-
摘要:
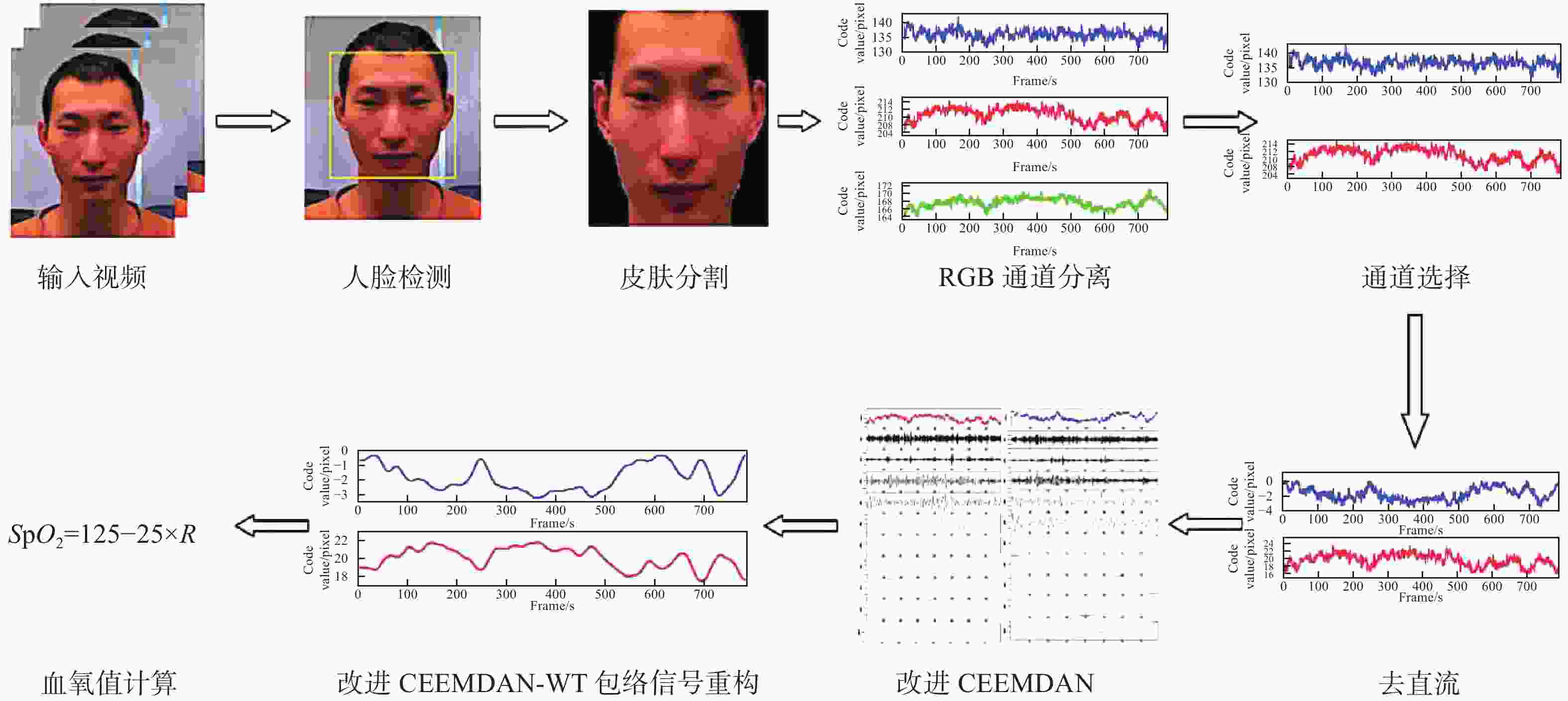
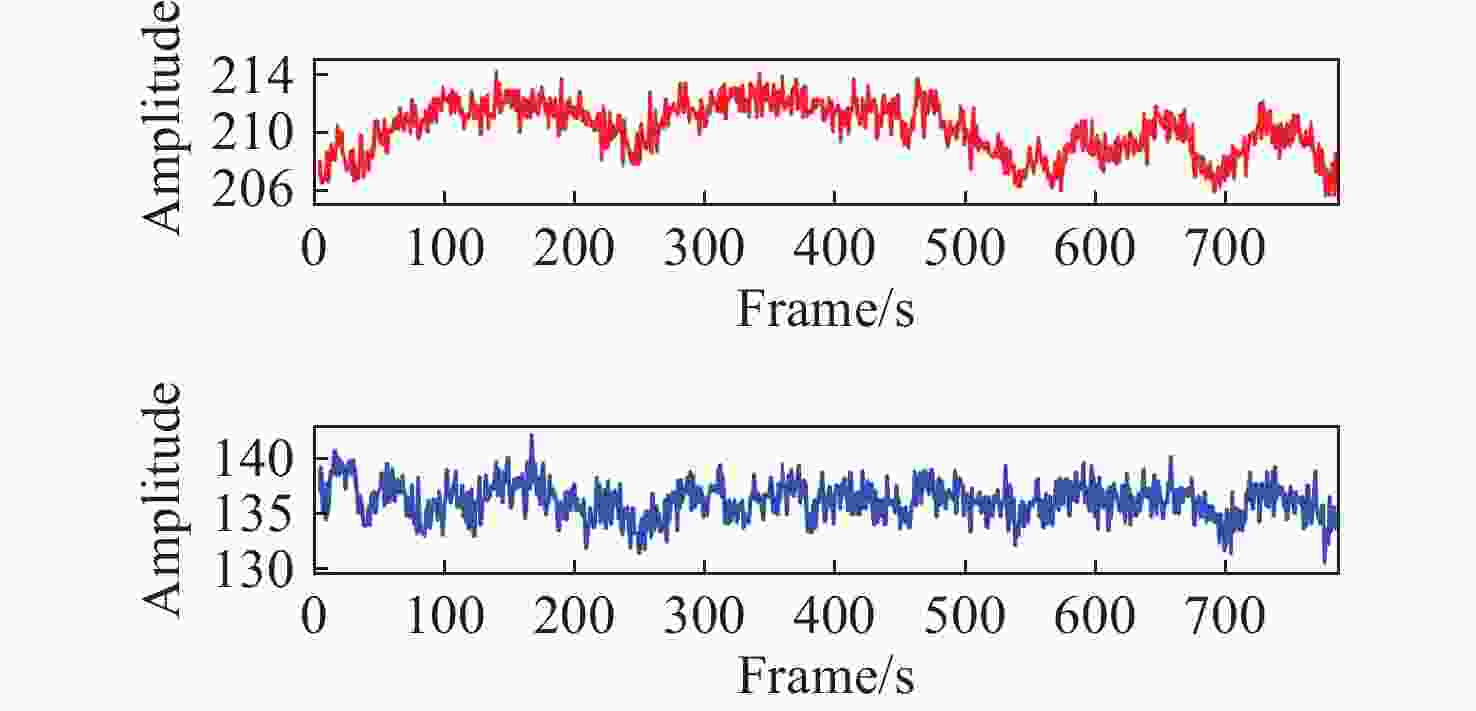
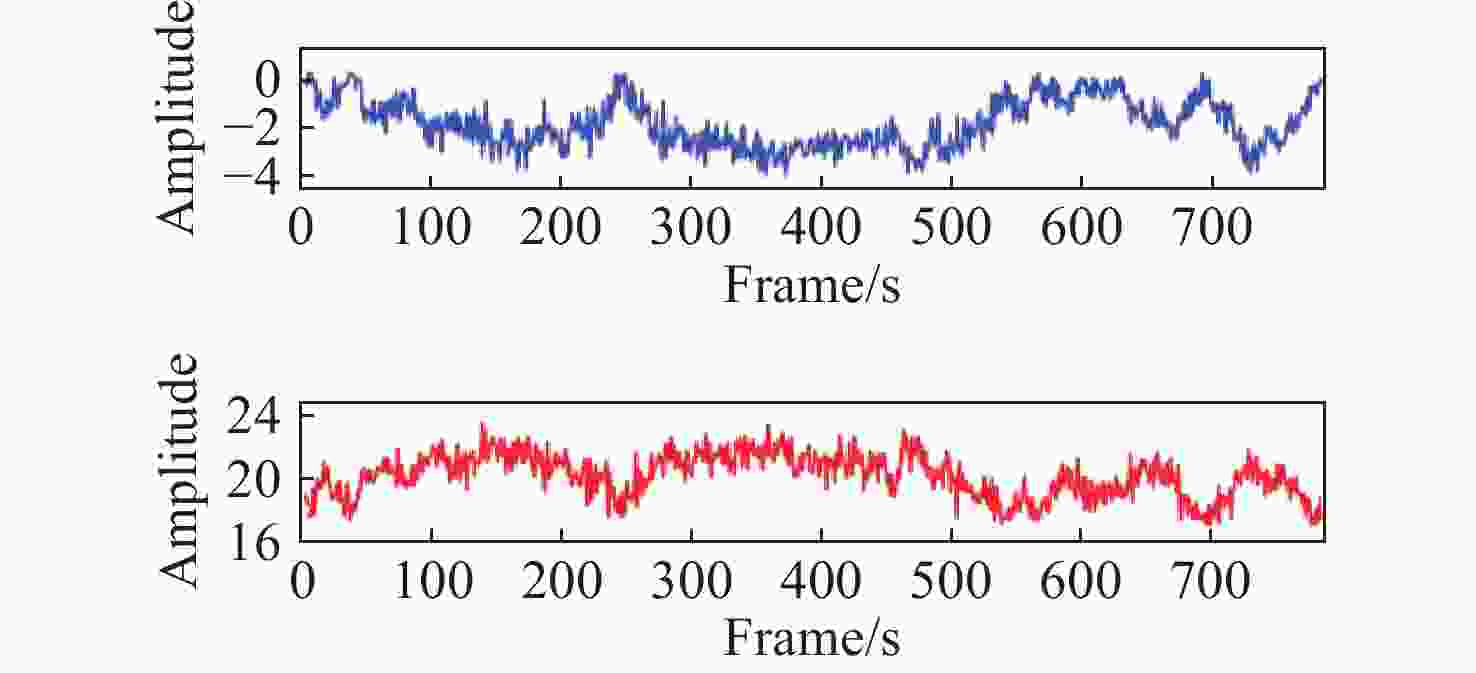
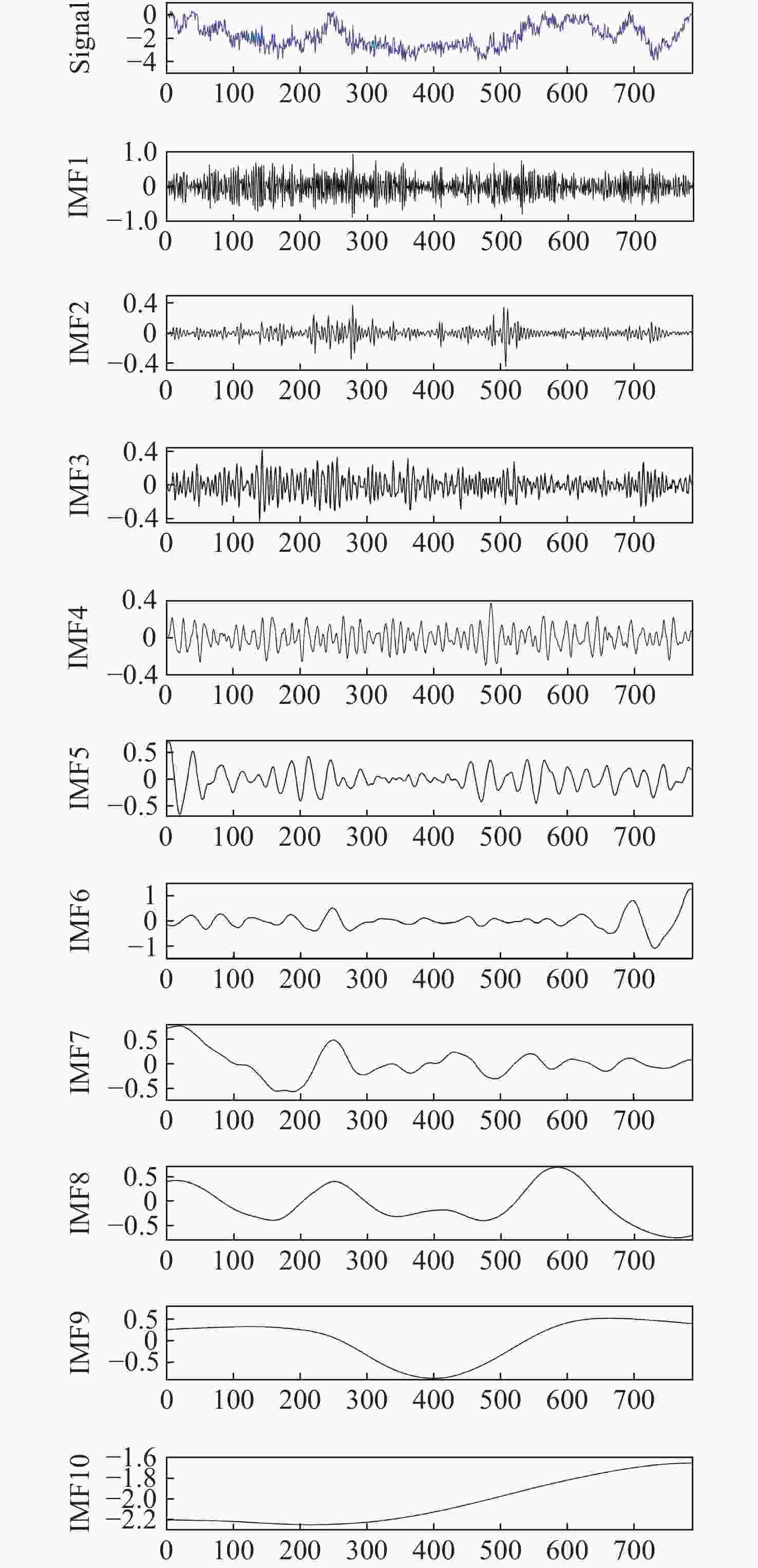
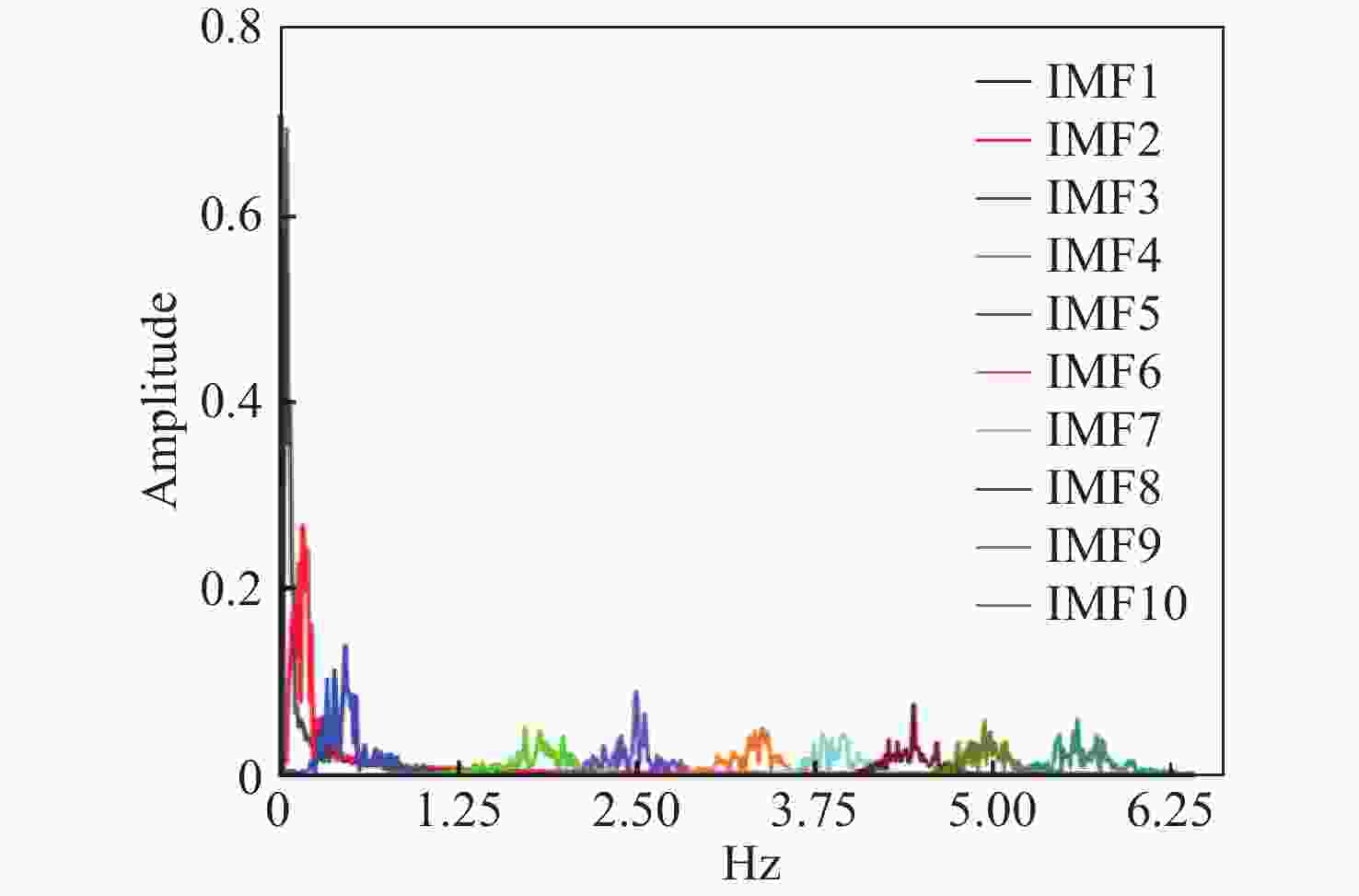
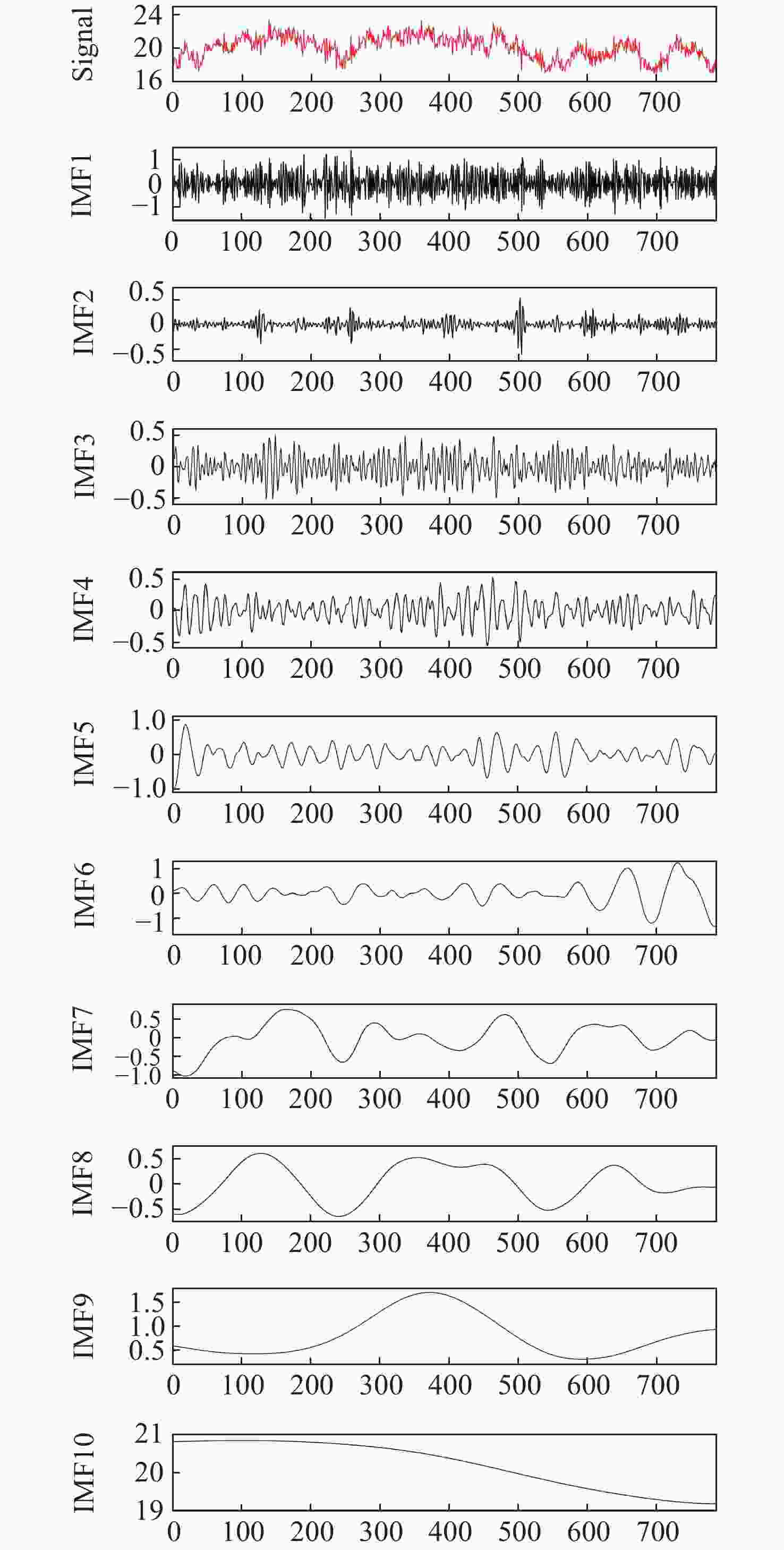
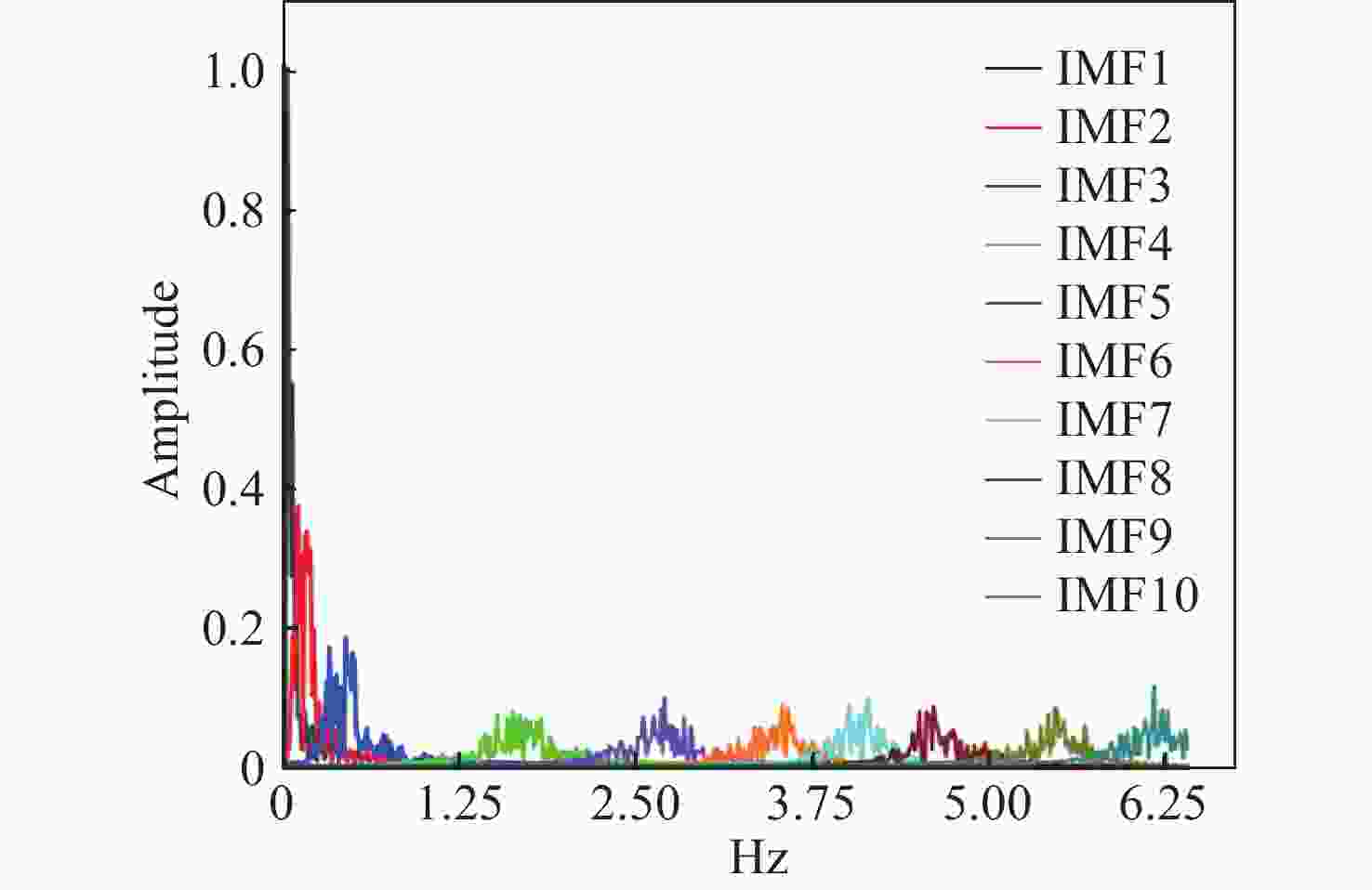
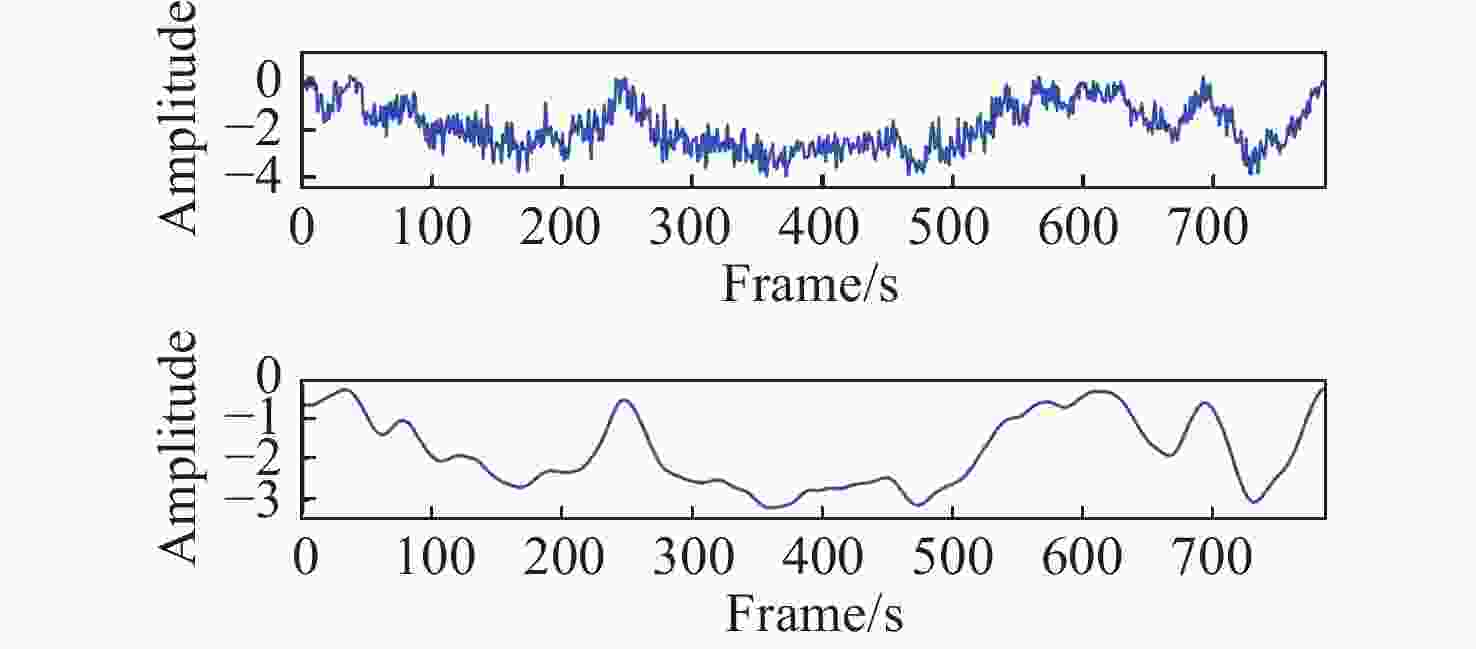
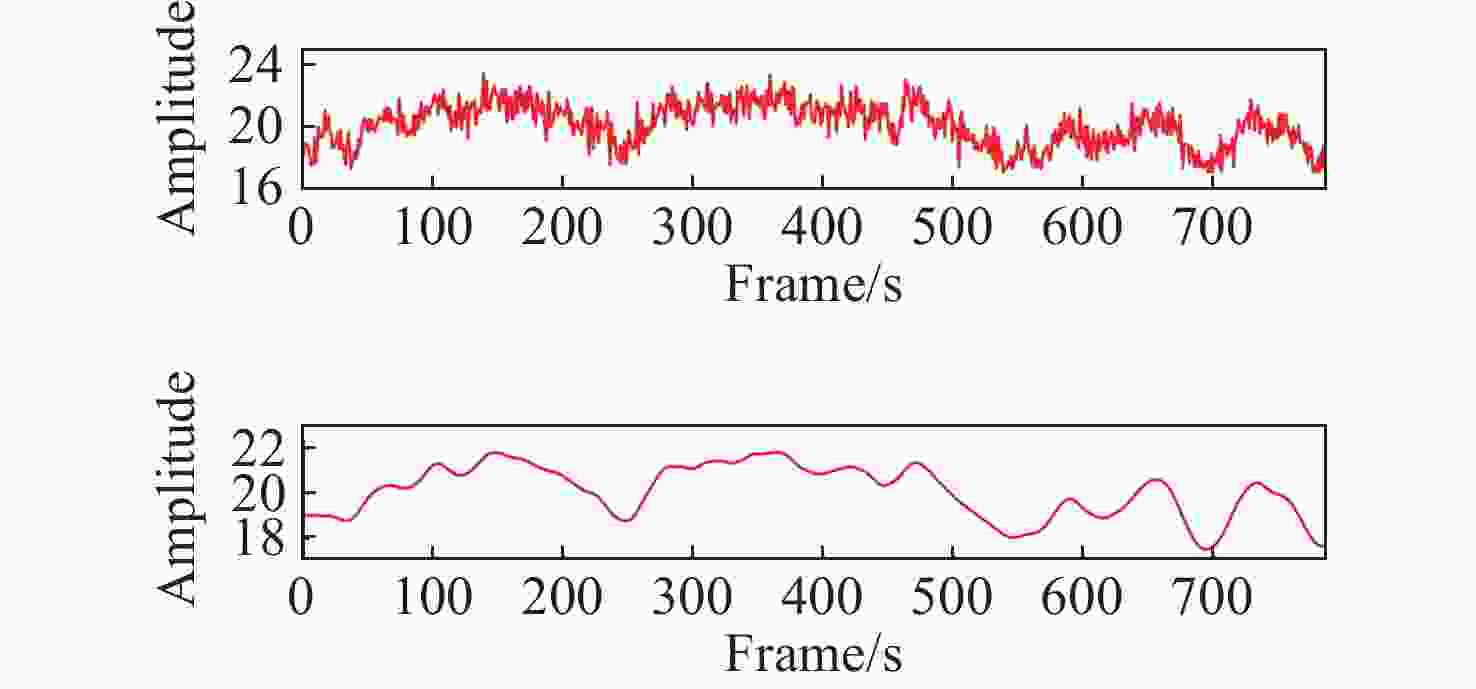
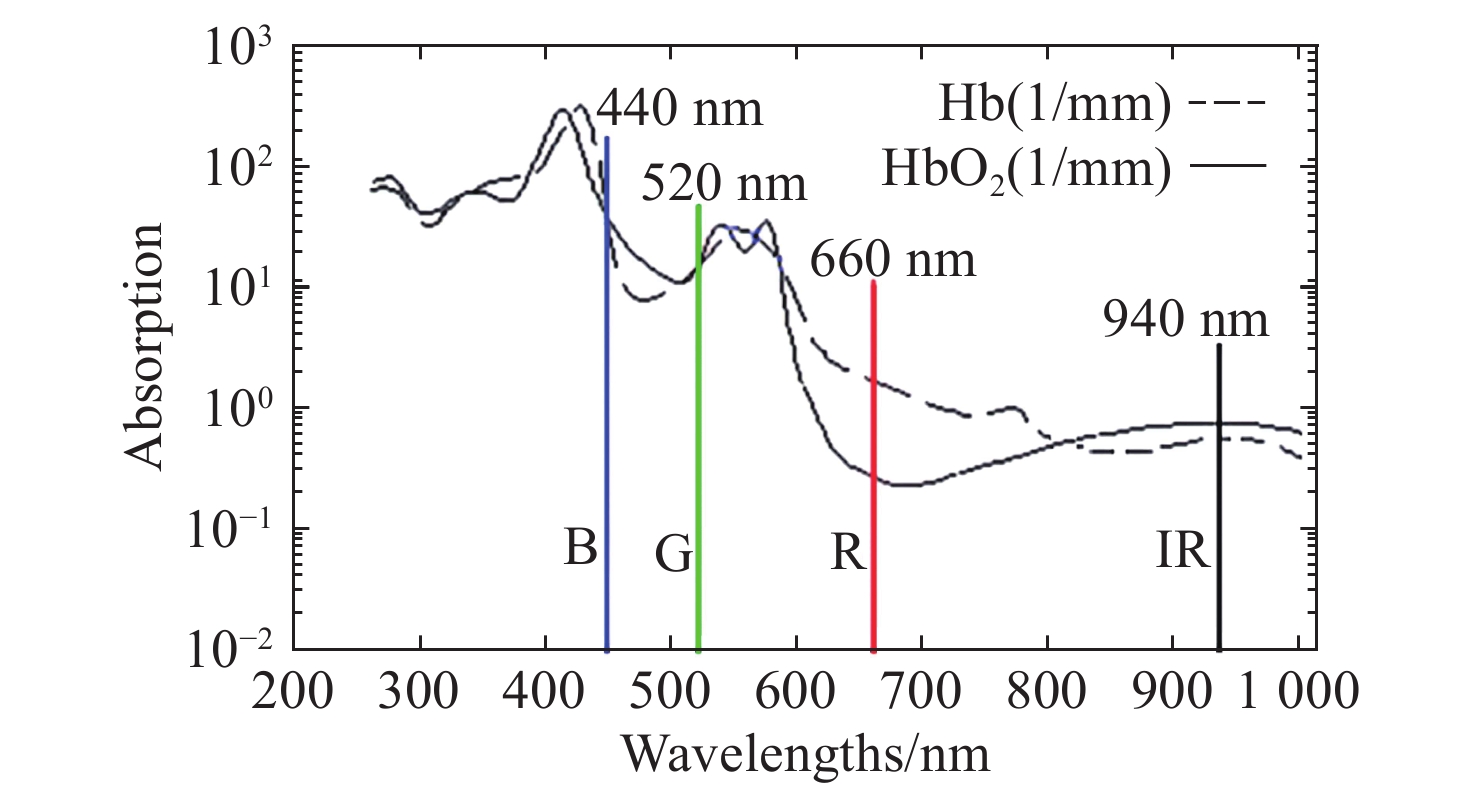
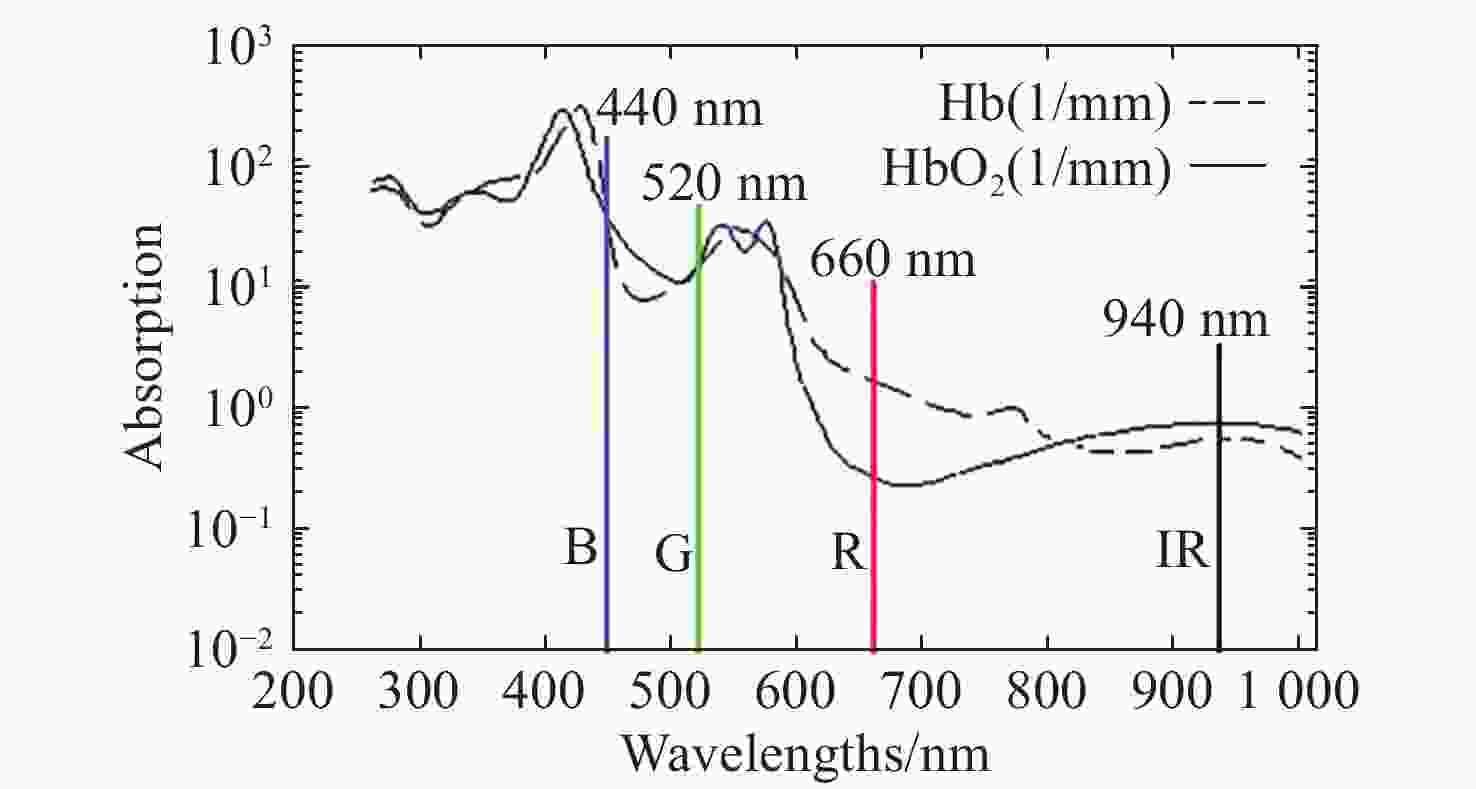
针对现有非接触式血氧饱和度测量方法在头部动态场景下准确性低的问题,提出一种基于改进的自适应噪声完全集合经验模态分解与小波阈值相结合的去噪方法,用于提取高信噪比的脉搏波信号。首先,为解决自适应噪声完全经验模态分解在分解重构早期产生虚假分量和模态混叠的问题,在分解过程中加入高斯白噪声,使其成为改进的自适应噪声完全集合经验模态分解(ICEEMDAN),从而减少模态分量中的残余噪声。然后,使用ICEEMDAN对红蓝色通道的脉搏波信号进行模态分解,并使用db8小波基函数对符合血氧频谱范围的分量进行3级分解和重构,将重构后的信号用于后续血氧值的计算。最后,将不同头部动态场景下测量的血氧饱和度结果进行实验对比分析。结果表明:不同头部场景下得到的血氧饱和度平均误差为0.73%,相较于其他算法平均误差降低1.93%。本文提出的去噪方法在不同头部场景下具有较好的稳定性,可满足日常血氧饱和度测量的需求。
Abstract:In dynamic head scenes, current non-contact blood oxygen saturation measurement methods have low accuracy. To solve this problem, we propose a denoising method based on improved adaptive noise complete set empirical mode decomposition and wavelet threshold. This method aims to extract pulse wave signals with a high signal-to-noise ratio. Firstly, in order to solve the problem of false components and mode aliasing in the early stage of decomposition and reconstruction, white Gaussian noise is added to the decomposition process to make it become an improved complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise (ICEEMDAN), to reduce the residual noise in the modal components. Then, ICEEMDAN is used to perform mode decomposition of pulse wave signals of red and blue channels. The db8 wavelet basis function is used to perform 3-stage decomposition and reconstruction on components within the blood oxygen spectrum range. The reconstructed signals are used for subsequent calculation of blood oxygen value. Finally, the experimental comparison and analysis of the blood oxygen saturation results measured in different dynamic head scenes show that the average error of blood oxygen saturation obtained in different head scenes is 0.73%, which is 1.93% lower than the average error of other algorithms. The denoising method proposed in this paper has good stability in different head scenes and can meet the needs of daily blood oxygen saturation measurement.
-
Key words:
- non-contact /
- oxygen saturation /
- head movement /
- wavelet threshold /
- decomposition and reconstruction
-
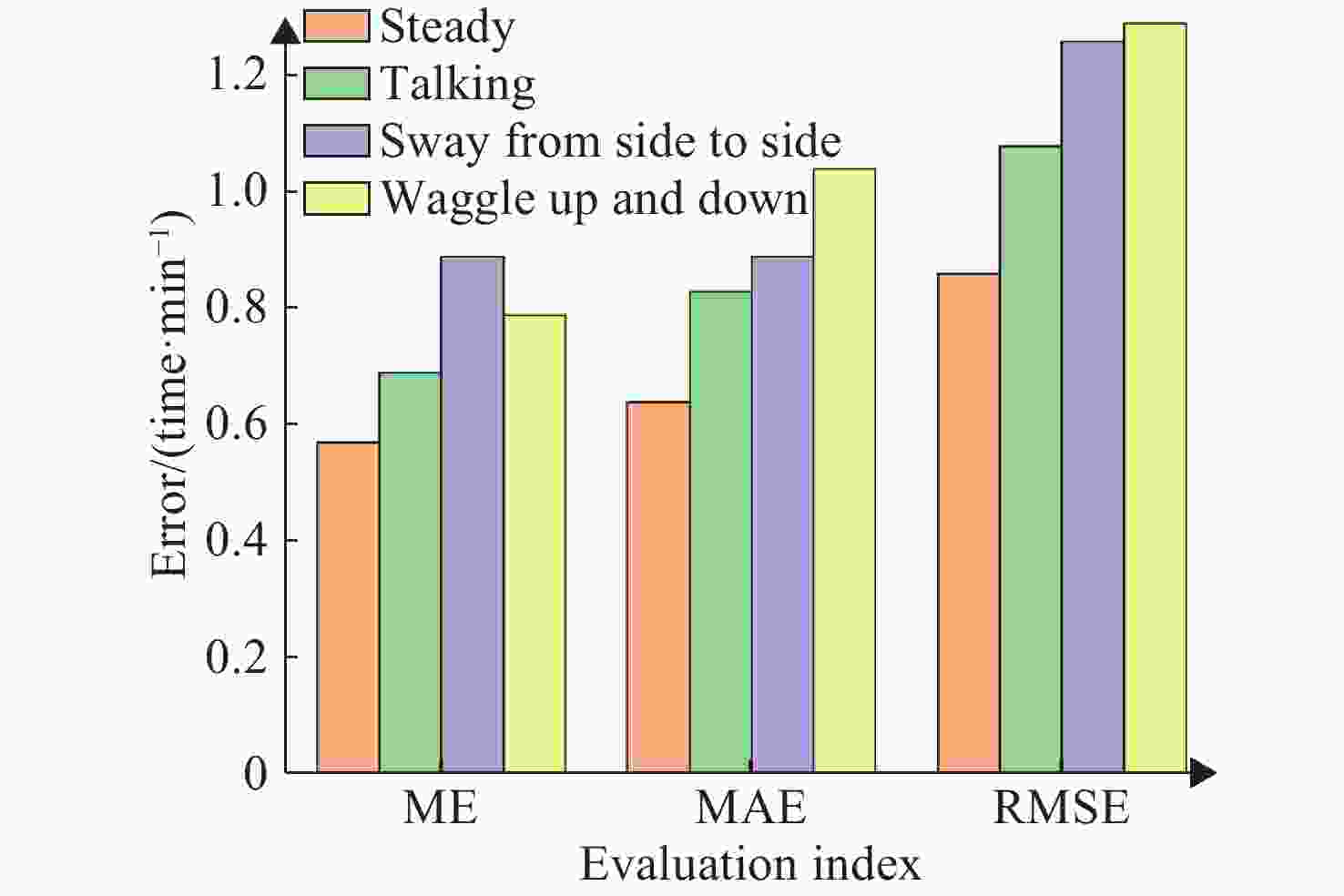
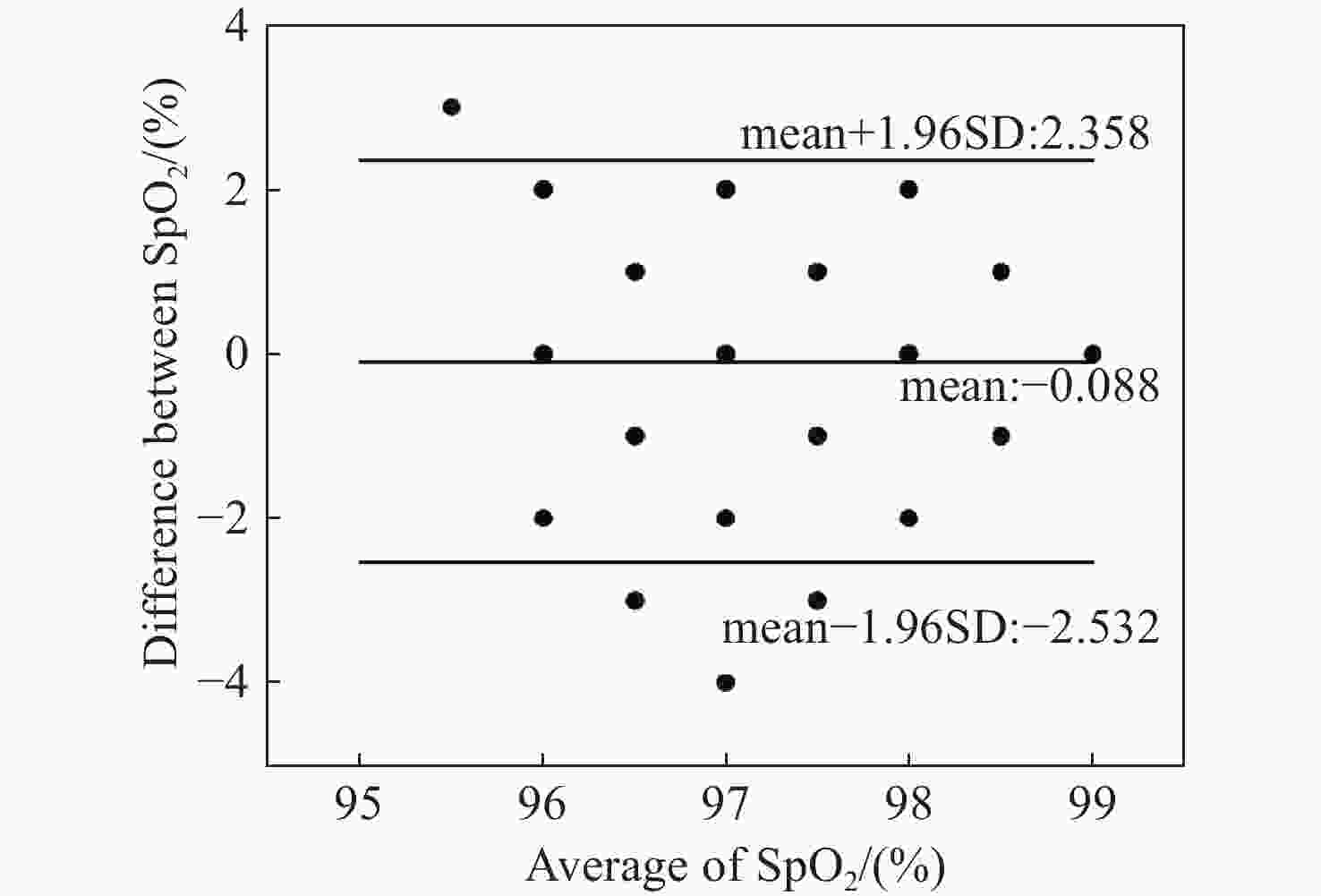
表 1 不同运动场景之下的SpO2结果
Table 1. Blood oxygen results under different exercise scenarios
(%) 实验场景 ME MAE RMSE 静态场景 0.57 0.64 0.86 说话场景 0.69 0.83 1.08 左右晃动 0.89 0.89 1.26 上下晃动 0.76 1.04 1.29 表 2 不同运动场景下算法性能对比
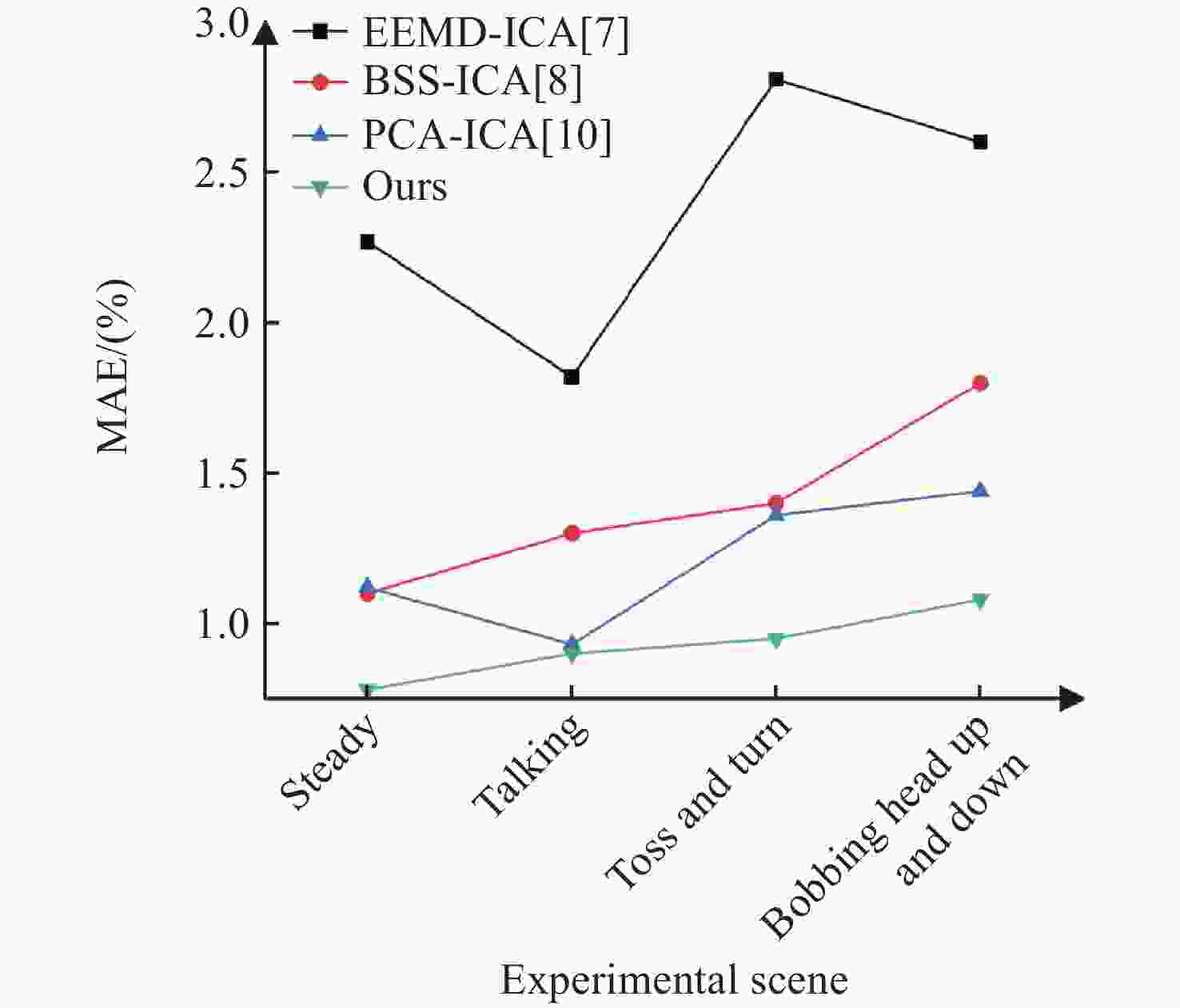
Table 2. Comparison of algorithm performances in different motion scenes (Unit: %)
方法 静态场景 说话场景 上下晃动场景 左右晃动场景 ME MAE RMSE ME MAE RMSE ME MAE RMSE ME MAE RMSE 文献[7] 1.55 2.27 2.74 2.23 1.82 2.88 3.28 2.81 4.32 3.56 2.6 4.41 文献[8] 0.70 1.10 1.30 1.13 1.30 1.72 1.33 1.40 1.93 1.70 1.80 2.23 文献[10] 0.51 1.12 1.23 0.63 0.93 1.12 1.11 1.36 1.75 1.27 1.44 1.92 本文方法 0.57 0.64 0.86 0.69 0.83 1.08 0.89 0.89 1.26 0.76 1.04 1.29 -
[1] STRUYF T, DEEKS J J, DINNES J, et al. Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19 disease[J]. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2020, 7(7): CD013665. [2] MORO E, PRIORI A, BEGHI E, et al. The international European Academy of Neurology survey on neurological symptoms in patients with COVID-19 infection[J]. European Journal of Neurology, 2020, 27(9): 1727-1737. doi: 10.1111/ene.14407 [3] TAMURA T. Current progress of photoplethysmography and SPO2 for health monitoring[J]. Biomedical Engineering Letters, 2019, 9(1): 21-36. doi: 10.1007/s13534-019-00097-w [4] ALHARBI S, HU S, MULVANEY D, et al. Oxygen saturation measurements from green and orange illuminations of multi-wavelength optoelectronic patch sensors[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(1): 118. [5] BAL U. Non-contact estimation of heart rate and oxygen saturation using ambient light[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2015, 6(1): 86-97. doi: 10.1364/BOE.6.000086 [6] 荣猛, 范强, 李凯扬. 基于IPPG非接触式生理参数测量算法的研究[J]. 生物医学工程研究,2018,37(1):27-31,35.RONG M, FAN Q, LI K Y. Study on the measurement algorithm of contactless physiological parameter based on imaging photoplenthysmography[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering Research, 2018, 37(1): 27-31,35. (in Chinese). [7] AL-NAJI A, KHALID G A, MAHDI J F, et al. Non-Contact SpO2 prediction system based on a digital camera[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(9): 4255. doi: 10.3390/app11094255 [8] WEI B, WU X P, ZHANG CH, et al. Analysis and improvement of non-contact SpO2 extraction using an RGB webcam[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2021, 12(8): 5227-5245. doi: 10.1364/BOE.423508 [9] 嵇晓强, 刘振瑶, 李炳霖, 等. 面部视频非接触式生理参数感知[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):276-285. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0157JI X Q, LIU ZH Y, LI B L, et al. Non-contact physiological parameters sensing in facial video[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 276-285. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0157 [10] PIRZADA P, MORRISON D, DOHERTY G, et al. Automated remote pulse oximetry system (ARPOS)[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(13): 4974. doi: 10.3390/s22134974 [11] HU M, WU X, WANG X H, et al. Contactless blood oxygen estimation from face videos: A multi-model fusion method based on deep learning[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2023, 81: 104487. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2022.104487 [12] KONG L Q, ZHAO Y J, DONG L Q, et al. Non-contact detection of oxygen saturation based on visible light imaging device using ambient light[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(15): 17464-17471. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.017464 [13] 吴其献, 胡玉斐, 李攻科. 可穿戴光谱传感器在医疗监测中的研究进展[J]. 分析化学,2024(4):449-459.WU Qi-Hsian, HU Yu-Fei, LI Tie-Ke. Research progress of wearable spectroscopic sensors in medical monitoring[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2024(4): 449-459. (in Chinese). [14] VIOLA P, JONES M J, SNOW D. Detecting pedestrians using patterns of motion and appearance[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2005, 63(2): 153-161. doi: 10.1007/s11263-005-6644-8 [15] MSTAFA R J, ELLEITHY K M. A video steganography algorithm based on Kanade-Lucas-Tomasi tracking algorithm and error correcting codes[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2016, 75(17): 10311-10333. doi: 10.1007/s11042-015-3060-0 [16] KHANAM F T Z, AL-NAJI A, CHAHL J. Remote monitoring of vital signs in diverse non-clinical and clinical scenarios using computer vision systems: A review[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(20): 4474. doi: 10.3390/app9204474 [17] 向宪昕, 孙华悦, 柴会宁, 等. 基于智能手机的可视化生物传感器在即时检测中的研究进展[J]. 分析化学,2024(2):145-156.XIANXIN XIANG, HUAYUE SUN, HUINING CHAI, et al. Advances in smartphone-based visual biosensors for immediate detection[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2024(2): 145-156. (in Chinese). [18] NIU X S, HU H, SHAN SH G, et al. VIPL-HR: A multi-modal database for pulse estimation from less-constrained face video[C]. Proceedings of the 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2018: 562-576. [19] NIU X S, SHAN SH G, HAN H, et al. RhythmNet: End-to-end heart rate estimation from face via spatial-temporal representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 2409-2423. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2947204 -





 下载:
下载: