-
摘要:
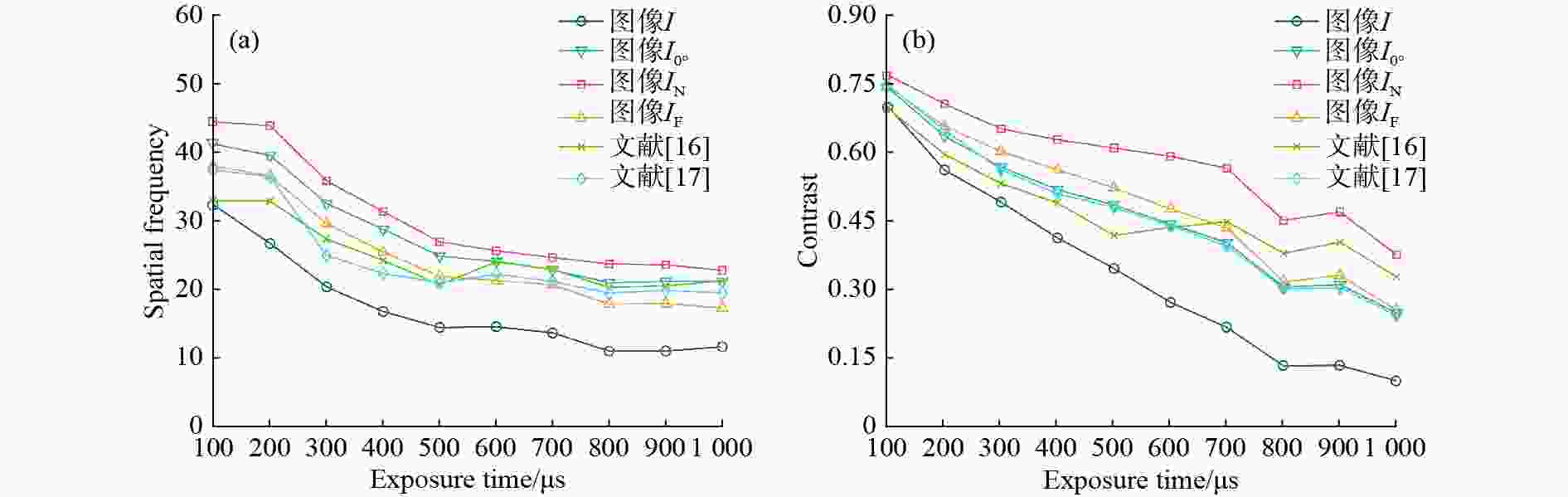
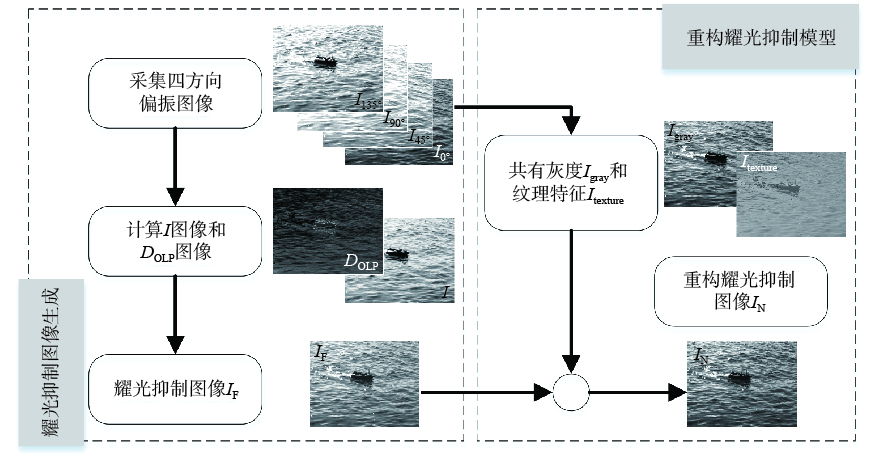
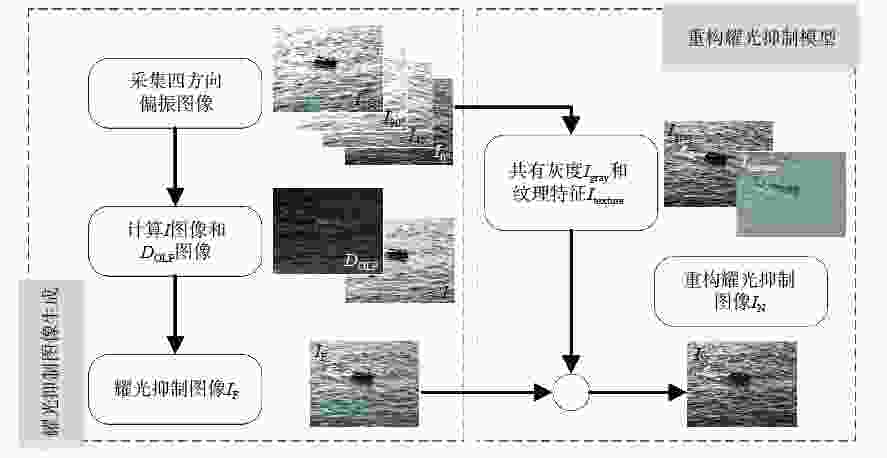
太阳耀光是海面目标探测过程中的重要影响因素,本文针对陆地观测平台,利用耀光的偏振特性,提出一种基于线偏振图像共有成分与特征成分重构的海面耀光抑制方法。该方法利用分焦平面偏振相机获取四通道线偏振辐射图像,计算场景的偏振度信息,生成耀光抑制图像。在以偏振信息抑制场景耀光的基础上,结合线偏振辐射图像的特点,将耀光抑制辐射图像的光强分量分解为共有成分与特征成分,重新赋予二者新的权重因子得到重构后的耀光抑制图像。外场偏振实验的结果表明,在3组典型实验数据中,重构耀光抑制图像相比于光强图像的饱和像素占比最多降低79.07%,空间频率与对比度提升可达73.77%和172.73%。本文所提方法有效抑制了海面场景中的耀光噪声且在背景细节信息恢复方面具有良好表现。
Abstract:Sun glint is a significant factor influencing sea surface target detection. For land observation platforms, a sea surface glint suppression method based on the reconstruction of common and feature components of linearly polarized images is proposed using the polarization characteristics of glints. We use a focal plane polarization camera to obtain four-channel linear polarized images, calculate the scene’s polarization information, and generate a glint suppression image. Based on suppressing scene glint with polarization information combined with the characteristics of linear polarization images, the light intensity components of the glint suppression image are decomposed into common and characteristic components, and new weight factors are reassigned to obtain the reconstructed glint suppression image. The glint polarization imaging experiments show that in the three sets of typical experimental data, the proportion of saturated pixels in the reconstructed glint suppressed image is decreased by up 79.07%. Compared to the intensity image, and the spatial frequency and contrast are increased by up to 73.77% and 172.73%, respectively. The method proposed in this paper effectively suppresses the glint noise in the sea scene and performs well in restoring background detail information.
-
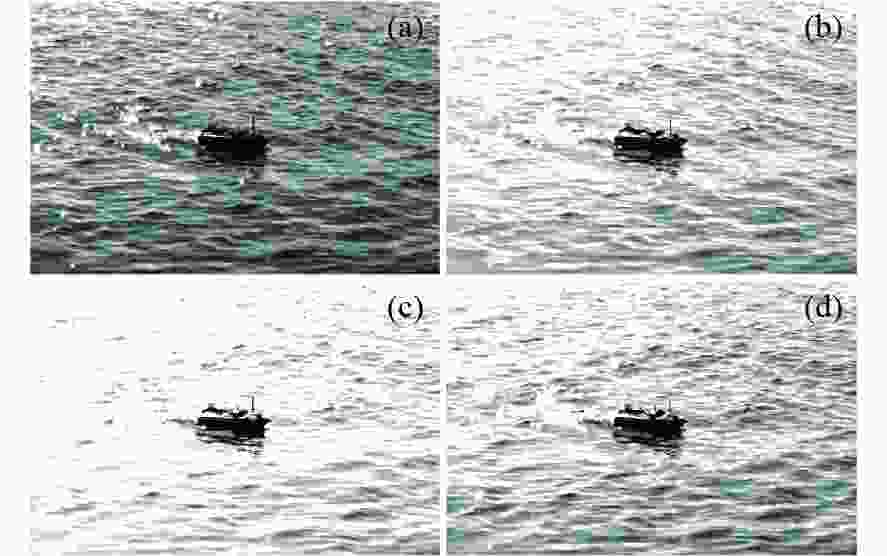
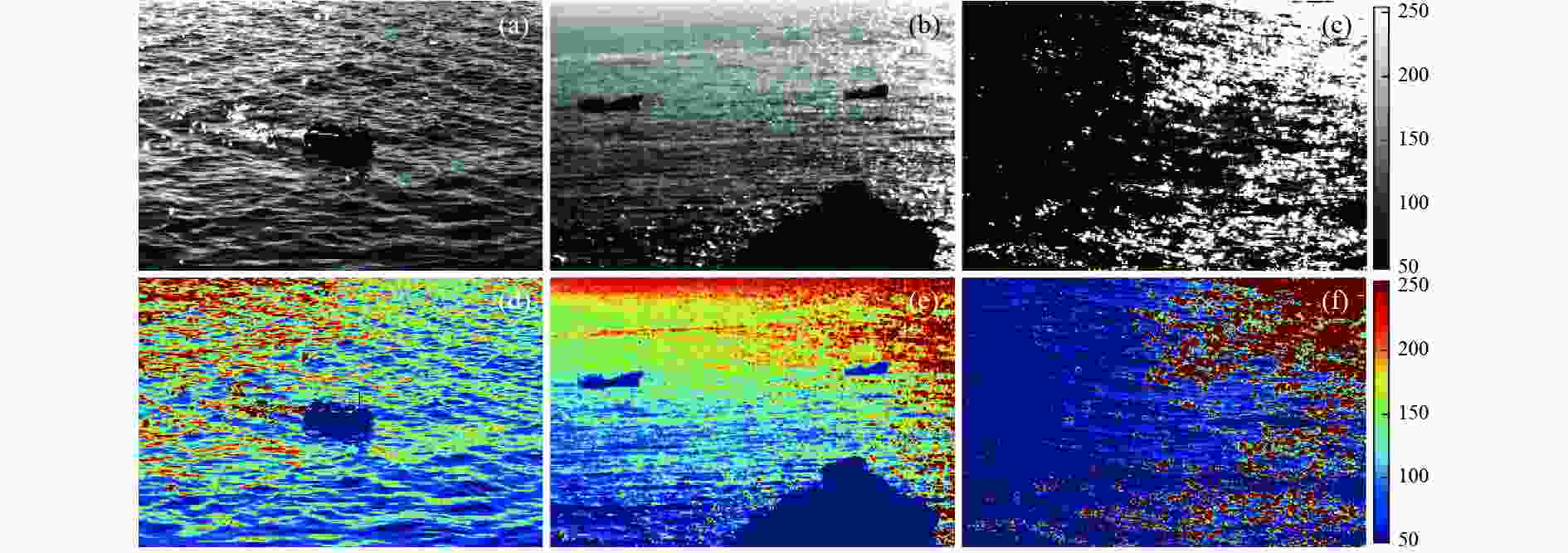
图 3 四通道线偏振光图像。(a)
${I_{{\text{0}}\text{°} }}$ 图像;(b)${I_{{\text{45}}\text{°} }}$ 图像;(c)${I_{{\text{90}}\text{°} }}$ 图像;(d)${I_{{\text{135}}\text{°} }}$ 图像Figure 3. Four-channel linearly polarized light images. (a) Image
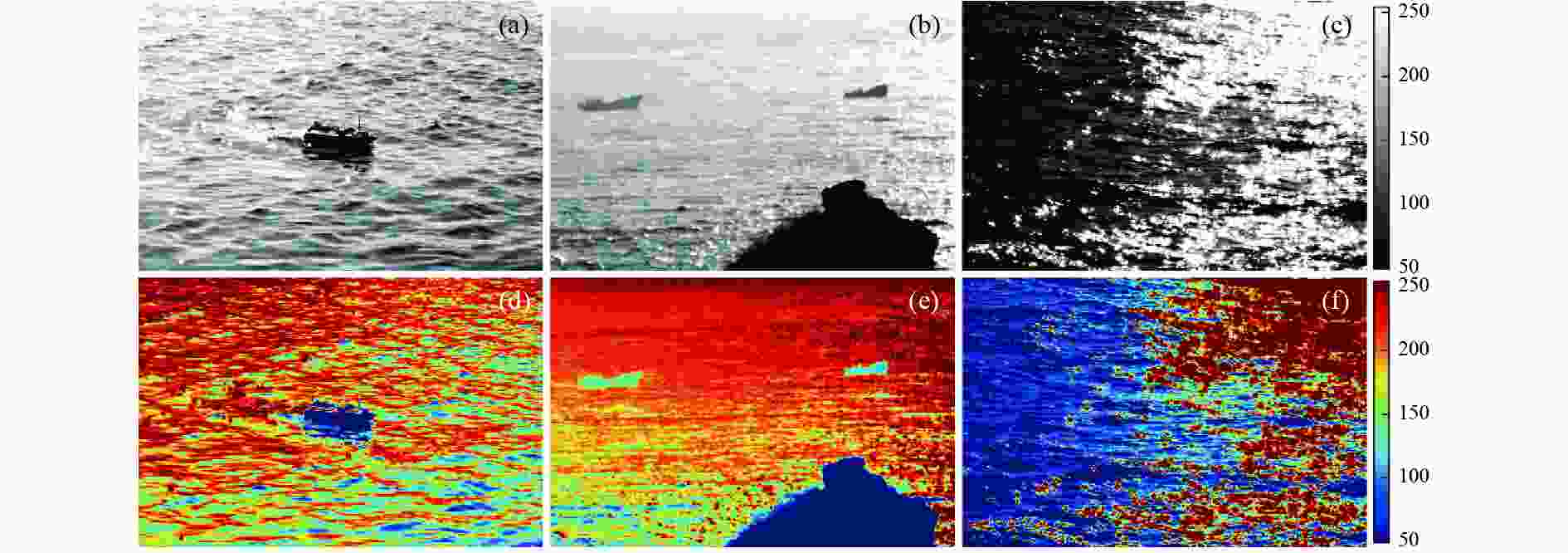
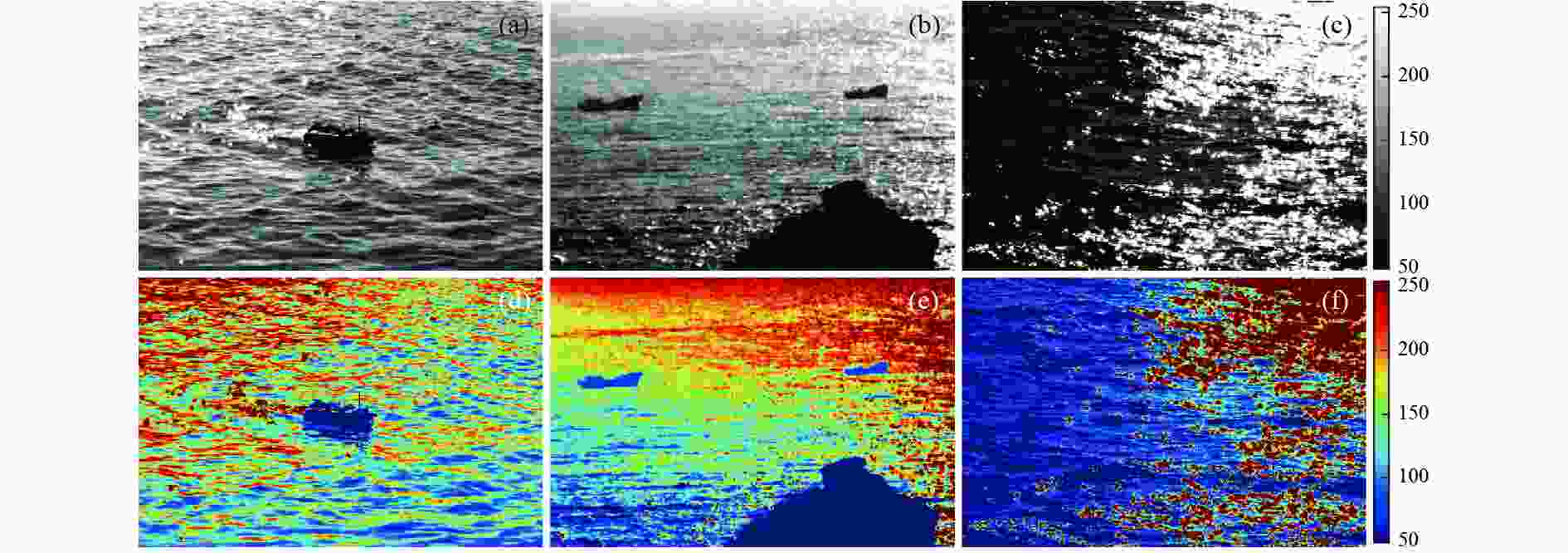
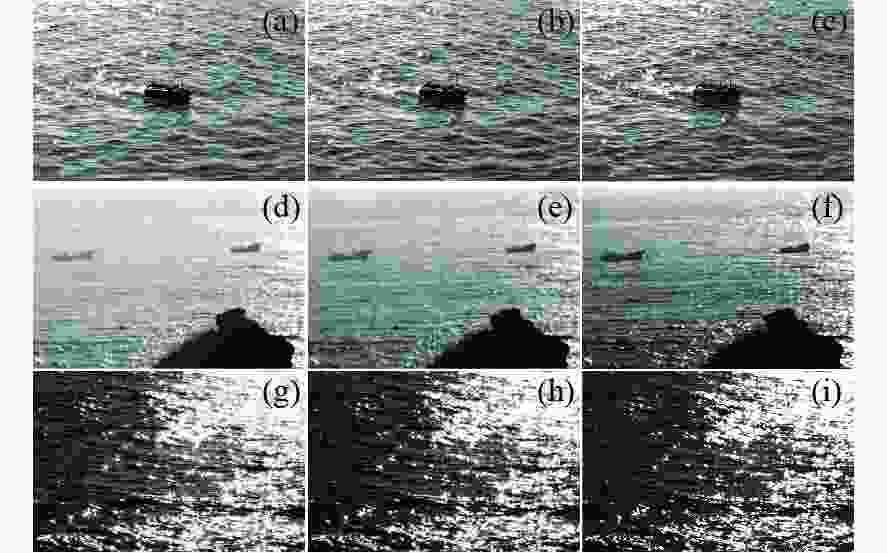
${I_{{\text{0}}\text{°} }}$ ; (b) image${I_{{\text{45}}\text{°} }}$ ; (c) image${I_{{\text{90}}\text{°} }}$ ; (d) image${I_{{\text{135}}\text{°} }}$ 图 8 耀光抑制图像对比结果。(a)(d)(g)为文献[16]中的算法结果;(b)(e)(h)为文献[17]中的算法结果;(c)(f)(i)为重构耀光抑制模型
Figure 8. Comparative results of glint suppression images. (a) (d) (g) Results obtained by the algorithm in Ref. [16]. (b) (e) (h) Results obtained by the algorithm in Ref. [17]. (c) (f) (i) Reconstruction obtained by the glint suppression model
表 1 线偏振图像评价指标
Table 1. Evaluation index of linearly polarized image
评价指标 ${I_{{\text{0}}\text{°} }}$ ${I_{45\text{°} }}$ ${I_{{\text{90}}\text{°} }}$ ${I_{135\text{°} }}$ 空间频率 42.33 39.87 30.94 43.69 对比度 0.48 0.39 0.37 0.35 表 2 图像的评价指标
Table 2. Image quality evaluation index
实验区域 评价指标 $ I $ $ I_{{\mathrm{F}}} $ $ I_{\mathrm{N}} $ 文献[16] 文献[17] 场景1 饱和像素占比/% 48.55 20.71 10.16 14.04 11.12 空间频率 32.12 39.45 45.29 39.57 42.57 对比度 0.39 0.51 0.54 0.47 0.47 场景2 饱和像素占比/% 59.79 24.92 14.91 41.62 18.57 空间频率 17.69 26.87 30.74 19.26 21.45 对比度 0.11 0.26 0.30 0.10 0.17 场景3 饱和像素占比/% 31.07 24.72 22.33 25.49 22.49 空间频率 33.10 38.29 46.37 34.94 32.12 对比度 — — — — — -
[1] LYNCH D K, DEARBORN D S P, LOCK J A. Glitter and glints on water[J]. Applied Optics, 2011, 50(28): F39-F49. doi: 10.1364/AO.50.000F39 [2] OTTAVIANI M, MERCK C, LONG S, et al. Time-resolved polarimetry over water waves: relating glints and surface statistics[J]. Applied Optics, 2008, 47(10): 1638-1648. doi: 10.1364/AO.47.001638 [3] 李岩松, 赵慧洁, 李娜, 等. 基于中红外偏振的海面太阳耀光背景下的目标探测[J]. 中国激光,2022,49(19):1910004. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1910004LI Y S, ZHAO H J, LI N, et al. Detection of marine targets covered in sun glint based on mid-infrared polarization[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(19): 1910004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1910004 [4] KAY S, HEDLEY J, LAVENDER S. Sun glint estimation in marine satellite images: a comparison of results from calculation and radiative transfer modeling[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(23): 5631-5639. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.005631 [5] SCHOLL V, GERACE A. Removing glint with video processing to enhance underwater target detection[C]. IEEE Western New York Image Processing Workshop (WNYIPW), IEEE, 2013: 18-21. [6] COX C, MUNK W. Measurement of the roughness of the sea surface from photographs of the Sun’s glitter[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1954, 44(11): 838-850. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.44.000838 [7] COOPER A W, LENTZ W J, WALKER P L, et al. Infrared polarization measurements of ship signatures and background contrast[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1994, 2223: 300-309. doi: 10.1117/12.177924 [8] WANG G C, WANG J L, ZHANG ZH D, et al. Performance of eliminating sun glints reflected off wave surface by polarization filtering under influence of waves[J]. Optik, 2016, 127(5): 3143-3149. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.12.057 [9] LIANG J A, WANG X, HE S, et al. Sea surface clutter suppression method based on time-domain polarization characteristics of sun glint[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(3): 2142-2158. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.002142 [10] AVRAHAMY R, MILGROM B, ZOHAR M, et al. Improving object imaging with sea glinted background using polarization method: analysis and operator survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8764-8774. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2922827 [11] 周俊焯, 郝佳, 余晓畅, 等. 面向偏振成像的超构表面研究进展[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(5):973-995. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0234ZHOU J ZH, HAO J, YU X CH, et al. Recent advances in metasurfaces for polarization imaging[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 973-995. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0234 [12] DE JONG A N, SCHWERING P B W, FRITZ P J, et al. Optical characteristics of small surface targets, measured in the False Bay, South Africa; June 2007[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2009, 7300: 730003. doi: 10.1117/12.816859 [13] ZHAO H J, JI ZH, ZHANG Y, et al. Mid-infrared imaging system based on polarizers for detecting marine targets covered in sun glint[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(15): 16396-16409. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.016396 [14] 张卫国. 海面太阳耀光背景下的偏振探测技术[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(2):231-236. doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0231ZHANG W G. Application of polarization detection technology under the background of sun flare on sea surface[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(2): 231-236. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0231 [15] 朱鹤骞, 曲宏松. 海面背景耀光的自适应抑制系统[J]. 光学学报,2022,42(12):1201006. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.1201006ZHU H Q, QU H S. Adaptive suppression system of sea background flare[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(12): 1201006. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.1201006 [16] 陈卫, 乔延利, 孙晓兵, 等. 基于偏振辐射图融合的水面太阳耀光抑制方法[J]. 光学学报,2019,39(5):0529001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0529001CHEN W, QIAO Y L, SUN X B, et al. Method for water surface sun glint suppression based on polarized radiation image fusion[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(5): 0529001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0529001 [17] LIANG J A, WANG X, FANG Y J, et al. Water surface-clutter suppression method based on infrared polarization information[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(16): 4649-4658. (in Chinese). doi: 10.1364/AO.57.004649 [18] 叶松, 屈文学, 李树, 等. 基于偏振时域特性的海面耀光抑制方法[J]. 光学学报,2021,41(10):1001003. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1001003YE S, QU W X, LI SH, et al. Sea surface glint-suppression method based on the polarization time-domain characteristics[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(10): 1001003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1001003 [19] 赵峰, 程喜萌, 冯斌, 等. 分焦平面偏振图像插值算法的比较研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2020,57(16):161014.ZHAO F, CHENG X M, FENG B, et al. Comparison research of interpolation algorithms for division of focal plane polarization image[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(16): 161014. (in Chinese). [20] 史浩东, 许家伟, 张健, 等. 强光背景下主动偏振成像方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(5):1075-1086. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0151SHI H D, XU J W, ZHANG J, et al. Active polarization imaging method under strong light background[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(5): 1075-1086. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0151 [21] 宿德志, 刘亮, 王坤, 等. 基于偏振差分图像的海天线检测方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(3):596-606. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0181SU D ZH, LIU L, WANG K, et al. Sea-sky-line detection method based on polarization difference images[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(3): 596-606. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0181 -





 下载:
下载: