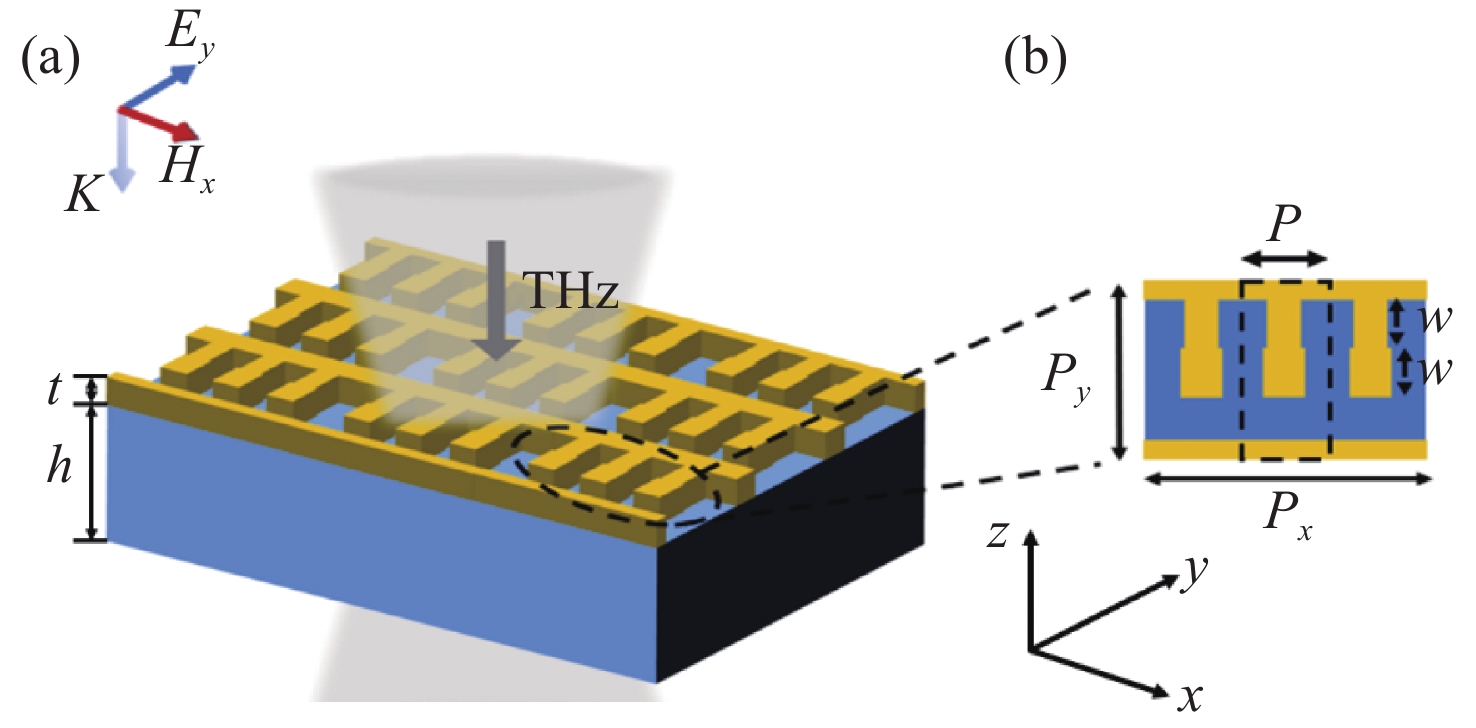
Coplanar excitation of terahertz spoof surface plasmon and high-Q sensing
doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0204
-
摘要:
本文提出使用单层光栅超表面结构耦合的方式实现太赫兹人工表面等离子体激元(SSP)共面激发,克服了通过介质耦合器在实际应用时需要反射测量等缺点。在单层金属结构上同时构造周期性光栅和太赫兹SSP复合结构,当太赫兹波垂直入射时,可实现光栅波矢和SSP波矢相匹配,激发SSP模式,在透射谱中可以产生高
Q 值谐振峰,其Q 因子可以达到1923。分析了结构参数对光栅耦合超表面透射谱以及色散特性的影响。基于该结构透射谱中的高Q 谐振峰进行传感研究,在谐振中心频率为0.22 THz时,实现传感灵敏度为67 GHz/RIU。本文所提出的光栅耦合超表面复合结构仅使用单层超表面结构实现了太赫兹SSP模式的激发以及高Q 传感,在诸多实际应用领域具有较大的研究潜力。-
关键词:
- 太赫兹超表面 /
- 人工表面等离子体激元 /
- 高Q谐振 /
- 传感
Abstract:In this paper, the coplanar excitation of terahertz Spoof Surface Plasmon (SSP) realized by using a single-layer grating meta-surface coupling method is proposed, which overcomes the disadvantages such as the reflection measurement when applying the medium couplers. The periodic grating and terahertz SSP composite structure are simultaneously constructed on the monolayer metal structure. When the terahertz waves are incident vertically, the wave vector of grating structures and the wave vector of SSPs are matched, and the SSP mode can be excited. The high
Q value resonant peaks can be generated in the transmission spectrum, and theQ factor can reach 1923. The effects of the structural parameters on the grating-coupled meta-surface transmission spectrum and dispersion characteristics are also analyzed. In addition, based on the highQ resonant peak in the transmission spectrum of the designed structure, the high sensing sensitivity is about 67 GHz/RIU at the resonant center frequency of 0.22 THz. The structure proposed in this paper, which realizes terahertz SSP excitation and highQ sensing by treating a single-layer meta-surface structure, exhibits great application potential in many practical applications.-
Key words:
- terahertz meta-surface /
- spoof surface plasmon /
- high Q resonance /
- sensing
-
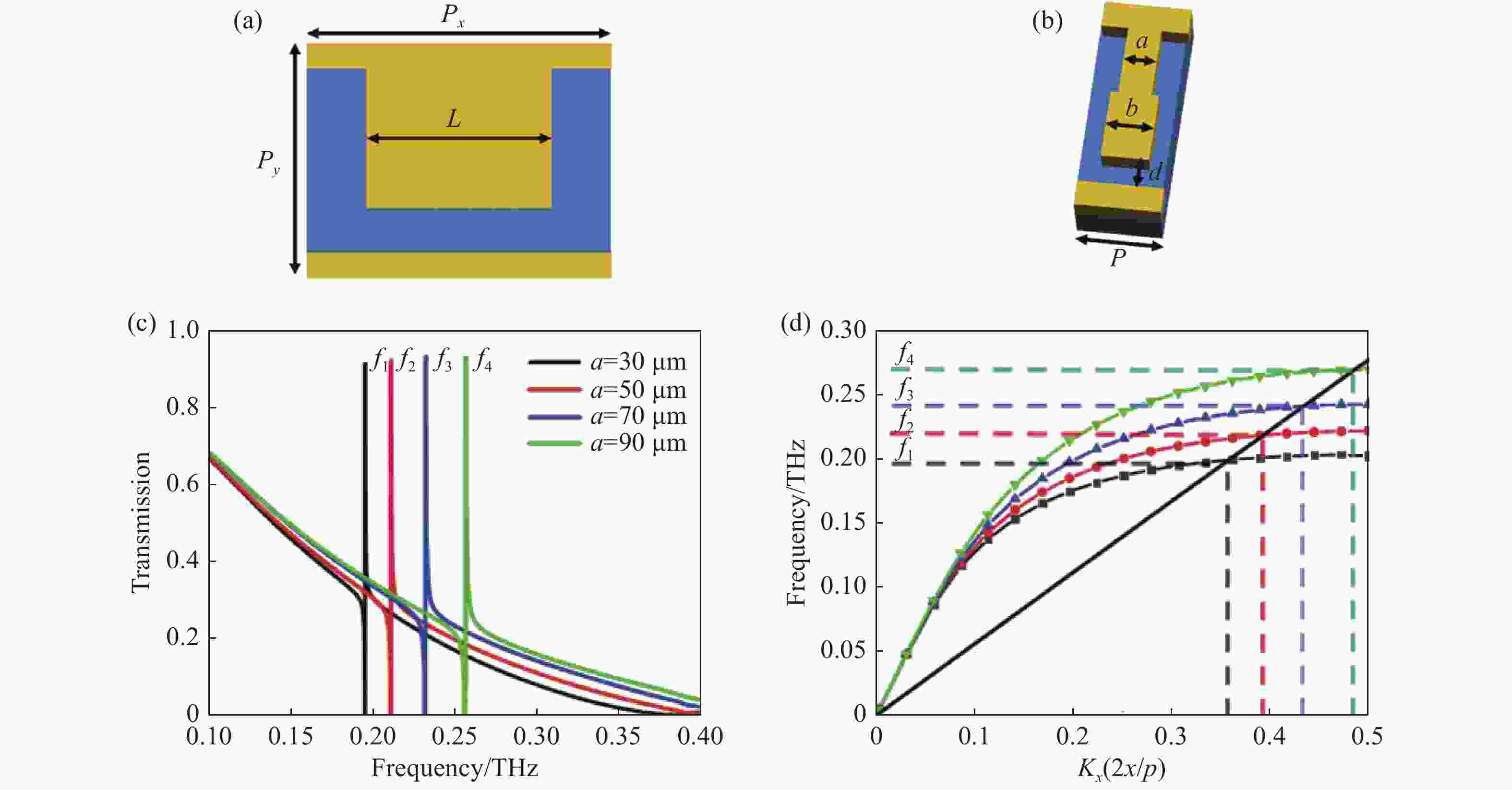
图 2 超表面结构及透射性能。(a)等效光栅耦合器结构示意图;(b)金属棒单元结构示意图;(c)不同结构参数a对应的透射谱;(d)结构参数a不同时对应的光栅及金属棒的色散关系
Figure 2. The meta-surface structure and transmission properties. (a) Schematic diagram of the equivalent grating coupler; (b) schematic diagram of the metal bar unit; (c) transmission spectra corresponding to different a; (d) dispersion characteristics of the grating and metal bar with different a
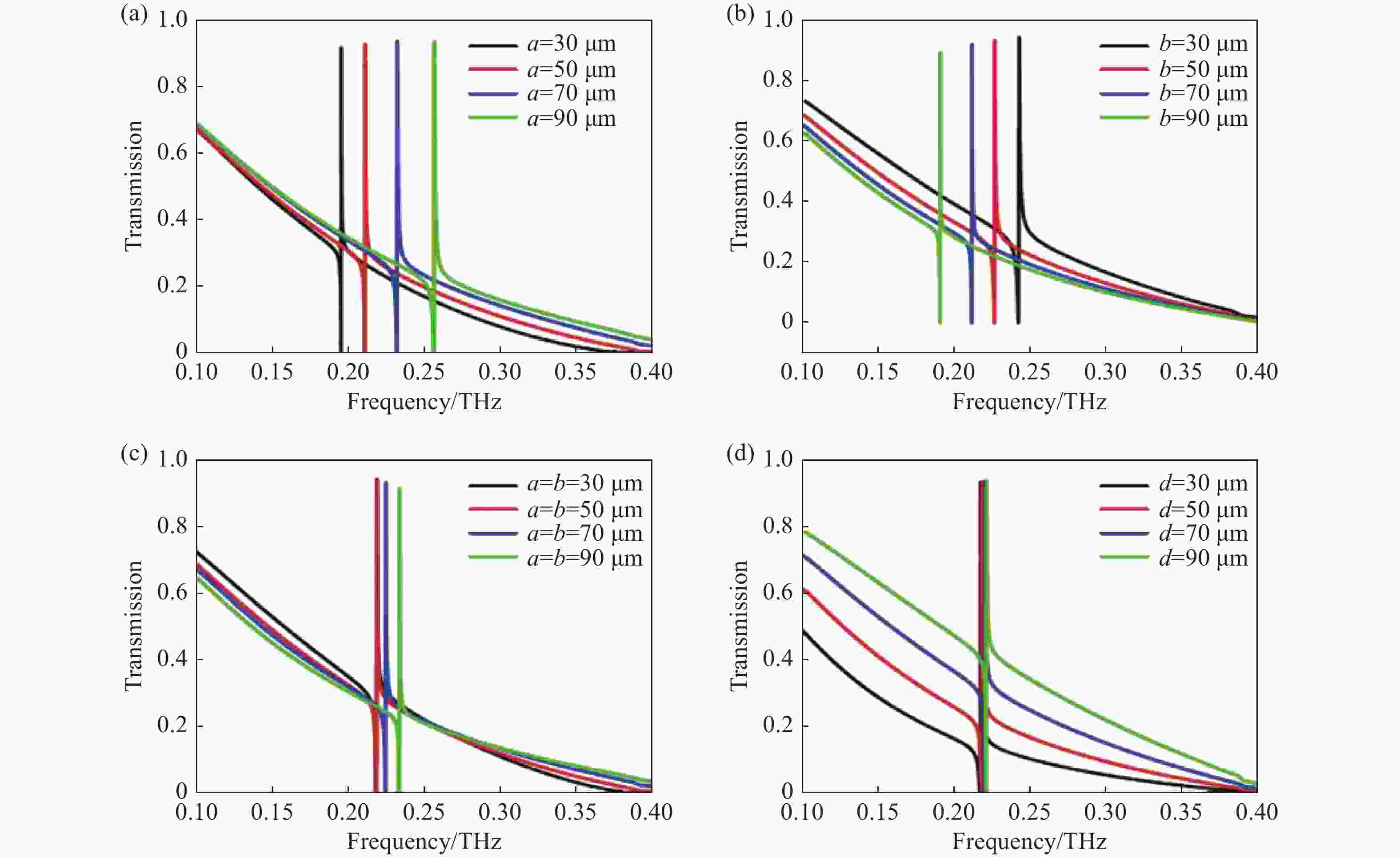
图 3 不同结构参数对光栅耦合超表面结构透射特性的影响。(a)参数a不同时的透射谱;(b)参数b不同时的透射谱;(c)参数a和b同时变化时的透射谱;(d)参数d不同时的透射谱
Figure 3. Effects of different structural parameters on the transmission spectrum of grating-coupled meta-surface structures. (a) Transmission spectra with different a; (b) transmission spectra with different b; (c) transmission spectra with the simultaneous variation of a and b; (d) transmission spectra with different d
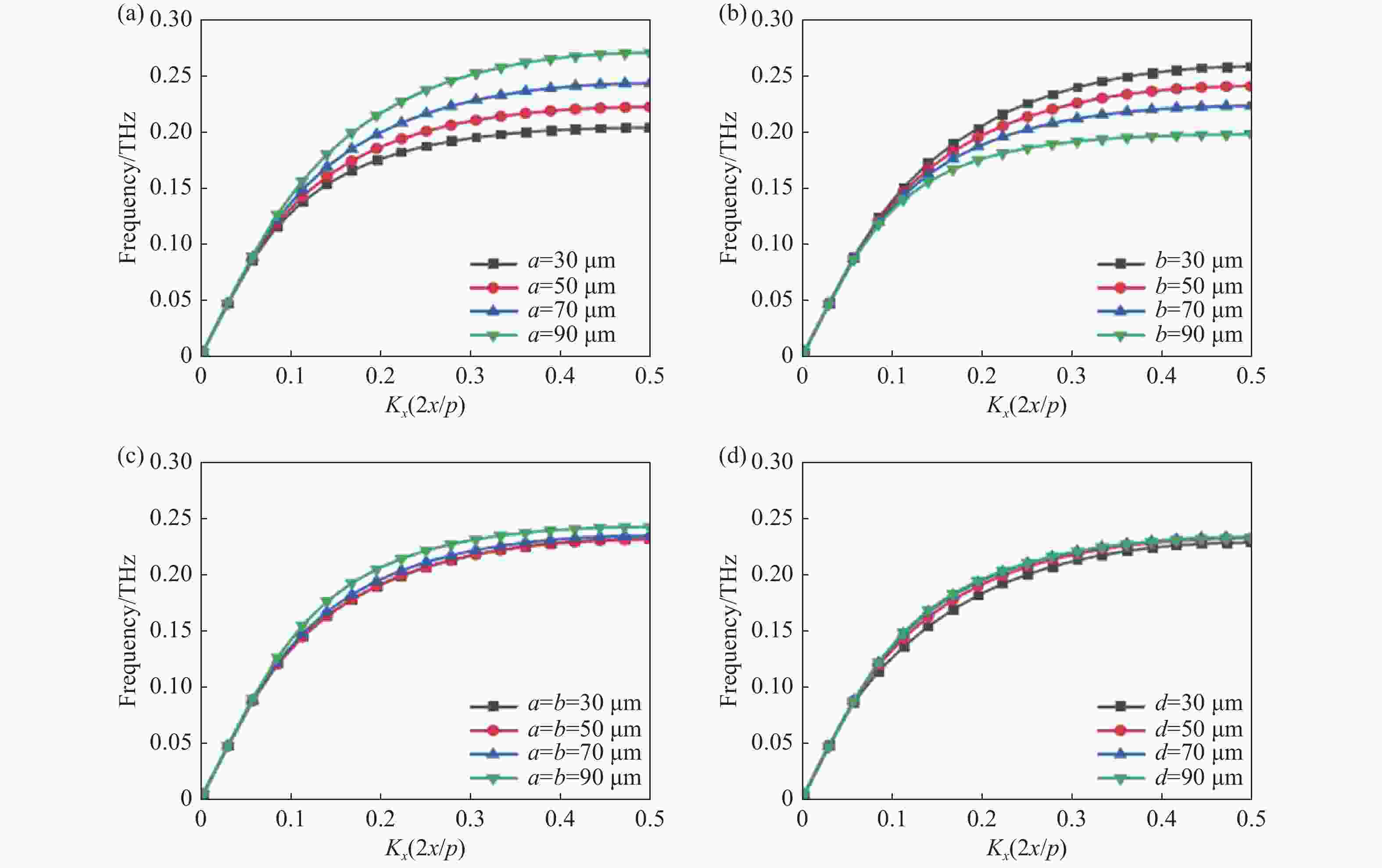
图 4 结构参数对周期性金属结构色散特性的影响结果。(a)参数a不同时的色散特性;(b)参数b不同时的色散特性;(c)参数a和b同时变化时的色散特性;(d)参数d不同时的色散特性
Figure 4. Effects of structural parameters on the dispersion characteristics of periodic metal structures. (a) Dispersion characteristics with different a; (b) dispersion characteristics with different b; (c) dispersion characteristics with the simultaneous variation of a and b; (d) dispersion characteristics with different d
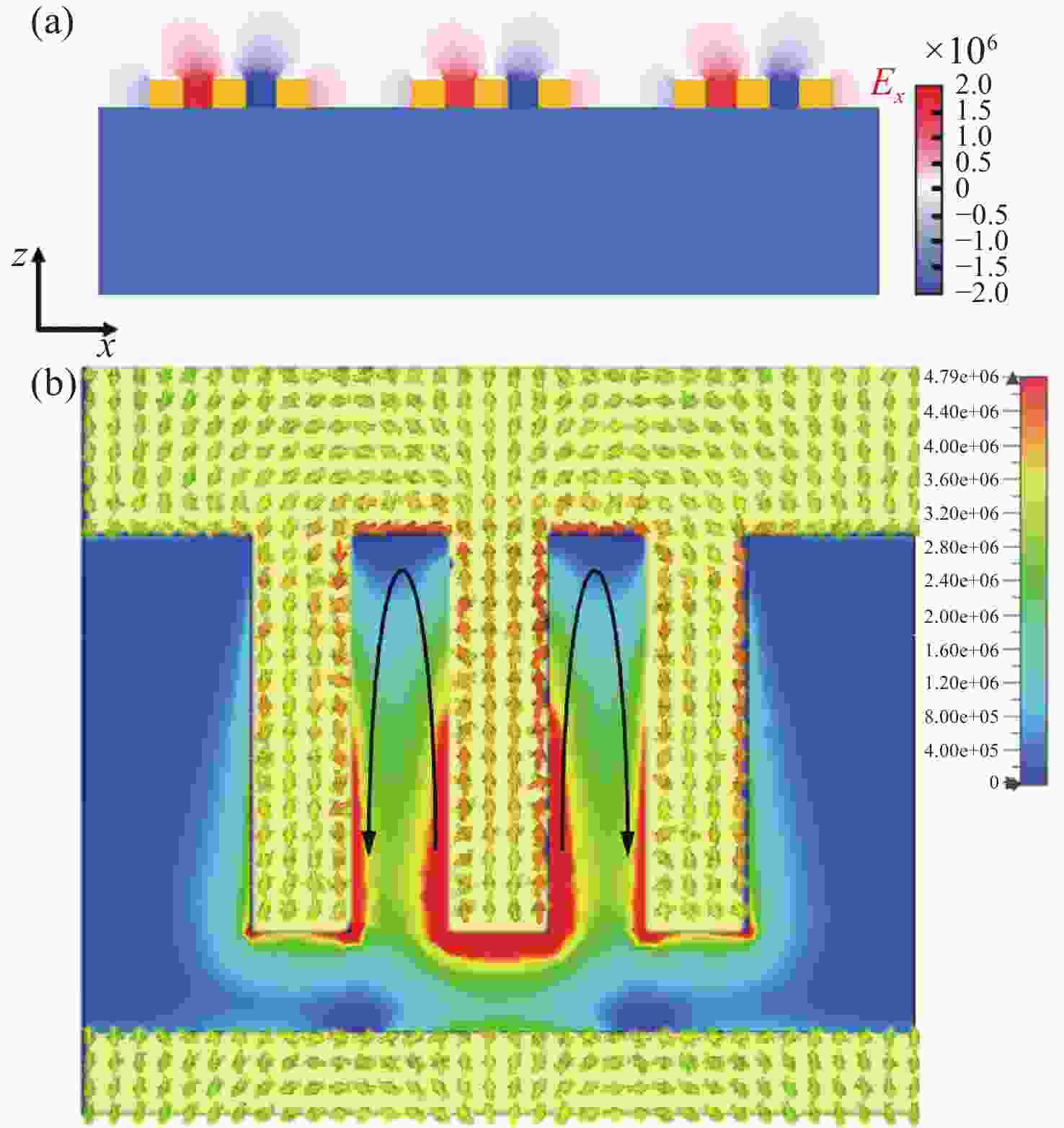
图 5 (a)光栅耦合超表面结构实现人工表面等离子体电场分布图;(b)超表面结构在谐振频率下的电场分布和表面电流分布。黑色箭头表示表面电流方向
Figure 5. (a) Electric field distribution of the SSP modes realized by the grating-coupled meta-surface structure. (b) Electric field and surface current distributions of the meta-surface structure at resonant frequency. The black arrows indicate the surface current direction
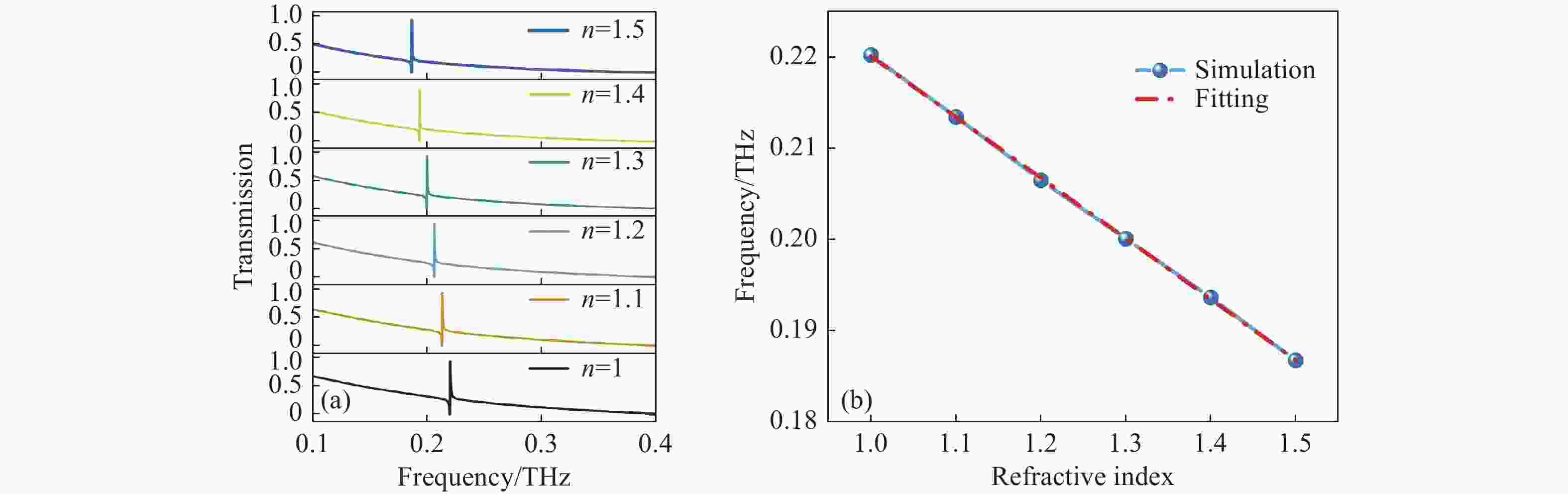
图 6 改变光栅耦合超表面周围环境折射率所得到的透射率变化以及相应的传感灵敏度。(a)不同折射率所对应的透射谱;(b)计算得到的传感灵敏度
Figure 6. Changes in transmissivity and the corresponding sensing sensitivity obtained by changing the ambient refractive index around the grating-coupled meta-surface. (a) Transmission spectra with different refractive indices; (b) the calculated sensing sensitivity
-
[1] SUN SH L, HE Q, HAO J M, et al. Electromagnetic metasurfaces: physics and applications[J]. Advances in Optics and Photonics, 2019, 11(2): 380-479. doi: 10.1364/AOP.11.000380 [2] LIU Q, JIANG Y, HU CH J, et al.. High-sensitivity surface plasmon resonance sensor based on the ten-fold eccentric core quasi-D-shaped photonic quasi-crystal fiber coated with indium tin oxide[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(1): 101-110. [3] ZHU Y CH, YUAN W ZH, YU Y T. Planar plasmonic lenses and their applications[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(2): 149-163. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20171002.0149 [4] LIU Y Q, LI L SH, YIN H CH. Long-range spoof surface plasmons (LRSSP) on the asymmetric double metal gratings[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2021, 13(2): 4800209. [5] YAO H Z, ZHANG W W, LIU W F, et al. Resolved terahertz spectroscopy of tiny molecules employing tunable spoof plasmons in an otto prism configuration[J]. Journal of Optics, 2022, 24(4): 045301. doi: 10.1088/2040-8986/ac5537 [6] BAI Y K, LIU S. A novel dual-beam terahertz leaky-wave antenna based on spoof surface Plasmon waveguide[J]. Optoelectronics Letters, 2022, 18(7): 404-407. doi: 10.1007/s11801-022-1151-5 [7] GAO ZH, WU L, GAO F, et al. Spoof plasmonics: from metamaterial concept to topological description[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(31): 1706683. doi: 10.1002/adma.201706683 [8] TANG H H, MA T J, LIU P K. Experimental demonstration of ultra-wideband and high-efficiency terahertz spoof surface Plasmon polaritons coupler[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 108(19): 191903. doi: 10.1063/1.4948928 [9] LI X J, CHENG G, YAN D X, et al. One-dimensional terahertz dielectric gradient metasurface for broadband spoof surface Plasmon polaritons couplers[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(2): 290-293. doi: 10.1364/OL.412229 [10] YIN L ZH, HUANG T J, WANG D, et al. Terahertz dual phase gradient metasurfaces: high-efficiency binary-channel spoof surface Plasmon excitation[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(2): 411-414. doi: 10.1364/OL.380771 [11] YAN D X, LI X J, MA CH, et al. Terahertz refractive index sensing based on gradient Metasurface coupled confined spoof surface Plasmon Polaritons mode[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(1): 324-329. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3130266 [12] LI X J, WANG L Y, CHENG G, et al. Terahertz spoof surface Plasmon sensing based on dielectric metagrating coupling[J]. APL Materials, 2021, 9(5): 051118. doi: 10.1063/5.0048491 [13] SUN SH L, HE Q, XIAO SH Y, et al. Gradient-index meta-surfaces as a bridge linking propagating waves and surface waves[J]. Nature Materials, 2012, 11(5): 426-431. doi: 10.1038/nmat3292 [14] MENG Y Y, MA H, WANG J F, et al. Broadband spoof surface Plasmon polaritons coupler based on dispersion engineering of metamaterials[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111(15): 151904. doi: 10.1063/1.4995505 [15] CHEN X, FAN W H. Ultrasensitive terahertz metamaterial sensor based on spoof surface Plasmon[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 2092. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01781-6 [16] NG B, WU J F, HANHAM S M, et al. Spoof Plasmon surfaces: a novel platform for THz sensing[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2013, 1(8): 543-548. doi: 10.1002/adom.201300146 [17] NG B, HANHAM S M, WU J F, et al. Broadband terahertz sensing on spoof Plasmon surfaces[J]. ACS Photonics, 2014, 1(10): 1059-1067. doi: 10.1021/ph500272n [18] HUANG Y, ZHONG SH C, SHI T T, et al. Terahertz plasmonic phase-jump manipulator for liquid sensing[J]. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(9): 3011-3021. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2020-0247 [19] SATHUKARN A, YI C H, BOONRUANG S, et al. The simulation of a surface Plasmon resonance metallic grating for maximizing THz sensitivity in refractive index sensor application[J]. International Journal of Optics, 2020, 2020: 3138725. [20] CHEN L, YIN H H, CHEN L, et al. Ultra-sensitive fluid fill height sensing based on spoof surface Plasmon polaritons[J]. Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 2018, 32(4): 471-482. doi: 10.1080/09205071.2017.1395367 [21] YIN L ZH, HUANG T J, HAN F Y, et al. High-efficiency terahertz spin-decoupled meta-coupler for spoof surface Plasmon excitation and beam steering[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(13): 18928-18939. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.018928 [22] HAN ZH H, ZHANG Y SH, BOZHEVOLNYI S I. Spoof surface Plasmon-based stripe antennas with extreme field enhancement in the terahertz regime[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(11): 2533-2536. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.002533 -





 下载:
下载: