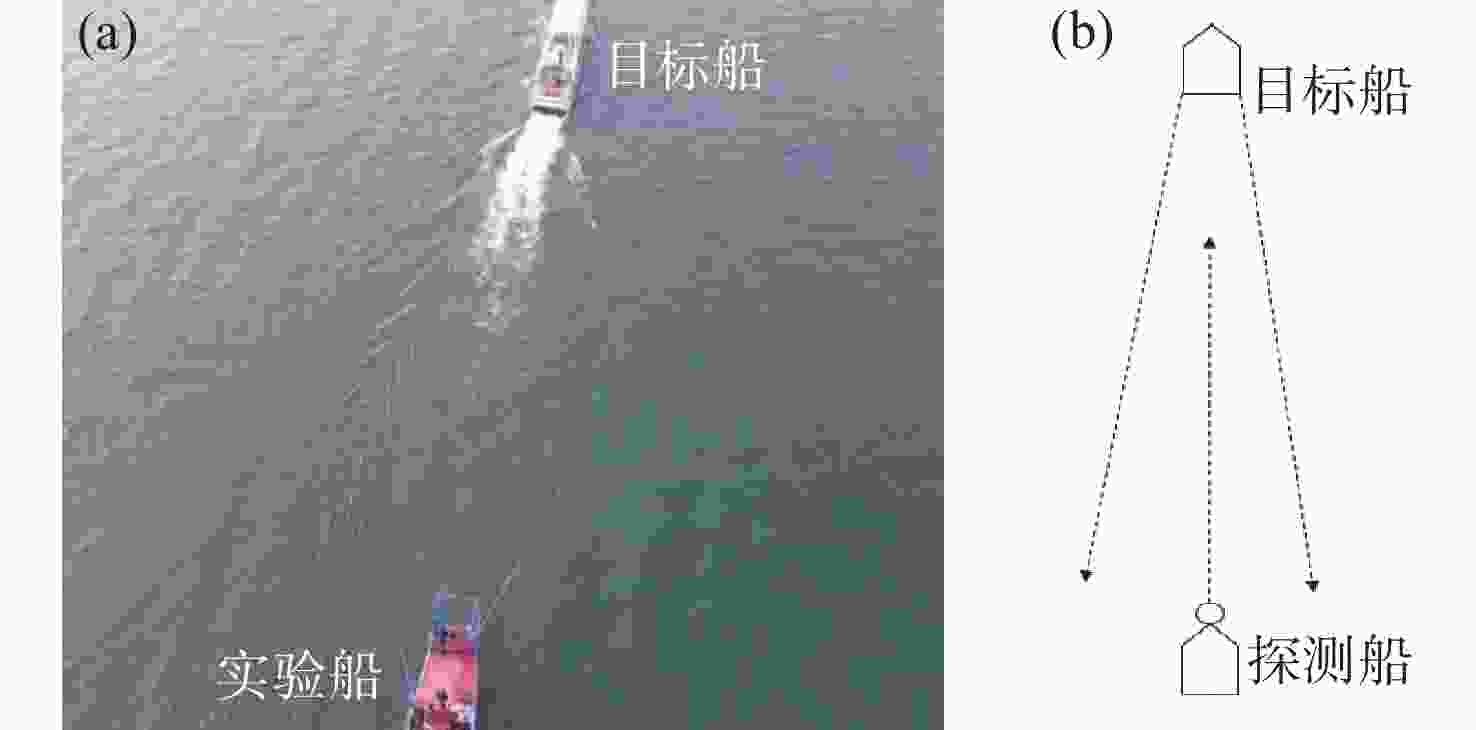
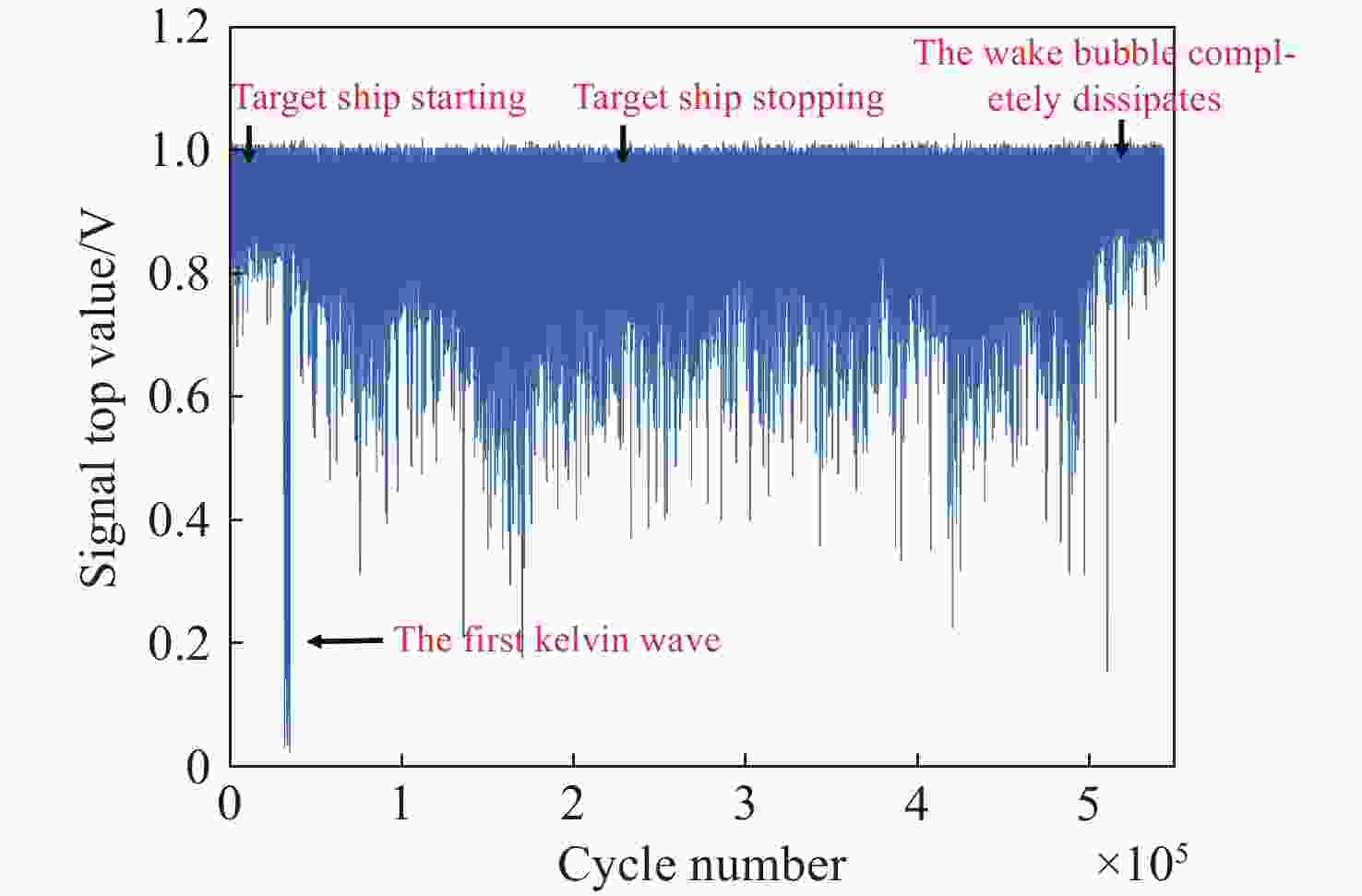
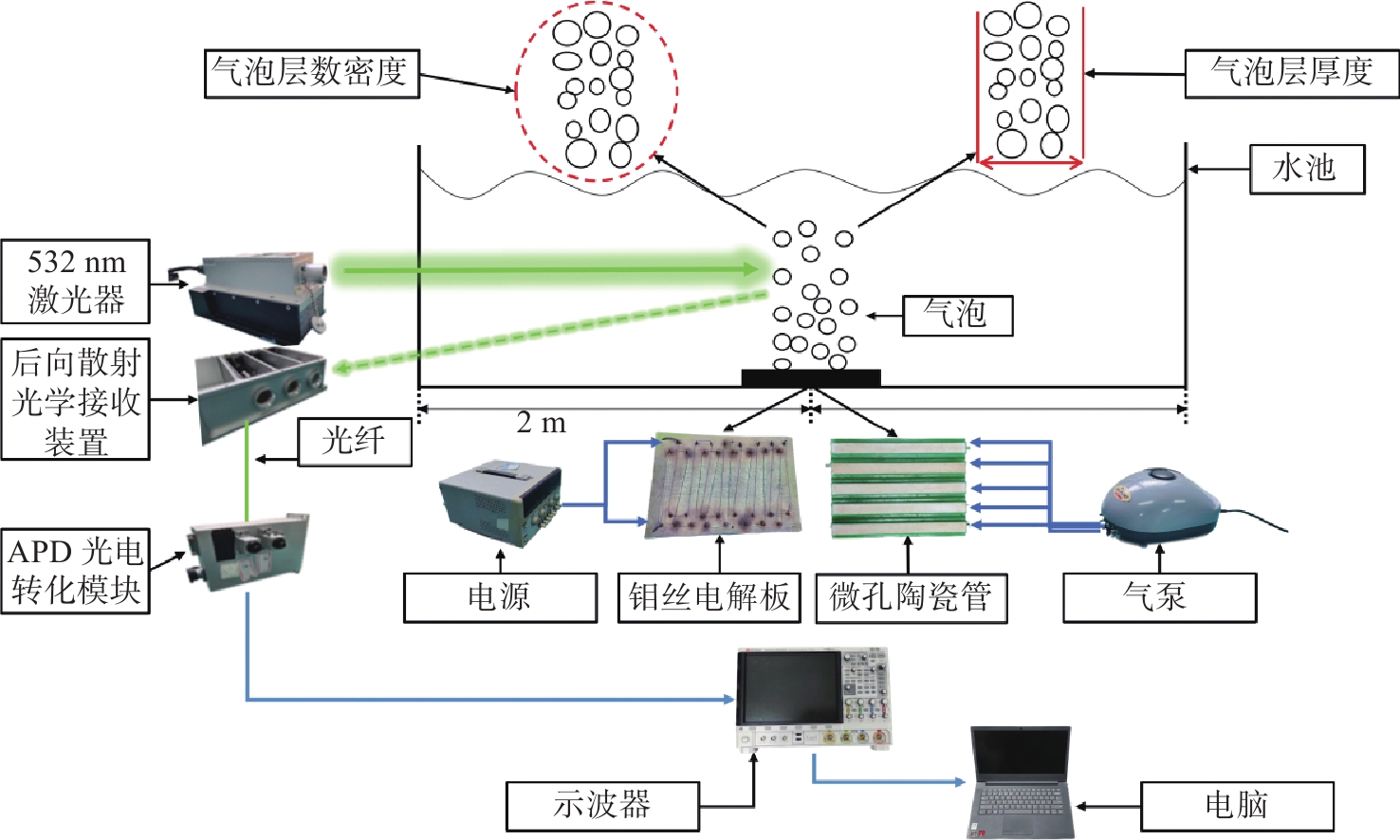
Detection method of weak ship wake signals based on the synchronous accumulation method
-
摘要:
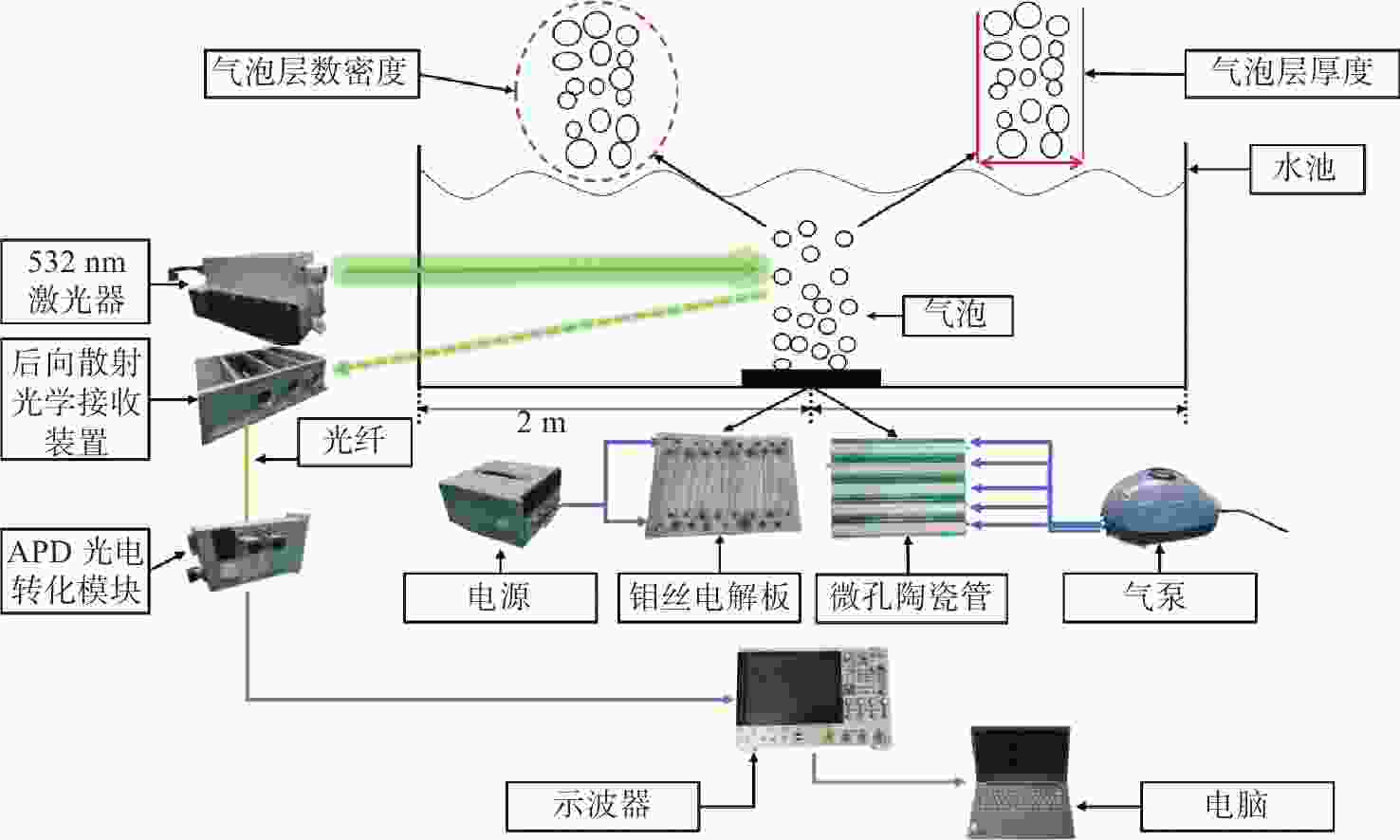
为适应复杂的动态变化的尾流气泡场环境,提高水下探测装置对舰船尾流微弱信号的探测信噪比与检出率,本文提出了一种基于同步累积法的舰船尾流微弱信号检测方法。利用周期信号的重复性与噪声的随机性,对连续多个周期信号做累积归一化处理,降低随机噪声对探测性能的干扰,提升探测信噪比。建立了针对舰船尾流微弱信号多时间尺度检测能力评估模型,评估本方法在多参量耦合下的探测性能。通过在室内水池、室外湖泊条件下开展大量模拟舰船尾流探测实验,验证了该方法适配稀疏微小的远场尾流气泡至高湍流扰动下的大尺度近场气泡检测。本文方法可实现全时域舰船尾流的跟踪检测,有效提升水下兵器的打击能力,为舰船尾流激光探测识别工程实践提供支撑。
Abstract:In order to adapt to the complex dynamic changing wake bubble field environment, improve the detection signal-to-noise ratio and detection rate of the weak ship wake signals, and expand the detection range, a method of detecting weak ship wake signals based on the synchronous accumulation method is proposed. By taking advantage of the repeatability of periodic signals and the randomness of noise, cumulative normalization is performed on successive periodic signals, effectively improving the detection signal-to-noise ratio and reducing the interference of random noise on detection performance. In order to evaluate the detection performance of the algorithm under multi-parameter coupling, a multi-time scale detection capability evaluation model for weak ship wake signals is established. By conducting many simulated ship wake detection experiments in large indoor pools and typical outdoor lakes, it is verified that the algorithm is suitable for the detection of various bubbles from smaller ones in sparse and discrete tiny far-field wakes to larger near-field ones under high turbulence disturbance, thus realizing full-time ship wake tracking and detection. This can effectively improve underwater weapon strike capability. It can support ship wake laser detection and identification engineering practice.
-
Key words:
- laser detection /
- ship wake /
- signal processing
-
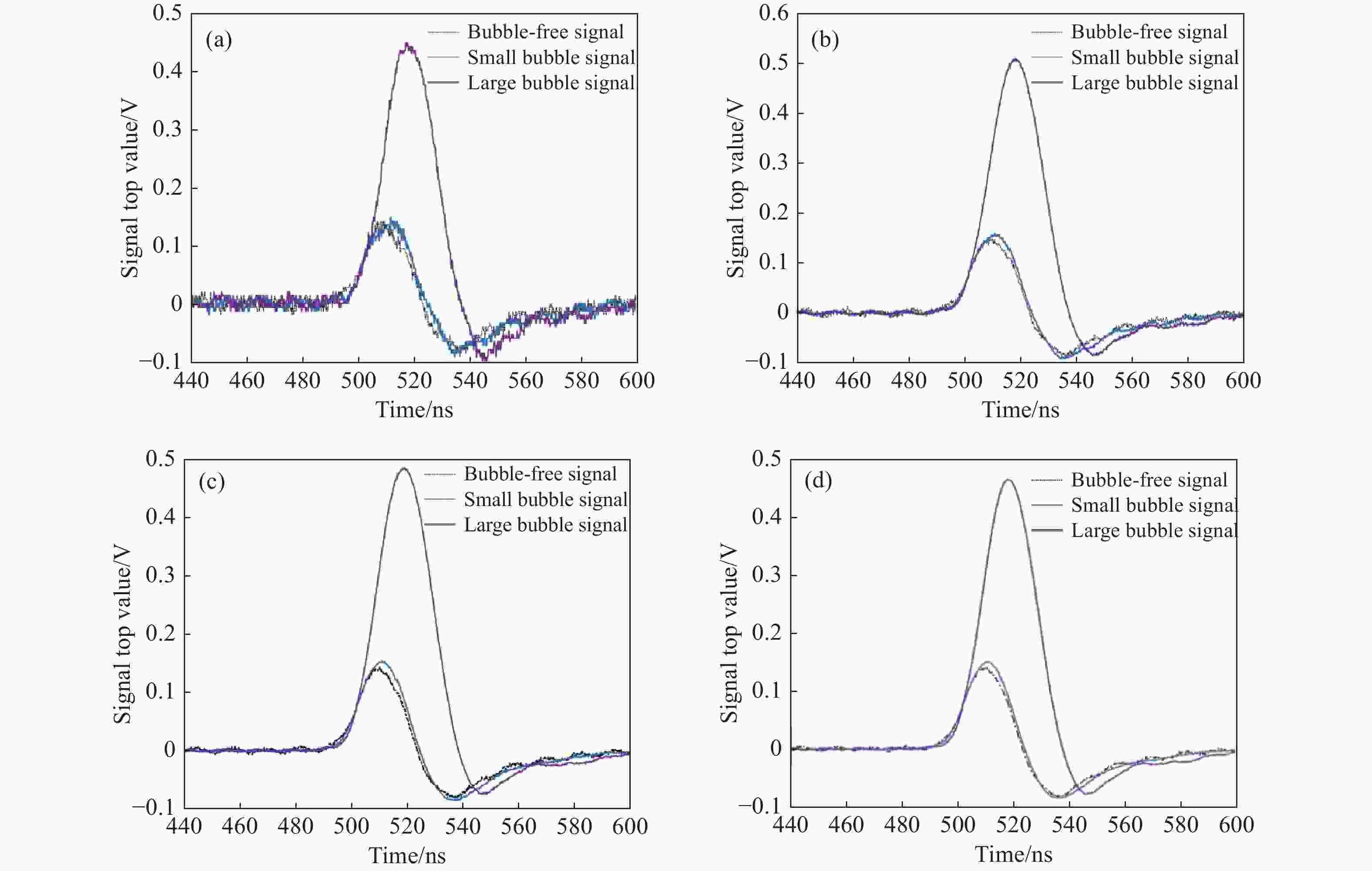
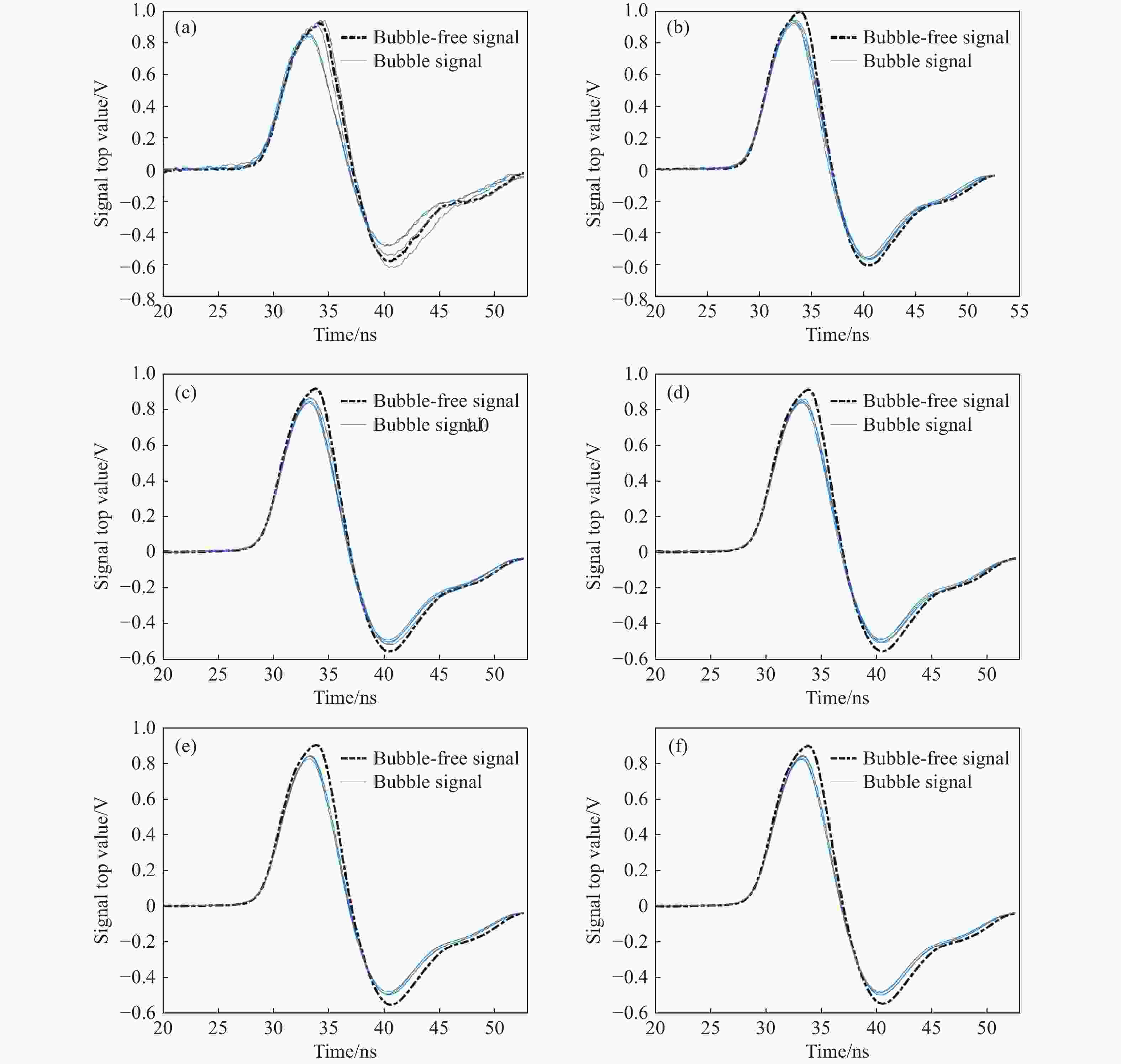
图 8 湖泊水域尾流气泡探测回波及信号处理波形。(a) 原始信号;(b) 10周期累积信号;(c) 50周期累积信号;(d) 100周期累积信号;(e) 500周期累积信号;(f)
1000 周期累积信号Figure 8. Waveforms of wake bubble echo detection and signal process in a lake. (a) The original signal; (b) 10-cycle cumulative signal; (c) 50-cycle cumulative signal; (d) 100-cycle cumulative signal; (e) 500-cycle cumulative signal; (f)
1000 -cycle cumulative signal表 1 室内水池尾流气泡探测信号处理效果评估结果
Table 1. Evaluation results of signal processing effectiveness of wake bubble detection in an indoor pool
累积
周期数信噪比 信背比 检出率 小气泡 大气泡 小气泡 大气泡 全探测过程 原始 0.3182 14.0000 1.0493 3.1690 65.36% 10 0.7905 34.2381 1.0549 3.3792 72.50% 30 1.8034 57.8258 1.0743 3.3815 84.62% 50 2.1925 75.6432 1.0655 3.2582 87.50% 表 2 湖泊水域尾流气泡探测信号处理效果评估
Table 2. Evaluation results of signal processing effectiveness of wake bubble detection in a lake
叠加周
期数信噪比 信背比 检出率
全过程2 min 4 min 6 min 8 min 2 min 4 min 6 min 8 min 1 3.9828 6.0263 4.9828 1.7403 0.9240 0.9872 0.9049 1.0188 79.88% 10 7.0033 8.1485 7.3742 5.9902 0.9348 0.9430 0.9266 0.9442 89.26% 50 11.7589 12.5028 11.7459 6.0344 0.9147 0.9413 0.9238 0.9463 89.32% 100 11.7314 18.4155 11.7865 7.6769 0.9242 0.9322 0.9208 0.9439 89.19% 500 15.9158 19.0482 12.9746 12.0893 0.9288 0.9151 0.9321 0.9337 89.06% 1000 15.9447 17.6144 11.6551 13.0707 0.9248 0.9168 0.9383 0.9351 88.97% -
[1] 韩彪, 刘继芳, 刘昆仑, 等. 舰船尾流气泡后向光学检测方法研究[J]. 光学学报,2012,32(1):9-13. doi: 10.3788/AOS201232.0101001HAN B, LIU J F, LIU K L, et al. Study of backward optical detection method for ship wake bubbles[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2012, 32(1): 9-13. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201232.0101001 [2] 彭晓雷, 马傲玲, 刘翼民. 舰船尾流后向光学检测方法研究[J]. 舰船科学技术,2016,38(22):133-135.PENG X L, MA A L, LIU Y M. The study on backward optical detection method for ship wake bubbles[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2016, 38(22): 133-135. (in Chinese). [3] 宗思光, 张鑫, 曹静, 等. 舰船尾流激光探测跟踪方法与试验[J]. 红外与激光工程,2023,52(3):205-216.ZONG S G, ZHANG X, CAO J, et al. Method and experiment of laser detection and tracking of ship wake[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52(3): 205-216. (in Chinese). [4] 王赟, 刘继芳, 鲁振中, 等. 尾流气泡群的激光多普勒检测方法[J]. 中国激光,2014,41(8):0813002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.0813002WANG Y, LIU J F, LU ZH ZH, et al. Laser Doppler method for the detection of wake bubbles[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(8): 0813002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.0813002 [5] 张晓晖, 雷选华, 饶炯辉, 等. 舰船尾流激光制导方法的研究[J]. 激光技术,2005,29(5):494-496,500.ZHANG X H, LEI X H, RAO J H, et al. Study of homing means for laser-wake-homing torpedoes[J]. Laser Technology, 2005, 29(5): 494-496,500. (in Chinese). [6] 张群, 王英民. 尾流中多气泡模型及有限元分析[J]. 鱼雷技术,2014,22(4):316-320.ZHANG Q, WANG Y M. Multi-bubble models in ship wake and finite element analysis[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2014, 22(4): 316-320. (in Chinese). [7] 顾建农, 张志宏, 王冲, 等. 舰船尾流气泡数密度分布的实验模拟[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2012,40(10):78-81.GU J N, ZHANG ZH H, WANG CH, et al. Simulating density distribution of bubble number in a ship’s far field wakes[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(10): 78-81. (in Chinese). [8] 高江, 张静远, 杨力. 舰船气泡尾流特性研究现状[J]. 舰船科学技术,2008,30(4):27-32. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2008.04.003GAO J, ZHANG J Y, YANG L. The present situation of research on shipwake characteristic[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2008, 30(4): 27-32. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2008.04.003 [9] 高可心, 金良安, 苑志江, 等. 舰船气泡尾流场气泡数密度衰减模型研究[J]. 中国测试,2019,45(8):61-66. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2019010085GAO K X, JIN L A, YUAN ZH J, et al. Research on bubble number density attenuation model of ship’s bubble wake field[J]. China Measurement & Test, 2019, 45(8): 61-66. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2019010085 [10] CHEN Y ZH, XIA M, LI W, et al. Comparison of point spread models for underwater image restoration[J]. Optik, 2012, 123(9): 753-757. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2011.06.010 [11] HE H L, XIA M, LI W, et al. Light scattering by a spheroid bubble with ray tracing method[J]. Optik, 2013, 124(10): 871-875. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2012.02.012 [12] 宗思光, 张鑫, 杨劭鹏, 等. 舰船尾流气泡目标激光后向散射特性研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(6):1333-1342.ZONG S G, ZHANG X, YANG SH P, et al. Laser backscattering characteristics of ship wake bubble target[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(6): 1333-1342. (in Chinese). [13] 刘罡, 李永胜, 刘礼文, 等. 基于时频分析和迁移学习的舰船尾流检测方法[J]. 水下无人系统学报,2022,30(4):465-473. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.202108013LIU G, LI Y SH, LIU L W, et al. Method of ship wake detection based on time-frequency analysis and transfer learning[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2022, 30(4): 465-473. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.202108013 [14] 顾建农, 张志宏, 张晓晖. 舰船远场尾流气泡分布特性的数值模拟[J]. 光子学报,2007,36(8):1504-1509.GU J N, ZHANG ZH H, ZHANG X H. Numerical simulation of bubble distribution characters in ship’s far field wakes[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2007, 36(8): 1504-1509. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: