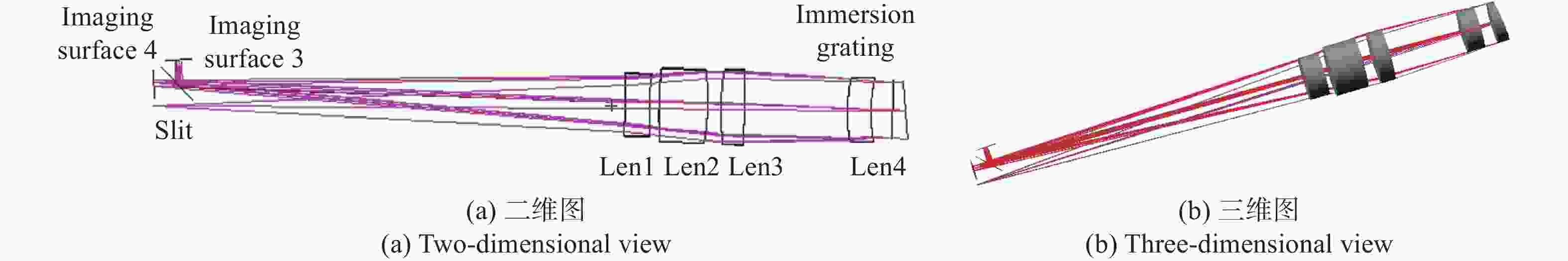
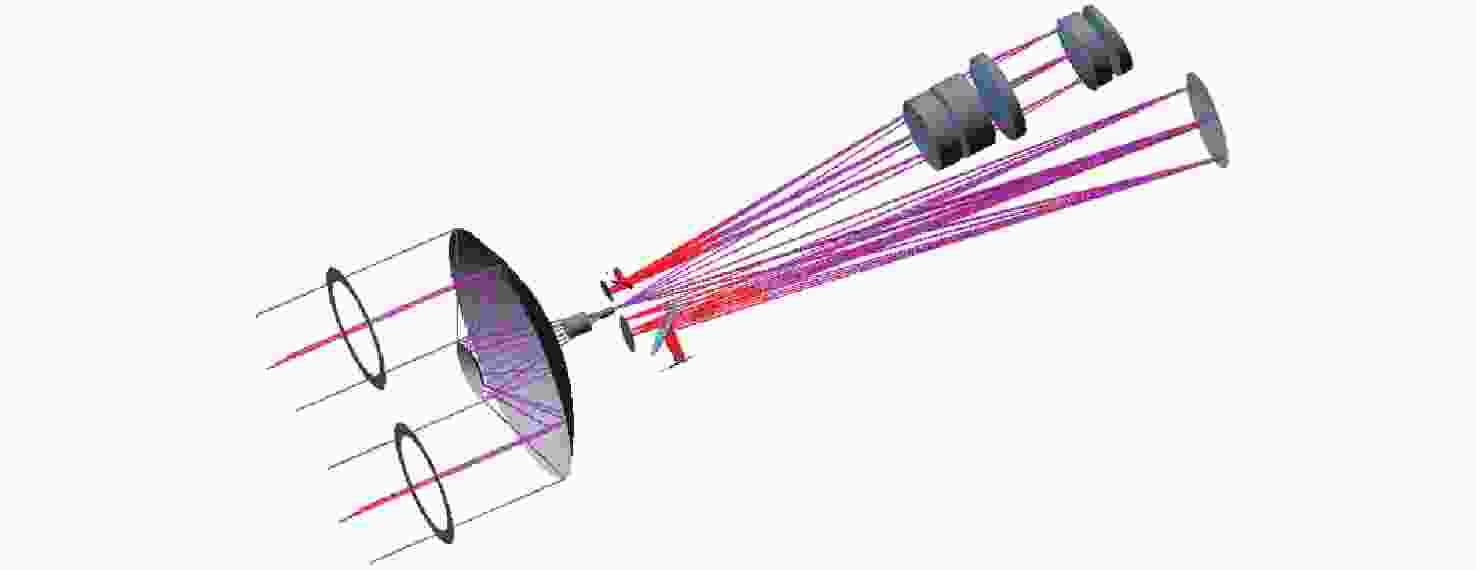
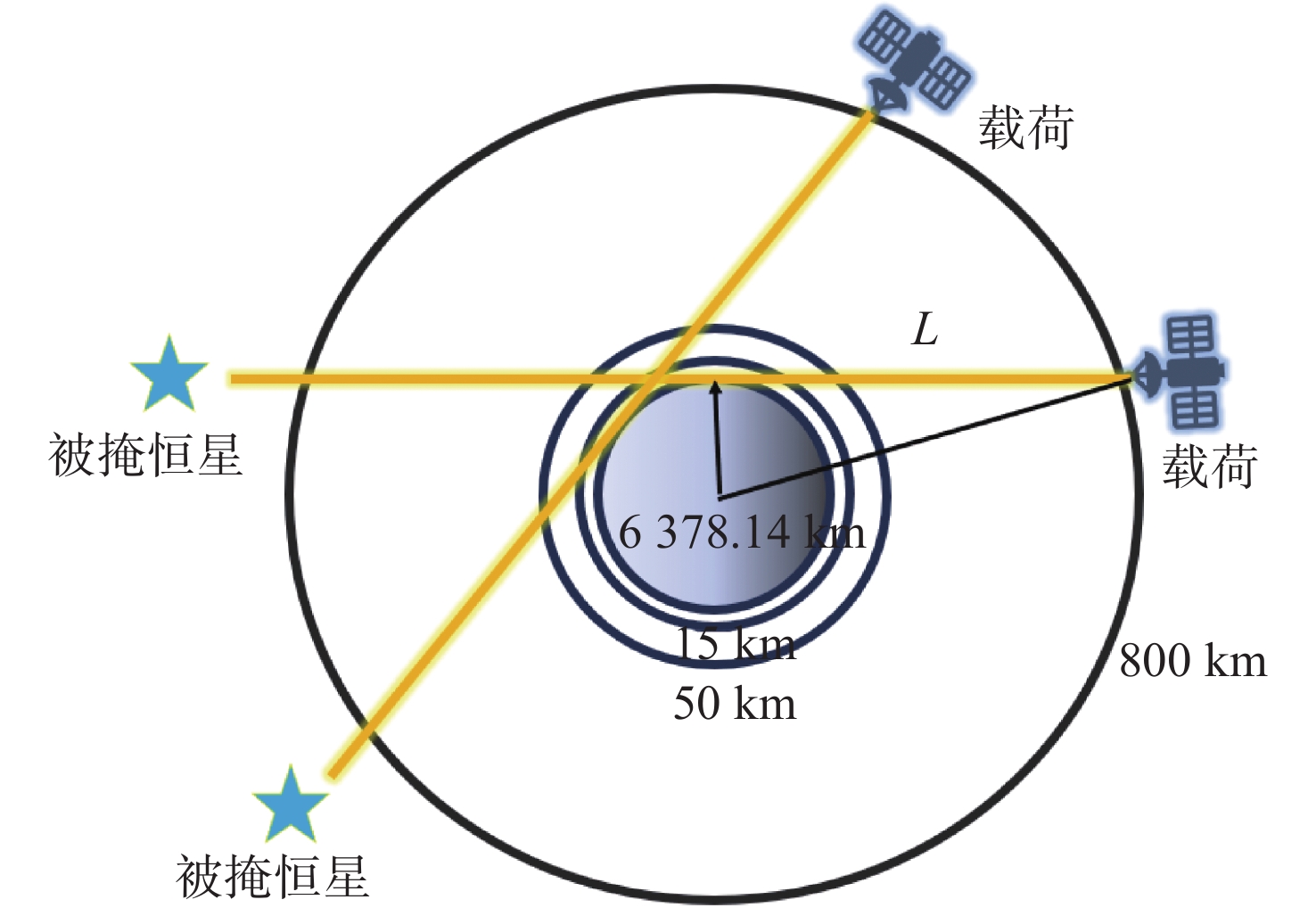
Optical system design of hyperspectral imaging spectrometer for trace gas occultation detection
-
摘要:
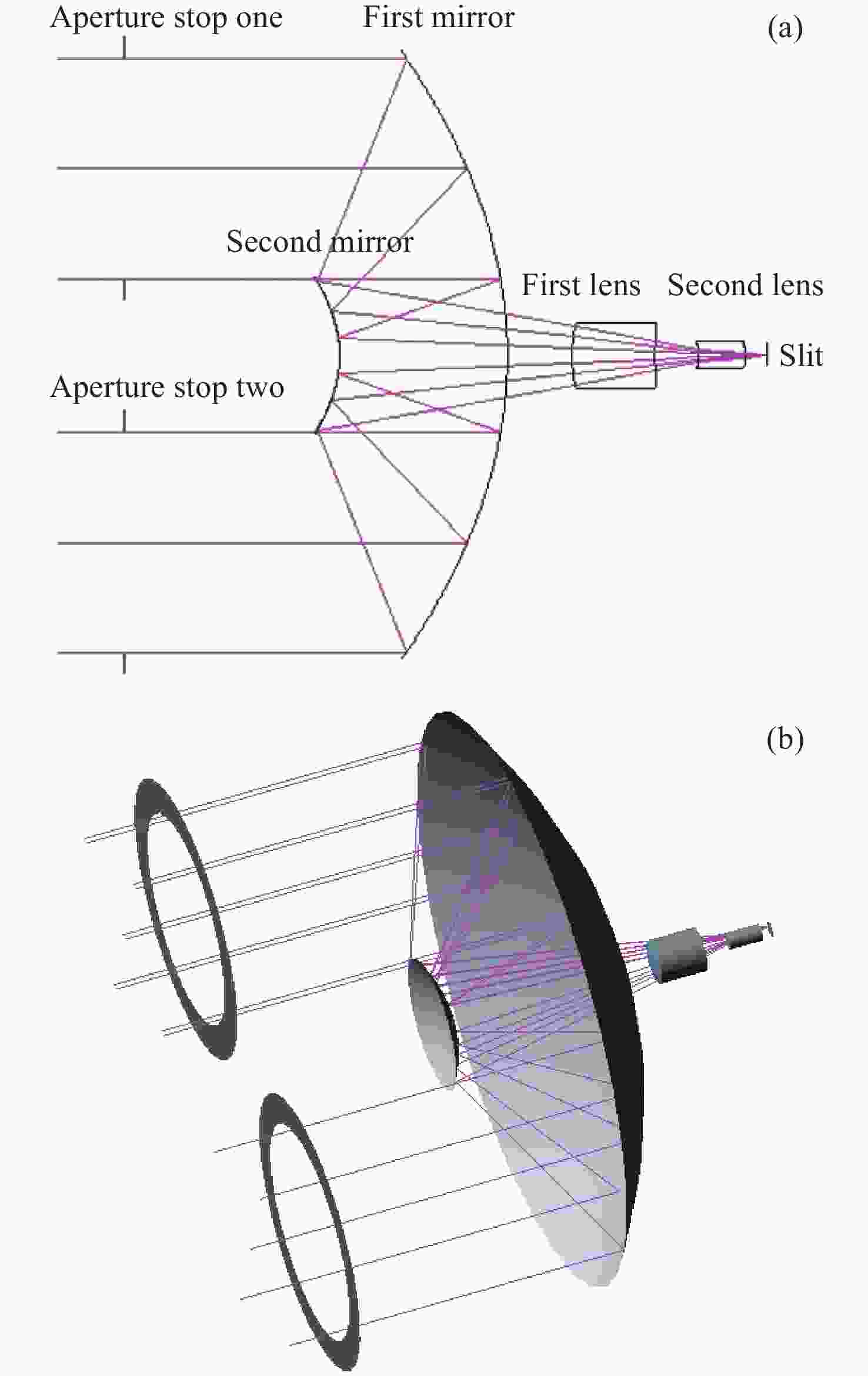
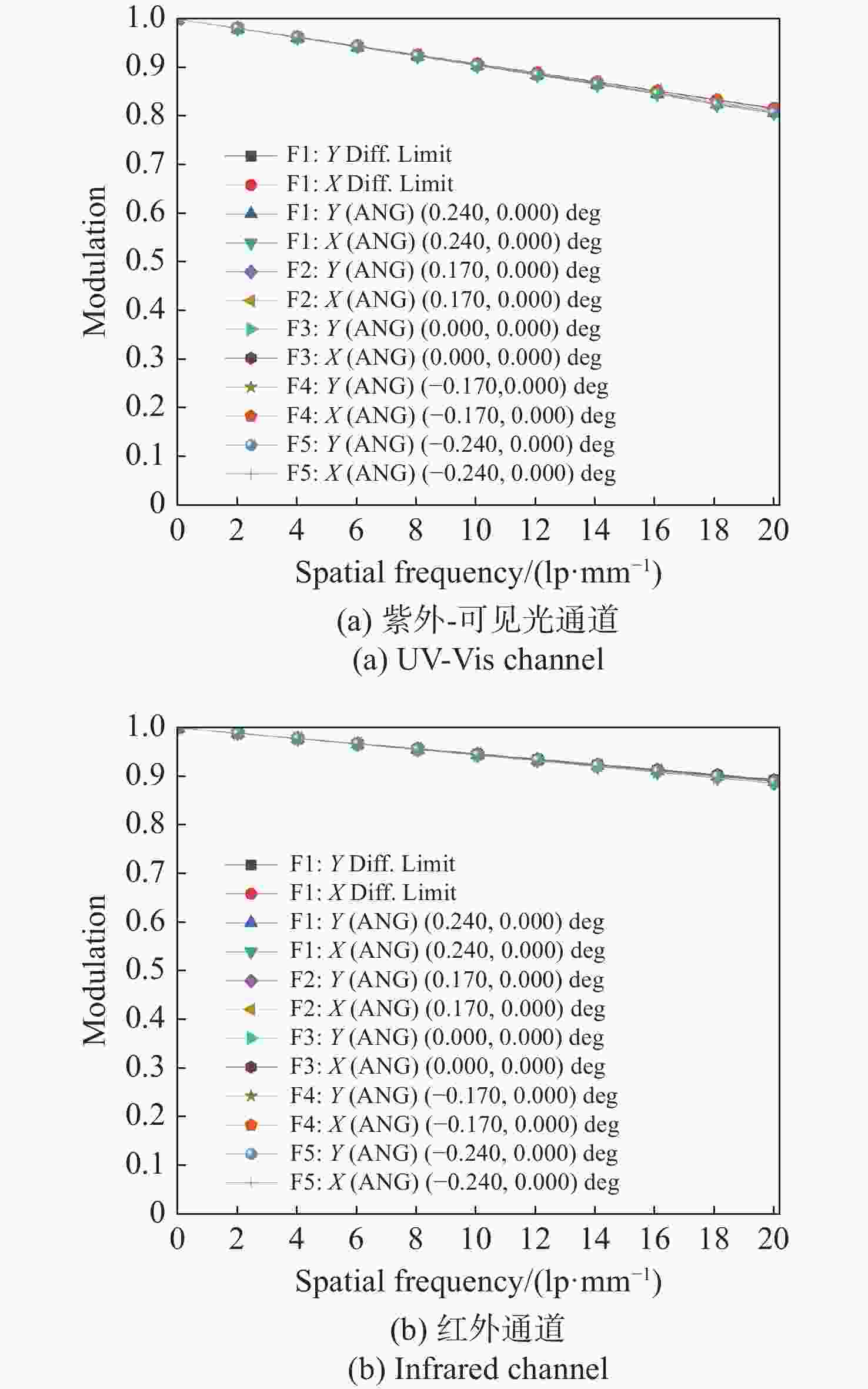
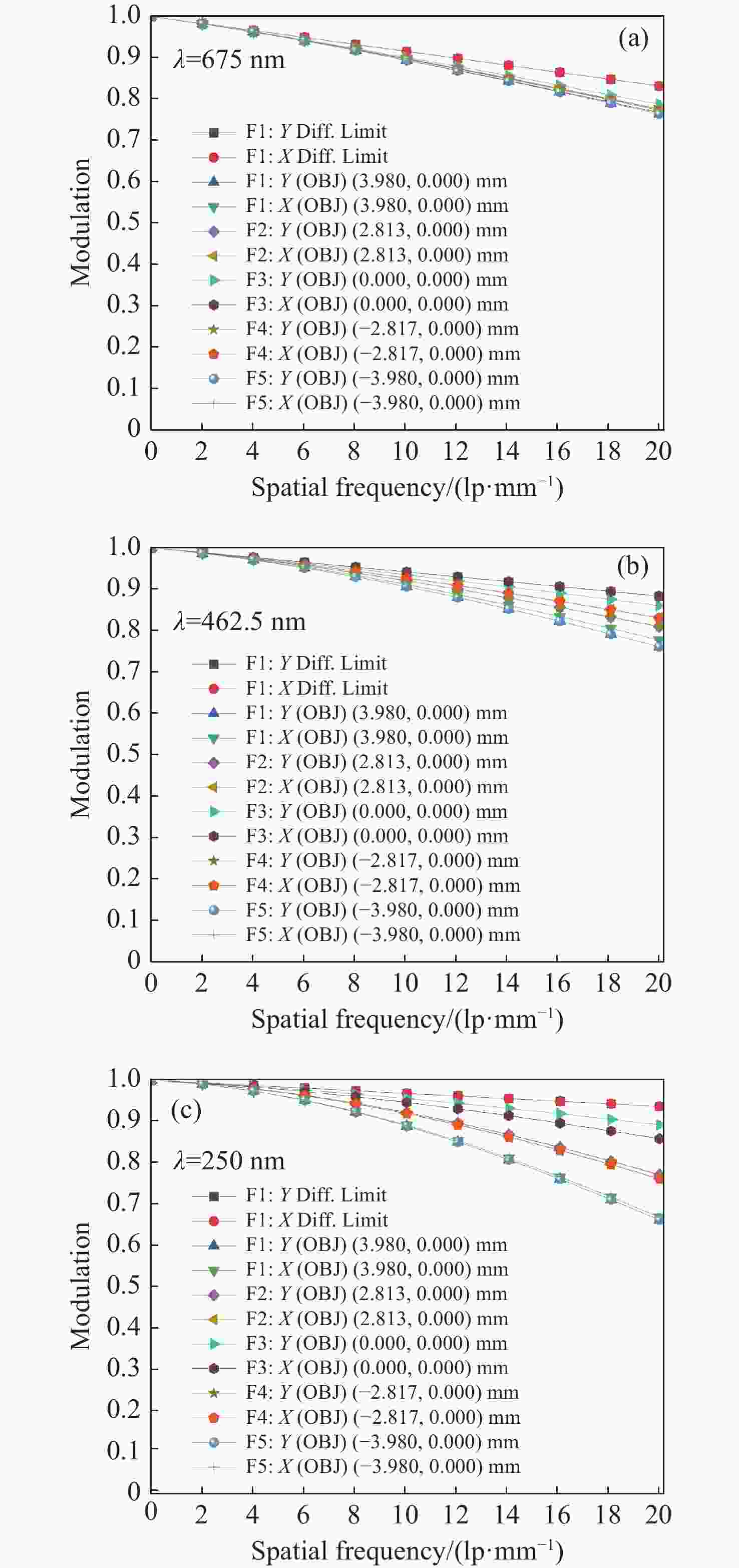
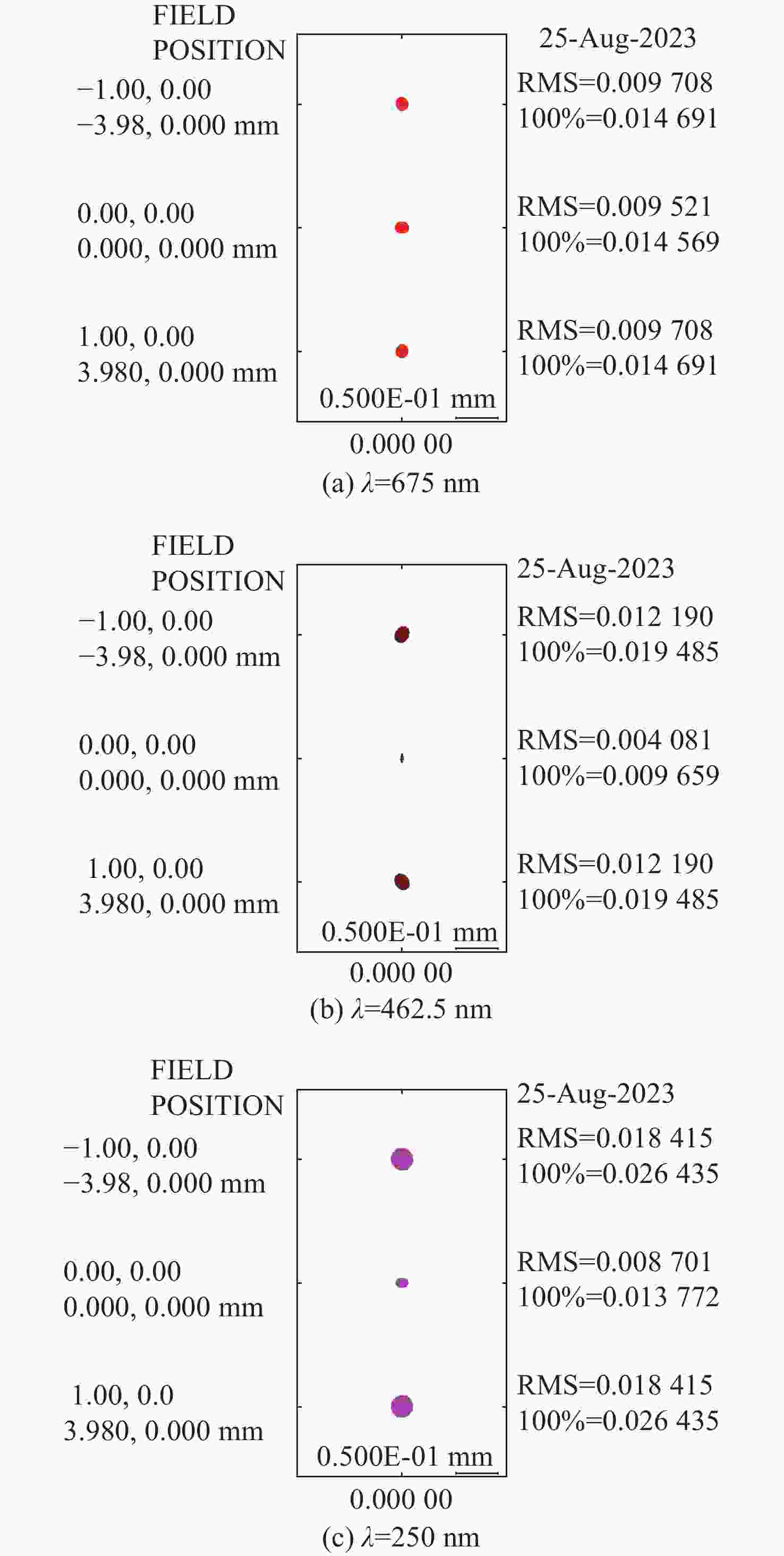
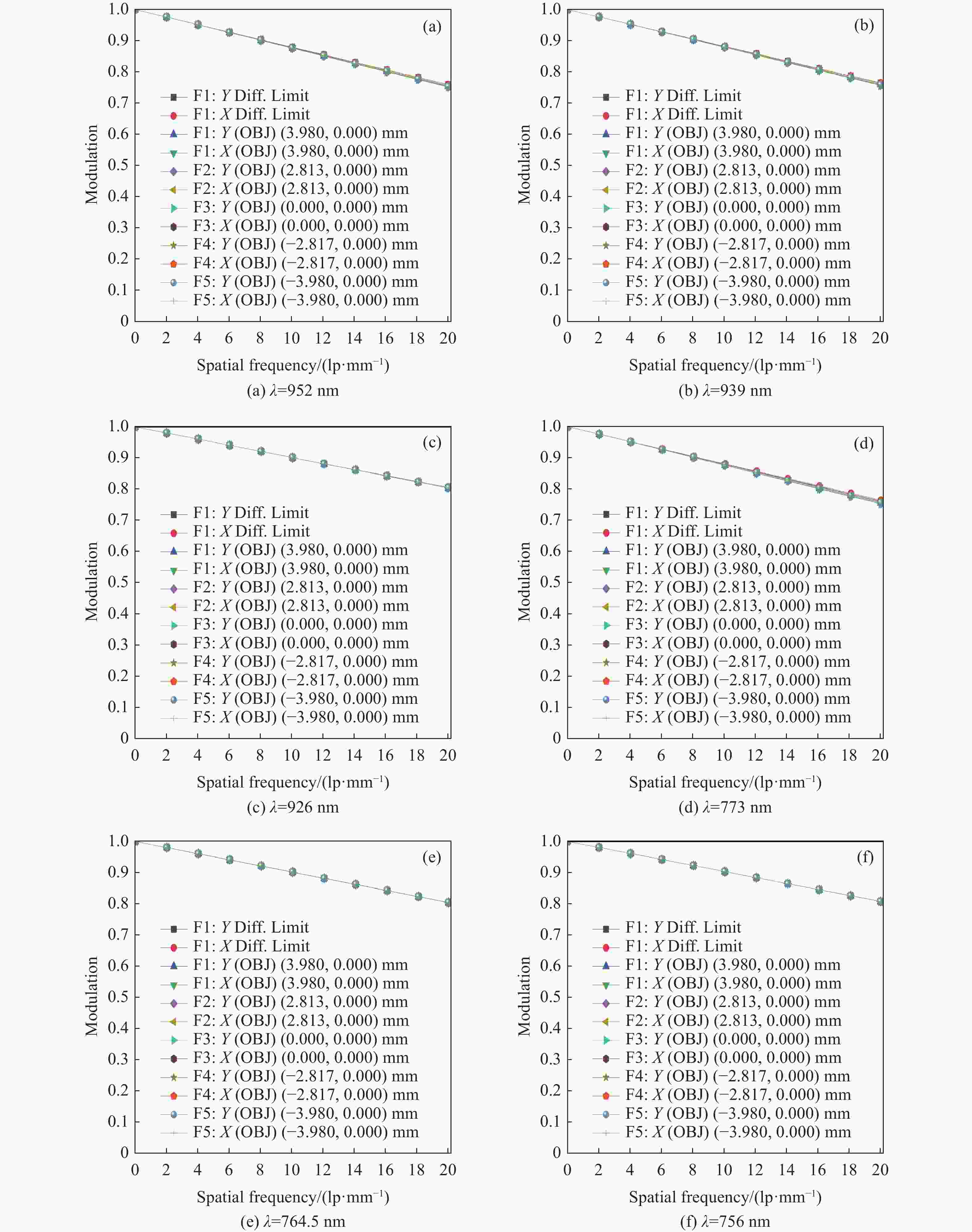
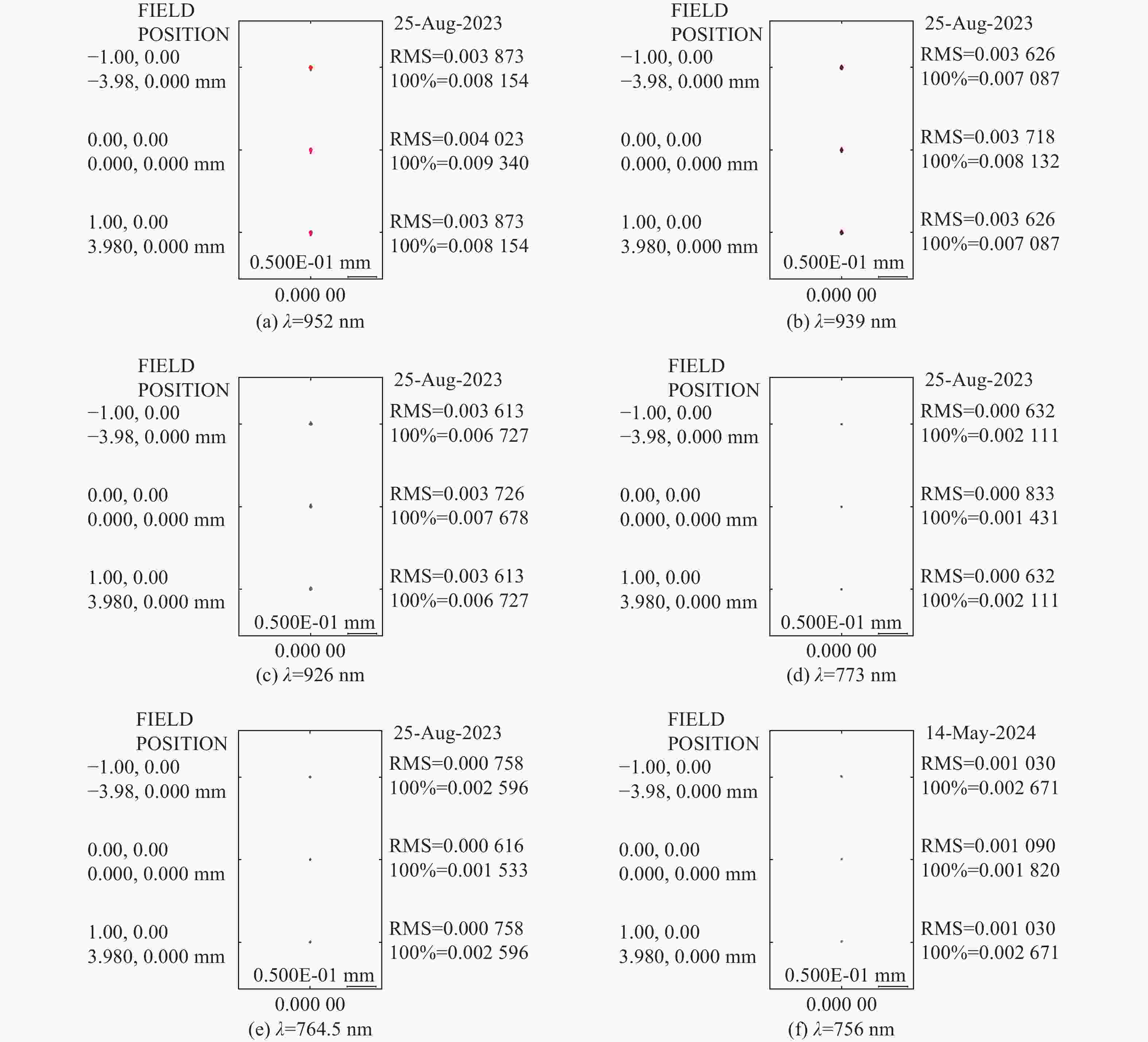
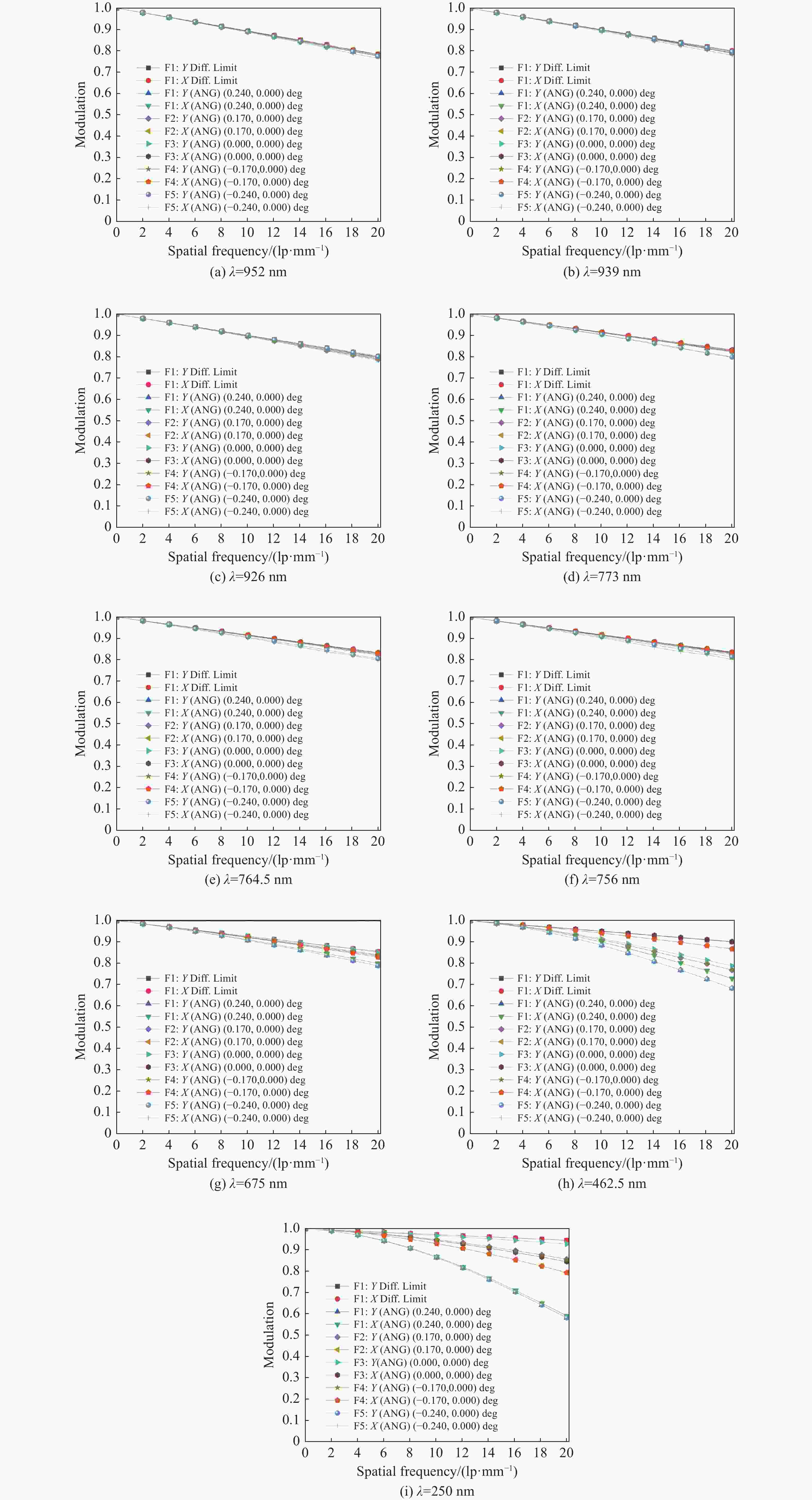
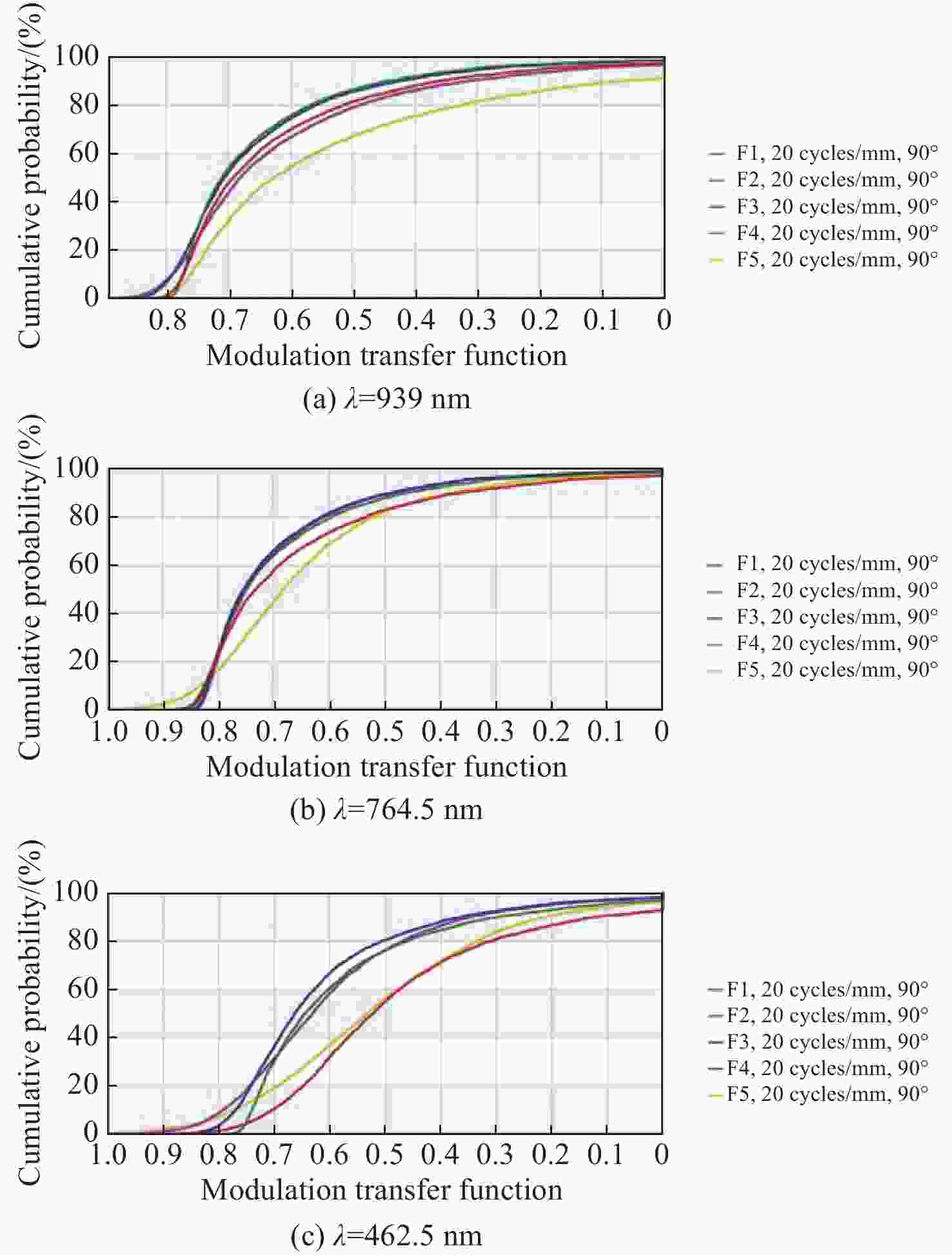
痕量气体作为大气的重要成份,对地球的生态起着重要作用。为了实现宽波段、高光谱全天时连续测量,本文设计了一款在掩星探测模式下工作的高光谱成像光谱仪。该系统为共狭缝的双通道结构,紫外-可见光通道采用单凹面光栅结构、红外通道采用利特罗与浸没光栅结合结构,有效地减小了体积。利用软件对光学结构进行优化,优化结果表明:光谱仪在250~952 nm波段范围内工作,其中紫外-可见光通道工作波段为250~675 nm、光谱分辨率优于1 nm、MTF在奈奎斯特频率为20 lp/mm处均高于0.58、全视场各波长处RMS值均小于21 μm;红外通道工作波段为756~952 nm、光谱分辨率优于0.2 nm、MTF在奈奎斯特频率为20 lp/mm处均高于0.76、全视场各波长处RMS值均小于6 μm,均满足设计要求。结果表明该高光谱成像光谱仪系统可以实现对痕量气体的掩星探测。
Abstract:Trace gases, as important constituents of the atmosphere, play an important role in the ecology of the planet. In order to realize the requirements of wide-band, hyperspectral and all-weather continuous measurement, a hyperspectral imaging spectrometer operating in occultation detection mode is designed in this paper. The system is a dual-channel structure with a common slit, the UV-visible channel adopts a single concave grating, and the infrared channel adopts a structure combining Littrow and immersion grating, which effectively reduces the volume. The software is used to optimize the optical structure, and the optimization results show that the spectrometer operates in the range of 250−952 nm wavelengths, of which the UV-visible channel operates in the wavelength range of 250−675 nm, the spectral resolution is better than 1 nm, the MTFs are all higher than 0.58 at a Nyquist frequency of 20 lp/mm, and the RMS values at various wavelengths of the full-field-of-view are all less than 21 μm; the infrared channel operates in the wavelength band of 756−952 nm, the spectral resolution is better than 0.2 nm, the MTF is higher than 0.76 at the Nyquist frequency of 20 lp/mm, and the RMS value at each wavelength in the whole field of view is less than 6 μm, all of them meet the design requirements. It can be seen that the hyperspectral imaging spectrometer system can realize the occultation detection of trace gases.
-
表 1 成像光谱仪的主要技术指标
Table 1. Main technical indicators of imaging spectrometer
参数 指标 系统波段/nm 250~952 视场/(°) 0.48 焦距/mm 950 F数 8.26 光谱分辨率/nm 0.2~1 狭缝长度/mm 7.96 MTF >0.58@20 lp/mm 探测器像元数/pixel 1024×1024 探测器像元尺寸/μm 13×13 -
[1] YE X, YI X L, LIN CH, et al. Instrument development: Chinese radiometric benchmark of reflected solar band based on space cryogenic absolute radiometer[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(17): 2856. doi: 10.3390/rs12172856 [2] 刘明言, 石秀顶, 李天国, 等. 电化学分析方法检测重金属离子研究进展[J]. 应用化学,2023,40(4):463-475.LIU M Y, SHI X D, LI T G, et al. Research progress in detection of heavy metal ions by electrochemical analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2023, 40(4): 463-475. (in Chinese). [3] THUILLIER G, ZHU P, SNOW M, et al. Characteristics of solar-irradiance spectra from measurements, modeling, and theoretical approach[J]. Light:Science & Applications, 2022, 11(1): 79. [4] 朱嘉诚, 陆伟奇, 赵知诚, 等. 静止轨道中波红外成像光谱仪分光成像系统[J]. 光学学报,2021,41(11):1122001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1122001ZHU J CH, LU W Q, ZHAO Z CH, et al. Spectroscopic imaging system in mid-wave infrared imaging spectrometer on geostationary orbit[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(11): 1122001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1122001 [5] FENG A W, ZHAO SH J, HAN J ZH, et al. High spectral resolution compact Offner spectrometer based on the aberration-reduced convex holographic gratings recorded by spherical waves under Rowland circle mounting[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(13): 3893-3900. doi: 10.1364/AO.458391 [6] 谭奋利, 曾晨欣, 冯安伟, 等. 基于Dyson结构的新型快照式分光成像系统光学设计[J]. 光学学报,2022,42(4):0422002. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.0422002TAN F L, ZENG CH X, FENG A W, et al. Optical design of novel snapshot spectral imaging system based on Dyson structure[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(4): 0422002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.0422002 [7] DILS B, BUCHWITZ M, REUTER M, et al. The greenhouse gas climate change initiative (GHG-CCI): comparative validation of GHG-CCI SCIAMACHY/ENVISAT and TANSO-FTS/GOSAT CO2 and CH4 retrieval algorithm products with measurements from the TCCON[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2014, 7(6): 1723-1744. doi: 10.5194/amt-7-1723-2014 [8] REMUND Q P, NEWELL D, RODRIGUEZ J V, et al. The Ozone Mapping and Profiler Suite (OMPS): on-orbit calibration design[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5652: 165-173. doi: 10.1117/12.579016 [9] SOUCY M A A, CHATEAUNEUF F, DEUTSCH C, et al. ACE-FTS instrument detailed design[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2002, 4814: 70-81. doi: 10.1117/12.451701 [10] 钟美, 皮波, 佘勇, 等. FY-3B TOU与Aura OMI卫星臭氧总量产品的比对分析[J]. 气象研究与应用,2021,42(2):29-34.ZHONG M, PI B, SHE Y, et al. Comparative analysis of total ozone products between FY -3B TOU and Aura OMI satellite[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research and Application, 2021, 42(2): 29-34. (in Chinese). [11] 邵春沅, 顾明剑, 漆成莉, 等. 风云三号D星红外高光谱大气探测仪零光程差检测[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(12):2573-2580. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202812.2573SHAO CH Y, GU M J, QI CH L, et al. Detection of zero path difference position for FY-3D hyper-spectral in frared atmospheric sounder[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(12): 2573-2580. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202812.2573 [12] 曹西凤, 李小英, 罗琪, 等. 星载红外高光谱传感器温度廓线反演综述[J]. 遥感学报,2021,25(2):577-598. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20210009CAO X F, LI X Y, LUO Q, et al. Review of temperature profile inversion of satellite-borne infrared hyperspectral sensors[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2021, 25(2): 577-598. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jrs.20210009 [13] 张璐, 李博, 李寒霜, 等. 超光谱分辨率紫外双通道共光路成像光谱仪设计[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(5):1029-1037.ZHANG L, LI B, LI H SH, et al. Hyperspectral resolution ultraviolet dual channel common optical path imaging spectrometer[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(5): 1029-1037. (in Chinese). [14] 李寒霜, 李博, 李昊晨, 等. 基于一种透镜材料的宽谱段紫外成像仪光学设计[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(1):65-71.LI H SH, LI B, LI H CH, et al. Optical design of a wide-spectrum ultraviolet imager based on a single material[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(1): 65-71. (in Chinese). [15] SZUMSKI R, WALKER D D. The immersed echelle-I. Basic properties[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 1999, 302(1): 139-144. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-8711.1999.02107.x [16] CU-NGUYEN P H, GREWE A, FEßER P, et al. An imaging spectrometer employing tunable hyperchromatic microlenses[J]. Light:Science & Applications, 2016, 5(4): e16058. -





 下载:
下载: