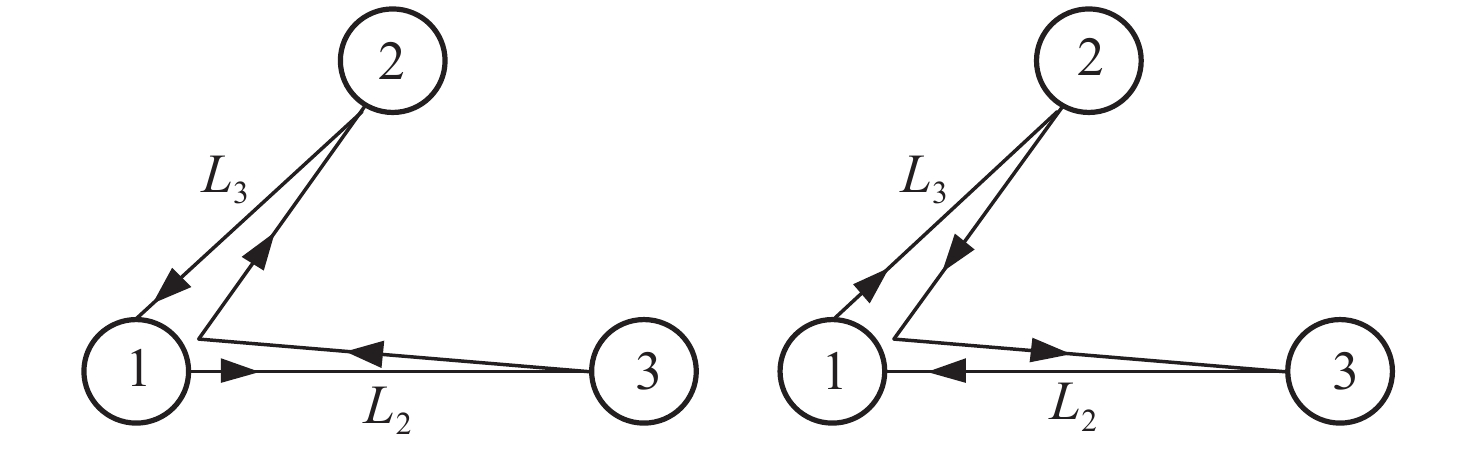
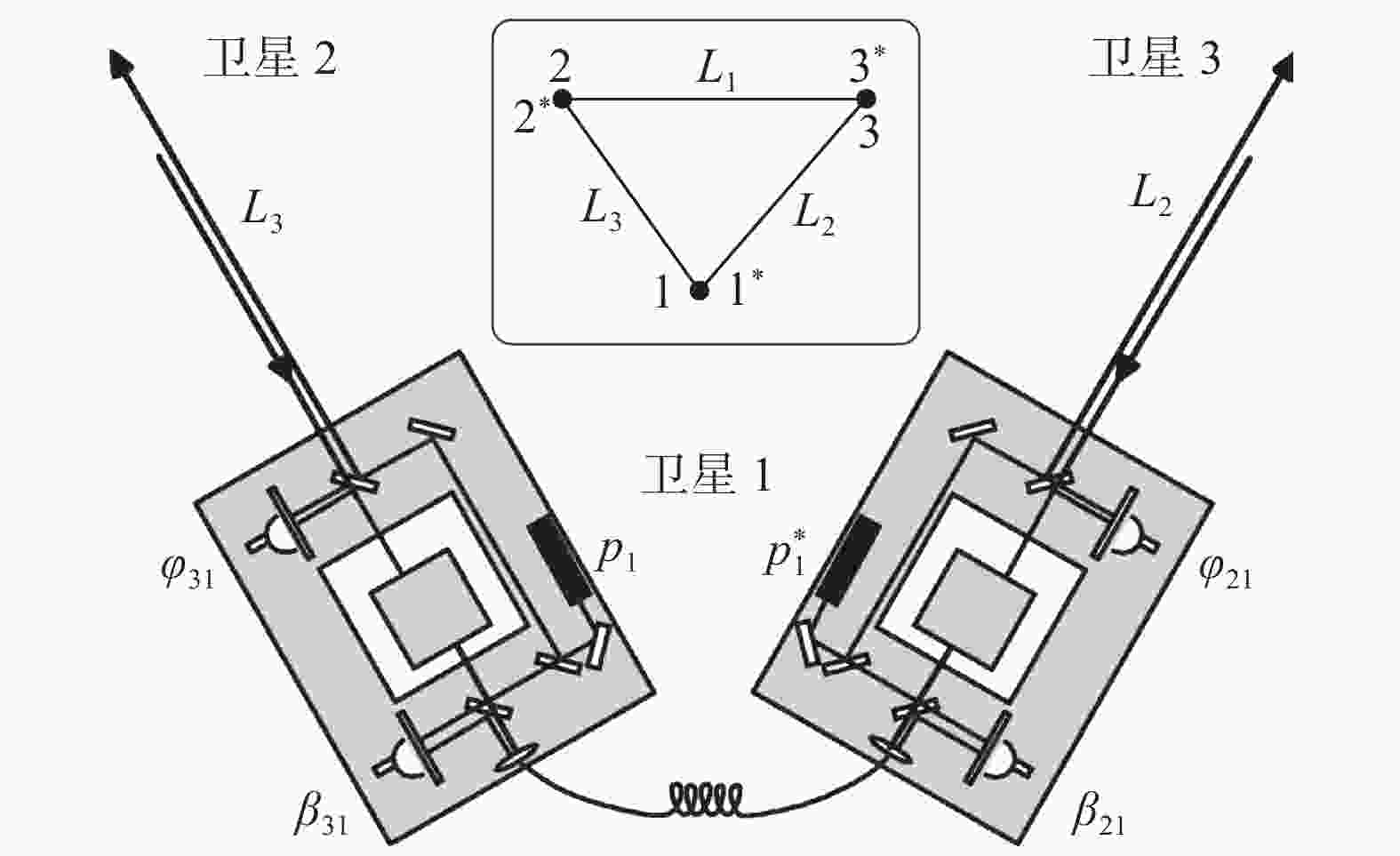
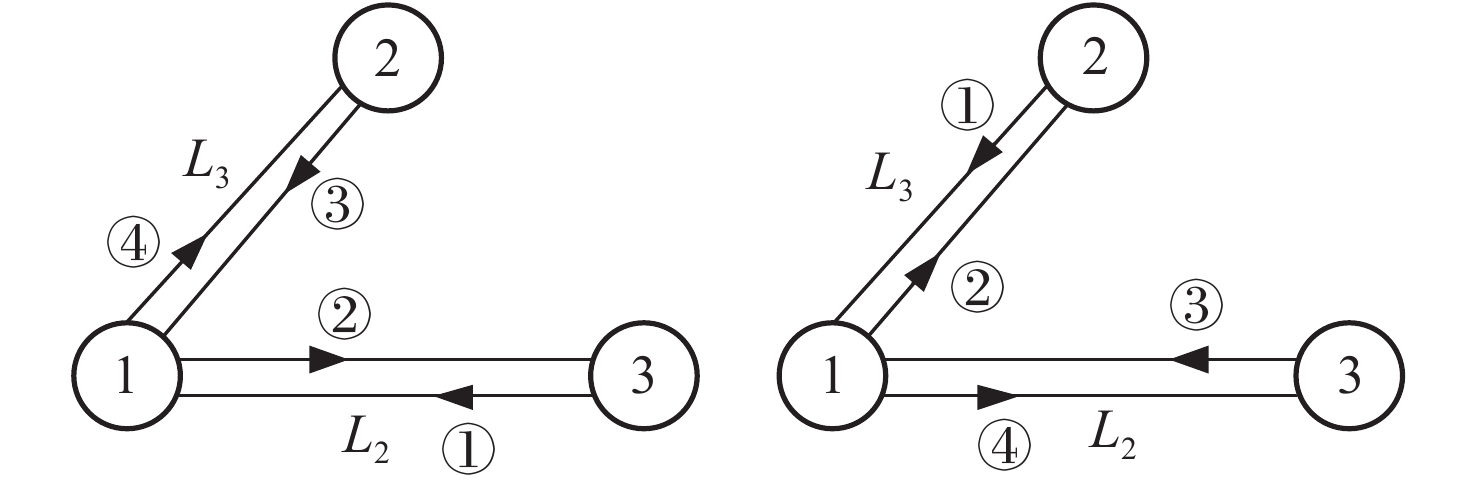
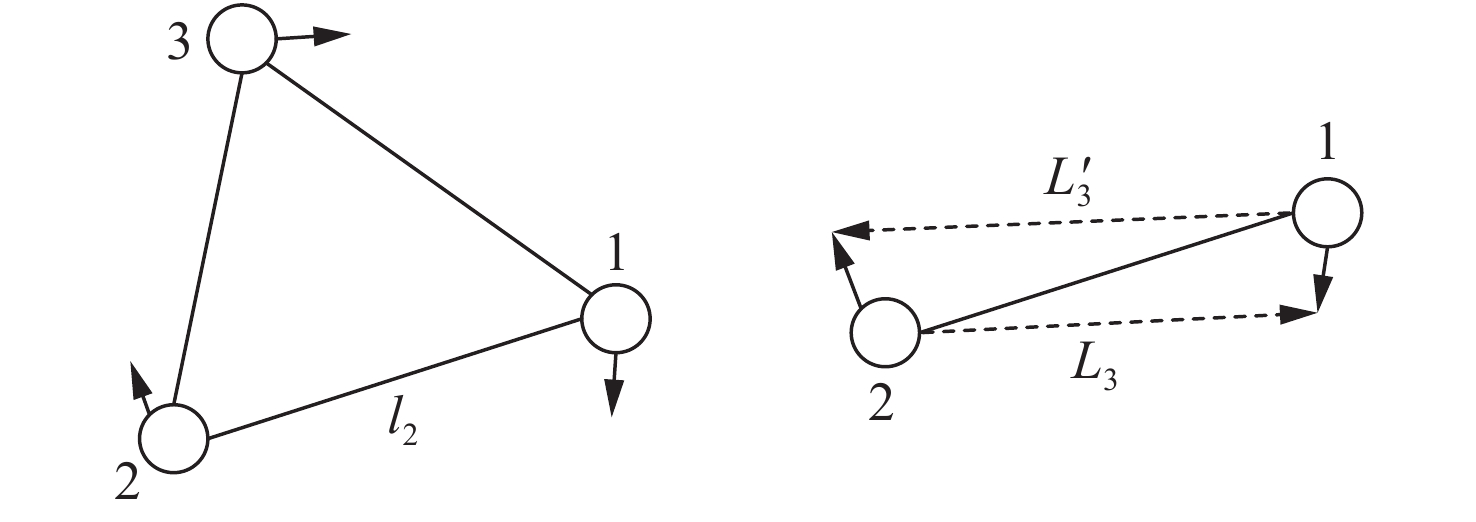
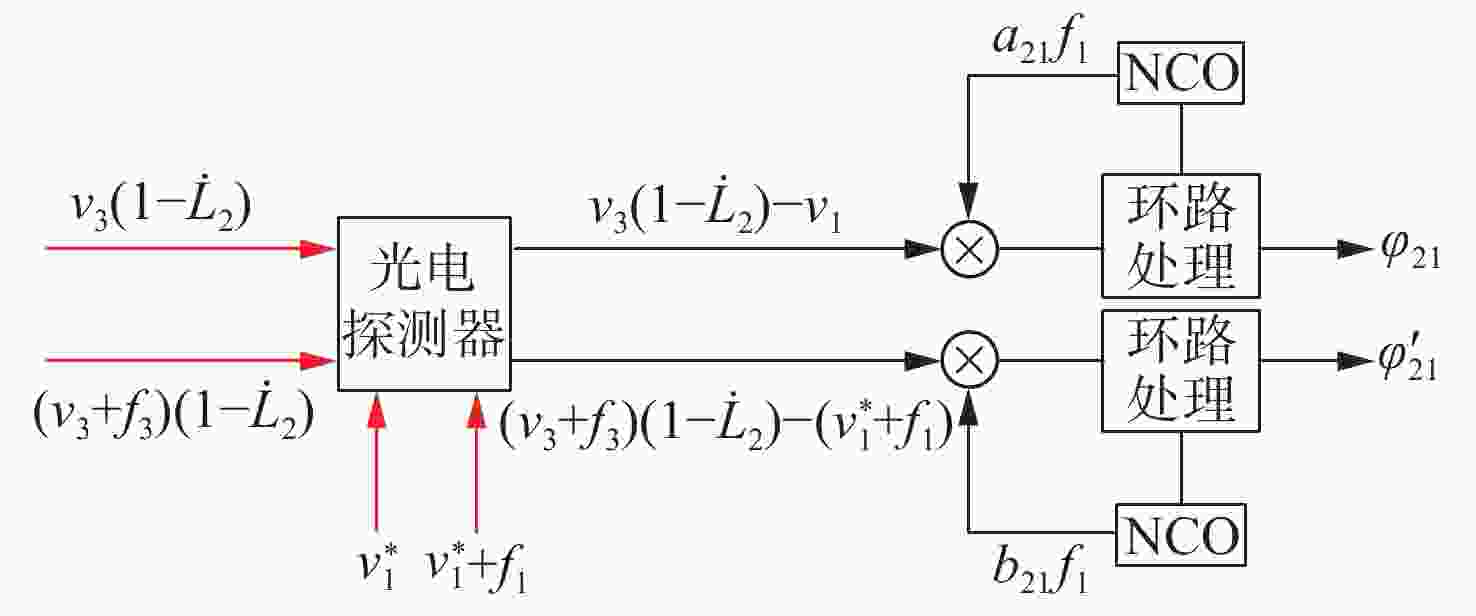
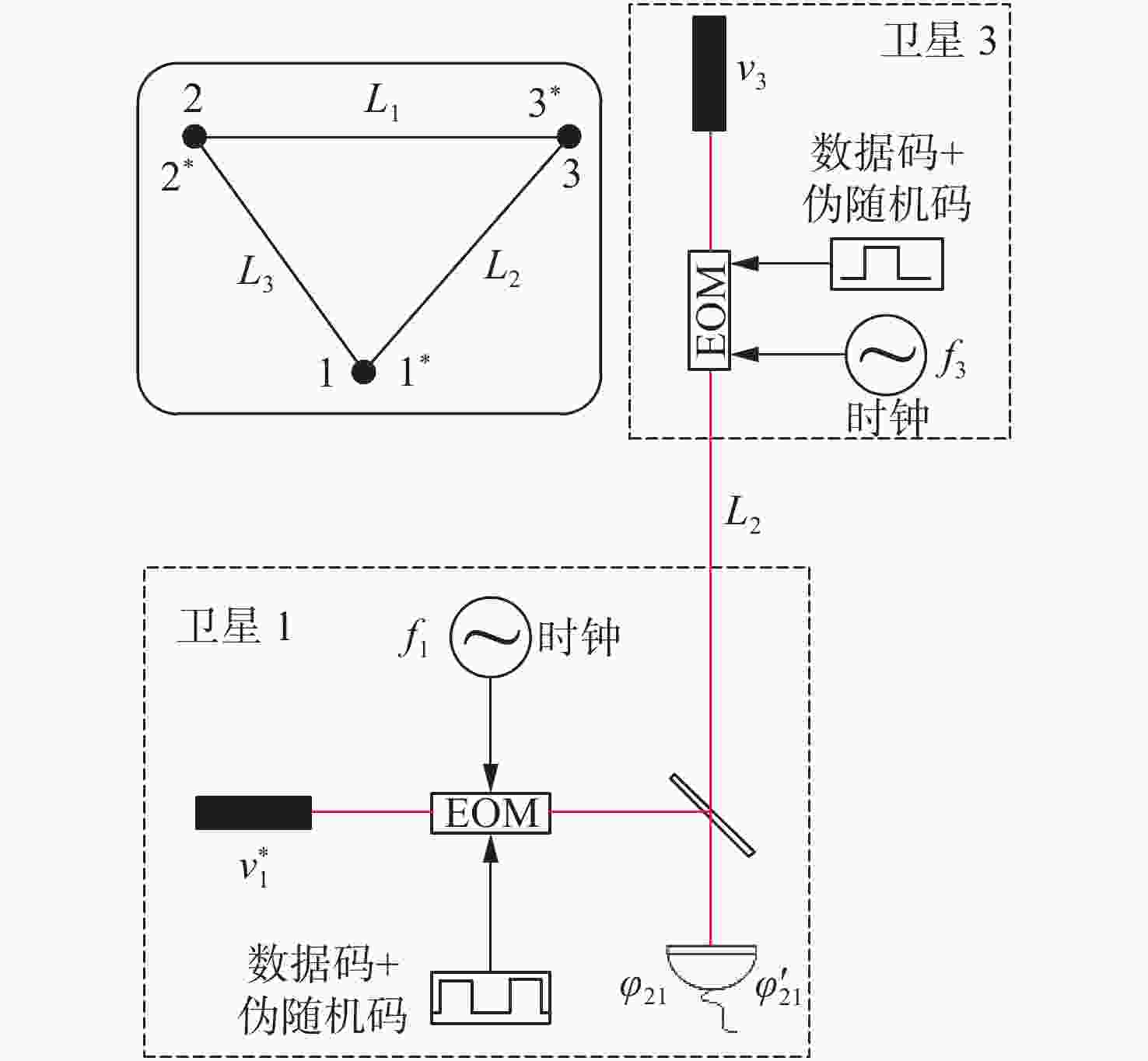
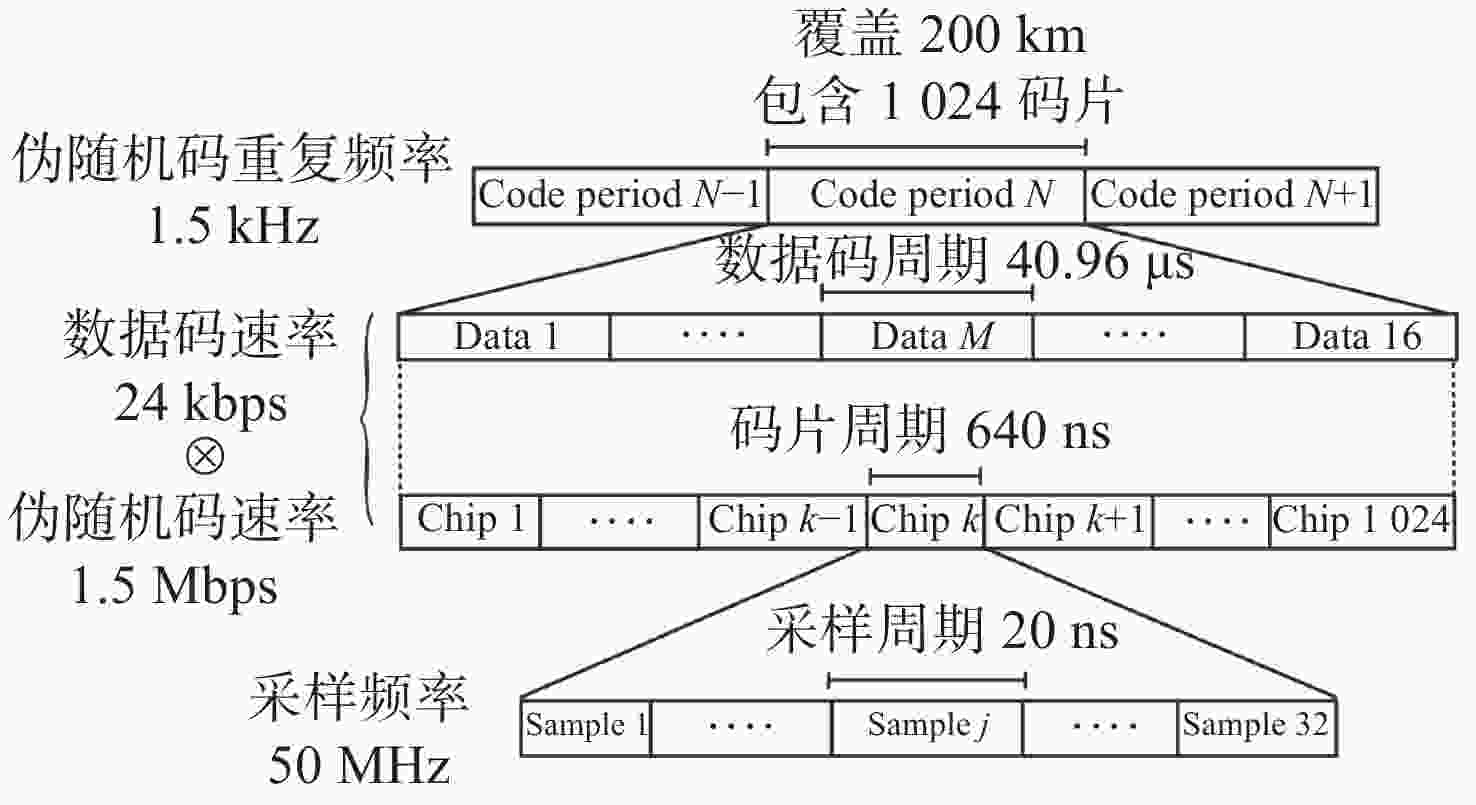
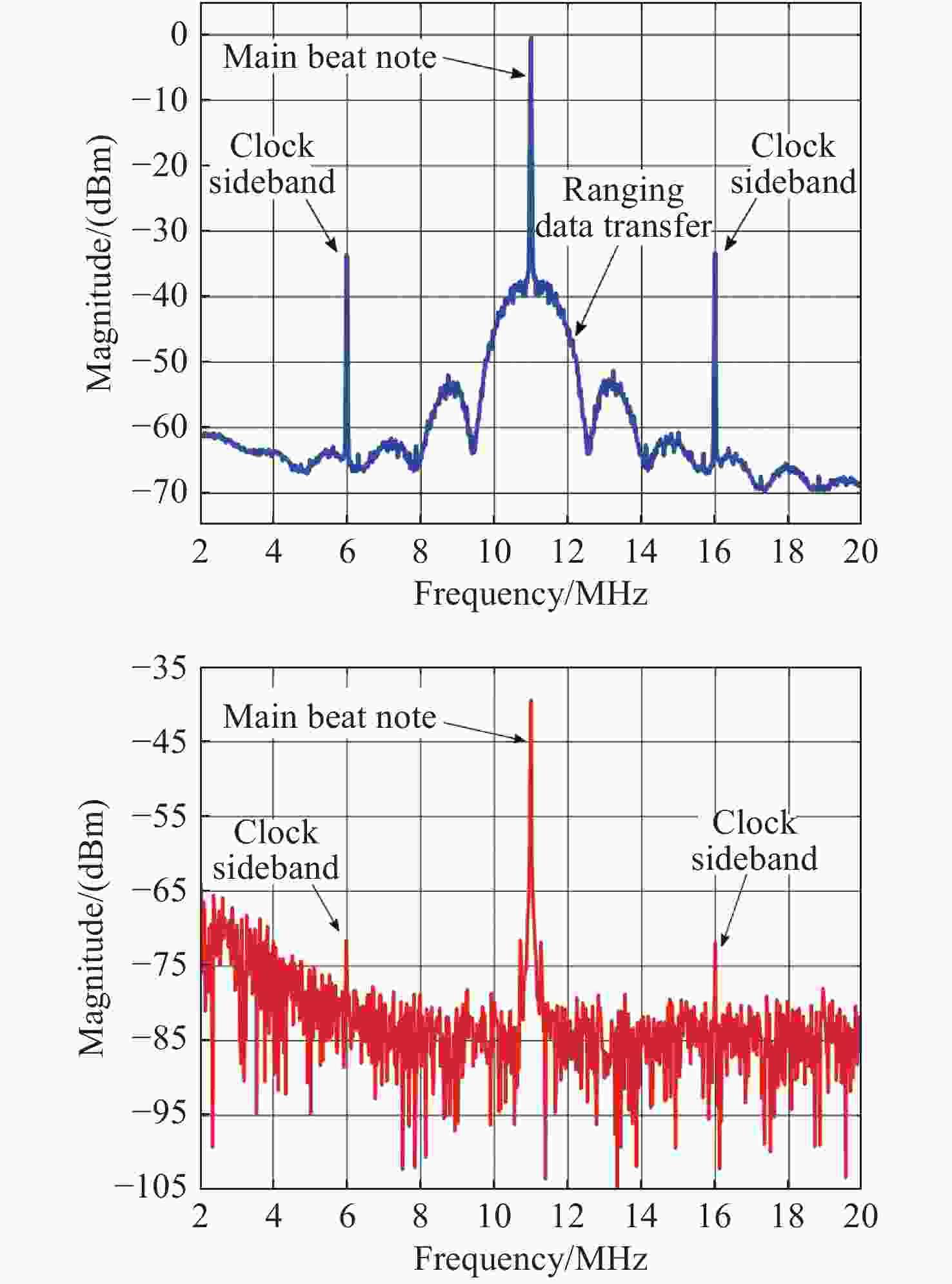
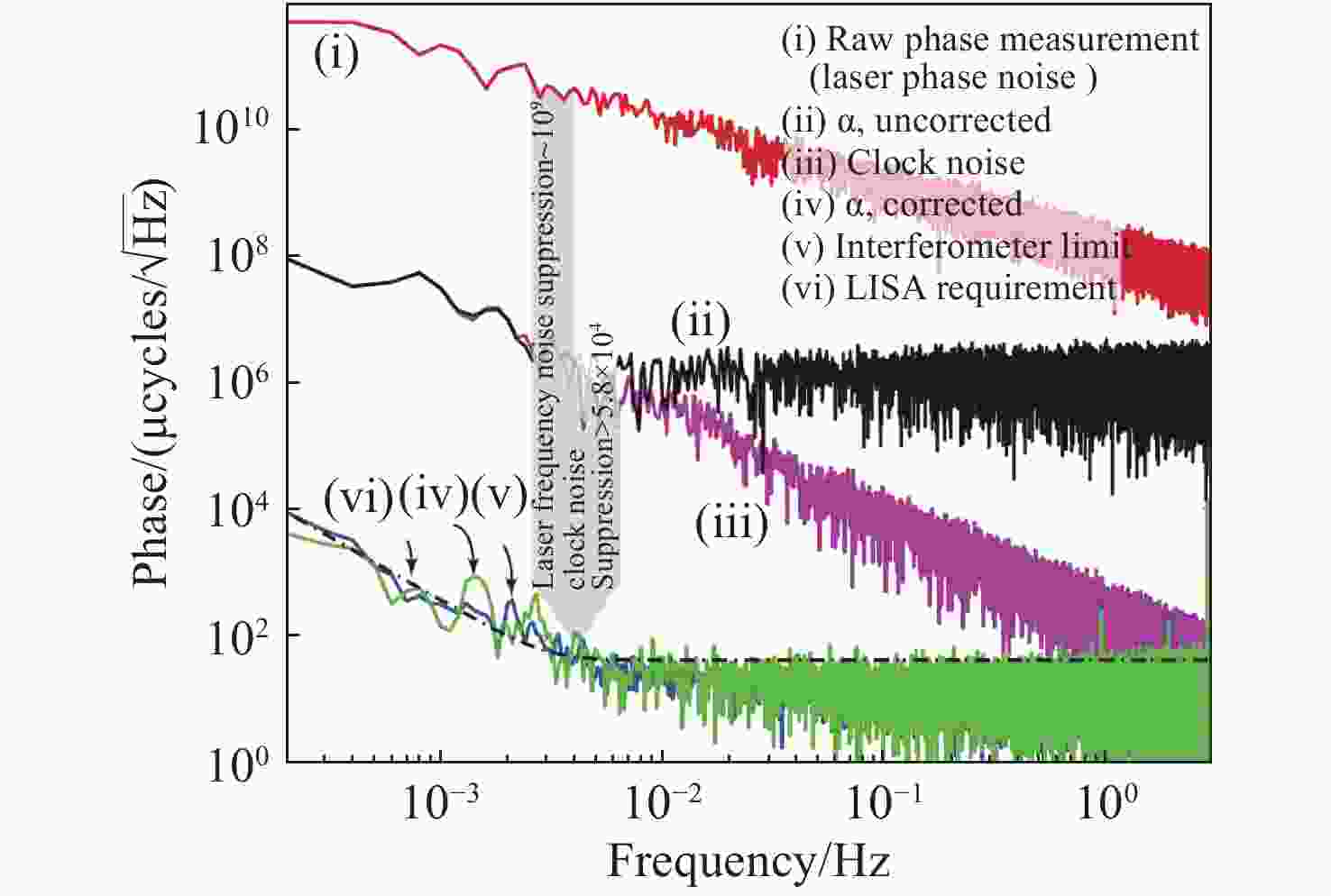
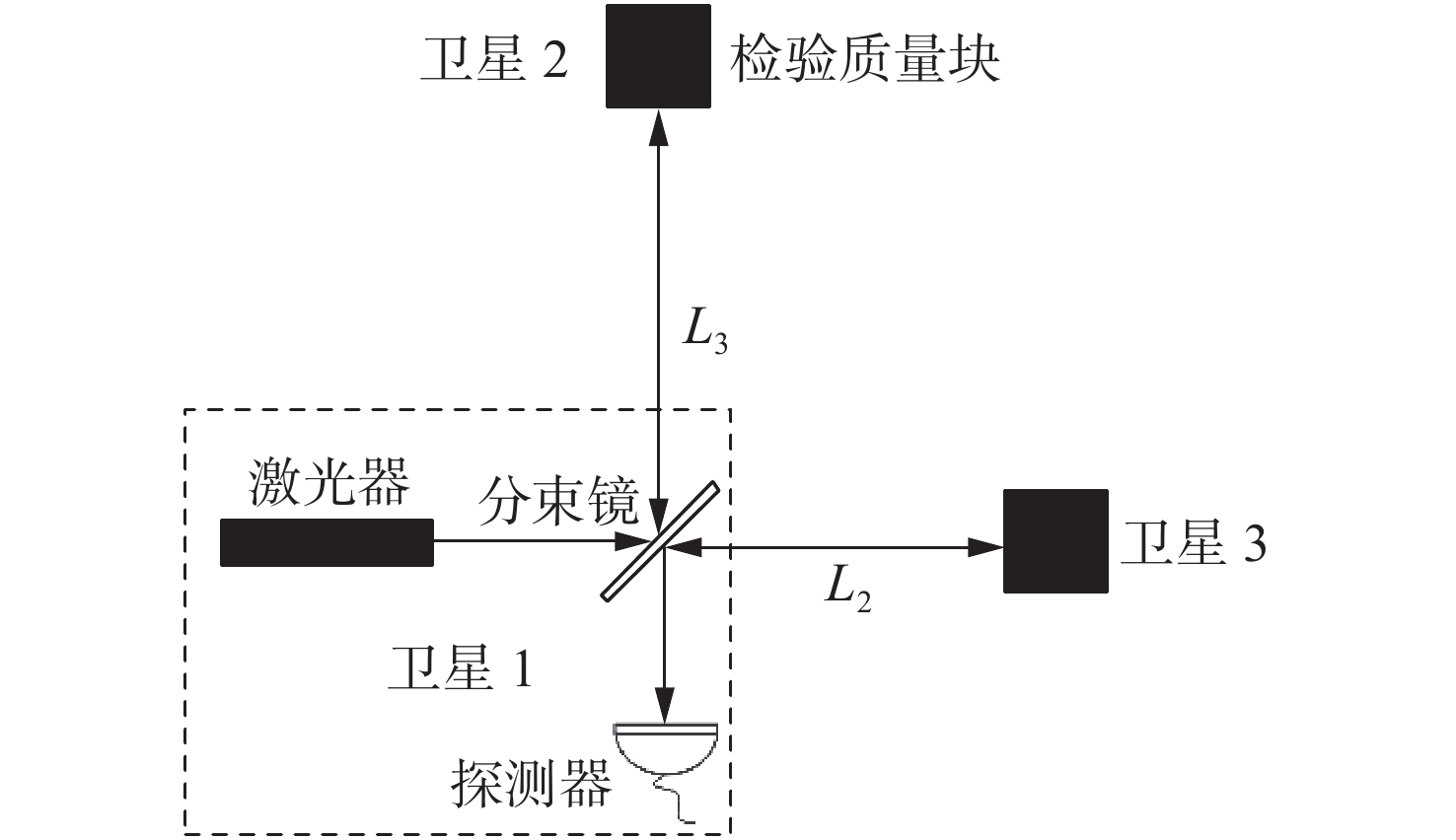
| [1] |
ABBOTT B P, ABBOTT R, ABBOTT T D et al. Observation of gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2016, 116(6): 061102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.061102
|
| [2] |
ABBOTT B P, ABBOTT R, ABBOTT T D et al. GW170817: Observation of gravitational waves from a binary neutron star inspiral[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2017, 119(16): 161101.
|
| [3] |
BARACK L, CARDOSO V, NISSANKE S, et al. Black holes, gravitational waves and fundamental physics: a roadmap[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2019, 36(14): 143001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/ab0587
|
| [4] |
DANZMANN K, RUDIGER A. LISA technology-concept, status, prospects[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2003, 20(10): S1-S9. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/20/10/301
|
| [5] |
WANNER G. Space-based gravitational wave detection and how LISA Pathfinder successfully paved the way[J]. Nature Physics, 2019, 15(3): 200-202. doi: 10.1038/s41567-019-0462-3
|
| [6] |
ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, BAIRD J, et al. LISA pathfinder platform stability and drag-free performance[J]. Physical Review D, 2019, 99(8): 082001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.99.082001
|
| [7] |
ABICH K, BRAXMAIER C, GOHLKE M, et al. In-orbit performance of the GRACE follow-on laser ranging interferometer[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 123(3): 031101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.031101
|
| [8] |
王智, 沙巍, 陈哲, 等. 空间引力波探测望远镜初步设计与分析[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(1):131-151. doi: 10.3788/co.20181101.0131WANG ZH, SHA W, CHEN ZH, et al. Preliminary design and analysis of telescope for space gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(1): 131-151. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20181101.0131
|
| [9] |
LUO Z R, LIU H SH, JIN G. The recent development of interferometer prototype for Chinese gravitational wave detection pathfinder mission[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2018, 105: 146-151.
|
| [10] |
刘河山, 高瑞弘, 罗子人, 等. 空间引力波探测中的绝对距离测量及通信技术[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(3):486-492. doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0486LIU H SH, GAO R H, LUO Z R, et al. Laser ranging and data communication for space gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 486-492. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0486
|
| [11] |
LI Y P, LIU H SH, ZHAO Y, et al. Demonstration of an ultraprecise optical bench for the Taiji space gravitational wave detection pathfinder mission[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(10): 2087. doi: 10.3390/app9102087
|
| [12] |
罗子人, 张敏, 靳刚, 等. 中国空间引力波探测“太极计划”及“太极1号”在轨测试[J]. 深空探测学报,2020,7(1):3-10.LUO Z R, ZHANG M, JIN G, et al. Introduction of Chinese space-borne gravitational wave detection program “Taiji” and “Taiji-1” satellite mission[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2020, 7(1): 3-10. (in Chinese)
|
| [13] |
LUO J, CHEN L SH, DUAN H Z, et al. TianQin: a space-borne gravitational wave detector[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2016, 33(3): 035010. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/33/3/035010
|
| [14] |
SHI CH F, BAO J H, WANG H T, et al. Science with the TianQin observatory: preliminary results on testing the no-hair theorem with ringdown signals[J]. Physical Review D, 2019, 100(4): 044036. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.100.044036
|
| [15] |
ZHANG J Y, MING M, JIANG Y Z, et al. Inter-satellite laser link acquisition with dual-way scanning for Space Advanced Gravity Measurements mission[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89(6): 064501. doi: 10.1063/1.5019433
|
| [16] |
FALLER J E, BENDER P L. A possible laser gravitational wave experiment in space[C]. Program and Abstracts of Second International Conference on Precision Measurement and Fundamental Constants (PMFC-II), National Bureau of Standards, 1981: 689-690.
|
| [17] |
TINTO M, DHURANDHAR S V. Time-delay interferometry[J]. Living Reviews in Relativity, 2014, 17: 6. doi: 10.12942/lrr-2014-6
|
| [18] |
ESTABROOK F B, TINTO M, ARMSTRONG J W. Time-delay analysis of LISA gravitational wave data: elimination of spacecraft motion effects[J]. Physical Review D, 2000, 62(4): 042002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.62.042002
|
| [19] |
TINTO M, ESTABROOK F B, ARMSTRONG J W. Time-delay interferometry for LISA[J]. Physical Review D, 2002, 65(8): 082003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.65.082003
|
| [20] |
TINTO M, HARTWIG O. Time-delay interferometry and clock-noise calibration[J]. Physical Review D, 2018, 98(4): 042003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.98.042003
|
| [21] |
DE VINE G, RABELING D S, SLAGMOLEN B J J, et al. Picometer level displacement metrology with digitally enhanced heterodyne interferometry[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(2): 828-837. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.000828
|
| [22] |
DE VINE G, WARE B, MCKENZIE K, et al. Experimental demonstration of time-delay interferometry for the laser interferometer space antenna[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 104(21): 211103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.211103
|
| [23] |
SPERO R, BACHMAN B, DE VINE G, et al. Progress in interferometry for LISA at JPL[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2011, 28(9): 094007. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/28/9/094007
|
| [24] |
ESTEBAN J J, GARCÍA A F, BARKE S, et al. Experimental demonstration of weak-light laser ranging and data communication for LISA[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(17): 15937-15946. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.015937
|
| [25] |
HEINZEL G, ESTEBAN J J, BARKE S, et al. Auxiliary functions of the LISA laser link: ranging, clock noise transfer and data communication[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2011, 28(9): 094008. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/28/9/094008
|
| [26] |
BRAUSE N C. Auxiliary function development for the LISA metrology system[D]. Hannover: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität, 2018.
|
| [27] |
ISLEIF K S. Laser interferometry for LISA and satellite geodesy missions[D]. Hannover: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität, 2018.
|
| [28] |
SCHWARZE T S, BARRANCO G F, PENKERT D, et al. Picometer-stable hexagonal optical bench to verify LISA phase extraction linearity and precision[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 122(8): 081104. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.081104
|
| [29] |
SHEARD B S, GRAY M B, MCCLELLAND D E, et al. Laser frequency stabilization by locking to a LISA arm[J]. Physics Letters A, 2003, 320(1): 9-21. doi: 10.1016/j.physleta.2003.10.076
|
| [30] |
SHADDOCK D, MCKENZIE K, SPERO R, et al.. LISA frequency control white paper[R]. 2009. https://atrium.in2p3.fr/nuxeo/nxfile/default/f6aa40dc-d83b-44b2-9bd7-ee4e93d88c82/file:content/FCSTWhitePaper.pdf.
|
| [31] |
KARLEN L, KUNDERMANN S, TORCHEBOEUF N, et al.. Laser system for the LISA mission[C]. 2019 Joint Conference of the IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium and European Frequency and Time Forum, IEEE, 2019: 1-2.
|
| [32] |
CORNISH N J, HELLINGS R W. The effects of orbital motion on LISA time delay interferometry[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2003, 20(22): 4851-4860. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/20/22/009
|
| [33] |
KULLMANN J. Development of a digital phase measuring system with microradian precision for LISA[D]. Hannover: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität, 2012.
|
| [34] |
GERBERDING O. Phase readout for satellite interferometry[D]. Hannover: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität, 2014.
|
| [35] |
POLLACK S E, STEBBINS R T. Demonstration of the zero-crossing phasemeter with a LISA test-bed interferometer[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2006, 23(12): 4189-4200. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/23/12/014
|
| [36] |
POLLACK S E, STEBBINS R T. A demonstration of LISA laser communication[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2006, 23(12): 4201-4213. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/23/12/015
|
| [37] |
GRÜNING P, HALLOIN H, PRAT P, et al. Status of the eLISA on table (LOT) electro-optical simulator for space based, long arms interferometers[J]. Experimental Astronomy, 2015, 39(2): 281-302. doi: 10.1007/s10686-015-9448-z
|
| [38] |
LAPORTE B M, HALLOIN H, BRÉELLE E, et al. Status of the LISA On table experiment: a electro-optical simulator for LISA[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2017, 840: 012014. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/840/1/012014
|
| [39] |
FRANCIS S P, SHADDOCK D A, SUTTON A J, et al. Tone-assisted time delay interferometry on GRACE Follow-On[J]. Physical Review D, 2015, 92(1): 012005. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.92.012005
|





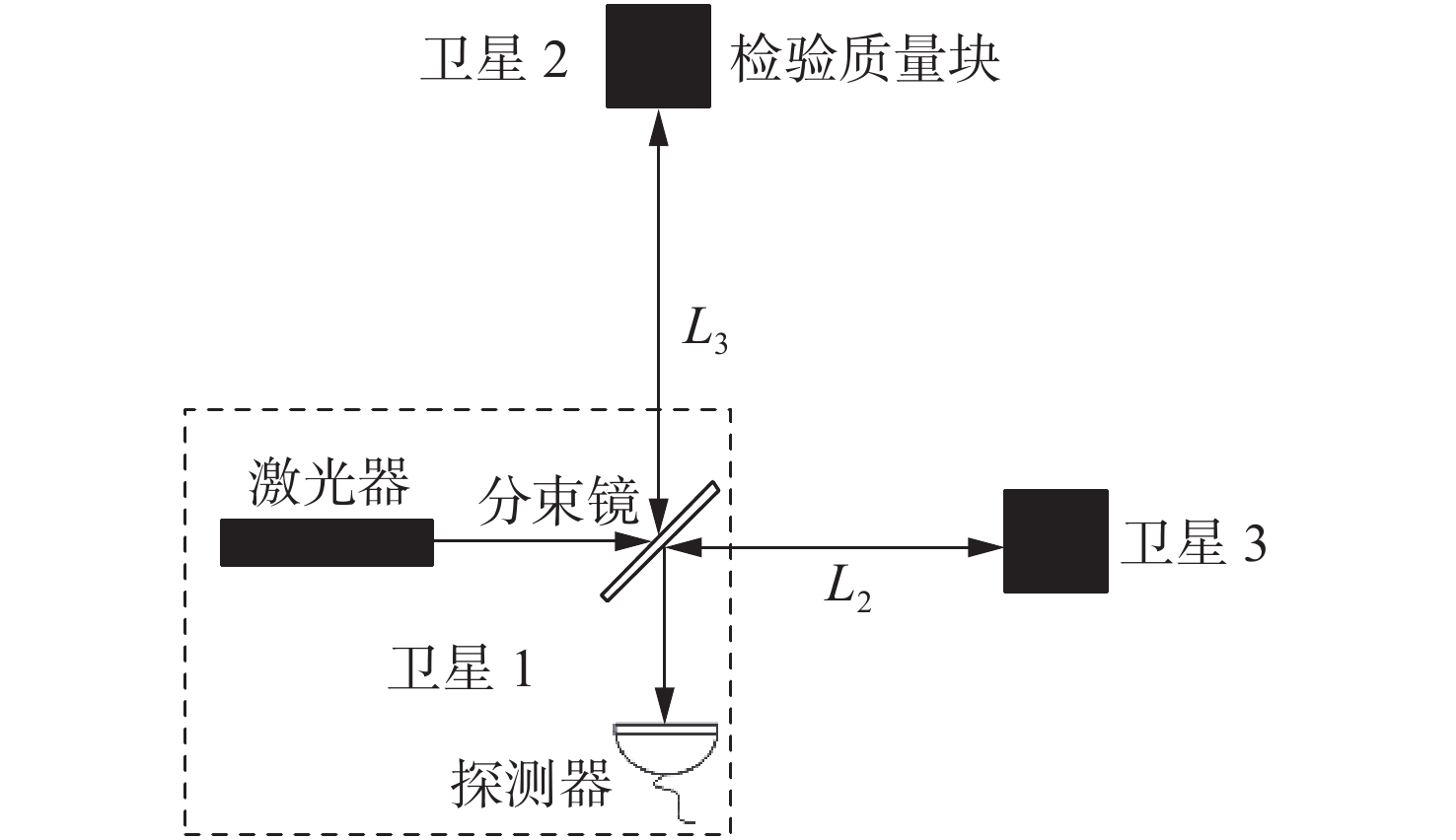
 下载:
下载: