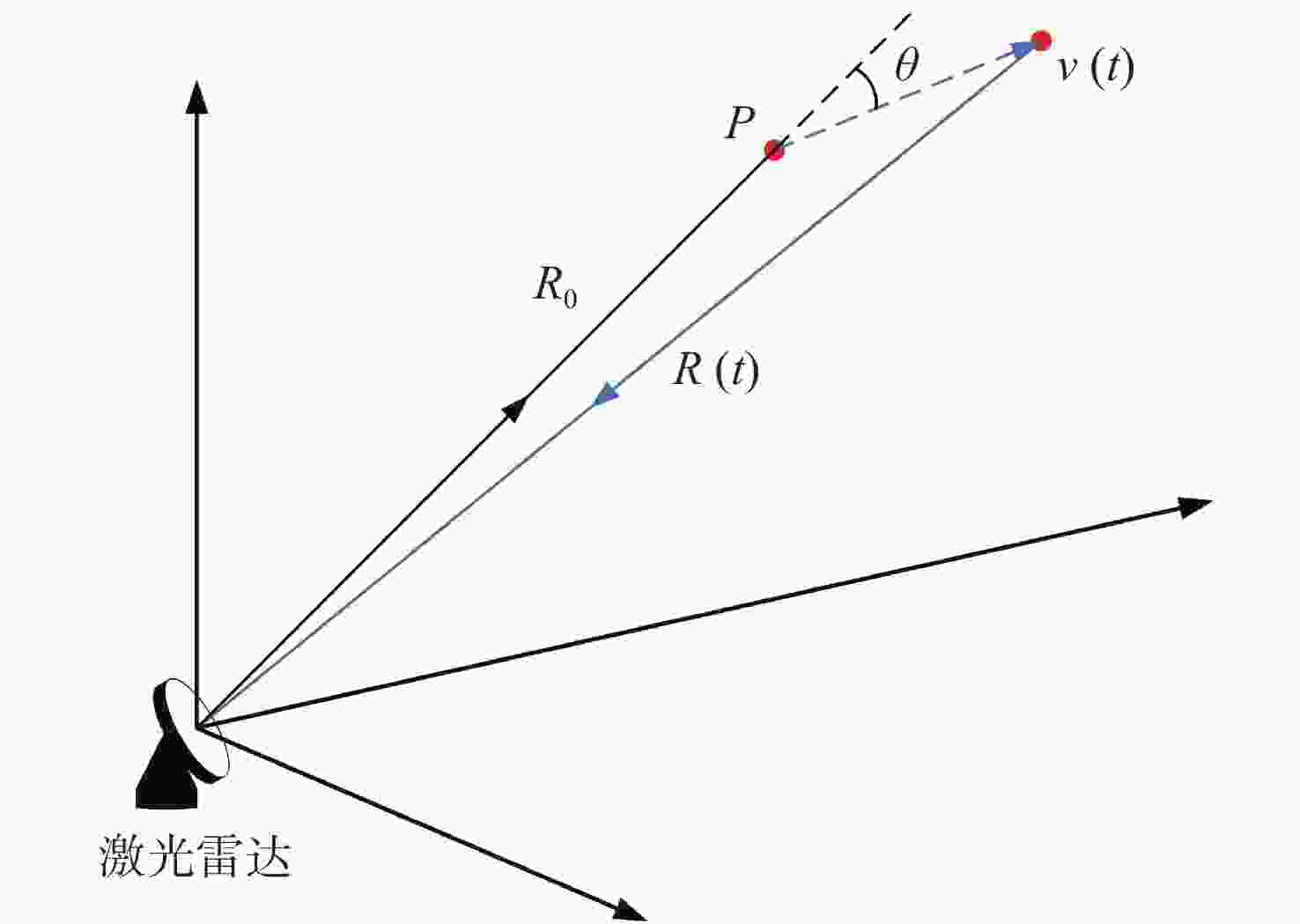
 下载:
下载: