Polarization changes of partially-coherent Airy-Gaussian beams in a slanted turbulent atmosphere
doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0095
-
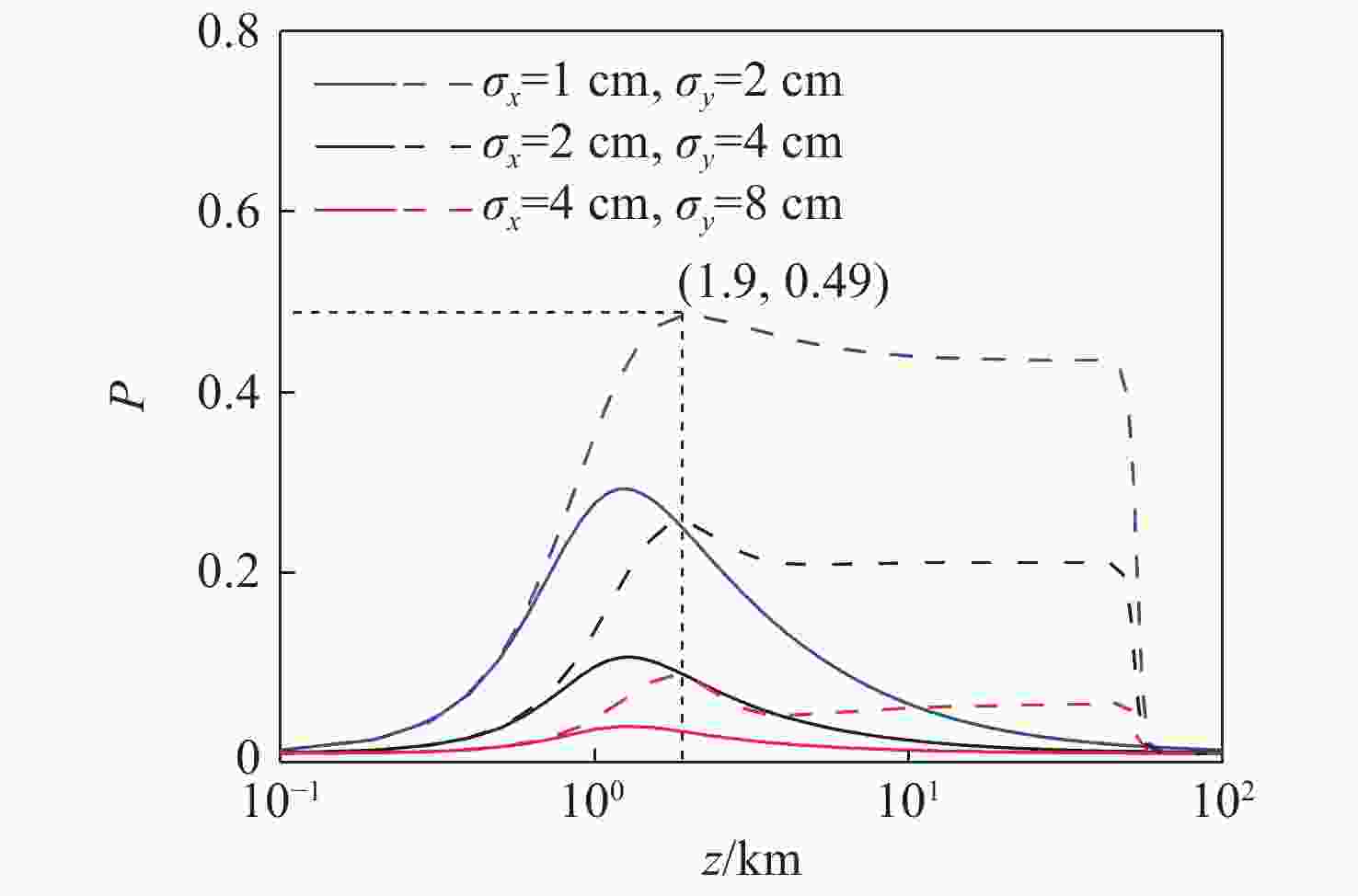
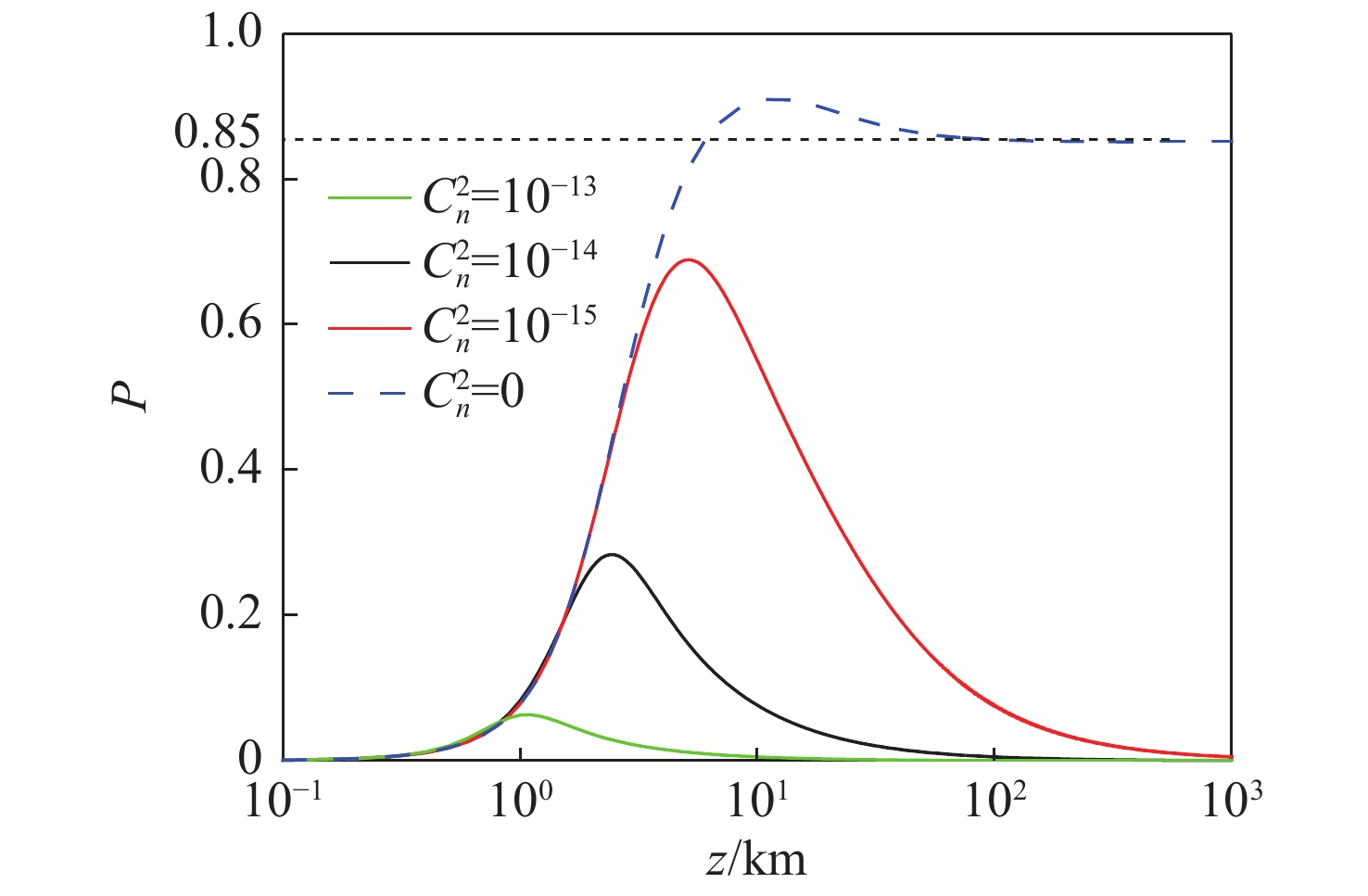
摘要: 偏振是激光通信中保密编码的重要参数,研究斜程湍流大气中的偏振特性对激光通信具有重要意义。利用广义惠更斯-菲涅尔原理和偏振-相干统一理论,推导了无衍射的部分相干艾里高斯光束在斜程湍流大气传输中的偏振度解析式,详细研究了湍流参数、相干长度、天顶角、截断因子和分布因子对偏振度的影响。研究结果表明:与水平湍流相比,光束在斜程湍流下恢复到初始偏振需要更长的传输距离。天顶角、接收高度、截断因子、分布因子越大和相干长度越小,光束偏振度峰值也越大。高相干性的高斯光束比艾里光束更易于保持偏振度不变。无衍射艾里光束中选取合适的光学参数更有利于信息传输与编码,本文结果对激光大气通信领域有着潜在的应用价值。Abstract: Investigating polarization changes in a turbulent atmosphere holds great significance because polarization is one of the most important parameters in laser communication. Based on the extended Huygens-Fresnel principle and the unified theory of coherence and polarization, an analytical expression for the degree of polarization (DoP) in partially-coherent Airy-Gaussian beams propagating in a slanted turbulent atmosphere is derived. It is then used to study the dependence of polarization changes in turbulent parameter, coherence length, zenith angle, truncation and distribution factor. The polarization between the slanted and horizontal paths is also compared. Compared with horizontal turbulence, the beams traverse a longer distance to recover their initial polarization in slanted turbulence. An increase in the zenith angle, receiving height and truncation factor, or a decrease in the coherence length can increase the DoP. A smaller distribution factor or a higher coherence length is beneficial to reducing the effect of the zenith angle on the polarization. Analysis of the influence of the distribution factor on polarization also shows that maintaining the polarization of a Gaussian beam with higher coherence in a horizontally turbulent atmosphere has a greater advantage to that of a pure Airy beam from the view of keeping polarization invariance. The results show that optical information encoding can be achieved by selecting appropriate parameters, which is useful for studying atmospheric communication.
-
Key words:
- degree of polarization /
- airy-gaussian beams /
- turbulent atmosphere /
- propagation
-
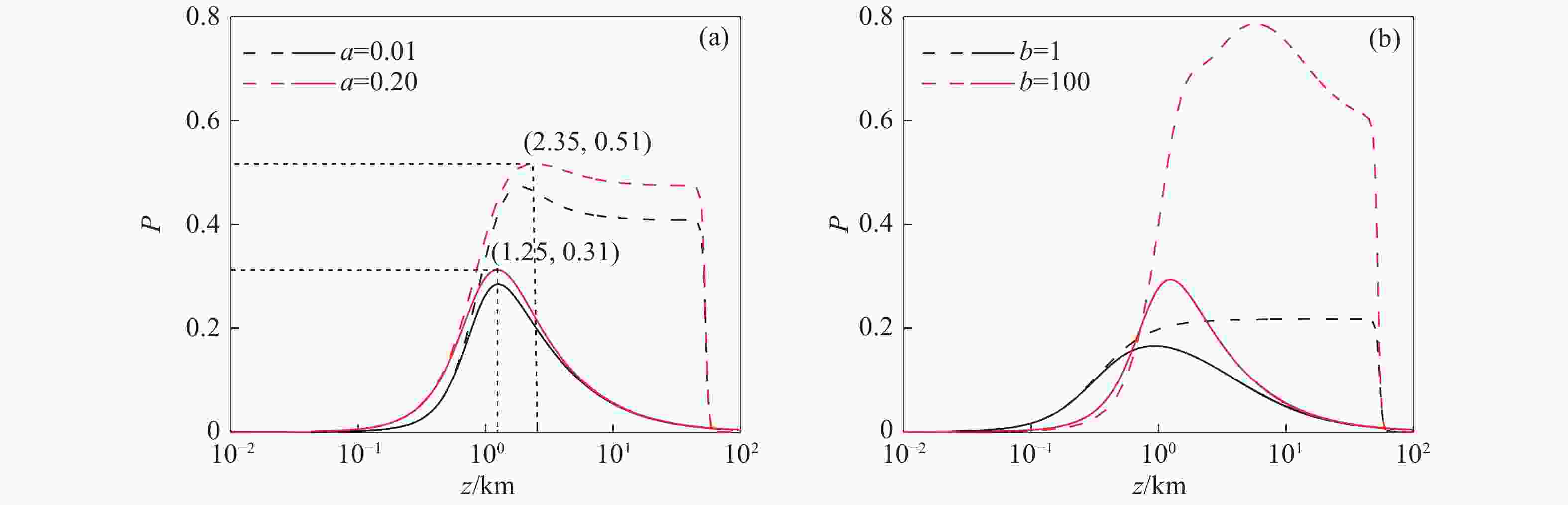
Figure 4. Change in DoP for partially coherent Airy-Gaussian beams over propagation distance z for different truncation or distribution factors, where the solid and dash lines show the horizontal and slanted paths, respectively. The fixed parameters are (a) b=20, H=10000 m and Cn2=10−14 m2/3; (b) a=0.05, H=10000 m and Cn2=10−14 m2/3.
-
[1] WOLF E. Unified theory of coherence and polarization of random electromagnetic beams[J]. Physics Letters A, 2003, 312(5/6): 263-267. doi: 10.1016/S0375-9601(03)00684-4 [2] SALEM M, KOROTKOVA O, DOGARIU A, et al. Polarization changes in partially coherent electromagnetic beams propagating through turbulent atmosphere[J]. Waves in Random Media, 2004, 14(4): 513-523. doi: 10.1088/0959-7174/14/4/003 [3] KOROTKOVA O, SALEM M, WOLF E. The far-zone behavior of the degree of polarization of electromagnetic beams propagating through atmospheric turbulence[J]. Optics Communications, 2004, 233(4/6): 225-230. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2004.01.005 [4] KOROTKOVA O, WOLF E. Changes in the state of polarization of a random electromagnetic beam on propagation[J]. Optics Communications, 2005, 246(1/3): 35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2004.10.078 [5] DU X Y, ZHAO D M. Polarization modulation of stochastic electromagnetic beams on propagation through the turbulent atmosphere[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(6): 4257-4262. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.004257 [6] AVRAMOV-ZAMUROVIC S, NELSON C, MALEK-MADANI R, et al. Polarization-induced reduction in scintillation of optical beams propagating in simulated turbulent atmospheric channels[J]. Waves in Random and Complex Media, 2014, 24(4): 452-462. doi: 10.1080/17455030.2014.944242 [7] GBUR G. Partially coherent beam propagation in atmospheric turbulence[Invited][J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2014, 31(9): 2038-2045. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.31.002038 [8] WANG F, LIU X L, CAI Y J. Propagation of partially coherent beam in turbulent atmosphere: a review (Invited review)[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2015, 150: 123-143. doi: 10.2528/PIER15010802 [9] RICKLIN J C, DAVIDSON F M. Atmospheric optical communication with a Gaussian Schell beam[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2003, 20(5): 856-866. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.20.000856 [10] JI X, ZHANG E, LU B D. Changes in the spectrum and polarization of polychromatic partially coherent electromagnetic beams in the turbulent atmosphere[J]. Optics Communications, 2007, 275(2): 292-300. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2007.03.038 [11] PU J X, KOROTKOVA O. Propagation of the degree of cross-polarization of a stochastic electromagnetic beam through the turbulent atmosphere[J]. Optics Communications, 2009, 282(9): 1691-1698. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2009.01.029 [12] CHU X X. Evolution of an Airy beam in turbulence[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(14): 2701-2703. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.002701 [13] CHEN R P, YIN CH F, CHU X X, et al. Effect of Kerr nonlinearity on an Airy beam[J]. Physical Review A, 2010, 82(4): 043832. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.82.043832 [14] EFREMIDIS N K. Airy trajectory engineering in dynamic linear index potentials[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(15): 3006-3008. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.003006 [15] YE ZH Y, LIU S, LOU C B, et al. Acceleration control of Airy beams with optically induced refractive-index gradient[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(16): 3230-3232. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.003230 [16] ZHOU G Q, CHEN R P, CHU X X. Propagation of Airy beams in uniaxial crystals orthogonal to the optical axis[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(3): 2196-2205. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.002196 [17] JI X L, EYYUBOGLU H T, JI G M, et al. Propagation of an Airy beam through the atmosphere[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(2): 2154-2164. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.002154 [18] BANDRES M A, GUTIÉRREZ-VEGA J C. Airy-Gauss beams and their transformation by paraxial optical systems[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(25): 16719-16728. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.016719 [19] DENG D M. Propagation of Airy-Gaussian beams in a quadratic-index medium[J]. The European Physical Journal D, 2011, 65(3): 553-556. doi: 10.1140/epjd/e2011-20479-2 [20] PIKSARV P, VALTNA-LUKNER H, VALDMANN A, et al. Temporal focusing of ultrashort pulsed Bessel beams into Airy-Bessel light bullets[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(15): 17220-17229. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.017220 [21] CHEN C D, CHEN B, PENG X, et al. Propagation of Airy-Gaussian beam in Kerr medium[J]. Journal of Optics, 2015, 17(3): 035504. doi: 10.1088/2040-8978/17/3/035504 [22] ZHOU M L, CHEN CH D, CHEN B, et al. Propagation of an Airy-Gaussian beam in uniaxial crystals[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2015, 24(12): 124102. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/24/12/124102 [23] HUANG J Y, LIANG Z J, DENG F, et al. Propagation properties of right-hand circularly polarized Airy-Gaussian beams through slabs of right-handed materials and left-handed materials[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2015, 32(11): 2104-2109. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.32.002104 [24] ZHOU J X, LIU Y C, KE Y G, et al. Generation of Airy vortex and Airy vector beams based on the modulation of dynamic and geometric phases[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(13): 3193-3196. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.003193 [25] DENG F, DENG D M. Three-dimensional localized Airy-Hermite-Gaussian and Airy-Helical-Hermite-Gaussian wave packets in free space[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(5): 5478-5486. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.005478 [26] YANG A L, LIN Q. Polarization characteristics of coherent partially Airy beams propagating in atmospheric turbulence[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(20): 204101. [27] MANDEL L, Wolf E. Optical Coherence and Quantum Optics[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001. [28] ANDREWS L C, PHILLIPS R L. Laser Beam Propagation Through Random Media[M]. Bellingham: SPIE Press, 2005. [29] DOU L Y, JI X L, LI P Y. Propagation of partially coherent annular beams with decentered field in turbulence along a slant path[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(8): 8417-8430. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.008417 [30] VALLÉE O, SOARES M. Airy Functions and Applications to Physics[M]. Hackensack: World Scientific Publishing Company, 2004. -





 下载:
下载: