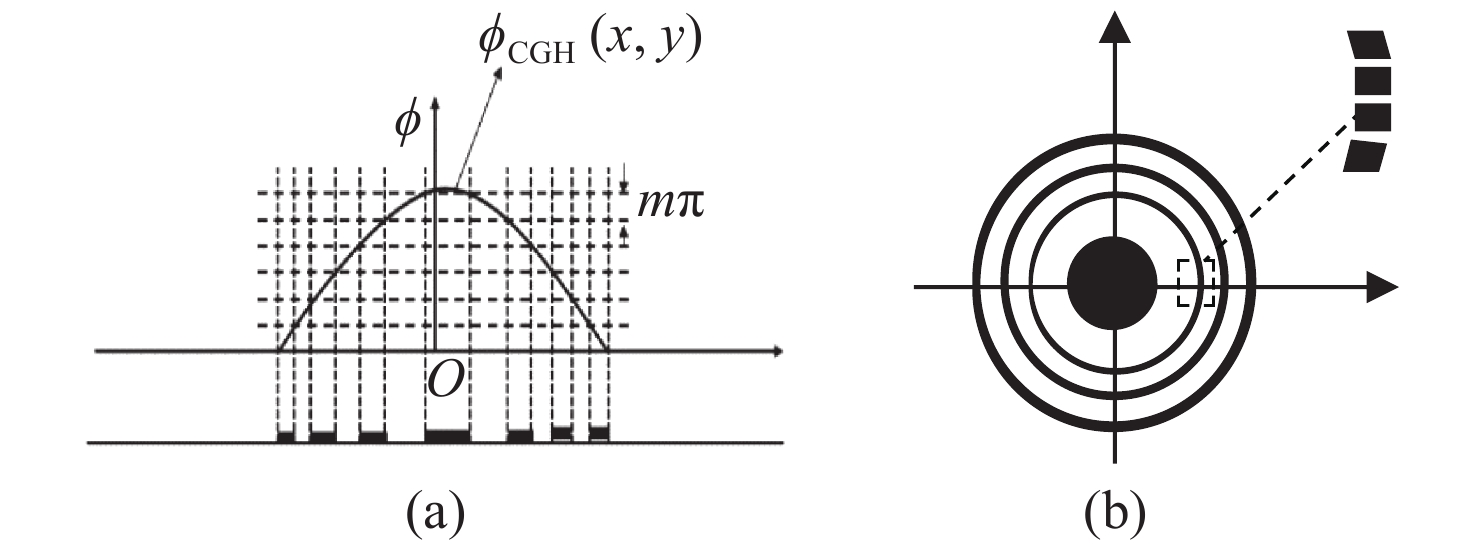
-
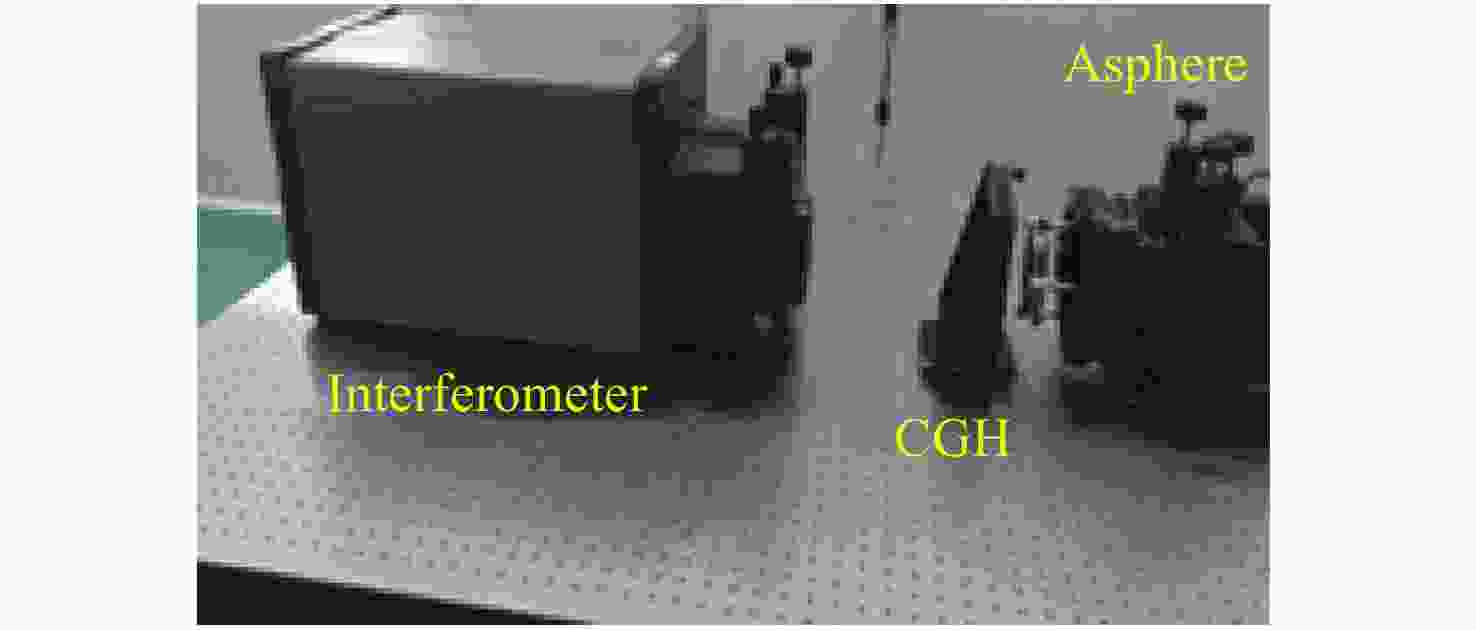
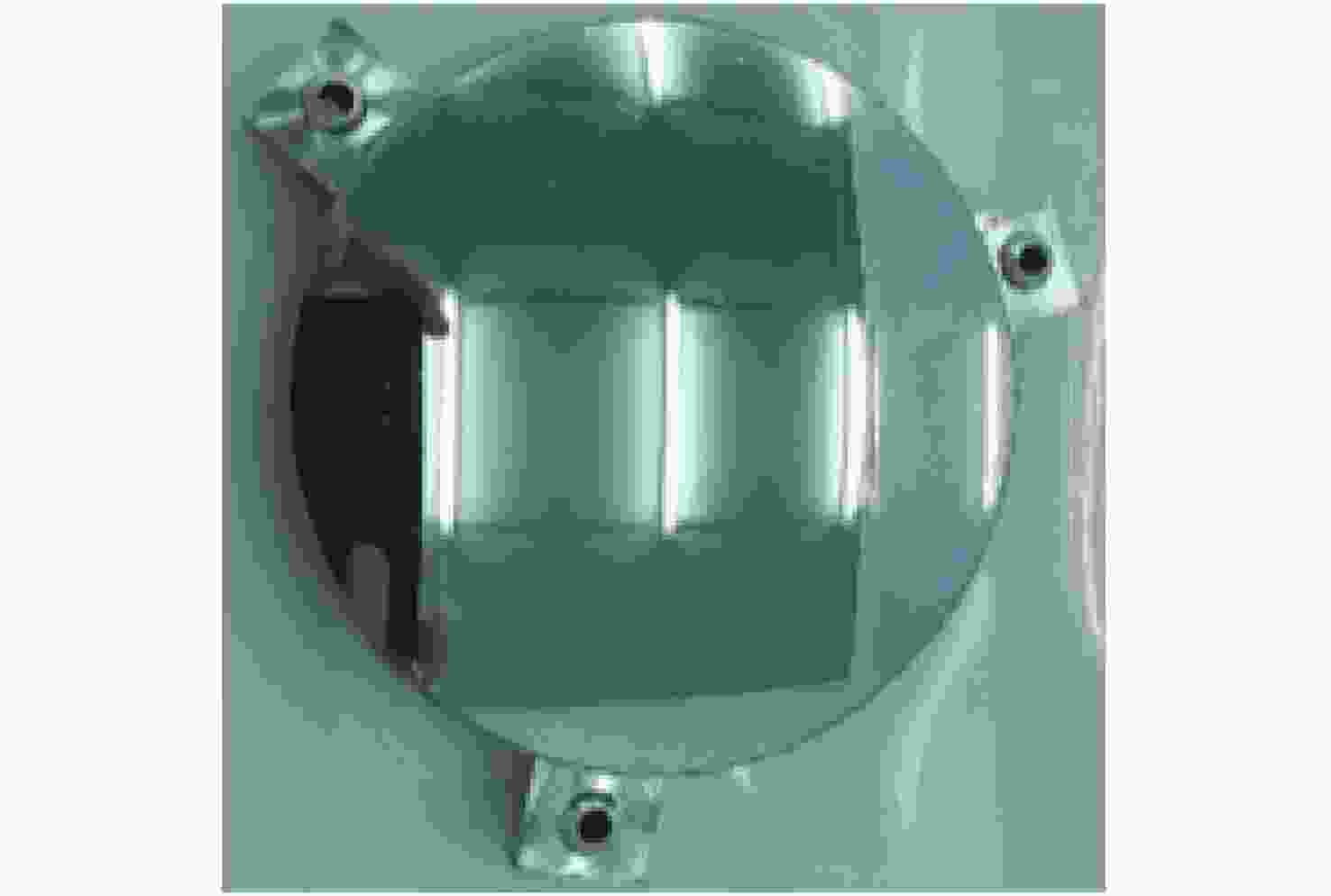
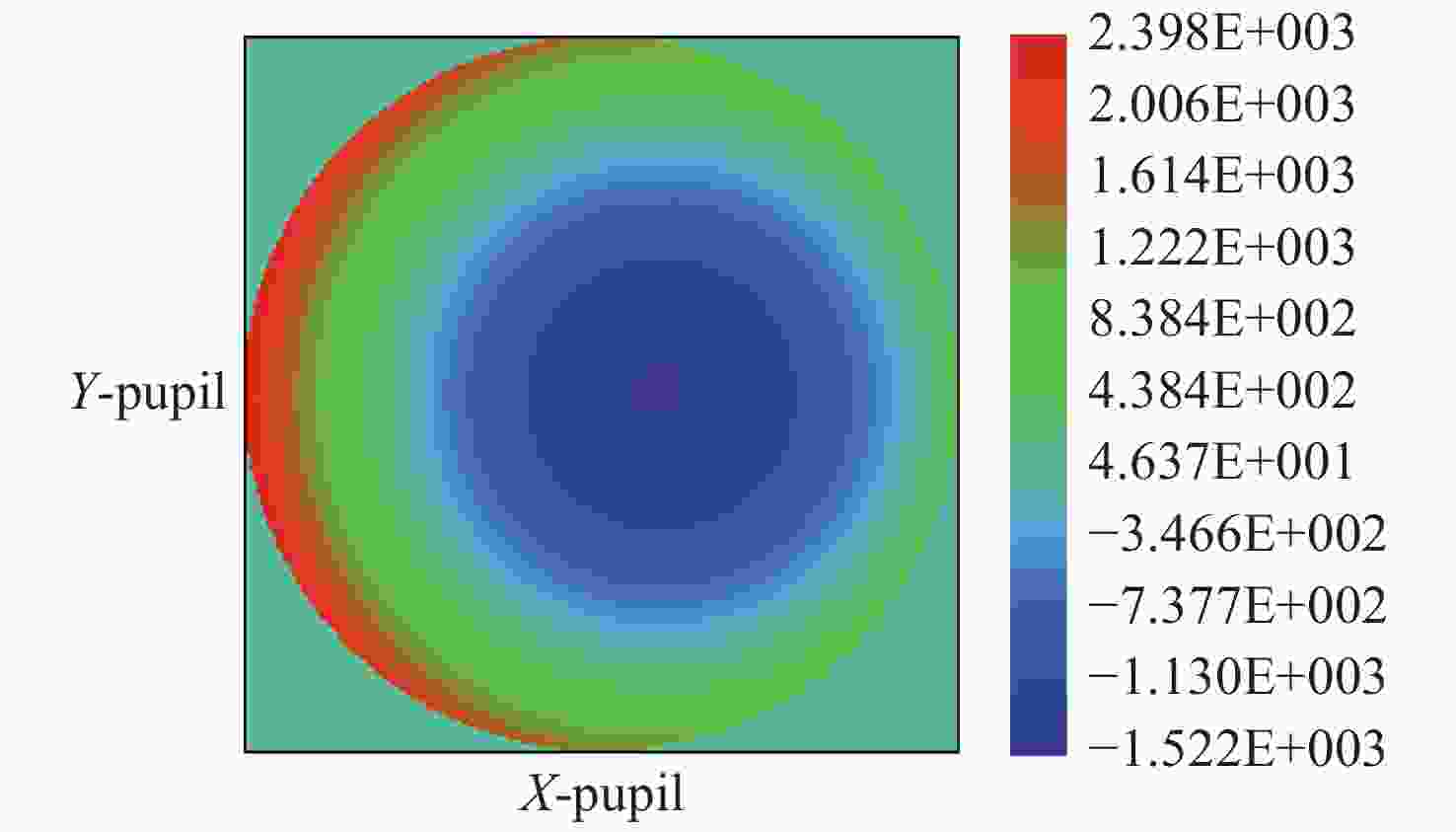
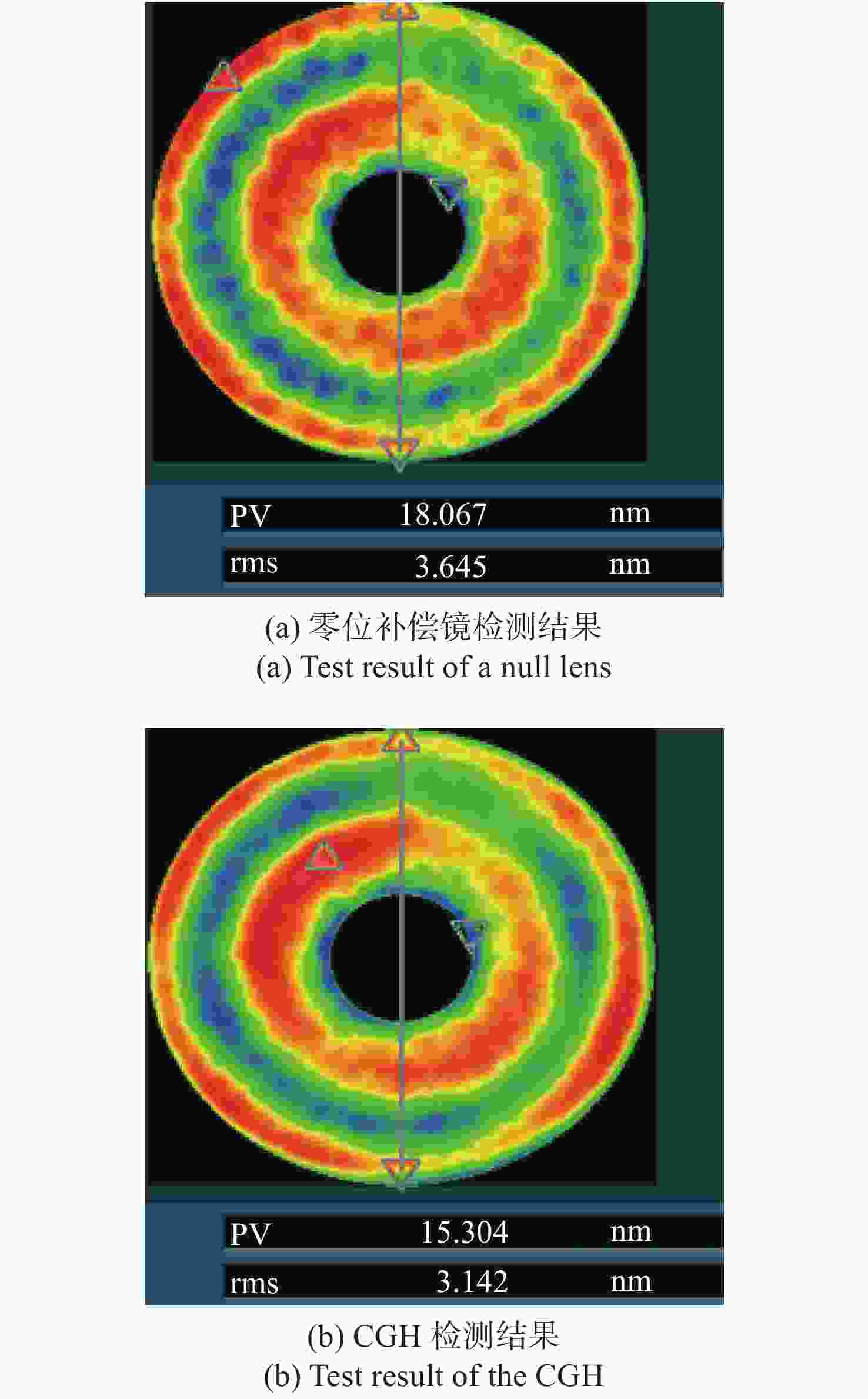
摘要: 基于计算全息图(Computer-Generated Hologram,CGH)的非球面检测技术通过控制衍射光相位来生成所需要的参考波前,从而实现非球面的零位检测,近年来,该技术已经发展成为非球面的主流检测技术。对于CGH编码,采用传统编码方法实现高精度编码,其数据量往往高达几十甚至上百GB。因此,为同时确保编码精度高及编码数据量小,本文提出了一种变步长CGH编码方法。该方法首先通过寻找等相位面的方法得到CGH条纹分布,然后通过计算相位分布梯度选取不同的取样步长,使CGH能利用尽可能少的点实现高精度编码。利用变步长搜索的编码方法进行编码并制作了CGH对非球面样品进行检测,检测结果为3.142 nm (RMS)。为验证检测结果可信度,本文设计并制作了补偿器对同一非球面进行检测,其检测结果为3.645 nm (RMS)。对两检测结果点对点做差,RMS值为1.291 nm,结果表明该编码方法可满足非球面高精度检测需求。Abstract: In the field of aspheric testing, Computer-Generated Hologram (CGH) technology has been widely used. For CGH encoding, when applying the conventional encoding method to achieve highly accurate coding, it will use an amount of data that is often up to tens or even hundreds of GB. Therefore, in order to achieve high encoding accuracy with a small amount of encoded data, we propose a variable step size CGH encoding method. This method first obtains CGH fringe distribution through finding isophase surface, then selects different sampling steps by calculating the phase distribution gradient so that the CGH achieves high precision coding using as few points as possible. Finally, the method was used to CGH encode, then the resulting CGH was manufactured to test an aspheric surface. The test result is 3.142 nm (RMS). In order to verify the credibility of the test results, we design and make a compensator to test the same aspheric surface. The test result is 3.645 nm (RMS). The difference between the two results is 1.291 nm (RMS), and shows that the encoding method can meet the requirements of high-precision testing of aspheric surfaces.
-
Key words:
- computer-generated hologram /
- CGH encoding /
- aspheric test
-
表 1 非球面参数
Table 1. Parameters of the aspheric lens
R D K A1 A2 −310.08 63 3.275 −2.148×10−8 −1.137×10−12 -
[1] 高松涛, 隋永新, 杨怀江. 用计算全息图对非球面的高精度检测与误差评估[J]. 光学学报,2013,33(6):0612003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201333.0612003GAO S T, SUI Y X, YANG H J. High precise testing of asphere with computer-generated hologram and error evaluation[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2013, 33(6): 0612003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201333.0612003 [2] ZHANG H D, WANG X K, XUE D L, et al. Modified surface testing method for large convex aspheric surfaces based on diffraction optics[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(34): 9398-9405. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.009398 [3] 何宇航, 李强, 高波, 等. 基于计算全息元件的大口径非球面透镜透射波前检测方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2019,56(2):021202.HE Y H, LI Q, GAO B, et al. Measurement of the transmission wavefront of a large-aperture aspheric lens based on computer-generated hologram[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(2): 021202. (in Chinese) [4] 闫公敬, 张宪忠. 非零位凸非球面自控精拼接检测技术研究[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(5):798-803. doi: 10.3788/CO.20181105.0798YAN G J, ZHANG X ZH. Research on non-null convex aspherical sub-aperture stitching detection technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(5): 798-803. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CO.20181105.0798 [5] 高松涛. 超高精度非球面自控精拼接检测技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2014.GAO S T. Research on ultra-precise aspheric surface testing[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014. (in Chinese). [6] 彭建涛. 基于计算全息的拼接式大口径光学系统检测与共相技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2017.PENG J T. Research on the optical testing and Co-phasing technology for large aperture segmented mirror systems based on computer-generated holograms[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. (in Chinese). [7] 张海东, 王孝坤, 薛栋林, 等. 一种针对超大口径凸非球面的面形检测方法[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(5):1147-1154. doi: 10.3788/CO.20191205.1147ZHANG H D, WANG X K, XUE D L, et al. Surface testing method for ultra-large convex aspheric surfaces[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(5): 1147-1154. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CO.20191205.1147 [8] XIAO X SH, YU Q H, ZHU ZH T, et al. Encoding method of CGH for highly accurate optical measurement based on non-maxima suppression[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2017, 15(11): 111201. doi: 10.3788/COL201715.111201 [9] 虞祖良, 金国藩. 计算机制全息图[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1984.YU Z L, JIN G F. Computer-Generated Hologram[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1984. (in Chinese) [10] JIAO F, DAVID Z, URQUHART K S, et al. Efficient encoding algorithms for computer-aided design of diffractive optical elements by the use of electron-beam fabrication[J]. Applied Optics, 1995, 34(14): 2522-2533. doi: 10.1364/AO.34.002522 [11] MA J, GAO Z S, ZHU R H, et al. Problems on fabrication of computer-generated holograms for testing aspheric surfaces[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2009, 7(1): 70-73. doi: 10.3788/COL20090701.0070 [12] CAI W R, ZHOU Z, ZHAO CH Y, et al. Analysis of wavefront errors introduced by encoding computer-generated holograms[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(34): 8324-8331. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.008324 [13] DHARMAVARAPU R, BHATTACHARYA S, JUODKAZIS S. GDOESII: software for design of diffractive optical elements and phase mask conversion to GDS II lithography files[J]. SoftwareX, 2019, 9: 126-131. doi: 10.1016/j.softx.2019.01.012 [14] 尹放, 尹冀波. CIF和GDSⅡ格式版图数据的直接转换[J]. 微处理机,2001(3):14-15, 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2279.2001.03.005YIN F, YIN J B. The direct conversion for CIF and GDSⅡ[J]. Microprocessors, 2001(3): 14-15, 19. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2279.2001.03.005 -






 下载:
下载: