Enhanced dye-sensitized up-conversion luminescence of neodymium-sensitized multi-shell nanostructures
doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0097
-
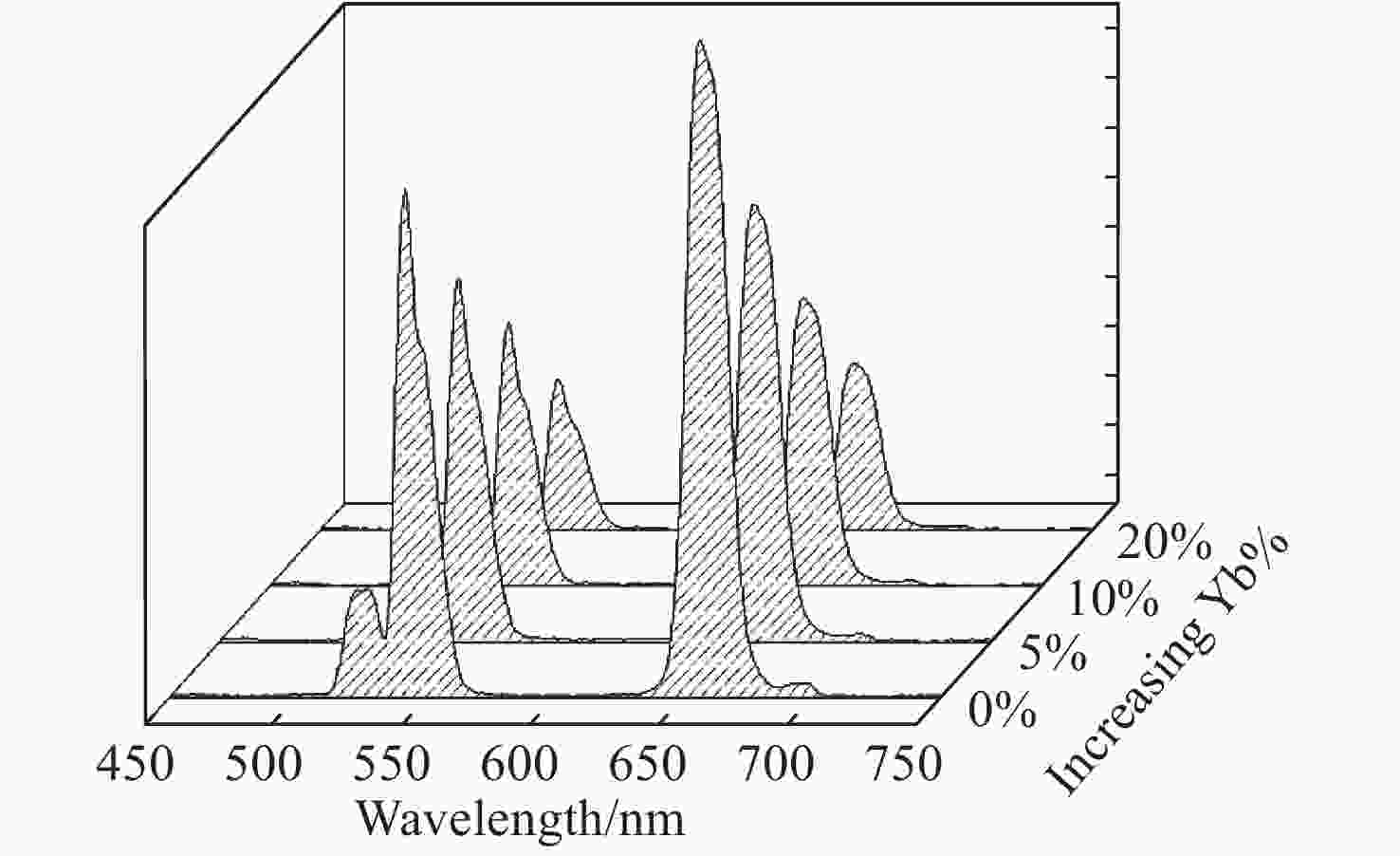
摘要: 对于稀土离子掺杂的上转换发光,由于稀土离子吸收截面小、吸收范围窄,导致其发光强度受限。最近,在稀土上转换纳米粒子的表面连接近红外染料分子敏化发光,被证实是提高上转换发光强度的有效策略。然而,将染料分子连接经典的稀土Yb掺杂纳米粒子,并不能有效利用染料分子的敏化能力。针对这一问题,本文通过高温热分解法成功制备了Nd3+敏化的核/壳/壳 (NaYF4:Yb/Er (20/2%)@ NaYF4:Yb (10 %)@ NaYF4:Nd (80 %))纳米结构,与经典的IR-806敏化的NaYF4:Yb/Er纳米结构相比,IR-806敏化的Nd3+掺杂的核/壳/壳纳米结构的上转换发光(500~700 nm)强度增强了约38倍。通过荧光光谱及荧光寿命分析证实,上转换发光强度增强源于Nd的吸收与近红外染料分子的有效交叠,以及壳层结构对发光中心的保护作用(Er3+ (4S3/2→4I15/2)的寿命延长了1.7倍)。另外,研究发现纳米壳层结构中最外层掺杂的Yb3+离子将导致染料敏化发光减弱。进一步,这种IR-806敏化的Nd掺杂的核/壳/壳纳米结构可实现增强发光中心为Ho及Tm的上转换发光。本文研究为提高染料敏化上转换发光及应用提供了新途径。Abstract: Lanthanide-ion-doped upconversion luminescence is limited by the small absorption cross-section and narrow absorption band of lanthanide ions, which results in weak luminescence. Recently, a dye-sensitized method has proven to be an effective strategy of increasing upconversion luminescence. However, simply attaching dye molecules to nanoparticles with classic Yb-doped nanostructures cannot effectively activate the sensitizing ability of the dye molecules. In response to this problem, we designed Nd-sensitized core/shell/shell (NaYF4:Yb/Er (20/2%)@ NaYF4:Yb (10 %)@ NaYF4:Nd (80 %)) nanostructures, compared with the classic IR-806 sensitized NaYF4:Yb/Er nanostructure, their upconversion luminescence (500 to 700 nm) was approximately enhanced by a factor of 38. Through analysis of the nanostructure’s emission and luminescence lifetime data, the enhancement was confirmed by the effective overlap of Nd absorption with the emission of near-infrared dye molecules and the protective effects of the shell structure on the luminescent center (the lifetime of Er (4S3/2→4I15/2) was increased by 1.7 times). In addition, we found that the doping Yb3+ in the outermost layer will decrease the dye-sensitized luminescence intensity. Furthermore, this Nd-sensitized core/shell/shell structure also achieved enhancement in the sensitized upconversion luminescence of the luminescence centers of Ho and Tm, which establishes a foundation for enhanced dye-sensitized upconversion luminescence.
-
Key words:
- upconversion luminescence /
- dye-sensitized /
- lanthanide ion /
- nanoparticles
-
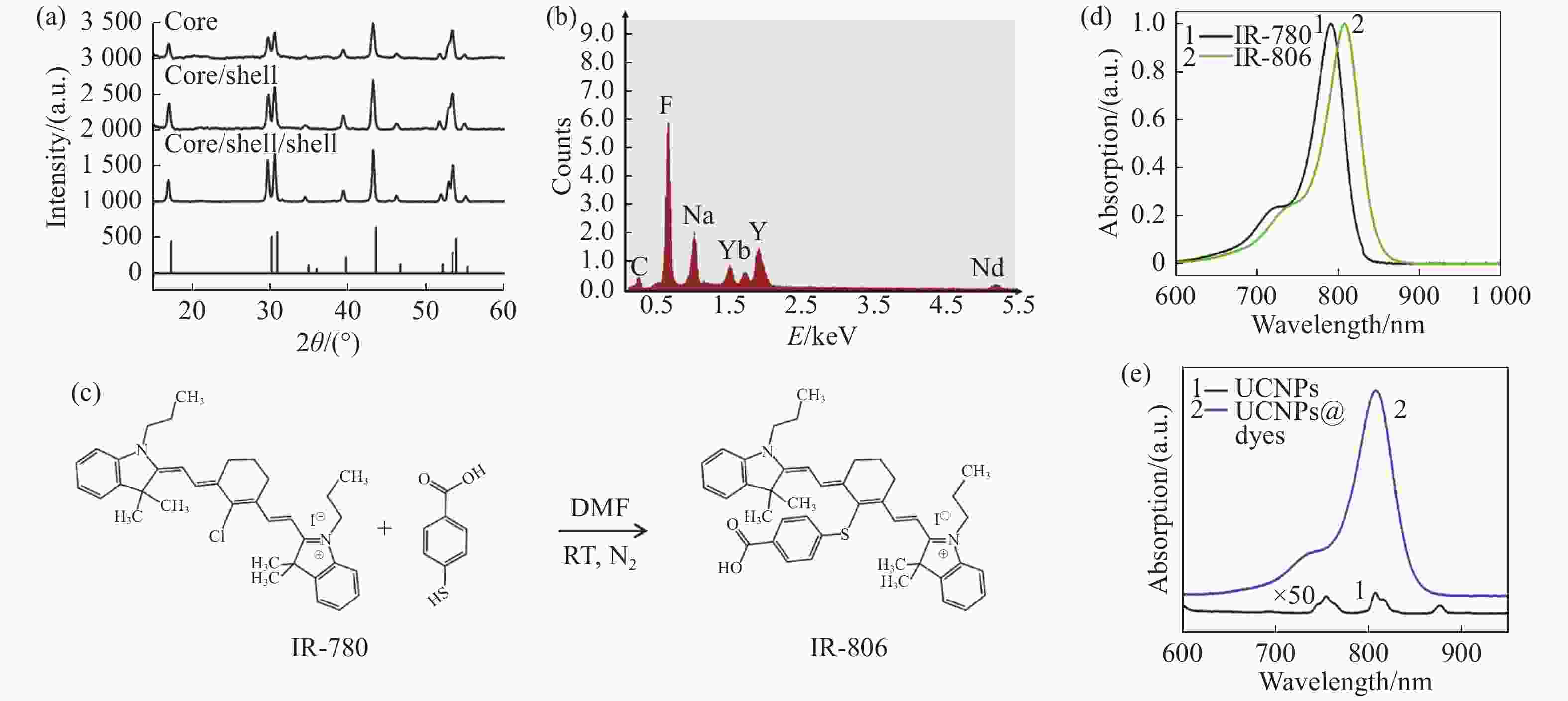
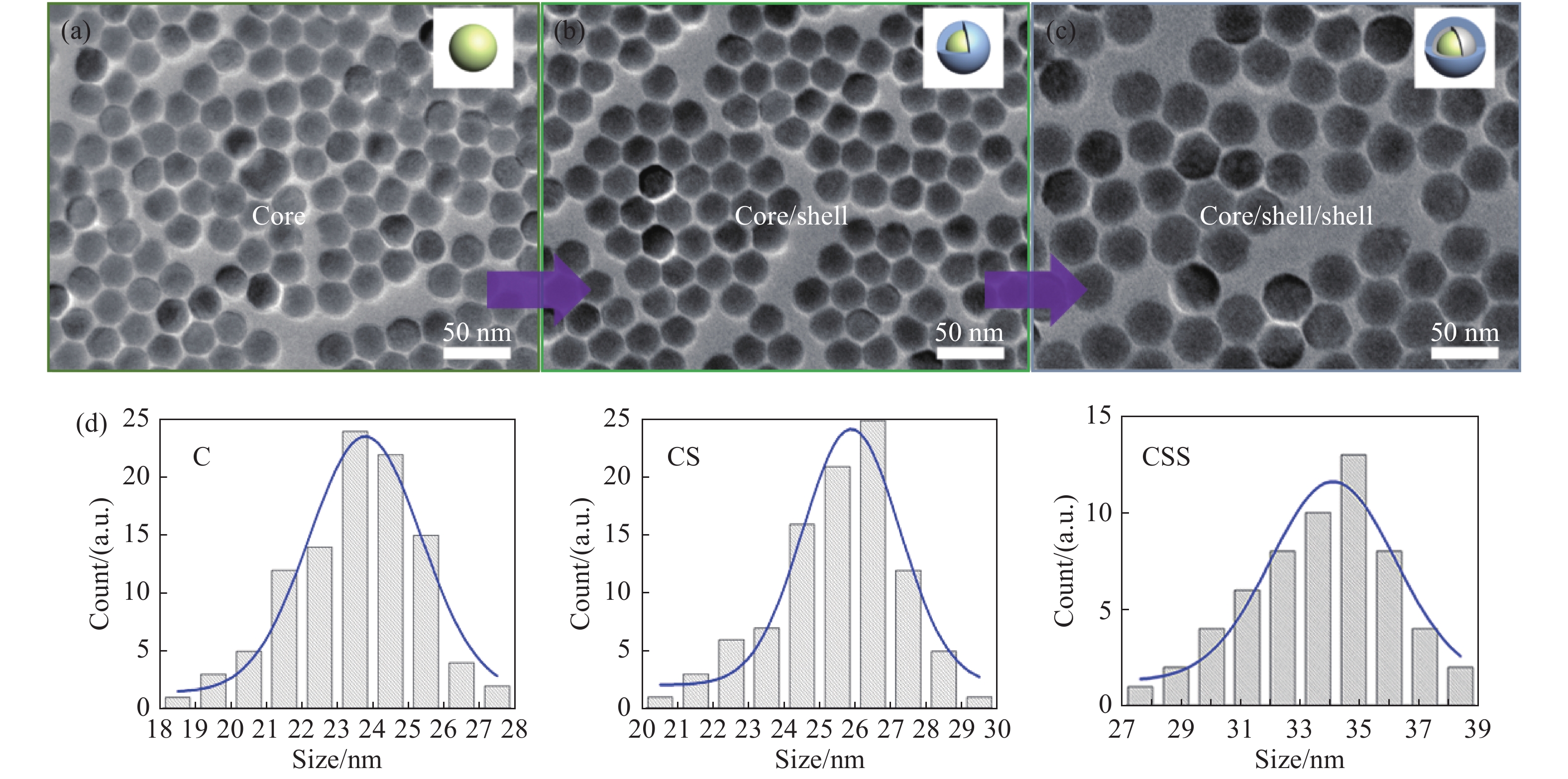
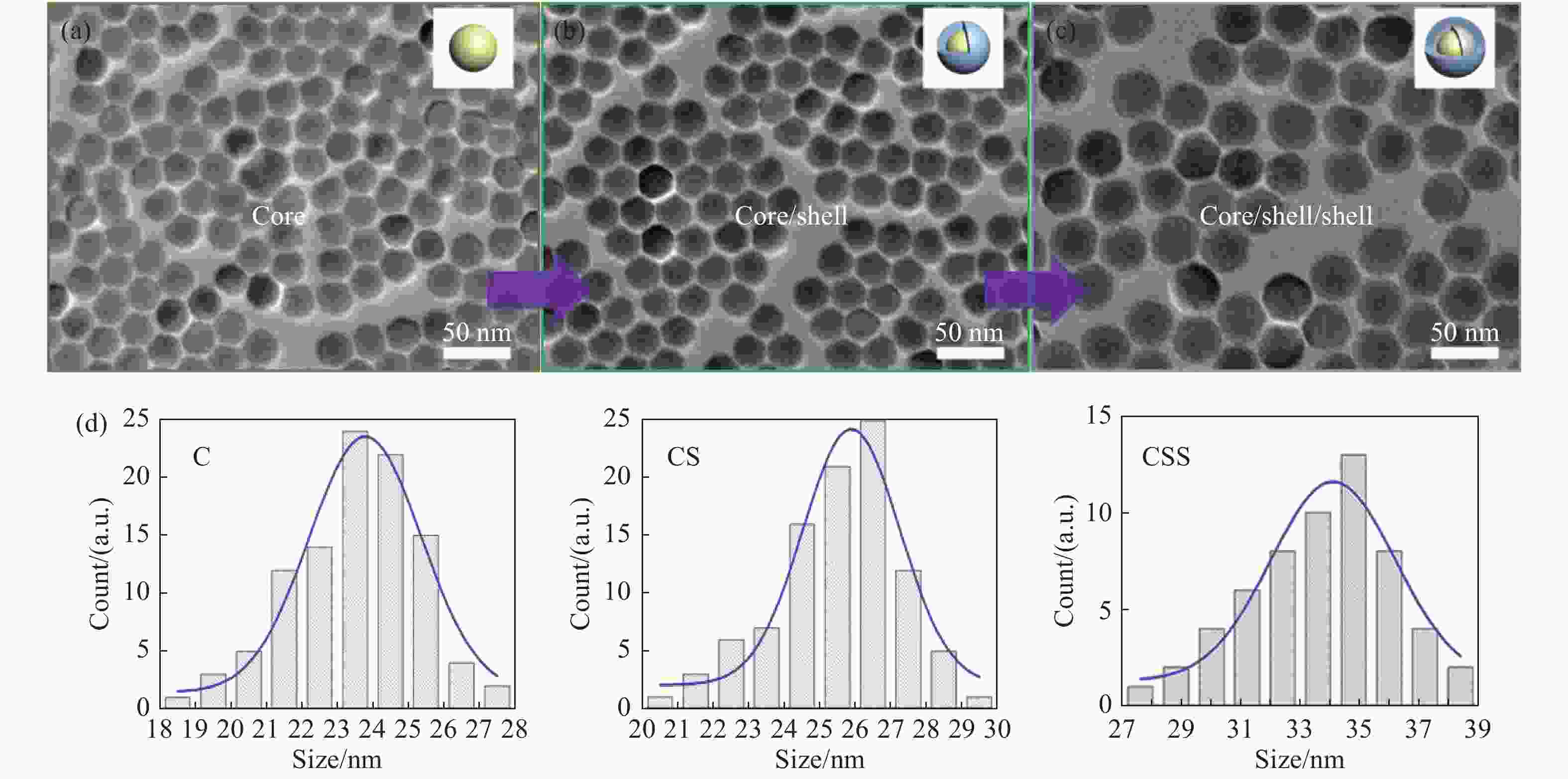
图 2 (a)上转换纳米粒子的核、核/壳、核/壳/壳XRD及标准卡片β-NaYF4 (JCPDS-16-0334, 底部)结果,(b)上转换CSS的EDS数据,(c)IR-806 合成过程图,(d)合成前后IR-780 和 IR-806的吸收,(e)连接IR-806之后UCNPs吸收和UCNPs本身的吸收
Figure 2. (a) XRD data of C, CS and CSS of UCNPs and the β-NaYF4 (JCPDS-16-0334, bottom); (b) EDS data of CSS; (c) IR-806 synthesis process; (d) absorptions of IR-780 and IR-806 before and after synthesis; (e) absorption of UCNPs and dye conjugated UCNPs after IR-806 connection
图 3 (a)IR-806敏化CSS结构的上转换光谱及IR-806敏化核结构的上转换光谱,激发波长为808 nm,(b)808 nm激发下的IR-806敏化的CSS结构的上转换发光强度随功率变化的log-log关系
Figure 3. (a) Up-conversion luminescence (UCL) spectra of IR-806-sensitized CSS structure and IR-806-sensitized core structure under 808 nm excitation wavelength; (b) log-log plots of the UCL intensity versus laser power for the IR-806 dye-sensitized CSS under 808 nm excitation
图 4 (a)IR-806分子的发射光谱与Nd3+的吸收交叠图;(b) 980 nm激发下,测试得到的核纳米粒子(黑色, NaYF4: Yb/Er (20/2%)),染料敏化核纳米粒子(红色)及染料敏化的CSS纳米结构(蓝色)的Er3+ (4S3/2→4I15/2)的寿命测试结果;(c)808 nm激发下CSS纳米结构及染料敏化的CSS纳米结构的Er3+ (4S3/2→4I15/2)的寿命测试结果
Figure 4. (a) Overlap between the emission spectrum of IR-806 molecules and the absorption spectrum of Nd3+; (b) the lifetimes of Er3+ (4S3/2→4I15/2) in core nanoparticles (black, NaYF4:Yb/Er (20/2%), dye-sensitized core nanoparticles (red) and dye-sensitized CSS nanostructure (blue) under 980 nm excitation; (c) the lifetimes of Er3+ (4S3/2→4I15/2) in CSS nanostructure and dye-sensitized CSS nanostructure under 808 nm excitation
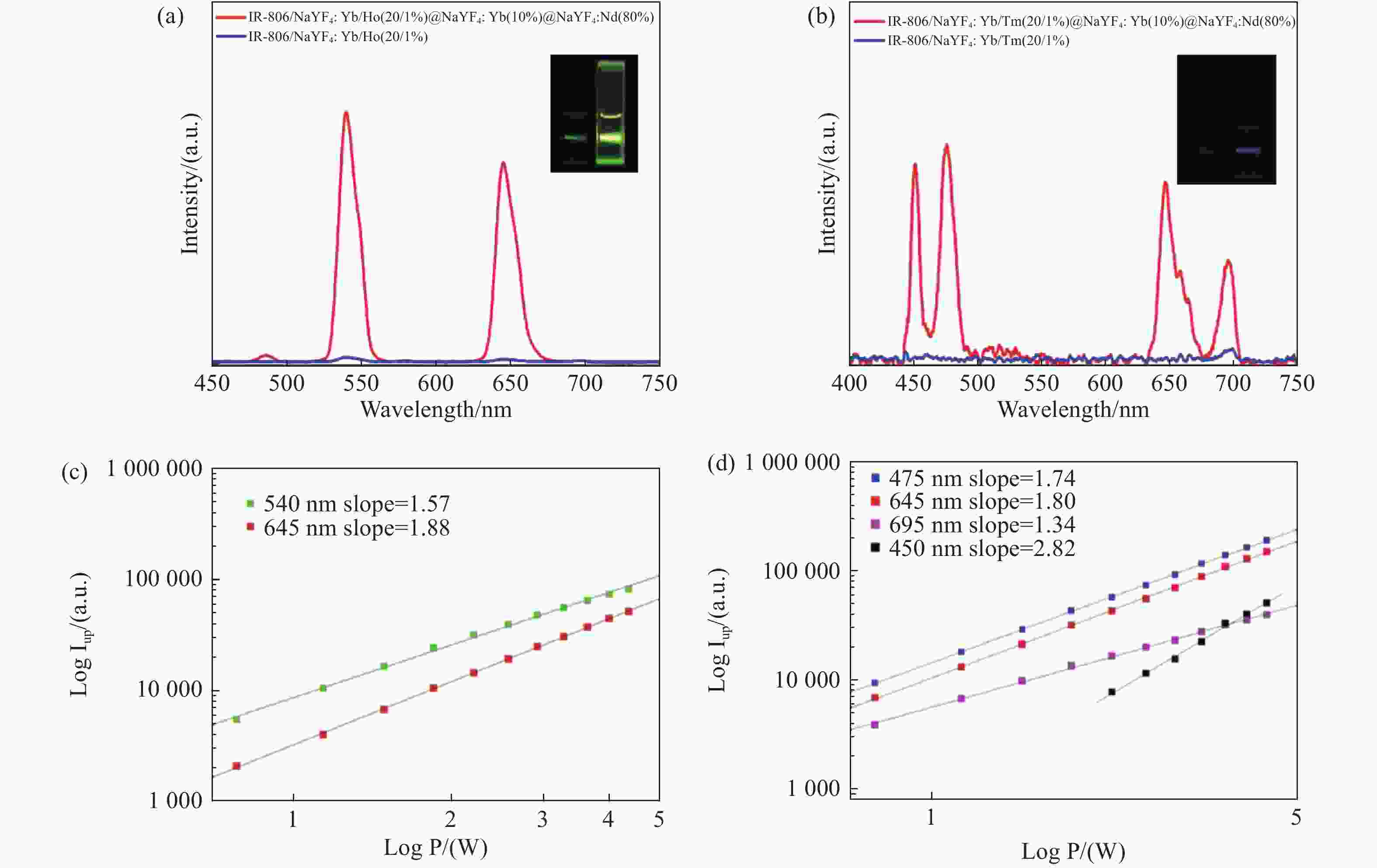
图 6 (a)IR-806敏化Ho核结构及IR-806敏化Ho-CSS结构的上转换光谱,(b) IR-806敏化Tm核结构及IR-806敏化Tm-CSS结构的上转换光谱,(c) 808 nm激发下的IR-806敏化的Ho-CSS结构的上转换发光强度随功率变化的log-log关系,(d) 808 nm激发下的IR-806敏化的Tm-CSS结构的上转换发光强度随功率变化的log-log关系
Figure 6. (a) The UCL of the IR-806 sensitized Ho core nanostructure and IR-806 sensitized Ho-CSS nanostructure, (b) the UCL of the IR-806 sensitized Tm core nanostructure and IR-806 sensitized Tm-CSS nanostructure, (c) log-log plots of the UCL intensity over laser power for the green and red emissions of the dye-sensitized Ho-CSS under 808 nm excitation, (d) log-log plots of the UCL intensity versus laser power for the green and red emissions of the dye-sensitized Tm-CSS under 808 nm excitation
-
[1] AUZEL F. Upconversion and anti-stokes processes with f and d ions in solids[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104(1): 139-174. doi: 10.1021/cr020357g [2] LI X X, LI Y Q, WANG X, et al. Highly sensitive down-conversion optical temperature-measurement material: NaGd(WO4)2:Yb3+/Er3 +[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 596-605. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0596 [3] HE F, GAI SH L, YANG P P, et al. Luminescence modification and application of the lanthanide upconversion fluorescence materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 39(1): 92-106. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183901.0092 [4] WANG F, WEN SH H, HE H, et al. Microscopic inspection and tracking of single upconversion nanoparticles in living cells[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2018, 7(4): e18007. [5] CHEN SH, WEITEMIER A Z, ZENG X, et al. Near-infrared deep brain stimulation via upconversion nanoparticle-mediated optogenetics[J]. Science, 2018, 359(6376): 679-684. [6] LIU Y J, LU Y Q, YANG X S, et al. Amplified stimulated emission in upconversion nanoparticles for super-resolution nanoscopy[J]. Nature, 2017, 543(7644): 229-233. doi: 10.1038/nature21366 [7] WANG D, XUE B, OHULCHANSKYY T Y, et al. Inhibiting tumor oxygen metabolism and simultaneously generating oxygen by intelligent upconversion nanotherapeutics for enhanced photodynamic therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2020, 251: 120088. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120088 [8] XUE B, WANG D, ZHANG Y L, et al. Regulating the color output and simultaneously enhancing the intensity of upconversion nanoparticles via a dye sensitization strategy[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(28): 8607-8615. doi: 10.1039/C9TC02293G [9] TU L P, LIU X M, WU F, et al. Excitation energy migration dynamics in upconversion nanomaterials[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(6): 1331-1345. doi: 10.1039/C4CS00168K [10] XU W, CHEN X, SONG H W. Manipulation of local electromagnetic field in upconversion luminescence of rare earth ions[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 39(1): 1-26. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183901.0001 [11] ZOU W Q, VISSER C, MADURO J A, et al. Broadband dye-sensitized upconversion of near-infrared light[J]. Nature Photonics, 2012, 6(8): 560-564. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.158 [12] CHEN G Y, DAMASCO J, QIU H L, et al. Energy-cascaded upconversion in an organic dye-sensitized core/shell fluoride nanocrystal[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(11): 7400-7407. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02830 [13] WANG D, WANG D, KUZMIN A, et al. ICG-sensitized NaYF4:Er nanostructure for theranostics[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2018, 6(12): 1701142. doi: 10.1002/adom.201701142 [14] WANG D, XUE B, KONG X G, et al. 808 nm driven Nd3+-sensitized upconversion nanostructures for photodynamic therapy and simultaneous fluorescence imaging[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(1): 190-197. doi: 10.1039/C4NR04953E [15] WANG D, XUE B, SONG J, et al. Compressed energy transfer distance for remarkable enhancement of the luminescence of Nd3+-sensitized upconversion nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(24): 6597-6604. doi: 10.1039/C8TC00936H [16] ZHONG Y T, TIAN G, GU Z J, et al. Elimination of photon quenching by a transition layer to fabricate a quenching-shield sandwich structure for 800 nm excited upconversion luminescence of Nd3+ -sensitized nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(18): 2831-2837. doi: 10.1002/adma.201304903 [17] XUE B, WANG D, TU L P, et al. Ultrastrong absorption meets ultraweak absorption: unraveling the energy-dissipative routes for dye-sensitized upconversion luminescence[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2018, 9(16): 4625-4631. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b01931 [18] LI J, LIU L, GUO H Q, et al. An upconversion fluorescent method for rapid detection of perfluorooctane sulfonate in water samples based on fluorine- fluorine interaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(3): 380-387. (in Chinese) [19] SHAO SH, DING B B, ZHU ZH L, et al. Preparation of water-soluble up-conversion nano-drug by host-guest chemistry and its application in tumor diagnosis and treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(6): 823-831. (in Chinese) [20] CUI L, ZHAO M H, ZHANG CH Y. Recent advance in applications of host-guest interaction in biochemical analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 48(7): 817-826. (in Chinese) [21] MENG ZH P, WU S L. Manipulating upconversion luminescence of rare earth by photonic crystals[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2020, 41(8): 913-925. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/fgxb20204108.0913 [22] SUN J F, YAN D, LIU L. Three-primary-color upconversion in single lanthanide based nanoparticle[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2020, 41(1): 1-8. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20204101.0001 [23] YU H Y, TU L P, ZHANG Y L, et al. Quantitative analysis of the surface quenching effect of lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles in solvents[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(6): 1288-1294. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191206.1288 [24] FISCHER S, BRONSTEIN N D, SWABECK J K, et al. Precise tuning of surface quenching for luminescence enhancement in core-shell lanthanide-doped nanocrystals[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(11): 7241-7247. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03683 -





 下载:
下载: