Calculation and experiment of tiny perturbations in electric field measurement for the laser-induced fluorescence-dip spectroscopy method
-
摘要:
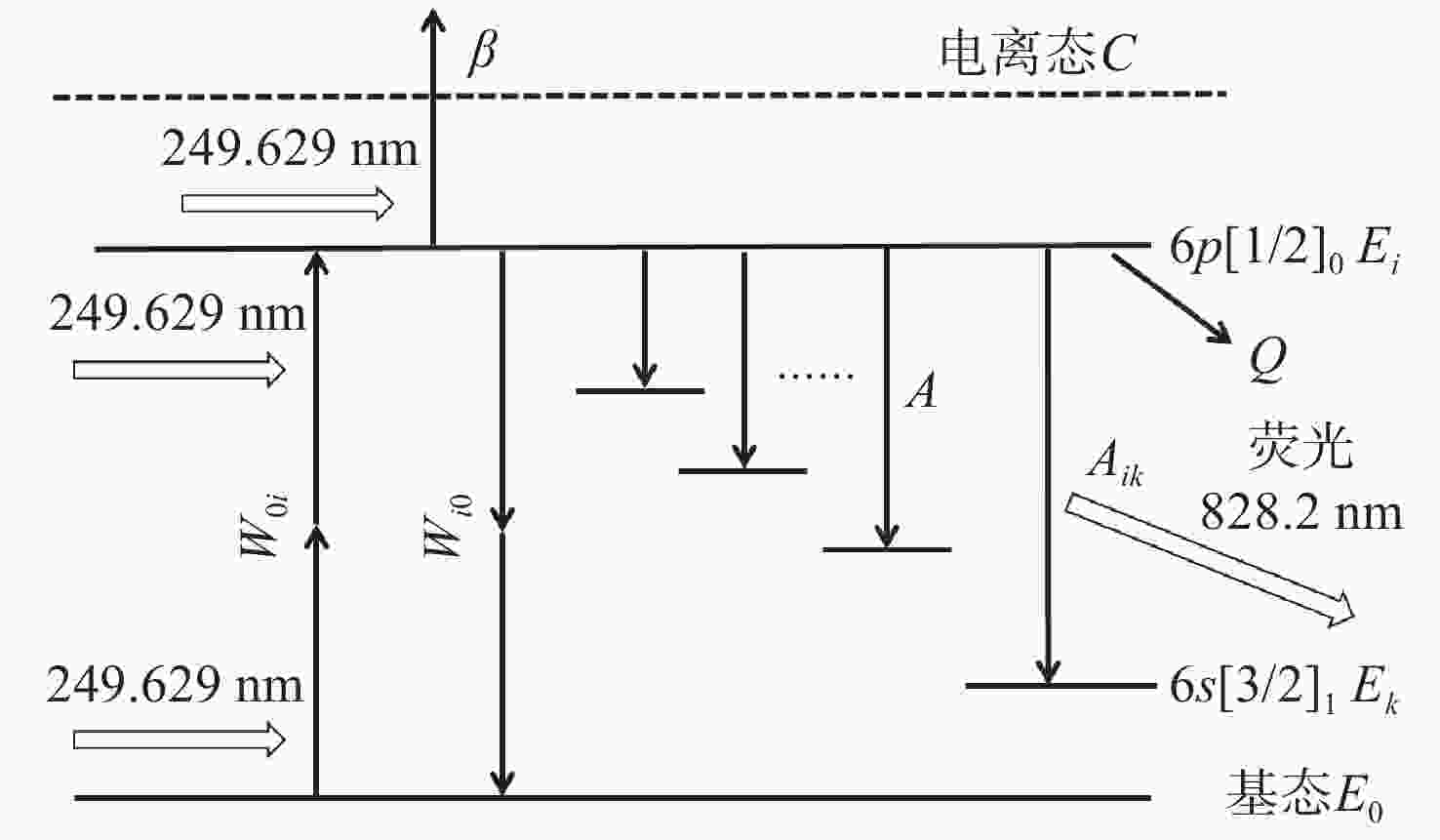
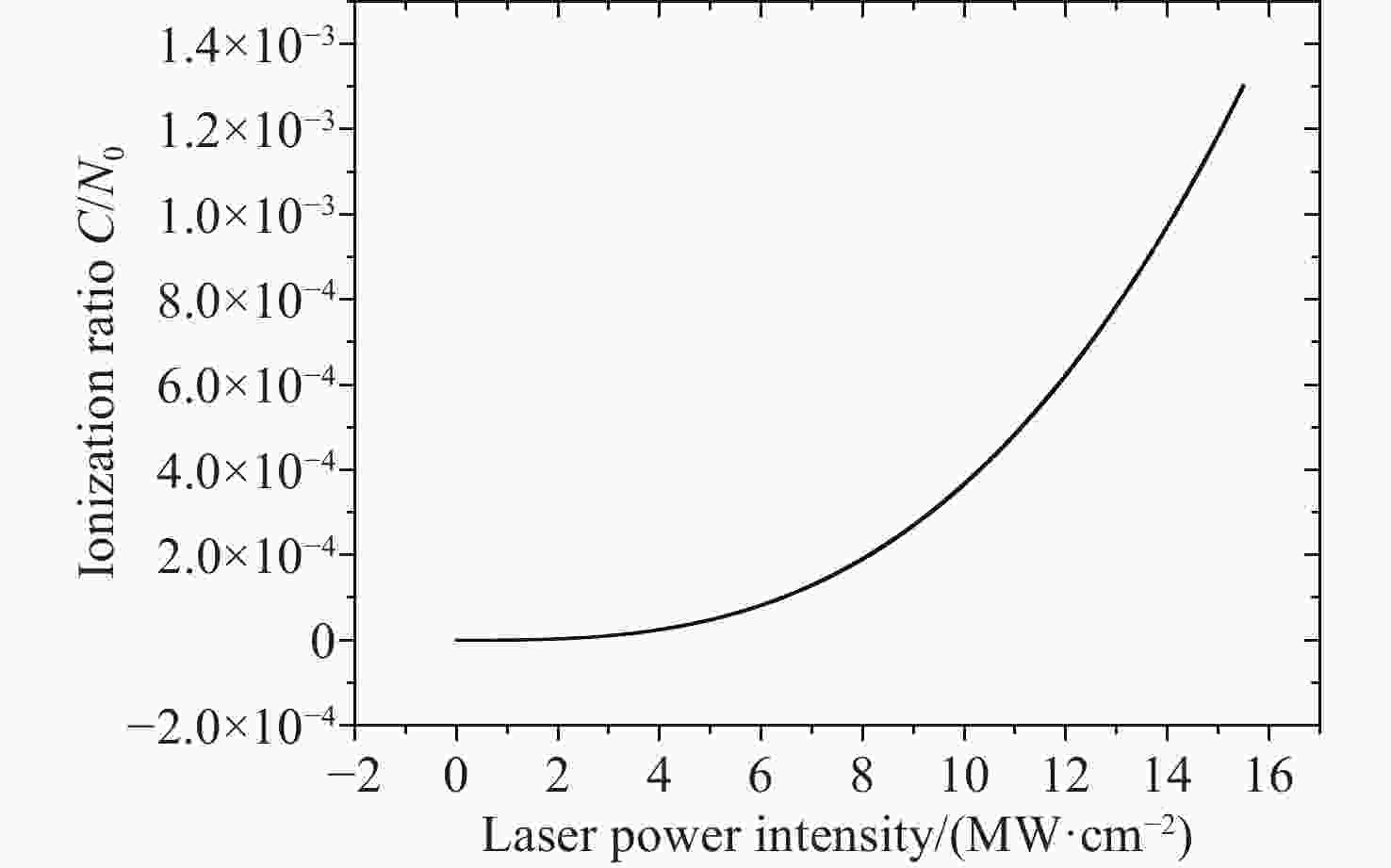
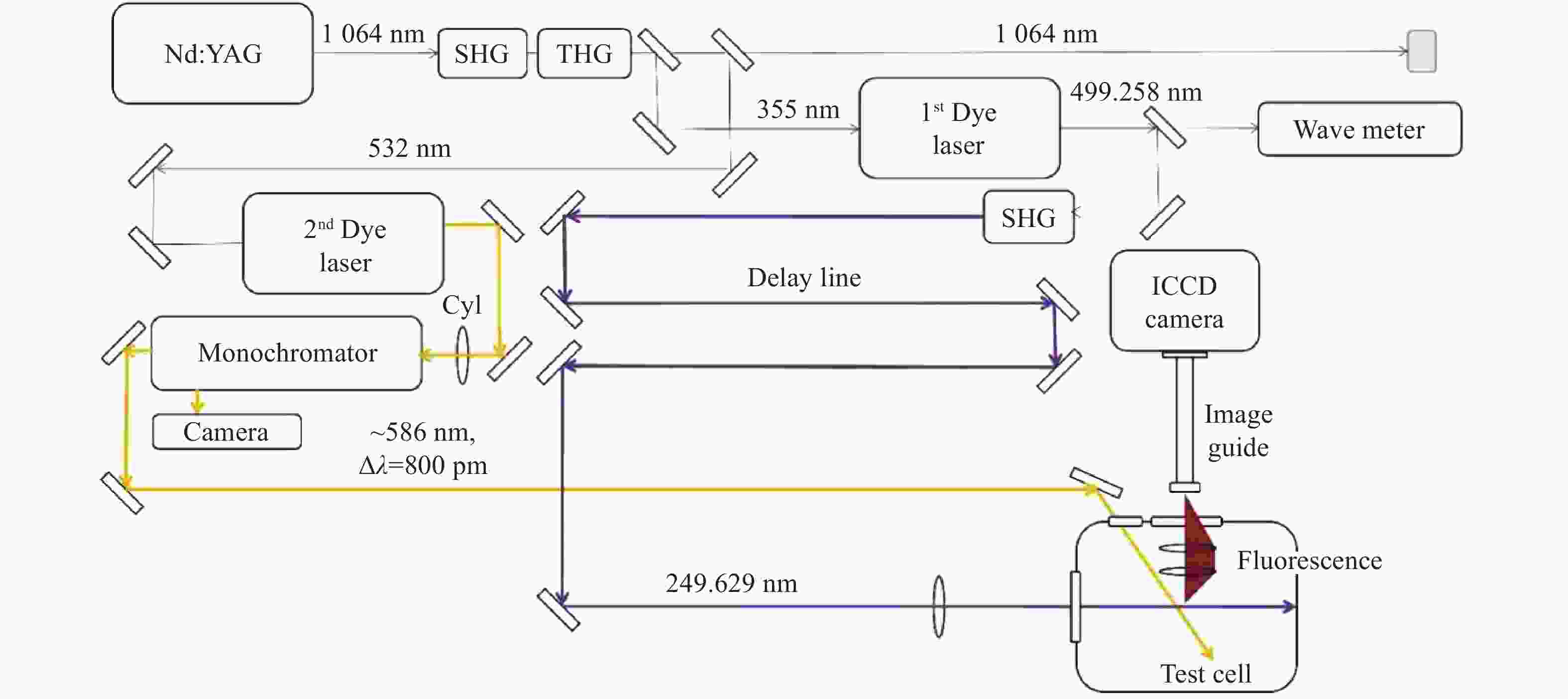
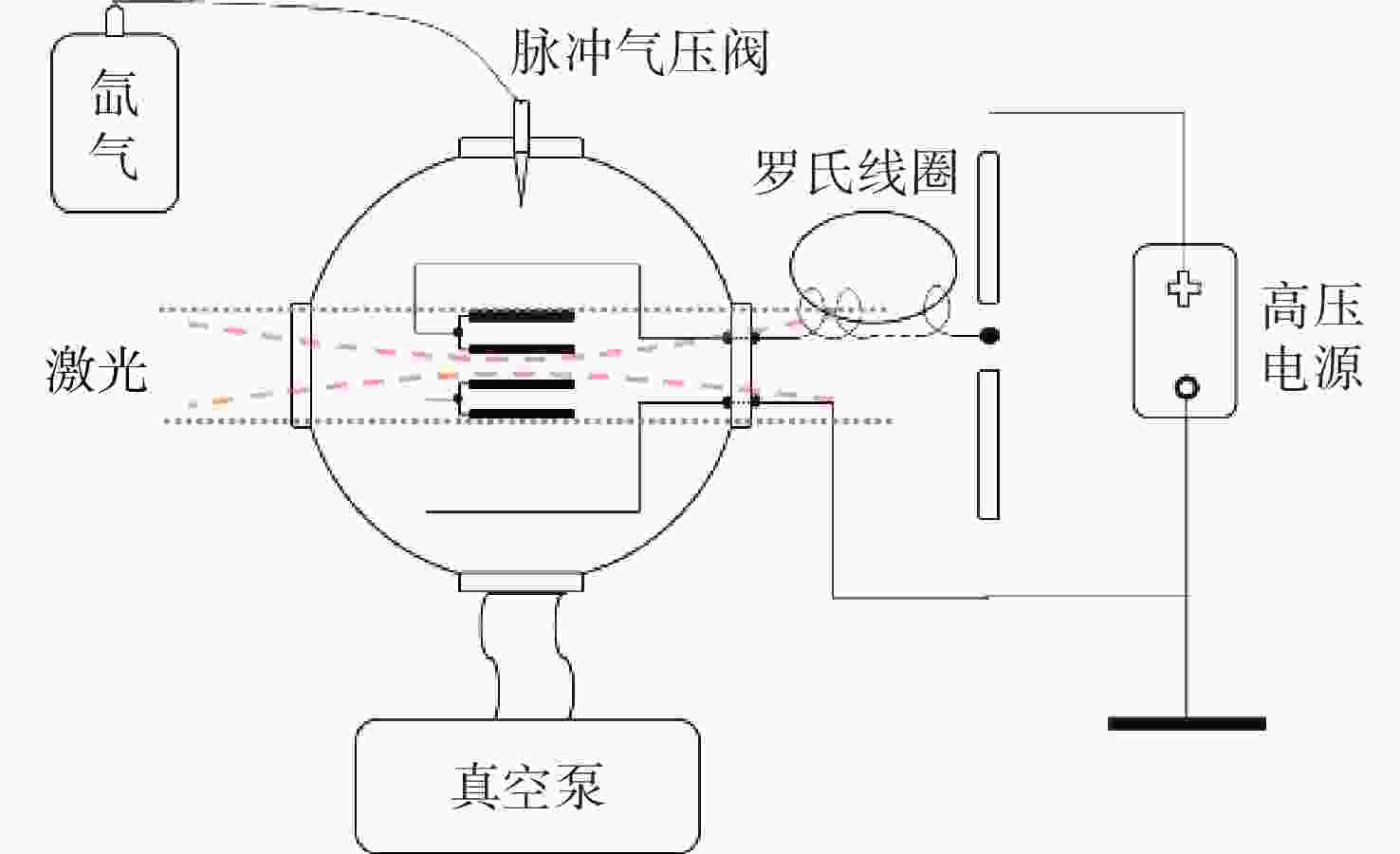
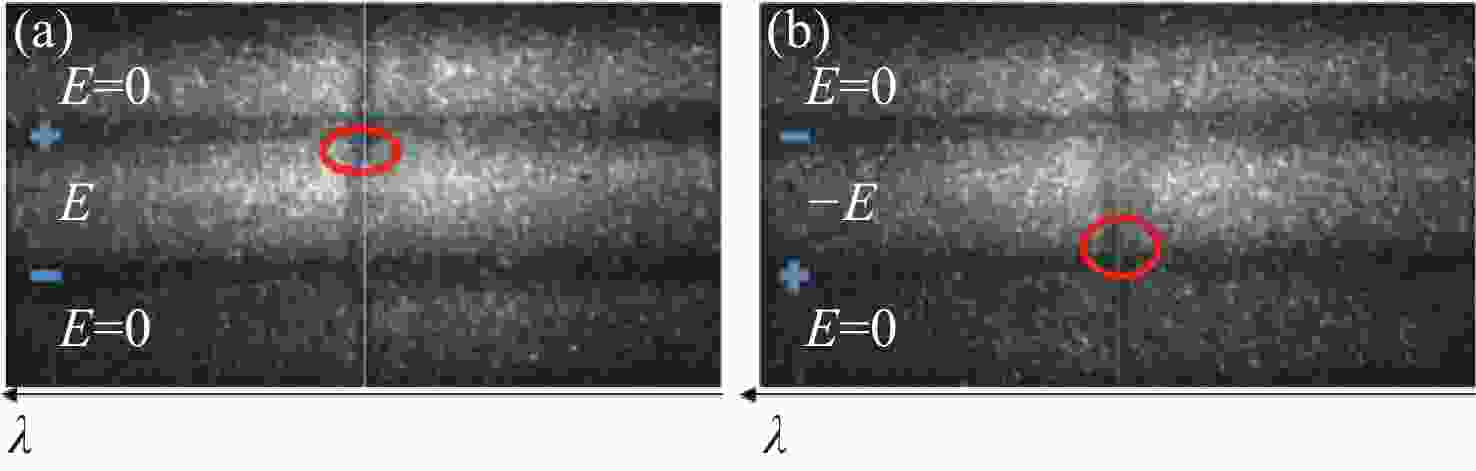
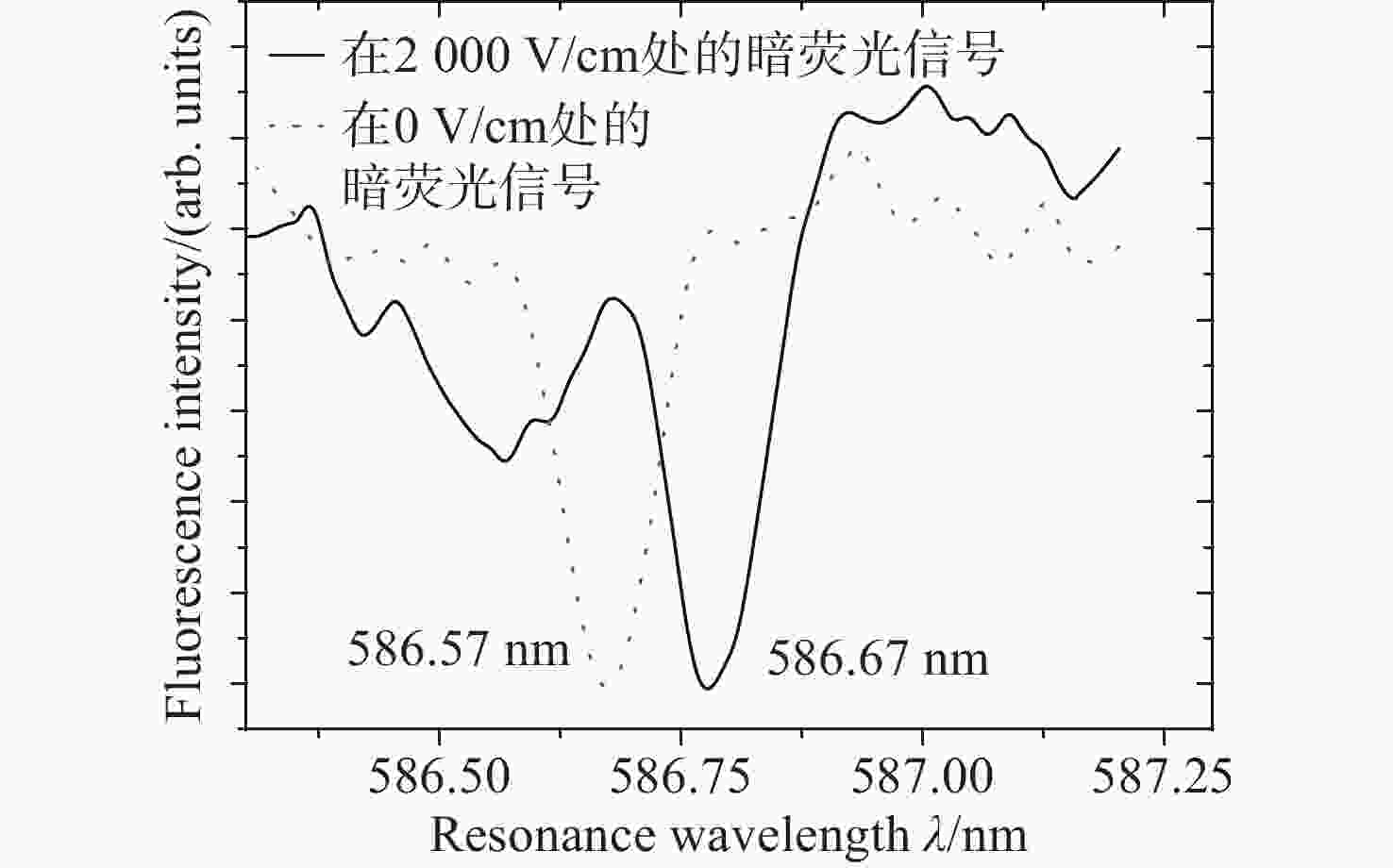
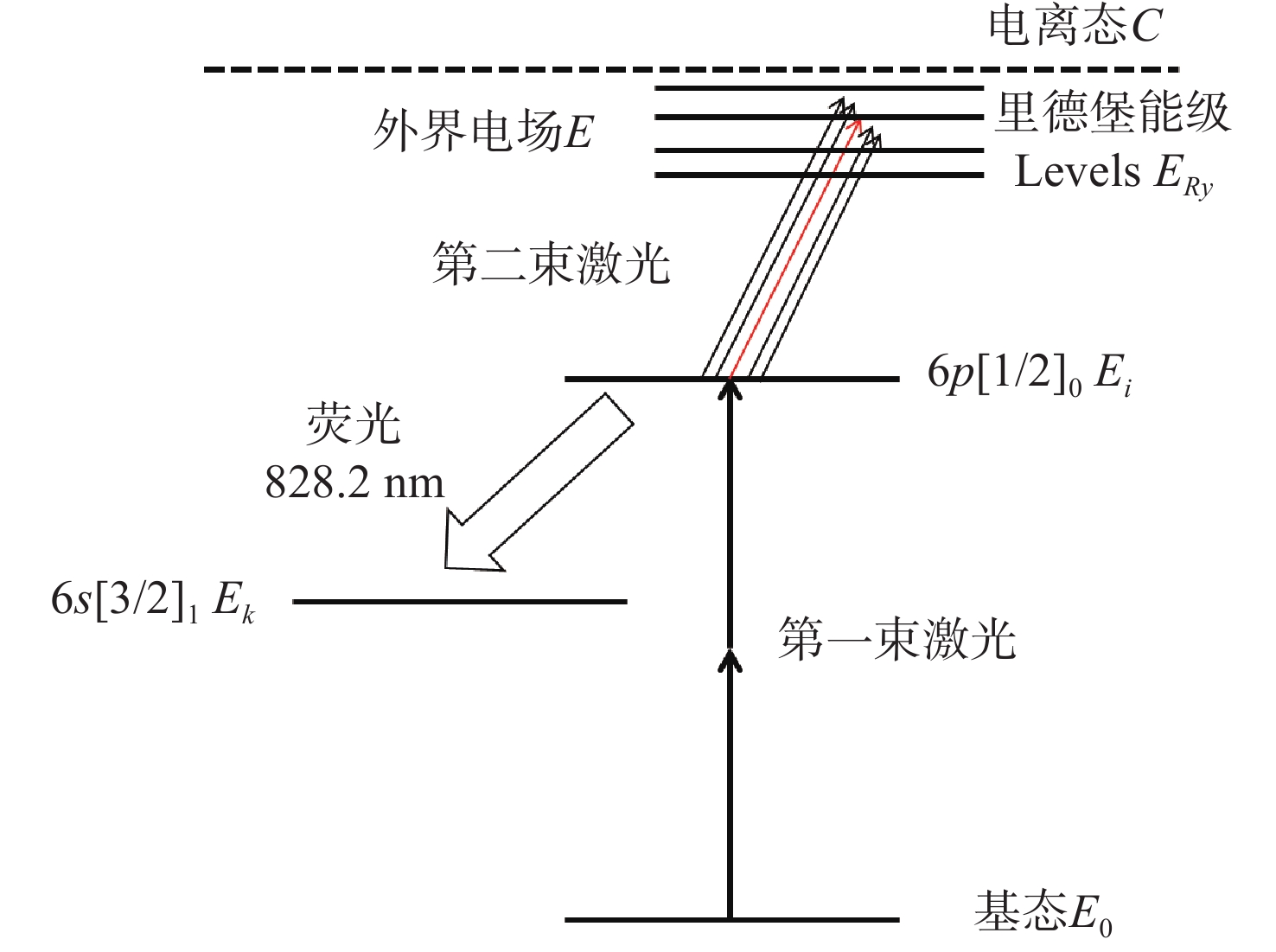
为了实现强流脉冲电子束对材料表面改性的工业化应用,需要对电子束的作用过程进行实时微扰监测。电场强度是反映电子束特性的关键参数之一,基于Stark效应的激光暗荧光光谱可实现对环境电场的微扰测量。因此,开展激光功率密度对环境电场的影响研究,对此类电场测量方法的参数设置和结果判断具有重要的理论和应用价值。通过理论分析和计算得出电场测量微扰状态下的激光功率密度与试验环境的关系模型。基于上述关系模型,搭建测试平台,验证激光功率密度对电场测量微扰的情况。实验结果表明:在示踪气体氙气压强为
$ 1.0\times {10}^{-4} $ mbar、电场强度不大于2 kV/cm的条件下,对电场测量微扰的激光功率密度值为5 MW/cm2,与理论计算值基本一致。研究结果填补了激光暗荧光光谱诊断方法中激光功率密度对电场影响定量分析的空白,可应用于同类电场测量方法中,为激光功率密度与实验参数的设置提供依据和参照,有效支撑电场测量实验的开展,有效提升电场测量的准确性。Abstract:In order to realize the industrial application of high-current pulsed electron beam on material surface modification, it is necessary to monitor tiny perturbation in real-time. The electric field strength is a critical parameter understanding the characteristics of electron beams. The laser-induced fluorescence-dip spectroscopy method based on the Stark effect can realize the tiny perturbation measurement of electric fields. Therefore, Studying laser power density influence on the electric field has significant theoretical and application value for the parameter setting and result interpretation of similar electric field measurement methods. The theoretical analysis and calculation are used to obtain the relationship model between excitation laser power density and the test environment parameters in the tiny perturbation state of electric field measurement. Then, based on the above relationship model and theoretical calculation, the influence of excitation laser power density on electric field measurement is verified experimentally. The experimental results show that under the conditions that the tracer gas xenon pressure is 1.0×10−4 mbar and the electric field strength is 2 kV/cm or below, the excitation laser power density of tiny perturbations on the electric field measurement is 5 MW/cm2, which is consistent with the theoretical calculation value. The research results provide a quantitative analysis method for studying the influence of laser power density on the electric field in the laser-induced fluorescence-dip spectroscopy. They can be applied to similar electric field measurement methods, open the way for the setting of laser power density and experimental parameters, support the development of electric field measurement experiments, and effectively improve the accuracy of electric field measurement.
-
-
[1] 杜昆, 陈麒好, 孟宪龙, 等. 陶瓷基复合材料在航空发动机热端部件应用及热分析研究进展[J]. 推进技术,2022,43(2):210380.DU K, CHEN Q H, MENG X L, et al. Advancement in application and thermal analysis of ceramic matrix composites in aeroengine hot components[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2022, 43(2): 210380. (in Chinese). [2] 赵传东, 李金燕, 张欢. 耐高温材料在航空发动机上的应用研究[J]. 内燃机与配件,2021(18):55-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-957X.2021.18.020ZHAO CH D, LI J Y, ZHANG H. Research on application of high temperature materials in aero-engine[J]. Internal Combustion Engines & Parts, 2021(18): 55-56. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-957X.2021.18.020 [3] SHAO L, LI W SH, LI D Y, et al. A review on combustion behavior and mechanism of Ti alloys for advanced aero-engine[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 960: 170584. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.170584 [4] 郑言. 2021年我国复合材料的行业发展态势、存在问题与发展建议[J]. 应用化学, 2022, 39(2): 351-352.ZHENG Y. Development trend, existing problems, and development suggestions of China's composite materials industry in 2021[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2022, 39(2): 351-352. (in Chinese). [5] 史和昌, 于彦存, 韩常玉. 聚乙烯/氧化铝复合材料形态、流变和力学性能[J]. 应用化学,2022,39(10):1593-1599.SHI H CH, YU Y C, HAN CH Y. Morphology, rheological and mechanical properties of polyethylene/aluminium oxide composites[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2022, 39(10): 1593-1599. (in Chinese). [6] 杨琦, 田娜娜, 关锦彤, 等. 强流脉冲电子束作用下Ti2AlNb微观结构状态与耐腐蚀性能研究[J]. 真空科学与技术学报,2023,43(10):870-878.YANG Q, TIAN N N, GUAN J T, et al. Microstructure and corrosion properties of Ti2AlNb irradiated by high current pulsed electron beam treatment[J]. Chinese Journal Vacuum Science and Technology, 2023, 43(10): 870-878. (in Chinese). [7] IVANOV K V, AKIMOV K O, FIGURKO M G. The effect of low-energy high-current pulsed electron beam irradiation on the structure, phase composition and mechanical properties of Ni3Al and Ni3Al-TiC composites[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024, 973: 172950. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.172950 [8] GUAN Q F, HAN J, ZHOU SH Y, et al. Improved mechanical and tribological properties of TiAlN coatings by high current pulsed electron beam irradiation[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2024, 118: 106435. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2023.106435 [9] MOORE C A, DAVIS G P, GOTTSCHO R A. Sensitive, nonintrusive, in-situ measurement of temporally and spatially resolved plasma electric fields[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1984, 52(7): 538-541. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.52.538 [10] CHNG T L, STARIKOVSKAIA S M, SCHANNE-KLEIN M C. Electric field measurements in plasmas: how focusing strongly distorts the E-FISH signal[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2020, 29(12): 125002. doi: 10.1088/1361-6595/abbf93 [11] ORR K, TANG Y, SIMENI M S, et al. Measurements of electric field in an atmospheric pressure helium plasma jet by the E-FISH method[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2020, 29(3): 035019. doi: 10.1088/1361-6595/ab6e5b [12] 李悦, 张国霞, 蔡朝晴, 等. 大气压辉光放电结合圆柱约束增强激光诱导击穿光谱应用于土壤中稀土元素的检测[J]. 分析化学,2022,50(9):1384-1390.LI Y, ZHANG G X, CAI ZH Q, et al. Atmospheric pressure glow discharge combined with cylindrical confinement enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for determination of rare earth in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 50(9): 1384-1390. (in Chinese). [13] 舒开强, 陈友元, 彭郑英, 等. 铀矿中多目标元素的激光诱导击穿光谱定量分析方法研究[J]. 分析化学,2023,51(7):1195-1203.SHU K Q, CHEN Y Y, PENG ZH Y, et al. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for quantitative analysis of multi-target elements in uranium ore[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(7): 1195-1203. (in Chinese). [14] CZARNETZKI U, LUGGENHÖLSCHER D, DÖBELE H F. Sensitive electric field measurement by fluorescence-dip spectroscopy of Rydberg states of atomic hydrogen[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1998, 81(21): 4592-4595. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.4592 [15] TAKIZAWA K, SASAKI K, KADOTA K. Observation of Stark spectra of argon high Rydberg states in well-defined electric fields by laser-induced fluorescence-dip spectroscopy[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 41(11B): L1285-L1287. [16] KAMPSCHULTE T, SCHULZE J, LUGGENHÖLSCHER D, et al. Laser spectroscopic electric field measurement in krypton[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2007, 9(1): 18. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/9/1/018 [17] WAGENAARS E, KROESEN G M W, BOWDEN M D. Investigations of Stark effects in xenon Rydberg states by laser-induced fluorescence-dip spectroscopy[J]. Physical Review A, 2006, 74(3): 033409. [18] AN W, WANG ZH, WEISENBURGER A, et al. Laser-induced fluorescence-dip spectroscopy of Rydberg states of xenon for electric field measurement in plasma[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2022, 93(2): 023503. doi: 10.1063/5.0064676 [19] STANCU G D. Two-photon absorption laser induced fluorescence: rate and density-matrix regimes for plasma diagnostics[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2020, 29(5): 054001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6595/ab85d0 [20] ZAKHEIM D S, JOHNSON P M. Rate equation modelling of molecular multiphoton ionization dynamics[J]. Chemical Physics, 1980, 46(3): 263-272. doi: 10.1016/0301-0104(80)85202-5 [21] KRÖLL S, BISCHEL W K. Two-photon absorption and photoionization cross-section measurements in the 5p56p configuration of xenon[J]. Physical Review A, 1990, 41(3): 1340-1349. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.41.1340 [22] LANGMUIR I. The interaction of electron and positive ion space charges in cathode sheaths[J]. Physical Review, 1929, 33(6): 954-989. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.33.954 [23] STEBBINGS R F, LATIMER C J, WEST W P, et al. Studies of xenon atoms in high Rydberg states[J]. Physical Review A, 1975, 12(4): 1453-1458. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.12.1453 -






 下载:
下载: