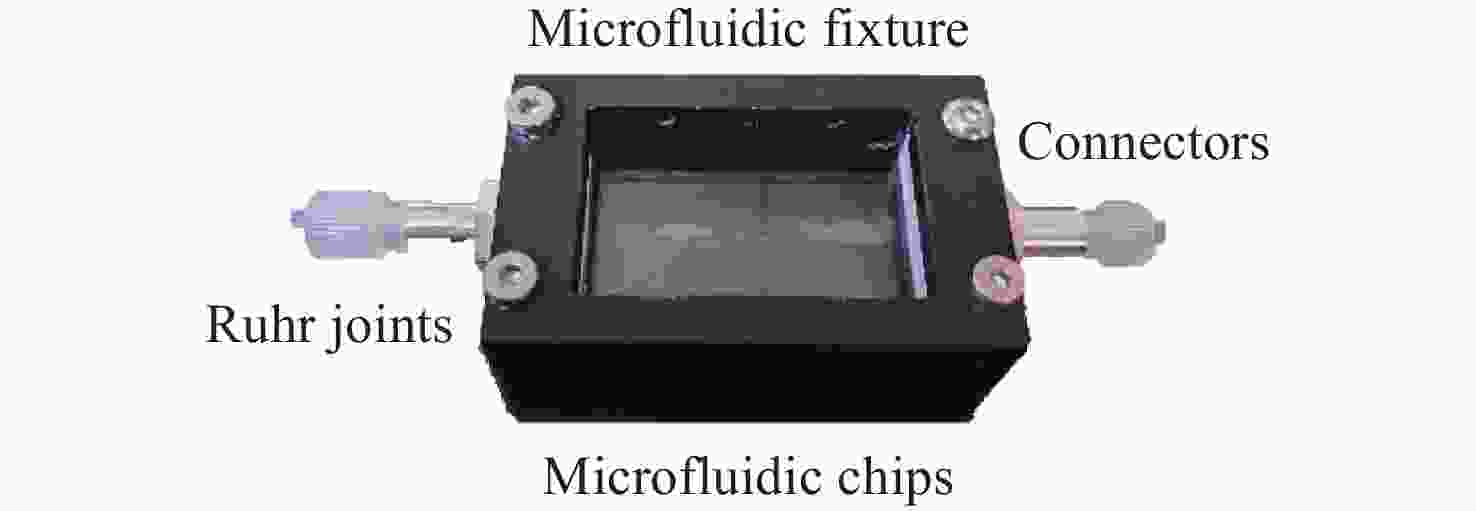
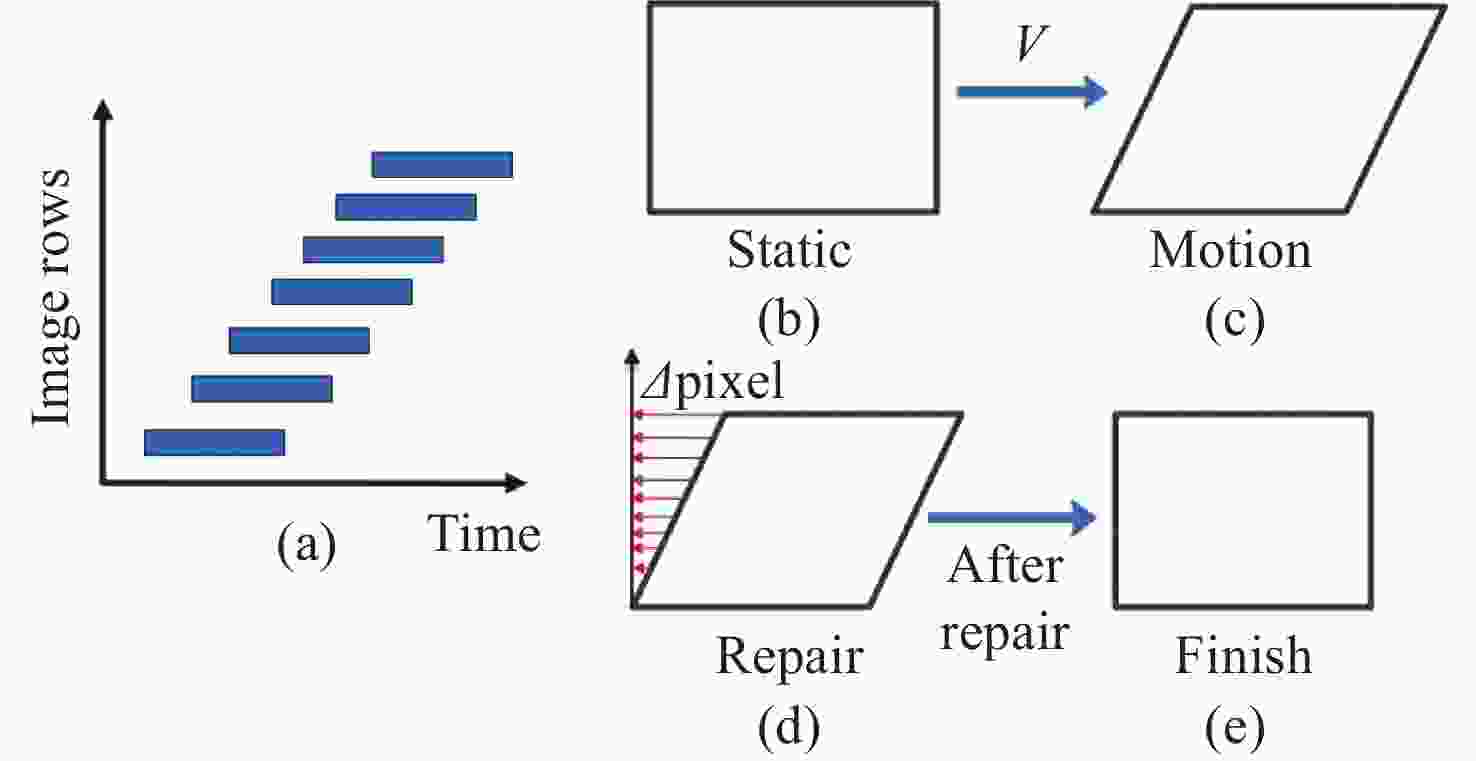
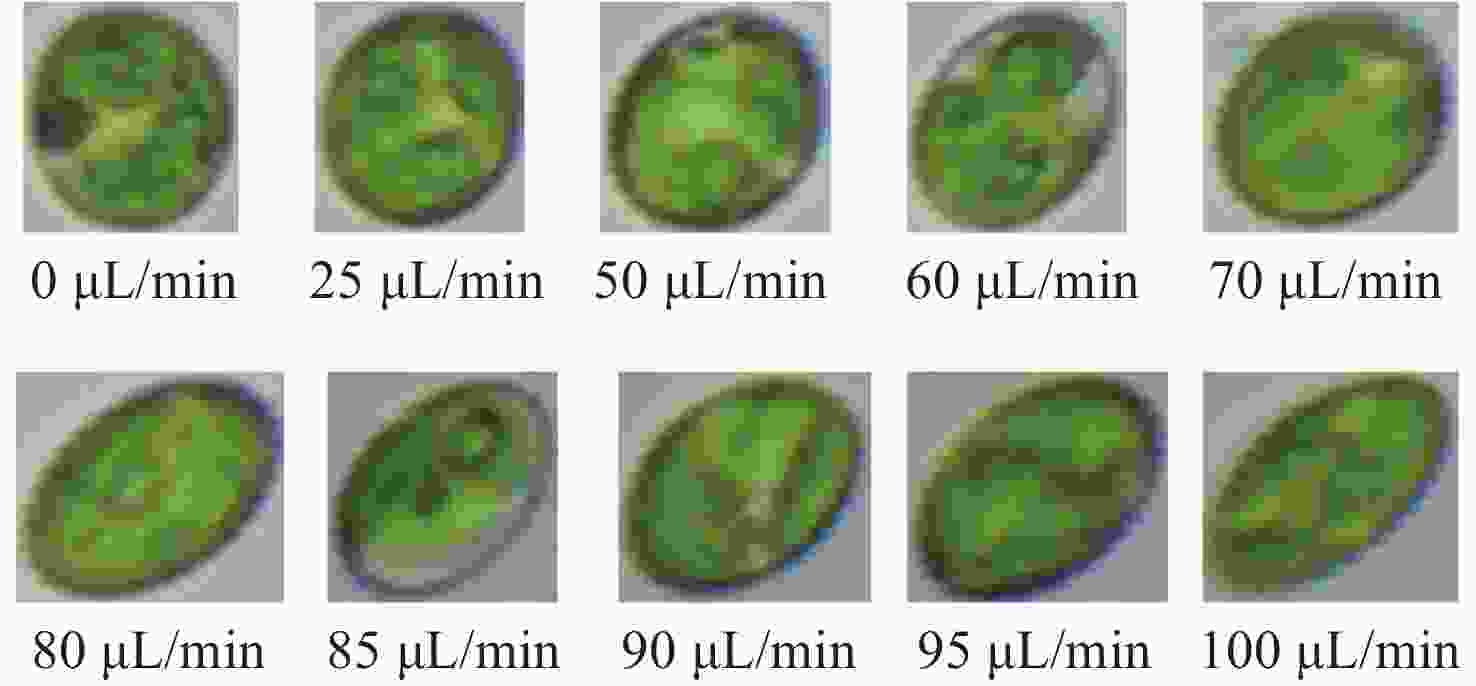
Microfluidic-microscopic image deformation correction method for planktonic algal cells
-
摘要:
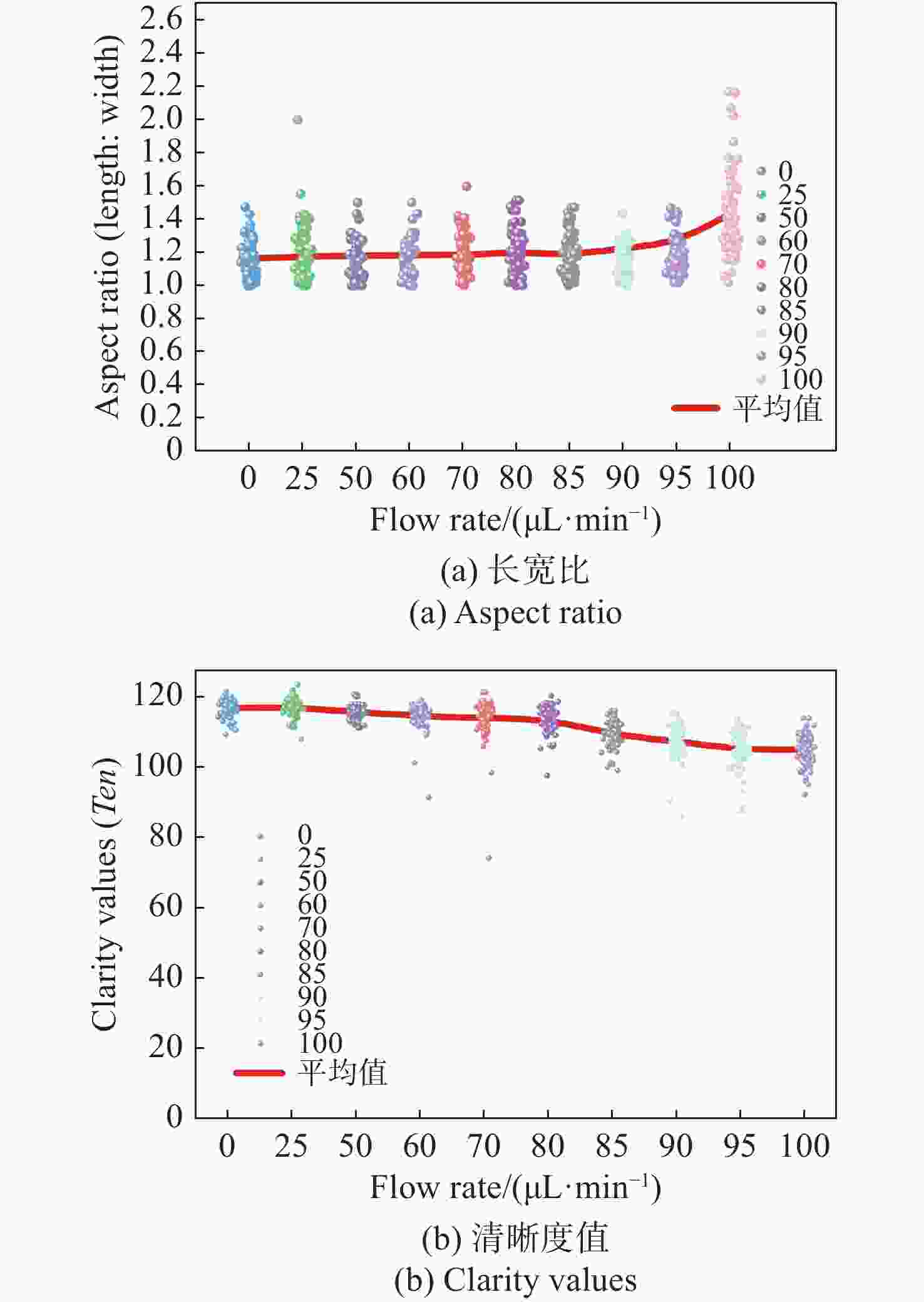
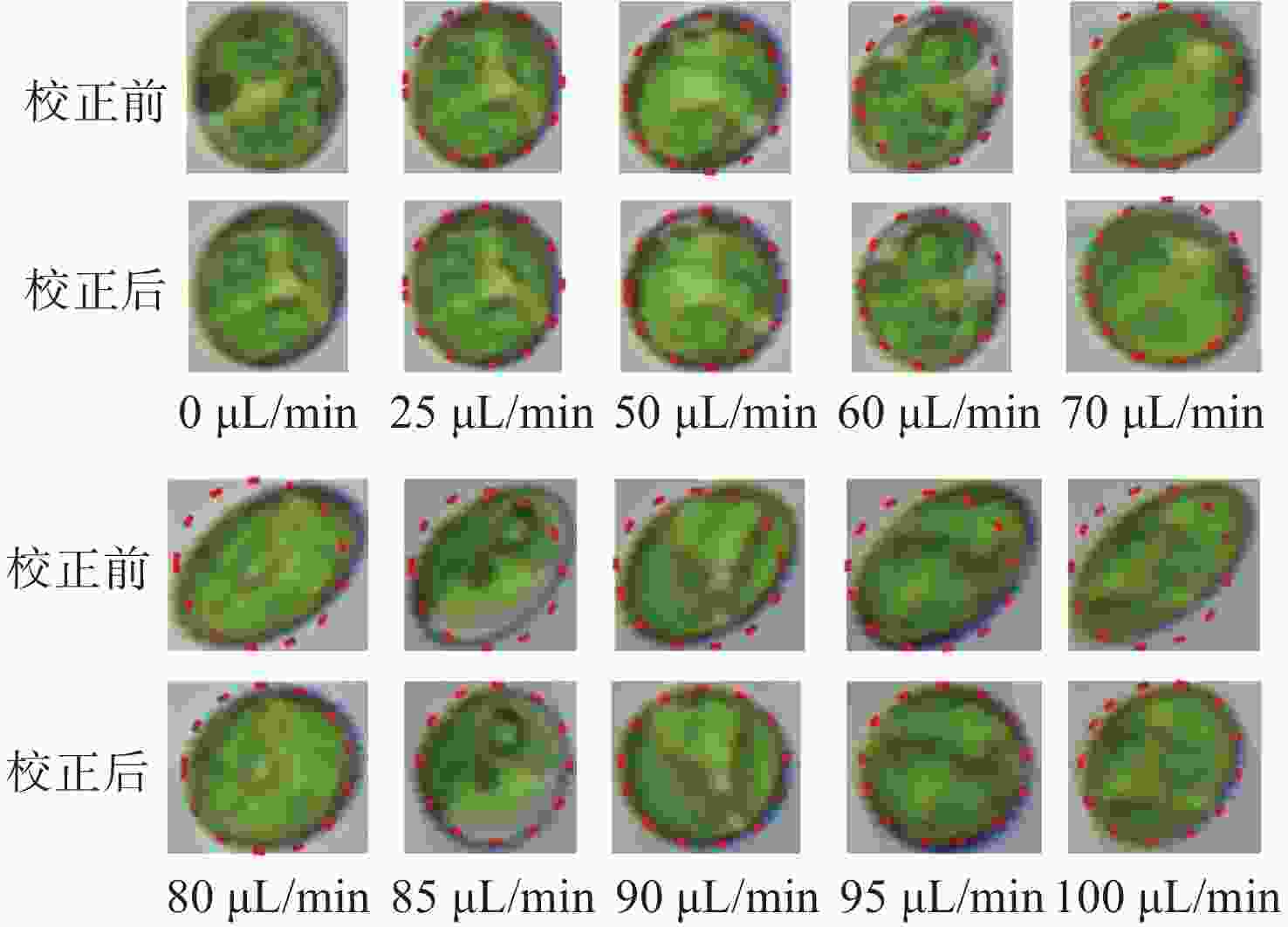
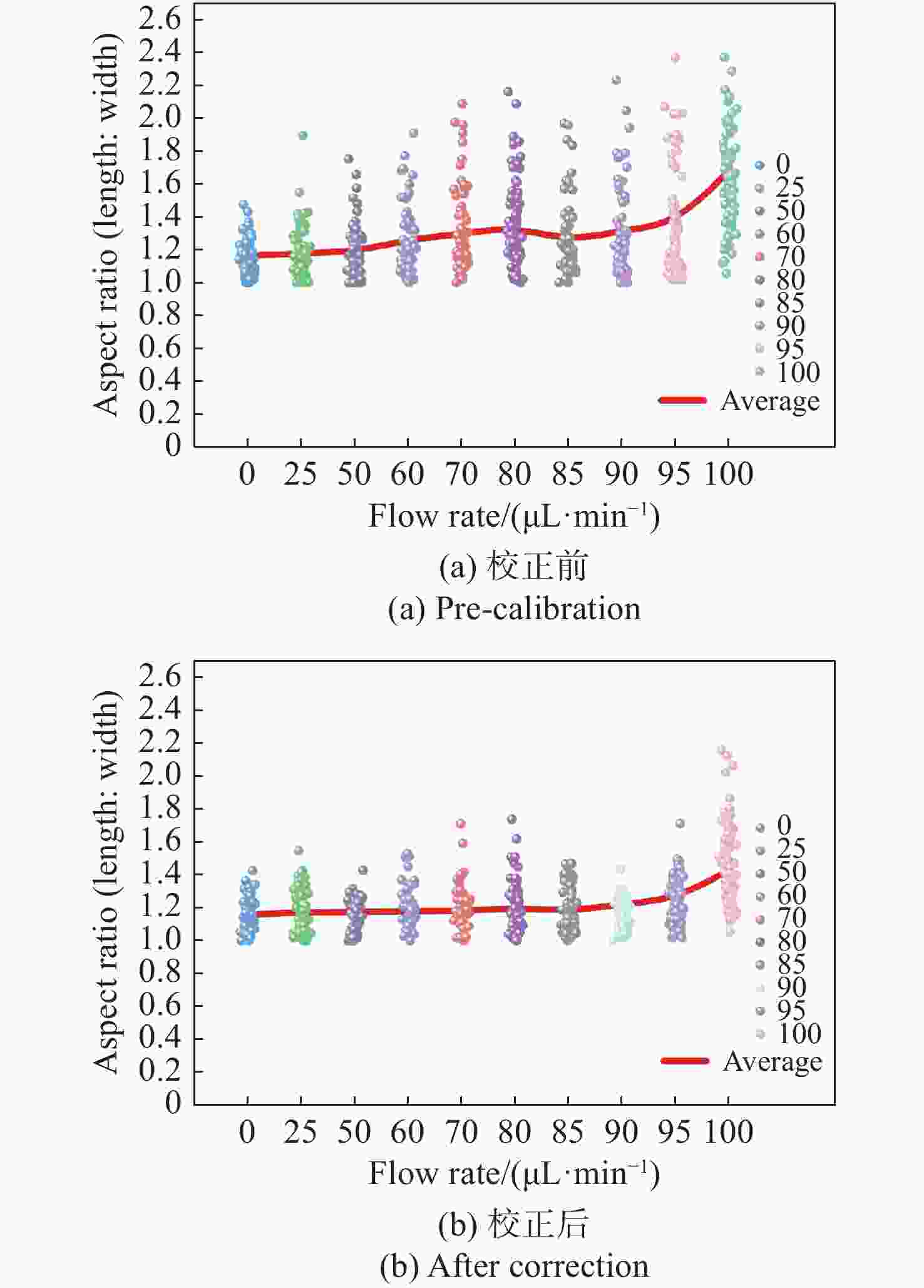
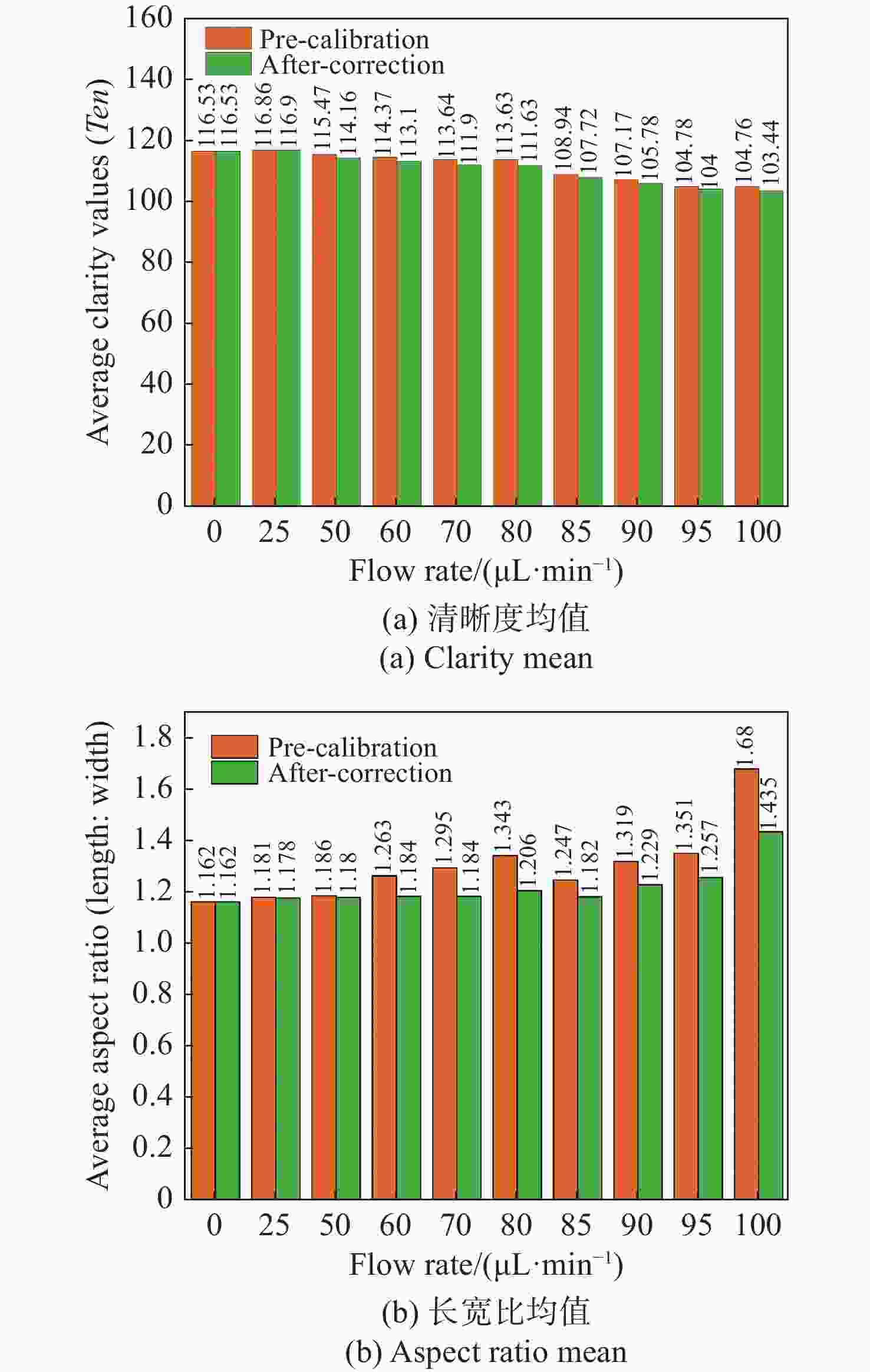
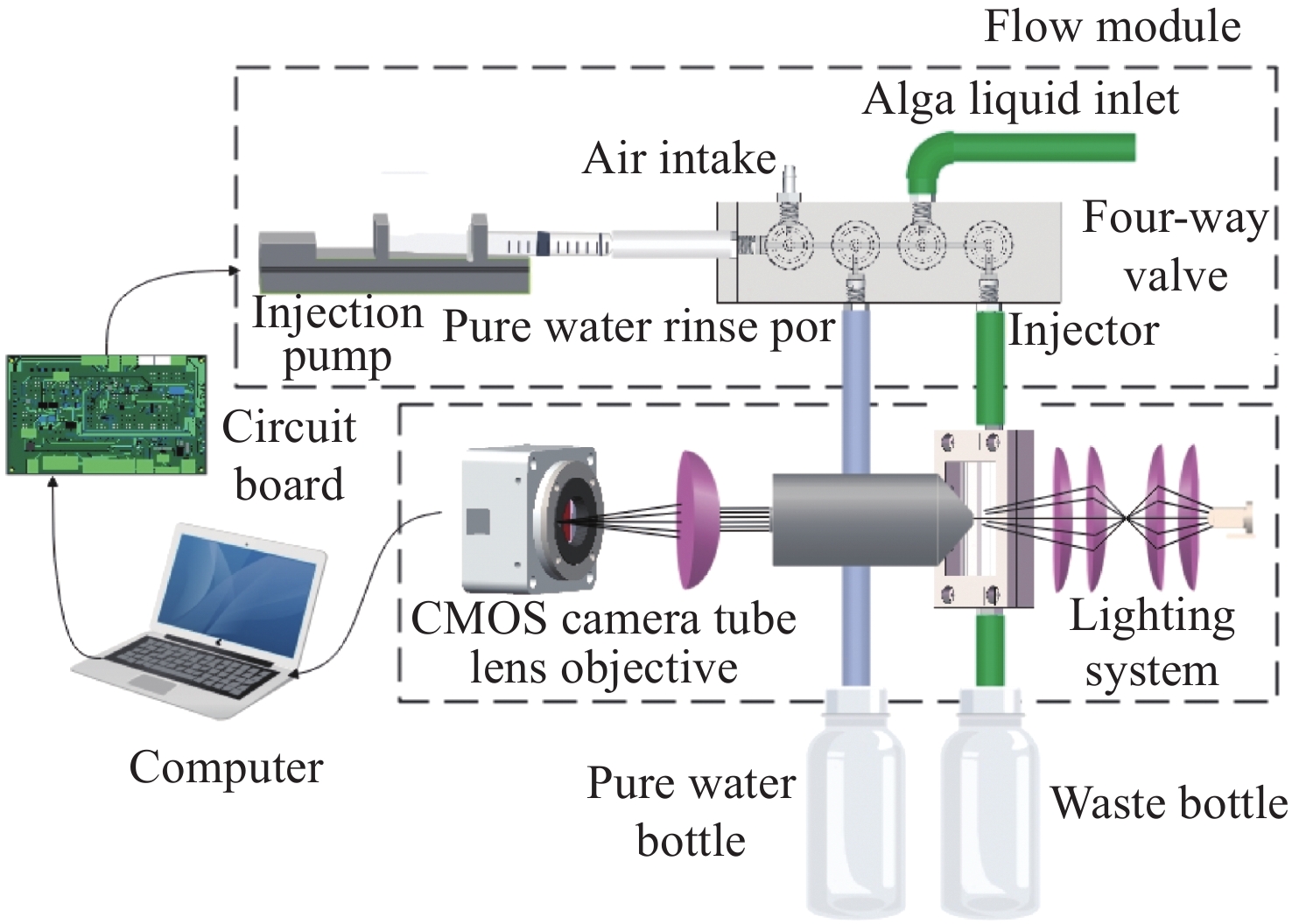
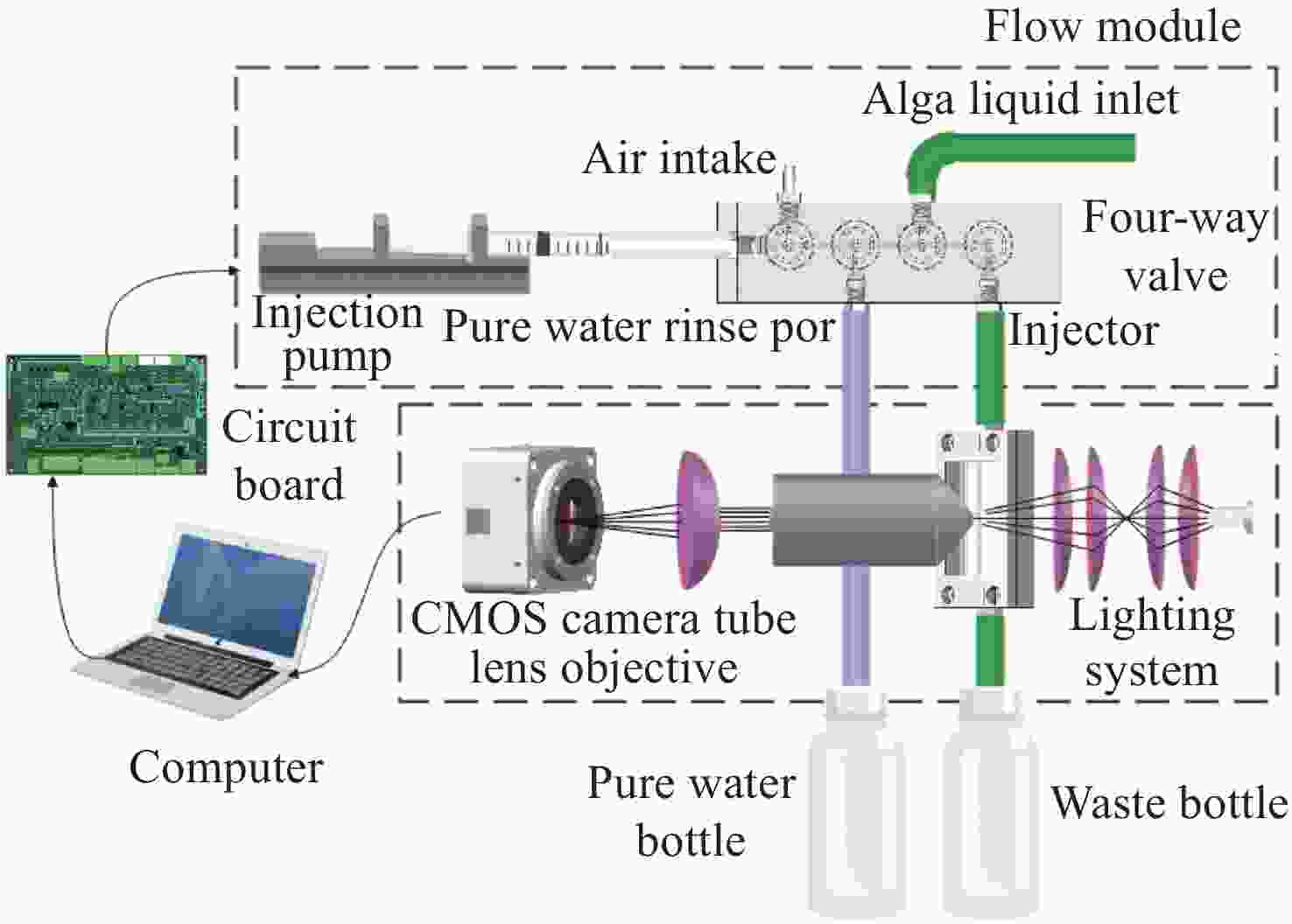
流式细胞显微图像分析法是水体浮游藻类自动鉴别的重要发展方向,快速进样条件下细胞显微图像将产生形变,影响浮游藻类自动鉴别准确率。本文基于搭建的浮游藻类微流控-显微成像实验系统,通过对不同进样流速下藻类细胞显微形变和图像清晰度的分析,研究了流速对显微成像形变的影响规律。分析基于卷帘快门拍摄运动物体产生形变原理,提出了单向偏移像素的图像形变校正方法,并与藻类细胞静态条件下获取的图像进行了对比分析。实验结果表明:静态条件下,湖生卵囊藻细胞的图像长宽比及清晰度均值分别为1.16和116.53;动态进样过程中,随着流速增大细胞图像形变(长宽比)逐渐增大、清晰度降低;95 µL/min进样流速下,校正前后细胞图像长宽比均值分别为1.35和1.26,形变离散程度由校正前的0.33降至0.1,与静态细胞形态接近且校正前后图像清晰度基本不变。本文研究结果为提升水体浮游藻类细胞自动鉴别准确率提供了依据。
Abstract:Flow cytomicrographic analysis is an important development in the automatic identification of planktonic algae in a water column, but the accuracy of this process is affected by the deformation of microscopic images under rapid injection conditions. Based on a microfluidic-microscopic imaging system for planktonic algae, the effects of flow rate on the deformation of microscopic images were investigated by analyzing the deformation of algal cells and image clarity at different injection flow rates. Based on the principle of deformation caused by photographing a moving object using a rolling shutter, a method of image deformation correction with unidirectional offset pixels is proposed and analyzed by comparing its results with images acquired under static conditions of algal cells. The experimental results showed that the average aspect ratio and sharpness of
L values for oocystis cell images under static conditions were 1.16 and 116.53, respectively; during the dynamic injection process, the deformation (aspect ratio) of the cell images gradually increased and the sharpness decreased as the flow rate increased; the average values of aspect ratio before and after correction were 1.35 and 1.26 respectively at 95µL/min injection flow rate, and the dispersion of deformation decreased from 0.33 before correction to 0.1. The results are close to that of static cell morphology and the image sharpness is basically same. The results provide a method for improving the accuracy of the automatic identification of planktonic algal cells in a water column. -
-
[1] 张春梅, 米武娟, 许元钊, 等. 南水北调中线总干渠浮游植物群落特征及水环境评价[J]. 水生态学杂志,2021,42(3):47-54. doi: 10.15928/j.1674-3075.201906280161ZHANG CH M, MI W J, XU Y ZH, et al. Phytoplankton community characteristics and water environment assessment in the main channel of the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2021, 42(3): 47-54. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15928/j.1674-3075.201906280161 [2] 张帅, 彭福利, 季雨来, 等. 耦合敏感参数实时识别的新型数据同化算法研究——以湖泊藻类模拟为例[J]. 湖泊科学,2022,34(6):1877-1889. doi: 10.18307/2022.0608ZHANG SH, PENG F L, JI Y L, et al. A new data assimilation method coupled with real-time detection of sensitive parameters: an example of phytoplankton modeling in lakes[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2022, 34(6): 1877-1889. (in Chinese) doi: 10.18307/2022.0608 [3] 唐诗俊. 藻类图像的精确识别算法的研究与应用[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2020.TANG SH J. Research and application of accurate recognition algorithm for algae image[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020. (in Chinese) [4] 王义强, 林方睿, 胡睿, 等. 大视场光学显微成像技术[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(6):1194-1210. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0098WANG Y Q, LIN F R, HU R, et al. Large field-of-view optical microscopic imaging technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(6): 1194-1210. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0098 [5] 张雯. 基于形态学与不完全树形小波分解的藻类图像纹理识别算法的研究 [D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2011.ZHANG W. Research of the algae image texture based on morphology and none entirely tree wavelet decomposition[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2020. (in Chinese) [6] 胡圣, 刘浩兵, 刘辉, 等. 基于深度学习技术的藻类智能监测系统开发[J]. 中国环境监测,2022,38(1):200-210. doi: 10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2022.01.19HU SH, LIU H B, LIU H, et al. Research on monitoring system of algae detection and classification based on deep learning[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2022, 38(1): 200-210. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2022.01.19 [7] QIAO X Y. Research on imbalanced microscopic image classification of harmful algae[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 125438-125446. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3007646 [8] 王立凯, 冯喜增. 微流控芯片技术在生命科学研究中的应用[J]. 化学进展,2005,17(3):482-498. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-281X.2005.03.015WANG L K, FENG X Z. Microfluidic network for research and application in life sciences[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2005, 17(3): 482-498. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-281X.2005.03.015 [9] 彭冉. 基于微流控芯片船舶压载水中微藻检测及分选研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2013.PENG R. Automatically detecting and sorting algae in ships’ ballast water on a microfluidic chip[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2013. (in Chinese) [10] 楚惠. 基于图像流式细胞技术的微藻检测系统设计[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2016.CHU H. Design of micro algae detection system based on image micro-fluidic[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2013. (in Chinese) [11] 陶淑苹, 冯钦评, 陈晓龙, 等. 数字域时间延迟积分CMOS遥感相机动态传函建模分析[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(5):983-991. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0111TAO SH P, FENG Q P, CHEN X L, et al. Dynamic MTF modeling and analysis of digital domain TDI CMOS remote sensing camera[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(5): 983-991. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0111 [12] HAN Y Y, GU Y, ZHANG A C, et al. Review: imaging technologies for flow cytometry[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(24): 4639-4647. doi: 10.1039/C6LC01063F [13] 张博研, 孔德柱, 刘金国, 等. 卷帘快门式CMOS探测器的星图像移补偿[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1276-1284. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0089ZHANG B Y, KONG D ZH, LIU J G, et al. Compensation of star image motion for a CMOS image sensor with a rolling shutter[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1276-1284. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0089 [14] 曾海飞, 韩昌佩, 李凯, 等. 改进的梯度阈值图像清晰度评价算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2021,58(22):2211001.ZENG H F, HAN CH P, LI K, et al. Improved gradient threshold image sharpness evaluation algorithm[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(22): 2211001. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: