-
摘要:
红外偏振成像技术具有探测距离远,目标识别率高等多种优势,但在复杂环境下目标偏振特性易受背景辐射影响,使得红外偏振设备的探测能力大幅降低。本文基于偏振双向反射分布函数,综合考虑目标和背景间的辐射耦合效应,建立了目标偏振度计算模型。对比研究了有强辐射背板和无强辐射背板两种情况下目标偏振度的变化情况,并针对陆基和机载探测等小角度探测情况,仿真研究了目标和背板的温度、夹角等参数对目标偏振度的影响规律。研究结果表明:目标和背板温度相同时,辐射耦合效应会显著降低目标的偏振度,但不会改变目标偏振度随温度升高而增大的趋势。当目标和背板温度为30 °C、40 °C和50 °C时,目标偏振度的最大值分别为无强辐射背板时的63.7%、44.9%和42.2%。可见温度越高,目标和背板间的辐射耦合效应越强,目标偏振度降低的比例越大。此外,辐射耦合效应的强弱不仅与温度有关,还与目标和背板的夹角有关。随着夹角的增大,目标偏振度先增大后减小,且在夹角约为105°处取得极大值。因此,辐射耦合效应会在一定程度上改变目标偏振度,从而影响红外偏振设备的探测能力。最后,通过搭建的长波红外偏振成像系统,对建立的目标偏振度计算模型进行了实验验证,实验结果与仿真分析结果基本一致。本文研究成果对提升陆基和机载红外偏振设备的探测和识别能力具有一定的指导意义。
-
关键词:
- 红外辐射 /
- 线偏振度 /
- 偏振双向反射分布函数 /
- 辐射耦合效应
Abstract:Infrared polarization imaging technology has the advantages of long detection range and high rate of target recognition. However, the polarization characteristics of targets are easily affected by background radiation in complex environments, which significantly reduces the detection capability of infrared polarization equipment. Based on the polarized Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (pBRDF), this paper establishes a calculation model for the target’s Degree of Linear Polarization (DoLP), comprehensively considering the radiation coupling effect between the target and the background. The variation of the target’s DoLP under two conditions - with and without a strong radiation backplate – is then comparatively studied. Additionally, in order to solve problems of land-based and airborne small-angle detection, simulation research is done to find out how the target’s DoLP is influenced by parameters such as the temperatures and the included angle between the target and the backplate. Research results show that the radiation coupling effect significantly reduces the target’s degree of polarization when the temperatures of the target and the backplate are the same, but it does not change the trend of the target’s degree of polarization, which increases with an increase in temperature. When the temperature of the target and the backplate is 30 °C, 40 °C, and 50 °C, the maximum degree of polarization of the target is 63.7%, 44.9%, and 42.2% of those without a strong radiation backplate, respectively. It can be concluded then that the higher the temperature, the stronger the radiation coupling effect between the target and the backplate, and the greater the reduction of the target’s degree of polarization; and that the strength of the radiation coupling effect is not only related to the temperature, but also to the included angle between the target and the backplate. With the increase of the included angle, the target’s DoLP first increases and then decreases, and the maximum value is obtained when the included angle is about 105°. Therefore, the radiation coupling effect changes the target’s DoLP to a certain extent, thereby affecting the detection ability of the infrared polarization equipment. Finally, through building a long-wave infrared polarization imaging system, the established calculation model of the target’s degree of polarization is verified by experiments, whose results are basically consistent with those of the simulation analysis. Overall, the research results in this paper have certain guiding significance for improving the detection and identification capabilities of land-based and airborne infrared polarization equipment.
-
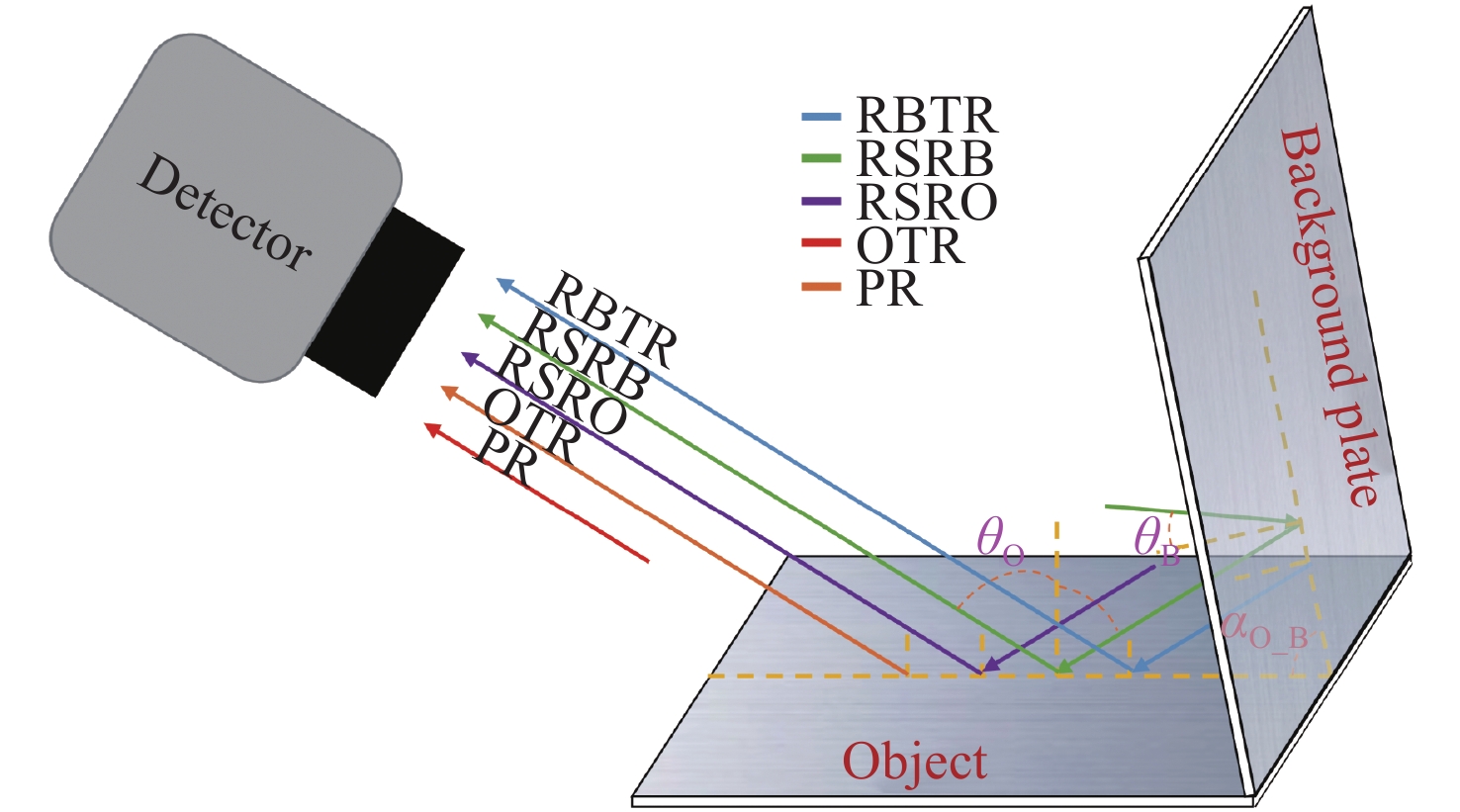
图 1 红外辐射模型。
${\theta _{\rm{O}}}$ 和${\theta _{\rm{B}}}$ 分别为目标和背板的入射角,${\alpha _{{\rm{O}}\_{\rm{B}}}}$ 为目标和背板的夹角Figure 1. The model of infrared radiation.
${\theta _{\rm{O}}}$ and${\theta _{\rm{B}}}$ are the incidence angle of the object and the background plate respectively;${\alpha _{{\rm{O}}\_{\rm{B}}}}$ is the angle between the object and the background plate图 6 不同温度下的目标偏振度。(a)仿真与实验结果对比;(b)30 °C对比结果;(c)40 °C对比结果;(d)50 °C对比结果
Figure 6. The DoLP of the object at different temperatures. (a) Comparison between the simulation results and the experimental results; (b) comparison results at 30 °C; (c) comparison results at 40 °C; and (d) comparison results at 50 °C
-
[1] 段锦, 付强, 莫春和, 等. 国外偏振成像军事应用的研究进展(上)[J]. 红外技术,2014,36(3):190-195. doi: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201403003DUAN J, FU Q, MO CH H, et al. Review of polarization imaging technology for international military application I[J]. Infrared Technology, 2014, 36(3): 190-195. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201403003 [2] HIOKI S, RIEDI J, DJELLALI M S. A study of polarimetric error induced by satellite motion: application to the 3MI and similar sensors[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2021, 14(3): 1801-1816. doi: 10.5194/amt-14-1801-2021 [3] LI S Y, JIAO J N, WANG CH. Research on polarized multi-spectral system and fusion algorithm for remote sensing of vegetation status at night[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(17): 3510. doi: 10.3390/rs13173510 [4] ZHOU Y, LU Y CH, SHEN Y F, et al. Polarized remote inversion of the refractive index of marine spilled oil from PARASOL images under Sunglint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2710-2719. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2953640 [5] 金伟其, 王霞, 曹峰梅, 等. 水下光电成像技术与装备研究进展(下)[J]. 红外技术,2011,33(3):125-132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8891.2011.03.001JIN W Q, WANG X, CAO F M, et al. Review of underwater Opto-electrical imaging technology and equipment (Ⅱ)[J]. Infrared Technology, 2011, 33(3): 125-132. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8891.2011.03.001 [6] ZHANG J H, ZHANG Y, SHI ZH G. Enhancement of dim targets in a sea background based on long-wave infrared polarisation features[J]. IET Image Processing, 2018, 12(11): 2042-2050. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2018.5607 [7] 宫剑, 吕俊伟, 刘亮, 等. 红外偏振图像的舰船目标检测[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2020,40(2):586-594.GONG J, LÜ J W, LIU L, et al. Ship target detection based on infrared polarization image[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(2): 586-594. (in Chinese) [8] 宫剑, 吕俊伟, 刘亮, 等. 红外偏振舰船目标自适应尺度局部对比度检测[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(1):223-233. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202801.0223GONG J, LÜ J W, LIU L, et al. Adaptive scale local contrast detection for infrared polarization ship targets[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(1): 223-233. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202801.0223 [9] 张弛, 吴鑫, 谢建. 基于双向反射分布函数的海面红外偏振特性表征模型[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(6):1303-1313. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202806.1303ZHANG CH, WU X, XIE J. Infrared polarization characteristics on sea surface based on bidirectional reflection distribution function[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(6): 1303-1313. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202806.1303 [10] 宿德志, 吴世永, 刘亮, 等. 基于海浪谱建模的海面偏振仿真研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2021,58(14):1411001.SU D ZH, WU SH Y, LIU L, et al. Ocean wave spectrum modeling-based sea surface polarization simulation[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(14): 1411001. (in Chinese) [11] GURTON K P, DAHMANI R, VIDEEN G. Measured degree of infrared polarization for a variety of thermal emitting surfaces[R]. Adelphi: Army Research Laborary, 2004: 1-19. [12] GURTON K P, DAHMANI R. Effect of surface roughness and complex indices of refraction on polarized thermal emission[J]. Applied Optics, 2005, 44(26): 5361-5367. doi: 10.1364/AO.44.005361 [13] 寻丽娜, 薛模根, 曾献芳, 等. 飞机材料及其伪装涂层的热红外偏振特性研究[J]. 红外技术,2016,38(9):783-787. doi: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201609013XUN L N, XUE M G, ZENG X F, et al. Research of infrared polarization characteristics of aircraft materials and its camouflage coating[J]. Infrared Technology, 2016, 38(9): 783-787. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201609013 [14] 谢琛, 王峰. 伪装涂层红外偏振辐射特性实验研究[J]. 红外技术,2015,37(10):890-894.XIE CH, WANG F. Research on infrared polarization radiation properties experiment of camouflage coating[J]. Infrared Technology, 2015, 37(10): 890-894. (in Chinese) [15] 王凯, 刘宏, 张修兴. 空间目标热控涂层材料偏振反射特性研究[J]. 光子学报,2020,49(12):1229003.WANG K, LIU H, ZHANG X X. Study on polarized reflection characteristics of space object thermal control coatings[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2020, 49(12): 1229003. (in Chinese) [16] FLYNN D S, ALEXANDER C. Polarized surface scattering expressed in terms of a bidirectional reflectance distribution function matrix[J]. Optical Engineering, 1995, 34(6): 1646-1650. doi: 10.1117/12.202105 [17] 徐文斌, 陈伟力, 李军伟, 等. 采用长波红外高光谱偏振技术的目标探测实验[J]. 红外与激光工程,2017,46(5):0504005. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.0504005XU W B, CHEN W L, LI J W, et al. Experiment of target detection based on long-wave infrared hyperspectral polarization technology[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(5): 0504005. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.0504005 [18] 柳祎, 史浩东, 姜会林, 等. 粗糙目标表面红外偏振特性研究[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(3):459-471.LIU Y, SHI H D, JIANG H L, et al. Infrared polarization properties of targets with rough surface[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(3): 459-471. (in Chinese) [19] 汪震, 洪津, 叶松, 等. 金属表面粗糙度对热红外偏振特性影响研究[J]. 光子学报,2007,36(8):1500-1503.WANG ZH, HONG J, YE S, et al. Study on effect of metal surface roughness on polarized thermal emission[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2007, 36(8): 1500-1503. (in Chinese) [20] 汪方斌, 伊龙, 王峰, 等. 基于漫反射优化的金属表面偏振双向反射分布函数[J]. 光学学报,2021,41(11):1129002. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1129002WANG F B, YI L, WANG F, et al. Polarization bidirectional reflection distribution function of metal surfaces based on diffuse reflection optimization[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(11): 1129002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1129002 [21] 管风, 张晓晖, 韩宏伟. 金属随机粗糙表面的散射光偏振特性的实验研究[J]. 海军工程大学学报,2020,32(6):101-107. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2020.06.017GUAN F, ZHANG X H, HAN H W. Experimental study of polarization properties of scattering light from metal random rough surfaces[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2020, 32(6): 101-107. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2020.06.017 [22] TYO J S, RATLIFF B M, BOGER J K, et al. The effects of thermal equilibrium and contrast in LWIR Polarimetric images[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(23): 15161-15167. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.015161 [23] FELTON M, GURTON K P, PEZZANITI J L, et al. Measured comparison of the crossover periods for mid- and long-wave IR (MWIR and LWIR) polarimetric and conventional thermal imagery[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(15): 15704-15713. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.015704 [24] LIU H ZH, SHI Z L, FENG B. An infrared DoLP computational model considering surrounding irradiance[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2020, 106: 103043. [25] 杨志勇, 陆高翔, 张志伟, 等. 热辐射环境下目标红外偏振特性分析[J]. 光学学报,2022,42(2):0220001.YANG ZH Y, LU G X, ZHANG ZH W, et al. Analysis of infrared polarization characteristics of target in thermal radiation environment[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(2): 0220001. (in Chinese) [26] SU D ZH, LIU L, LIU L SH, et al. An infrared DoLP model considering the radiation coupling effect[J]. Photonics, 2021, 8(12): 546. doi: 10.3390/photonics8120546 [27] 倪歆玥, 余书田, 唐玉俊, 等. 海雾中舰船目标的偏振探测能力研究[J]. 红外与毫米波学报,2021,40(1):96-101. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2021.01.014NI X Y, YU SH T, TANG Y J, et al. The research on polarimetric detection capability of ship targets in the sea fog[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2021, 40(1): 96-101. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2021.01.014 [28] 张景华, 张焱, 石志广. 基于长波红外的海面场景偏振特性分析与建模[J]. 红外与毫米波学报,2018,37(5):586-594. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2018.05.011ZHANG J H, ZHANG Y, SHI ZH G. Study and modeling of infrared polarization characteristics based on sea scene in long wave band[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2018, 37(5): 586-594. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2018.05.011 [29] PRIEST R G, GERMER T A. Polarimetric BRDF in the microfacet model: theory and measurements[C]. Proceedings of the Meeting of the Military Sensing Symposia Specialty Group on Passive Sensors, NIST, 2000: 169-181. [30] HYDE IV M W, SCHMIDT J D, HAVRILLA M J. A geometrical optics polarimetric bidirectional reflectance distribution function for dielectric and metallic surfaces[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(24): 22138-22153. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.022138 [31] PÉREZ J J G, OSSIKOVSKI R. Polarized Light and the Mueller Matrix Approach[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2016: 107-109. [32] THILAK V, VOELZ D G, CREUSERE C D. Polarization-based index of refraction and reflection angle estimation for remote sensing applications[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(30): 7527-7536. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.007527 [33] 朱达荣, 冯康康, 汪方斌, 等. 粗糙表面六参量偏振双向反射分布函数模型[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2020,57(9):092901.ZHU D R, FENG K K, WANG F B, et al. Six-parameter polarized bidirectional reflectance distribution function model for rough surfaces[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(9): 092901. (in Chinese) [34] 姚竞争, 韩端锋, 郑向阳. 某三体舰船外形雷达隐身性设计[J]. 舰船科学技术,2011,33(7):62-67. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2011.07.015YAO J ZH, HAN D F, ZHENG X Y. The shape optimal design considering the radar stealthy performance of a trimaran warship[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2011, 33(7): 62-67. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2011.07.015 -












 下载:
下载: