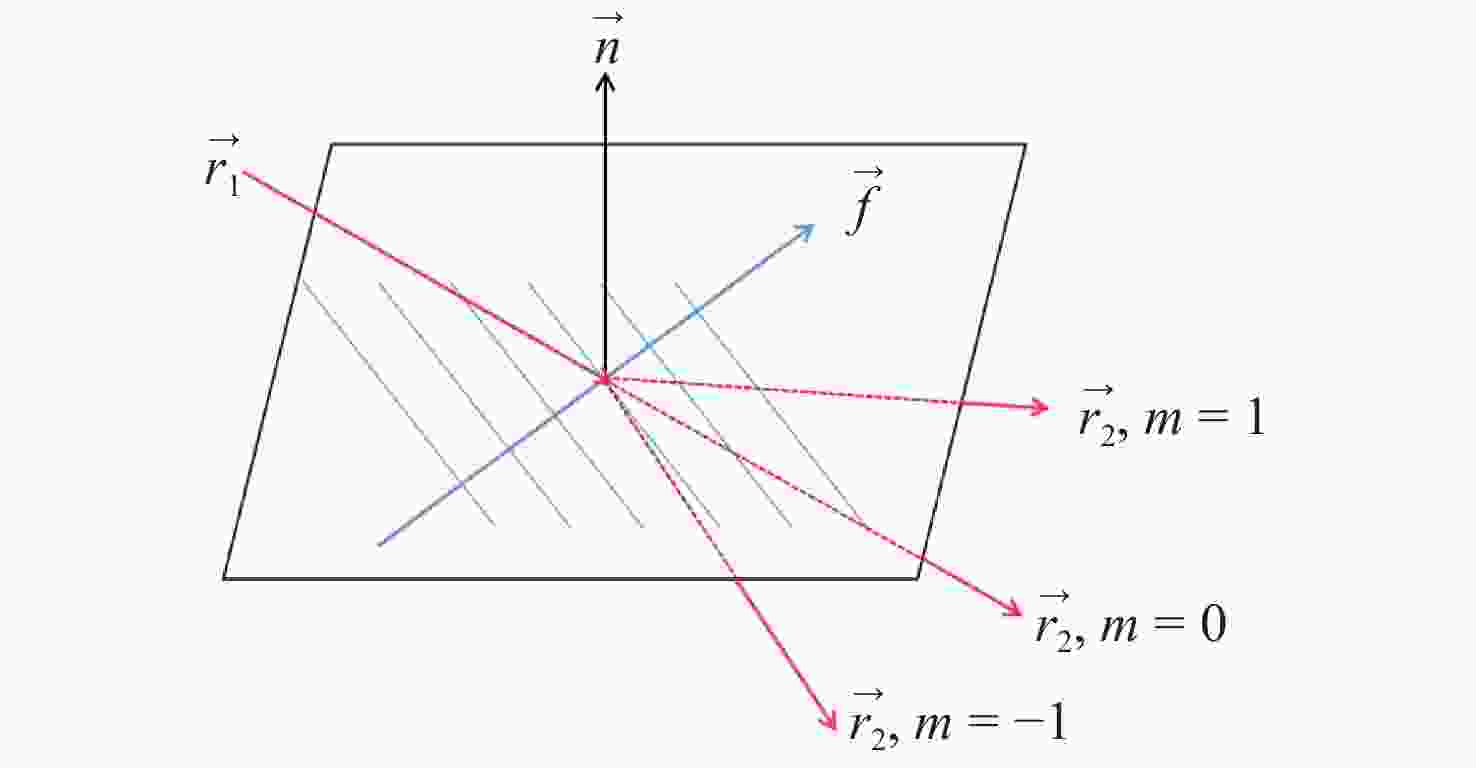
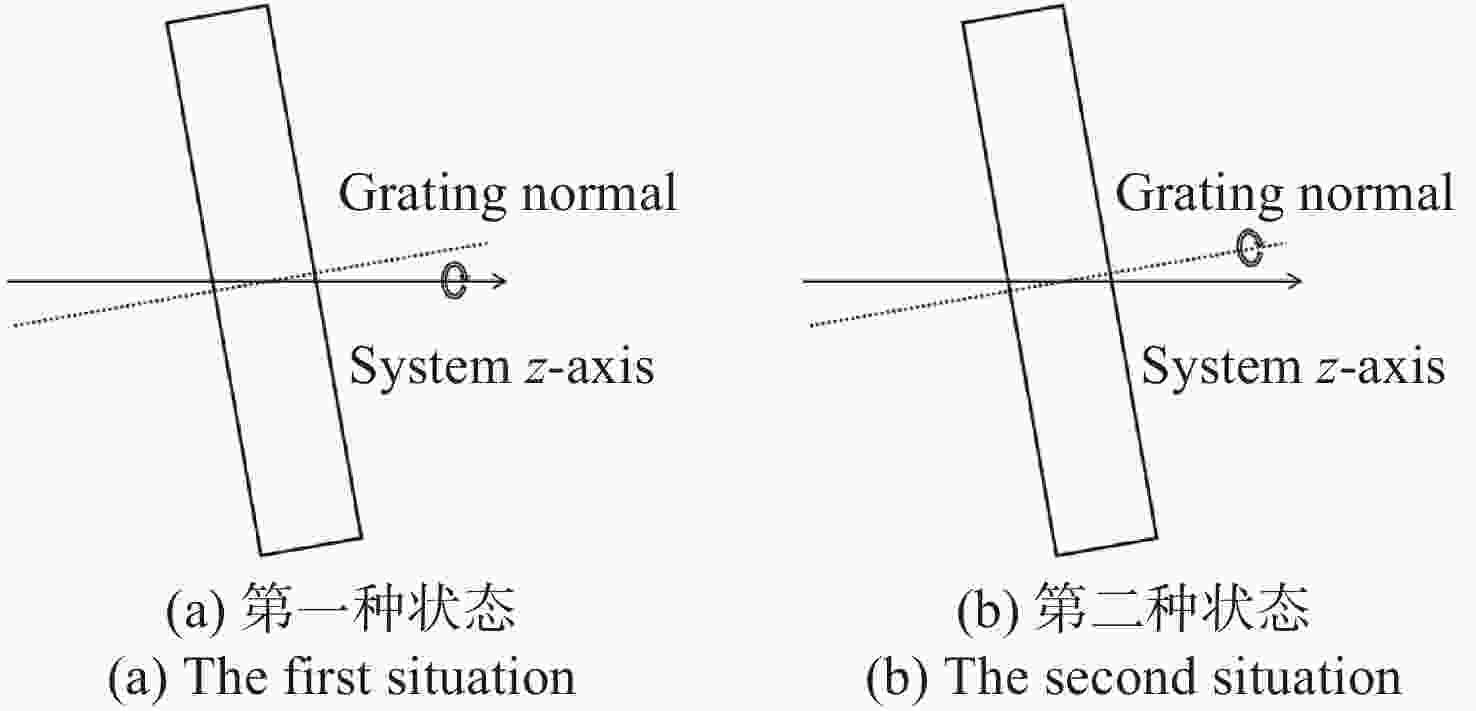
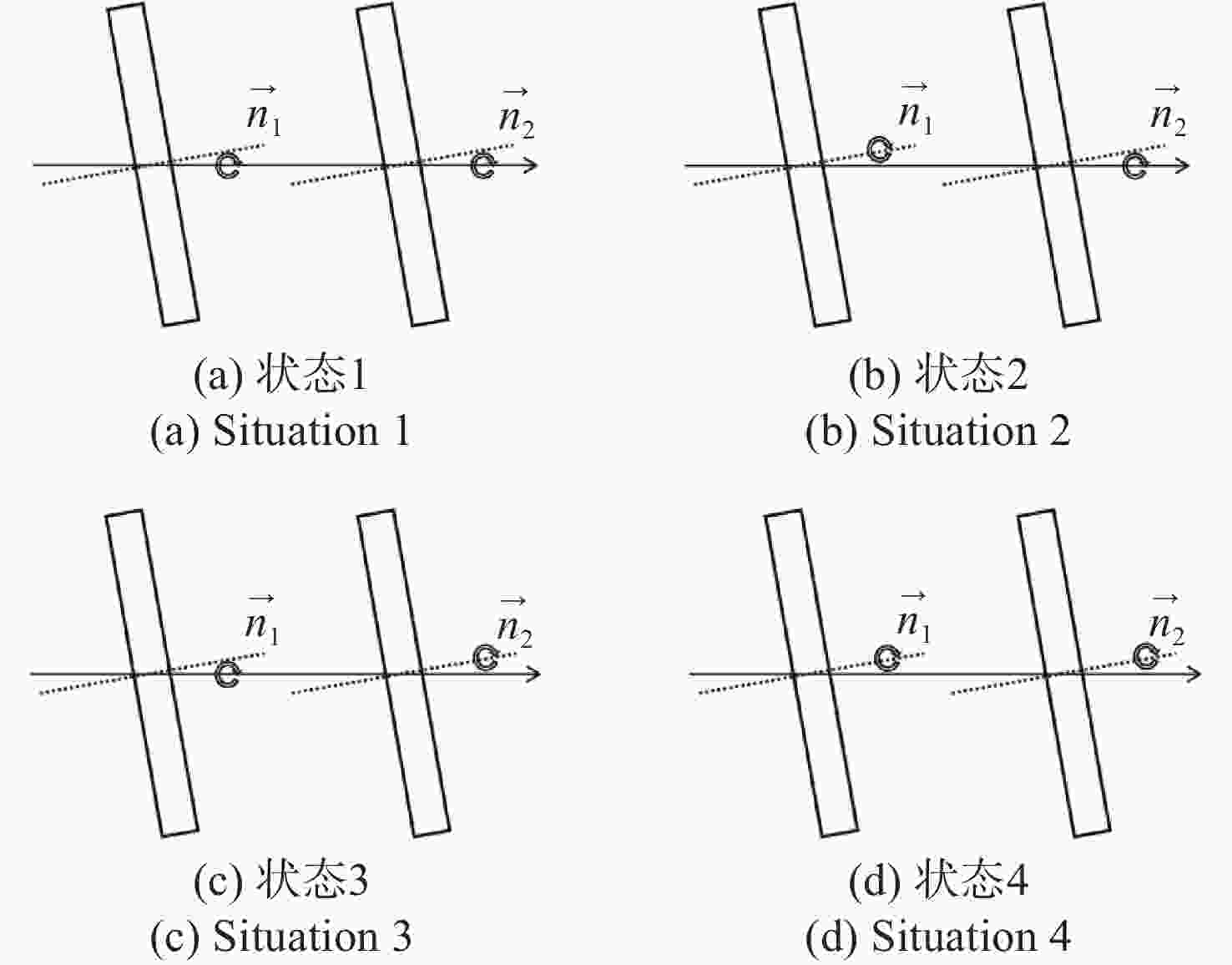
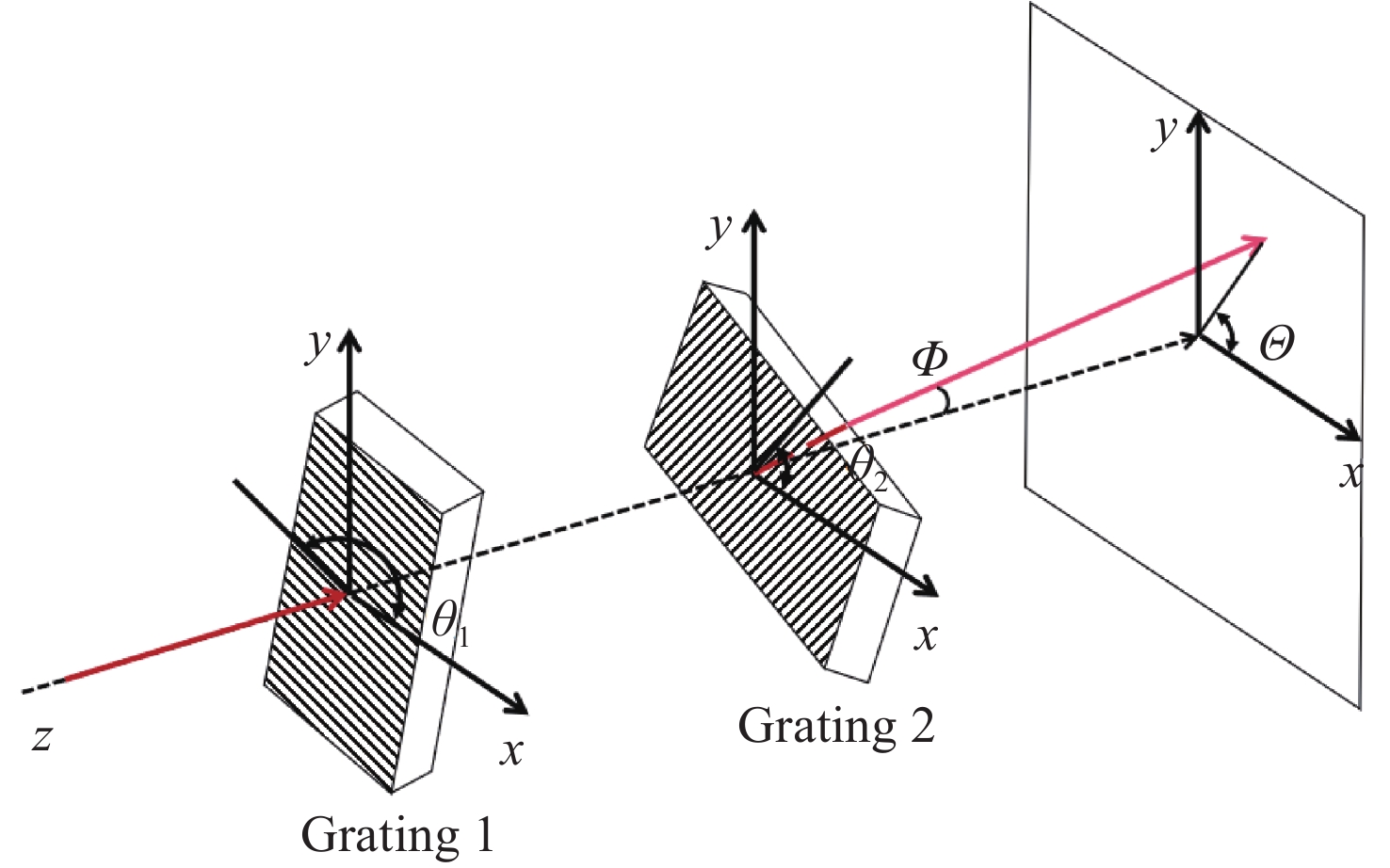
Tilt error’s characteristic analysis of dual liquid crystal polarization grating system
-
摘要:
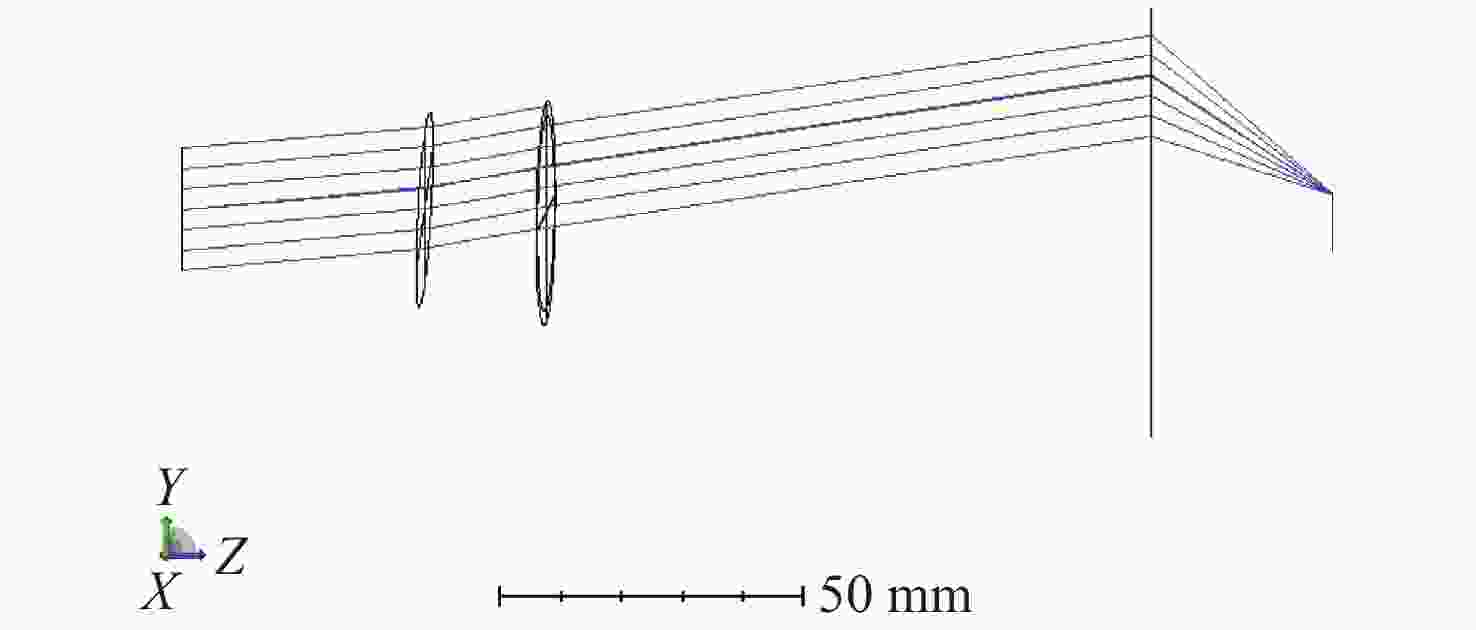
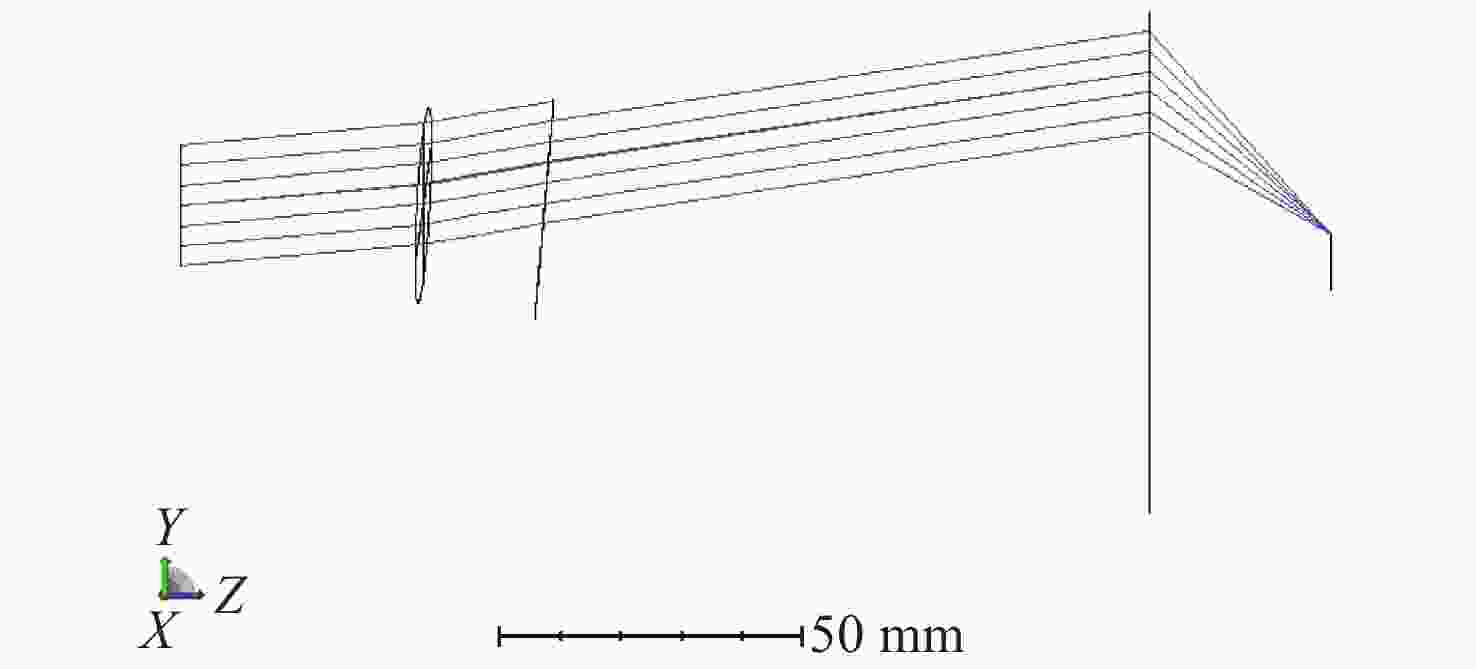
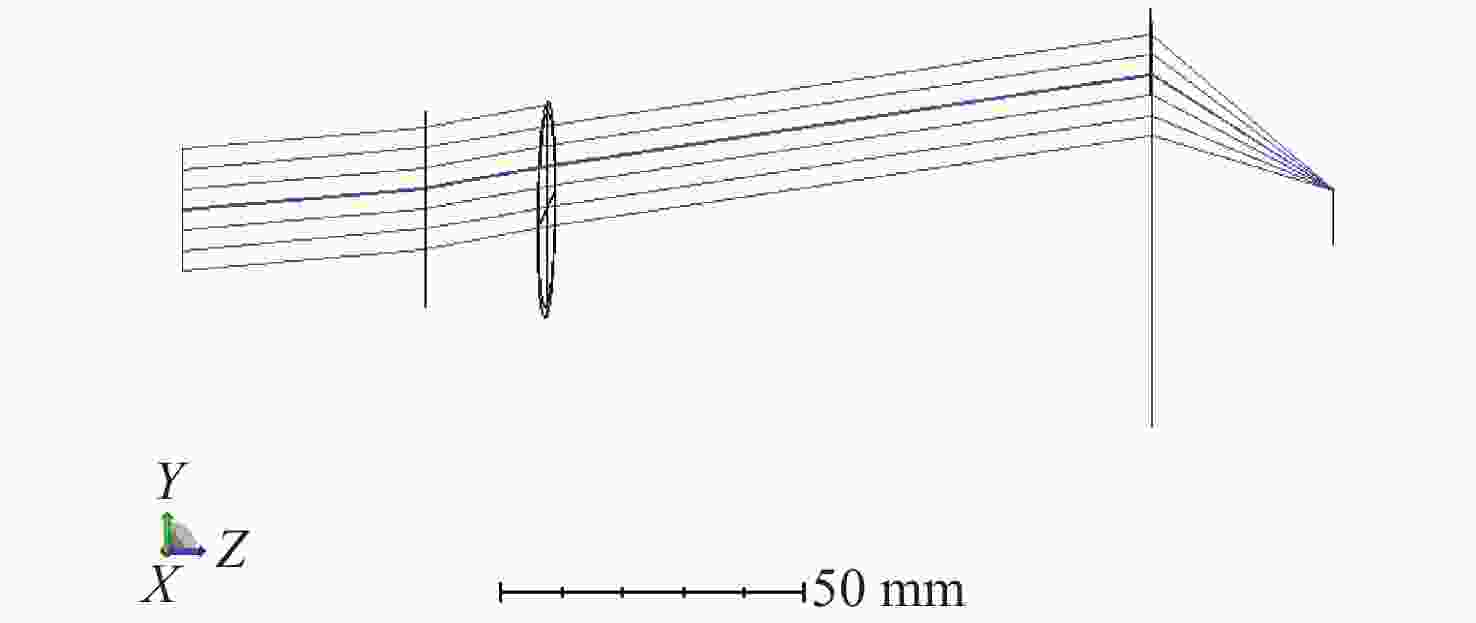
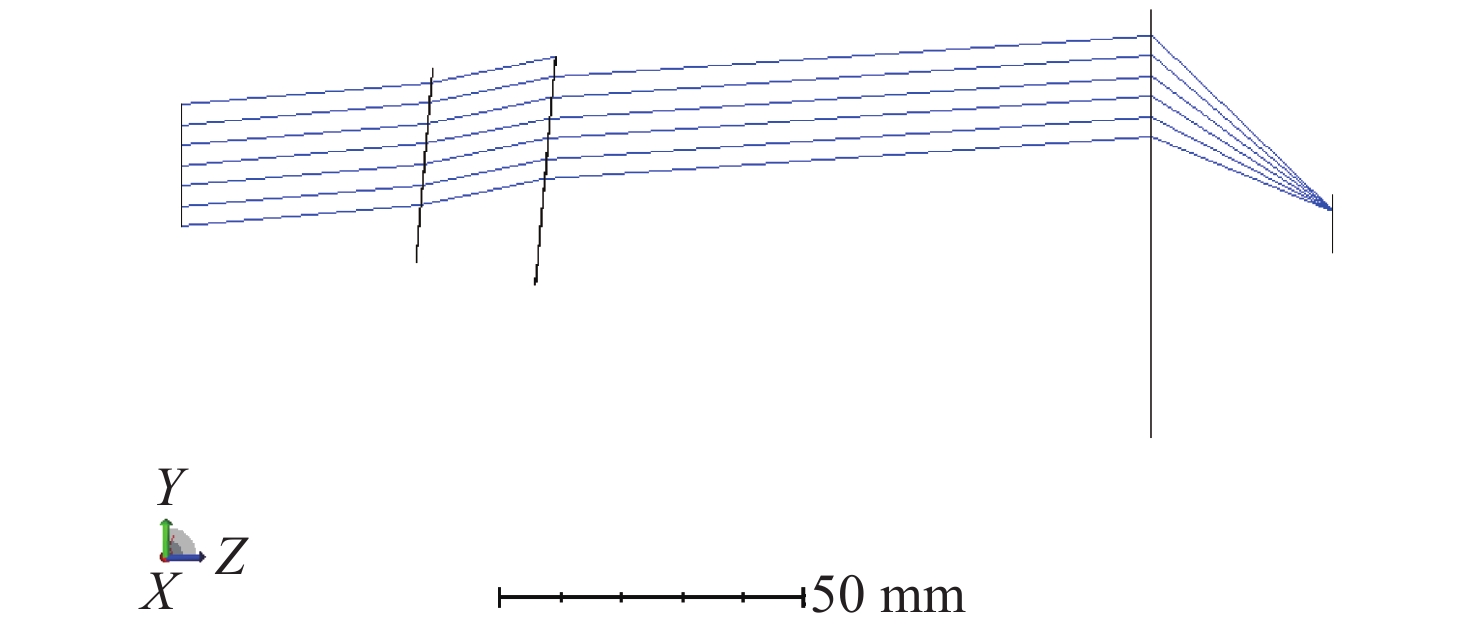
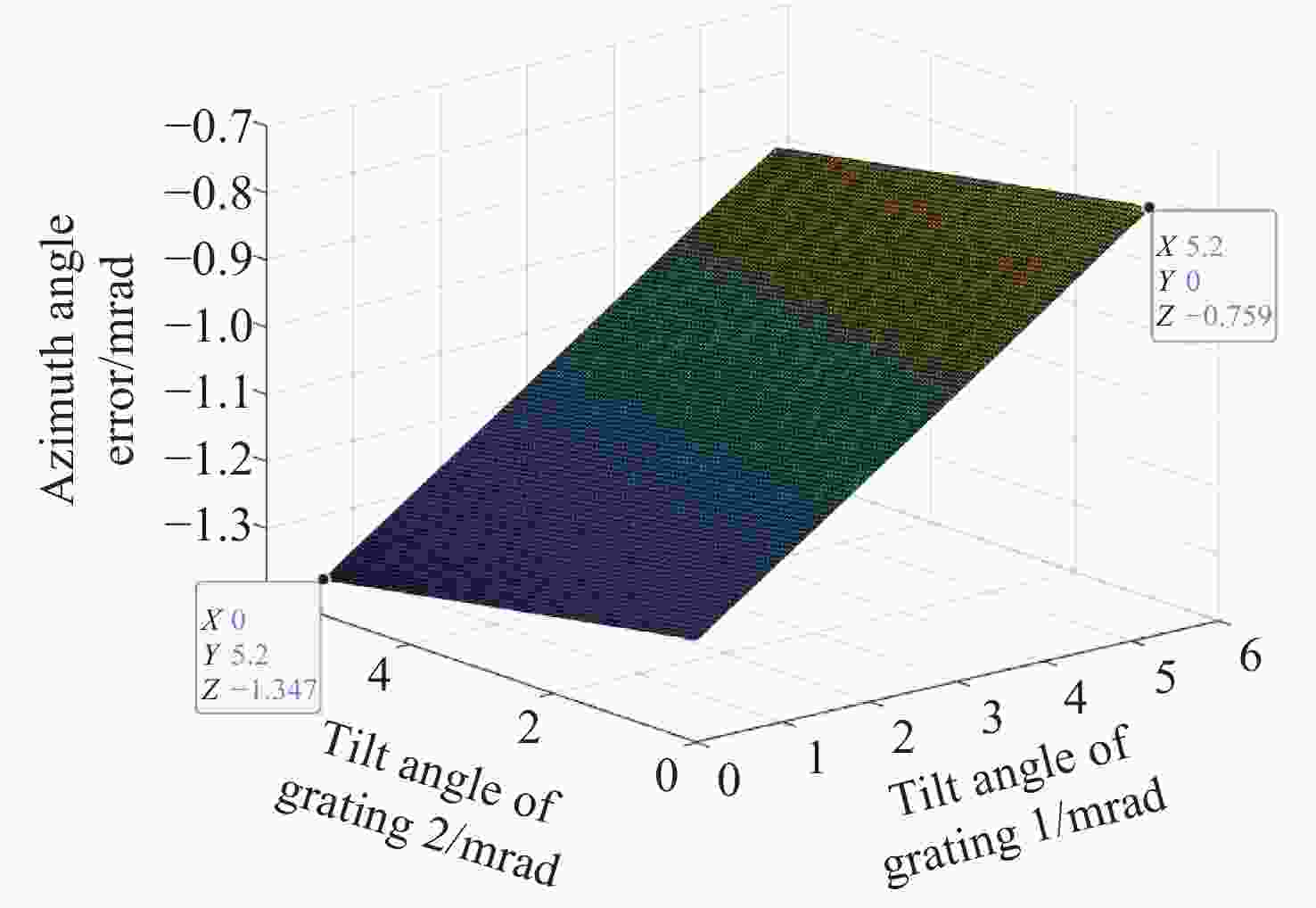
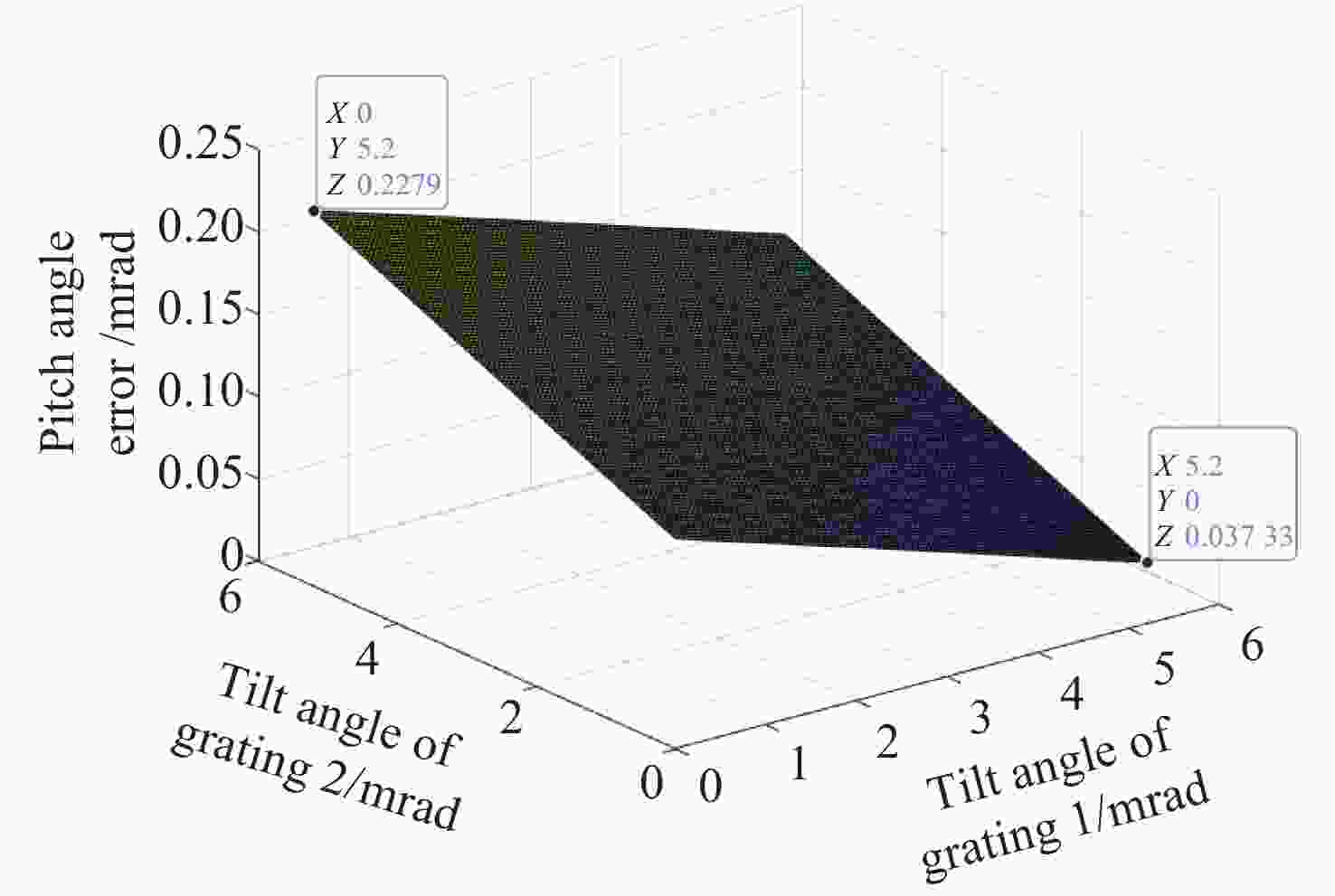
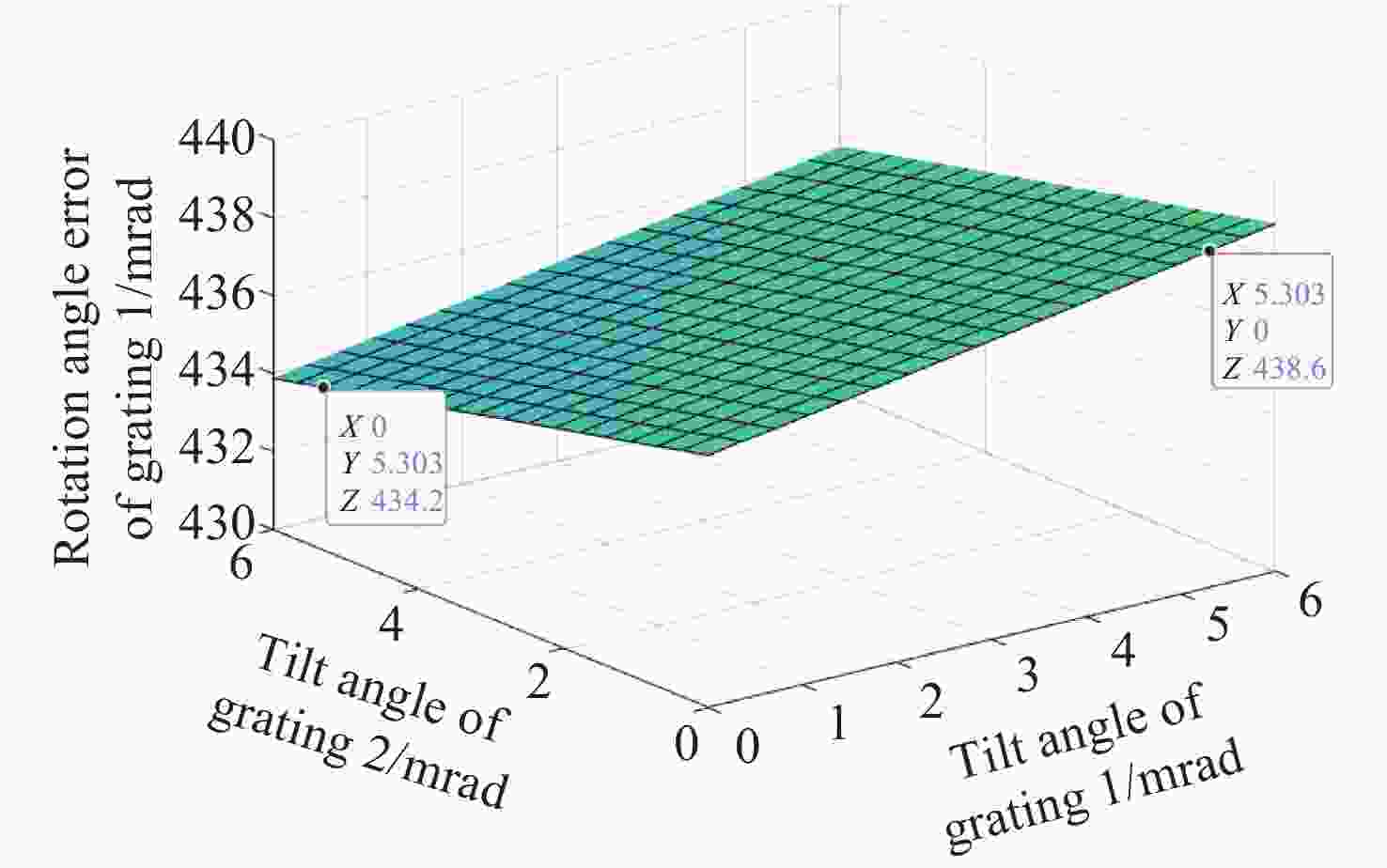
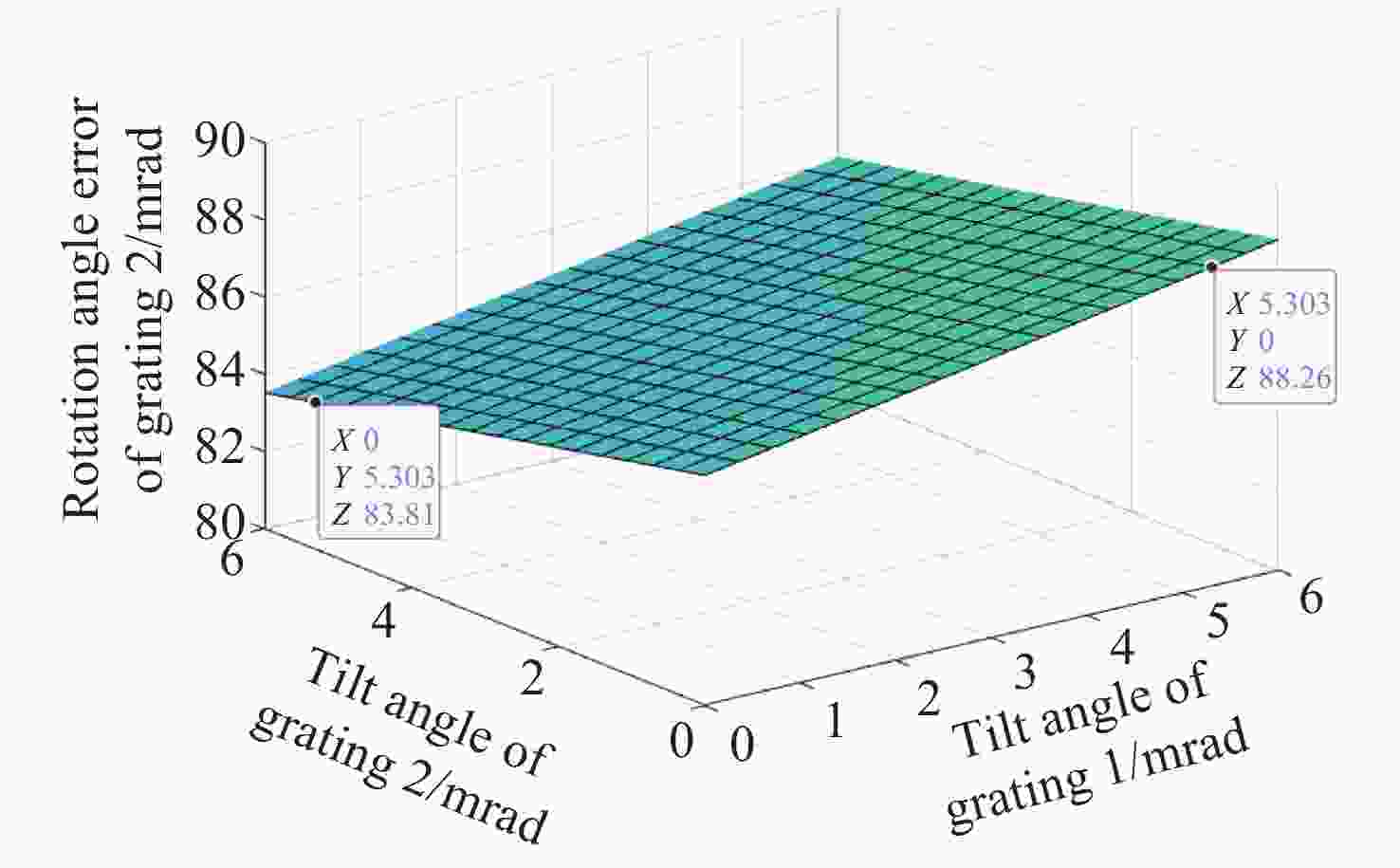
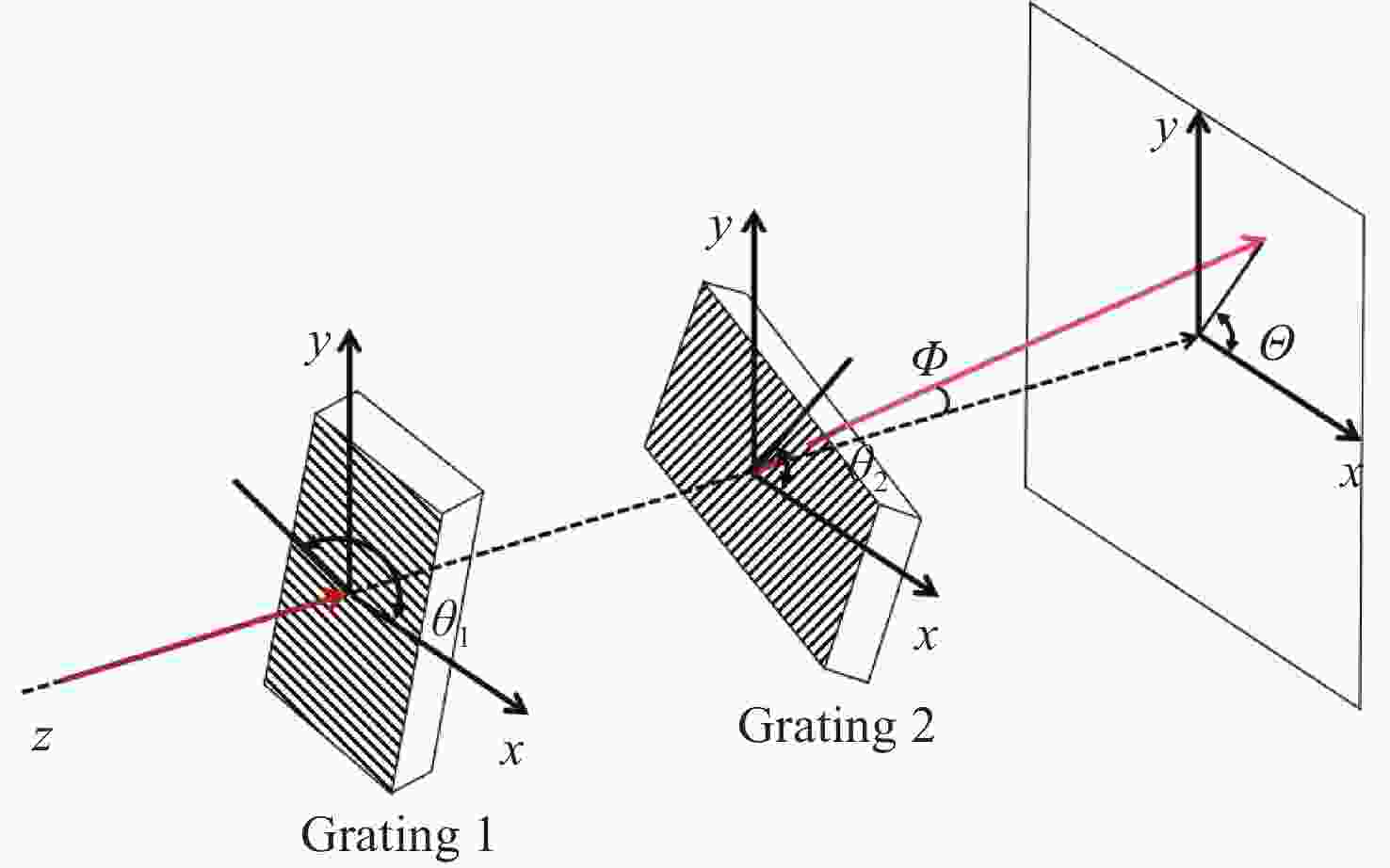
为了精确控制激光光束指向,本文基于双液晶偏振光栅系统的光束指向算法,分析了系统中因光栅倾斜产生的误差。首先,采用一种基于衍射光栅方程的光线追迹方法求解出射光束指向,引入了入射光束指向和光栅倾斜角,通过与仿真结果进行对比,验证了该方法的正确性和精度。其次,通过对光栅不同倾斜情况的分析,本文给出了不同倾斜情况下光栅姿态的表达式,并结合光线追迹法得到了相应的出射光束指向表达式,并进一步分析了光栅倾斜产生的调零误差和旋转误差。研究结果表明,在0°~0.3°光栅倾斜角范围内,调零误差分别在0.25 mrad和2 mrad以内,旋转误差分别在85 mrad和430 mrad左右。本文方法可实现对双液晶偏振光栅系统中出射光束指向和光栅倾斜误差的精确计算。
Abstract:In order to precisely control the direction of laser beams, we analyze the error caused by the grating tilt in the system based on the optical beam pointing algorithm of the dual liquid crystal polarization grating system. Firstly, a ray tracing method based on the diffraction grating equation is used to solve the outgoing beam pointing, introducing the incident beam pointing and grating tilt angle. The correctness and accuracy of this method are verified through comparison with simulation results. Secondly, by analyzing different cases of grating tilt, we provide expressions of the grating attitude under different tilt conditions, and in combination with the ray tracing method, obtain the expressions for the outgoing beam pointing for corresponding situations, analyzing the zeroing error and rotation error caused by grating tilt. The research results indicate that within the 0° to 0.3° grating tilt angle range, the zeroing errors are within 0.25 mrad and 2 mrad respectively, and the rotation errors are around 85 mrad and 430 mrad, respectively. We propose a method for accurately calculating the pointing direction and grating tilt errors in the exit beam of a dual liquid crystal polarization grating system.
-
表 1 光栅旋转角为变量时的验证结果
Table 1. Verification results when the grating’s rotation angle is variable
光栅1
旋转角
$ {\theta _1} $(°)光栅2
旋转角
$ {\theta _2} $(°)关系式(rad) 仿真(rad) $ \varTheta $ $ \varPhi $ $ \varTheta $ $ \varPhi $ 0 0 0 0.0873 0 0.0873 30 0 5.5260 0.0959 5.5260 0.0959 60 0 4.9022 0.1159 4.9022 0.1159 90 0 4.3944 0.1380 4.3944 0.1380 120 0 3.9514 0.1563 3.9514 0.1563 150 0 3.5401 0.1680 3.5401 0.1680 180 0 3.1416 0.1720 3.1416 0.1720 0 30 0.5585 0.1242 0.5585 0.1242 0 60 0.6339 0.1919 0.6339 0.1919 0 90 0.5331 0.2569 0.5331 0.2569 0 120 0.3733 0.3086 0.3733 0.3086 0 150 0.1907 0.3415 0.1907 0.3415 0 180 0 0.3528 0 0.3528 表 2 光栅倾斜角为变量时的验证结果
Table 2. Verification results when the grating’s tilt angle is variable
光栅1
倾斜角
$ {t_1} $(°)光栅2
倾斜角
$ {t_2} $(°)关系式(rad) 仿真(rad) $ \varTheta $ $ \varPhi $ $ \varTheta $ $ \varPhi $ 0 0 0.50004 0.22072 0.50004 0.22072 1 0 0.49900 0.22101 0.49900 0.22101 2 0 0.49784 0.22134 0.49784 0.22134 3 0 0.49656 0.22170 0.49656 0.22170 4 0 0.49515 0.22210 0.49515 0.22210 5 0 0.49363 0.22254 0.49363 0.22254 0 1 0.50007 0.22072 0.50007 0.22072 0 2 0.50028 0.22073 0.50028 0.22073 0 3 0.50065 0.22076 0.50065 0.22076 0 4 0.50119 0.22080 0.50119 0.22080 0 5 0.50190 0.22086 0.50190 0.22086 表 3 入射光束指向为变量时的验证结果
Table 3. Verification results when the pointing of the incident light beam is variable
入射光束
指向方位角
$ {\varTheta _0} $(°)入射光束
指向俯仰角
$ {\varPhi _0} $(°)关系式(rad) 仿真(rad) $ \varTheta $ $ \varPhi $ $ \varTheta $ $ \varPhi $ 45 1 0.6639 0.1512 0.6639 0.1512 90 1 0.6908 0.1382 0.6908 0.1382 135 1 0.7807 0.1322 0.7807 0.1322 180 1 0.8705 0.1378 0.8705 0.1378 225 1 0.8966 0.1506 0.8966 0.1506 270 1 0.8559 0.1626 0.8559 0.1626 315 1 0.7794 0.1676 0.7794 0.1676 360 1 0.7035 0.1631 0.7035 0.1631 0 1 0.7035 0.1631 0.7035 0.1631 0 2 0.6387 0.1771 0.6387 0.1771 0 3 0.5835 0.1918 0.5835 0.1918 0 4 0.5363 0.2070 0.5363 0.2070 0 5 0.4955 0.2227 0.4955 0.2227 -
[1] BUCK J, SERATI S, HOSTING L, et al. Polarization gratings for non-mechanical beam steering applications[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8395: 83950F. doi: 10.1117/12.921688 [2] DILLON T E, SCHUETZ C A, MARTIN R D, et al. Nonmechanical beam steering using optical phased arrays[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2011, 8184: 81840F. doi: 10.1117/12.898356 [3] 王灿进, 孙涛, 李正炜. 基于快速轮廓转动力矩特征的激光主动成像目标识别[J]. 中国光学,2015,8(5):775-784. doi: 10.3788/co.20150805.0775WANG C J, SUN T, LI ZH W. Target recognition in laser active imaging based on fast contour torque features[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(5): 775-784. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/co.20150805.0775 [4] 王新华, 黄玮, 欧阳继红. 多探测器拼接成像系统实时图像配准[J]. 中国光学,2015,8(2):211-219. doi: 10.3788/co.20150802.0211WANG X H, HUANG W, OUYANG J H. Real-time image registration of the multi-detectors mosaic imaging system[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(2): 211-219. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/co.20150802.0211 [5] 郭巳秋, 许廷发, 王洪庆, 等. 改进的粒子群优化目标跟踪方法[J]. 中国光学,2014,7(5):759-767.GUO S Q, XU T F, WANG H Q, et al. Object tracking method based on improved particle swarm optimization[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(5): 759-767. (in Chinese). [6] 潘国涛, 闫钰锋, 于信, 等. 矩形大口径激光光束质量评价光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):306-317. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0130PAN G T, YAN Y F, YU X, et al. Design of optical system for quality evaluation of a large rectangular aperture laser beam[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 306-317. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0130 [7] 张新荣, 王鑫, 王瑶, 等. 基于转动式二维激光扫描仪和多传感器的三维重建方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(3):663-672. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0159ZHANG X R, WANG X, WANG Y, et al. 3D reconstruction method based on a rotating 2D laser scanner and multi-sensor[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(3): 663-672. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0159 [8] TAN L. Liquid crystal polarization gratings and their applications[D]. Hong Kong, China: The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, 2013. [9] JONES W M. Development of switchable polarization gratings for highly efficient liquid crystal displays[D]. Raleigh: North Carolina State University, 2006. [10] KIM J, OH C, ESCUTI M J, et al. Wide-angle nonmechanical beam steering using thin liquid crystal polarization gratings[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7093: 709302. doi: 10.1117/12.795752 [11] OH C, KIM J, MUTH J F, et al. A new beam steering concept: Risley gratings[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2009, 7466: 74660J. doi: 10.1117/12.828005 [12] 赵志伟. 大偏转角液晶偏振光栅的研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2020.ZHAO ZH W. Study on liquid crystal polarization grating with large deflection angle[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. (in Chinese). [13] KIM J, MISKIEWICZ M N, SERATI S, et al. High efficiency quasi-ternary design for nonmechanical beam-steering utilizing polarization gratings[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7816: 78160G. doi: 10.1117/12.860885 [14] 李松振. 液晶偏振光栅的设计及其光偏转特性研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2019.LI S ZH. Design of liquid crystal polarization grating and study of its beam deflection characteristics[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019. (in Chinese). [15] 刘壮, 王启东, 王超, 等. 正交级联液晶偏振光栅角度偏转模型[J]. 光子学报,2021,50(11):1105003. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20215011.1105003LIU ZH, WANG Q D, WANG CH, et al. Deflection angular model of orthogonal cascade liquid crystal polarization gratings[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2021, 50(11): 1105003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20215011.1105003 [16] 刘壮, 王启东, 史浩东, 等. 正交级联液晶偏振光栅的收发分离结构设计[J]. 红外与激光工程,2021,50(11):20210551. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210551LIU ZH, WANG Q D, SHI H D, et al. Design of transceiver separation structure for orthogonal cascaded liquid crystal polarization gratings[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(11): 20210551. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210551 [17] 郑青泉, 王春阳, 王子硕, 等. 斜入射下液晶偏振光栅衍射特性研究[J]. 红外与激光工程,2022,51(7):20210511. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210511ZHENG Q Q, WANG CH Y, WANG Z SH, et al. Research on diffraction characteristics of liquid crystal polarization grating under oblique incidence[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(7): 20210511. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210511 [18] SAKAMOTO M, NHAN H T, NODA K, et al. Polarized beam steering using multiply-cascaded rotating polarization gratings[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(7): 2062-2068. doi: 10.1364/AO.416089 [19] WANG Z SH, WANG CH Y, LIANG SH N, et al. Diffraction characteristics of a non-mechanical beam steering system with liquid crystal polarization gratings[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(5): 7319-7331. doi: 10.1364/OE.452397 [20] WANG J, GAO L, JIANG L, et al. Establishment and verification of formulas of target tracking based on dual liquid crystal polarization gratings[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(24): 43062-43077. doi: 10.1364/OE.473947 -





 下载:
下载: