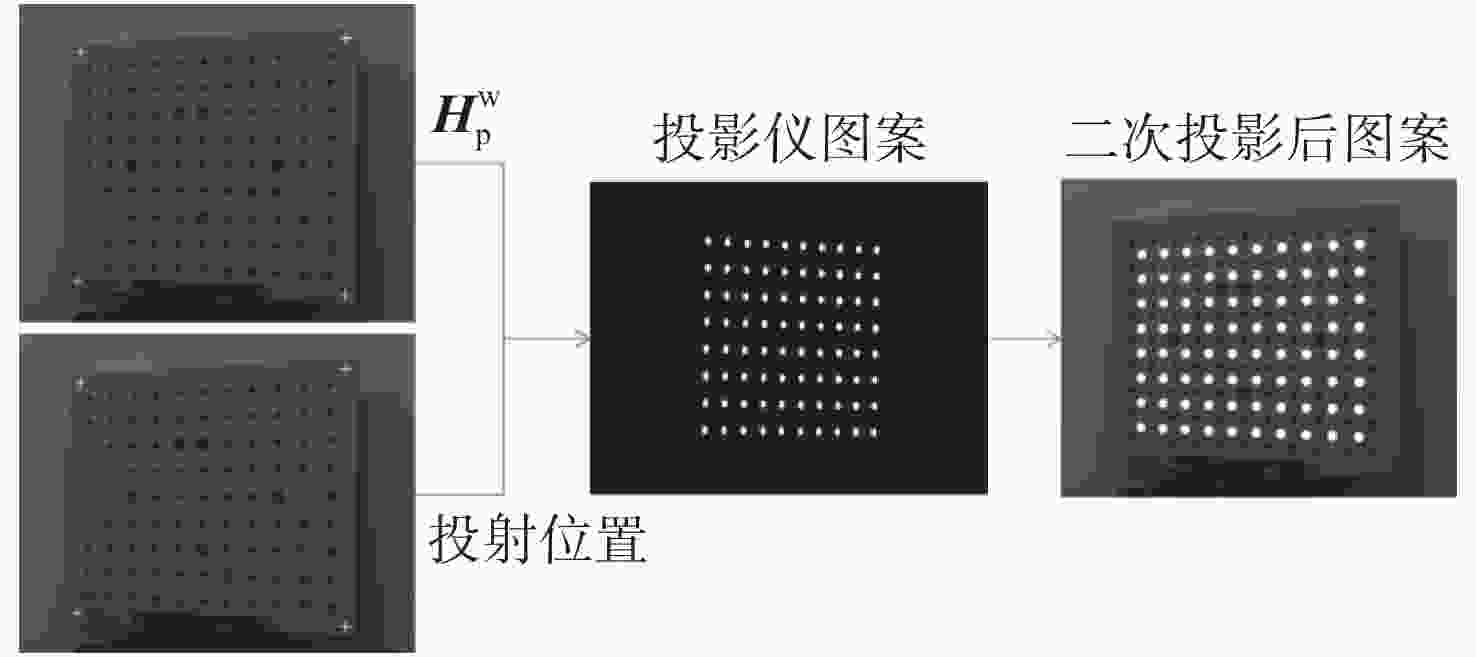
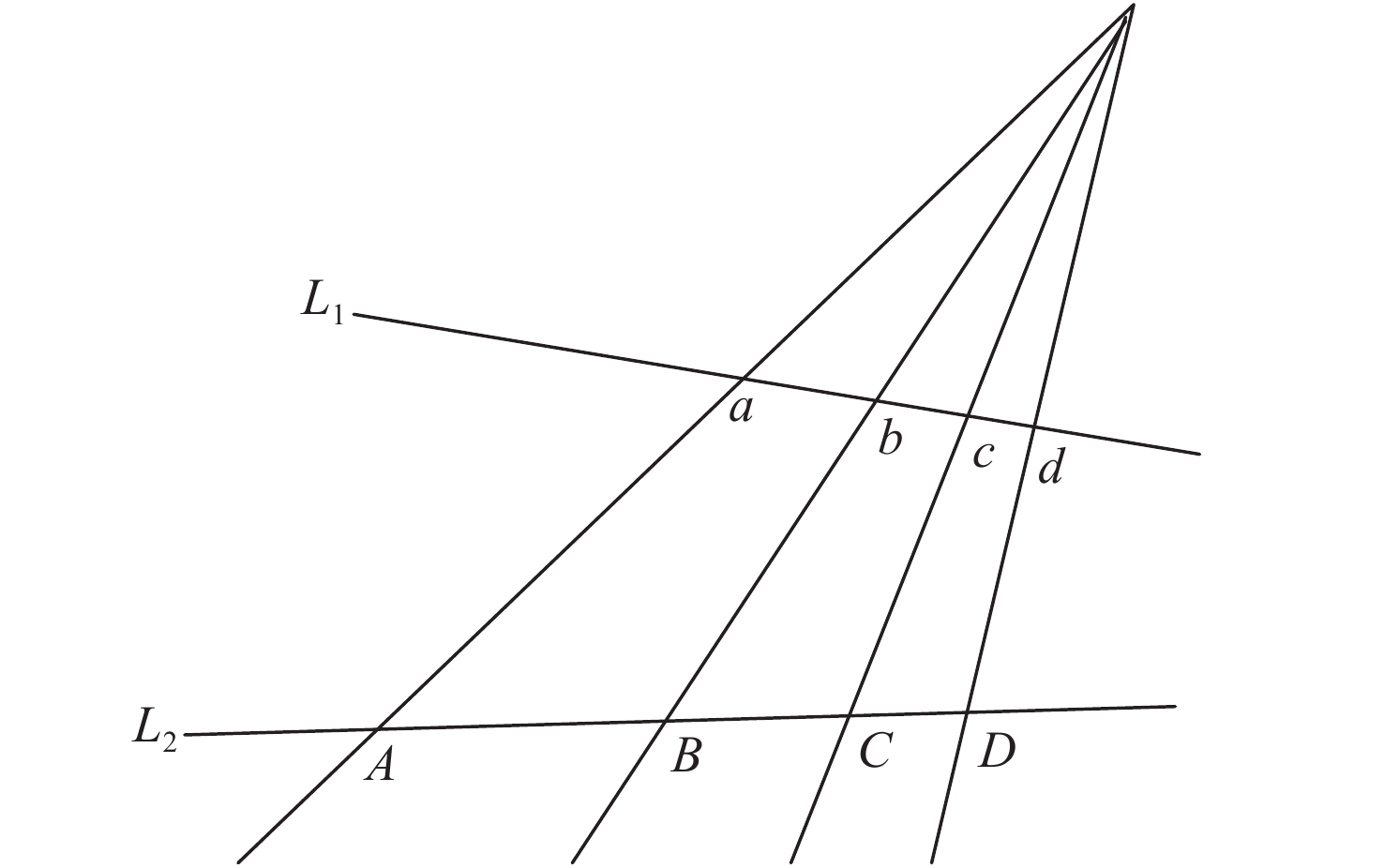
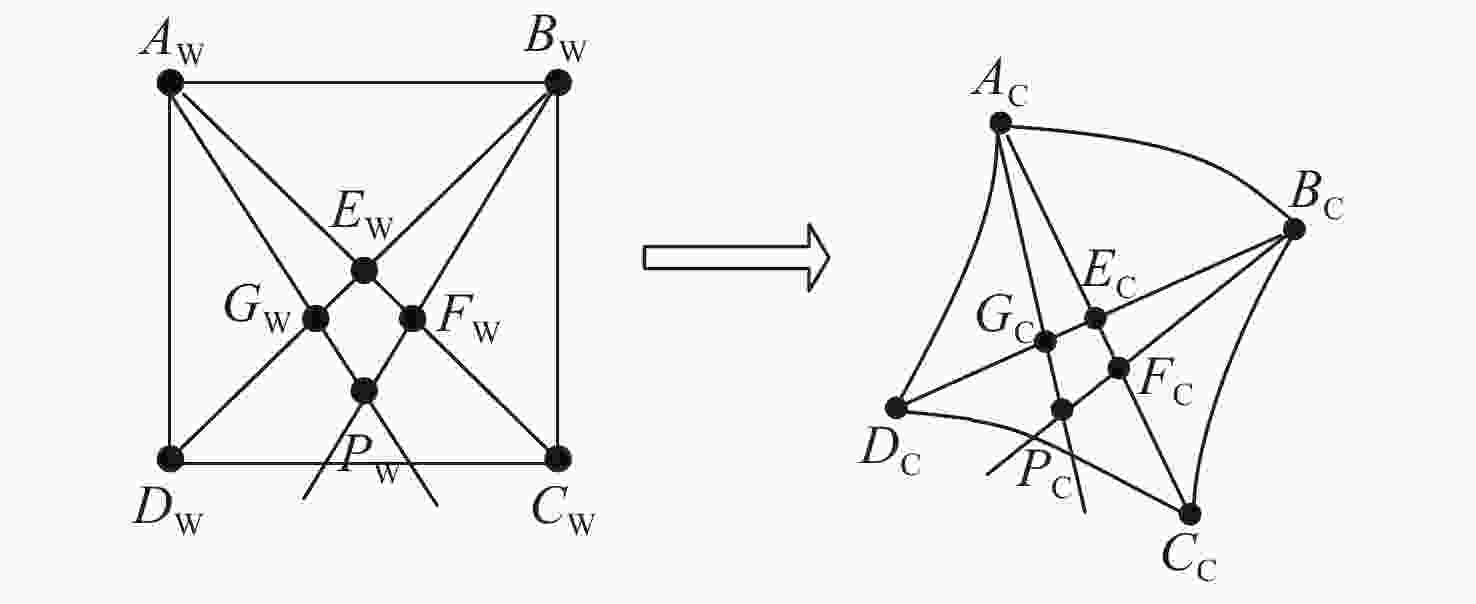
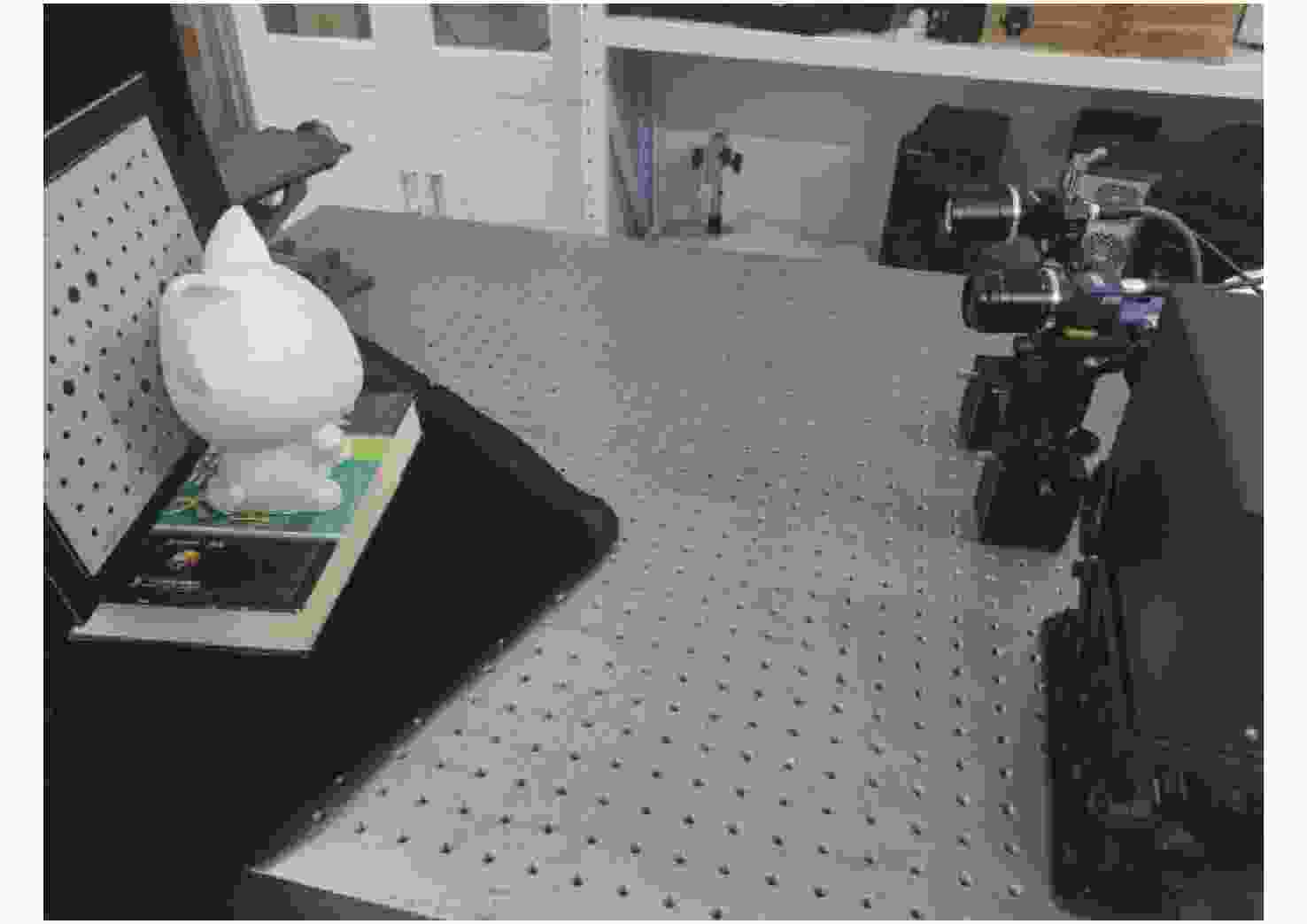
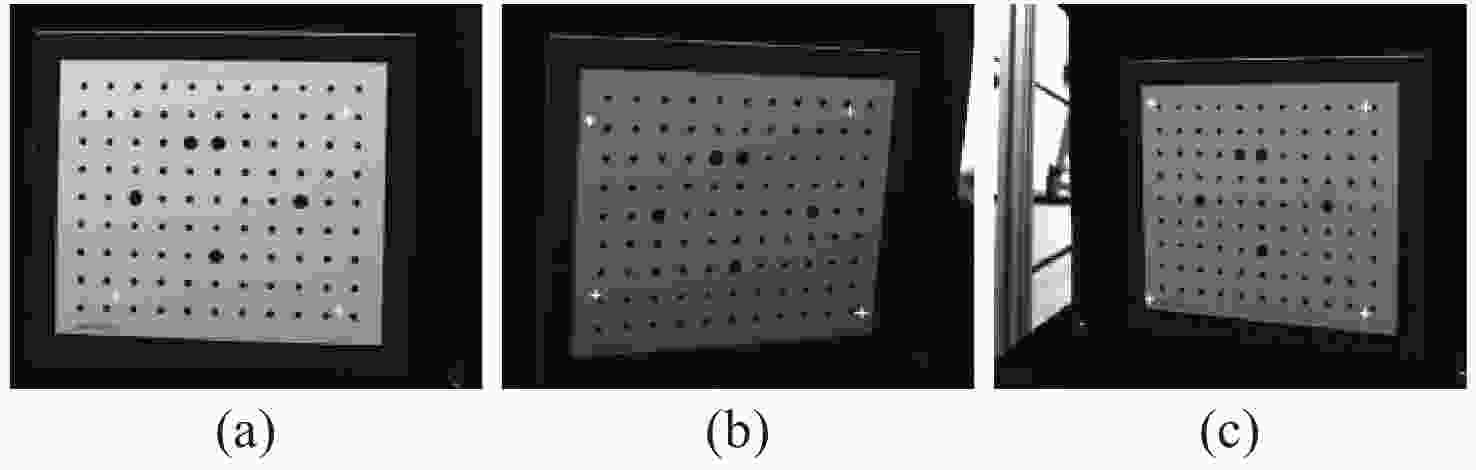
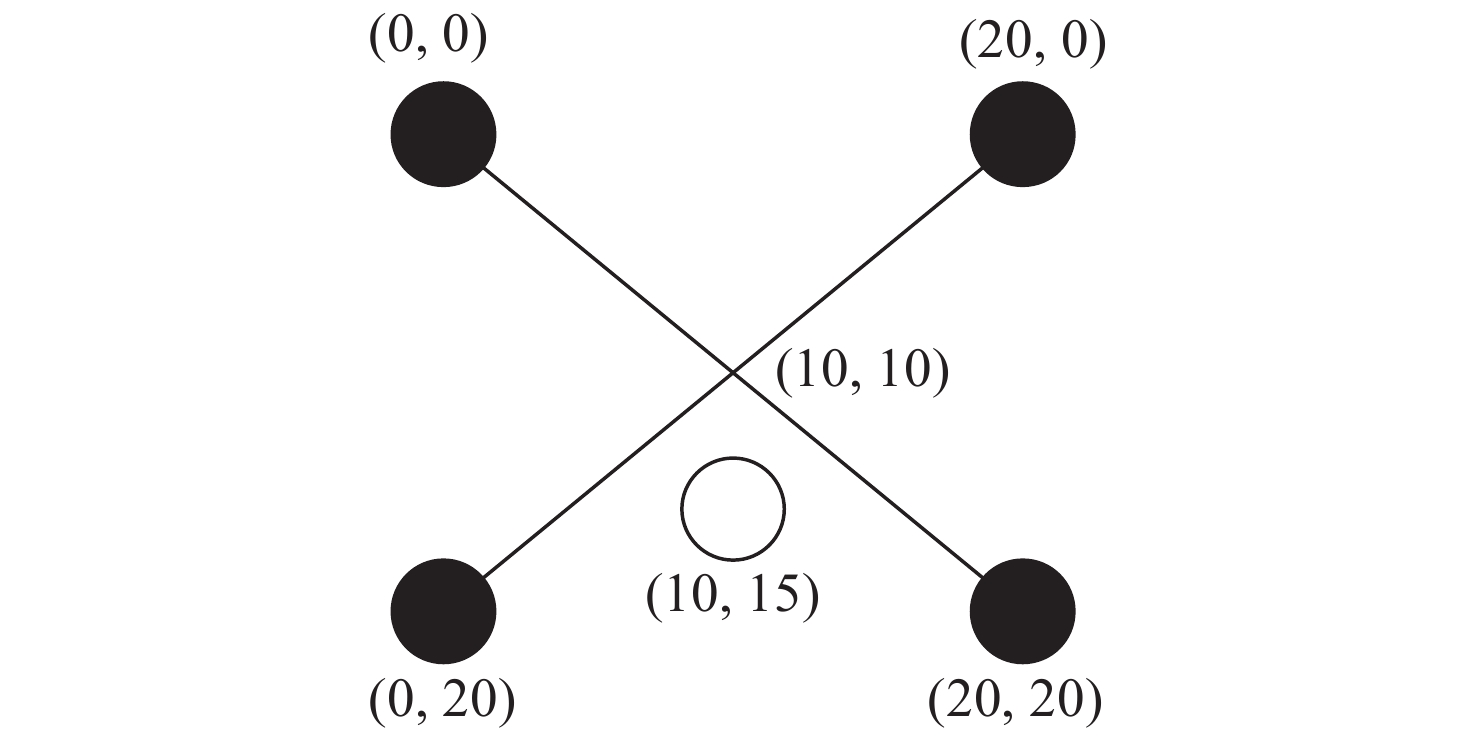
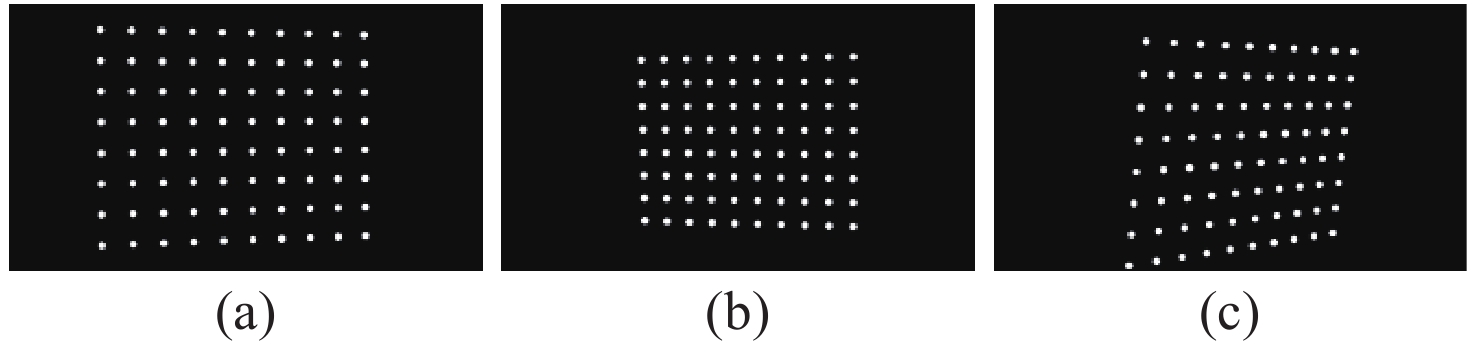
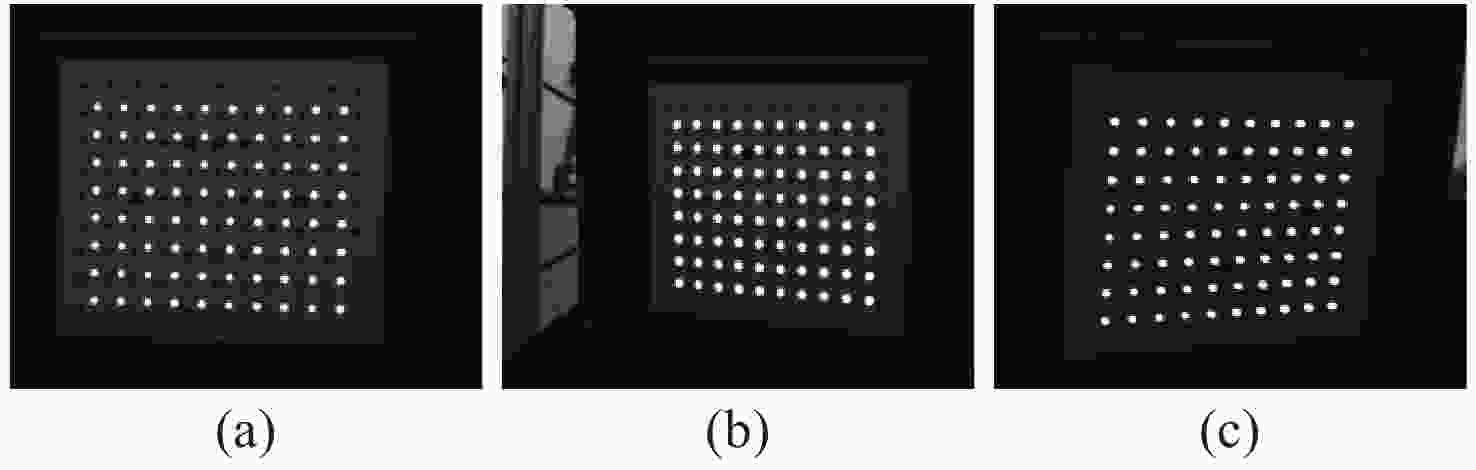
-
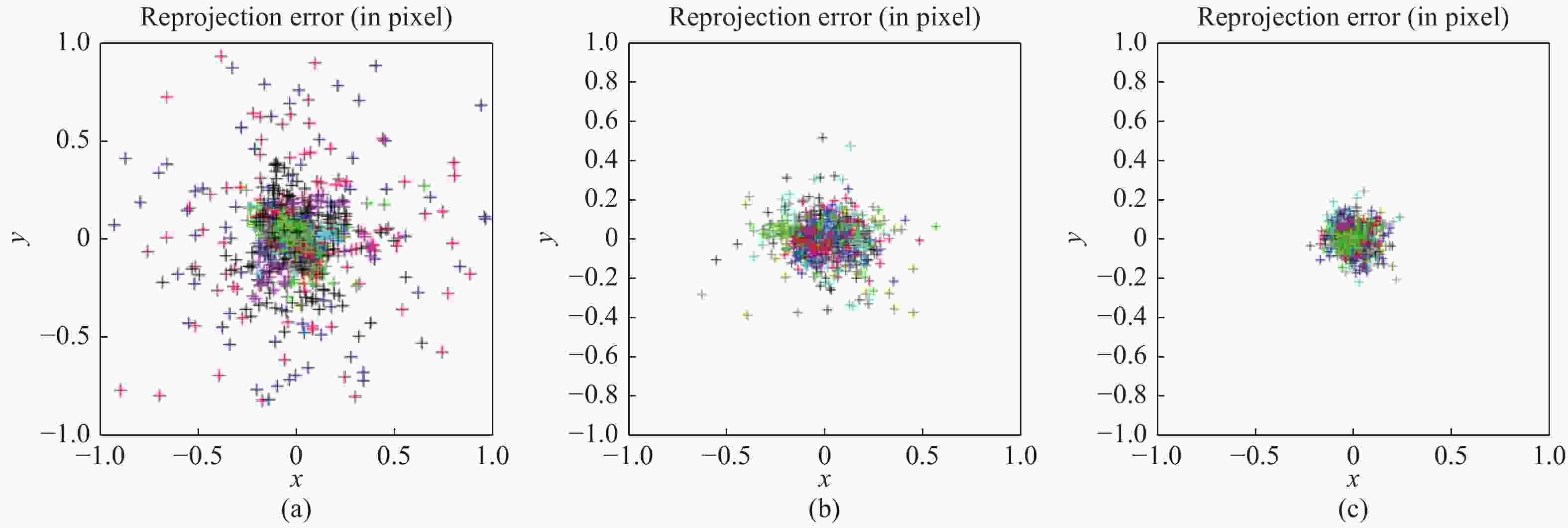
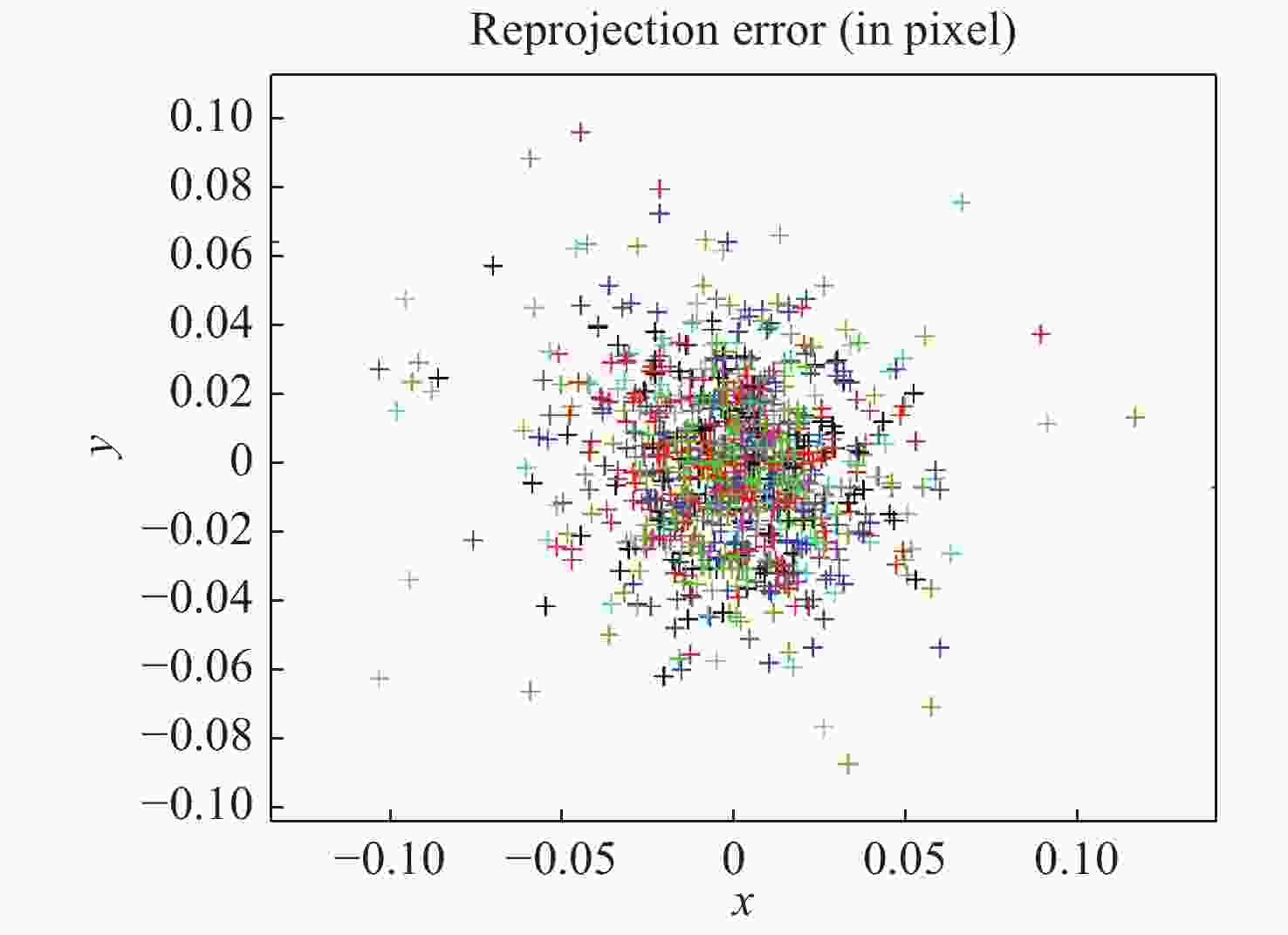
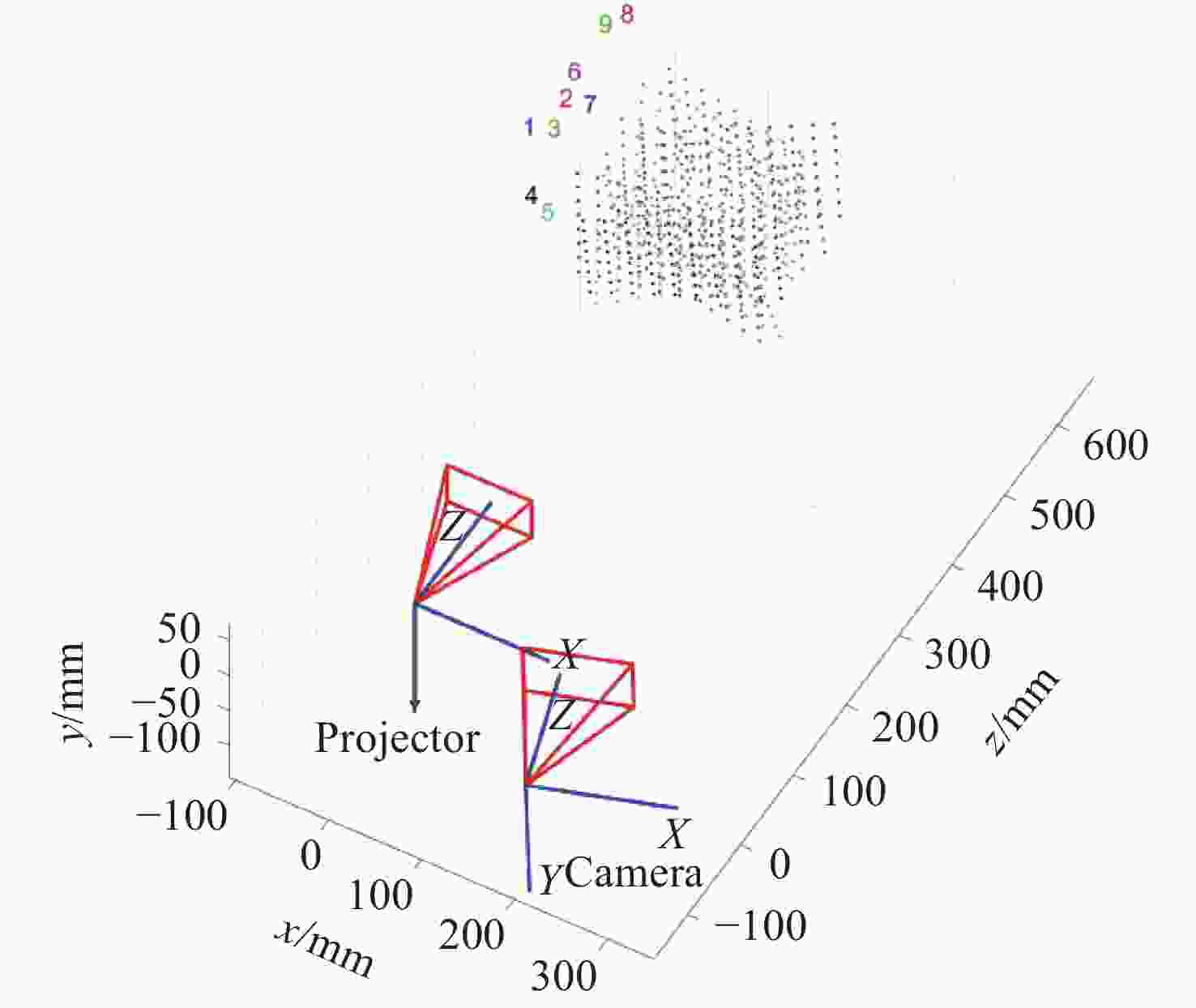
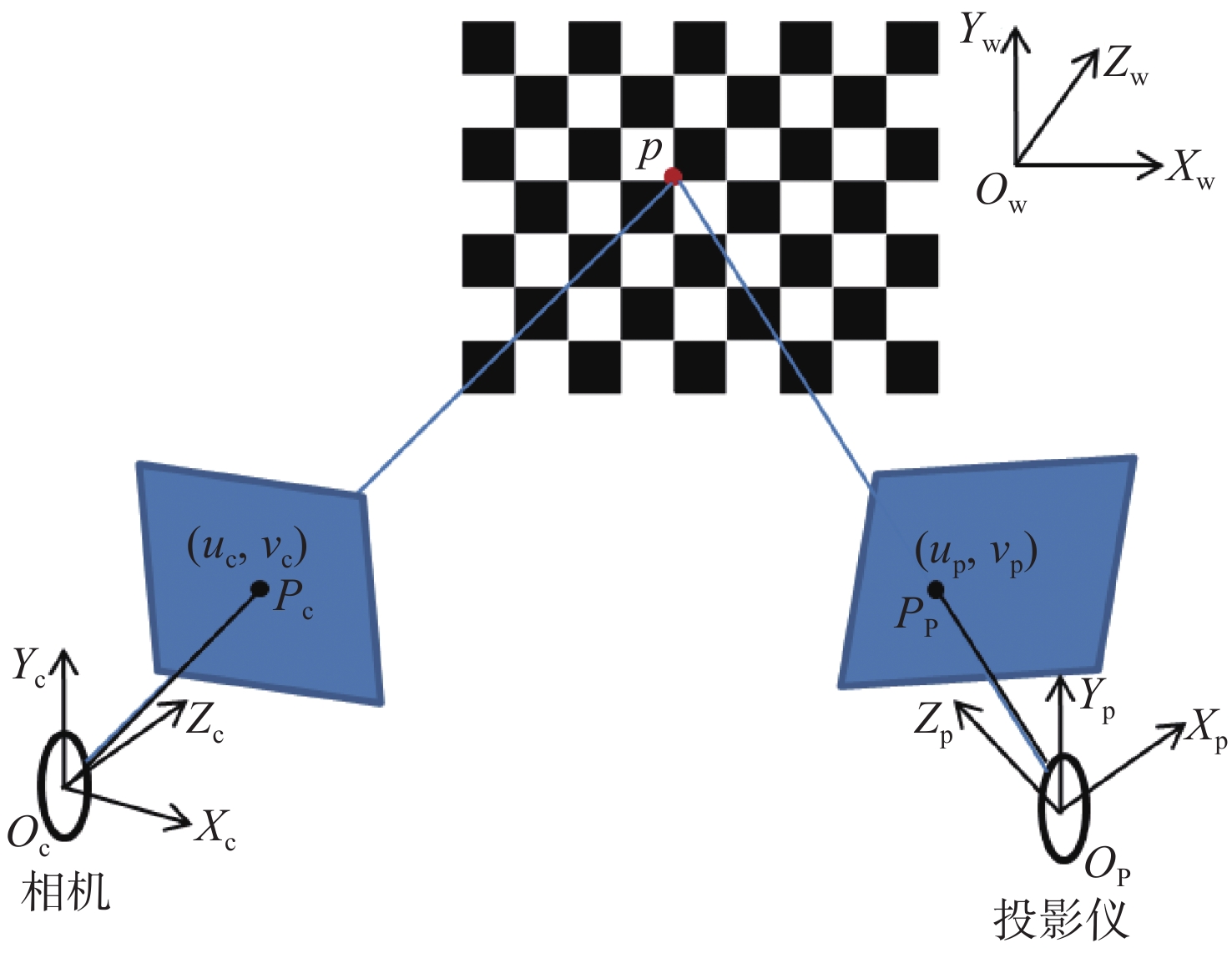
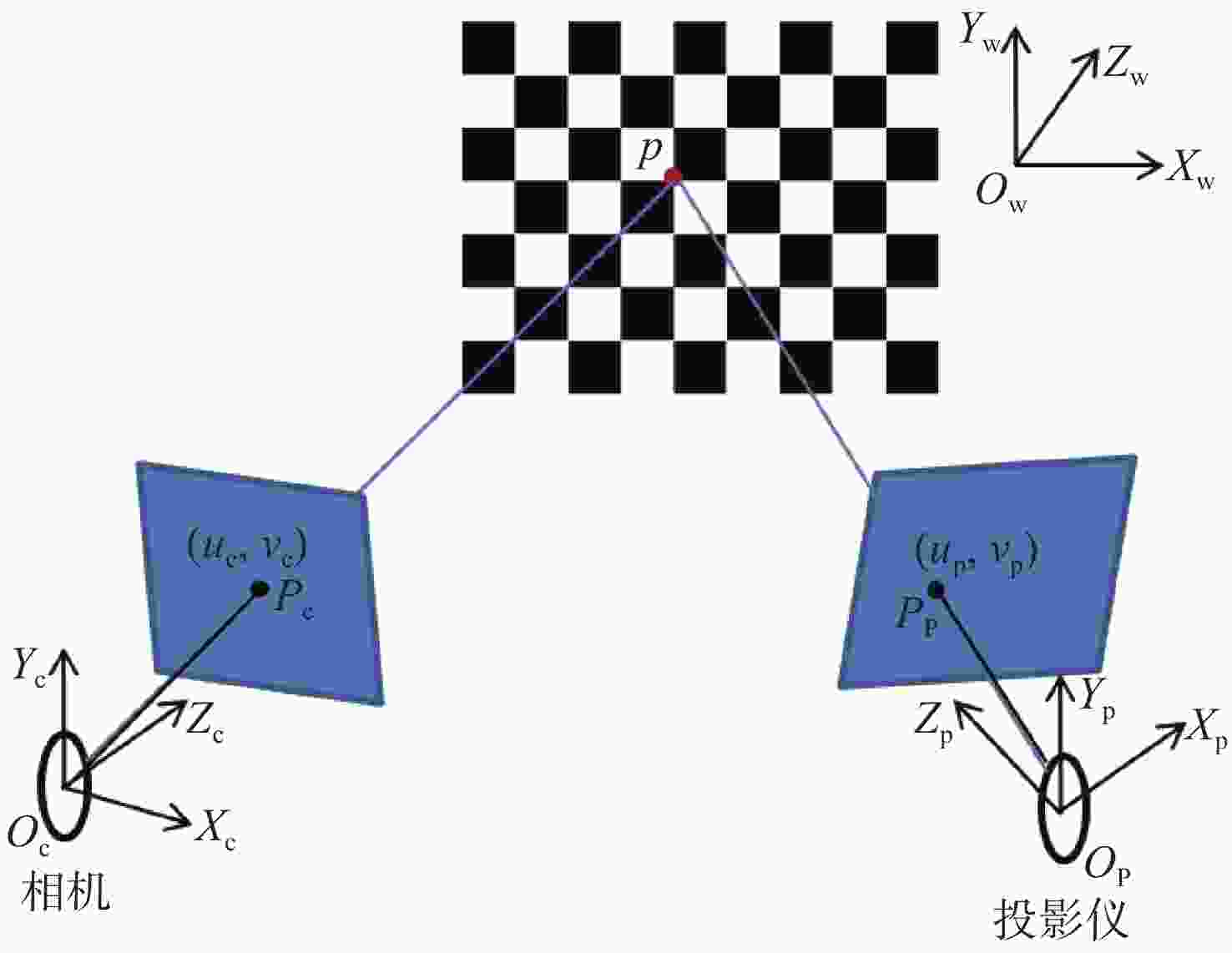
摘要: 提出了一种新的投影仪标定方法以提高数字光栅投影三维测量中投影仪标定的准确性。该方法结合二次投影技术和交比不变性进行投影仪标定。采用二次投影技术解决投射图案与标定板图案互相干扰的问题;采用交比不变性以避免引入相机的标定误差。接着进行了对比实验,以验证所提方法的有效性。选取需要相机参数的传统投影仪标定方法以及根据全局单应性的投影仪标定方法作为对比方法。结果显示,本方法的反投影误差标准差分别从(0.2275, 0.2264)像素和(0.1397, 0.0997)像素降低到(0.0645, 0.0601)像素,反投影误差的最大值分别从1.222像素和0.5617像素降低到0.2421像素。另外,该方法还可同时标定相机,从而获得整个三维测量系统的参数。本文提出的方法可以避免相机标定参数的误差传递,提高投影仪的标定精度。Abstract: In order to improve the accuracy of the projector calibration in 3D shape measurement using digital fringe projection, a new projector calibration method that combines secondary projection technology and cross-ratio invariance is proposed. The secondary projection technology is used to solve the mutual interference between the projection pattern and the calibration pattern, and the cross-ratio invariance method is used to avoid introducing camera calibration error. A comparative experiment is carried out to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. Compared with the traditional method of projector calibration that requires camera parameters and that using global homography, the RMS values of reprojection error of this method is reduced from (0.2275, 0.2264) and (0.1397, 0.0997) pixels to (0.0645, 0.0601) pixels, and the maximum value of the reprojection error is reduced from 1.222 pixels and 0.5617 pixels to 0.2421 pixels. In addition, this method allows the camera to be simultaneously calibrated during operation, and therefore the parameters of the entire 3D measurement system can be acquired. The above results show that the method proposed in this paper can prevent error propagation of camera calibration parameters and improve the calibration accuracy of a projector.
-
表 1 标定的投影仪内部参数
Table 1. Calibrated intrinsic parameters of the projector
(pixel) 方法 参数 fu fv u0 v0 需要相机参数标定法 3033.9020 3037.0319 976.0815 546.6816 全局单应性变换法 3040.3878 3042.7892 993.4626 553.0046 本文方法 3060.7594 3059.8479 1006.0491 540.8452 表 2 标定的投影仪镜头畸变系数
Table 2. Calibrated lens distortion coefficients of the projector
方法 系数 k1 k2 p1 p2 需要相机参数标定法 0.1102 −0.7058 0.0025 −0.0050 全局单应性变换法 0.0215 −0.4157 0.0033 −0.0014 本文方法 −0.1065 0.0058 0.0011 −0.0007 表 3 几种方法的反投影误差
Table 3. Reprojection errors of different methods (pixel)
x轴(MAX) y轴(MAX) x轴(STD) y轴(STD) 需要相机参数标定法 1.222 1.022 0.2275 0.2264 全局单应性变换法 0.5617 0.5130 0.1397 0.0997 本文方法 0.2345 0.2421 0.0645 0.0601 表 4 相机内部参数和畸变系数标定结果
Table 4. Calibration results of camera intrinsic parameters and distortion coefficients
fu fv u0 v0 k1 k2 p1 p2 2644.92 2644.11 646.56 508.34 −0.222 0.313 −0.0001 0.0001 -
[1] ZHANG S. High-speed 3D shape measurement with structured light methods: a review[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2018, 106: 119-131. [2] 安东, 陈李, 丁一飞, 等. 光栅投影相位法系统模型及标定方法[J]. 中国光学,2015,8(2):248-254. doi: 10.3788/co.20150802.0248AN D, CHEN L, DING Y F, et al. Optical system model and calibration of grating projection phase method[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(2): 248-254. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20150802.0248 [3] 孟晓亮, 于晓洋, 吴海滨, 等. 基于三维傅里叶变换的胸腹表面测量[J]. 光学 精密工程,2018,26(4):778-787. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182604.0778MENG X L, YU X Y, WU H B, et al. Measurement of thoraco-abdominal surface using 3D Fourier transform[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(4): 778-787. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182604.0778 [4] 张旭, 邵双运, 祝祥, 等. 光学三维扫描仪光强传递函数的测量和校正[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(1):123-130. doi: 10.3788/co.20181101.0123ZHANG X, SHAO SH Y, ZHU X, et al. Measurement and calibration of the intensity transform function of the optical 3D profilometry system[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(1): 123-130. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20181101.0123 [5] 吴坤帅, 魏仲慧, 何昕, 等. 基于笔划三维深度特征的签名识别[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(10):1013-1020. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193410.1013WU K SH, WEI ZH H, HE X, et al. Signatures recognition based on strokes 3 D depth feature[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(10): 1013-1020. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193410.1013 [6] 马国庆, 刘丽, 于正林, 等. 大型复杂曲面三维形貌测量及应用研究进展[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(2):214-228. doi: 10.3788/co.20191202.0214MA G Q, LIU L, YU ZH L, et al. Application and development of three-dimensional profile measurement for large and complex surface[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(2): 214-228. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191202.0214 [7] 任国印, 吕晓琪, 杨楠, 等. 心脏体素化三维模型感兴趣血管交互式显示方法研究[J]. 液晶与显示,2018,33(5):433-442. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20183305.0433REN G Y, LV X Q, YANG N, et al. Interactive display methods of vessel of interest within voxelized three-dimensional cardiac model[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2018, 33(5): 433-442. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20183305.0433 [8] ZHANG ZH Y. A flexible new technique for camera calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000, 22(11): 1330-1334. doi: 10.1109/34.888718 [9] 王谭, 王磊磊, 张卫国, 等. 基于张正友标定法的红外靶标系统[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(8):1828-1835. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192708.1828WANG T, WANG L L, ZHANG W G, et al. Design of infrared target system with Zhang Zhengyou calibration method[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(8): 1828-1835. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192708.1828 [10] 赵亚凤, 胡峻峰. 一种双正交消隐点的双目相机标定方法[J]. 液晶与显示,2016,31(10):958-966. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20163110.0958ZHAO Y F, HU J F. Binocular self calibration using two pairs of orthogonal vanishing points[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2016, 31(10): 958-966. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20163110.0958 [11] DAVIES E R. 计算机与机器视觉: 理论、算法与实践[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2013.DAVIES E R. Computer and Machine Vision: Theory, Algorithms, Practicalities[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2013. (in Chinese). [12] ZHANG S, HUANG P S. Novel method for structured light system calibration[J]. Optical Engineering, 2006, 45(8): 083601. doi: 10.1117/1.2336196 [13] LI ZH W, SHI Y SH, WANG C J, et al. Accurate calibration method for a structured light system[J]. Optical Engineering, 2008, 47(5): 053604. doi: 10.1117/1.2931517 [14] ZHANG W, LI W SH, YU L D, et al. Sub-pixel projector calibration method for fringe projection profilometry[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(16): 19158-19169. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.019158 [15] 吴海滨, 于晓洋. 应用市售设备的结构光系统模型及标定[J]. 光学 精密工程,2008,16(4):617-623.WU H B, YU X Y. Structured light system model using off-the-shelf components and its calibration[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2008, 16(4): 617-623. (in Chinese) [16] AUDET S, OKUTOMI M. A user-friendly method to geometrically calibrate projector-camera systems[C]. 2009 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, IEEE, 2009: 47-54. [17] ANWAR H. Calibrating projector flexibly for a real-time active 3D scanning system[J]. Optik, 2018, 158: 1088-1094. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.01.005 [18] 高治华, 王昭, 黄军辉, 等. 基于射影变换的结构光测量系统中投影仪标定方法[J]. 中国激光,2012,39(10):154-161.GAO ZH H, WANG ZH, HUANG J H, et al. Projector calibration method based on projective transformation for structured light measurement system[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2012, 39(10): 154-161. (in Chinese) [19] HARTLEY R, ZISSERMAN A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003. -





 下载:
下载: