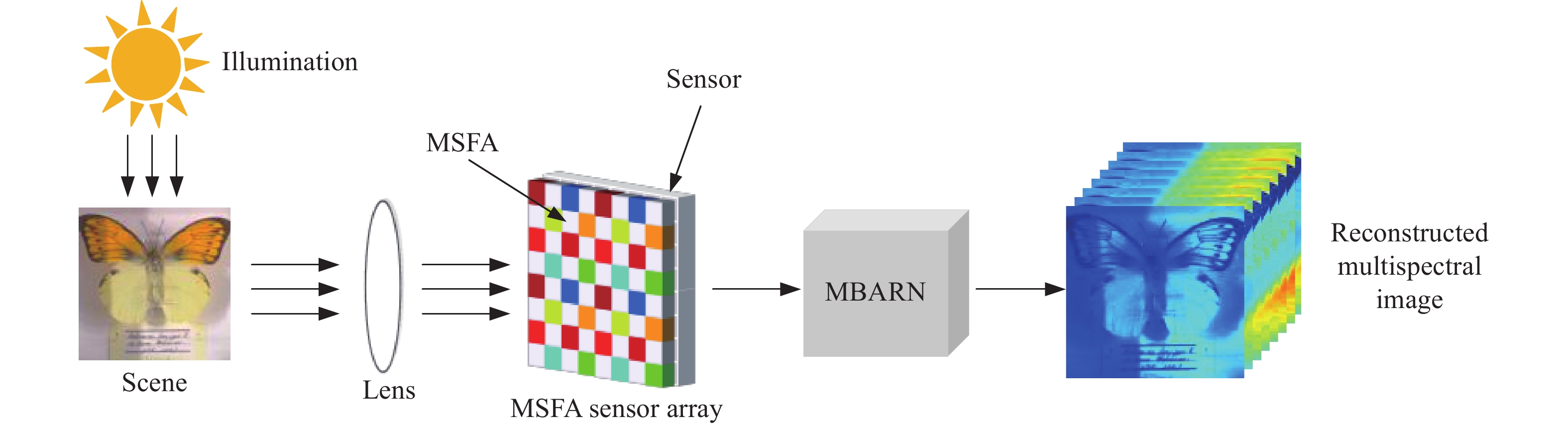
Image reconstruction of snapshot multispectral camera based on an attention residual network
-
摘要:
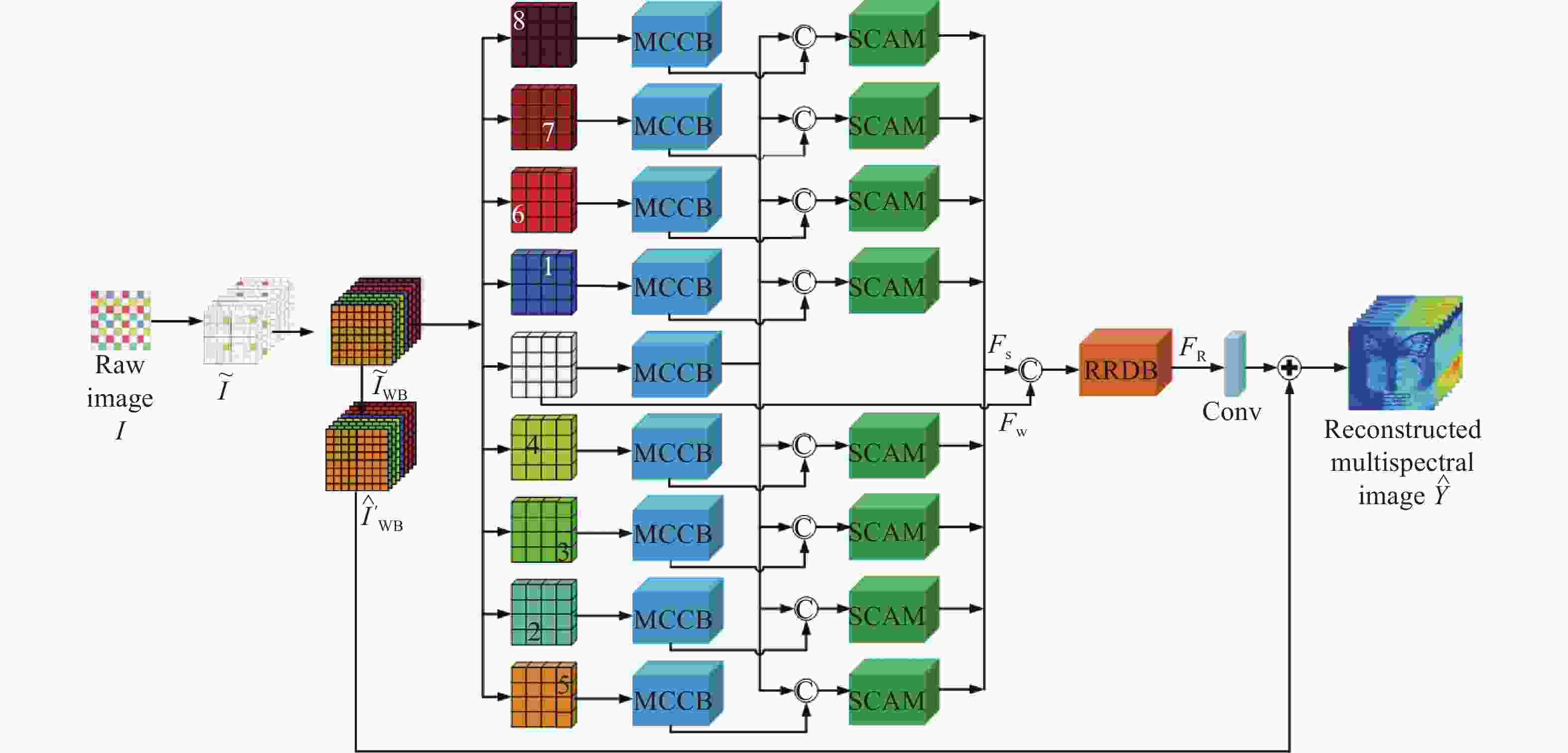
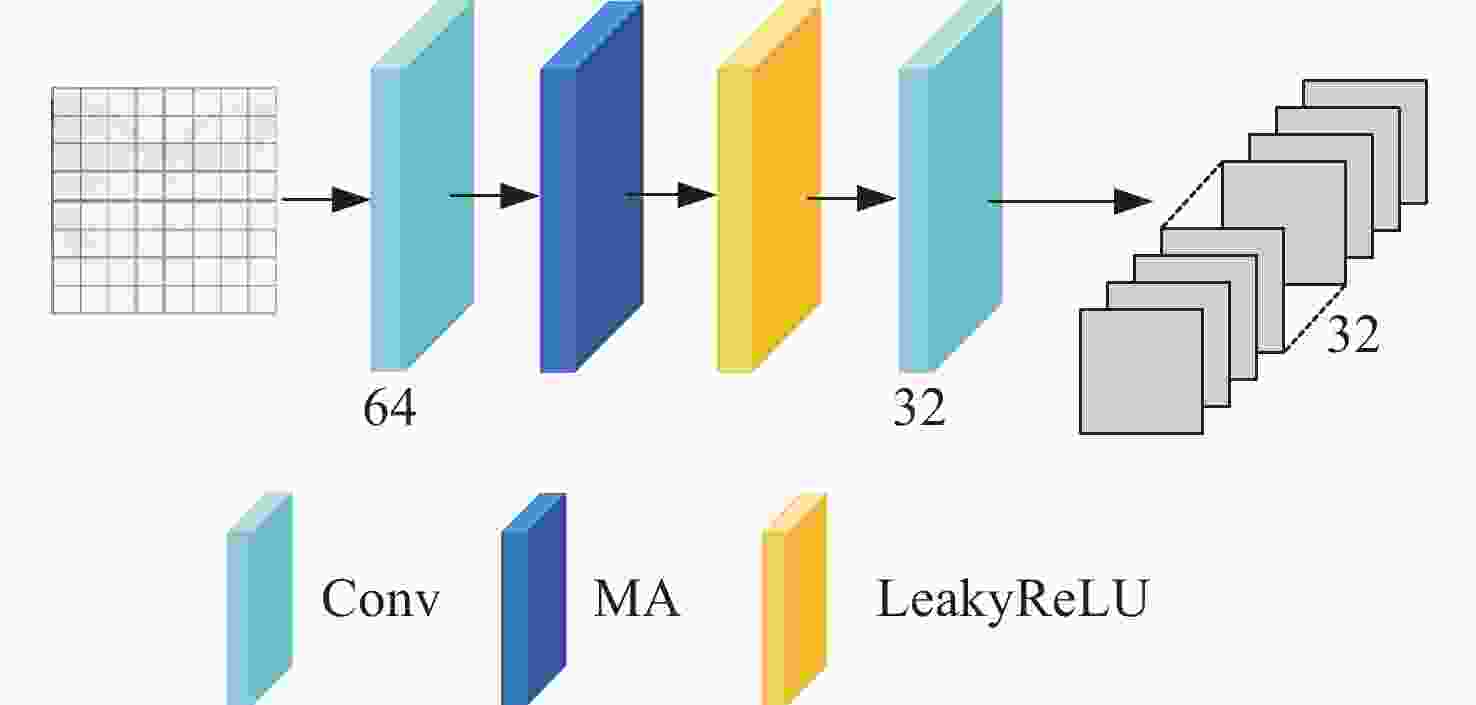
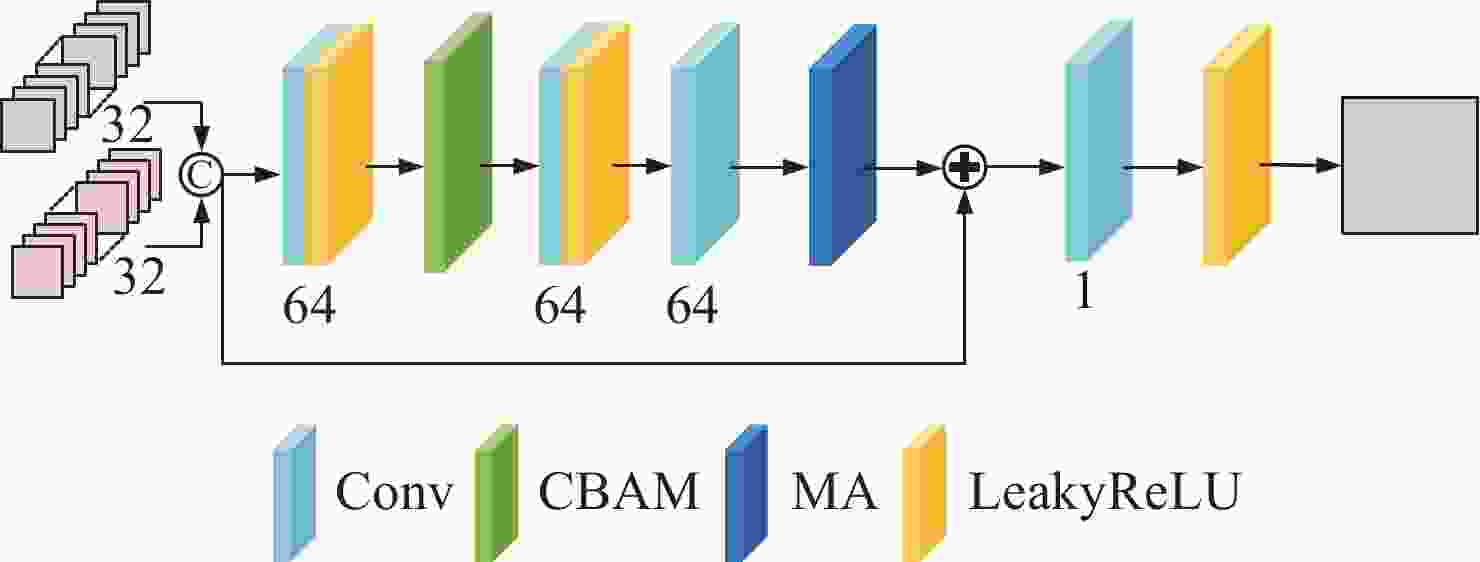
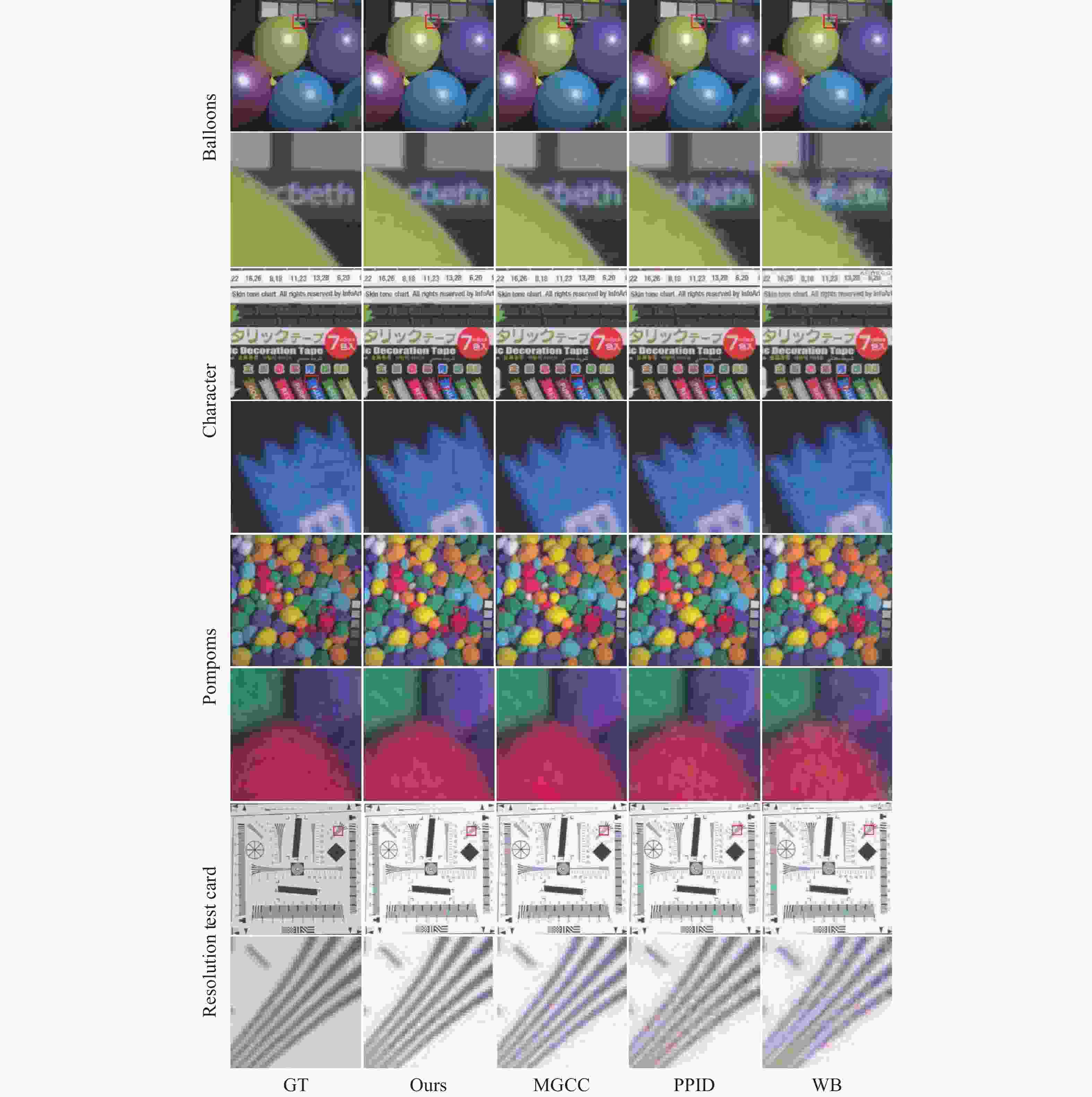
随着光谱成像技术的飞速发展,使用多光谱滤光片阵列(multispectral filter array,MSFA)采集多光谱图像的空间和光谱信息已经成为研究热点。如何利用低采样率且具有强频谱互相关性的原始数据进行重构成为制约其发展的瓶颈。本文基于一种含有全通波段的8波段4×4 MSFA,提出了一种空谱联合的多分支注意力残差网络模型。使用多分支模型对各个波段插值后的图像特征进行学习。利用本文设计的空间通道注意力模型对8个波段和全通波段的特征信息进行联合处理。该模型通过多层卷积和卷积注意力模块以及残差补偿机制,有效减小了各波段的颜色差异,增强了边缘纹理等相关特征信息。对于初步插值的全通波段和其他波段的特征信息,通过无需进行批量归一化的残差密集块对多光谱图像空间和光谱相关性进行特征学习,以匹配各个波段的光谱信息。实验结果表明,对于在D65光源下测试图像,本文所提模型的峰值信噪比、结构相似度和光谱角相似度分别较最先进的深度学习方法提升了3.46%、0.27%和6%。该方法不仅减少了伪影还获得了更多的纹理细节。
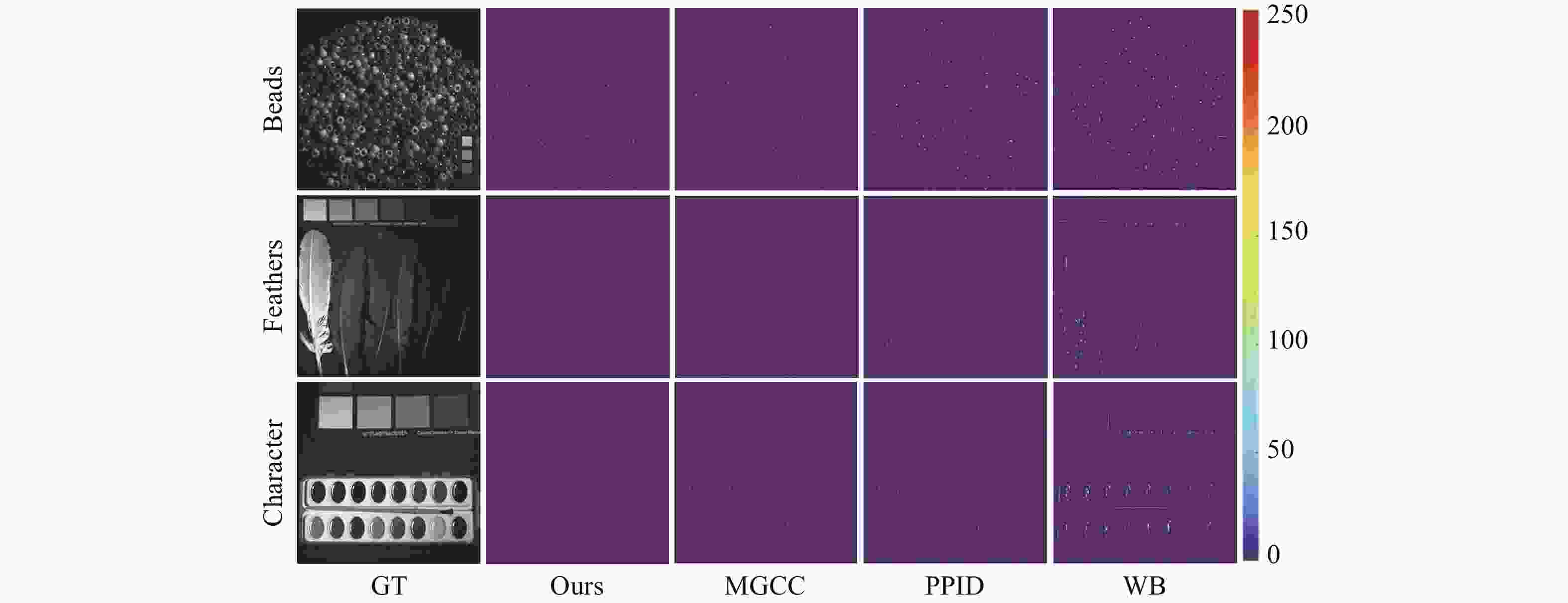
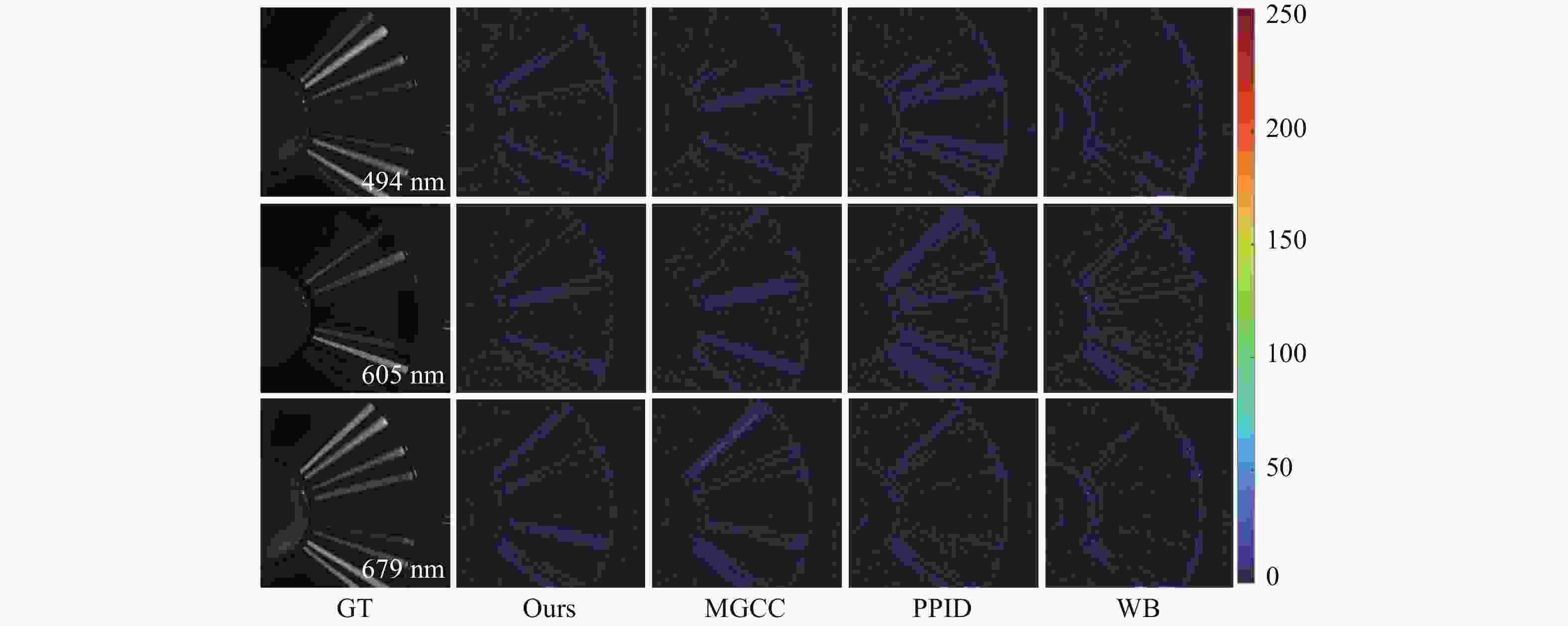
Abstract:With the rapid advancement of spectral imaging technology, the use of multispectral filter array (MSFA) to collect the spatial and spectral information of multispectral images has become a research hotspot. The uses of the original data are limited because of its low sampling rate and strong spectral inter-correlation for reconstruction. Therefore, we propose a multi-branch attention residual network model for spatial-spectral association based on an 8-band 4 × 4 MSFA with all-pass bands. First, the multi-branch model was used to learn the image features after interpolation in each band; second, the feature information of the eight bands and the all-pass band were united by the spatial channel attention model designed in this paper, and the application of multi-layer convolution and the convolutional attention module and the use of residual compensation effectively compensated the color difference of each band and enriched the edge texture-related feature information. Finally, the preliminary interpolated full-pass band and the rest of the band feature information were used for feature learning of the spatial and spectral correlations of multispectral images through residual dense blocks without batch normalization to match the spectral information of each band. Experimental results show that the peak signal-to-noise ratio, structural similarity, and spectral angular similarity of the test image under the D65 light source outperform the state-of-the-art deep learning method by 3.46%, 0.27%, and 6%, respectively. This method not only reduces artifacts but also obtains more texture details.
-
表 1 测试图像在A光源下的PSNR、SSIM和SAM值
Table 1. PSNR, SSIM, and SAM values of the test image under the A light source
PSNR ↑ SSIM ↑ SAM ↓ WB PPID MGCC Ours WB PPID MGCC Ours WB PPID MGCC Ours balloons 39.99 43.23 45.52 45.93 0.9977 0.9988 0.9992 0.9993 4.892 3.693 3.409 3.329 beads 28.35 31.03 32.75 33.57 0.9610 0.9768 0.9776 0.9858 10.087 8.002 7.571 6.182 Egyptian 35.22 40.77 40.96 43.65 0.9908 0.9947 0.9953 0.9972 11.358 10.648 8.653 7.570 feathers 32.38 36.32 37.03 38.48 0.9908 0.9962 0.9964 0.9976 8.351 6.782 6.036 5.960 paints 32.39 36.29 35.79 38.63 0.9939 0.9973 0.9973 0.9984 6.557 5.178 4.891 4.500 pompoms 36.37 38.28 40.54 41.02 0.9953 0.9968 0.9978 0.9987 4.395 3.524 3.003 2.916 CD 36.54 38.54 39.01 39.75 0.9939 0.9953 0.9956 0.9969 4.211 4.043 3.956 4.145 Character 29.27 34.91 38.91 39.51 0.9942 0.9981 0.9989 0.9992 6.103 3.811 3.119 3.049 ChartRes 30.24 31.26 31.45 32.63 0.9931 0.9976 0.9984 0.9996 3.962 2.761 2.529 1.300 Average 33.41 36.73 37.99 39.24 0.9900 0.9946 0.9951 0.9969 6.657 5.383 4.796 4.327 表 2 测试图像在D65光源下的PSNR、SSIM和SAM值
Table 2. PSNR, SSIM, and SAM values of the test image under the D65 light source
PSNR ↑ SSIM ↑ SAM ↓ WB PPID MGCC Ours WB PPID MGCC Ours WB PPID MGCC Ours balloons 40.73 44.16 46.94 48.36 0.9981 0.9991 0.9995 0.9997 3.629 3.114 2.700 2.539 beads 25.75 31.28 33.21 34.06 0.9662 0.9826 0.9808 0.9898 10.316 8.324 6.957 6.243 Egyptian 39.29 42.50 42.58 44.86 0.9929 0.9875 0.9965 0.9979 10.642 8.015 7.038 6.919 feathers 32.67 36.72 37.26 39.12 0.9916 0.9931 0.9966 0.9980 7.377 5.891 5.412 4.843 paints 31.18 36.07 36.41 38.90 0.9922 0.9974 0.9887 0.9986 6.408 4.788 3.974 3.905 pompoms 36.88 38.90 41.19 42.65 0.9962 0.9978 0.9985 0.9989 4.032 3.232 2.693 2.753 CD 34.54 38.21 40.61 41.53 0.9949 0.9952 0.9961 0.9967 3.209 2.942 2.772 2.726 Character 28.88 34.90 39.63 39.87 0.9936 0.9984 0.9994 0.9996 6.867 4.100 3.108 2.907 ChartRes 29.34 29.65 32.54 33.21 0.9951 0.9958 0.9969 0.9971 2.840 2.290 1.561 1.324 Average 33.25 36.93 38.93 40.28 0.9912 0.9941 0.9947 0.9974 6.147 4.744 4.023 3.795 表 3 测试图像在F12光源下的PSNR、SSIM和SAM值
Table 3. PSNR, SSIM, and SAM values of the test image under the F12 light source
PSNR ↑ SSIM ↑ SAM ↓ WB PPID MGCC Ours WB PPID MGCC Ours WB PPID MGCC Ours balloons 36.68 37.83 38.60 38.91 0.9937 0.9952 0.9961 0.9989 5.540 5.640 5.537 5.955 beads 25.84 27.65 27.67 29.92 0.9390 0.9566 0.9673 0.9720 14.958 13.669 13.532 11.424 Egyptian 36.23 37.46 38.23 39.47 0.9825 0.9857 0.9862 0.9913 6.150 5.740 4.763 3.795 feathers 30.61 32.76 33.51 34.70 0.9829 0.9887 0.9889 0.9928 11.526 11.194 11.251 10.897 paints 28.02 30.89 31.98 33.93 0.9761 0.9871 0.9912 0.9939 9.801 9.440 9.415 9.113 pompoms 32.17 32.81 33.92 33.97 0.9874 0.9889 0.9907 0.9909 6.776 6.355 6.150 5.936 CD 35.58 35.99 36.26 37.06 0.9869 0.9872 0.9898 0.9988 7.934 6.691 5.957 6.622 Character 26.11 28.86 32.33 32.64 0.9824 0.9908 0.9954 0.9962 7.794 6.881 6.835 6.767 ChartRes 25.81 26.32 27.61 29.33 0.9768 0.9814 0.9826 0.9916 3.845 3.157 2.837 1.859 Average 30.78 32.28 33.34 34.44 0.9786 0.9846 0.9875 0.9918 8.258 7.640 7.364 6.929 表 4 测试图像在3种光源下的PSNR、SSIM和SAM与不同去马赛克方法的定量比较
Table 4. Quantitative comparison of PSNR, SSIM, and SAM of test images processed by different de-mosaicing methods under three light sources
WB PPID MGCC Ours PSNR 29.37 34.56 35.69 37.81 SSIM 0.8926 0.9705 0.9902 0.9936 SAM 8.541 6.473 5.647 5.312 表 5 不同去马赛克方法运行时间比较
Table 5. Comparison of running times of different de-mosaicing methods(Unit:ms)
WB PPID MGCC Ours CPU 254.35 2134.5 - - GPU - - 2.65 2.12 表 6 不同网络架构的消融研究
Table 6. The ablation of different network architectures
多分支架构 残差密集块 PSNR SSIM SAM × × 36.94 0.9869 7.263 × √ 37.21 0.9907 6.726 √ √ 38.59 0.9938 6.218 表 7 不同注意力机制方案的消融研究
Table 7. The ablation of different attention mechanism schemes
注意力机制 PSNR SSIM SAM RN 36.24 0.9804 8.352 CA 36.79 0.9873 6.316 MAM 37.28 0.9927 6.047 SCAM 38.46 0.9951 5.247 -
[1] JUNIOR J D D, BACKES A R, ESCARPINATI M C. Detection of control points for UAV-multispectral sensed data registration through the combining of feature descriptors[C]. Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, SciTePress, doi: 10.5220/0007580204440451. [2] MANGAI U G, SAMANTA S, DAS S, et al. A hierarchical multi-classifier framework for landform segmentation using multi-spectral satellite images - a case study over the Indian subcontinent[C]. 2010 Fourth Pacific-Rim Symposium on Image and Video Technology, IEEE, 2010: 306-313, doi: 10.1109/PSIVT.2010.58. [3] LIU CH H, LIU W, LU X ZH, et al. Application of multispectral imaging to determine quality attributes and ripeness stage in strawberry fruit[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(2): e87818. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087818 [4] CHEN I T, LIN H Y. Detection, counting and maturity assessment of cherry tomatoes using multi-spectral images and machine learning techniques[C]. Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, SciTePress, 2020: 759-766, doi: 10.5220/0008874907590766. [5] CHANG K, LI H X, TAN Y F, et al. A two-stage convolutional neural network for joint demosaicking and super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(7): 4238-4254. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3129201 [6] SHINODA K, OGAWA S, YANAGI Y, et al. Multispectral filter array and demosaicking for pathological images[C]. 2015 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA), IEEE, 2015: 697-703, doi: 10.1109/APSIPA.2015.7415362. [7] ZENTENO O, TREUILLET S, LUCAS Y. 3D cylinder pose estimation by maximization of binary masks similarity: a simulation study for multispectral endoscopy image registration[C]. Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, SciTePress, 2019: 857-864, doi: 10.5220/0007400808570864. [8] 李云辉. 压缩光谱成像系统中物理实现架构研究综述[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(5):929-945. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0104LI Y H. Review of physical implementation architecture in compressive spectral imaging system[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(5): 929-945. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0104 [9] ZHUANG L N, NG M K, FU X Y, et al. Hy-demosaicing: hyperspectral blind reconstruction from spectral subsampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1-15. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3102136 [10] ZHANG J CH, CHEN J L, YU H W, et al. Polarization image demosaicking via nonlocal sparse tensor factorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1-10. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3093903 [11] RATHI V, GOYAL P. Multispectral image demosaicking based on novel spectrally localized average images[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022, 29: 449-453. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3139581 [12] RATHI V, GOYAL P. Generic multispectral demosaicking using spectral correlation between spectral bands and pseudo-panchromatic image[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2023, 110: 116893. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2022.116893 [13] LIU SH M, ZHANG Y G, CHEN J, et al. A deep joint network for multispectral demosaicking based on pseudo-panchromatic images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2022, 16(4): 622-635. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2022.3172865 [14] ZHANG Y, SUN W J, CHEN ZH ZH. Joint image demosaicking and denoising with mutual guidance of color channels[J]. Signal Processing, 2022, 200: 108674. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2022.108674 [15] AGGARWAL H K, MAJUMDAR A. Single-sensor multi-spectral image demosaicing algorithm using learned interpolation weights[C]. 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IEEE, 2014: 2011-2014, doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6946857. [16] CHINI M, CHIANCONE A, STRAMONDO S. Scale Object Selection (SOS) through a hierarchical segmentation by a multi-spectral per-pixel classification[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2014, 49: 214-223. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2014.07.012 [17] MIHOUBI S, LOSSON O, MATHON B, et al. Multispectral demosaicing using pseudo-panchromatic image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2017, 3(4): 982-995. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2017.2691553 [18] 齐海超, 宋延嵩, 张博, 等. 基于改进引导滤波器的多光谱去马赛克方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(5):1056-1065. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0231QI H CH, SONG Y S, ZHANG B, et al. Multispectral demosaicing method based on an improved guided filter[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 1056-1065. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0231 [19] CHEN L K, ZHAO Y Q, CHAN J C W, et al. Histograms of oriented mosaic gradients for snapshot spectral image description[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2022, 183: 79-93. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2021.10.018 [20] XIONG F CH, ZHOU J, QIAN Y T. Material based object tracking in hyperspectral videos: benchmark and algorithms[Z]. arXiv: 1812.04179, 2019. [21] WANG X H, CHEN J, WEI Q, et al. Hyperspectral image super-resolution via deep prior regularization with parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(4): 1708-1723. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3078559 [22] HU J, JIA X P, LI Y S, et al. Hyperspectral image super-resolution via intrafusion network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(10): 7459-7471. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2982940 [23] KUMAR S P P, PETER K J, KINGSLY C S. De-noising and demosaicking of Bayer image using deep convolutional attention residual learning[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2023, 82(13): 20323-20342. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-14334-z [24] KURNIAWAN E, PARK Y, LEE S. Noise-resistant demosaicing with deep image prior network and random RGBW color filter array[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(5): 1767. doi: 10.3390/s22051767 [25] SHINODA K, YOSHIBA S, HASEGAWA M. Deep demosaicking for multispectral filter arrays[Z]. arXiv: 1808.08021, 2018. [26] PAN ZH H, LI B P, BAO Y Z, et al. Deep panchromatic image guided residual interpolation for multispectral image demosaicking[C]. 2019 10th Workshop on Hyperspectral Imaging and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), IEEE, 2019: 1-5, doi: 10.1109/WHISPERS.2019.8920868. [27] FENG K, ZHAO Y Q, CHAN J C W, et al. Mosaic convolution-attention network for demosaicing multispectral filter array images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2021, 7: 864-878. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2021.3102052 [28] DIJKSTRA K, VAN DE LOOSDRECHT J, SCHOMAKER L R B, et al. Hyperspectral demosaicking and crosstalk correction using deep learning[J]. Machine Vision and Applications, 2019, 30(1): 1-21. doi: 10.1007/s00138-018-0965-4 [29] WANG ZH, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600-612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [30] KRUSE F A, LEFKOFF A B, BOARDMAN J W, et al. The spectral image processing system (SIPS)-interactive visualization and analysis of imaging spectrometer data[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1993, 283(1): 192-201. [31] WANG X T, YU K, WU SH X, et al. ESRGAN: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2018: 63-79. [32] ZHAO H, GALLO O, FROSIO I, et al. Loss functions for image restoration with neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2017, 3(1): 47-57. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2016.2644865 [33] KIM J, LEE J K, LEE K M. Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2016. [34] KINGMA D P, BA L J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), ICLR, 2017. [35] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[M]. FERRARI V, HEBERT M, SMINCHISESCU C, et al. Computer Vision – ECCV 2018. Cham: Springer, 2018: 3-19, doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1. [36] YASUMA F, MITSUNAGA T, ISO D, et al. Generalized assorted pixel camera: postcapture control of resolution, dynamic range, and spectrum[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(9): 2241-2253. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2046811 [37] MONNO Y, KIKUCHI S, TANAKA M, et al. A practical one-shot multispectral imaging system using a single image sensor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(10): 3048-3059. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2436342 [38] HU J, SHEN L, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011-2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372 -





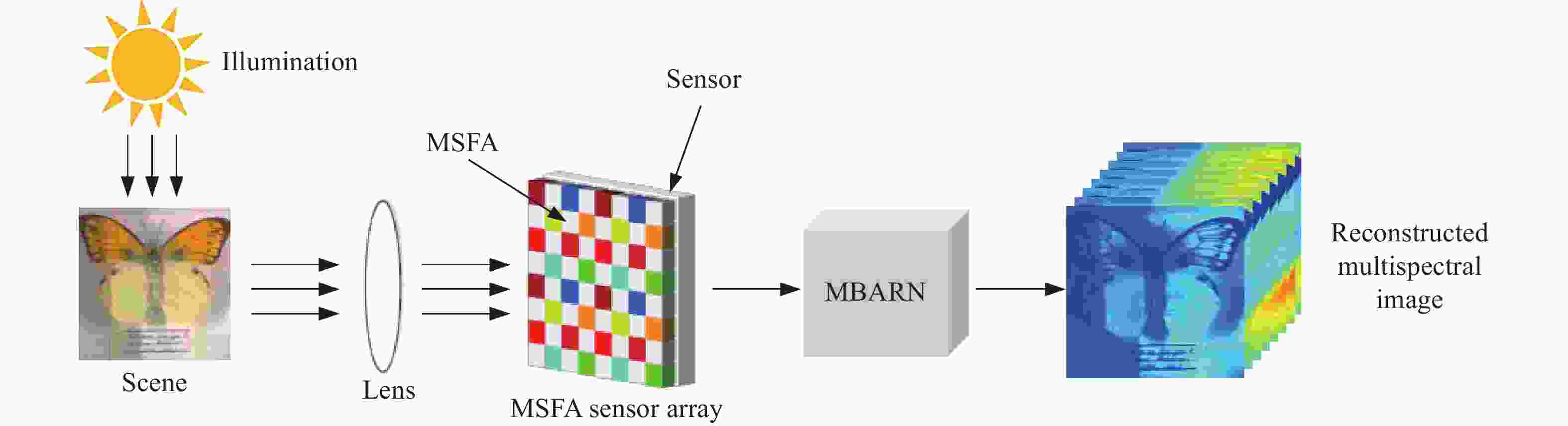
 下载:
下载: