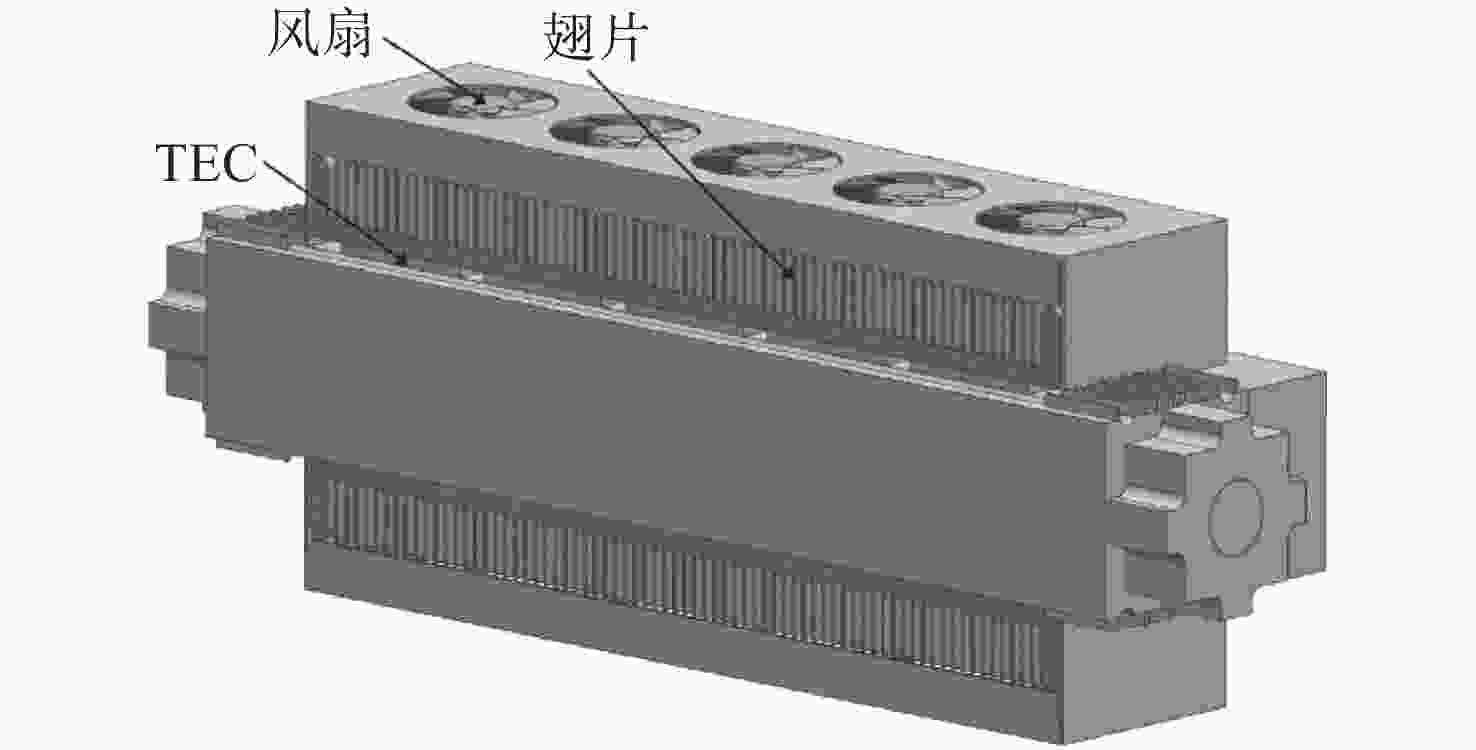
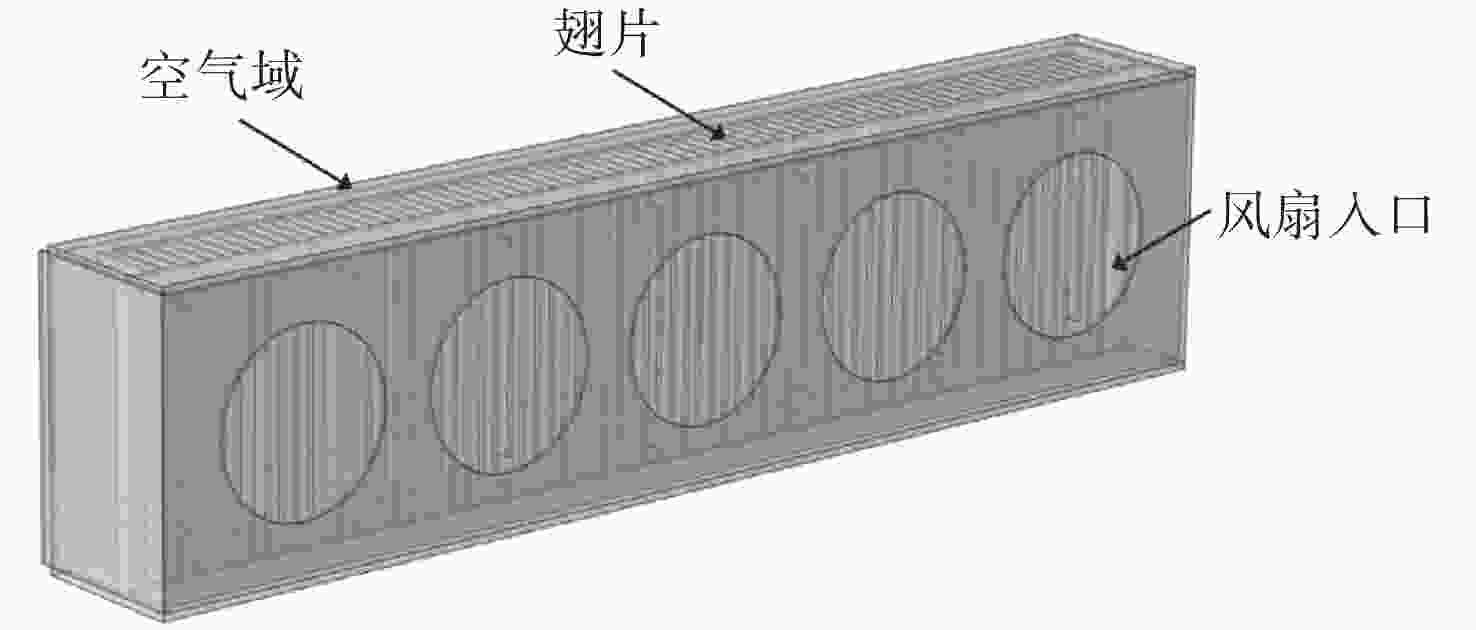
Temperature control method of CO2 laser operating in airborne wide temperature range
-
摘要:
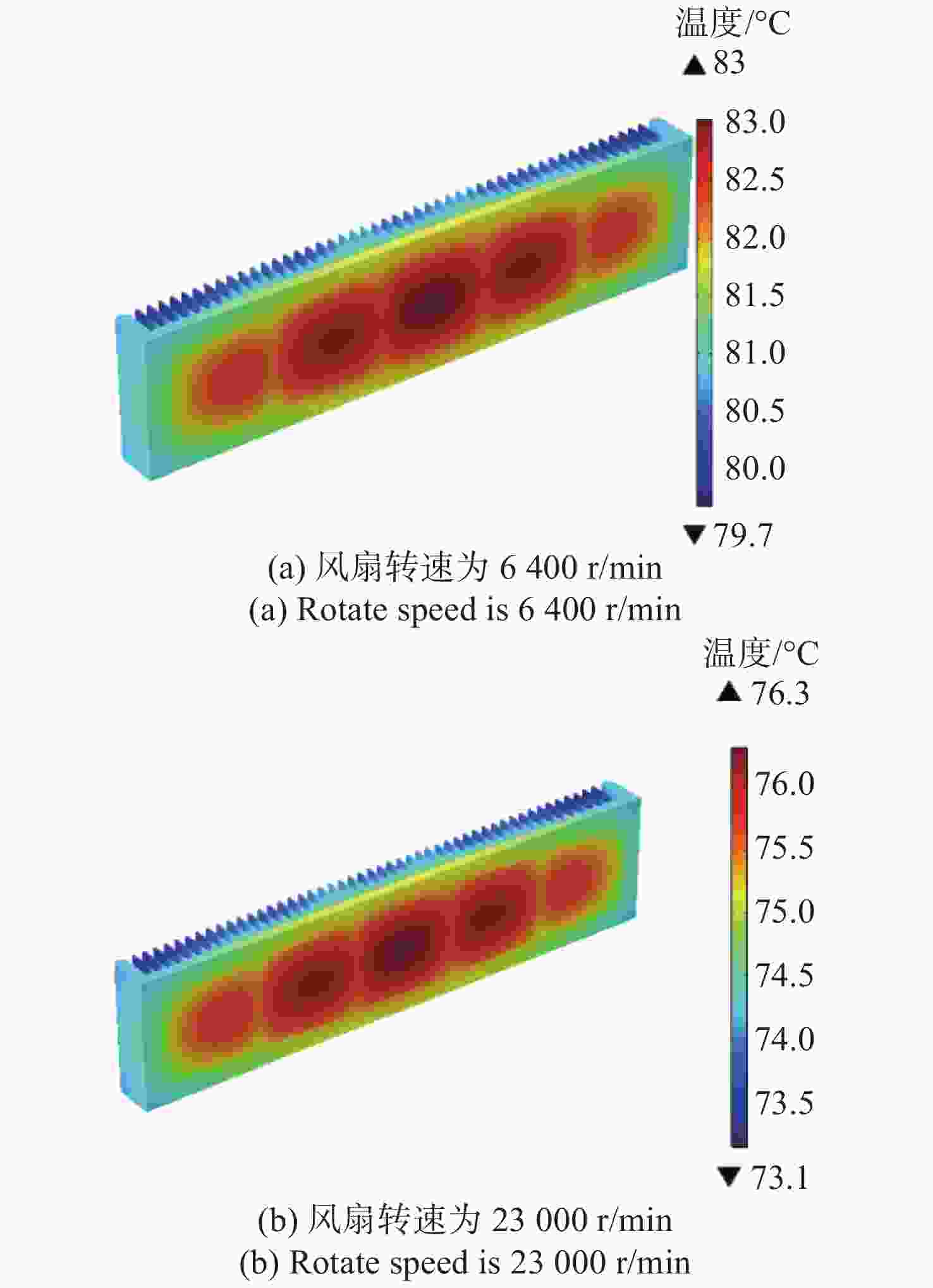
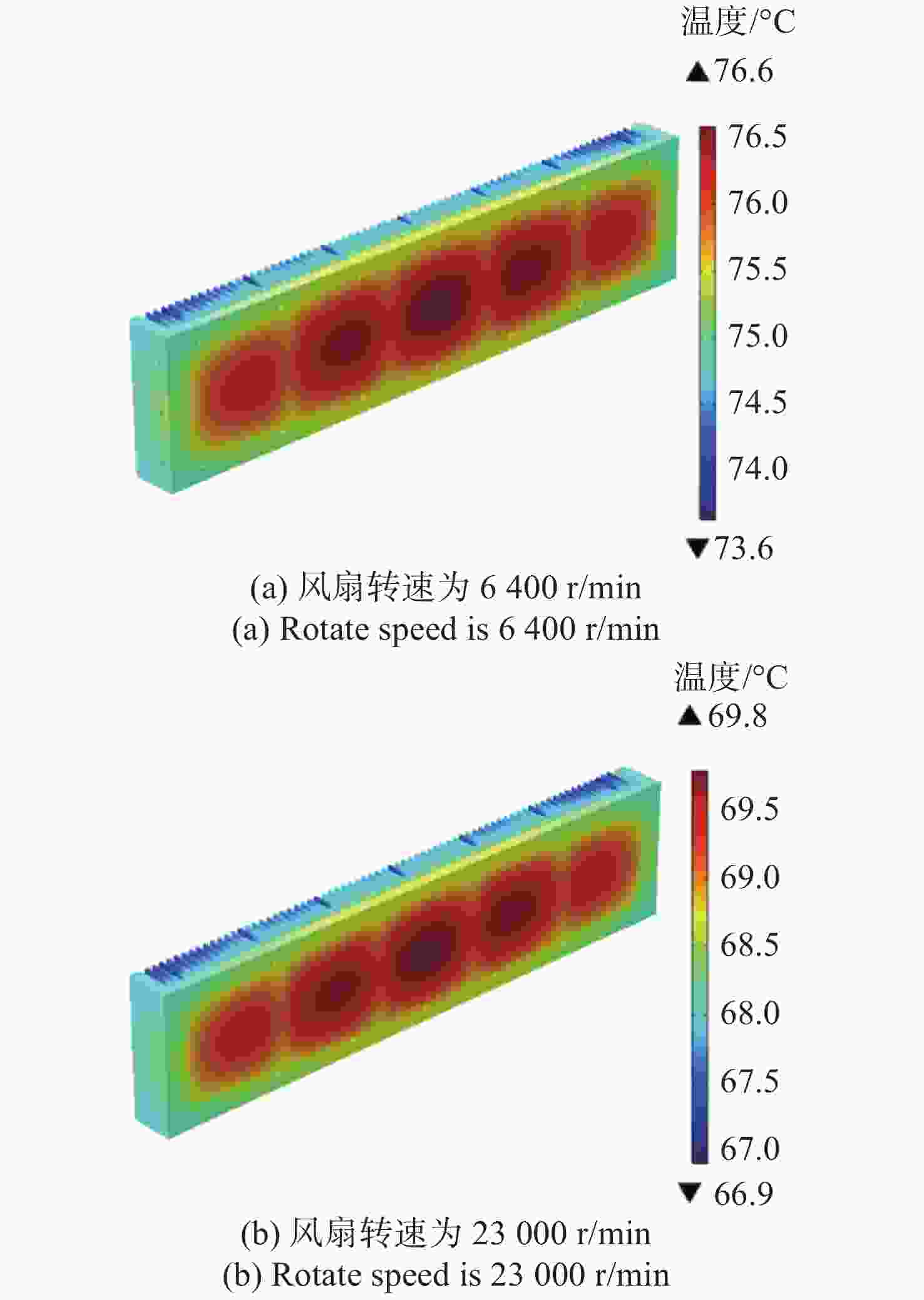
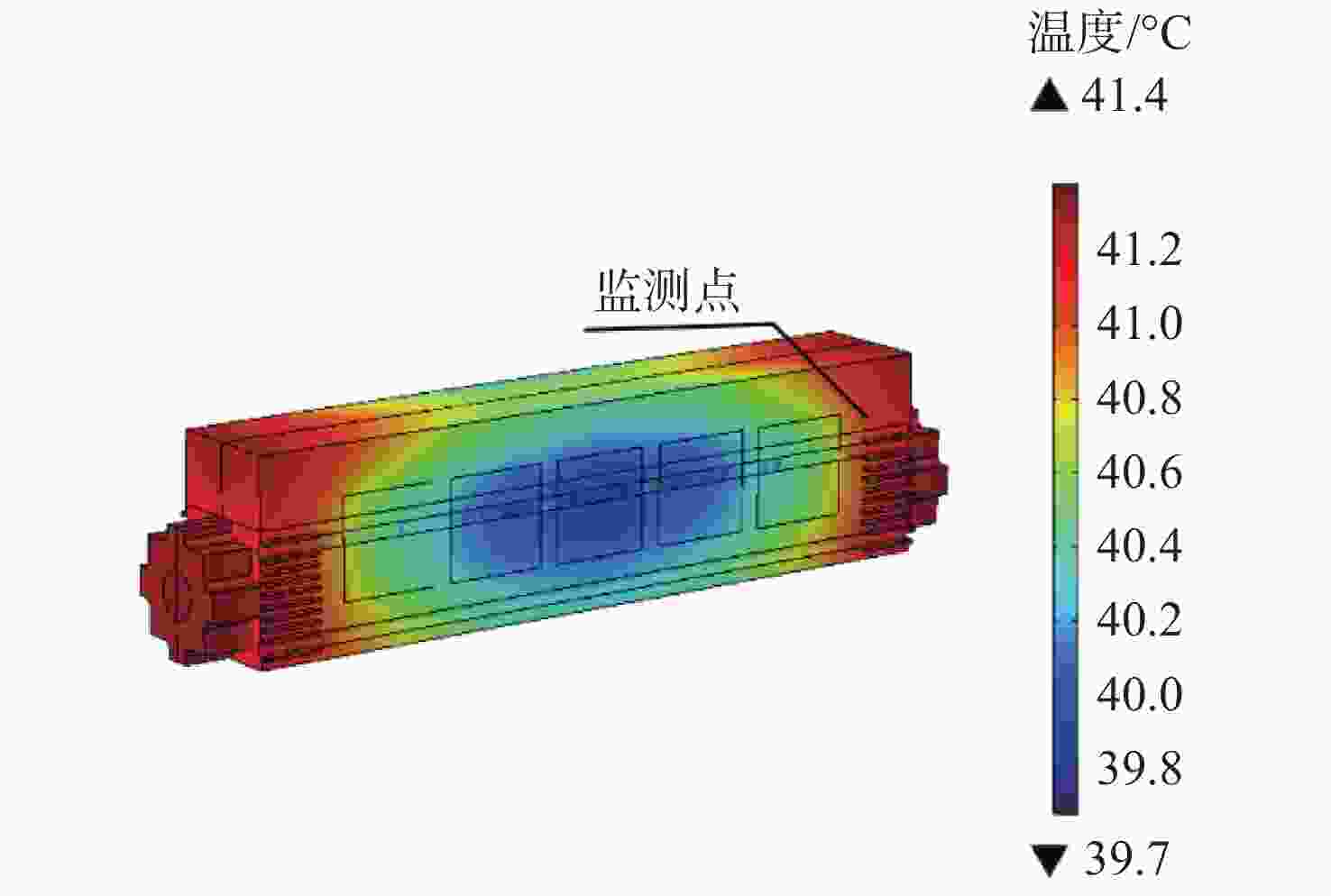
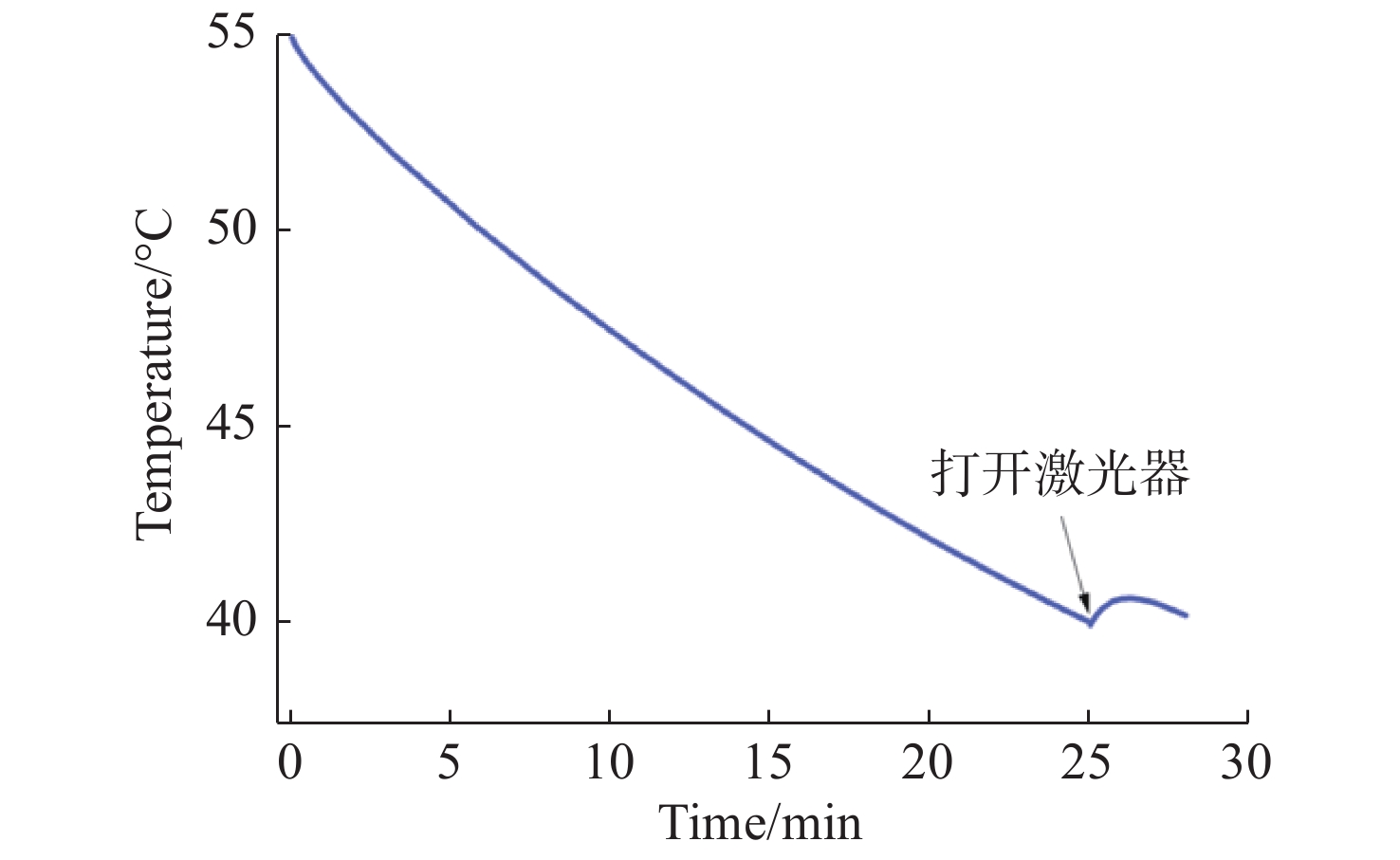
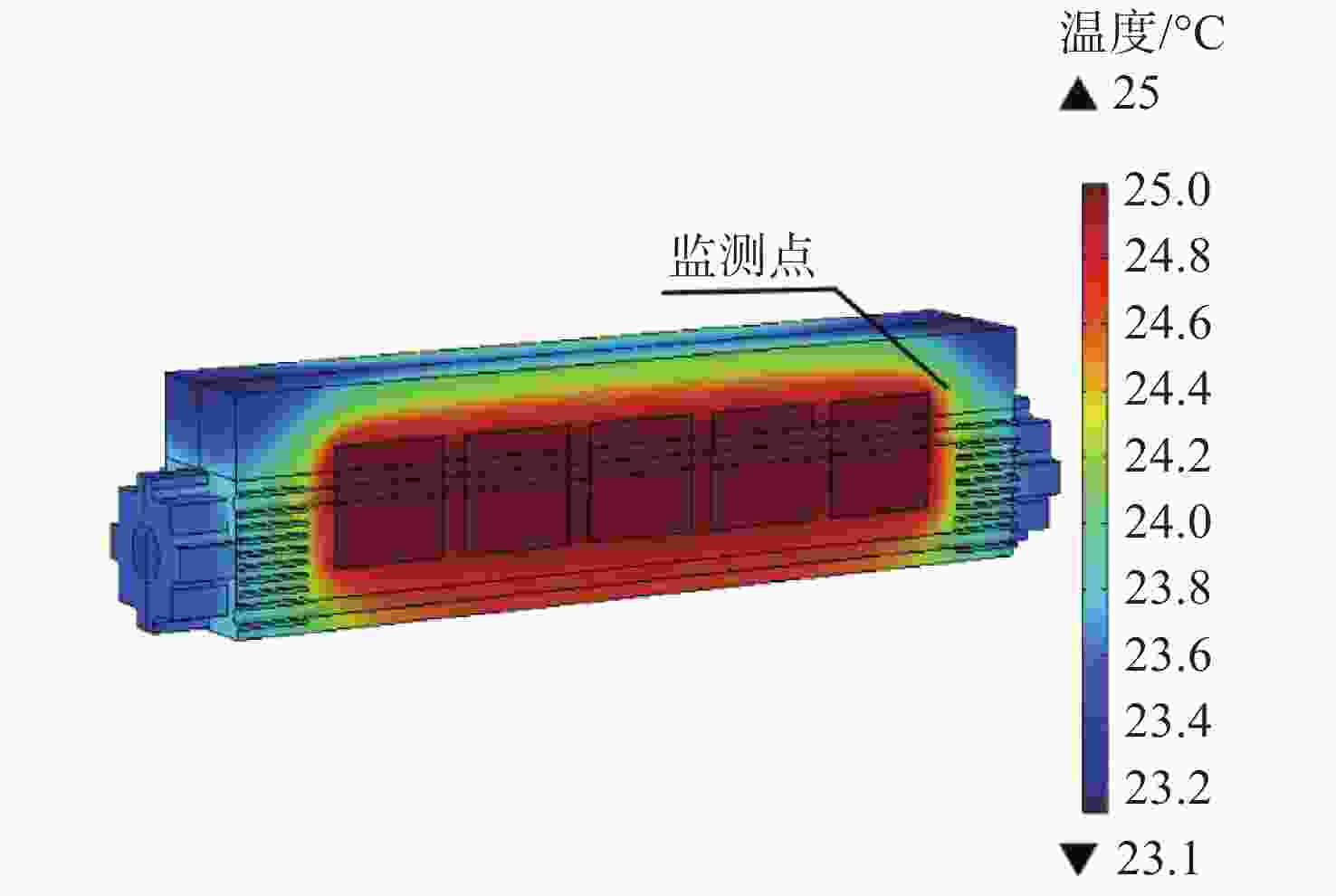
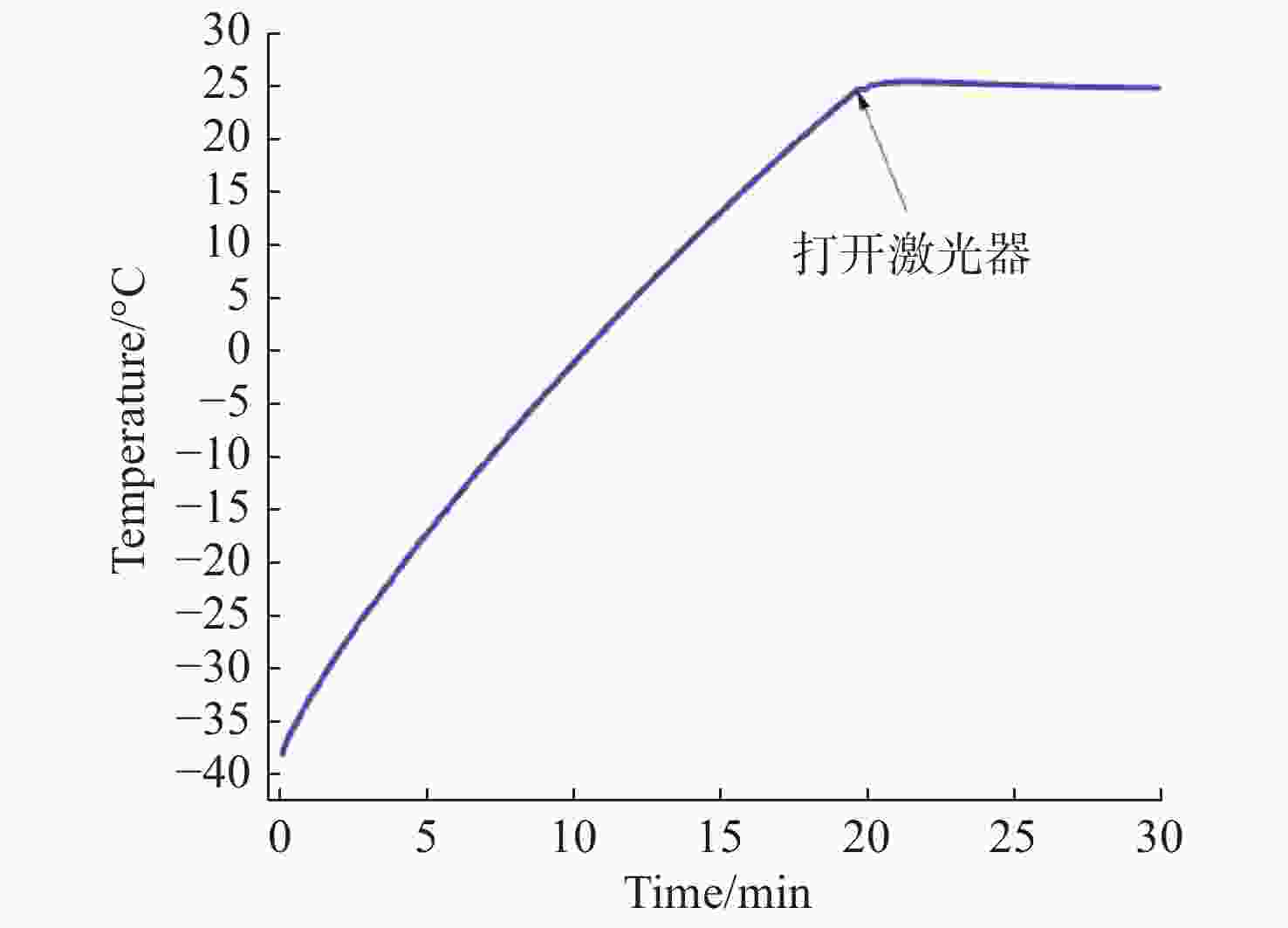
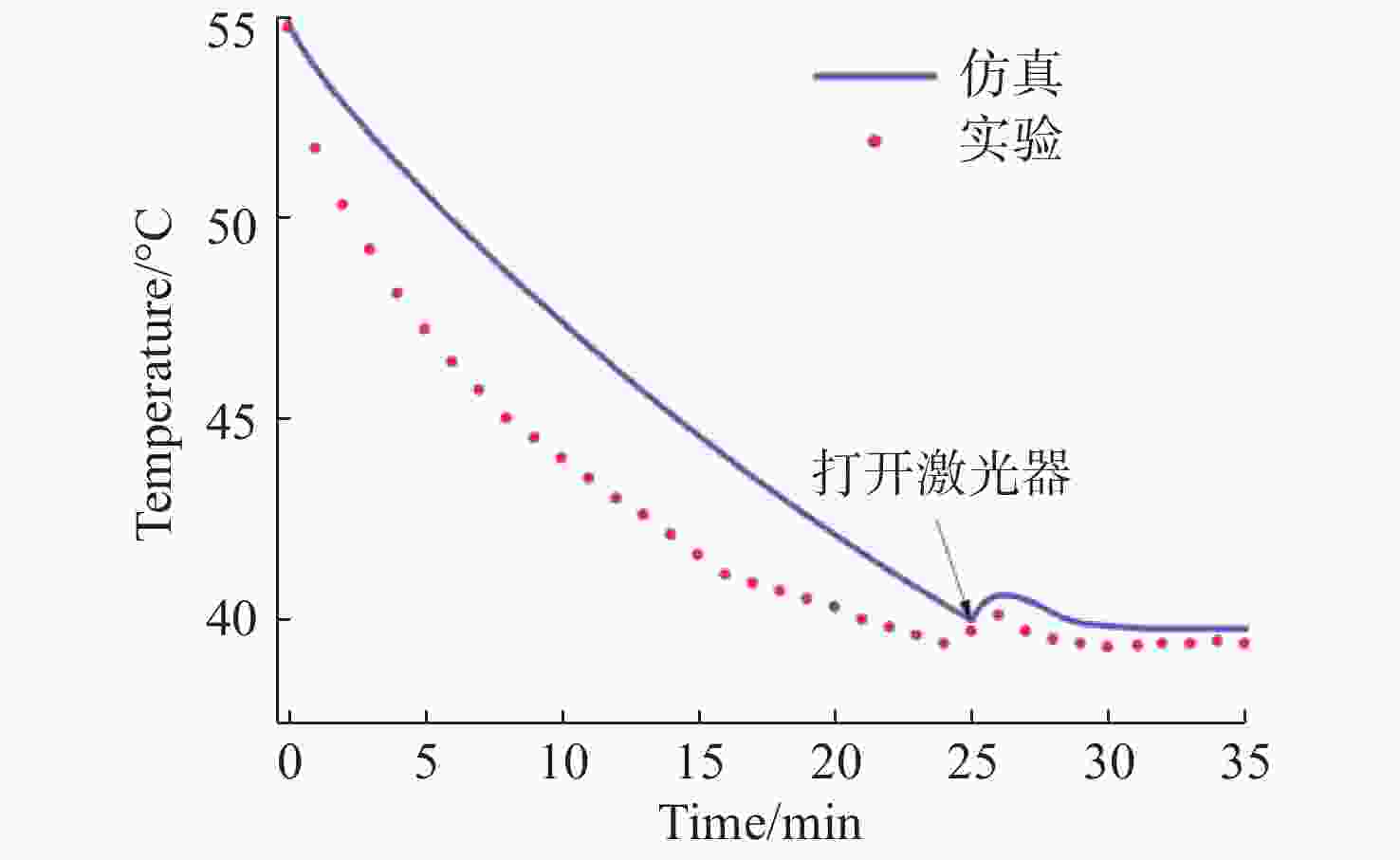
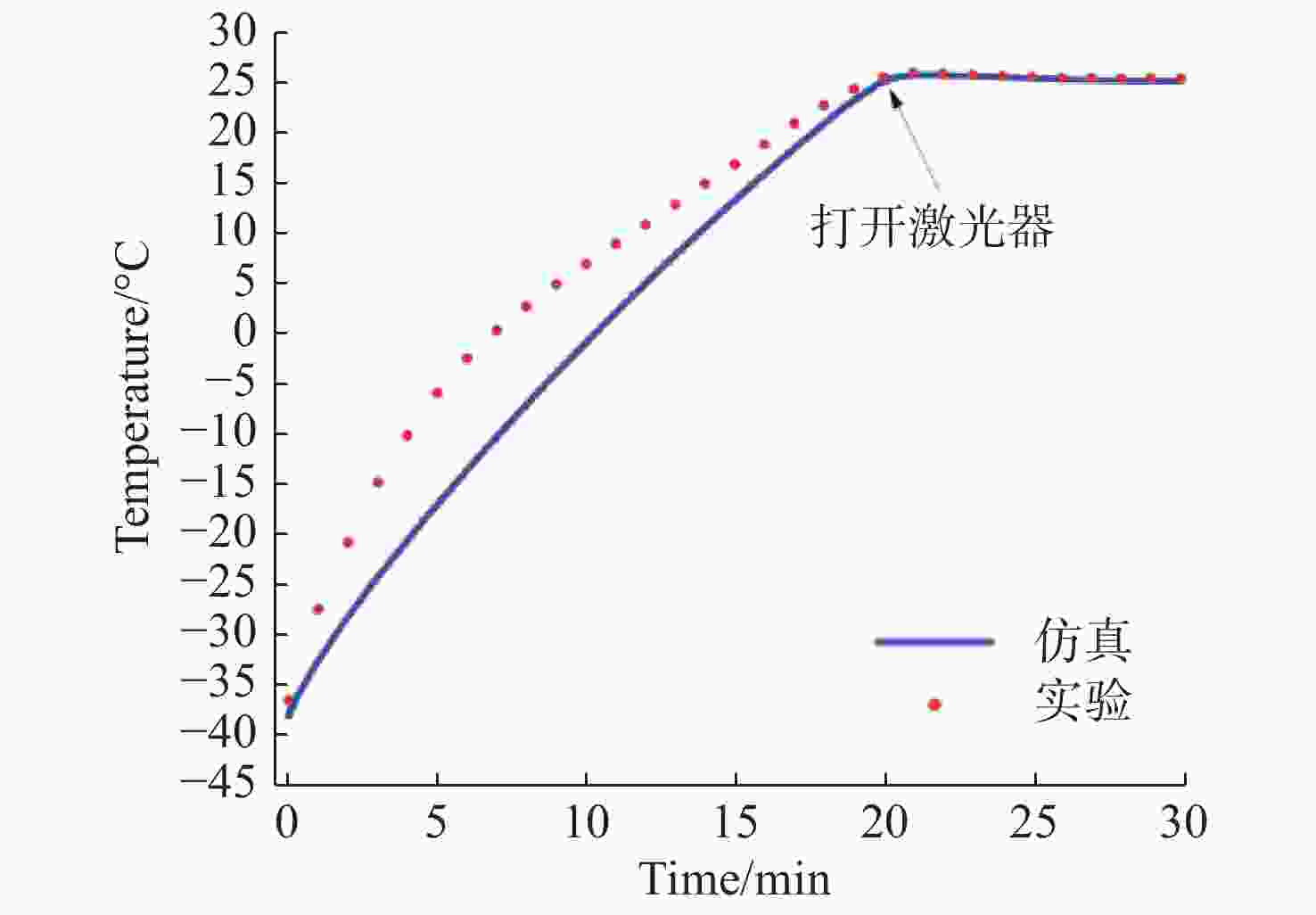
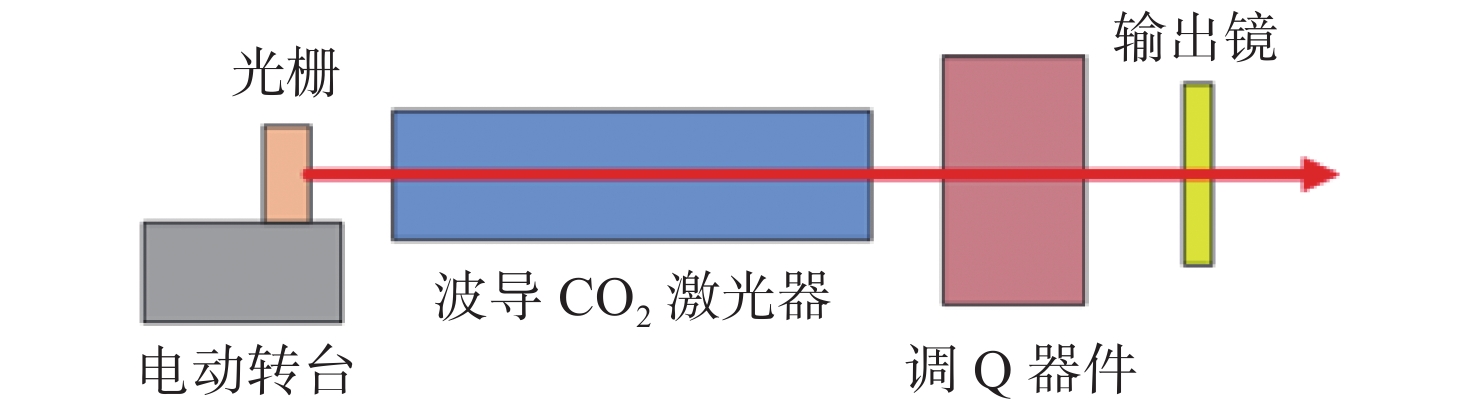
机载激光雷达是实现远距离大气精准监测的重要手段,CO2激光器工作谱段与部分大气污染物和化学物质吸收谱一致,是大气监测激光雷达的重要光源。面向机载要求,在控制体积重量的条件下实现−40 °C~55 °C宽温域工作是机载CO2激光器温控系统的设计难点。因此,本文提出一种以激光器性能和环境温度为设计输入,半导体热电制冷与强制风冷相结合的闭环温控方法。根据激光器、半导体热电制冷和强制风冷等的结构与传热特性,建立温控方法的有限元模型,基于此模型对激光器温控性能进行研究。对于55 °C高温环境,温控系统工作25 min后,激光器温度控制在40 °C;对于−40 °C低温环境,温控系统在工作20 min后,激光器温度控制在25 °C,满足激光器正常工作要求。根据激光器及建立的温控方法,开展高低温环境下激光器工作能力实验研究,采集实验过程中的激光器温度数据,测量高低温条件下激光输出能力。实验结果表明:实测激光器温度与有限元仿真温度数据基本吻合,两者误差小于10%;采用所提出的温控方法,激光器在高低温条件下可以正常工作,输出功率与室温条件下一致。
Abstract:Airborne lidar is an important means to achieve long-range accurate atmospheric monitoring. Its laser wavelength is consistent with the absorption spectrum of most atmospheric pollutants and chemical substances, which makes it an important laser source for airborne lidar. However, it is difficult to design a temperature control system for airborne CO2 lasers to work in the −40 °C−55 °C temperature range under the controlled volume and weight conditions. In this paper, we propose a temperature closed-loop control method, in which the laser characteristic and environment temperature are used as input, and a thermo electric cooler and forced air cooling are combined. According to the structure and heat transfer characteristics of the laser, the thermo-electric cooler and the level of forced air cooling, the finite element model of temperature control method is established to optimize the temperature control performance of the laser. In a high temperature environment of 55 °C, the temperature of the laser is controlled at 40 °C after the temperature control system operates for 25 min. In a low temperature environment of −40 °C, the laser temperature is controlled at 25 °C after the temperature control system operates for 20 minutes, which meets the normal working requirements of the laser. According to the laser and the established temperature control method, the experimental research on the working ability of the laser in high and low temperature environment is carried out, the temperature data of the laser in the experimental process is collected, and the laser output power is measured under high and low temperature conditions. The experimental results show that the experimental measured temperature data is consistent with the finite element simulation results and the error between them is less than 10%. The laser using the proposed temperature control method can work steadily, and the output power of the laser is consistent with that of the laser at room temperature.
-
-
[1] 潘其坤, 俞航航, 陈飞, 等. 声光偏转快调谐脉冲CO2激光器实验研究[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(2):355-361. doi: 10.3788/co.20191202.0355PAN Q K, YU H H, CHEN F, et al. Experimental research on acousto-optic deflection rapid tuning pulsed CO2 lasers[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(2): 355-361. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191202.0355 [2] 郑义军, 朱子任, 谭荣清, 等. 双光路快速调谐脉冲CO2激光器[J]. 红外与激光工程,2020,49(1):0105001.ZHENG Y J, ZHU Z R, TAN R Q, et al. Rapidly tuned pulsed CO2 Laser with dual optical path[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(1): 0105001. (in Chinese) [3] 谭荣清, 万重怡, 吴谨, 等. 高重复频率可调谐TEA CO2激光研究[J]. 中国激光,2005,32(6):739-742. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2005.06.003TAN R Q, WAN CH Y, WU J, et al. Investigation on tunable high repetition rate TEA CO2 laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2005, 32(6): 739-742. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2005.06.003 [4] 吴世松, 张合勇, 王挺峰, 等. 基于透射式非稳腔的单纵模TEA CO2激光器[J]. 光学 精密工程,2018,26(2):293-299. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182602.0293WU SH S, ZHANG H Y, WANG T F, et al. Single longitudinal mode TEA CO2 laser based on transmissive unstable resonator[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(2): 293-299. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182602.0293 [5] WU F P, XIE X Y, LI SH P. A thermal dissipation design method for LED array structure illumination[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(3): 670-684. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0211 [6] 全伟, 李光慧, 陈熙, 等. 一体化半导体激光器的ANSYS热仿真及结构设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2016,24(5):1080-1086. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162405.1080QUAN W, LI G H, CHEN X, et al. Structural design and ANSYS thermal simulation for semiconductor laser system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(5): 1080-1086. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162405.1080 [7] APOLLONOV V V, DERZHAVIN S I, FILONENKO V A, et al. Highly efficient heat exchangers for laser diode arrays[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2000, 3889: 71-81. doi: 10.1117/12.380919 [8] 杨波, 高松信, 刘军, 等. 高功率二极管激光器喷雾冷却实验研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束,2014,26(7):071001. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.071001YANG B, GAO S X, LIU J, et al. Spray cooling of high power diode laser[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26(7): 071001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.071001 [9] 吴胤禛, 柳祎, 高全宝, 等. 碳化硅过渡热沉对C-mount封装激光器散热的影响[J]. 中国科技论文,2019,14(12):1362-1368.WU Y ZH, LIU Y, GAO Q B, et al. Effect of silicon carbide transition heat sink on heat dissipation of C-mount package laser[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2019, 14(12): 1362-1368. (in Chinese) [10] 张龙, 陈建生, 高静, 等. 大功率半导体激光器驱动电源及温控系统设计[J]. 红外与激光工程,2018,47(10):1005003. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.1005003ZHANG L, CHEN J SH, GAO J, et al. Design of driving power and temperature control system for high power semiconductor laser[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(10): 1005003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.1005003 [11] 张志军, 刘云, 付喜宏, 等. 百瓦级半导体激光器模块的风冷散热系统分析[J]. 发光学报,2012,33(2):187-191. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20123302.0187ZHANG ZH J, LIU Y, FU X H, et al. Analysis of air-cooled heat system in hundred-watt level semiconductor laser module[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2012, 33(2): 187-191. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20123302.0187 [12] 张阔, 于德洋, 何洋, 等. 紧凑型中红外固体激光器散热性能分析[J]. 中国激光,2017,44(3):0301002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201744.0301002ZHANG K, YU D Y, HE Y, et al. Analysis on cooling performance of compact mid-infrared solid state laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(3): 0301002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201744.0301002 [13] ZHANG W, SHEN L M, YANG Y X, et al. Thermal management for a micro semiconductor laser based on thermoelectric cooling[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 90: 664-673. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.07.027 [14] 刘玉华. RF激励全金属CO2波导激光器散热系统的设计[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版),2013,43(3):400-402.LIU Y H. Devising of an inner hydro-cooling circulation system of RF-excited the all metal CO2 waveguide laser[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 43(3): 400-402. (in Chinese) [15] 陆培华, 王润文. 高功率CO2激光器热平衡分析及热交换器换热计算[J]. 中国激光,2001,28(9):775-778. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2001.09.003LU P H, WANG R W. Heat balance analysis of high power CO2 laser and calculation to the heat exchanger[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2001, 28(9): 775-778. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2001.09.003 [16] 李岩, 张艺轩, 纳全鑫, 等. Tm: YLF激光器温度场分布计算与实验[J]. 红外与激光工程,2017,46(5):0506001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.0506001LI Y, ZHANG Y X, NA Q X, et al. Temperature distribution calculation and experiments of Tm: YLF laser[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(5): 0506001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.0506001 -





 下载:
下载: