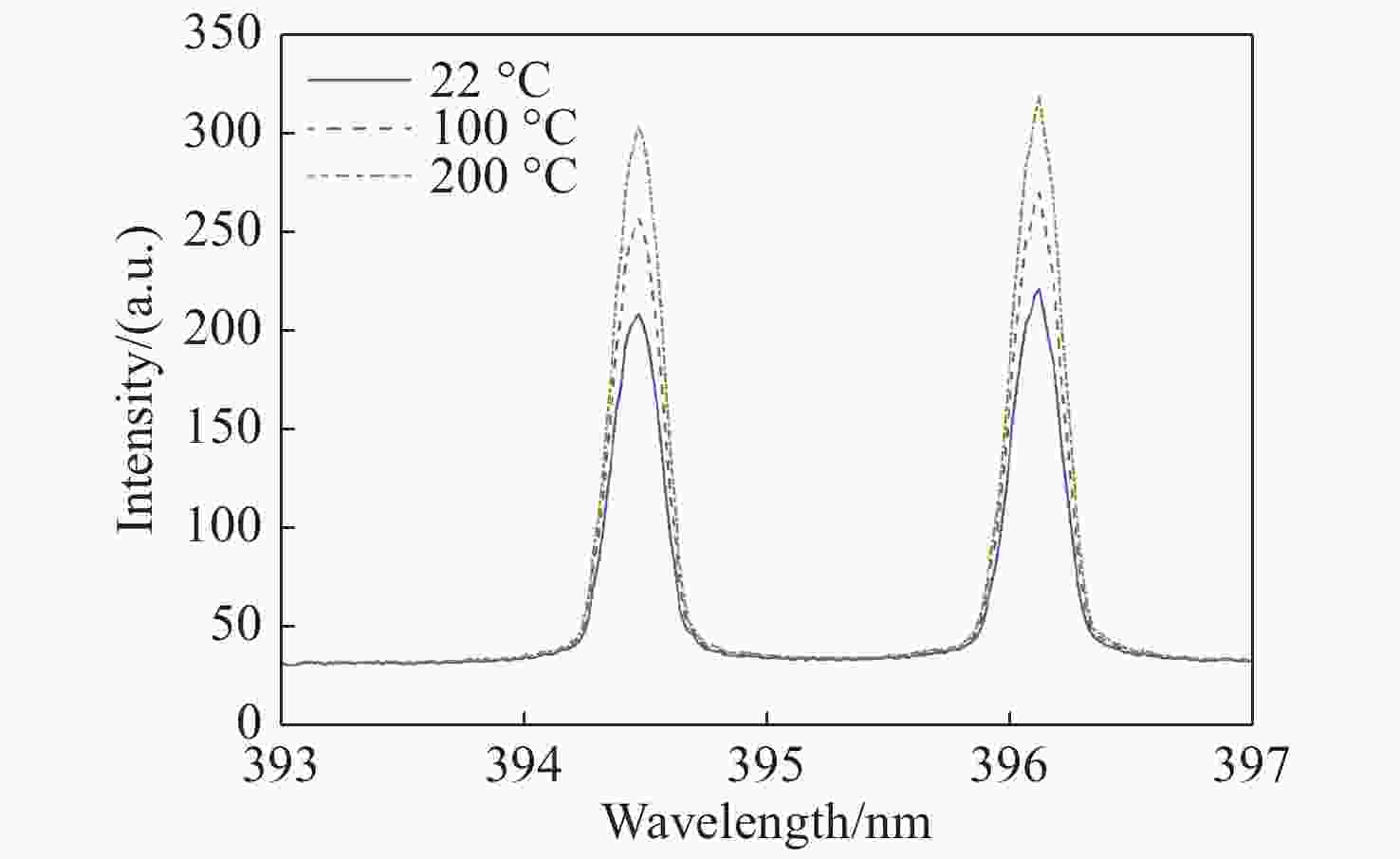
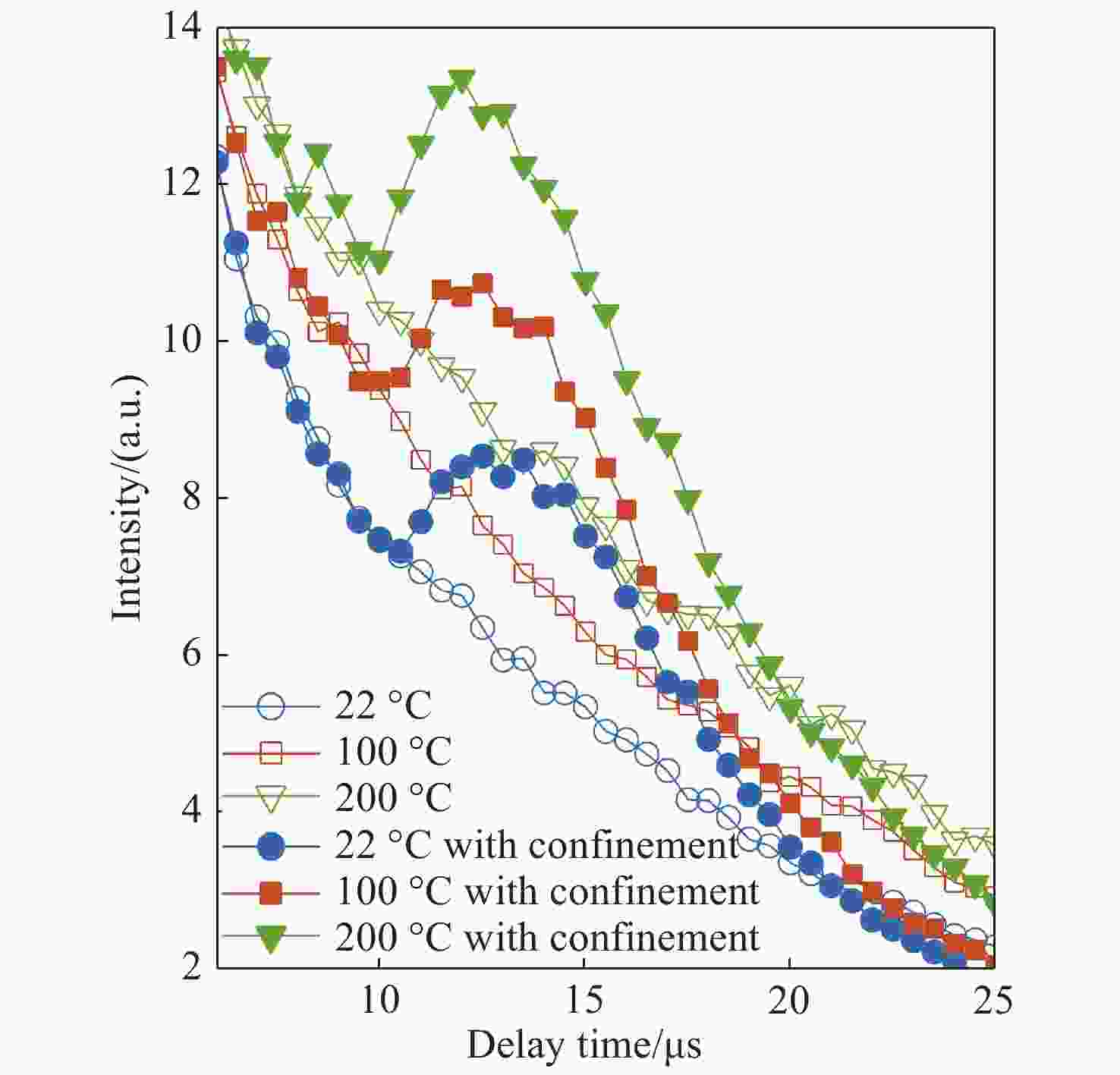
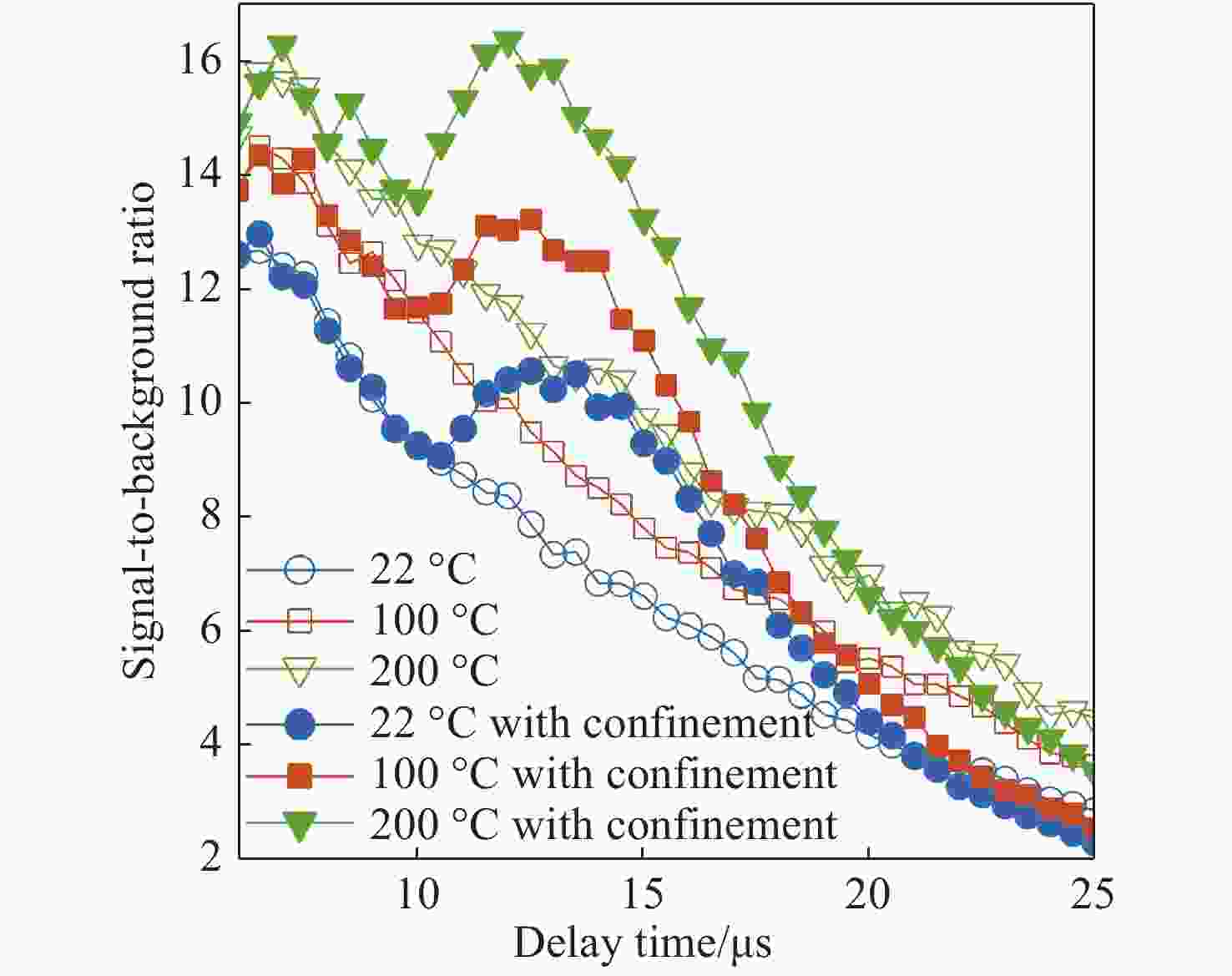
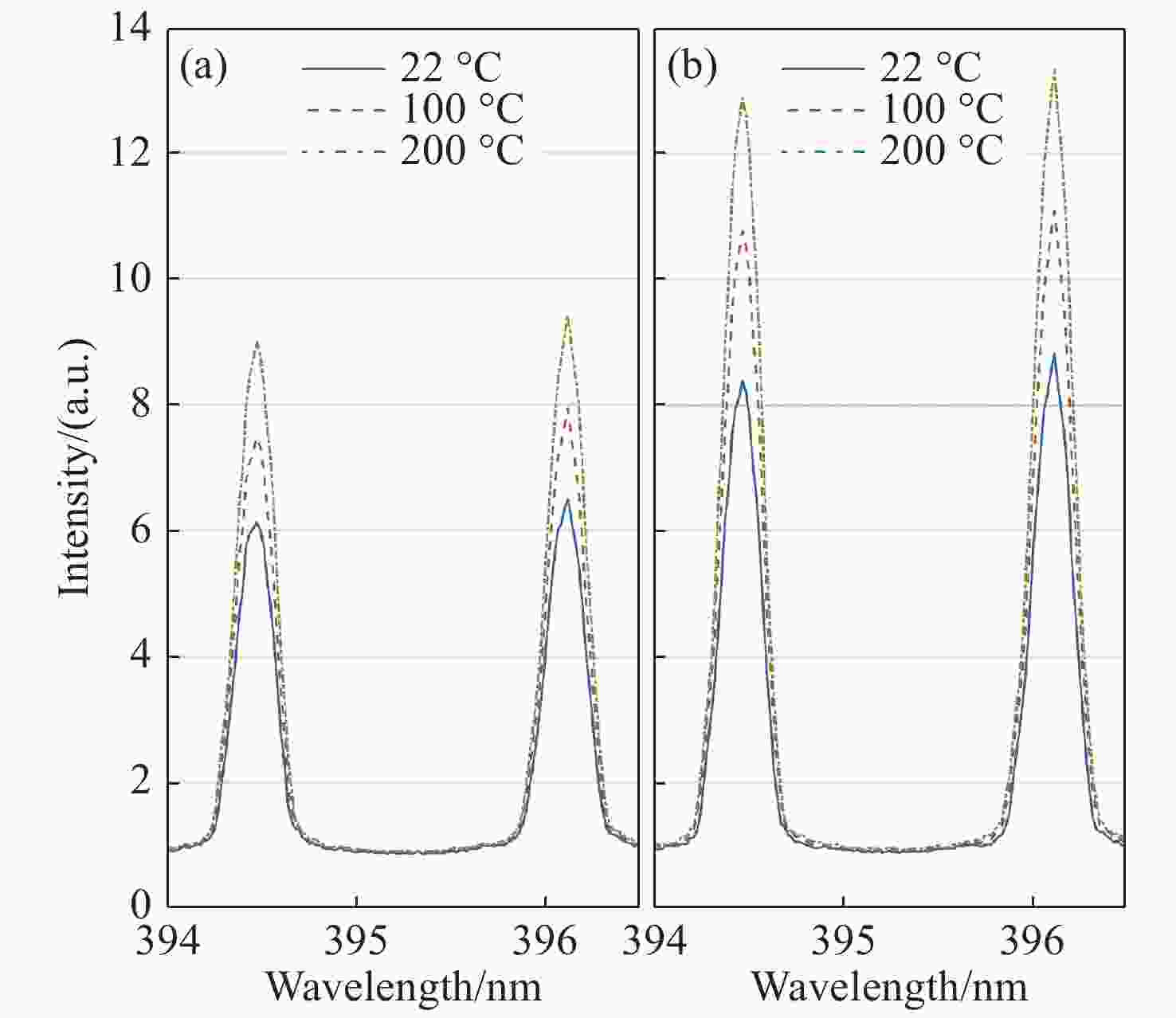
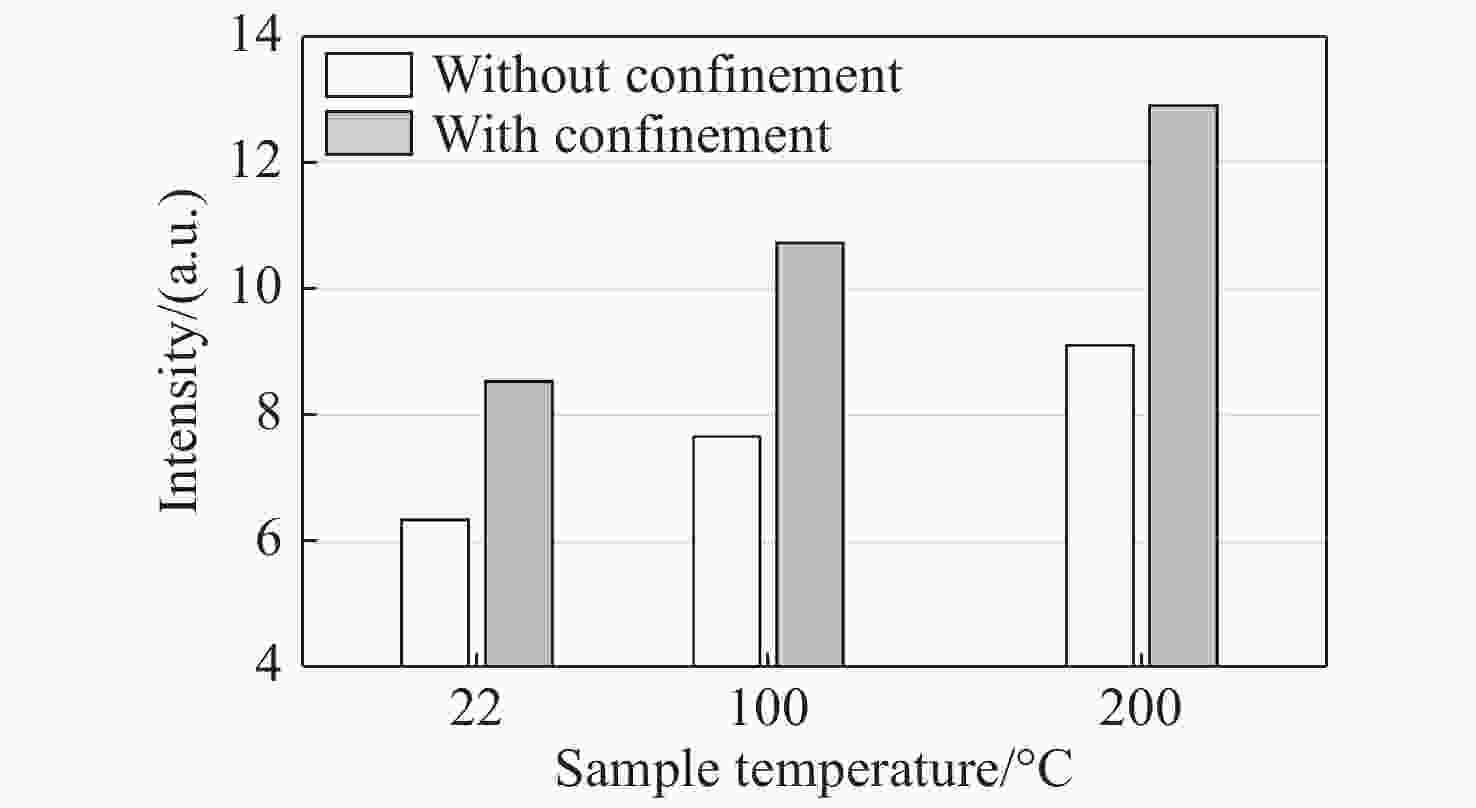
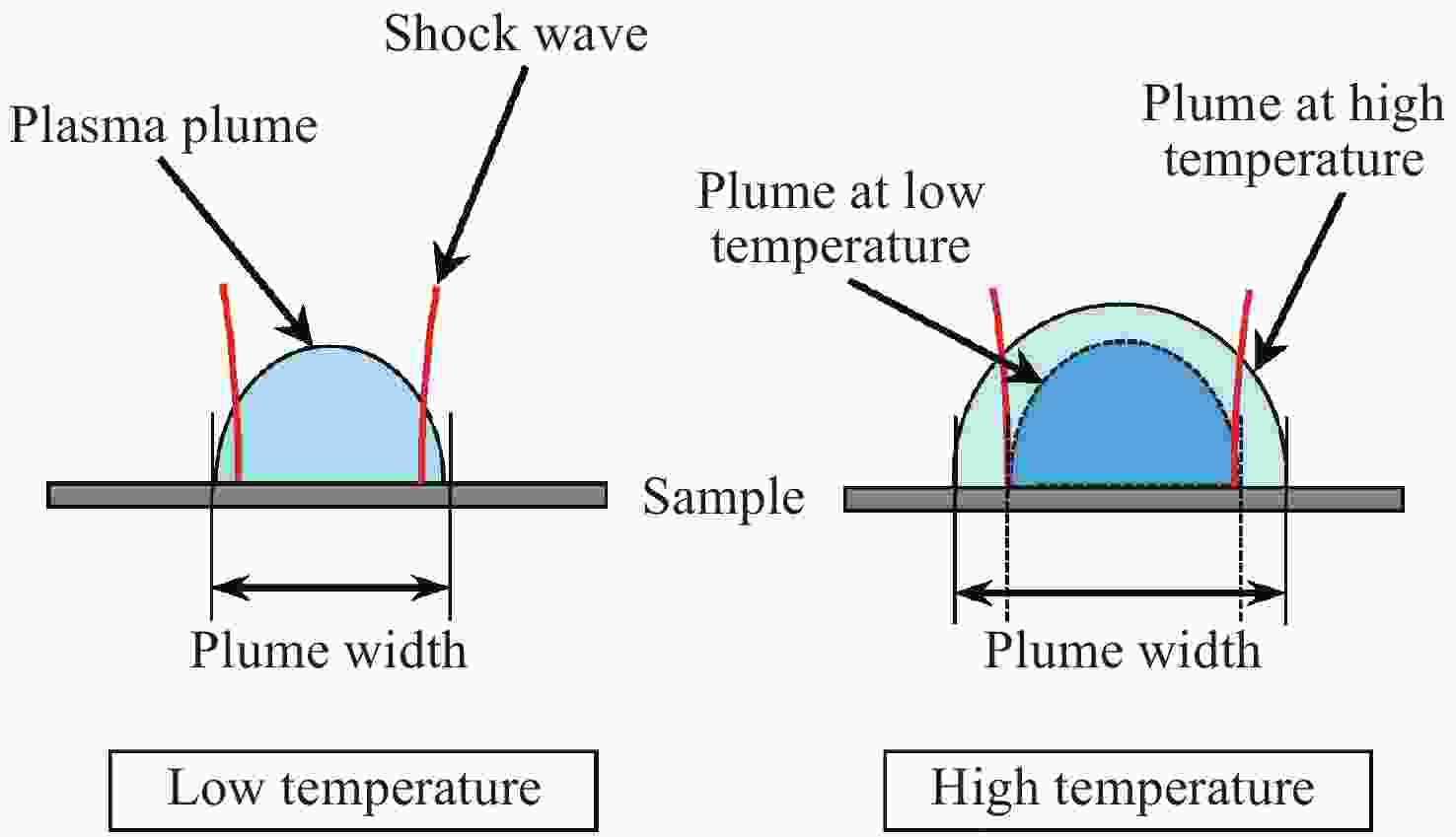
| [1] |
刘津, 孙通, 甘兰萍. 基于内标法和CARS变量优选的倍硫磷含量LIBS检测[J]. 发光学报,2018,39(5):737-744. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183905.0737LIU J, SUN T, GAN L P. Detection of fentshion content by LIBS combined with internal standard and CARS variable selection method[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 39(5): 737-744. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183905.0737
|
| [2] |
王慧丽, 王建伟, 周强, 等. 激光诱导击穿光谱法定量分析水泥中的铜元素[J]. 发光学报,2017,38(11):1553-1558. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20173811.1553WANG H L, WANG J W, ZHOU Q, et al. Quantitative analysis of Cu in cement by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2017, 38(11): 1553-1558. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20173811.1553
|
| [3] |
李占锋, 王芮雯, 邓琥, 等. 黄连、附片和茯苓内铜元素激光诱导击穿光谱分析[J]. 发光学报,2016,37(1):100-105. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20163701.0100LI ZH F, WANG R W, DENG H, et al. Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy of Cu in coptis chinensis, aconite root and poria cocos[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2016, 37(1): 100-105. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20163701.0100
|
| [4] |
李安, 王亮伟, 郭帅, 等. 激光诱导击穿光谱增强机制及技术研究进展[J]. 中国光学,2017,10(5):619-640. doi: 10.3788/co.20171005.0619LI A, WANG L W, GUO SH, et al. Advances in signal enhancement mechanism and technology of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(5): 619-640. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20171005.0619
|
| [5] |
李昂泽, 王宪双, 徐向君, 等. 激光诱导击穿光谱技术对烟草快速分类研究[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(5):1139-1146. doi: 10.3788/co.20191205.1139LI A Z, WANG X SH, XU X J, et al. Fast classification of tobacco based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(5): 1139-1146. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191205.1139
|
| [6] |
王宪双, 郭帅, 徐向君, 等. 基于激光诱导击穿光谱和拉曼光谱对四唑类化合物的快速识别和分类实验研究[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(4):888-895. doi: 10.3788/co.20191204.0888WANG X SH, GUO SH, XU X J, et al. Fast recognition and classification of tetrazole compounds based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(4): 888-895. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191204.0888
|
| [7] |
侯冠宇, 王平, 佟存柱. 激光诱导击穿光谱技术及应用研究进展[J]. 中国光学,2013,6(4):490-500.HOU G Y, WANG P, TONG C ZH. Progress in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and its applications[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(4): 490-500. (in Chinese)
|
| [8] |
WANG Y, CHEN A M, ZHANG D, et al. Enhanced optical emission in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy by combining femtosecond and nanosecond laser pulses[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2020, 27(2): 023507. doi: 10.1063/1.5131772
|
| [9] |
GUO L B, HU W, ZHANG B Y, et al. Enhancement of optical emission from laser-induced plasmas by combined spatial and magnetic confinement[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(15): 14067-14075. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.014067
|
| [10] |
LU Y, ZHOU Y S, QIU W, et al. Magnetic field enhancement for femtosecond-laser-ablation mass spectrometry in ambient environments[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2015, 30(11): 2303-2306. doi: 10.1039/C5JA00225G
|
| [11] |
WANG Y R, JIANG Y H, HE X Y, et al. Triggered parallel discharge in laser-ablation spark-induced breakdown spectroscopy and studies on its analytical performance for aluminum and brass samples[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2018, 150: 9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2018.10.001
|
| [12] |
LIU L, LI S, HE X N, et al. Flame-enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(7): 7686-7693. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.007686
|
| [13] |
YANG F, JIANG L, WANG S M, et al. Emission enhancement of femtosecond laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy by combining nanoparticle and dual-pulse on crystal SiO2[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2017, 93: 194-200.
|
| [14] |
YANG X Y, HAO ZH Q, SHEN M, et al. Simultaneous determination of La, Ce, Pr, and Nd elements in aqueous solution using surface-enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Talanta, 2017, 163: 127-131. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.10.094
|
| [15] |
王旭朝, 郝中骐, 郭连波, 等. 基于共振激发的激光诱导击穿光谱技术研究进展[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2015,35(5):1159-1164.WANG X ZH, HAO ZH Q, GUO L B, et al. Research progress on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy based on resonance excitation[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(5): 1159-1164. (in Chinese)
|
| [16] |
SHEN X K, SUN J, LING H, et al. Spectroscopic study of laser-induced Al plasmas with cylindrical confinement[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102(9): 093301. doi: 10.1063/1.2801405
|
| [17] |
WANG Y, CHEN A M, SUI L ZH, et al. Two sequential enhancements of laser-induced Cu plasma with cylindrical cavity confinement[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2016, 31(10): 1974-1977. doi: 10.1039/C6JA00260A
|
| [18] |
GAO X, LIU L, SONG CH, et al. The role of spatial confinement on nanosecond YAG laser-induced Cu plasma[J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 2015, 48(17): 175205. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/48/17/175205
|
| [19] |
SANGINÉS R, SOBRAL H, ALVAREZ-ZAUCO E. Emission enhancement in laser-produced plasmas on preheated targets[J]. Applied Physics B, 2012, 108(4): 867-873. doi: 10.1007/s00340-012-5130-6
|
| [20] |
LIU Y, TONG Y, LI S Y, et al. Effect of sample temperature on laser-induced semiconductor plasma spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2016, 14(12): 123001. doi: 10.3788/COL201614.123001
|
| [21] |
LIU Y, TONG Y, WANG Y, et al. Influence of sample temperature on the expansion dynamics of laser-induced germanium plasma[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2017, 19(12): 125501. doi: 10.1088/2058-6272/aa8acc
|
| [22] |
齐洪霞, 赵亮, 金川琳, 等. 样品温度对纳秒激光诱导铝等离子体光谱强度的影响[J]. 中国激光,2019,46(2):0211002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0211002QI H X, ZHAO L, JIN CH L, et al. Influence of sample temperature on spectral intensity of nanosecond laser-induced aluminum plasma[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2019, 46(2): 0211002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0211002
|
| [23] |
SU X J, ZHOU W D, QIAN H G. Optical emission character of collinear dual pulse laser plasma with cylindrical cavity confinement[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2014, 29(12): 2356-2361. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00296B
|
| [24] |
GUO L B, ZHANG B Y, HE X N, et al. Optimally enhanced optical emission in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy by combining spatial confinement and dual-pulse irradiation[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(2): 1436-1443. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.001436
|
| [25] |
HOU Z Y, WANG ZH, LIU J M, et al. Combination of cylindrical confinement and spark discharge for signal improvement using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(11): 12909-12914. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.012909
|
| [26] |
SANGINÉS R, SOBRAL H, ALVAREZ-ZAUCO E. The effect of sample temperature on the emission line intensification mechanisms in orthogonal double-pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2012, 68: 40-45. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2012.01.011
|
| [27] |
UJIHARA K. Reflectivity of metals at high temperatures[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1972, 43(5): 2376-2383. doi: 10.1063/1.1661506
|
| [28] |
ZHANG D, CHEN A M, WANG Q Y, et al. Influence of distance between sample surface and focal point on the expansion dynamics of laser-induced silicon plasma under different sample temperatures in air[J]. Optik, 2020, 202: 163511. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.163511
|
| [29] |
王秋云, 陈安民, 李苏宇, 等. 圆柱形空间约束腔直径和深度对激光诱导硅等离子体光谱的影响[J]. 光子学报,2018,47(8):0847007. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20184708.0847007WANG Q Y, CHEN A M, LI S Y, et al. Influence of diameter and depth on spatially confined laser-induced silicon plasma spectroscopy with cylindrical cavity[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2018, 47(8): 0847007. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20184708.0847007
|
| [30] |
FU Y T, HOU Z Y, WANG ZH. Physical insights of cavity confinement enhancing effect in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(3): 3055-3066. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.003055
|






 下载:
下载: