Line-scanning confocal microscopic imaging based on virtual structured modulation
doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0120
-
摘要: 共聚焦显微镜的分辨率受光学衍射极限限制。已经证明结构调制在共聚焦显微镜中可以实现超分辨成像,但是由于图像采集速度有限,导致该方法的实际应用具有局限性。为了提高系统的成像速度,本文介绍了一种将线扫描应用到结构调制共焦显微镜的方法。利用柱面透镜产生线照明,余弦数字掩模用于探测端的解扫描线斑图像调制,与虚拟结构探测方法不同之处在于无需后续的移频过程。为了提高各项同性分辨率,采用样本转动的方式实现0°、90°两角度扫描。仿真和实验结果表明,相干传递函数频谱宽度增大,成像分辨率达到传统共聚焦显微镜的1.4倍。与采集单点图像的结构调制共焦显微镜相比,图像采集速度提高了104倍。Abstract: Resolution in a confocal microscope is limited by the diffraction limit. Structured modulation has been proven to be able to achieve super-resolution in confocal microscopy, however, its limited speed in image acquisition limits its applicability in practical applications. In order to improve its imaging speed, we introduce a method that can achieve rapid super-resolution confocal microscopy by combining line-scanning and structured detection. A cylindrical lens is used to focus the light into a line, and a digital mask with a sinusoidal function is used to modulate the descanned image in the light detection arm. Unlike the virtual structured method, there is no need for a subsequent frequency shift process. In order to improve the isotropic resolution of the system, a scanning angle of 0 ° and 90 ° is achieved by rotating the sample. Simulation and experiment results indicate that the spectrum width of coherent transfer function expands and the resolution is 1.4 times as large as that of a conventional confocal microscope. This method increases the system’s imaging acquisition speed 104-fold when compared with a confocal structured modulation microscope that uses spot-scanning.
-
Key words:
- line-scanning confocal /
- super-resolution /
- virtual structured modulation
-
图 3 系统CTF仿真。(a) 传统线扫描共聚焦(CLSM) 的CTF,(b) 线扫描结构调制共聚焦(LVSM)的CTF,(c) 黑色曲线为(a)中Y方向归一化频率分布(WM),蓝色和红色曲线分别为(a)、(b)中X方向归一化频率分布(CLSM、LVSM)
Figure 3. System CTF simulation. (a) CTF of traditional confocal line scanning microscopy (for CLSM); (b) CTF of line-scanning confocal microscopy with structure modulation (for LVSM); (c) black curve is the normalized frequency distribution along the Y direction in (a) (for WM), and blue and red curves are the normalized frequency distributions along the X direction in (a) and (b), respectively (for CLSM and LVSM)
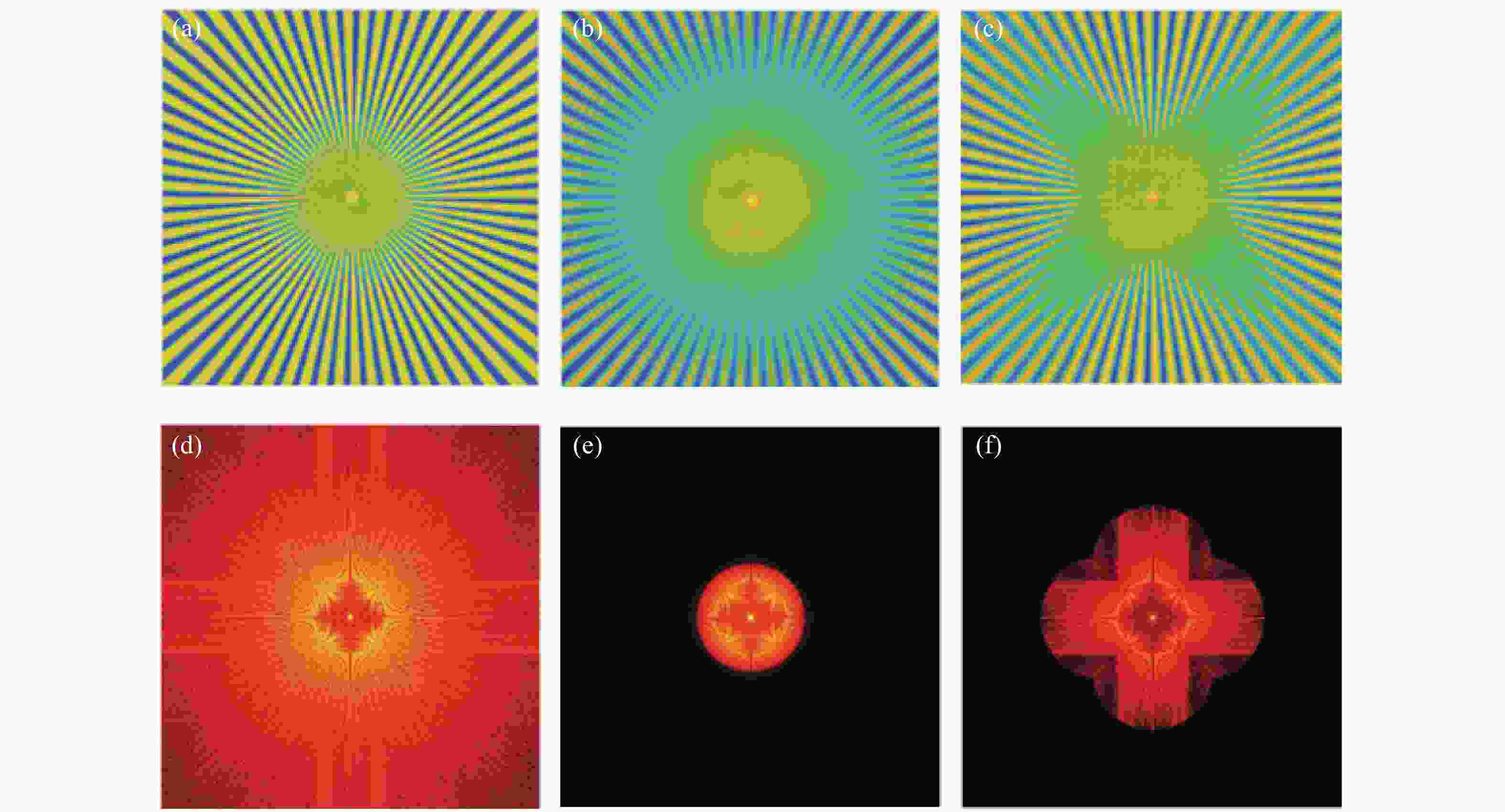
图 5 线扫描共聚焦虚拟结构调制仿真(LVSM)。(a)仿真使用的辐条状样品。(b)普通共聚焦图像。(c)取0°、90°两个扫描方向,结合对应方向上的结构检测函数重建后图像。(d)、(e)、(f)分别是(a)、(b)、(c)的傅立叶变换,即对应的频域图像
Figure 5. Simulation of line-scanning confocal microscopy with virtual structure modulation (for LVSM). (a) Spoke-like sample for simulation; (b) image of conventional confocal microscopy; (c) image reconstructed with the structure detection functions in the two scanning directions of 0° and 90°; (d), (e) and (f) are the Fourier transforms i.e. frequency domain images of (a), (b) and (c), respectively
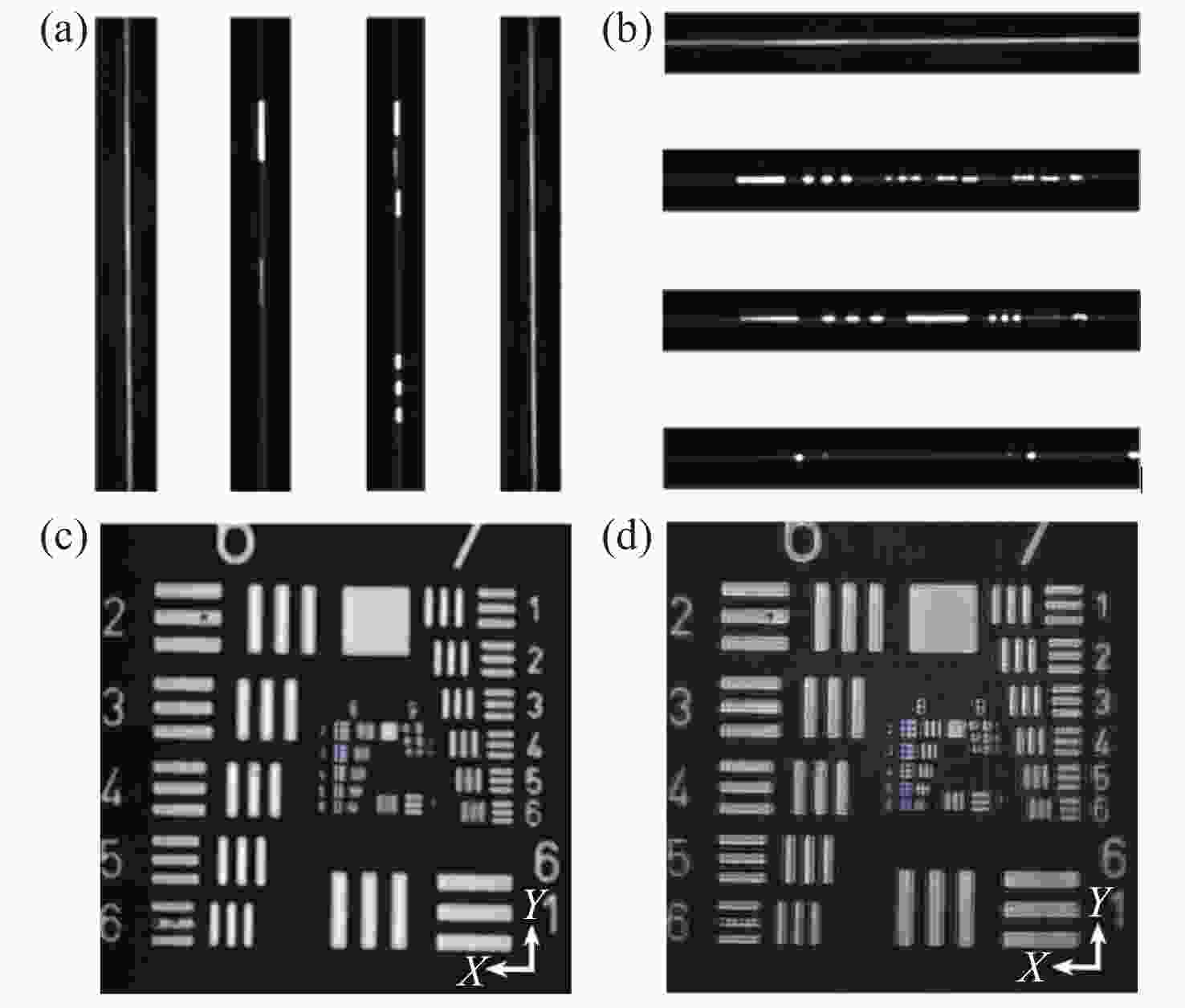
图 7 分辨率测试目标的线扫描虚拟结构调制共聚焦实现。(a)扫描方向为0°时,采集的第20、205、360、490条线斑图像。(b)扫描方向为90°时,采集的第20、205、360、490条线斑图像。(c)扫描方向为90°时,常规线扫描共聚焦获得的分辨率测试靶图片。(d) LVSM超分辨重建后图像
Figure 7. Implementation of line-scanning confocal virtual structure modulation imaging on the resolution test target. (a) The 20th, 205th, 360th and 490th line spot images collected in the 0° scanning direction; (b) the 20th, 205th, 360th and 490th line spot images collected in the 90° scanning direction; (c) the image of resolution test target obtained by conventional line-scanning confocal method in the 90° scanning direction; (d) reconstructed super-resolution image by LVSM
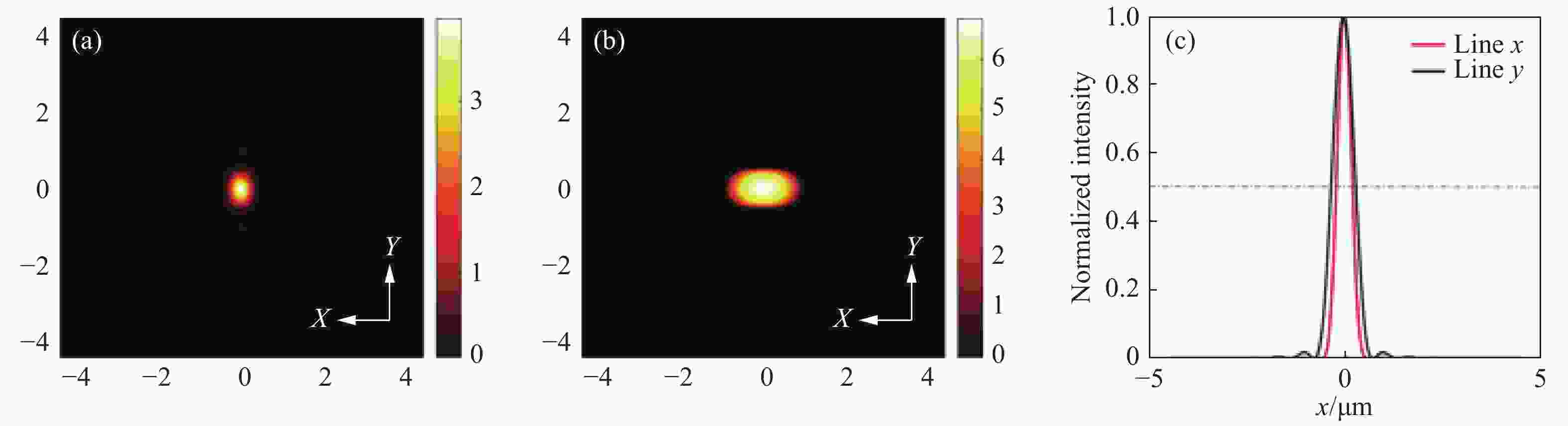
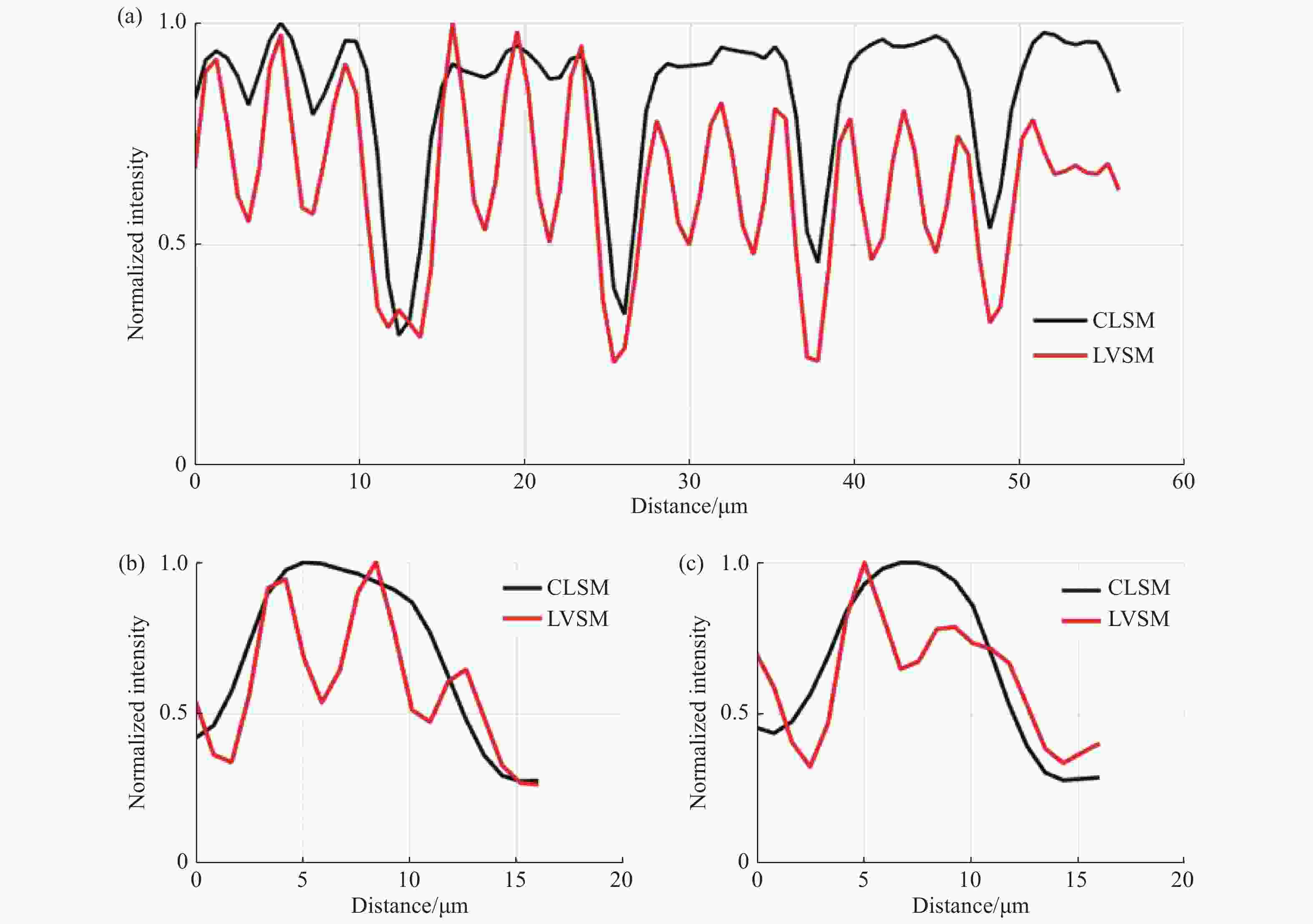
图 8 常规线扫描共聚焦和线扫描虚拟结构调制共聚焦在特定区域的归一化强度曲线。图7(c)、7(d)中(a)蓝色线段标记区域(b)黄色线段标记区域及(c)绿色线段标记区域的归一化强度分布对比
Figure 8. Normalized intensity curves of conventional line-scanning confocal microscope and line-scanning confocal microscope with virtual structure modulation in specified areas. Comparison between the normalized intensities of the area marked by (a) blue curve, (b) yellow curve and (c) green curve in Fig. 7(c) and Fig. 7(d)
-
[1] HELL S W. Microscopy and its focal switch[J]. Nature Methods, 2009, 6(1): 24-32. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1291 [2] WANG X, LIU H Y, LU X CH, et al. Cell imaging by holographic lens-free microscopy[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(8): 1644-1650. (in Chinese) [3] XU B T, YANG X B, LIU J L, et al. Image correction for high speed scanning confocal laser endomicroscopy[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(1): 60-68. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202801.0060 [4] MIAO X, ZHANG Y H, HUANG W. Image brightness adaptive adjustment during skin imaging by reflectance confocal microscopy[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(6): 1270-1276. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192706.1270 [5] WANG F M, XIAO Y, ZHAO M M, et al. 3D resolution improvement in confocal microscopy by mirror refection interference and fluorescence emission difference[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 134: 106198. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106198 [6] WILSON T, CARLINI A R. Size of the detector in confocal imaging systems[J]. Optics Letters, 1987, 12(4): 227-229. doi: 10.1364/OL.12.000227 [7] HELL S W, WICHMANN J. Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: stimulated-emission-depletion fluorescence microscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 1994, 19(11): 780-782. [8] GUSTAFSSON M G L. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 2000, 198(2): 82-87. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2818.2000.00710.x [9] SALES T R M, MORRIS G M. Fundamental limits of optical superresolution[J]. Optics Letters, 1997, 22(9): 582-584. doi: 10.1364/OL.22.000582 [10] RUST M J, BATES M, ZHUANG X W, et al. Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM)[J]. Nature Methods, 2006, 3(10): 793-796. doi: 10.1038/nmeth929 [11] HESS S T, GIRIRAJAN T P K, MASON M D. Ultra-high resolution imaging by fluorescence Photoactivation localization microscopy[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2006, 91(11): 4258-4272. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.091116 [12] GUSTAFSSON M G L. Nonlinear structured-illumination microscopy: wide-field fluorescence imaging with theoretically unlimited resolution[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2005, 102(37): 13081-13086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406877102 [13] NI H, ZOU L M, GUO Q Y, et al. Lateral resolution enhancement of confocal microscopy based on structured detection method with spatial light modulator[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(3): 2872-2882. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.002872 [14] LU J, MIN W, CONCHELLO J A, et al. Super-resolution laser scanning microscopy through spatiotemporal modulation[J]. Nano Letters, 2009, 9(11): 3883-3889. doi: 10.1021/nl902087d [15] LU R W, WANG B Q, ZHANG Q X, et al. Super-resolution scanning laser microscopy through virtually structured detection[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2013, 4(9): 1673-1682. doi: 10.1364/BOE.4.001673 [16] ZHI Y A, LU R W, WANG B Q, et al. Rapid super-resolution line-scanning microscopy through virtually structured detection[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(8): 1683-1686. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.001683 [17] WANG B K, ZOU L M, ZHANG S, et al. Super-resolution confocal microscopy with structured detection[J]. Optics Communications, 2016, 381: 277-281. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.07.005 [18] WOLLESCHENSKY R, ZIMMERMANN B, KEMPE M, et al. High-speed confocal fluorescence imaging with a novel line scanning microscope[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2006, 11(6): 064011. doi: 10.1117/1.2402110 [19] GUSTAFSSON M G L, SHAO L, CARLTON P M, et al. Three-dimensional resolution doubling in wide-field fluorescence microscopy by structured illumination[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2008, 94(12): 4957-4970. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.120345 -





 下载:
下载: