-
摘要:
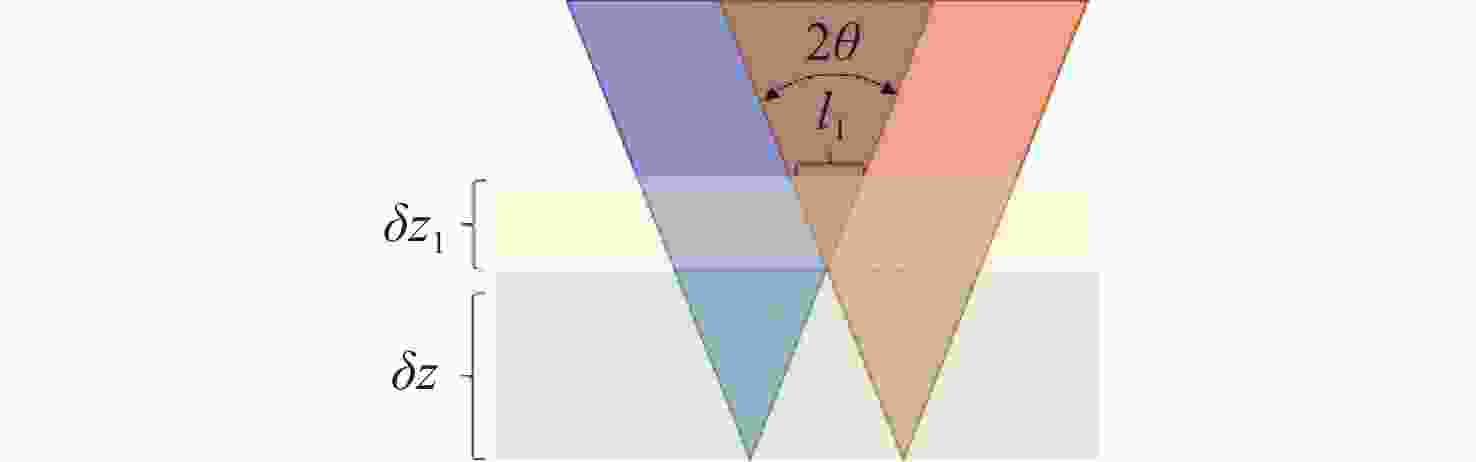
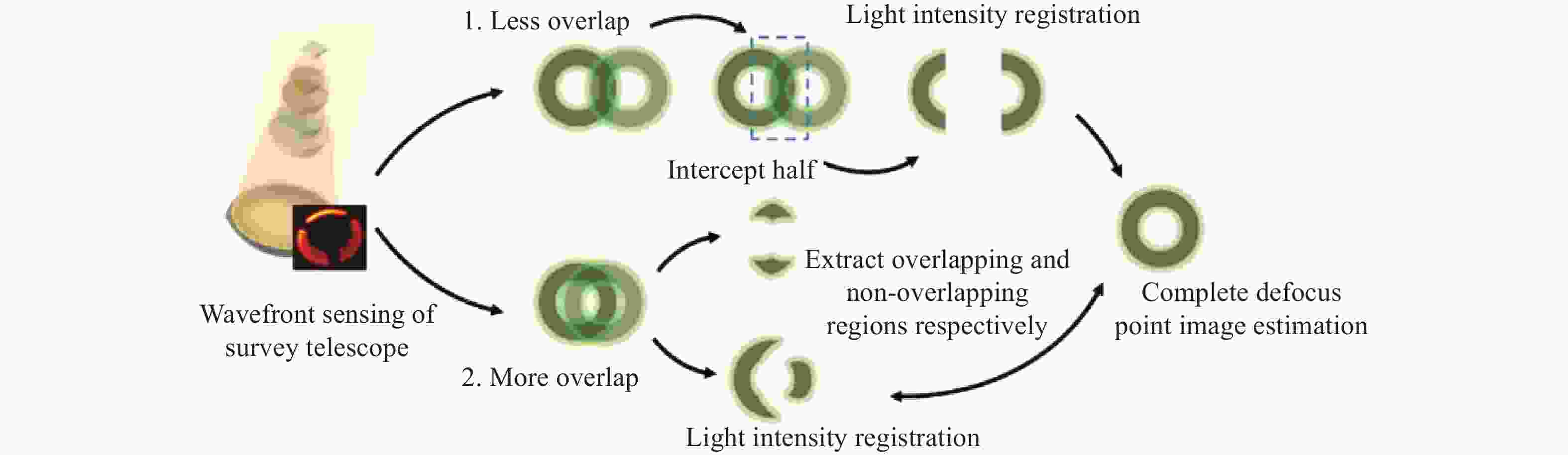
大口径巡天望远镜需要基于波前传感系统的反馈,进行主动光学闭环校正,以更好地发挥其极限探测能力。本文面向大口径巡天望远镜波前传感过程中,离焦星点像重合所导致的导星数量下降的问题,首先针对分区域曲率传感的基本理论表达进行了推导,之后,通过建立联合仿真模型,利用光学设计软件与数值计算软件之间的通讯交互,对分区域曲率传感的过程进行了仿真分析。最后,通过搭建桌面实验,分别就单目标与多目标的曲率传感进行了交叉比对,验证了算法的正确性。针对标准波前,本文所提出的方法与单导星曲率传感相比,误差为0.02个工作波长(RMS),误差在10%以内,可在传统主动光学技术的基础上,通过扩展可用导星,提升探测信噪比与采样速度,有效提升主动光学系统校正能力。
Abstract:The large aperture sky survey telescope needs closed-loop error correction based on the feedback of its wavefront sensing system, so as to give it a better conform to its limit detection ability. In this paper, firstly, the basic theoretical expression of sub region curvature sensing is derived. Then, a joint simulation model is established. The process of sub region curvature sensing is simulated and analyzed by using a combination of optical design software and numerical calculation software. Finally, by setting up a desktop experiment, the cross-comparison of single- and multi-target curvature sensors is carried out to verify the correctness of the algorithm. Compared to the traditional active optical technology, the method proposed in this paper can improve the detection signal-to-noise ratio and sampling speed by expanding the available guide stars. For the standard wavefront, compared with the single guide star curvature sensor, the error is 0.02 operating wavelengths (RMS), and the error is less than 10%, which can effectively improve the correction ability of the active optical system.
-
Key words:
- large aperture survey telescope /
- active optics /
- curvature sensing /
- natural guide star
-
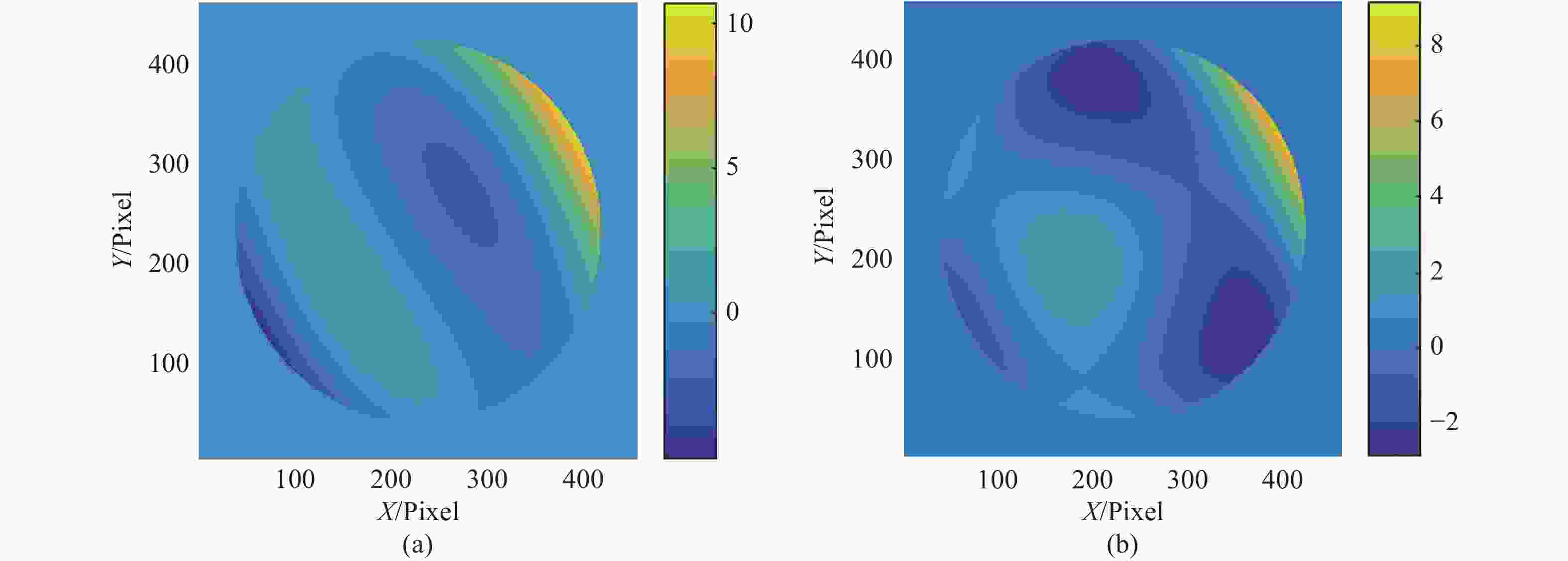
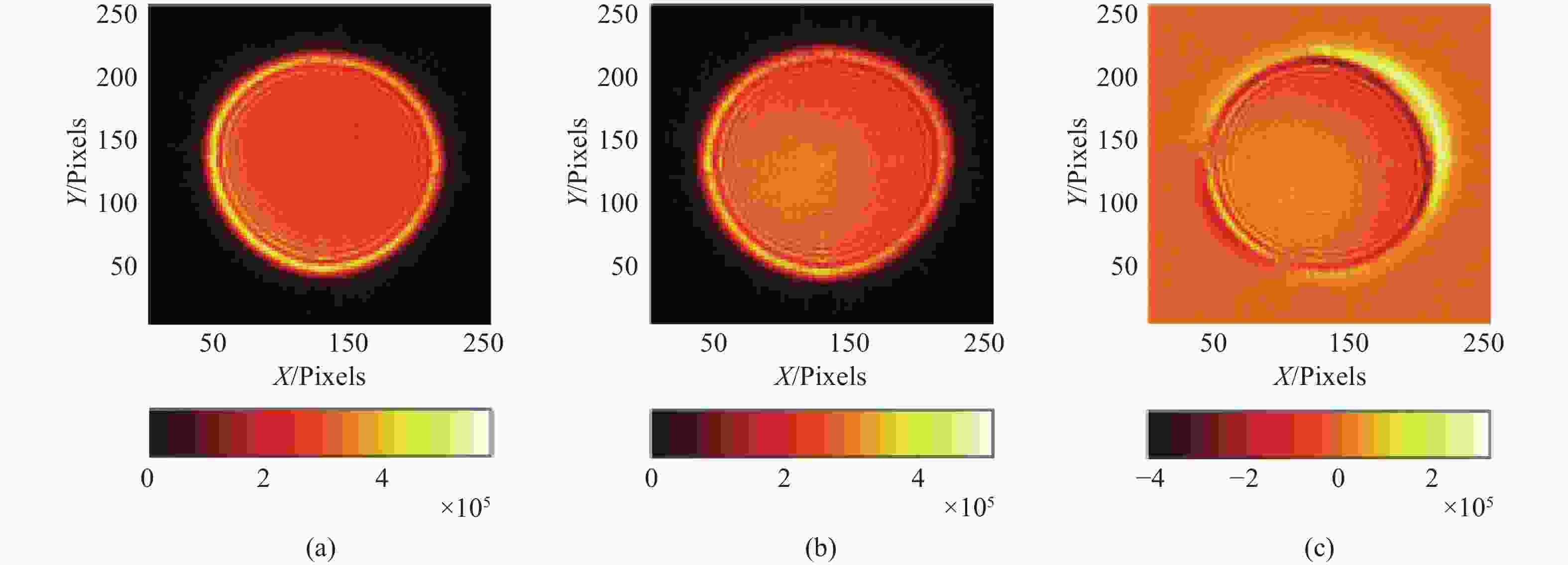
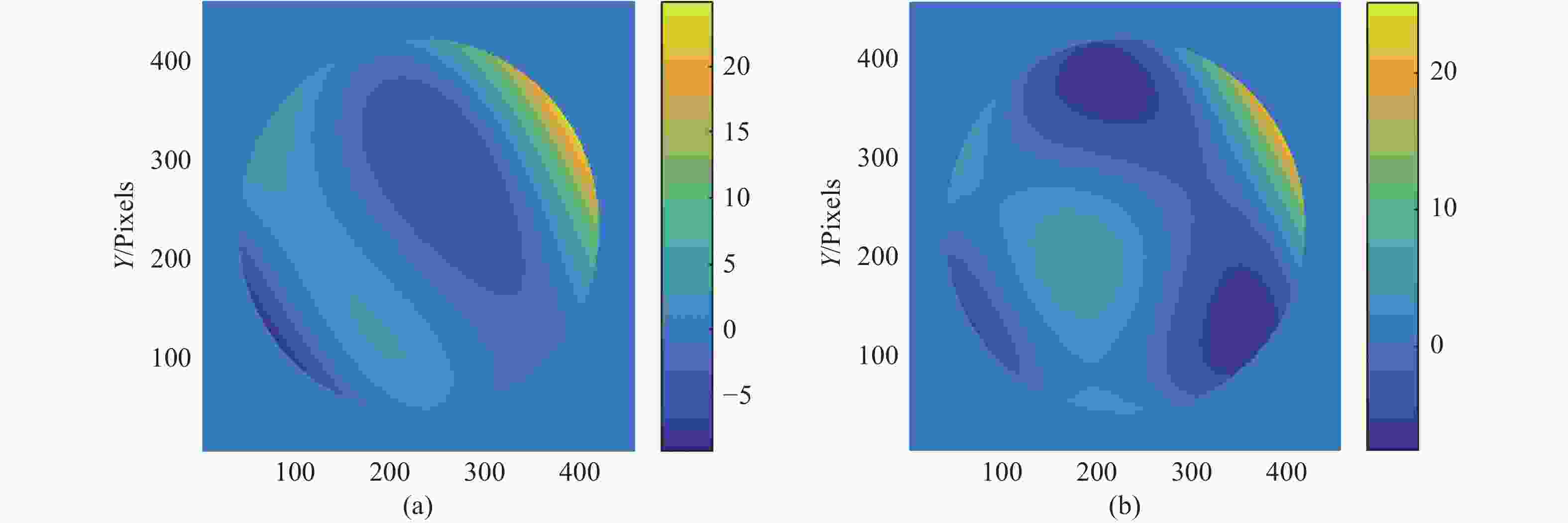
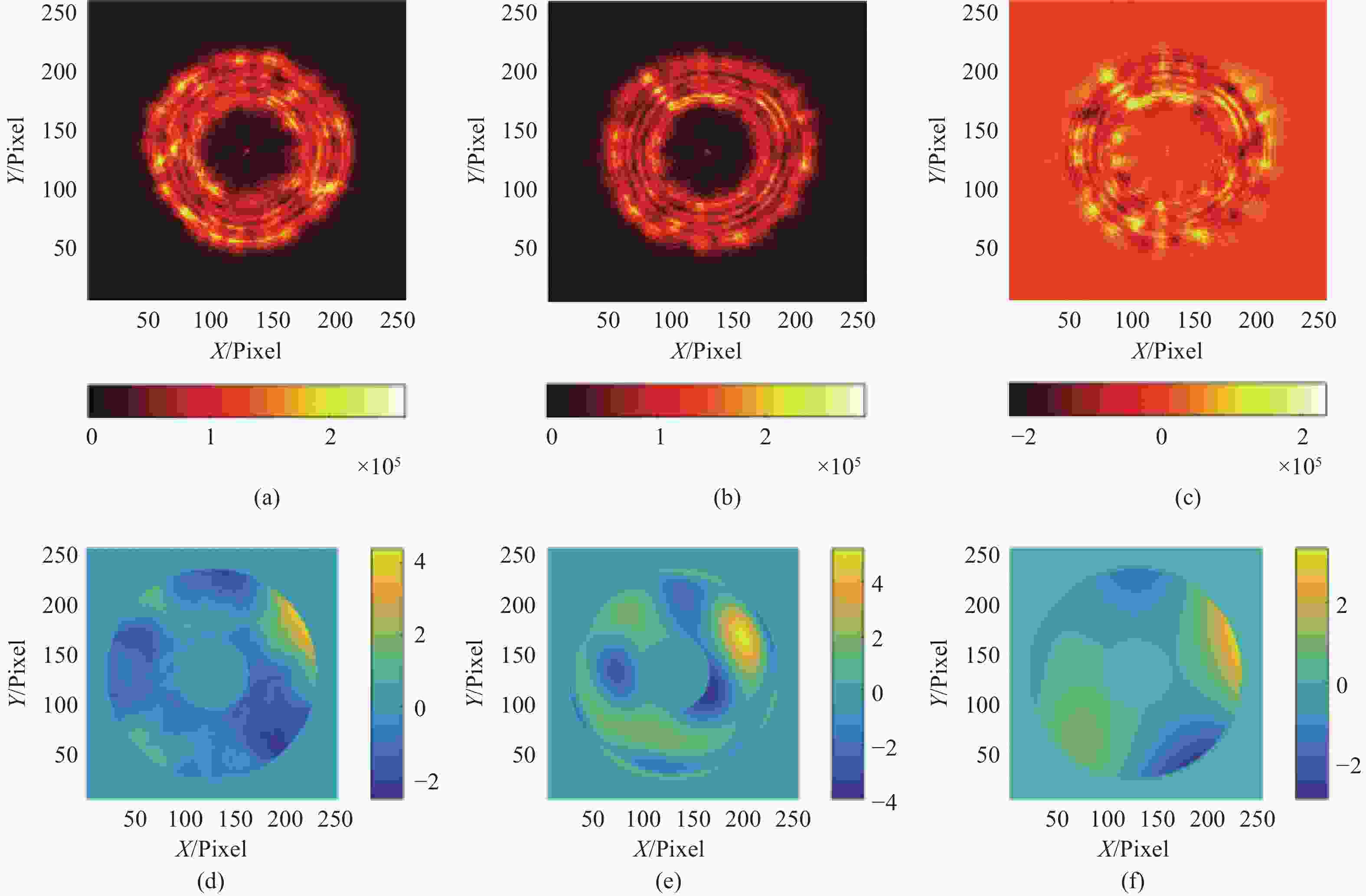
图 10 5 cm相干长度下湍流对像差提取的影响。(a)焦前能量分布;(b)焦后能量分布;(c)光强分布差分;(d)短曝光重建波前(10 ms);(e)长曝光重建波前(100 ms);(f)原始波前
Figure 10. Influence of turbulence on aberration extraction at 5 cm coherence length. (a) Pre-focal energy distribution; (b) post-focal energy distribution; (c) light intensity distribution difference; (d) short exposure reconstruction wavefront (10 ms); (e) long exposure reconstruction wavefront (100 ms); (f) original wavefront
-
[1] GANSICKE B T, SCHREIBER M R, TOLOZA O, et al. Accretion of a giant planet onto a white dwarf star[J]. Nature, 2019, 576(7785): 61-64. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1789-8 [2] EGDALL I M. Manufacture of a three-mirror wide-field optical system[J]. Optical Engineering, 1985, 24(2): 242285. doi: 10.1117/12.7973470 [3] SEBRING T A, DUNHAM E W, MILLIS R L, et al. The discovery channel telescope: a wide-field telescope in northern Arizona[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5489: 658-666. doi: 10.1117/12.551720 [4] ROODMAN A, REIL K, DAVIS C. Wavefront sensing and the active optics system of the dark energy camera[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9145: 914516. [5] HOLZLÖHNER R, TAUBENBERGER S, RAKICH A P, et al. Focal-plane wavefront sensing for active optics in the VST based on an analytical optical aberration model[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9906: 99066E. [6] GUNN J E, SIEGMUND W A, MANNERY E J, et al. The 2.5 m telescope of the Sloan digital sky survey[J]. The Astronomical Journal, 2006, 131(4): 2332-2359. doi: 10.1086/500975 [7] WOODS D F, SHAH R Y, JOHNSON J A, et al. Space Surveillance Telescope: focus and alignment of a three mirror telescope[J]. Optical Engineering, 2013, 52(5): 053604. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.52.5.053604 [8] HARBECK D R, BOROSON T, LESSER M, et al. The WIYN one degree imager 2014: performance of the partially populated focal plane and instrument upgrade path[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9147: 91470P. [9] PINIARD M, SORRENTE B, HUG G, et al. Melt pool monitoring in laser beam melting with two-wavelength holographic imaging[J]. Light:Advanced Manufacturing, 2022, 3(1): 11. doi: 10.37188/lam.2022.011 [10] 张天宇, 王钢, 张熙, 等. 基于焦面复制方法的自适应光学系统静态像差校正技术[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(3):545-551. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0182ZHANG T Y, WANG G, ZHANG X, et al. Statica berration correction technique for adaptive optics system based on focal-plane copy approach[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(3): 545-551. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0182 [11] GENG Z CH, TONG ZH, JIANG X Q. Review of geometric error measurement and compensation techniques of ultra-precision machine tools[J]. Light:Advanced Manufacturing, 2021, 2(2): 14. [12] SU R, LEACH R. Physics-based virtual coherence scanning interferometer for surface measurement[J]. Light:Advanced Manufacturing, 2021, 2(2): 9. [13] 王丰璞, 李新南, 徐晨, 等. 大型光学红外望远镜拼接非球面子镜反衍补偿检测光路设计[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(5):1184-1193. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0218WANG F P, LI X N, XU CH, et al. Optical testing path design for LOT aspheric segmented mirrors with reflective-diffractive compensation[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(5): 1184-1193. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0218 [14] 张磊, 吴金灵, 刘仁虎, 等. 光学自由曲面自适应干涉检测研究新进展[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(2):227-244. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0126ZHANG L, WU J L, LIU R H, et al. Research advances in adaptive interferometry for optical freeform surfaces[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(2): 227-244. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0126 [15] 陈波, 杨靖, 李新阳, 等. 波前曲率传感自适应光学的模式型控制技术[J]. 光学学报,2016,36(2):0201002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0201002CHEN B, YANG J, LI X Y, et al. Modal control technique of adaptive optics with wavefront curvature sensing[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(2): 0201002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0201002 -





 下载:
下载: