-
摘要: 光学自由曲面因其表面自由度较多而难于进行检测。干涉检测法具有高精度非接触的特点,但传统干涉仪中的静态补偿器在自由曲面加工过程中未知面形不断变化的情况下,难以实现原位检测。因此,可编程控制的大动态范围自适应补偿器成为近年来自由曲面干涉检测中的研究热点。结合课题组在自由曲面自适应干涉检测领域的工作,介绍了光学自由曲面自适应干涉检测的最新研究进展,详细分析了基于可变形镜和空间光调制器的自适应干涉检测技术,介绍了针对干涉图目标的自适应控制算法,总结了两大类自适应检测方法的优点以及发展瓶颈,并对未来自由曲面的自适应检测技术进行了展望。Abstract: Optical free-form surfaces are difficult to detect due to their rich degrees of freedom. Interference detection methods are both highly precise and non-contact. However, the static compensator in a traditional interferometer faces difficulty in achieving in-situ tests of unknown surface shapes or those changing during fabrication. Therefore, programmable adaptive compensators for large dynamic ranges have become a well-researched topic in recent years. Combined with the research work in the field of freeform surface metrology, we introduce the latest research progress in adaptive interferometry for optical freeform surfaces. Adaptive interferometers based on a Deformable Mirror (DM) or Liquid Crystal Spatial Light Modulator (LC-SLM) are analyzed in detail. An adaptive controlling algorithm in the adaptive interferometer is introduced as well. Finally, the advantages and development bottleneck of the above two kinds of adaptive interferometry are summarized and the prospects for the future development of freeform surface adaptive interferometers are proposed.
-
Key words:
- freeform surface testing /
- adaptive interferometry /
- DM /
- LC-SLM
-
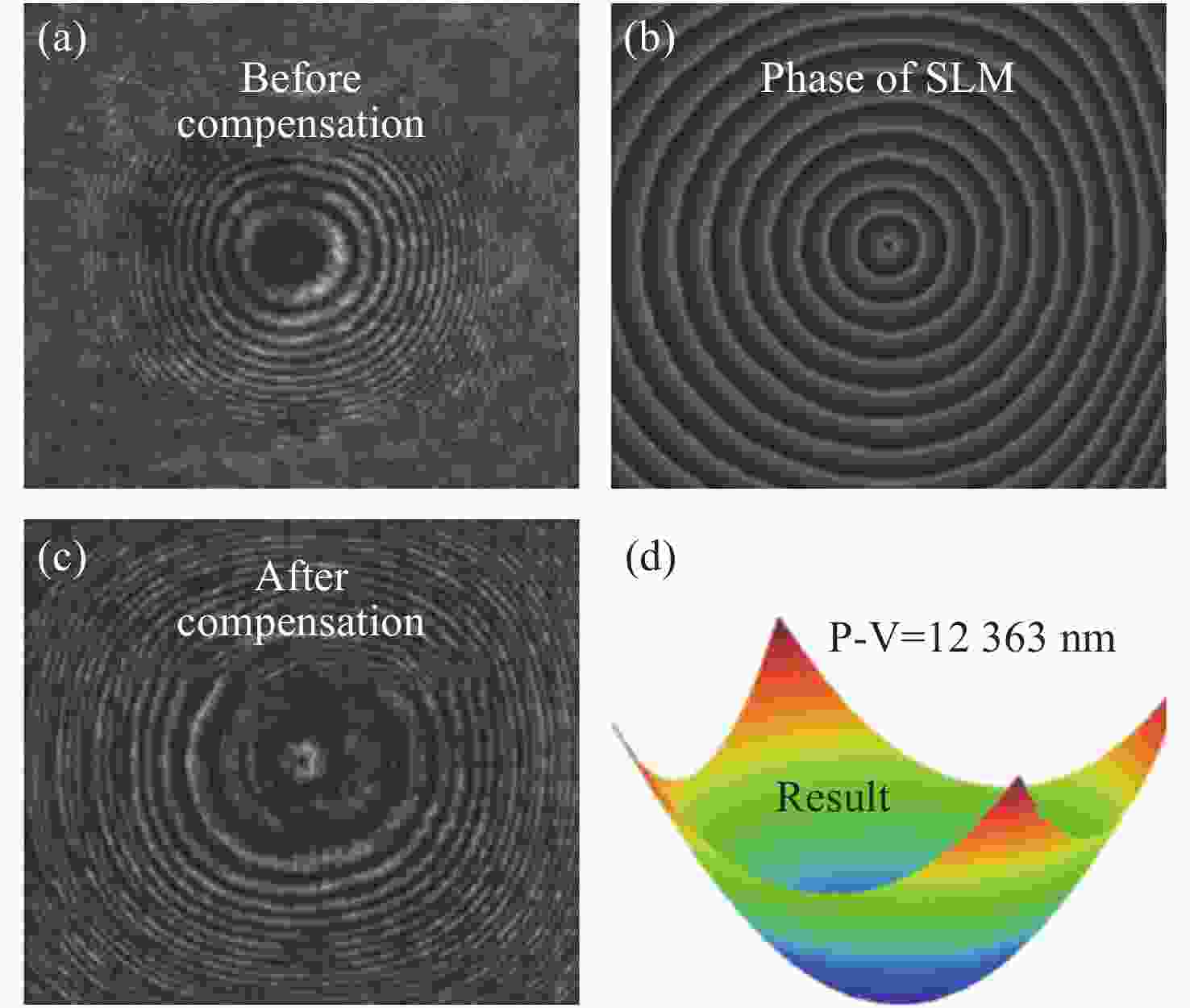
图 2 LC-SLM替代泰曼格林干涉仪的参考镜时的薄膜检测结果。(a)补偿前干涉图,(b)LC-SLM产生的参考相位,(c)补偿后的干涉图,(d)SLM波前调制量[33]
Figure 2. Thin-film interferometry results when LC-SLM replaces the reference mirror in the Twyman-Green interferometer. (a) The pre-compensated interferogram, (b) the reference phase generated by the LC-SLM, (c) the compensated interferogram, (d) the final detection result[33]
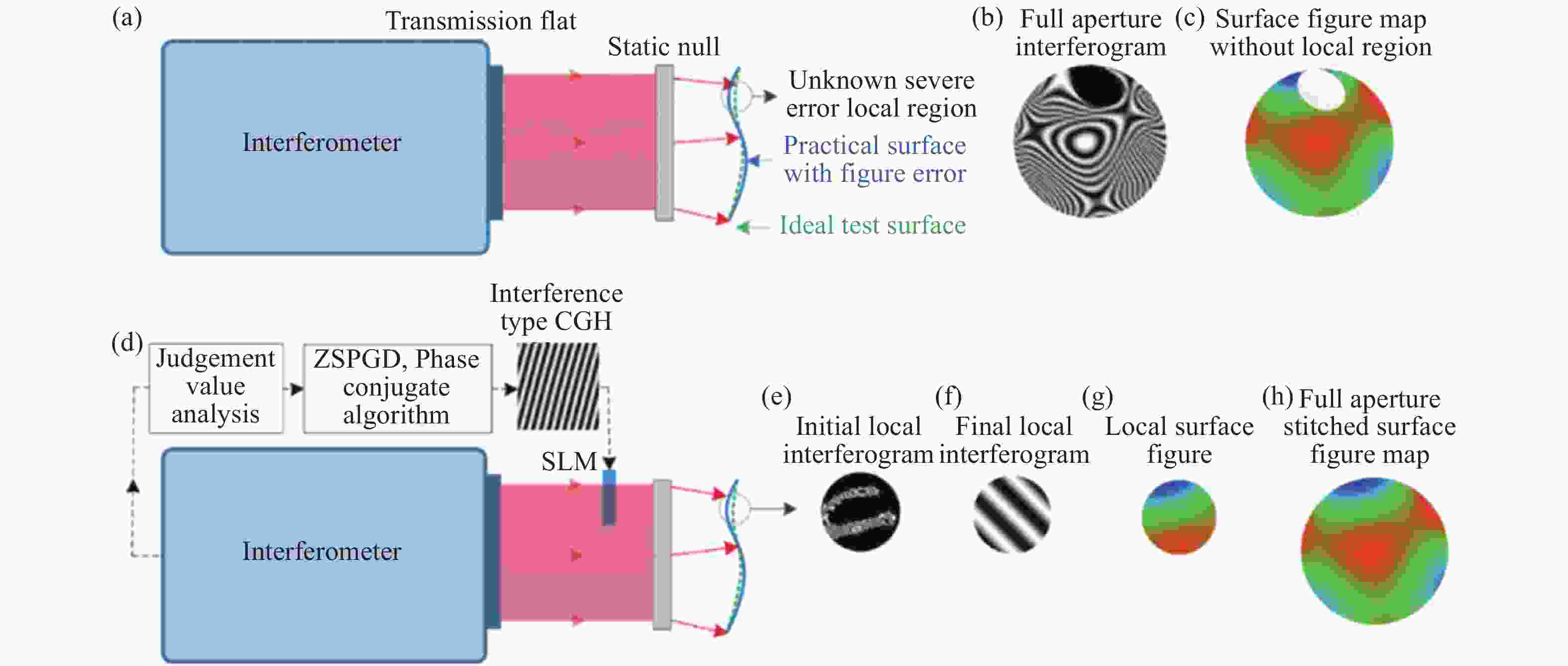
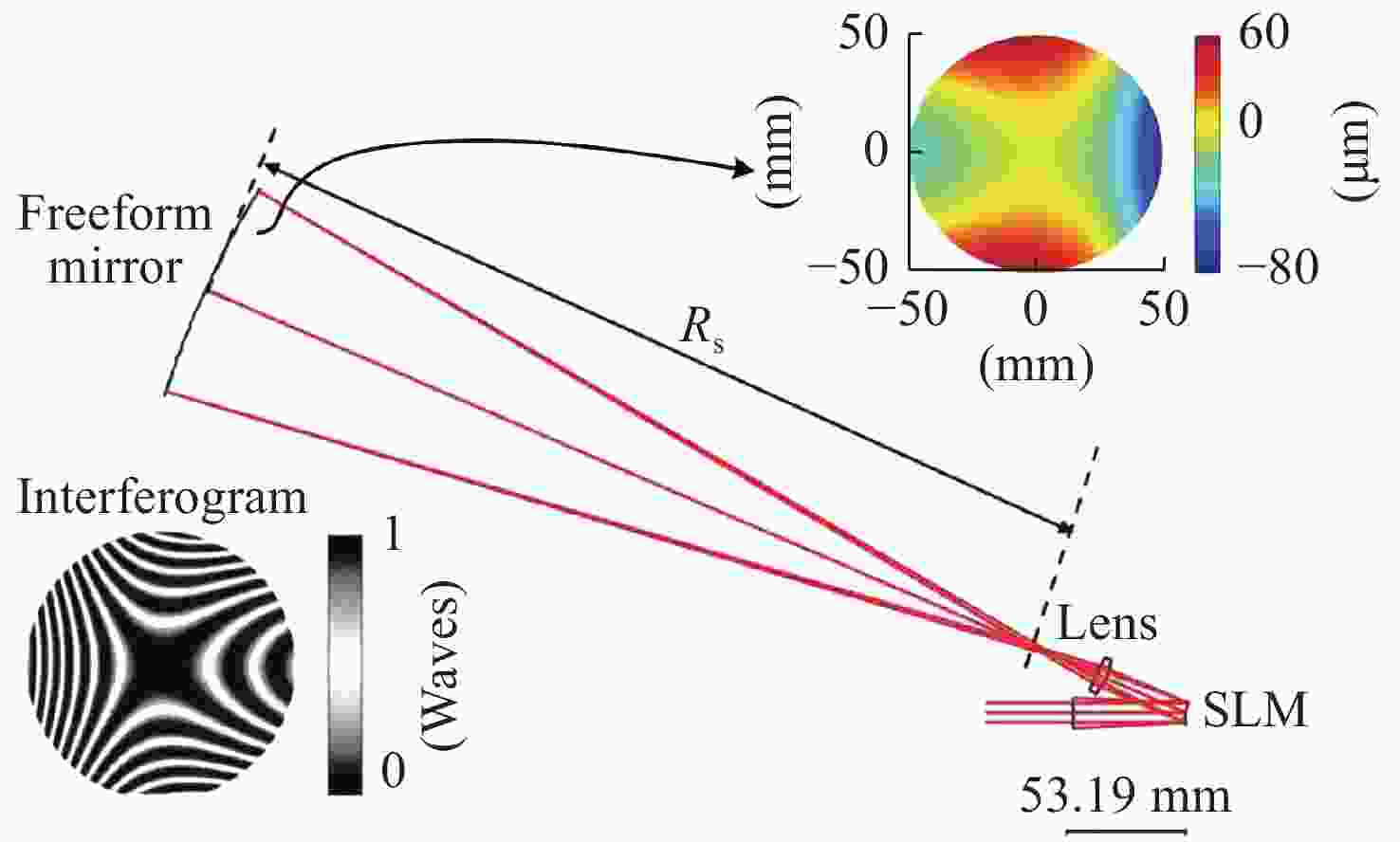
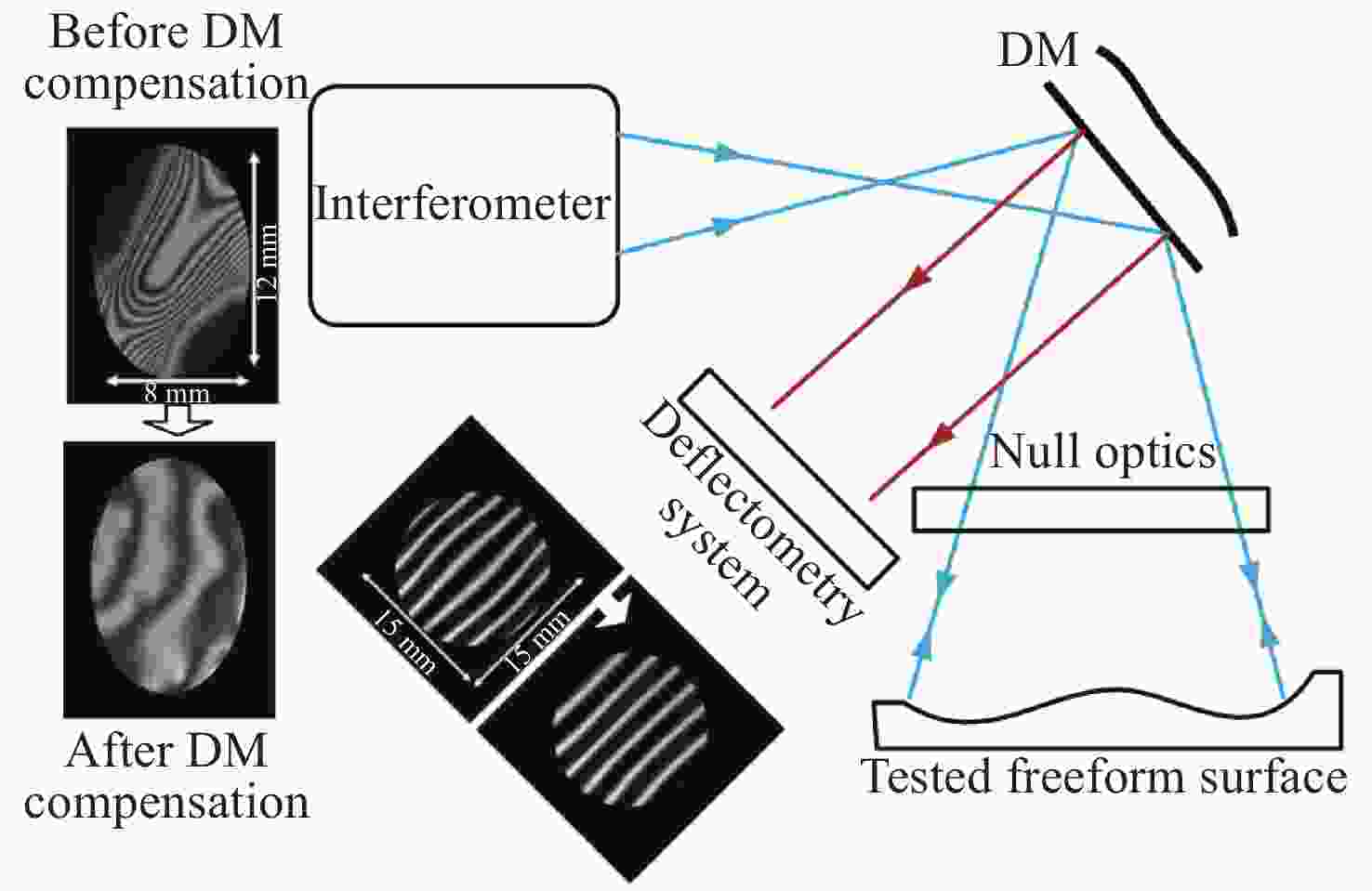
图 4 基于SLM的自适应波前干涉仪对大面形误差自由曲面检测示意图。(a)利用静态零位镜对自由曲面进行的常规检测;(b)全孔径干涉图中部分条纹不能分辨;(c)表面面形误差分布具有部分数据缺失;(d)基于SLM的自由曲面检测;(e)局部区域的初始不能分辨干涉图;(f)被SLM补偿的局部区域的最终干涉图;(g)局部区域的曲面面形误差;(h)全孔径曲面面形误差图拼接结果[38]
Figure 4. Illustration of the SLM-based Adaptive Wave-front Interferometer (AWI) for freeform surfaces with severe surface figure error. (a) The conventional test of a freeform surface utilizing a static null. (b) The full aperture interferogram when the upper region cannot be resolved by the interferometer. (c) The surface figure error map when the upper region is not available. (d) The SLM-based AWI. (e) The initial interferogram of the local region. (f) The final interferogram of the local region nulled by the SLM. (g) The surface figure error of the local region. (h) The full aperture surface figure error map stitching result[38]
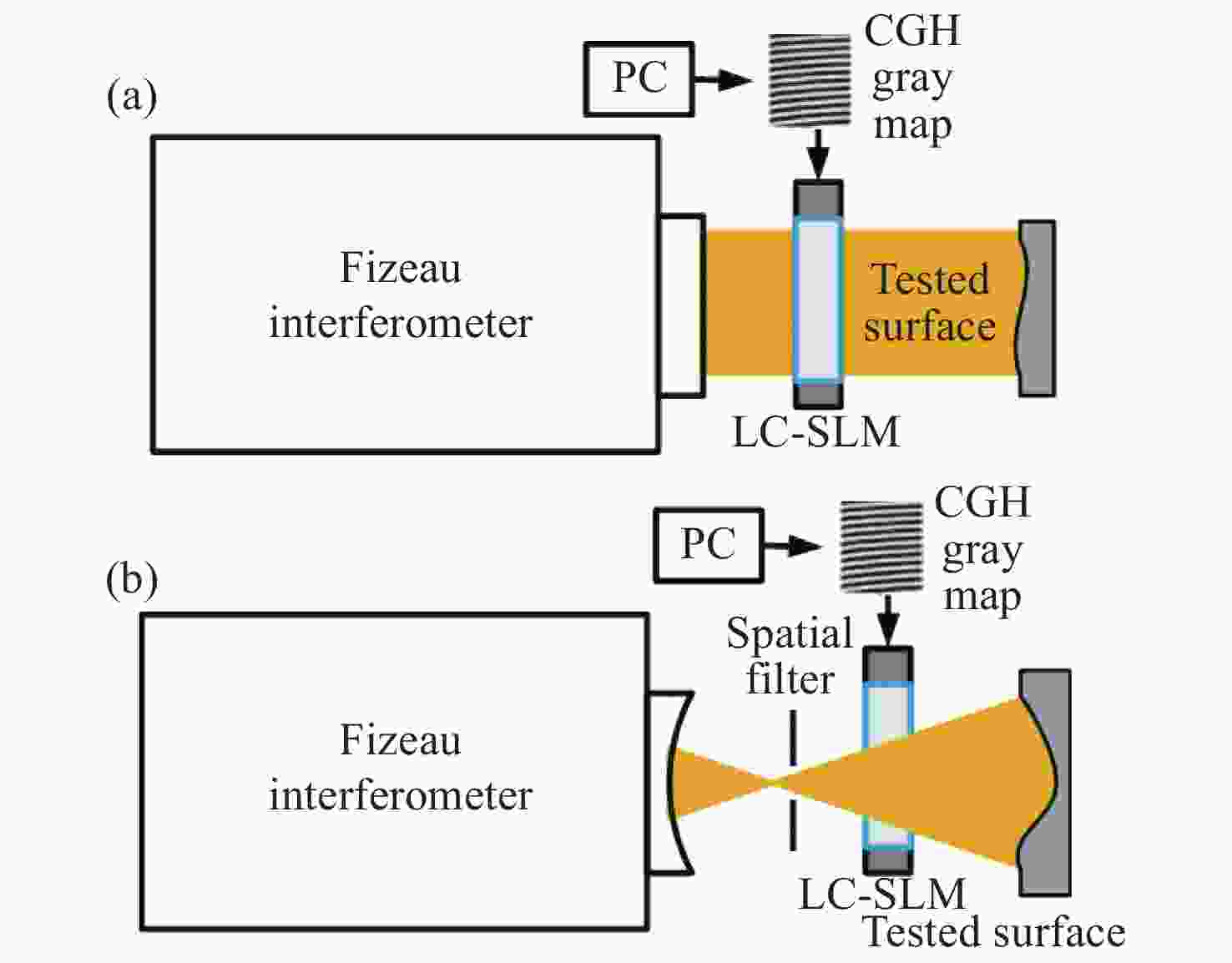
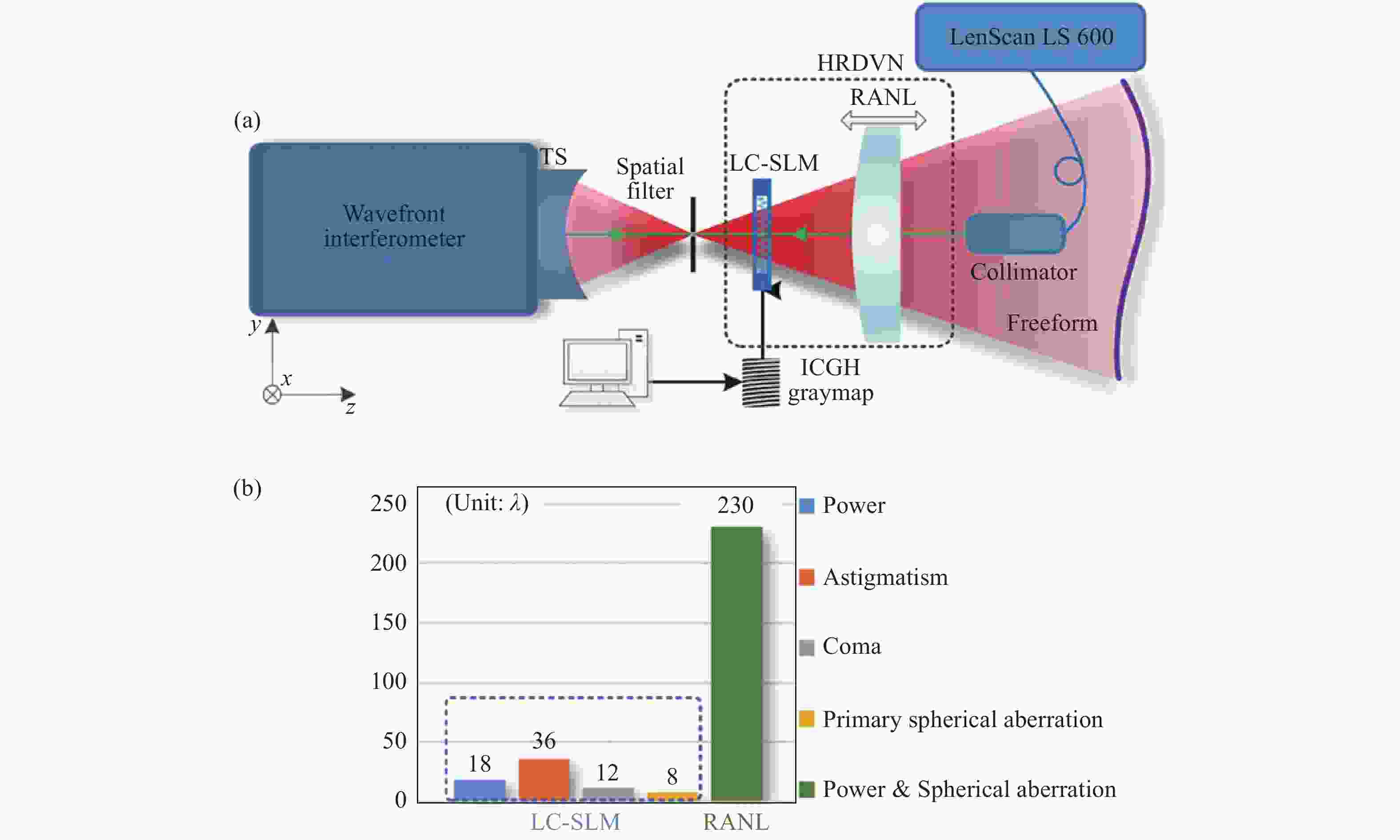
图 6 利用LC-SLM作为可重构的多级干涉型计算全图产生对自由曲面进行全口径零位检测。(a)准直光入射,(b)汇聚(发散)光入射[39]
Figure 6. LC-SLM is used as a reconfigurable multistage interferometric CGH to perform a full-aperture null test on the freeform surface, with (a) the collimating light incident and (b) the converging (divergent) light incident[39]
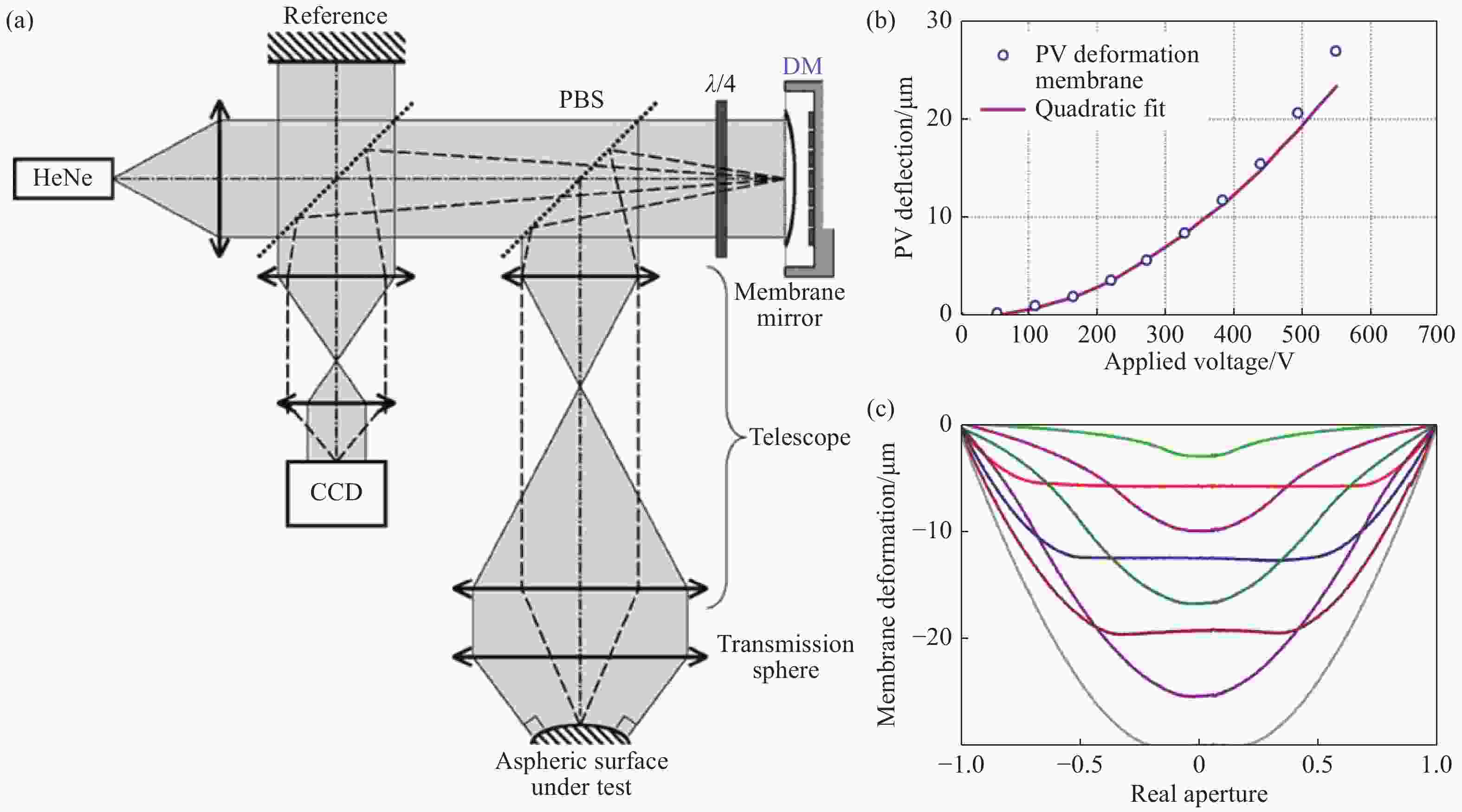
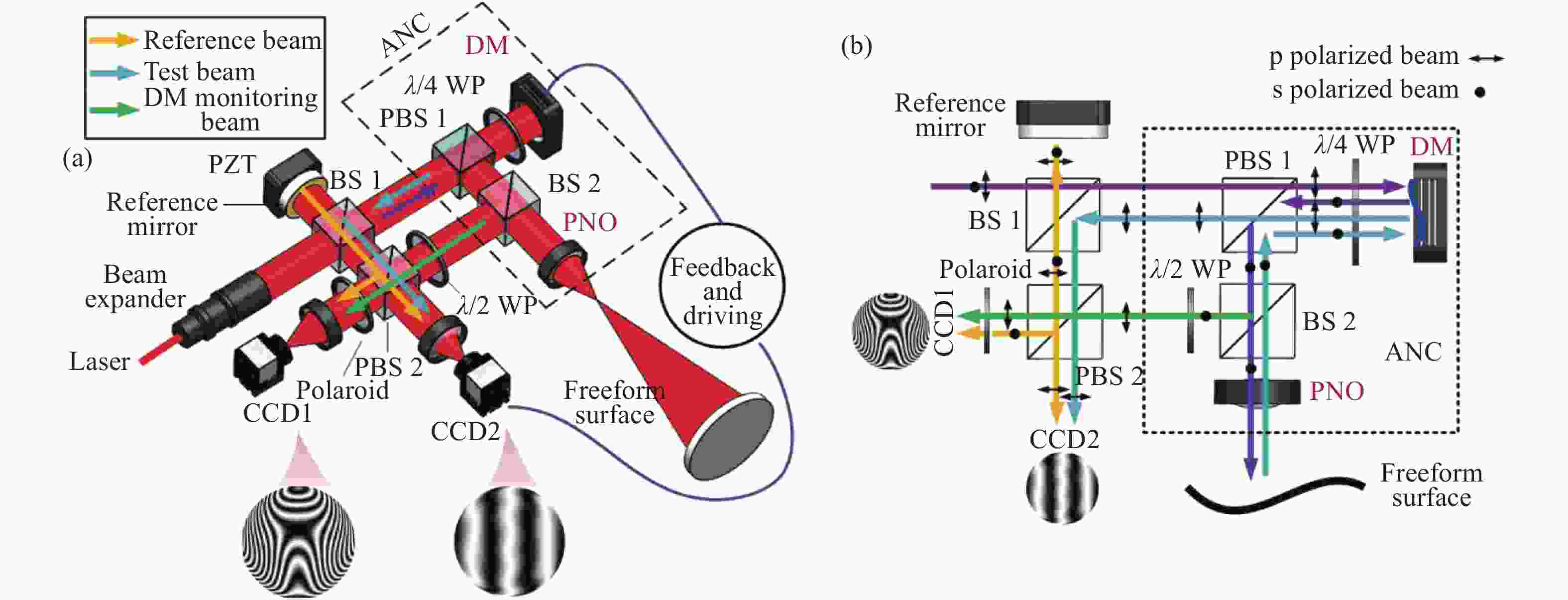
图 9 基于薄膜DM的非球面动态干涉检测。(a)干涉检测系统布局;(b)驱动电压与DM反射波前PV的模型预测值和实际测量值之间的关系;(c)不同驱动电压下DM全口径形变量(截面)[47]
Figure 9. Aspheric dynamic interferometer based on a thin film DM. (a) Layout of the system; (b) the relationship between the model predicted value and the actual measured value for PV of the DM- reflected wavefront with applied voltage and (c) the DM’s full aperture shapes (section) under different driving voltages[47]
图 17 SPGD搜索过程中,以优化指标J作为条纹恢复判据的一维演示。(a)为条纹缺失状态,(b)为优化中间过程,(c)为最终条纹及其J值[50]
Figure 17. One-dimensional demonstration showing the judgment value J as the fringe restoration criterion during the SPGD search process. (a) The case without the fringe, (b) the middle of the restoration process, and (c) the final fringe with its J value[50].
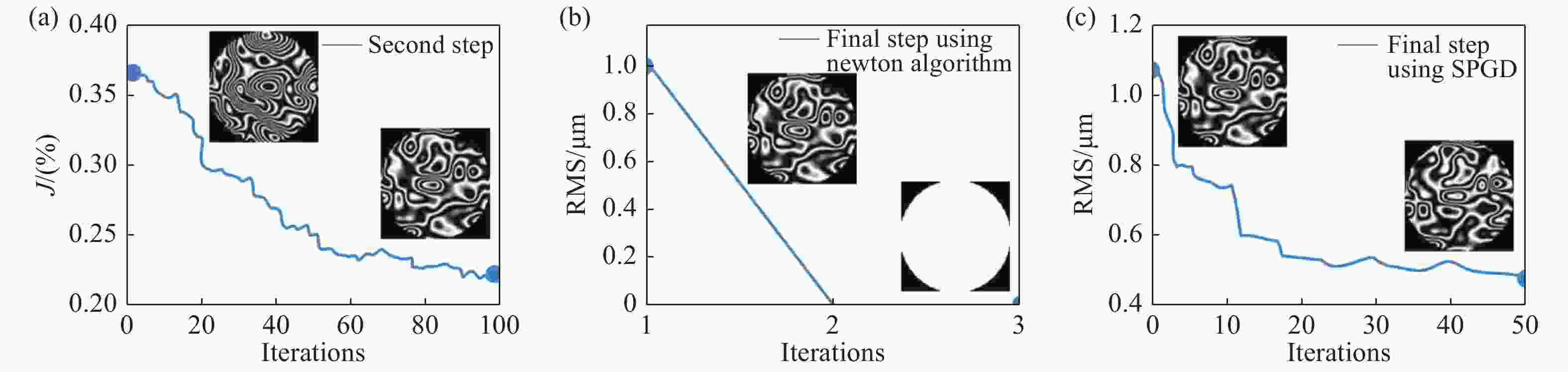
图 18 实验中优化收敛曲线。(a) SPGD算法的收敛曲线(第二步) ;(b) 最后一步采用牛顿迭代算法时的收敛曲线;(c) 最后一步采用SPGD算法时的收敛曲线[72]
Figure 18. Experimental convergence curves between the second and final steps. (a) The convergence curve using the SPGD algorithm (the second step); (b) the convergence curve using the Newton iteration algorithm in the final step; (c) the convergence curve using the SPGD algorithm in the final step[72]
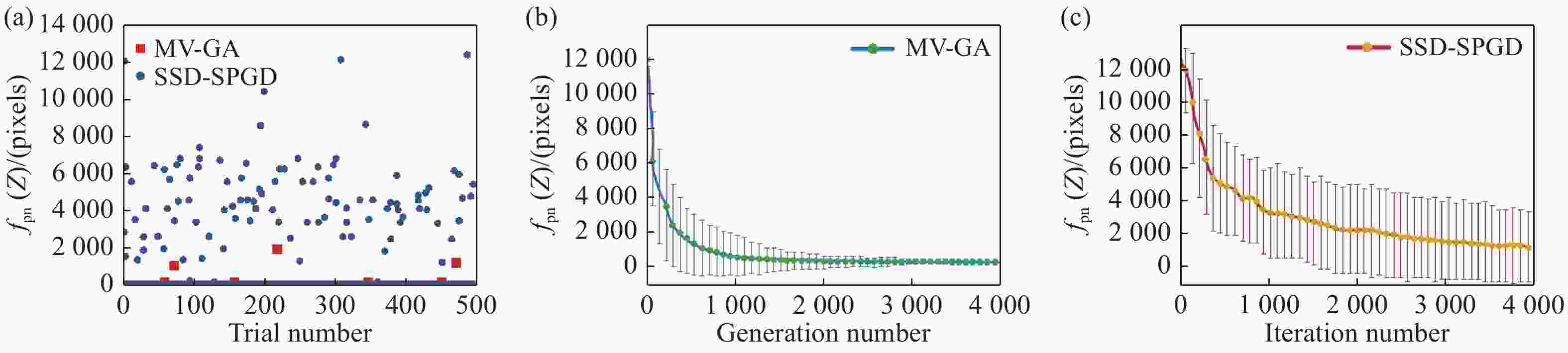
图 19 MV-GA和SSD-SPGD算法对比[71]。(a) 500次实验中MV-GA和SSD-SPGD算法优化后的目标函数值(最终干涉图中不可分辨条纹子区域的像素数),(b) MV-GA法中500个试验目标函数值的均值变化,(c) SSD-SPGD算法500次试验目标函数值的均值随迭代次数的变化
Figure 19. Comparison of the MV-GA and SSD-SPGD algorithms[71]. (a) The objective function values optimized by MV-GA and SSD-SPGD in 500 experiments. (b) Variation of the mean value & standard deviation of the 500 trials’ objective function values with a generation number for the MV-GA method. (c) Variation of the mean value & standard deviation of the 500 trials’ objective function values with the iteration number for the SSD-SPGD method.
表 1 相关文献研究中使用的SLM参数及自由曲面检测指标
Table 1. SLM parameters used in relevant literatures and freeform surface detection indexes
表 2 相关文献研究中使用的DM参数及自由曲面检测指标
Table 2. DM parameters used in relevant literatures and freeform surface detection indexes
-
[1] REIMERS J, BAUER A, THOMPSON K P, et al. Freeform spectrometer enabling increased compactness[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2017, 6(7): e17026. [2] 王欣, 刘强, 舒嵘. 大视场快焦比施密特系统在星载光谱仪中的应用[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(3):533-541. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192703.0533WANG X, LIU Q, SHU R. Application of Schmidt optical system with wide-field of view and fast focal ratio to aerospace imaging spectrometer[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(3): 533-541. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192703.0533 [3] BAUER A, SCHIESSER E M, ROLLAND J P. Starting geometry creation and design method for freeform optics[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1756. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04186-9 [4] YANG T, JIN G F, ZHU J. Automated design of freeform imaging systems[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2017, 6(10): e17081. [5] 赵星, 肖流长, 张赞, 等. 基于面形斜率的高斯径向基自由曲面优化设计及公差分析[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(12):2499-2508. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192712.2499ZHAO X, XIAO L CH, ZHANG Z, et al. Optimization and tolerance analysis of freeform surface using Gaussian RBF-Slope model[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(12): 2499-2508. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192712.2499 [6] GISSIBL T, THIELE S, HERKOMMER A, et al. Sub-micrometre accurate free-form optics by three-dimensional printing on single-mode fibres[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 11763. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11763 [7] HONG ZH H, LIANG R G. IR-laser assisted additive freeform optics manufacturing[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 7145. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07446-8 [8] 徐领娣, 房安利, 于建海, 等. 微晶材质自由曲面反射镜精密超声铣磨加工技术[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(12):2564-2570. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192712.2564XU L D, FANG A L, YU J H, et al. Ultrasonic-vibration assisted grinding of a zerodour freeform optical mirror[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(12): 2564-2570. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192712.2564 [9] GREIVENKAMP J E, GAPPINGER R O. Design of a nonnull interferometer for aspheric wave fronts[J]. Applied Optics, 2004, 43(27): 5143-5151. doi: 10.1364/AO.43.005143 [10] HAO Q, WANG SH P, HU Y, et al. Two-step carrier-wave stitching method for aspheric and freeform surface measurement with a standard spherical interferometer[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(17): 4743-4750. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.004743 [11] LIU D, SHI T, ZHANG L, et al. Reverse optimization reconstruction of aspheric figure error in a non-null interferometer[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(24): 5538-5546. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.005538 [12] TIAN CH, YANG Y Y, ZHUO Y M. Generalized data reduction approach for aspheric testing in a non-null interferometer[J]. Applied Optics, 2012, 51(10): 1598-1604. doi: 10.1364/AO.51.001598 [13] 高松涛, 武东城, 苗二龙. 大偏离度非球面检测畸变校正方法[J]. 中国光学,2017,10(3):383-390. doi: 10.3788/co.20171003.0383GAO S T, WU D CH, MIAO E L. Distortion correcting method when testing large-departure asphere[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(3): 383-390. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20171003.0383 [14] 何宇航, 李强, 高波, 等. 基于计算全息元件的大口径非球面透镜透射波前检测方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2019,56(2):021202.HE Y H, LI Q, GAO B, et al. Measurement of the transmission Wavefront of a large-aperture aspheric lens based on computer-generated hologram[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(2): 021202. (in Chinese) [15] 李明, 闫力松, 薛栋林, 等. 计算机再现全息与辅助球面混合补偿检测凸非球面方法研究[J]. 光学学报,2015,35(11):1122001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201535.1122001LI M, YAN L S, XUE D L, et al. Hybrid compensation testing of convex Asphere with computer generated holograms and fold sphere[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2015, 35(11): 1122001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201535.1122001 [16] 师途, 杨甬英, 张磊, 等. 非球面光学元件的面形检测技术[J]. 中国光学,2014,7(1):26-46.SHI T, YANG Y Y, ZHANG L, et al. Surface testing methods of aspheric optical elements[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(1): 26-46. (in Chinese) [17] 王孝坤. 子孔径拼接检测非球面时调整误差的补偿[J]. 中国光学,2013,6(1):88-95.WANG X K. Compensation of misalignment error on testing aspheric surface by subaperture stitching interferometry[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(1): 88-95. (in Chinese) [18] OFFNER A. A null corrector for Paraboloidal mirrors[J]. Applied Optics, 1963, 2(2): 153-155. doi: 10.1364/AO.2.000153 [19] NOVAK M, ZHAO C, BURGE J H. Distortion mapping correction in aspheric null testing[J]. Proceeding of SPIE, 2008, 7063: 706313. doi: 10.1117/12.798151 [20] SULLIVAN J J, GREIVENKAMP J E. Design of partial nulls for testing of fast aspheric surfaces[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6671: 66710W. doi: 10.1117/12.734874 [21] ZHANG L, LIU D, SHI T, et al. Aspheric subaperture stitching based on system modeling[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(15): 19176-19188. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.019176 [22] MURPHY P, DEVRIES G, FLEIG J, et al. Measurement of high-departure aspheric surfaces using subaperture stitching with variable null optics[J]. Proceeding of SPIE, 2009, 7426: 74260P. doi: 10.1117/12.826544 [23] CHEN SH Y, LI SH Y, DAI Y F, et al. Lattice design for subaperture stitching test of a concave paraboloid surface[J]. Applied Optics, 2006, 45(10): 1112007. [24] 黄亚, 马骏, 朱日宏, 等. 基于计算全息的光学自由曲面测量不确定度分析[J]. 光学学报,2015,35(11):1112007-172. doi: 10.3788/AOS201535.1112007HUANG Y, MA J, ZHU R H, et al. Investigation of measurement uncertainty of optical freeform surface based on computer-generated hologram[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2015, 35(11): 1112007-172. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201535.1112007 [25] 苏萍, 谭峭峰, 康果果, 等. 自由曲面零补偿计算全息图离散相位的B样条拟合[J]. 光学学报,2010,30(6):1767-1771. doi: 10.3788/AOS20103006.1767SU P, TAN Q F, KANG G G, et al. B-spline interpolation of scattered phase data of computer generated hologram for null test of freeform surface[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2010, 30(6): 1767-1771. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS20103006.1767 [26] FORTMEIER I, STAVRIDIS M, WIEGMANN A, et al. Evaluation of absolute form measurements using a tilted-wave interferometer[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(4): 3393-3404. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.003393 [27] XUE SH, CHEN SH Y, TIE G P. Near-null interferometry using an aspheric null lens generating a broad range of variable spherical aberration for flexible test of aspheres[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(24): 31172-31189. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.031172 [28] CHEN SH Y, ZHAO CH Y, DAI Y F, et al. Reconfigurable optical null based on counter-rotating Zernike plates for test of aspheres[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(2): 1381-1386. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.001381 [29] TANONE A, ZHANG ZH, UANG C M, et al. Phase modulation depth for a real-time kinoform using a liquid crystal television[J]. Optical Engineering, 1993, 32(3): 517-521. doi: 10.1117/12.61038 [30] AMAKO J, SONEHARA T. Kinoform using an electrically controlled birefringent liquid-crystal spatial light modulator[J]. Applied Optics, 1991, 30(32): 4622-4628. doi: 10.1364/AO.30.004622 [31] DAVIS J A, VALADÉZ K O, COTTRELL D M. Encoding amplitude and phase information onto a binary phase-only spatial light modulator[J]. Applied Optics, 2003, 42(11): 2003-2008. doi: 10.1364/AO.42.002003 [32] CAO ZH L, XUAN L, HU L F, et al. Investigation of optical testing with a phase-only liquid crystal spatial light modulator[J]. Optics Express, 2005, 13(4): 1059-1065. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.13.001059 [33] KACPERSKI J, KUJAWINSKA M. Active, LCoS based laser interferometer for microelements studies[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(21): 9664-9678. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.009664 [34] ARES M, ROYO S, SERGIEVSKAYA I, et al. Active optics null test system based on a liquid crystal programmable spatial light modulator[J]. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(32): 6201-6206. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.006201 [35] NEIL M A A, BOOTH M J, WILSON T. Dynamic wave-front generation for the characterization and testing of optical systems[J]. Optics Letters, 1998, 23(23): 1849-1851. doi: 10.1364/OL.23.001849 [36] BORUAH B R, LOVE G D, NEIL M A A. Interferometry using binary holograms without high order diffraction effects[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(12): 2357-2359. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.002357 [37] CASHMORE M T, HALL S R G, LOVE G D. Traceable interferometry using binary reconfigurable holograms[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(24): 5353-5358. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.005353 [38] XUE SH, CHEN SH Y, FAN ZH B, et al. Adaptive wavefront interferometry for unknown free-form surfaces[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(17): 21910-21928. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.021910 [39] XUE SH, CHEN SH Y, TIE G P, et al. Adaptive null interferometric test using spatial light modulator for free-form surfaces[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(6): 8414-8428. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.008414 [40] XUE SH, CHEN SH Y, TIE G P, et al. Flexible interferometric null testing for concave free-form surfaces using a hybrid refractive and diffractive variable null[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(9): 2294-2297. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.002294 [41] CHAUDHURI R, PAPA J, ROLLAND J P. System design of a single-shot reconfigurable null test using a spatial light modulator for freeform metrology[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(8): 2000-2003. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.002000 [42] HOLOEYE[EB/OL]. GAEA-210 Mega pixel phase only LCOS-SLM (reflective). https://holoeye.com/gaea-4k-phase-only-spatiallight-modulator/. [43] 杨慧珍, 李新阳, 姜文汉. 自适应光学技术在大气光通信系统中的应用进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2007,44(10):61-68.YANG H ZH, LI X Y, JIANG W H. Applications of adaptive optics technology in atmospheric laser communications system[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2007, 44(10): 61-68. (in Chinese) [44] 饶长辉, 姜文汉, 凌宁, 等. 自适应光学系统对实际大气湍流波前的时域校正效果[J]. 光学学报,2001,21(8):933-938. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2001.08.009RAO CH H, JIANG W H, LING N, et al. Temporal correction effectiveness of adaptive optical system for light wave atmospheric propagation[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2001, 21(8): 933-938. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2001.08.009 [45] FERNÁNDEZ E J, VABRE L, HERMANN B, et al. Adaptive optics with a magnetic deformable mirror: applications in the human eye[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(20): 8900-8917. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.008900 [46] 张雨东, 姜文汉, 史国华, 等. 自适应光学的眼科学应用[J]. 中国科学 G辑: 物理学 力学 天文学,2007,37(S1):68-74.ZHANG Y D, JIANG W H, SHI G H, et al. Ophthalmology applications of adaptive optics[J]. Science in China Series G:Physics,Mechanics &Astronomy, 2007, 37(S1): 68-74. (in Chinese) [47] PRUSS C, TIZIANI H J. Dynamic null lens for aspheric testing using a membrane mirror[J]. Optics Communications, 2004, 233(1-3): 15-19. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2004.01.030 [48] BOOTH M, WILSON T, SUN H B, et al. Methods for the characterization of deformable membrane mirrors[J]. Applied Optics, 2005, 44(24): 5131-5139. doi: 10.1364/AO.44.005131 [49] FUERSCHBACH K, THOMPSON K P, ROLLAND J P. Interferometric measurement of a concave, φ-polynomial, Zernike mirror[J]. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(1): 18-21. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.000018 [50] HUANG L, CHOI H, ZHAO W CH, et al. Adaptive interferometric null testing for unknown freeform optics metrology[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(23): 5539-5542. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.005539 [51] WANG D D, ZHANG S, WU R M, et al. Computer-aided high-accuracy testing of reflective surface with reverse Hartmann test[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(17): 19671-19681. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.019671 [52] HUANG L, XUE J P, GAO B, et al. Modal phase measuring deflectometry[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(21): 24649-24664. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.024649 [53] 陈惠颖, 王卫兵, 王挺峰, 等. 随机并行梯度下降算法性能与变形镜排布规律的关系研究[J]. 中国光学,2016,9(4):432-438. doi: 10.3788/co.20160904.0432CHEN H Y, WANG W B, WANG T F, et al. Relationship between performance of stochastic parallel gradient descent algorithm and distribution rule of deformable mirror[J]. Chinese Optics, 2016, 9(4): 432-438. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20160904.0432 [54] WANG W B, WANG T F, GUO J. Simulation on the law of wave-front shaping with stochastic parallel gradient descent algorithm for adaptive optics[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(3): 411-420. [55] ZHANG L, ZHOU SH, LI D, et al. Pure adaptive interferometer for free form surfaces metrology[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(7): 7888-7898. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.007888 [56] ZHANG L, ZHOU S, LI D, et al. Model-based adaptive non-null interferometry for freeform surface metrology[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2018, 16(8): 081203. doi: 10.3788/COL201816.081203 [57] CHENG T, LIU W J, PANG B Q, et al. A slope-based decoupling algorithm to simultaneously control dual deformable mirrors in a woofer-tweeter adaptive optics system[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2018, 27(7): 070704. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/27/7/070704 [58] LIU W J, DONG L ZH, YANG P, et al. A Zernike mode decomposition decoupling control algorithm for dual deformable mirrors adaptive optics system[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(20): 23885-23895. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.023885 [59] LIU W J, DONG L ZH, YANG P, et al. Zonal decoupling algorithm for dual deformable mirror adaptive optics system[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2016, 14(2): 020101. doi: 10.3788/COL201614.020101 [60] ZOU W Y, QI X F, BURNS S A. Wavefront-aberration sorting and correction for a dual-deformable-mirror adaptive-optics system[J]. Optics Letters, 2008, 33(22): 2602-2604. doi: 10.1364/OL.33.002602 [61] ZHANG L, LI CH, HUANG X L, et al. Compact adaptive interferometer for unknown freeform surfaces with large departure[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(2): 1897-1913. doi: 10.1364/OE.380889 [62] ALPAO. Deformable mirrors[EB/OL]. (2019). https://www.alpao.com/adaptive-optics/deformable-mirrors.html. [63] BITENC U. Software compensation method for achieving high stability of Alpao deformable mirrors[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(4): 4368-4381. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.004368 [64] ZHANG L, ZHANG Y K. Freeform surface interferometry with an adaptive ring-cavity compensator[J]. Surface Topography:Metrology and Properties, 2020, 8(2): 025036. doi: 10.1088/2051-672X/ab9e43 [65] 杨华峰, 饶长辉, 张雨东, 等. 自适应光学系统中变形镜和波前传感器共轭位置要求的分析[J]. 光电工程,2009,36(4):27-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2009.04.006YANG H F, RAO CH H, ZHANG Y D, et al. Analysis of the conjugation request between the wavefront sensors and the deformable mirrors in adaptive optics system[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2009, 36(4): 27-34. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2009.04.006 [66] LEI X, WANG SH, YAN H, et al. Double-deformable-mirror adaptive optics system for laser beam cleanup using blind optimization[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(20): 22143-22157. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.022143 [67] DOU R SH, VORONTSOV M A, SIVOKON V P, et al. Iterative technique for high-resolution phase distortion compensation in adaptive interferometers[J]. Optical Engineering, 1997, 36(12): 3327-3335. doi: 10.1117/1.601591 [68] HU Q T, ZHEN L L, MAO Y, et al. Adaptive stochastic parallel gradient descent approach for efficient fiber coupling[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(9): 13141-13154. doi: 10.1364/OE.390762 [69] VORONTSOV M A, CARHART G W. Adaptive wavefront control with asynchronous stochastic parallel gradient descent clusters[J]. Journal of Optics Society of America A, 2006, 23(10): 2613-2622. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.23.002613 [70] WU K N, SUN Y, HUAI Y, et al. Multi-perturbation stochastic parallel gradient descent method for wavefront correction[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(3): 2933-2944. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.002933 [71] XUE SH, DENG W X, CHEN SH Y. Intelligence enhancement of the adaptive wavefront interferometer[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(8): 11084-11102. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.011084 [72] ZHANG Y, TIAN X B, LIANG R G. SPGD and Newton iteration mixed algorithm used in freeform surface metrology[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 129: 106050. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106050 [73] LIMA N C, MISHRA K, MUGELE F. Aberration control in adaptive optics: a numerical study of arbitrarily deformable liquid lenses[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(6): 6700-6711. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.006700 [74] OLIKER V, DOSKOLOVICH L L, BYKOV D A. Beam shaping with a plano-freeform lens pair[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(15): 19406-19419. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.019406 [75] DING Z Q, WANG CH H, HU ZH X, et al. Surface profiling of an aspherical liquid lens with a varied thickness membrane[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(4): 3122-3132. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.003122 [76] ZHOU H, ZHANG X F, XU Z J, et al. Universal membrane-based tunable liquid lens design for dynamically correcting spherical aberration over user-defined focal length range[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(26): 37667-37679. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.037667 [77] XU ZH X, YANG P, HU K, et al. Deep learning control model for adaptive optics systems[J]. Applied Optics, 2019, 58(8): 1998-2009. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.001998 [78] GUZMÁN D, DE COS JUEZ F J, MYERS R, et al. Modeling a MEMS deformable mirror using non-parametric estimation techniques[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(20): 21356-21369. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.021356 [79] BLAIN C, GUYON O, BRADLEY C, et al. Fast Iterative Algorithm (FIA) for controlling MEMS deformable mirrors: principle and laboratory demonstration[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(22): 21271-21294. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.021271 [80] BLAIN C, CONAN R, BRADLEY C, et al. Open-loop control demonstration of micro-electro-mechanical-system MEMS deformable mirror[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(6): 5433-5448. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.005433 [81] STEWART J B, DIOUF A, ZHOU Y P, et al. Open-loop control of a MEMS deformable mirror for large-amplitude wavefront control[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2007, 24(12): 3827-3833. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.24.003827 [82] DIOUF A, LEGENDRE A P, STEWART J B, et al. Open-loop shape control for continuous microelectromechanical system deformable mirror[J]. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(31): G148-G154. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.00G148 -






 下载:
下载: